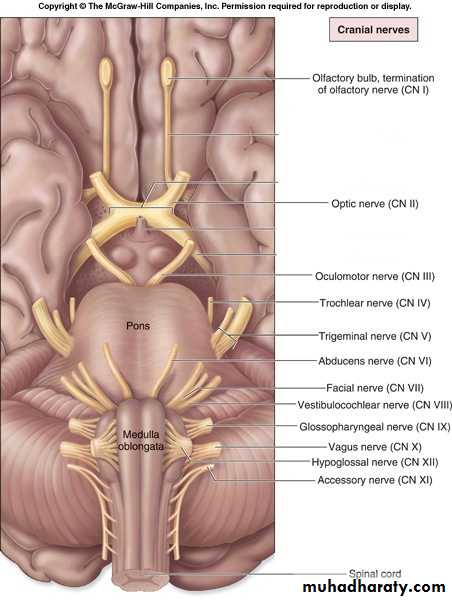
Cranial Nerves Dr.Haythem Ali Alsayigh
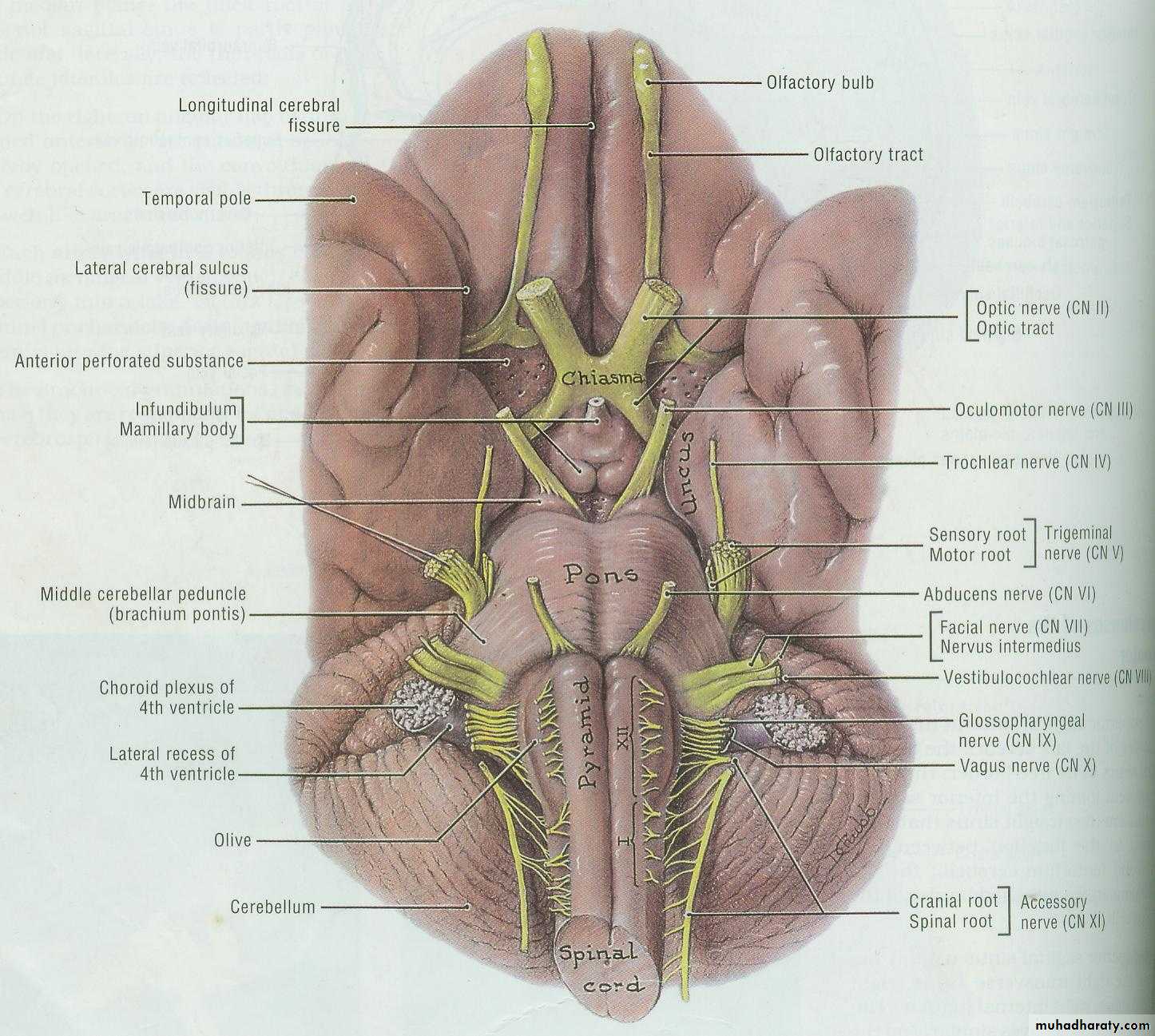
12 pairs of cranial nervesIII to XII attached to brain stem
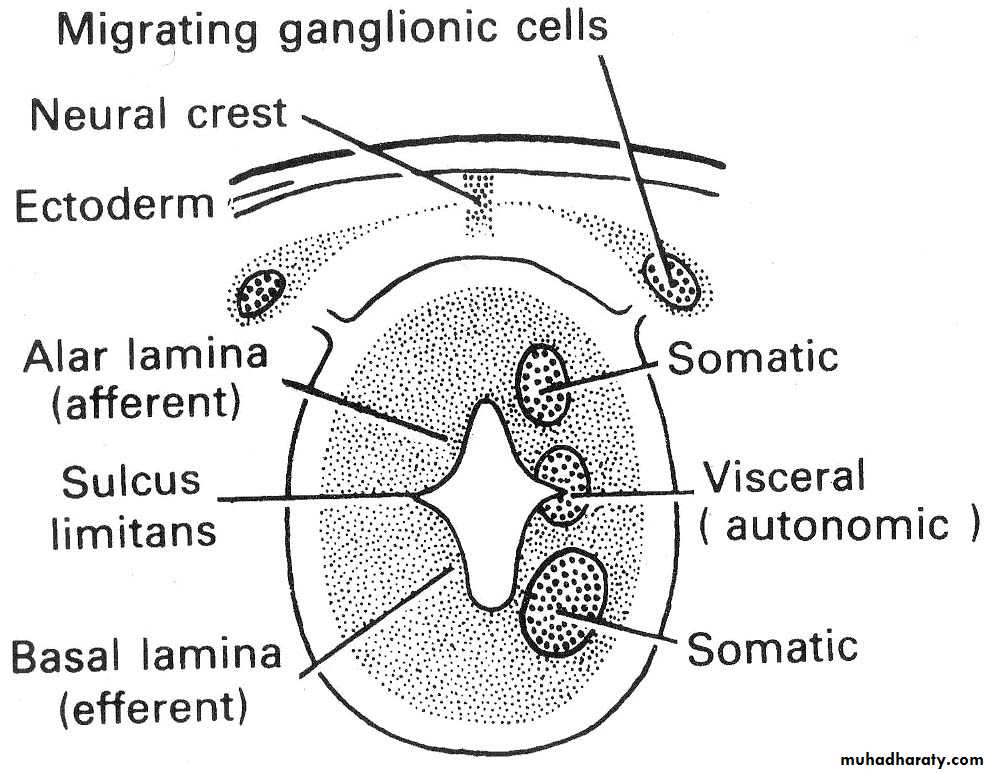
Their cell bodies form nuclei in the brain stemFirst cell body of sensory nerves lie out side CNS
(form ganglia)Summary of cranial nerves
• Aspects to study• Position of nucleus
• Emerging point from brain stem
• Intracranial course
• Point of exit from the cranial cavity
• Extracranial course
• Distribution
• Few terms: Somatic, branchial and visceral
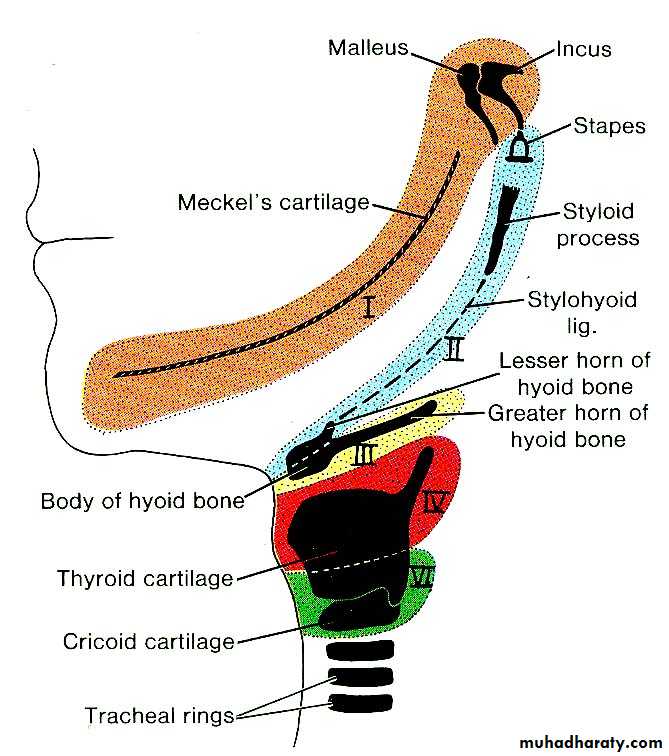
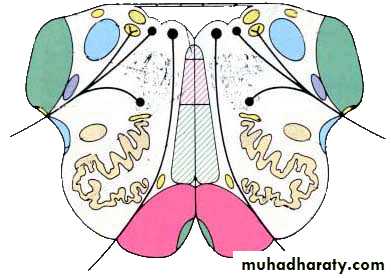
Branchial (Pharyngeal) Arches
Core of mesodermal tissue covered by ectoderm and endodermEach of the arch will have its own bone/cartilage, muscles, nerve and artery
endoderm
ectoderm• Branchial
Premaxilla, maxilla, zygomatic bone, part of temporal bone and mandible
Mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve (V)
Facial nerve (VII)
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Superior laryngeal branch of vagus nerve (X)
Recurrent laryngeal branch of vagus nerve (X)
• Visceral
In relation to internal organsHeart
Lung
Intestines
………………
……………..
• Few hints
Nerve ANerve B
Posterior horn
Lateral hornAnterior horn
Motor
SensoryMotor
SensoryPosterior
Spinal cord (thoracic or lumbar)Somatic sensory
Visceral sensory
Visceral motor
Somatic motor
SM
VM
VS
BM
SS
Brain stem
SpS
GSS
• Types of sensations
Visceral sensorySomatic sensory
General Visceral sensory
pain, temperature, touch, viration
position sense
Special Visceral sensory
taste
General Somatic sensory
pain, temperature, touch, vibration
position sense
Special Somatic sensory
hearing
SM
VM
VS
BM
SS
SpS
SM
VM
VS
BM
SpS
SS
SM
VS
GSS
SS
III
IV
VI
XII
BM
V
VII
IX
X
XI
VM
III
VII
IX
X
VII
IX
X
V
VII
IX
X
VIII
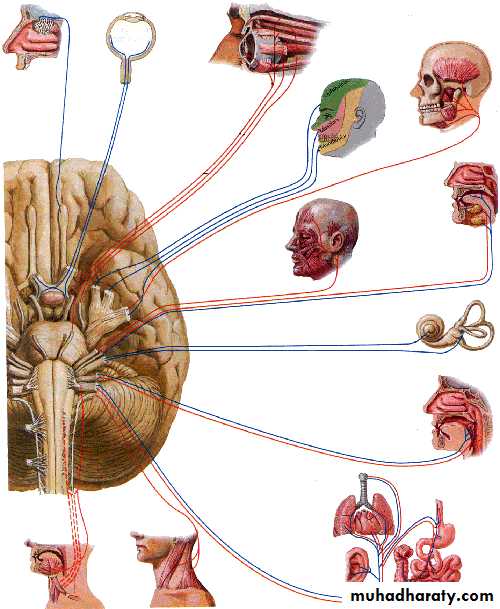
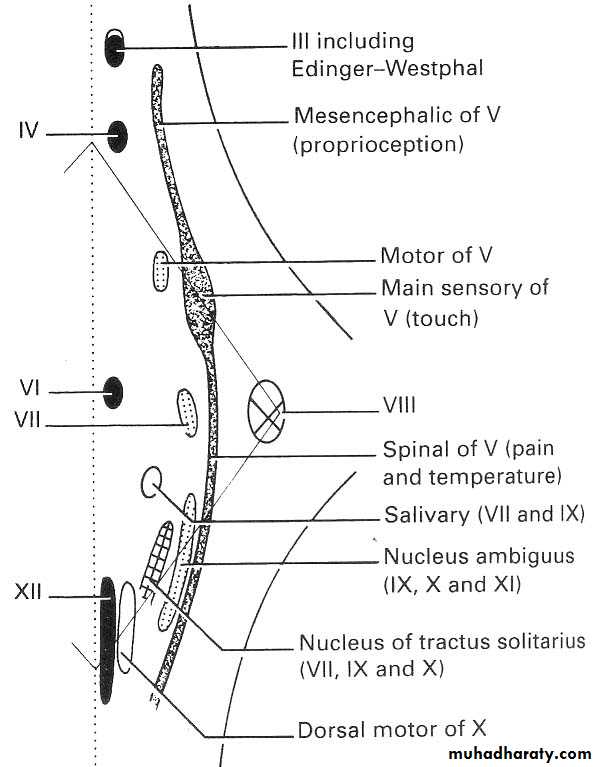
Functional components of cranial nerves
Somatic MotorMuscles of the orbit (III, IV, VI)
Muscles of tongue (XII)III
IV
VI
XII
Branchial Motor
Muscles of mastication (V)Facial muscles (VII)
Pharyngeal and laryngeal muscles (Nucleus ambiguus via IX, X, XI nerves)
Visceral Motor
Edinger Westphal nucleus(accessory oculomotor)
Salivary nuclei (NI part of VII, IX)
Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus(for cardiac muscles, smooth muscles of alimentary tract)
Sensory
Consists of single nuclei for visceral and somatic sensoryVisceral sensory with taste
Nucleus of tractus solitarious which receives taste fibres from the tongue through VII, IX
and sensory from heart, lungs and other viscera through X
General somatic sensory
Sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve extending from the midbrain to the cervical spinal cordSpecial somatic sensory
Hearing via VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve)SM
VM
VS
BM
GSS
SS
V
VII
IX
X
XI
III
IV
VI
XII
III
VII
IX
X
VII
IX
X
V
VII
IX
X
VIII
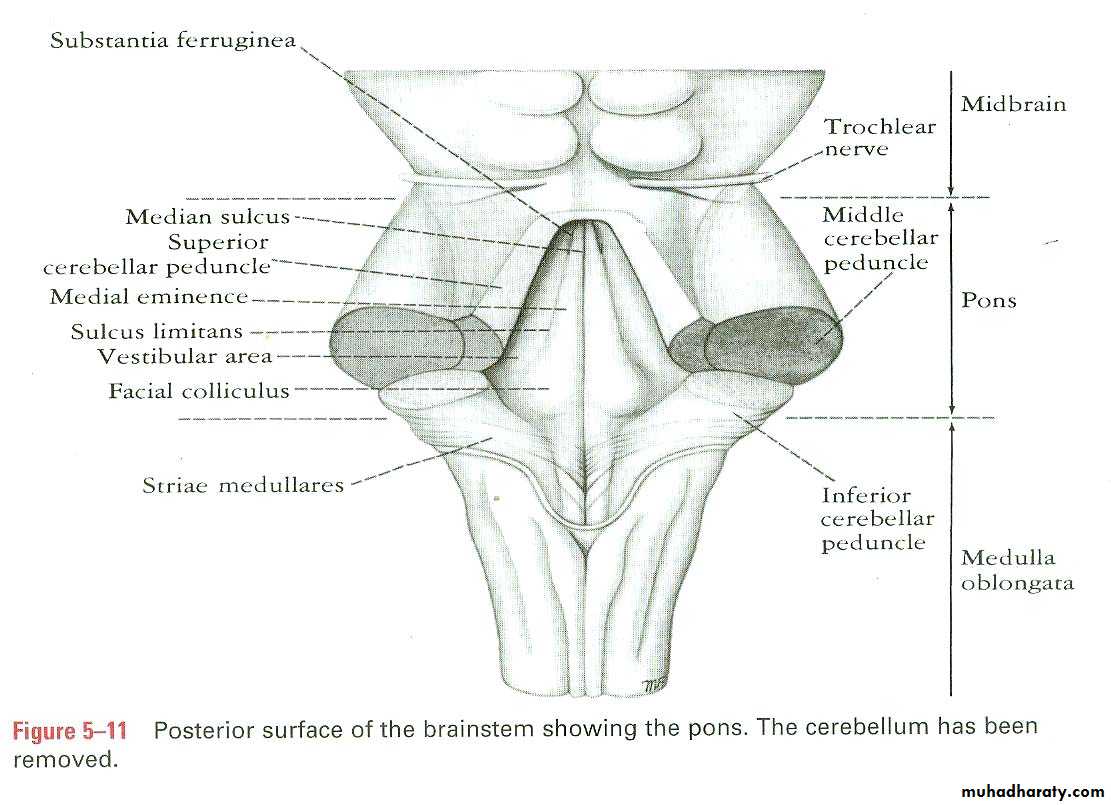
Intracranial course and exitNames of cranial nerves
Ⅰ Olfactory nerveⅡ Optic nerve
Ⅲ Oculomotor nerve
Ⅳ Trochlear nerve
Ⅴ Trigeminal nerve
Ⅵ Abducent nerve
Ⅶ Facial nerve
Ⅷ Vestibulocochlear nerve
Ⅸ Glossopharyngeal nerve
Ⅹ Vagus nerve
Ⅺ Accessory nerve
Ⅻ Hypoglossal nerve
Functional components
General somatic afferent fibers (GSA): transmit exteroceptive and proprioceptive impulses from head and face to somatic sensory nucleiSpecial somatic afferent fibers (SSA): transmit sensory impulses from special sense organs of vision, equilibrium and hearing to the brain
General visceral afferent fibers (GVA): transmit interoceptive impulses from the viscera to the visceral sensory nuclei
Special visceral afferent fibers (SVA): transmit sensory impulses from special sense organs of smell and taste to the brain
General somatic efferent fibers (GSE): innervate skeletal muscles of eye and tongue
Special visceral efferent fibers (SVE): transmit motor impulses from the brain to skeletal muscles derived from brachial (gill) arches of embryo. These include the muscles of mastication, facial expression and swallowing
General visceral efferent fibers (GVE): transmit motor impulses from the general visceral motor nuclei and relayed in parasympathetic ganglions. The postganglionic fibers supply cardiac muscles,smooth muscles and glands
Classification of cranial nerves
Sensory cranial nerves: contain only afferent (sensory) fibersⅠOlfactory nerve
ⅡOptic nerve
Ⅷ Vestibulocochlear nerve
Motor cranial nerves: contain only efferent (motor) fibers
Ⅲ Oculomotor nerve
Ⅳ Trochlear nerve
ⅥAbducent nerve
Ⅺ Accessory nerv
Ⅻ Hypoglossal nerve
Mixed nerves: contain both sensory and motor fibers---
ⅤTrigeminal nerve,
Ⅶ Facial nerve,
ⅨGlossopharyngeal nerve
ⅩVagus nerve
Sensory cranial nerves
• N.
• Location of cell body and axon categories
• Cranial exit
• Terminal nuclei
• Main action
• Ⅰ
• Olfactory cells (SVA)
• Cribrifom
• foramina
• Olfactory bulb
• Smell
• Ⅱ
• Ganglion cells (SSA)
• Optic canal
• Lateral geniculate body
• Vision
• Ⅷ
• Vestibular ganglion(SSA)
• Internal acoustic meatus
• Vestibular nuclei
• Equilibrium
• Cochlear ganglion (SSA)
• Cochlear nuclei
• HearingMotor cranial nerves
• N.• Nucleus of origin and axon categories
• Cranial exit
• Main action
• Ⅲ
• Nucleus of oculomotor (GSE)
• Superior orbital fissure
• Motot to superior, inferior and medial recti; inferior obliquus; levator palpebrae superioris
• Accessory nucleus of oculomotor (GVE)
• Parasympathetic to sphincter pupillea and ciliary muscl• Ⅳ
• Nucleus of trochlear nerve (GSE)
• Superior orbital fissure
• Motor to superior obliquus
• Ⅵ
• Nucleus of abducent nerve (GSE)
• Superior orbital fissure
• Motor to lateral rectus
• Ⅺ
• Nucleus of accessory nerve (SVE)
• Jugular foramen
• Motor to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
• Ⅻ
• Nucleus of hypoglossal nerve( GSE)
• Hypoglossal canal
• Motot to muscles of tongue
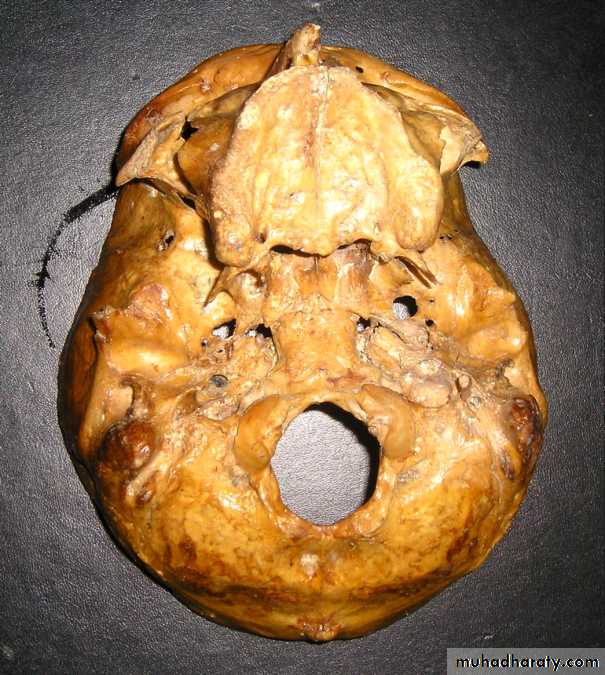
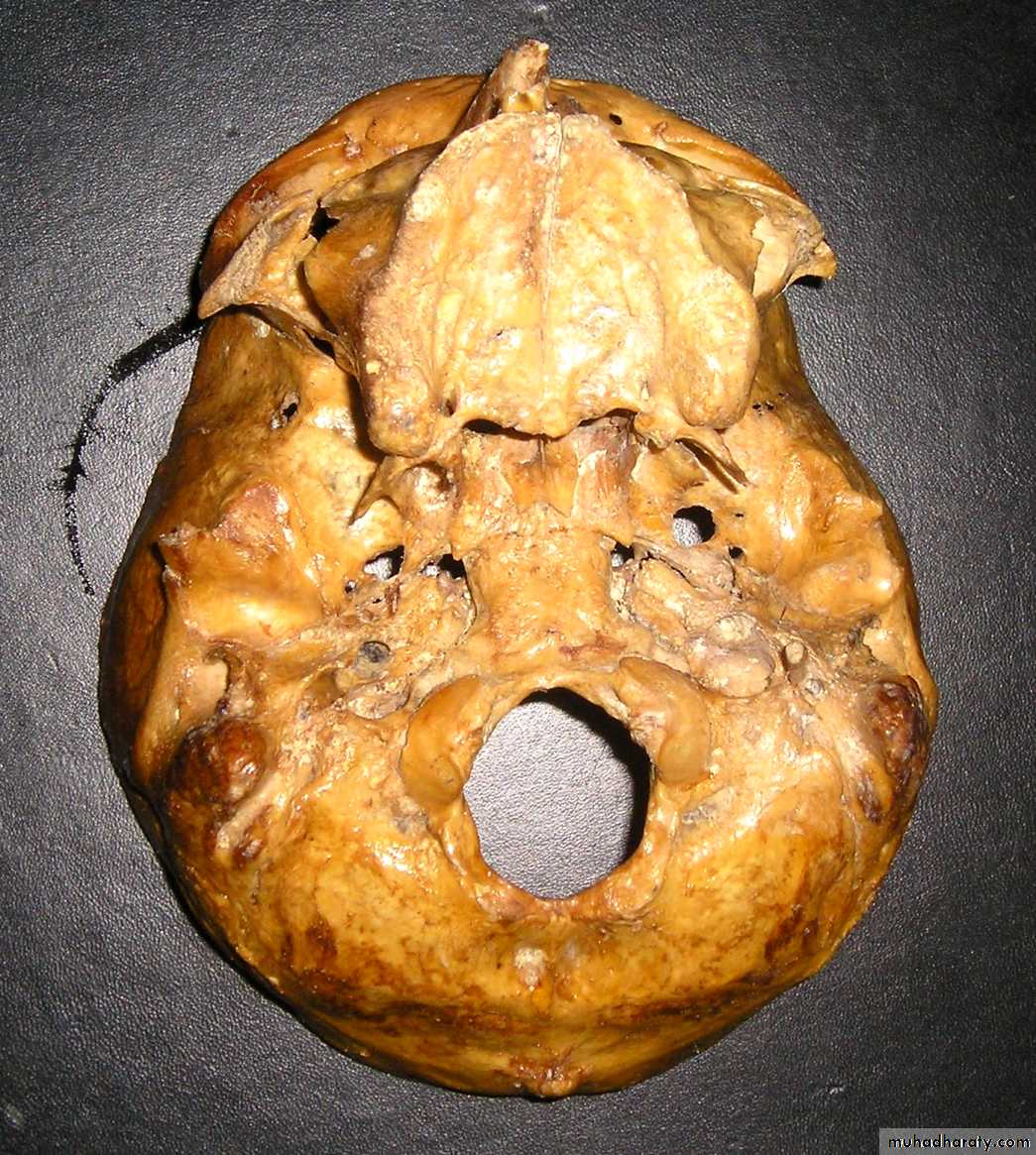
Superior orbital fissure
(III, IV, V1, VI)Foramen rotundum
(V2)
Foramen ovale
(V3)
Foramen spinosum
Foramen lacerum
Internal acoustic meatus
(VII, VIII)
Jugular foramen
(IX, X, XI)
Hypoglossal canal
(XII)
Optic canal
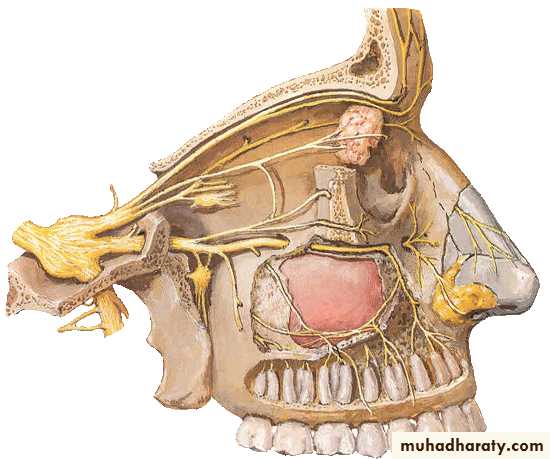
(II)Olfactory Nerve (I)
Olfactory bulb
Olfactory tractAnterior perforated
substanceUncus
Bypass thalamus and goes directly into the taste areaNerve filaments
Cribriform plate of
ethmoid boneOlfactory nerve
Olfactory mucosa (SVA)→ Cribriform foramina → Olfactory bulbOptic Nerve (II)
T
N
T
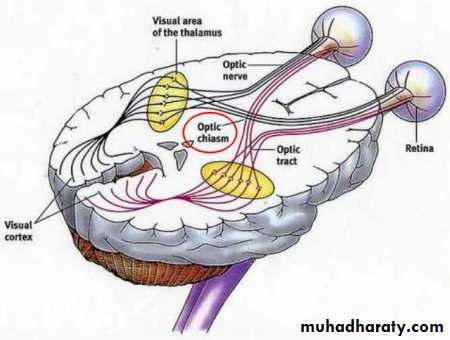
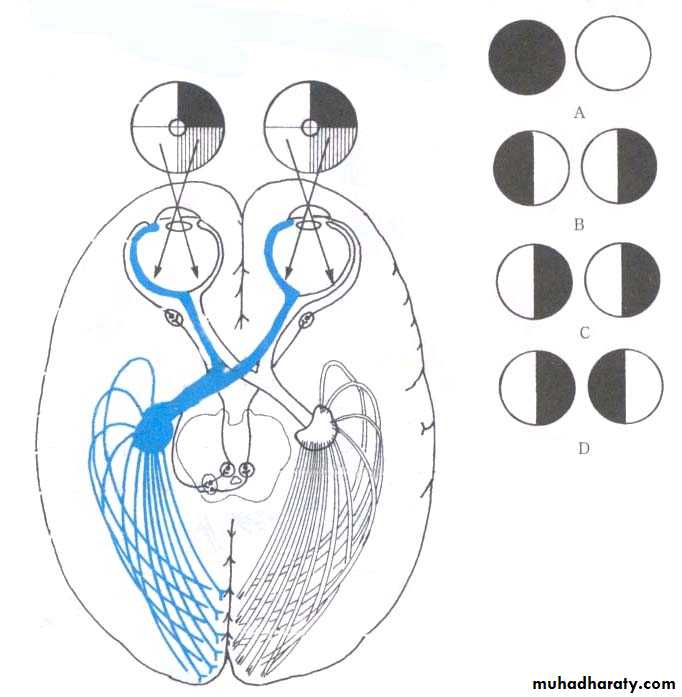
Optic Nerve (II)
Optic nerveOptic chiasma
Optic tractSuperior colliculus
(body reflexes)
Pretectal nucleus
(pupillary reflexes)
Lateral geniculate body
of thalamusInternal
capsule
Optic
radiation
Optic nerve
Ganglion cell (SSA) → Optic canal → Lateral geniculate body
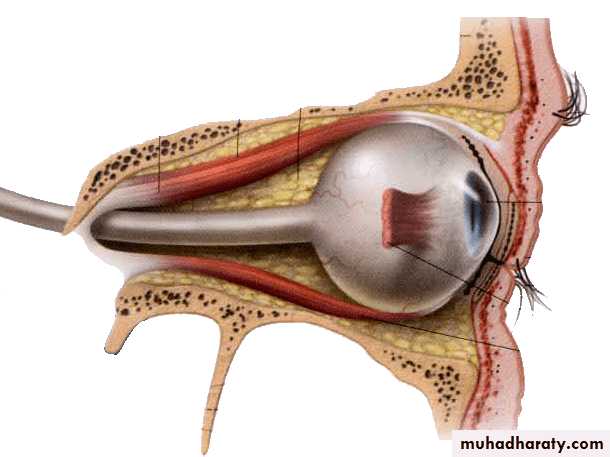
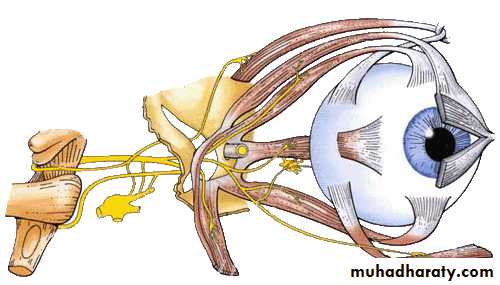
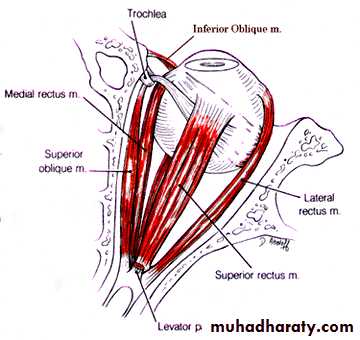
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Somatic motor nucleusVisceral motor nucleus
(Edinger westphal nucleus)
Nerve emerges from ventral aspect of midbrain
travel’s in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus
Oculomotor Nerve… cont.
Levator palpabrae superioris
Dilator pupillae
Superior rectusMedial rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique
Ciliary muscle
Sphincter pupillaeCiliary ganglion
Superior division
Inferior divisionSympathetic from
Internal carotid plexus
Parasympathetic from
EW nucleusOculomotor nerve
ComponentsGeneral somatic efferent fibers (GSE)
General visceral efferent fibers (GVE)
Main action-supplies
Superior, inferior and medial recti; inferior obliquus; levator palpebrae superioris
Sphincter pupillea and ciliary muscle
Ciliary ganglion: lies between optic nerve and lateral rectus
Oculomotor nerve
Abducent nerve
Accessory nerveTrochlear Nerve (IV)
Somatic motor nucleusEmerges from the dorsal aspect of midbrain
Travels in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus
Supplies the superior oblique muscle
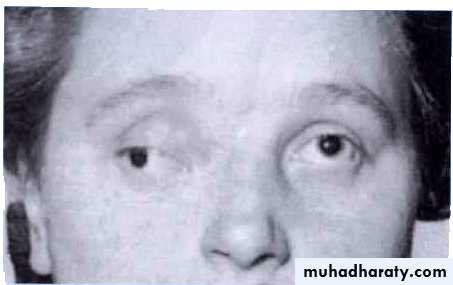
Abducens Nerve (VI)
Somatic motor nucleus
Nucleus lies in lower pons near midline
Emerge between pons and pyramid of medulla
Travels through the cavernous sinus
Supply the lateral rectus muscle
Oculamotor paralysis
Abducent nerve injuryOculomotor N (III)
Ventralmidbrain
Lateral wall
Cavernous S
Divide
Sup. & Inf.
divisions
Sup/infraorbital fissure
Trochlear N (IV)
Dorsal
midbrain
Lateral wall
Cavernous S
Superior orbital fissure
Abducent N (VI)
BetweenPons & pyramid of medulla
within
Cavernous S
Superior orbital fissure
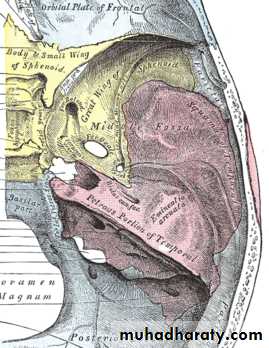
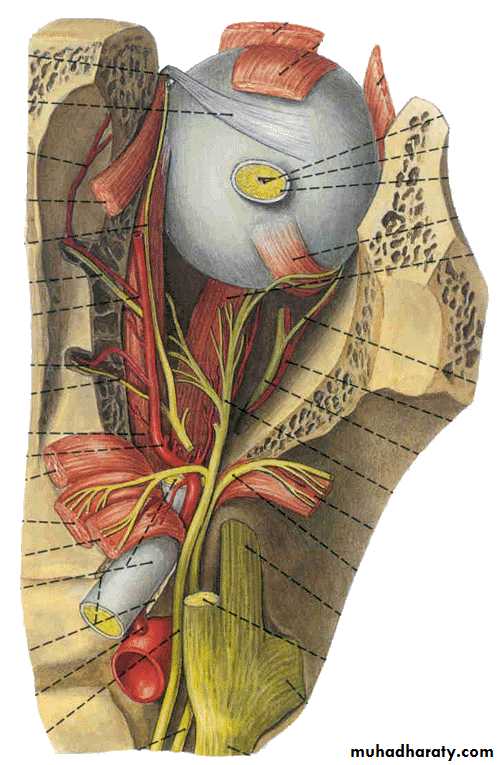
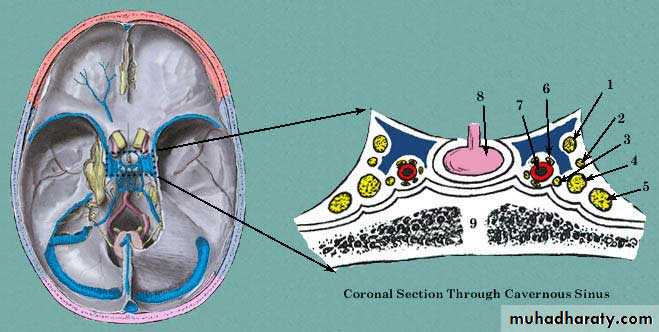
Cavernous sinus
1- Oculomotor N
2- Trochlear N3- Abducent N
4- Ophthalmic branch of TN
5- Maxillary branch of TN
6- Sympathetic plexus of N
7- Internal carotid A
8- Pituitary gland
LR6(SO4)3
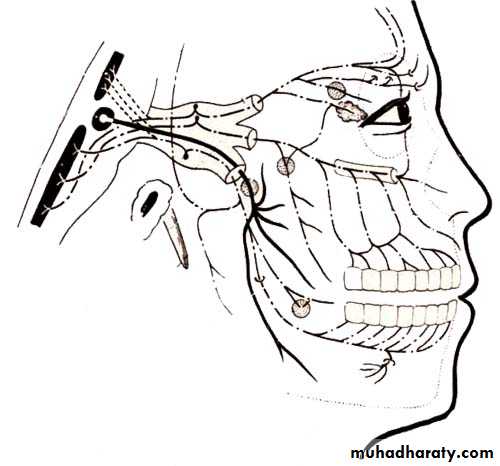
Trigeminal nerve (V)Branchial motor nucleus
Somatic sensory nucleus
Emerge from the ventral aspect of pons
Sensory and motor roots emerge separately
Trigeminal nerve… cont.
Cell bodies of 1st orderSA fibres
Trigeminal ganglion
Somatic sensory
nucleusBranchial motor
nucleus
Foramen ovale
Ophthalmic division
Maxillary divisionLat. Wall of
cavernoussinous
Mandibulardivision
Mandibularnerve
(mixed)Trigeminal nerve
Components of fibersSVE fibers: originate from motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve, and supply masticatory muscles
GSA fibers: transmit facial sensation to sensory nuclei of trigeminal nerve, the GSA fibers have their cell bodies in trigeminal ganglion, which lies on the apex of petrous part of temporal bone
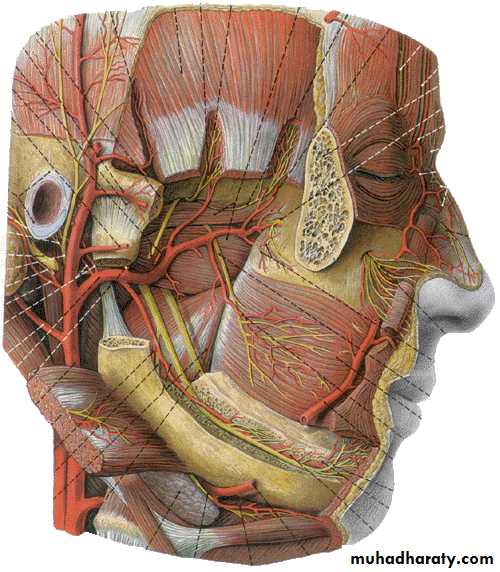
Branches
Ophthalmic nerve (Ⅴ1, sensory) leave the skull through the superior orbital fissure, to enter orbital cavityBranches
Frontal nerve
Supratrochlear nerve
Supraorbital nerve Lacrimal nerve Nasociliary nerve
Distribution:
Sensation from cerebral dura materVisual organ
Mucosa of nose
Skin above the eye and back of nose
Maxillary nerve
(Ⅴ2, sensory)Leave skull through foramen rotundum
Branches
Infraorbital nerve
Zygomatic nerve
Superior alveolar nerve
Pterygopalatine nerve
Distribution:
Sensation from cerebral dura materMaxillary teeth
Mucosa of nose and mouth
Skin between eye and mouth
Mandibular nerve (Ⅴ3, mixed)
Leave the skull through the foramen ovale to enter the infratemporal fossaBranches
Auriculotemporal nerve Buccal nerve
Lingual nerve
Inferior alveolar nerve
Nerve of masticatory muscles
Distribution:
Sensation from cerebral dura materTeeth and gum of lower jaw
Mucosa of floor of mouth
Anterior 2/3 of tongue
Skin of auricular and temporal regions and below the mouth
Motor to masticatory muscles, mylohyoid, and anterior belly of digastric
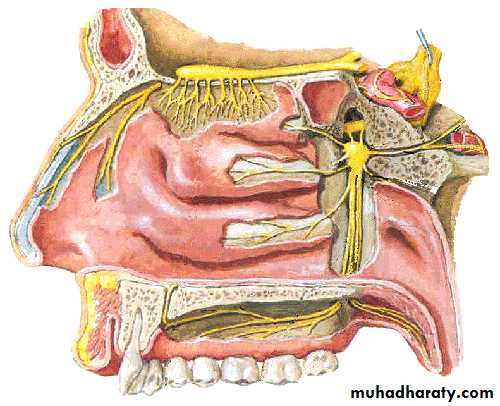
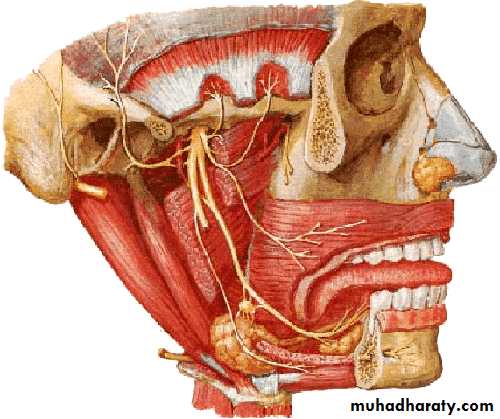
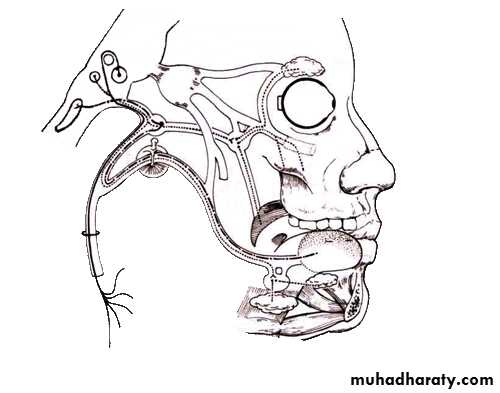
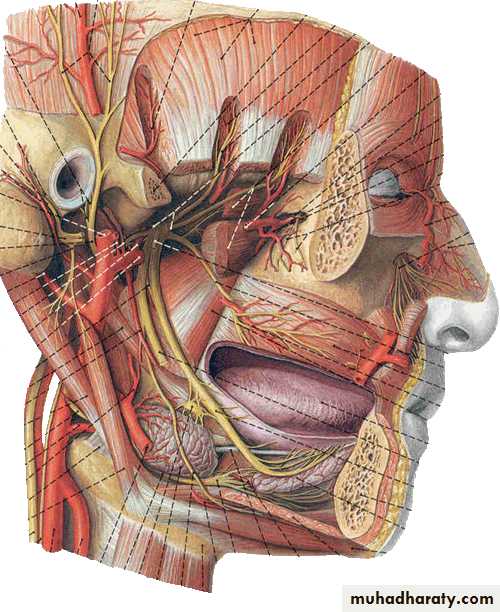
Facial Nerve (VII)
Branchial motor nucleusVisceral motor nucleus
(Superior salivary nucleus)Taste sensory nucleus (Tractus solitarius)
Main facial nerve and the nervous intermedius parts emerge from the cerebellopontine angle
Geniculate ganglion
(taste 1st order cell bodies)Nucleus of
Tractus solitariousChorda tympani
nerve
Taste from anterior tongue
Nervousintermedius
Facial Nerve…cont.
Branchial motor
nucleus
Nerve to stapedius
Stylomastoid foramen
Pure branchial motor facial nerveSupply muscles of facial expression
Ear drum
VE to submandibular gland and glands on the mouth floorGreater petrosal nerve
Sup. salivary
nucleusInternal acoustic meatus
Facial nerve (Ⅶ)Components of fibers
SVE fibers originate from nucleus of facial nerve, and supply facial muscles
GVE fibers derived from superior salivatory nucleus and relayed in pterygopalatine ganglion and submandibular ganglion. The postganglionic fibers supply lacrimal, submandibular and sublingual glands
SVA fiber from taste buds of anterior two-thirds of tongue which cell bodies are in the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve and end by synapsing with cells of nucleus of solitary tract
GSA fibers from skin of external ear
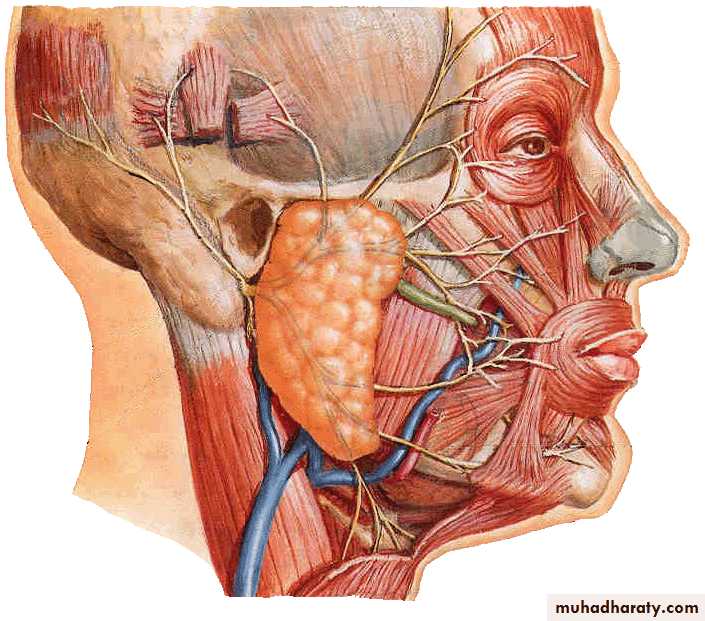
Course: leaves skull through internal acoustic meatus, facial canal and stylomastoid foramen, it then enters parotid gland where it divides into five branches which supply facial muscles
Branches within the facial canal
Chorda tympani : joins lingual branch of mandibular nerveTo taste buds on anterior two-thirds of tongue
Relayed in submandibular ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply submandibular and sublingual glands
Greater petrosal nerve: GVE fibers pass to pterygopalatine ganglion and there relayed through the zygomatic and lacrimal nerves to lacrimal gland
Stapedial nerve : to stapedius
Branches outside of facial canal
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Marginal mandibular
Cervical
Pterygopalatine ganglion: lies in pterygopalatine fossa under maxillary nerve
Submandibular ganglion : lies between lingual nerve and submandibular glandInjury to the facial nerve
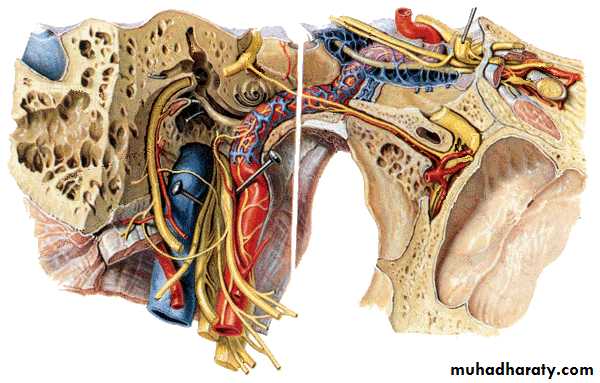
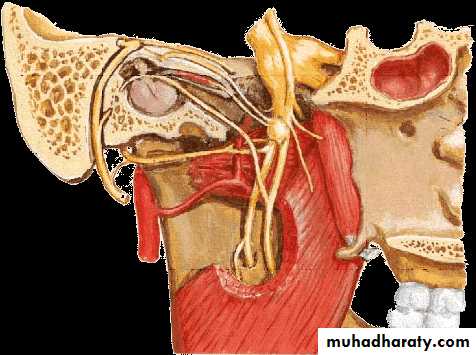
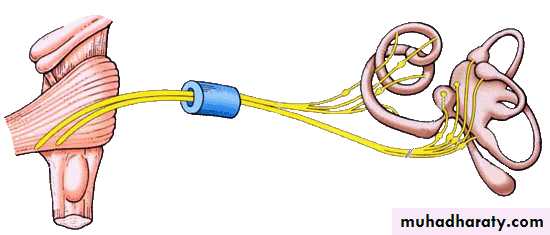
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
Cochlear nerve
Vestibular nerve
Hair cells of spiral organ
Hair cells of utricle, saccule and semilunar canals
Spiral ganglion of cochlea
Vestibular ganglionInternal acoustic meatus
Cerebellopontine angleCochlear nuclei
in ponsVestibular nuclei
in medullaVestibulocochlear nerve
Vestibular ganglion(SSA) ↘ ↗ Vestibular nucleiInternal acoustic meatus
Cochlear ganglion (SSA) ↗ ↘ Cochlear nuclei
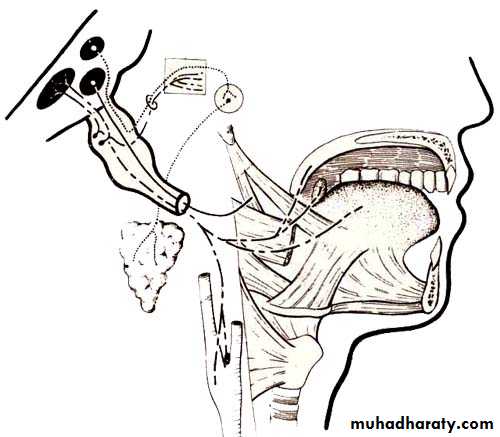
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Branchial motor nucleus (Nucleus ambiguus)supplies stylopharyngeus muscle
Parasympathetic nucleus (Inferior salivary nucleus)
supplies parotid gland
Sensory nuclei
GSS from posterior tongue goes to sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve
Taste from the posterior tongue goes to the tractus solitarius
VS from baroreceptors go to nucleus of tractus solitarius
Glossopharyngeal nerve (Ⅸ)
Components of fibersSVE fibers: originate from nucleus ambiguus, and supply stylopharygeus
GVE fibers: arise from inferior salivatory nucleus and ralyed in otic ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply parotid gland
SVA fibers: arise from the cells of inferior ganglion, the central processes of these cells terminate in nucleus of solitary tract, the peripheral processes supply the taste buds on posterior third of tongue
GVA fibers: visceral sensation from mucosa of posterior third of tongue, pharynx, auditory tube and tympanic cavity, carotid sinus and glomus, and end by synapsing with cells of nucleus of solitary tract
GSA fibers: sensation from skin of posterior surface of auricle and
Course: leaves the skull via jugular foramen
BranchesLingual branches : to taste buds and mucosa of posterior third of tongue
Pharyngeal branches : take part in forming the pharyngeal plexus
Tympanic nerve : GVE fibers via tympanic and lesser petrosal nerves to otic ganglion, with postganglionic fibers via auriculotemporal (Ⅴ3) to parotid gland
Carotid sinus branch : innervations to both carotid sinus and glomus
Others: tonsillar and stylophayngeal branches
Otic ganglion : situated just below foramen ovale
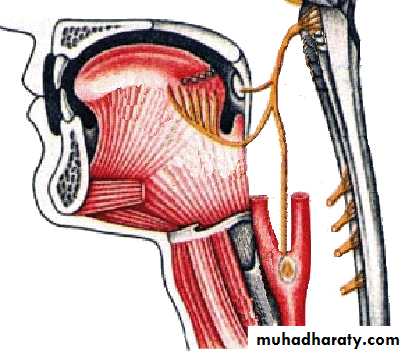
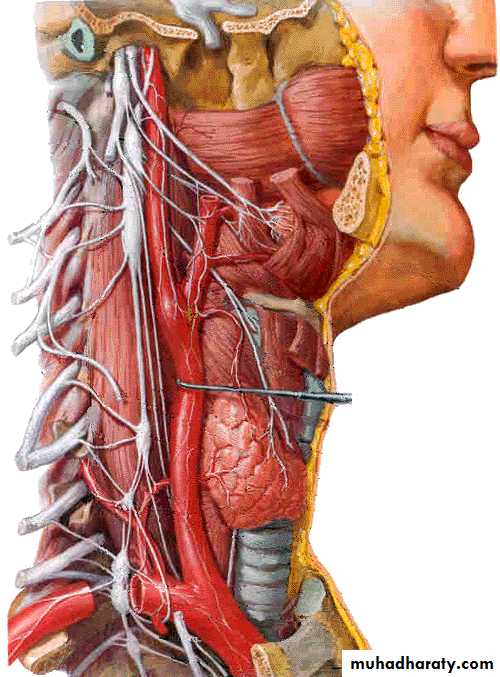
Vagus Nerve (X)
Branchial motor nucleus (Nucleus ambiguus)supplies pharyngeal constrictors
Visceral motor nucleus (Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus)
supplies muscles of heart, bronchi, oesophagus, stomach and intestines
Visceral sensory nucleus
VS from larynx, heart, lung… goes to nucleus of tractus solitarius
GSS goes to sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve
Vagus nerve (Ⅹ)
components of fibersGVE fibers: originate from dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve, synapse in parasympathetic ganglion, short postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscles, smooth muscles and glands of viscera
SVE fibers: originate from ambiguus, to muscles of pharynx and larynx
GVA fibers: carry impulse from viscera in neck, thoracic and abdominal cavity to nucleus of solitary tract
GSA fiber: sensation from auricle, external acoustic meatus and cerebral dura mater
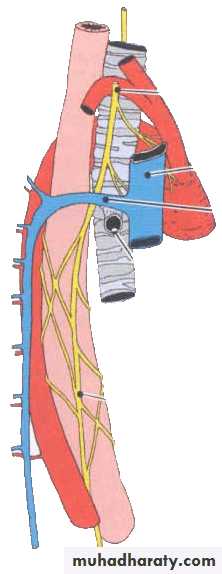
Course
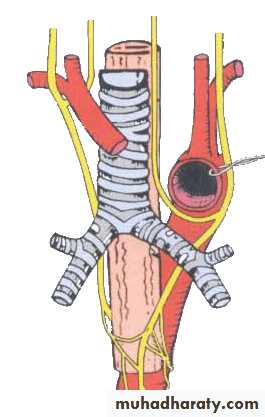
Exits the skull from jugular foramenDescends in the neck in carotid sheath between internal (or common) carotid artery and internal jugular vein
Right vagus nerve
Enter thoracic inlet on right side of trachea
Travels downward posterior to right brachiocephalic vein and superior vena cava
Passes posterior to right lung root
Forms posterior esophageal plexus
Forms posterior vagal trunk at esophageal hiatus where it leaves thorax and passes into abdominal cavity, then divides into posterior gastric and celiac branches
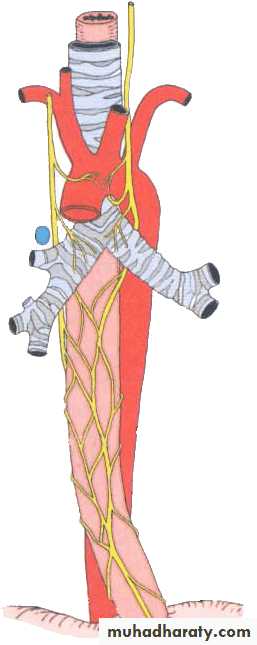
Left vagus nerve
Enter thoracic inlet between left common carotid and left subclavian arteries, posterior to left brachiocephalic veinCrosses aortic arch where left recurrent laryngeal nerve branches off
Passes posterior to left lung root
Forms anterior esophageal plexus
Forms anterior vagal trunk at esophageal hiatus where it leaves thorax and passes into abdominal cavity , then divides into anterior gastric and hepatic branches
Branches in neck
Superior laryngeal nerve: passes down side of pharynx and given rise toInternal branch, which pierces thyrohyoid membrane to innervates mucous membrane of larynx above fissure of glottis
External branch, which innervates cricothyroid
Cervical cardiac branches : descending to terminate in cardiac plexus
Others: auricular, pharyngeal and meningeal branches
Superior laryngeal nerve
External branchInternal branch
Branches in thoraxRecurrent laryngeal nerves
Right one hooks around right subclavian artery, left one hooks aortic arch
Both ascend in tracheo-esophageal groove
Nerves enter larynx posterior to cricothyroid joint, the nerve is now called inferior laryngeal nerve
Innervations: laryngeal mucosa below fissure of glottis , all laryngeal laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid
Bronchial and esophageal branches
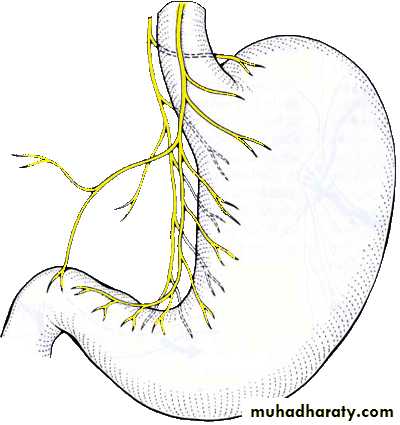
Branches in abdomen
Anterior and posterior gastric branchesRun close to lesser curvature and innervate anterior and posterior surfaces of stomach
As far as pyloric antrum to fan out into branches in a way like the digits of a crow’s foot to supply pyloric part
Hepatic branches: join hepatic plexus and then supply liver and gallbladder
Celiac branches: send branches to celiac plexus to be distributed with sympathetic fibers to liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, intestine as far as left colic flexure
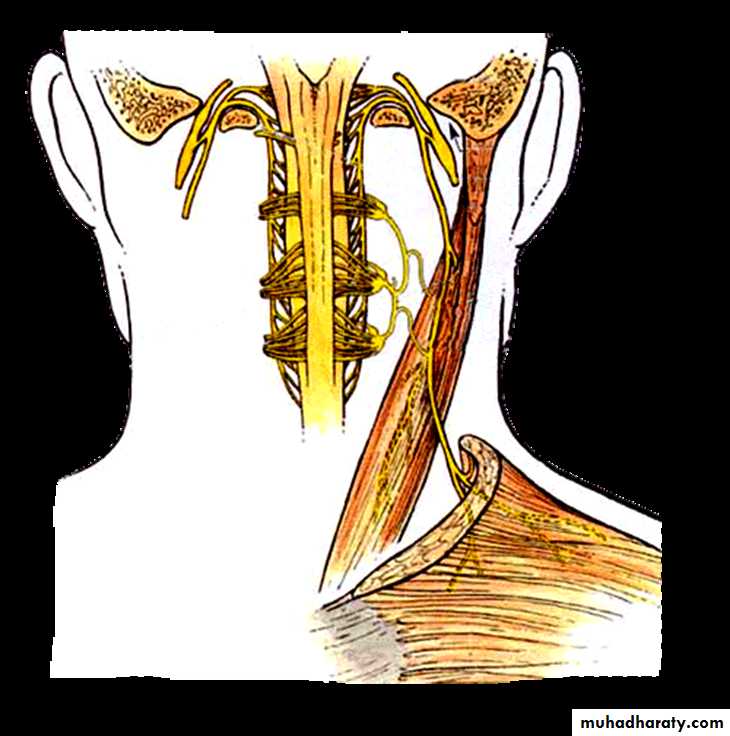
Accessory Nerve (XI)
Branchial motor nerveCranial root From nucleus ambiguus
Fibres in the cranial root join the vagus nerveSomatic motor nerve
Spinal root Anterior horn cells of upper 5-6 cervical spinal segmentsFibres in the spinal root supply sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Somatic motor nerveLeaves cranial cavity through the hypoglossal canal
Supplies all muscles (intrinsic and extrinsic) of tongue except palatoglossus
BE
VE
BA
GSA
BE
VE
BA
GSA