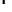Orthognathic surgery
Combined Surgical and Orthodontic Treatmentتقويم \ خامس اسنان
د. الاء م(3-4)9\ 5\ 2017
Orthognathic surgery
• Orthognathic surgery refers to the surgical repositioning of the maxilla, mandible, and the dentoalveolar segments to achieve facial and occlusal balance.• One or more segments of the jaw(s) can be simultaneously repositioned to treat various types of malocclusions and jaw deformities.
There are only three possible treatment ways to treat a jaw discrepancy problem 1. Modification of growth 2. Camouflage ( dental compensation for a skeletal problem ) 3. Surgical repositioning of the jaws and/or dentoalveolar segments
Limitations Of Orthodontic Treatment:
Both dental and orthopedic approaches to attain ideal occlusion through orthodontic appliances alone may be unsuccessful.1. Skeletal deformity may be too great.
2. Completion of jaw growth may limit
the amount of orthodontic treatment
possible.
Limitations of Orthodontic Treatment3. Patient may refuse to wear orthodontic appliances.4. Loss of posterior teeth may limit available anchorage.5. Some orthodontic movement are difficult or impossible (significant intrusion).6. Esthetic consideration (gummy smile).
Limitations Of Surgical Treatment:
Surgery alone is not enough and maybe unsuccessful due to:
1. Teeth need to be properly aligned.
2. Arch forms must be compatible.3. Dental compensations should be
eliminated, so that teeth are well
related with respect to individual jaws.
Indications for Surgery
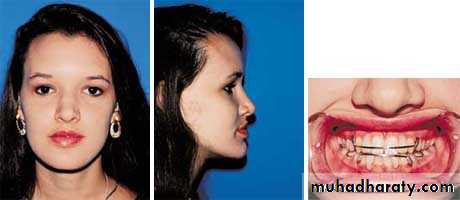
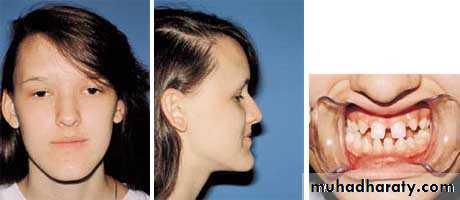
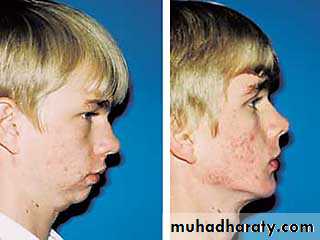
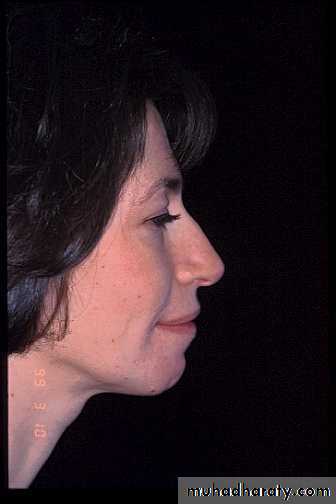
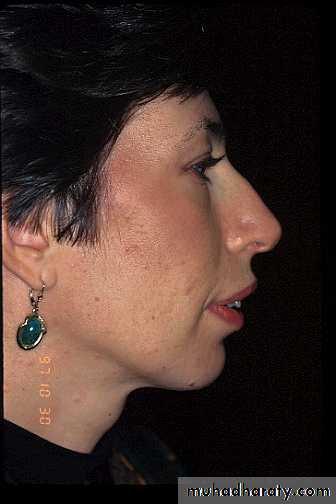
Severity of the skeletal malrelationship (the envelop of discrepancy).Esthetic and psychological considerations.
Severity of the skeletal malrelationship
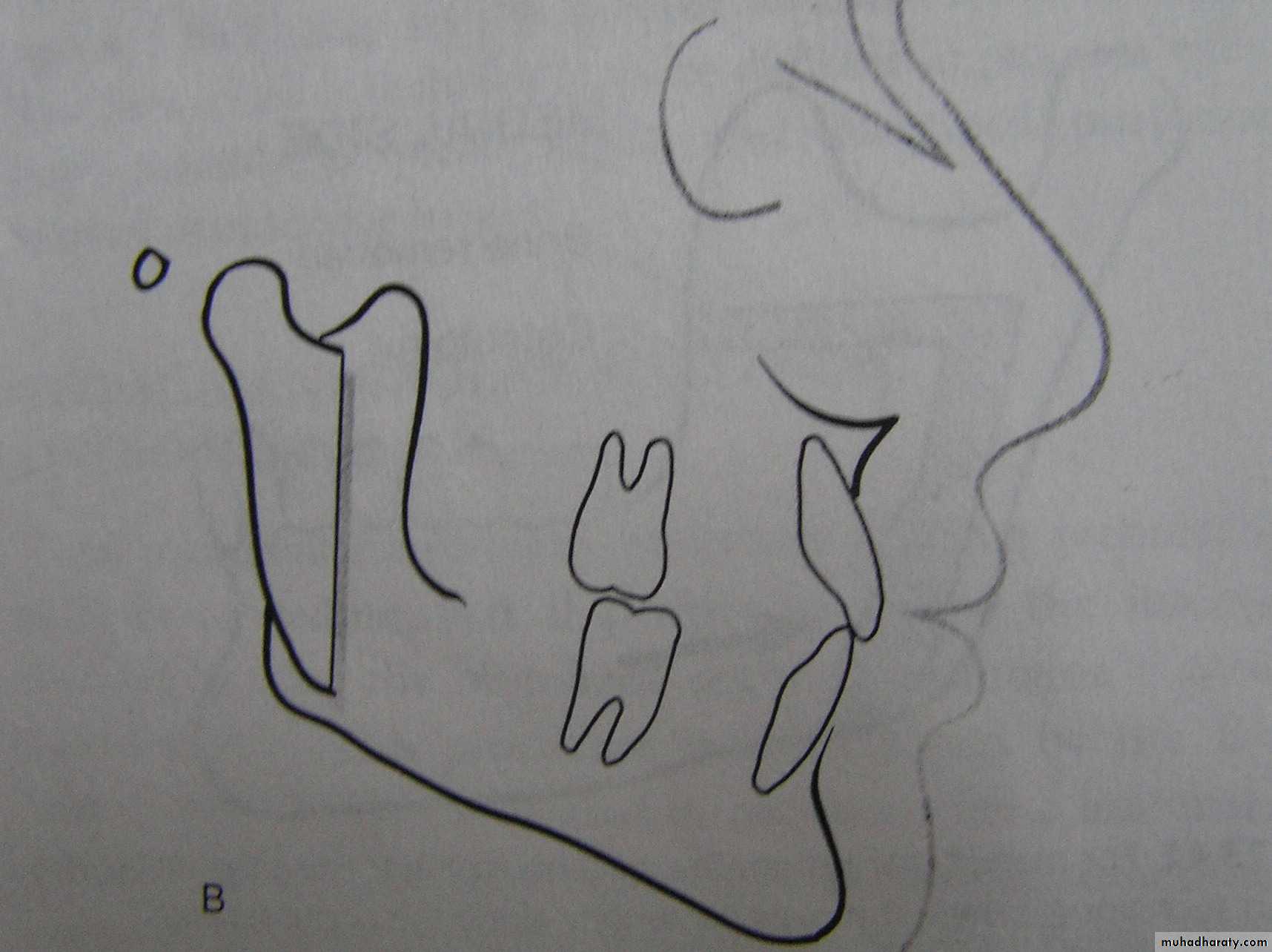
The envelop of Discrepancy
It shows the amount of change that could be produced by orthodontic tooth movement (inner envelop); orthodontic tooth movement + growth modification (the middle envelop); and orthognathic surgery (the outer envelop).
Esthetic and psychological considerations
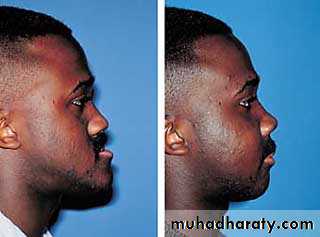
75 %-80% of individuals referred for orthognathic surgery seek esthetic improvement.Changes in the position of the nose and chin have a greater impact on facial esthetics than changes limited to the lips.
Surgical Procedures and Treatment Possibilities
Correction of anteroposterior
relationships
Correction of vertical relationships
Correction of transverse
relationships
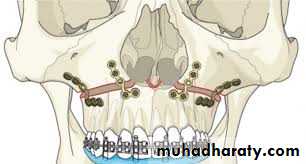
Correction of Anteroposterior Relationships
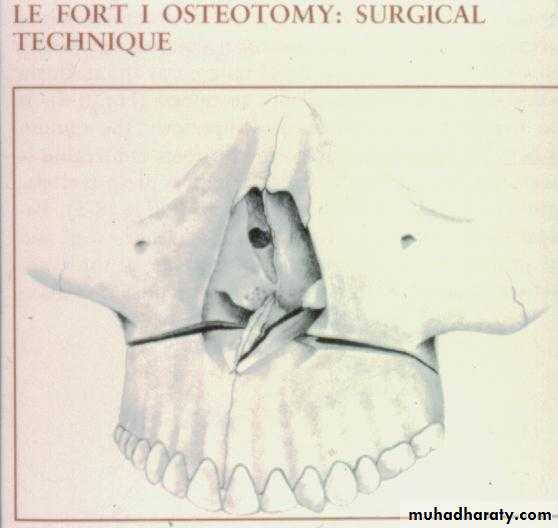
I. Maxillary Surgery:Maxillary advancement
Down fracture technique
Protraction of Maxilla
Correction of Anteroposterior Relationships
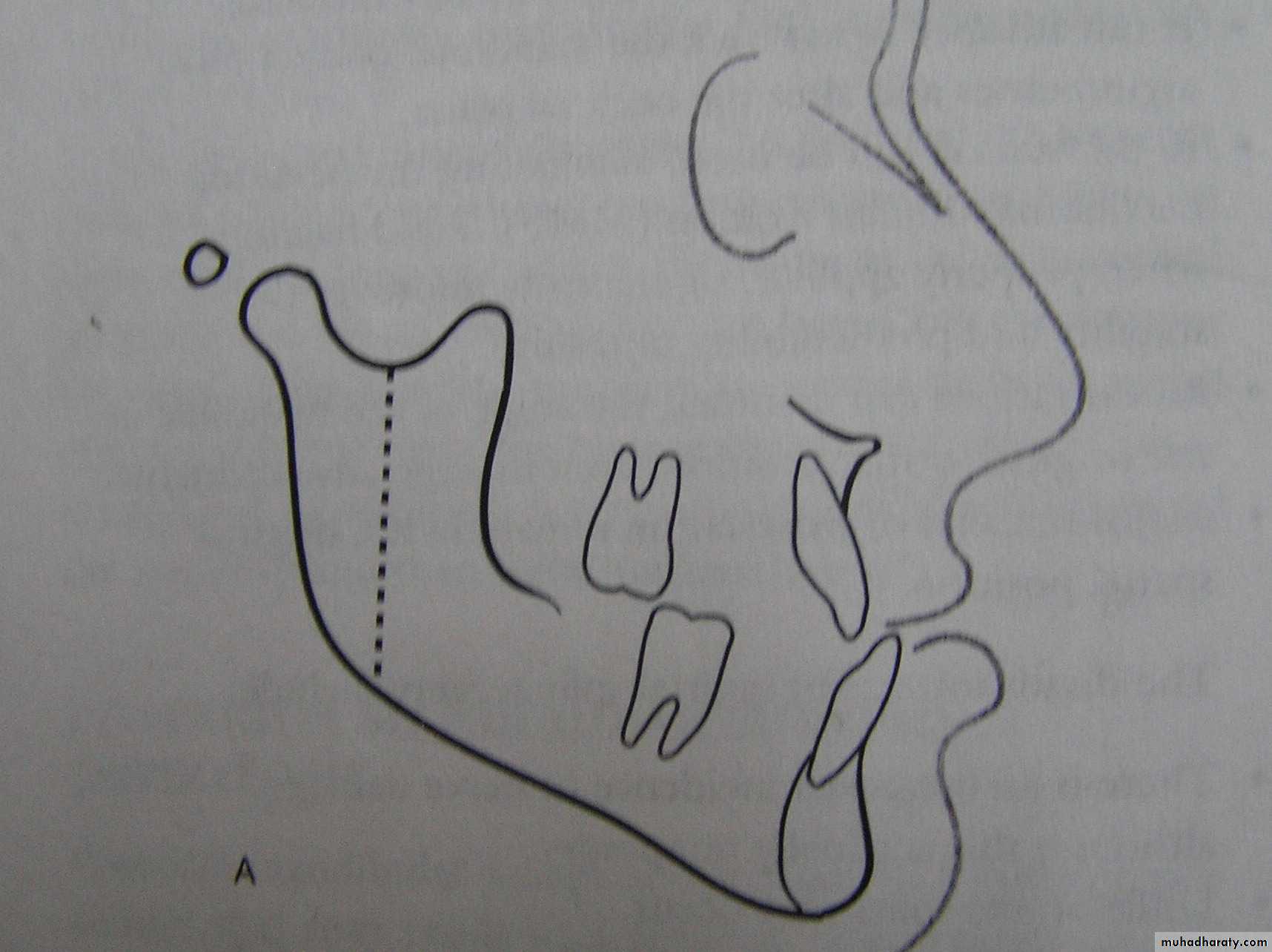
Maxillary retraction:
Down fracture technique: limited by
the anatomic structure immediately
distal to the pterygomaxillary fissure.
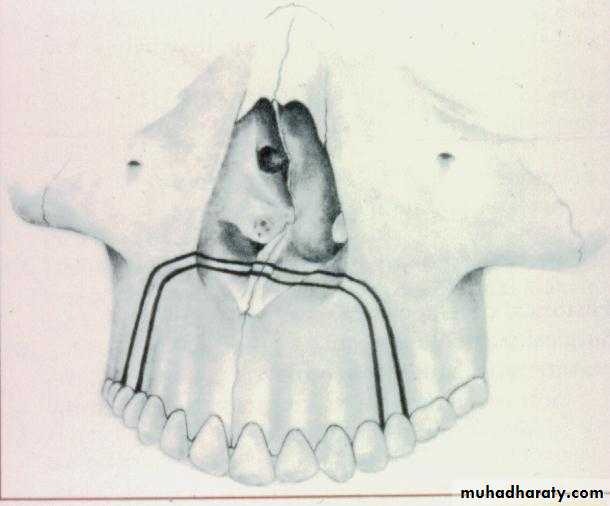
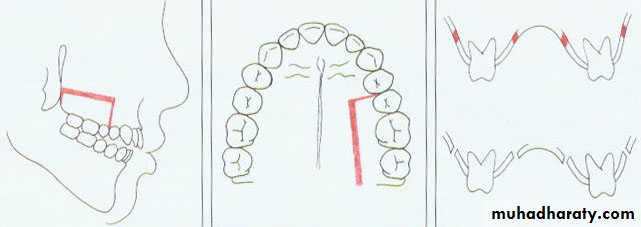
Retraction of anterior segment by a segmental osteotomy after (extraction of 2 first premolars).
Correction Of Anteroposterior Relationships:
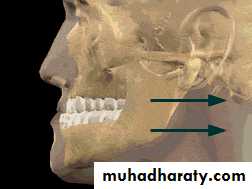
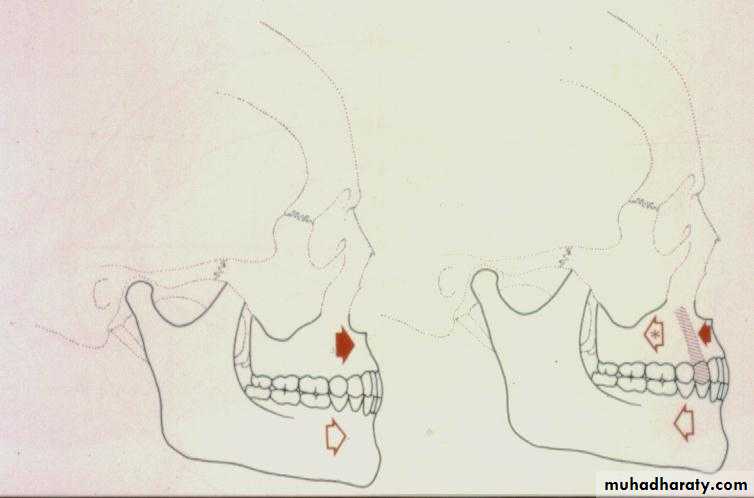
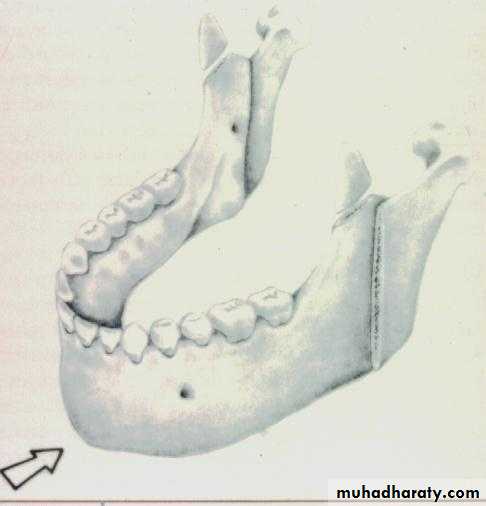
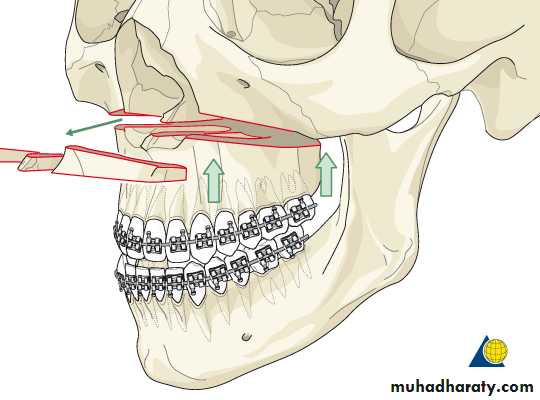
Mandibular SurgeryMandibular Advancement:
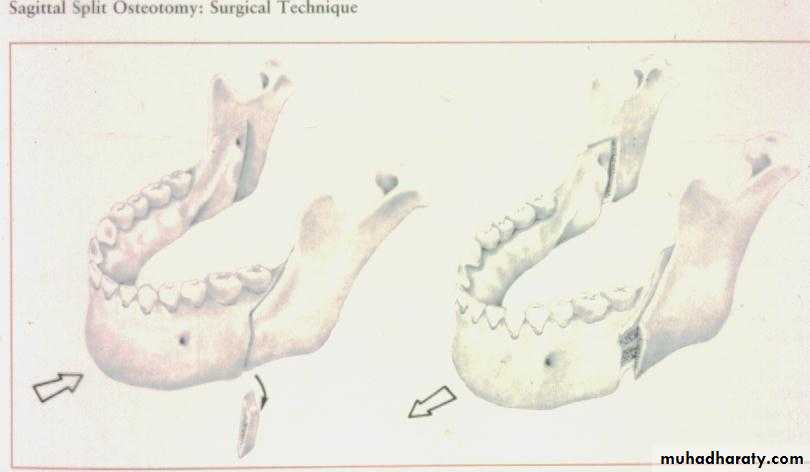
1. Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy (BSSO) of the mandibular ramus
Mandibular Advancement
Correction Of Anteroposterior Relationships
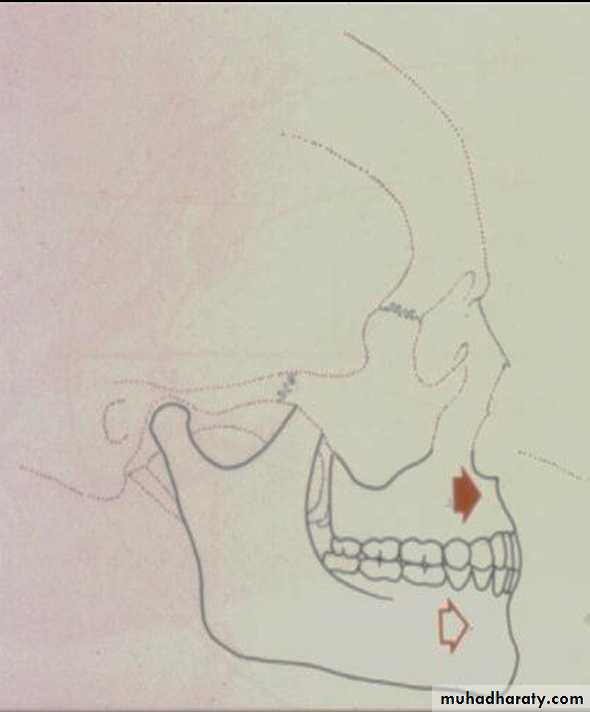
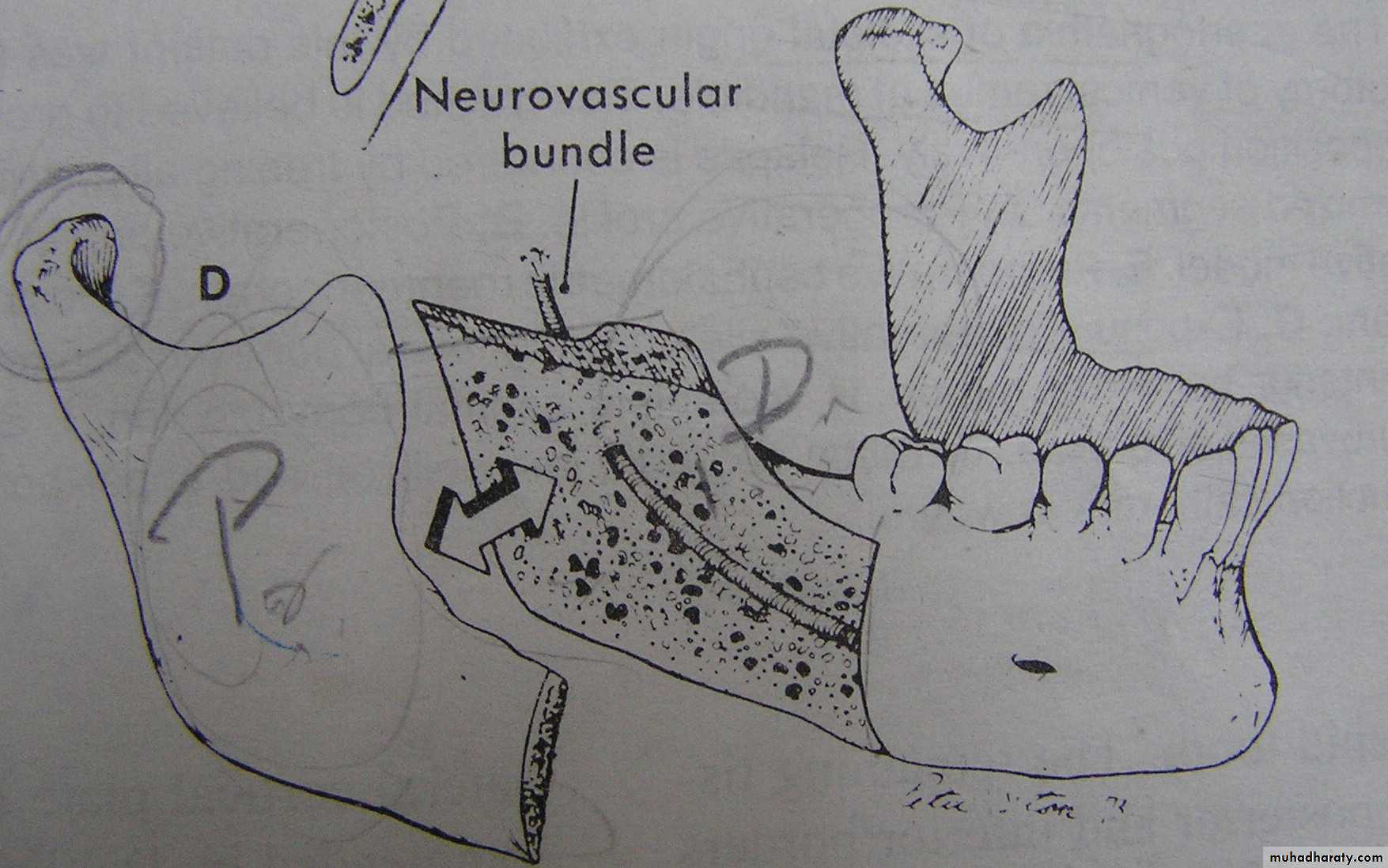
Bilateral sagital split osteotomyhas the following advantages:
Intra oral approach
Broad interface of medullar surface (Rapid healing)
Rigid internal fixation (RIF) with bone screws
Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy ( BSSO ) drawbacks Altered sensation in the lingual nerve distribution ( transient 2 - 6 months ). Paresthesia over the distribution of the inferior alveolar nerve.
Correction Of Anteroposterior Relationships
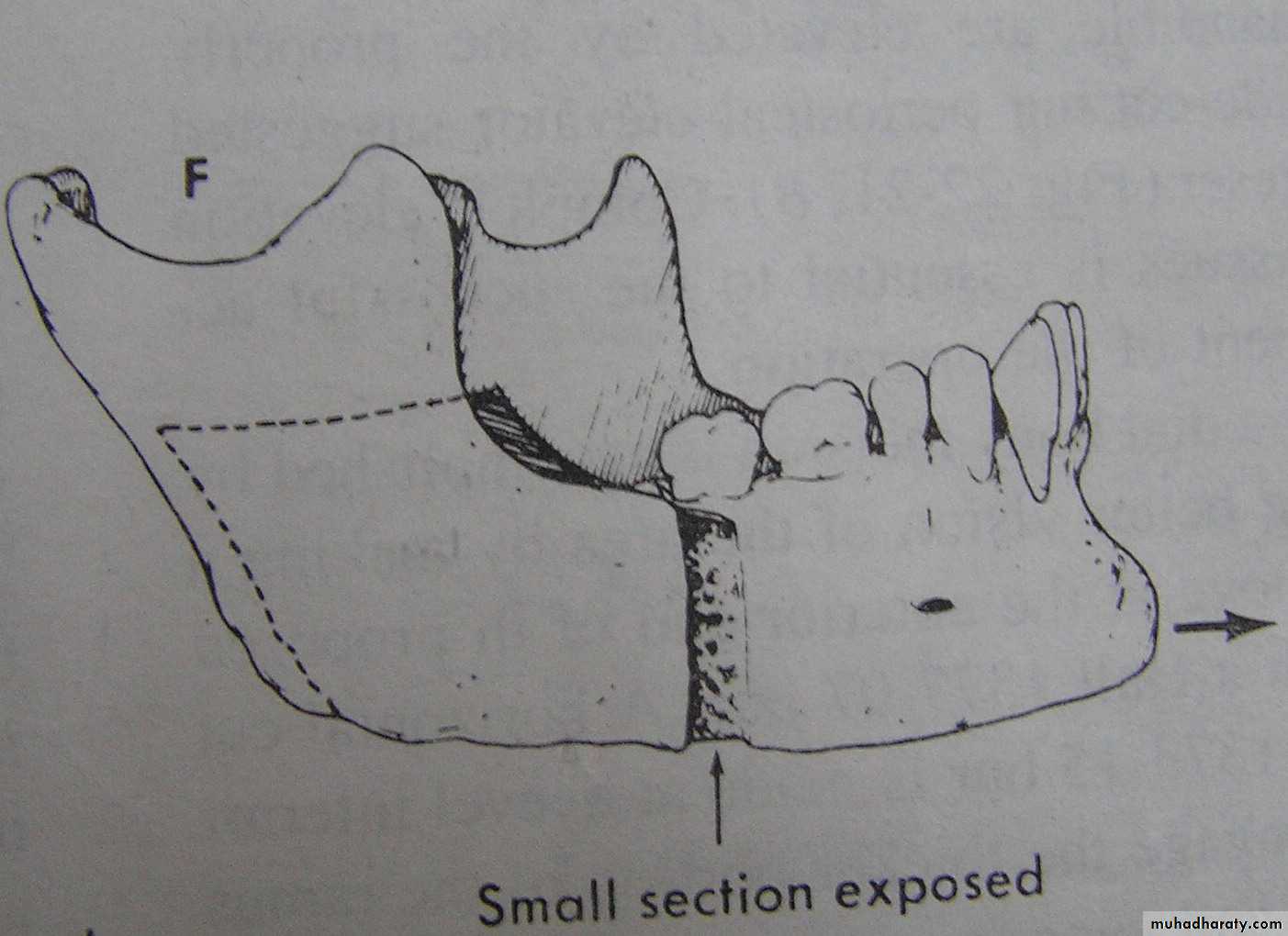
Mandibular Setback:
1. Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy
(BSSO)Excellent control of the condylar segment.
Osteosynthetic screws can be
employed for fixation.
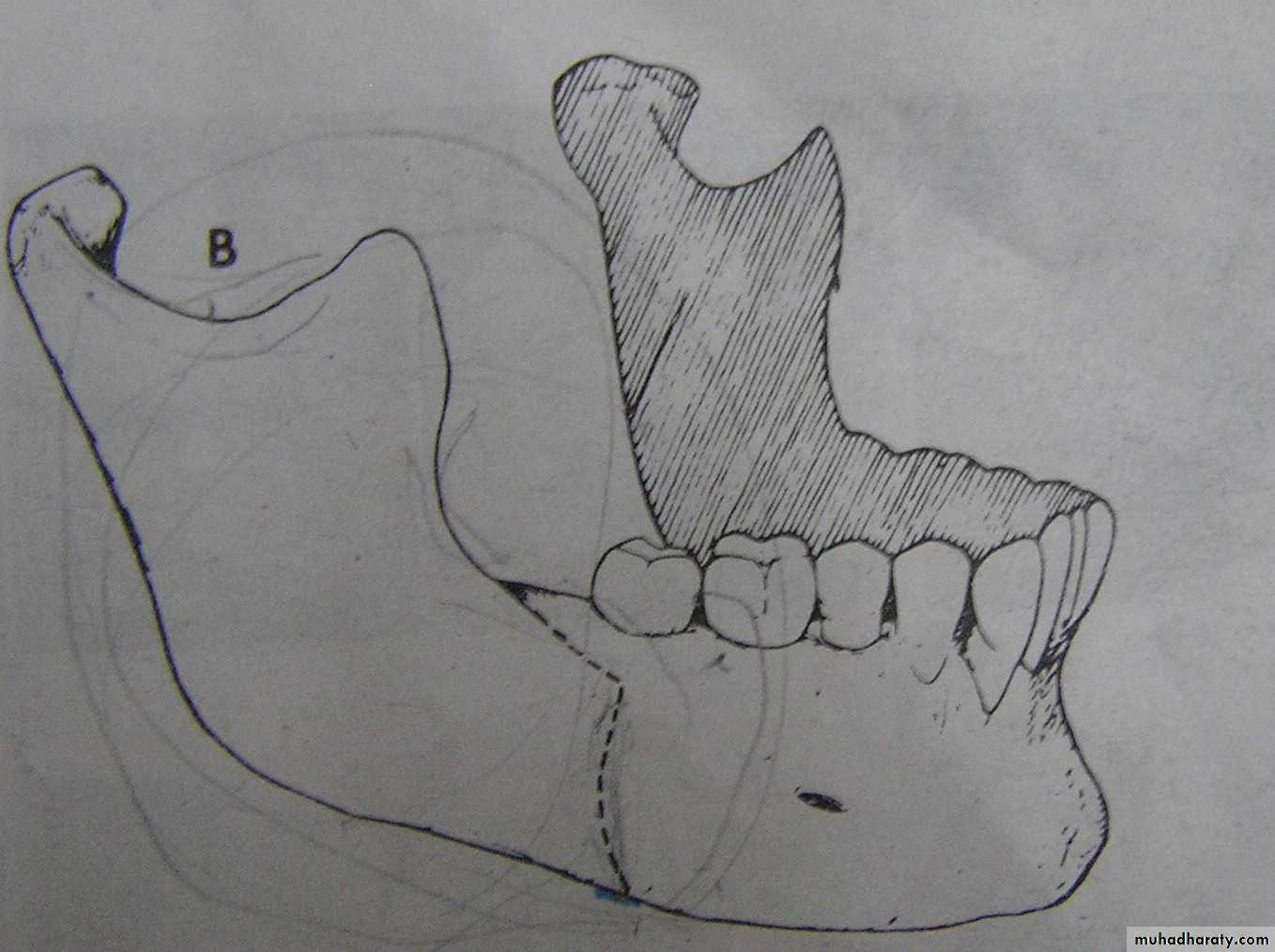
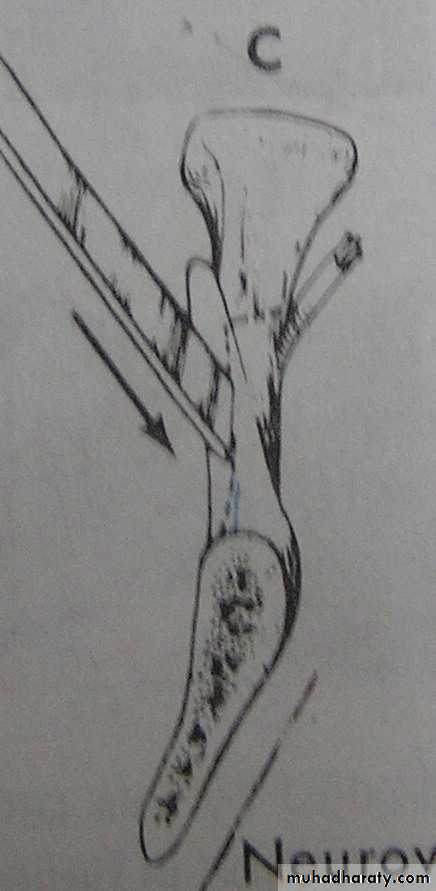
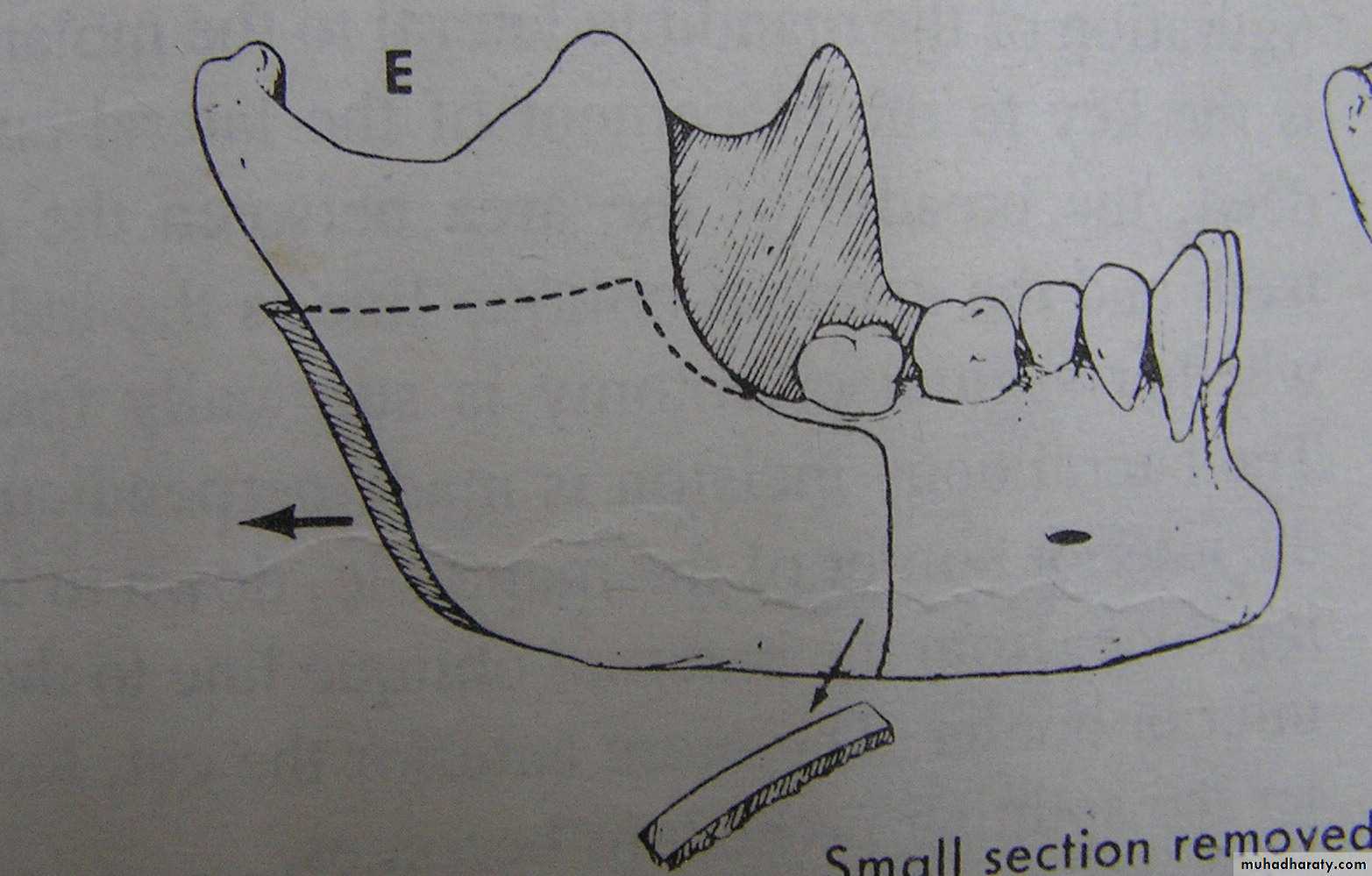
Mandibular set back: (cont’d.)
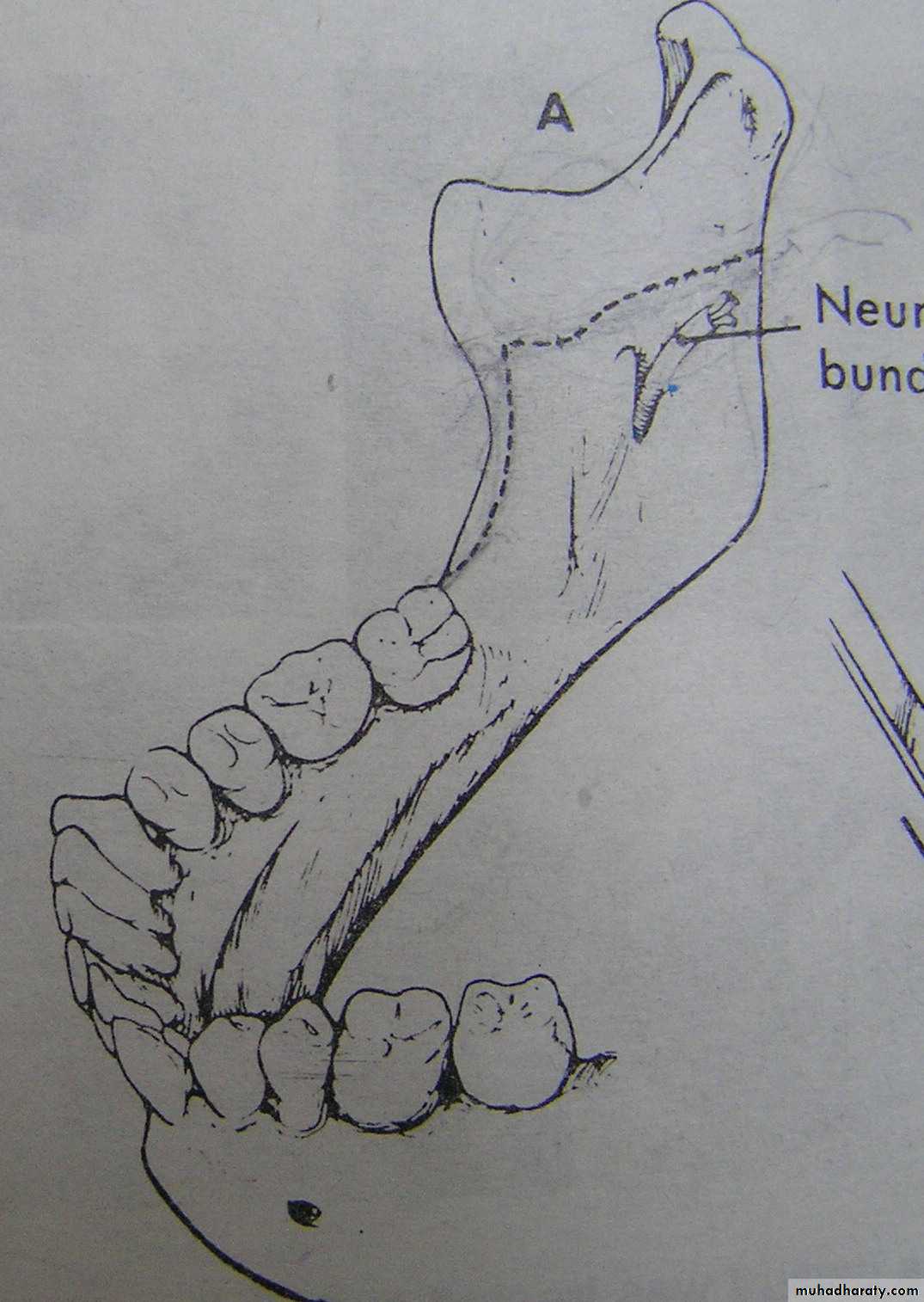
2.The Trans Oral Vertical Obliqueramus osteotomy (TORVO)
(limited to the reduction of
mandibular prognathism.)
Full thickness overlapping segments
Less likely to produce neurosensory changes
Jaws immobilization is necessary
Difficult control of the condyles
Correction Of Vertical Relationships
Maxillary Surgery:
Correction of skeletal open bite
(long face) deformity by:
Le Fort I down fracture of the maxilla with
superior repositioning of the maxilla (maxillaryimpaction) after removal of bone from the lateral
wall of the nose, sinus and nasal septum.
Correction Of Skeletal Open Bite (cont’d.)
Long- face problems are best treated by intrusion of the maxilla leading to
Mandibular rotation around the condyle (autorotation)
Reduction of mandibular plane angle
Shortening of the face
Closure of the open bite
Correction of Skeletal Open Bite
Correction Of The Vertical Relationships (cont’d.)
Mandibular Surgery1. Surgery to reduce mandibular plane angle
and close the open bite by rotating themandible down posteriorly and up anteriorly
is highly unstable due to:
a. Lengthening the ramus and stretching
the muscles of the pterygomandibular
sling( masseter, medial ptyregoid)
b. Lack of neuromuscular adaptation in
these powerful muscles.
Vertical maxillary excess
2- “Skeletal deep bite” or patients with a
“short face” problem (seen in Cl. II div.2cases) are characterized by a long
mandibular ramus, square gonial angle,
and short nose-chin distance.
Short - face problems are best treated by mandibular ramus surgery that allows the mandible to move downward only at the chin.
This will lead to:
increase in the mandibular plane angle
by shortening of the ramus
opening of the gonial angle
Short Face Problems Treated by Maxillary Surgery
Le Fort I down fracture of the maxilla to increase face height is not stable,therefore not used.
Correction Of Transverse Relationships
Expansion & narrowing of the dental arches
It is possible to move the maxillary segments both away from and toward the midline with relative ease and stability.
Correction Of Transverse Relationships ( cont’d. )
Rapid palatal expansion
Not feasible in adults, because
of the increasing resistance of
the midpalatal & lateral maxillary
sutures.
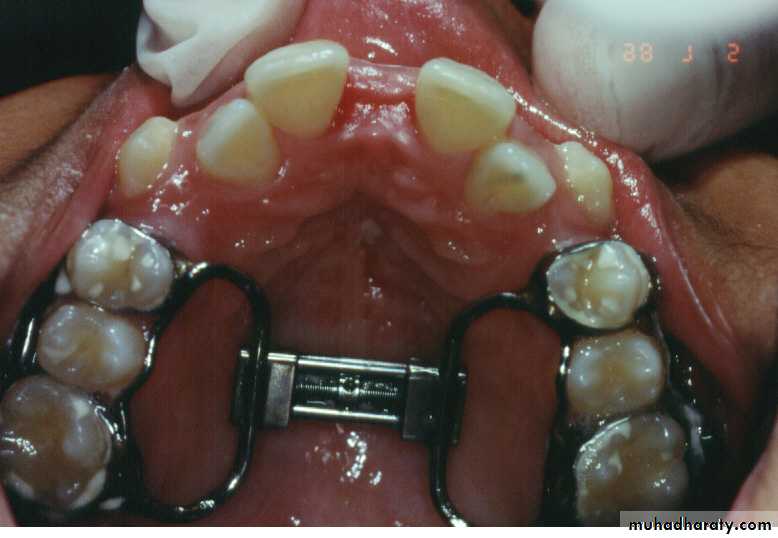
Correction Of Transverse Relationships
• Surgically-assisted palatal expansion
• to reduce the resistance of the• segments include:
• lateral antral wall. Mid
• palatal corticotomy.
• Corticotomies in the midline or
• Two para-midline vertical cuts
4. The jackscrew ( RPE ) is cemented before the surgery.
5. Activated after the bone cuts are made to continue for 10 -14 days followed by a period of stabilization.
Corticotomy to hasten the orthodontic movements.
Asymmetry
Mandibular asymmetry often leadsto a secondary maxillary deformity
ex: More vertical mandibular growth
produces:
compensatory changes in maxillary
growth
tilt of the occlusal plane
Asymmetry
Mandibular deviation also leads tocompensatory changes in the mandibular alveolar process and the chin deviates more than the dental midline.
Surgical correction of asymmetry often requires a Le Fort I osteotomy + BSSO for Mandibular ramus correction.
Repositioning the chin may also be needed.
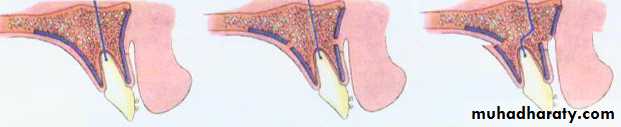
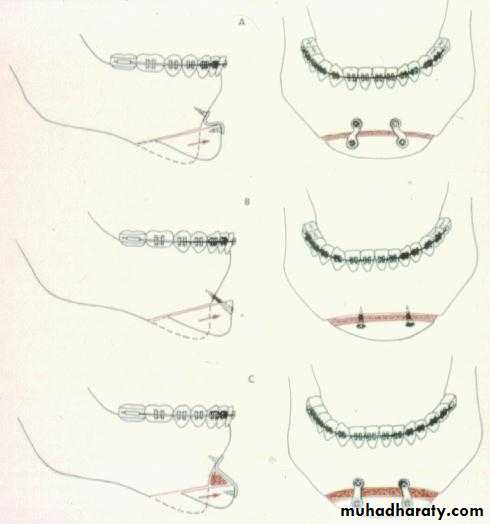
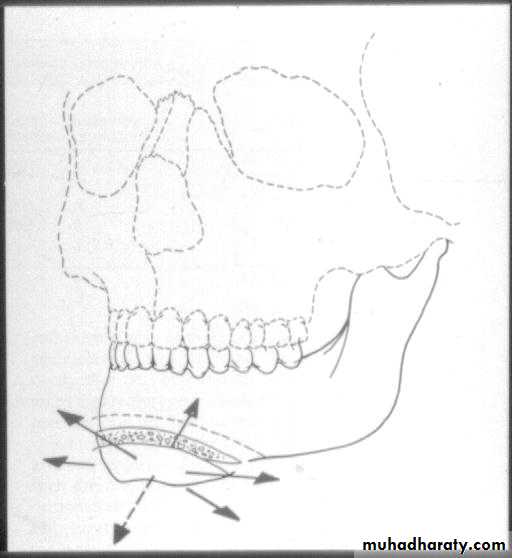
GENIOPLASTY
Is an osteotomy to free a wedge-shaped portion of the symphysis and inferior border that remains pedicled on the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles.GENIOPLASTY
Advanced (advancement genioplasty).Moved backward (reduction genioplasty).
Shifted sideways to correct asymmetry.
Down-grafted to increase lower face height.
By splitting the segment vertically, the wedge can be flared or compressed.
This segment can be:
Timing and Sequencing of Surgical Treatment
General rules:
Orthognathic surgery should be
delayed until growth is completed.Orthognathic surgery can be considered
earlier in growth deficiencies
TIMING OF TREATMENT
• Actively growing patients with mandibular prognathism can be expected to outgrow their correction. “Relapse`’• 2. Psychosocial problems may justify early surgery to correct prognathism, however retreatment may be needed
• 3. The Hand-wrist films to determine bone age are not accurate for planning the exact Timing of Surgery.
TIMING OF TREATMENT
• The best method is serial cephalometric tracings, until good documentations that the adult deceleration of growth has occurred.Diagnostic set-up
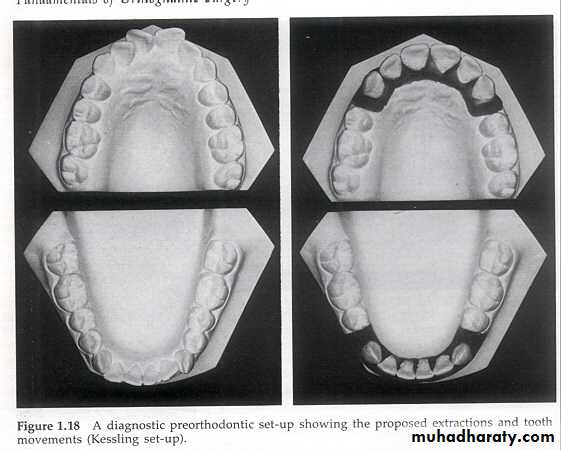
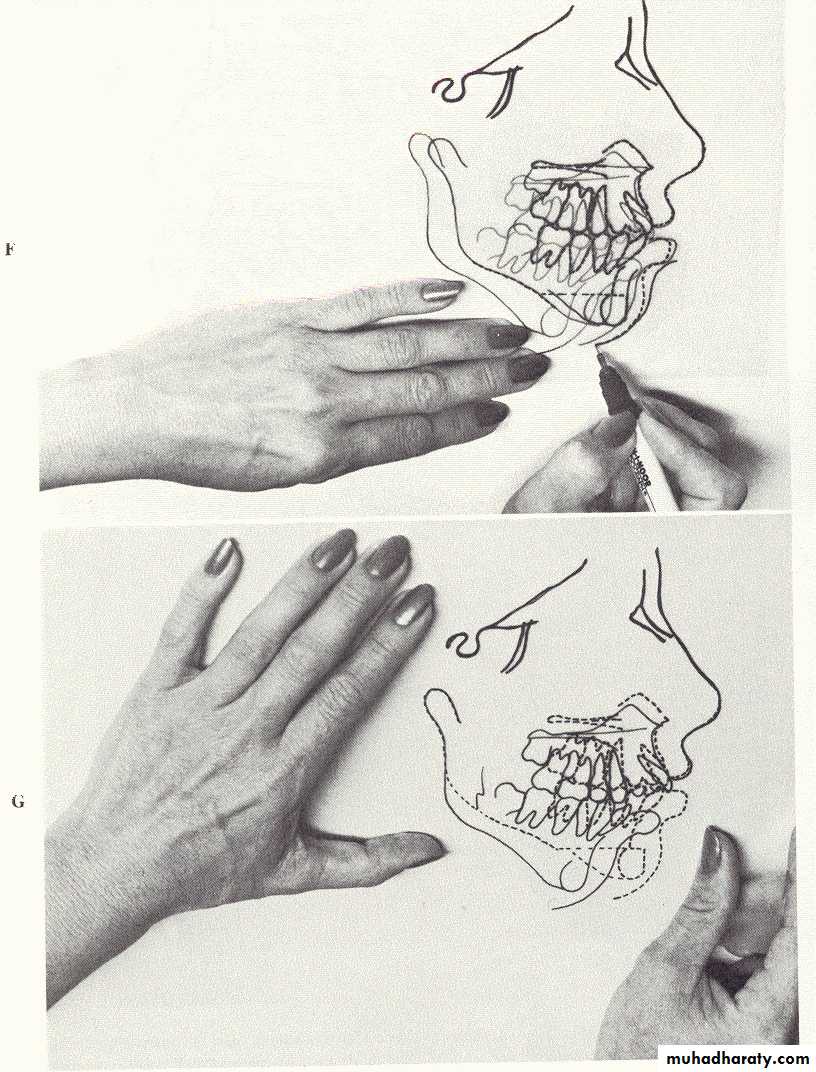
A diagnostic set up is employed to be sure that it will be possible to get the teeth to fit together if a given orthodontic treatment plan is employed.Diagnostic pre-orthodontic set-up showing the proposed extractions and tooth movements.
Sequence of an Orthodontic/Surgical PlanI. Sequence:
1. Orthodontics to correct alignment
and inclinations of teeth (no attempt
for skeletal correction.)
Note: Malocclusion may temporarily
look worse.
2. Surgery to reposition the jaws.
3. Finishing Orthodontics.Objectives Of Pre-Surgical Orthodontics
1.Place teeth in their properrelationships to mandible or maxilla.
i.e. decompensation of teeth
2. Level both arches independently:
It is sometimes necessary to level
teeth in segments, independently.
Pre-Treatment Evaluation:
Records Needed:
1. Dental casts
2. Dental radiographs3. Facial photographs (frontal and
profile)
4. Cephalometric radiographs
Check List for Treatment Planning
A-P relationships maxillary deficiency/protrusionmand prognathism/deficiency
amount of deficiency
Vertical relationships open bite
deep bite
Transverse relationships crossbites
before surgery expansion
surgically assisted expansion
during surgery
{
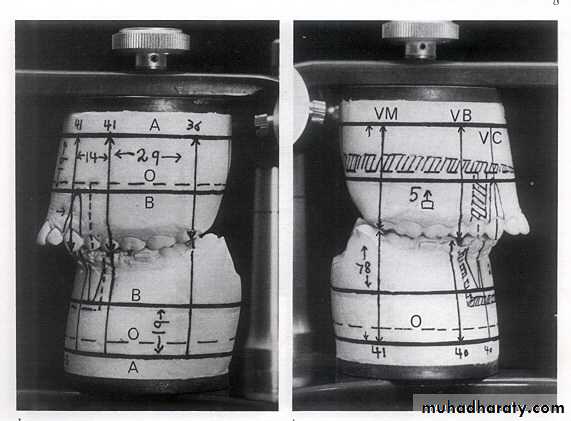
Mounting of the maxillary model
Models with completed skeletal and dental reference lines
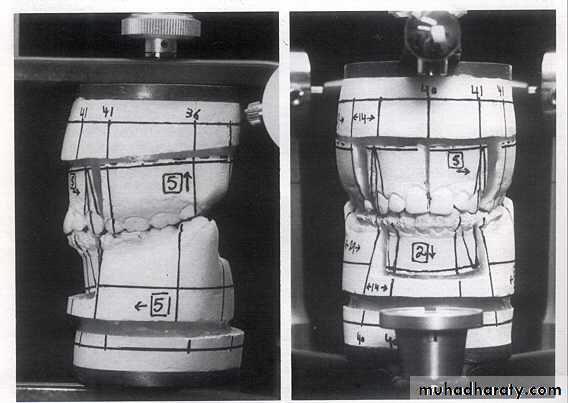
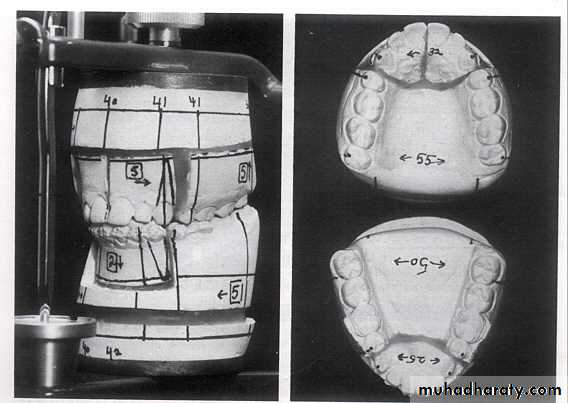
Model (Mock) surgery
Interrupted line is the proposed osteotomy site.
osteotomy linesAnterior view: models showing the upper midline split to widen the intercanine width and the lower anterior set-down.
The splint:A acrylic splint is made in the laboratory to transfer the model relationship to the patient during surgery