1
Fifth stage
Dermatology
Lec
Dr.Omar
2/3/2017
Vitiligo
Chronic skin disease
Other name = Leukoderma
White spots occur when the skin no longer forms melanin
(pigment that determines the color of your skin, hair, and
eyes)
The white patches of irregular shapes begin to appear on
your skin
Symptoms & Signs
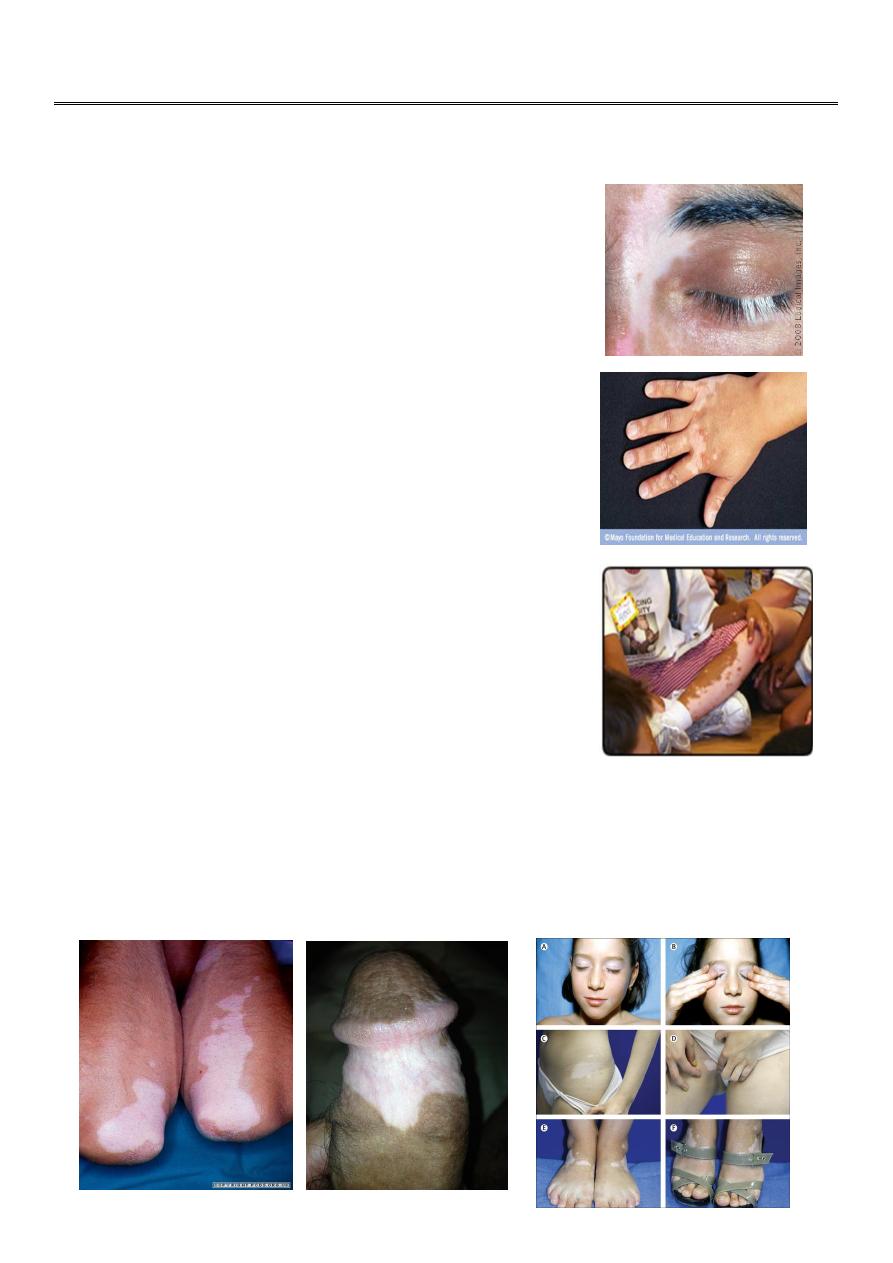
White patches of skin
Whitening or graying of the hair on your scalp, eyelashes,
eyebrows or beard
Loss of color in the tissues that line the inside of your
mouth
Loss or change in color of the inner layer of your eye
White Vitiligo Spots
Chalk white color
Convex margins
5mm to 5cm or more in diameter
Round, oval, or elongated in shape
3 patterns:
1. Focal pattern—the depigmentation is limited to one or only a few areas
2. Segmental pattern—depigmented patches develop on only one side of the body
3. Generalized pattern—(most common) depigmentation occurs symmetrically on both
sides of the body
Focal and segmental patterns do not spread. The generalized pattern is hard to predict and
can randomly stop

2
Facts:
Can appear at any age, usually first appears between the ages of 20 and 30
White patches may begin on your face above your eyes or on your neck, armpits,
elbows, genitals, hands or knees
1-200 of the world population develops
Affects both genders and all races equally
Causes:
1. When no melanin is produced, the involved patch of skin becomes white
2. When a white patch grows or spreads the cause may be Vitiligo
3. Exact cause is unknown
4. May be due to an immune disorder, heredity, or environmental causes like sunburn or
emotional distress that trigger the condition
Treatment
Vitiligo is difficult to treat
Early treatment options include:
Exposure to intense ultraviolet light, such as narrow-band UVB therapy
Photosensitizers taken by mouth such as trimethylpsoralen (Trisoralen) plus UVA
exposure
Topicals:
Corticosteroid creams (weak effect)
Immunosuppressants such as
pimecrolimus
(
Elidel
) and
tacrolimus
(
Protopic
)
Repigmenting agents such as
methoxsalen
(
Oxsoralen
)
Excimer lasres
Systemic steroids
If the affected body surface area is more than 40%, then it is better to bleach
(depigment) the remaining normal skin in order to unify the body’s color by using
20% monobenzone cream.
Psoralen photochemotherapy (Psorglen & Ultraviolet A Therapy & PUVA therapy)
Most effective treatment available in the United States.
PUVA therapy is to repigment the white patches
time-consuming, and care must be taken to avoid side effects
Psoralen is a drug that contains chemicals that react with ultraviolet light to cause
darkening of the skin.
Psoralen is taken orally or is applied to the skin
Then skin is carefully timed exposure to sunlight or to ultraviolet A (UVA) light that
comes from a special lamp.

3
Sun awareness and camouflage
Sunscreen
Helps protect the skin from sunburn and long-term damage
Minimizes tanning, which makes the contrast between normal and depigmented skin
less noticeable
Cosmetics
Dermablend
SH.J
ღ
