Sutures & ligatures
History of suture materials:In ancient Egyptian writings,48 cases of clinical surgery were described and Arabian surgeons took their sutures from twisted and sun-dried sheep intestines.
Suture: The term suture refer to either material used to close a wound such as gut or silk and the method used such as interrupted technique.
Ligature: It means a cord or band for tying vessels or the act of tying or binding (ligation).
Characteristics of ideal suture materials :
It should be suitable for using in many surgical operation.
It should be easy to handle.
It has adequate tensile strength.
It has security knot without slipping or cutting or fraying.
It should not be capillary, electrolytic, allergenic, toxic, carcinogenic and corrosive.
It's easy to sterilize and not shrink in the tissue.
It's non-irritant and absorbed with minimal tissue reaction after having served its purpose.
It should be monofilament and very strong but simply dissolved in body fluids.
It's totally biologically inert.
It's not favorable for bacterial growth.
Classification of suture materials:
A. According to their behavior in tissue:1. Absorbable suture materials.
2. Nonabsorbable suture materials.
B. According to their structures:
Monofilament S.M.:
is made of single strand and they have less tissue drag and don’t have interistics that may be harbor bacteria and very damaging by needle holder.
2. Multifilament S.M.:
It is made of several filaments twisted or braided together and more pliable and flexible and they may be coated to reduce tissue drag and enhances handling characteristics.
C. According to their origin:
1. Natural.
2. Synthetic.
3. Metallic.
Examples of Absorbable suture materials
(according to its origin )
Examples of
Non-absorbable suture materials(according to its origin )
Absorbable:
this suture undergo degradation and rapid loss of tensile strength within 60 days.Nonabsorbable:
it is not absorbed by the body and the retain to its tensile strength more than60 days.
Indications of absorbable suture material:
A hallow viscous is entered and non-absorbable suture might serve as a nidius for stone formation (as in the urinary bladder).
Contamination can not be eliminated (such as gut).
It is desired to have the body remove the suture (such as deep sutures in liver, spleen and kidney).
Subcutaneous suturing must be performed.
Natural absorbable surgical gut (cat gut)
It is derived from the submucosal layer of sheep or the serosa of cattle intestine and it is consist of 4 types:1. TYPE A (plain cat gut untreated) absorbed within 3-7 days.
2. TYPE B (mild chromic treatment) with in 14days.
3. TYPE C (medium chromic treatment) within 20 days.
4. TYPE D (extra chromic treatment) within 40 days.
Type B,C,D are treated by chromic acid for:
1. Increase the time of absorption.
2. Increase the tensile strength.
3. Decrease the soft tissue reaction to suture material.
Mechanism of absorption:
1. Loss of tensile strength due to destruction of molecular bonds by acid and hydrolytic and collagenolytic enzymes. exp: polyglycolic acid.2. Digestion and absorption by proteolytic enzymes which occur during the last stage of implantation. Exp: catgut.
Advantage:
good handling when its wet.
Disadvantages:
1. Weakness and poor knot security.
2. Induce inflammatory reaction.
3. Some time can induce sensitivity reaction.
4. Capillarity.
COLLAGEN :
It is multifilament process from the bovine flexor tendons, absorption like catgut and use in ophthalmic surgery less inflammatory reaction because of uniformity of the tissue components.Kangaroo tendon:
Is obtained from the tail of the kangaroo and is quite expensive, thus it is rarely used as suture and it has higher tensile strength.
FASCIA LATA:
Is obtained from beef cattle and is prepared in strips that are used to provide additional supports to weakened facial layers.
Synthetic Absorbable S.M.:
POLYGLYCOLIC ACID:
It is braided and multifilament resulting from polymer of glycolic acid or called glycosetic acid.
Characteristic:
1. It is absorbed by hydrolysis.
2. It is relatively strong and high tensile strength than catgut.
3. It is good suture material when infection is present.
Polygalactin: (vicryl)
It is braided fiber composed of glycolic and lactic acid in ratio 9-1 and
characterized By :
1. Hydrolysis.
2. Tensile strength loss in high temperature and under alkaline condition.
3. It is stronger than catgut.
POLY DIXANON OR DEXON:
It is monofilaments suture derived from the polymer of paradioxanone.
Characterized by :
1. Hydrolysis absorption .
2. It is cause minimal tissue reaction.
3. It is safe for use in urologic surgery.
Non absorbable suture material:
SILK:It is obtained from the cocoon of silk worm and it is braided or tested multifilament ,it may be treated by emersion either wax or oil or silicone to decrease the natural capillarity.
CHARACTERISTIC:
1. It is higher tensile strength.
2. Easy to handle.
3. Has good knot security.
4. It is in an expensive .
DISADVANTAGE:
IT cause ulceration in GIT if the suture is protruded in the lumen of the GIT.
Contraindication:
not used in urinary bladder and gall bladder because it is serve as nidus for the formation of calculi.
Mechanism of absorption:
are not absorbed but encapsulated or walled by fibrous tissue.
Cotton:
the most common use of cotton in large animal is as umbilical cotton tap it is produced from the filament of cotton plant ,it is well tolerated by the tissue and causes less tissue reaction than silk, it is in ex pensive with capillarity and has good knot security and can be autoclave but prolonged autoclaving will decrease the tensile strength and not security when wet.
Disadvantage:
1. it is capillarity and may be lead to formation of sinuses and pustules.
2. it is sticks to wet surgical gloves macking it more difficult to handle .it is use in suture of perineal region for prolapsed of uterus vagina and rectum.
NYLON: (DERMALON):
It is either monofilament or multifilament it has minimal tissue reaction (inert) when implanted to tissue and has more tensile strength.
DISADVANTAGE:
1.it is more handling with it.
2.it is knot is not good and mostly used in skin suture.
Polymerized caprolactum:
use in veterinary surgery only and it is twisted multifilament of nylon family:, the twisted fiber are made from material related to nylon of coated to minimize capillarity, it has more tensile strength than nylon and used in skin suture.
Polyester fiber:
It is braided multifilament and derived from a synthetic polymer with less tissue reaction and it is either plain (uncoated form) or coating such as polybutilate or Teflon or silicone to reduce the drag and facillatating the suturing.
Characteristics by:
1. It is one the strong suture material and high tensile strength, bad handling, minimal capillarity and withstands sterilization well.
2. Poor knot security.
3. High tissue reaction and using for skin and cardiovascular surgery.
Polypropylene:
It is polymerized and monofilament and it is derived from polymer propylene.
Characteristic:
High tensile strength(inert) but has great knot security and lead to less thrombogenic sutures and use in vascular surgery.
Disadvantage:
slippery.
Polyethelene:
It is polymerized monofilament with highly tensile strength and can be reputed autoclave and have poor knot security.
Stainless steel:
It should contains the following metallic foramen:
Iron, chromium(17%),nickel(10%)and molybdenum(2-4%),it is available either monofilament or multifilament, it isbilogical inert and non capillary,easly sterilized and autoclave and it has the high tensile strength ,greater knot security ,it is good for suture of the tissue that healing slowly such as tendon, flat bone.
Disadvantage:
It is tendency to the cut of the suture ,poor handling specialty knot of it, it cannot stand repeated bending.
Tentalum, Silver, Aluminium
Use as a mesh for hernia repair and knot security highly with stand repeating bonding.
METAL CLIPS AND STAPLES:
Are made from silver and stainless steel clips are used to ligate small vessels ,wound edges and secure accessory drapes to the edges of wounds and can easily sterilized (external use).
TITANUM CLIPS:
Using for ligation of internal blood vessels (internal use).
SURGICAL NEEDLE:
It is essential for the placement of suture in tissue.
Characterized:
1. It should be designed to place suture with minimal amount of trauma.
2. should be rigid enough to prevent excessive bending.
3. flexible enough to bend before breaking.
4. sharp enough to penetrate tissue with minimum of resistance.
5. clean and corrosion resistant made from stainless steel and smooth coated.
The selection of needle is determined by:
1. Type of tissue and location.
2. Size of suture material.
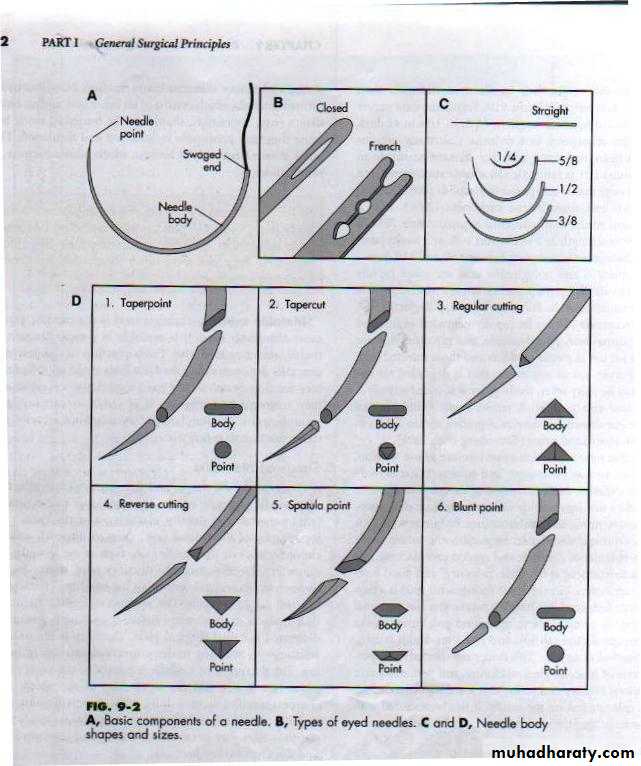
PARTS OF NEEDLE:
A. Needle eye:
1. Closed : round, square
2. French eye: it have a slit from inside the eye of the needle to facilitate threading and they tend to release the suture unless large sizes of suture are used (economy).
3. Swaged eye (eye less): The needle eye is fused with thread and it have the same size of suture material in order to minimize tissue trauma and increased ease of use.
B. Body or shaft:
it is varies in gauge or wide ,length and shape such as: round, oval, flat, triangular, straight and curved such as (one fourth1\4used in ophthalmic surgery), (three eight3\8,one half1\2,fifty eight5\8circle and1\2 curve for abdominal surgery).
C. Needle point:
Either taper cut using for muscle, tendon, vascular graft and soft tissue, blunt point using for spleen, liver, kidney, reverse, regular cutting using for skin, spatula for ophthalmic procedures (figure 1).SIZE OF SUTURE MATERIAL:
There are two grades.
1. USP
2. METRIC
TYPES OF SURGICAL KNOT
1. half hitch knot
2. square knot
3. granny knot
4. surgeon knot