
1
Fifth stage
Gynecology
Lec-6
د. احمد جاسم
6/4/2016
Germ cell tumor
– Origin : cells derived form oocytes
– Incidence: 15- 20% of all ovarian tumors, 5% malignant
• Age: young age
• A germ cell tumor
( GCT )is a neoplasm derived from germ cells .Germ cells normally
occur inside the gonads
( ovary and testis .)Germ cell tumors that originate outside
the gonads may be birth defects resulting from errors during development of
development of the embryo.
Etiology
• Some investigators suggest that this distribution arises as a consequence of abnormal
migration of germ cells during embryogenesis. Others hypothesize a widespread
distribution of germ cells to multiple sites during normal embryogenesis, with these
cells conveying genetic information or providing regulatory functions at somatic
sites.
Classification
• Germ cell tumors are classified by their histology,regardless of location in the body.
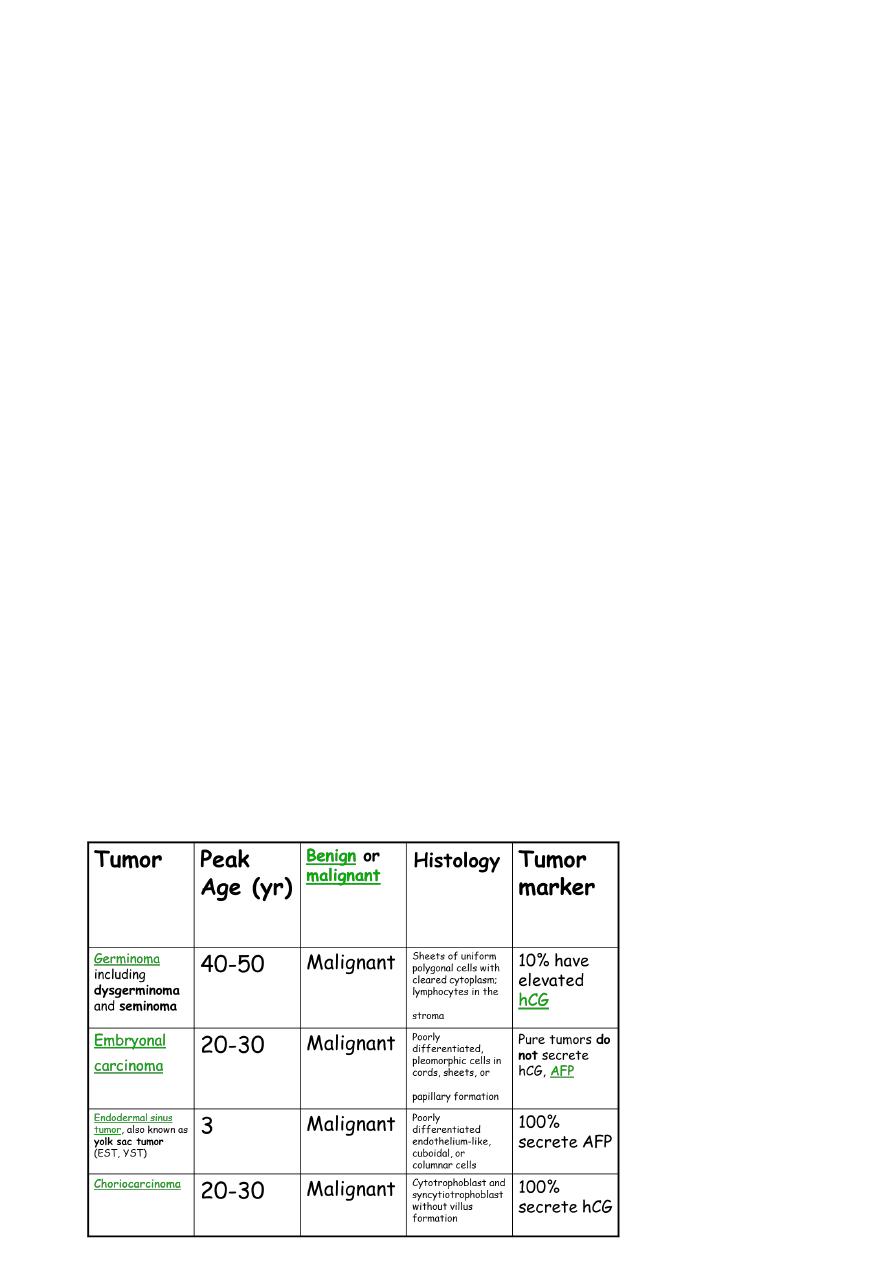
• Dysgerminoma
– Incidence : very common
• Age : 20 – 20 yrs
– Bilateral : 10 – 15 %
– Macroscopic features :
• Solid tumors, elastic rubbery consistency having smooth, firm capsule
2
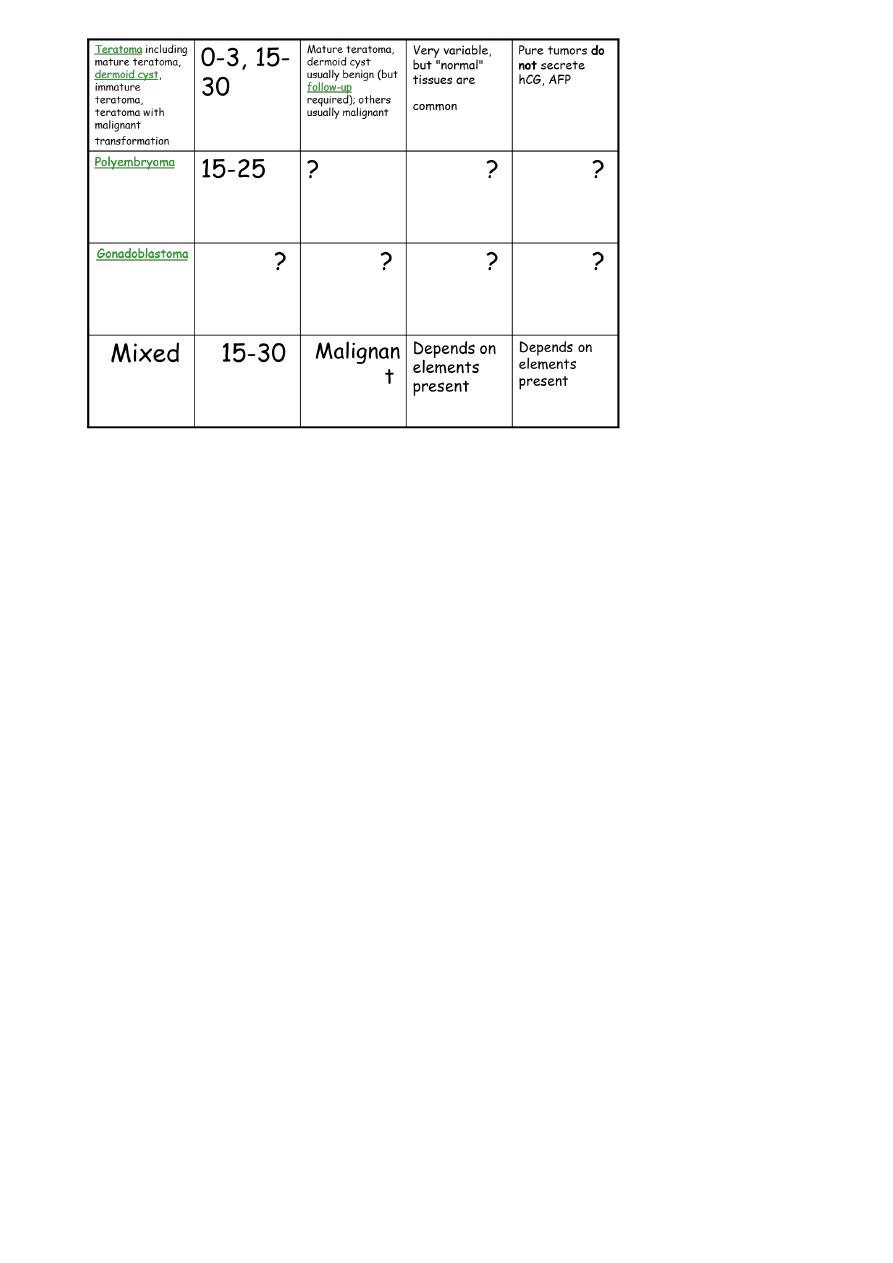
• Teratoma
– Derived from cells of all three germ layers
– Types:
• Mature or benign type (e.g. Dermoid cysts)
• Immature or malignant type (e.g. Solid Teratoma)
• Monodermal or highly specialized (e.g. Struma ovarii)
• Choriocarcinoma and Embryonal Cell Carcinoma
– Choriocarcinoma mostly of placental origin occurs in prepubertal girls. Highly
malignant
• Contains syncytiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts
• Secretes large quantities of the tumor marker - HCG
– Embryonal cell carcinoma
• Incidence : rare
– Highly malignant
• Ovarian Fibroma:
– Meig’s syndrome
• Ascites
• Right sided effusion
3
• Germ cell tumors are broadly divided in two classes:
• The germinomatous or seminomatous germ cell tumors (GGCT, SGCT) include only
germinoma and its synonyms dysgerminoma and seminoma .
• The nongerminomatous or nonseminomatous germ cell tumors (NGGCT, NSGCT)
include all other germ cell tumors, pure and mixed .
• The two classes reflect an important clinical difference. Compared to germinomatous
tumors, nongerminomatous tumors tend to grow faster, have an earlier mean age at
time of diagnosis (~25 years versus ~35 years, in the case of testicular cancers ,)and
have a lower 5 year survival rate. The survival rate for germinomatous tumors is
higher in part because these tumors are exquisitely sensitive to radiation, and they
also respond well to chemotherapy. The prognosis for nongerminomatous has
improved dramatically, however, due to the use of platinum-based chemotherapy
regimens.
Mixed
• Mixed germ cell tumors occur in many forms. Among these, a common form is
teratoma with endodermal sinus tumor.
• Teratocarcinoma refers to a germ cell tumor that is a mixture of teratoma with
embryonal carcinoma ,or with choriocarcinoma ,or with both.This kind of mixed
germ cell tumor may be known simply as a teratoma with elements of embryonal
carcinoma or choriocarcinoma, or simply by ignoring the teratoma component and

4
referring only to its malignant component: embryonal carcinoma and/or
choriocarcinoma.
Location
• Despite their name, germ cell tumors occur both within and outside the ovary and
• In females ,germ cell tumors account for 30% of ovarian tumors, but only 1 to 3% of
ovarian cancers in North America .In younger women germ cell tumors are more
common, thus in patients under the age of 21, 60% of ovarian tumors are of the
germ cell type, and up to one-third are malignant .In males ,germ cell tumors of the
testis occur typically after puberty and are malignant
neonates ,infants ,and children younger than 4 years, the majority of germ cell
tumors are sacrococcygeal teratomas.
• Males with Klinefelter's syndrome have a 50 times greater risk of germ cell tumors
(GSTs).In these persons, GSTs usually contain nonseminomatous elements, present at
an earlier age, and seldom are gonadal in location.
Prognosis
• The 1997 International Germ Cell Consensus Classification is a tool for estimating the
risk of relapse after treatment of malignant germ cell tumor.
• A small study of ovarian tumors in girls reports a correlation between cystic and
benign tumors and, conversely, solid and malignant tumors. Because the cystic
extent of a tumor can be estimated by ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan before surgery,
this permits selection of the most appropriate surgical plan to minimize risk of
spillage of a malignant tumor.
