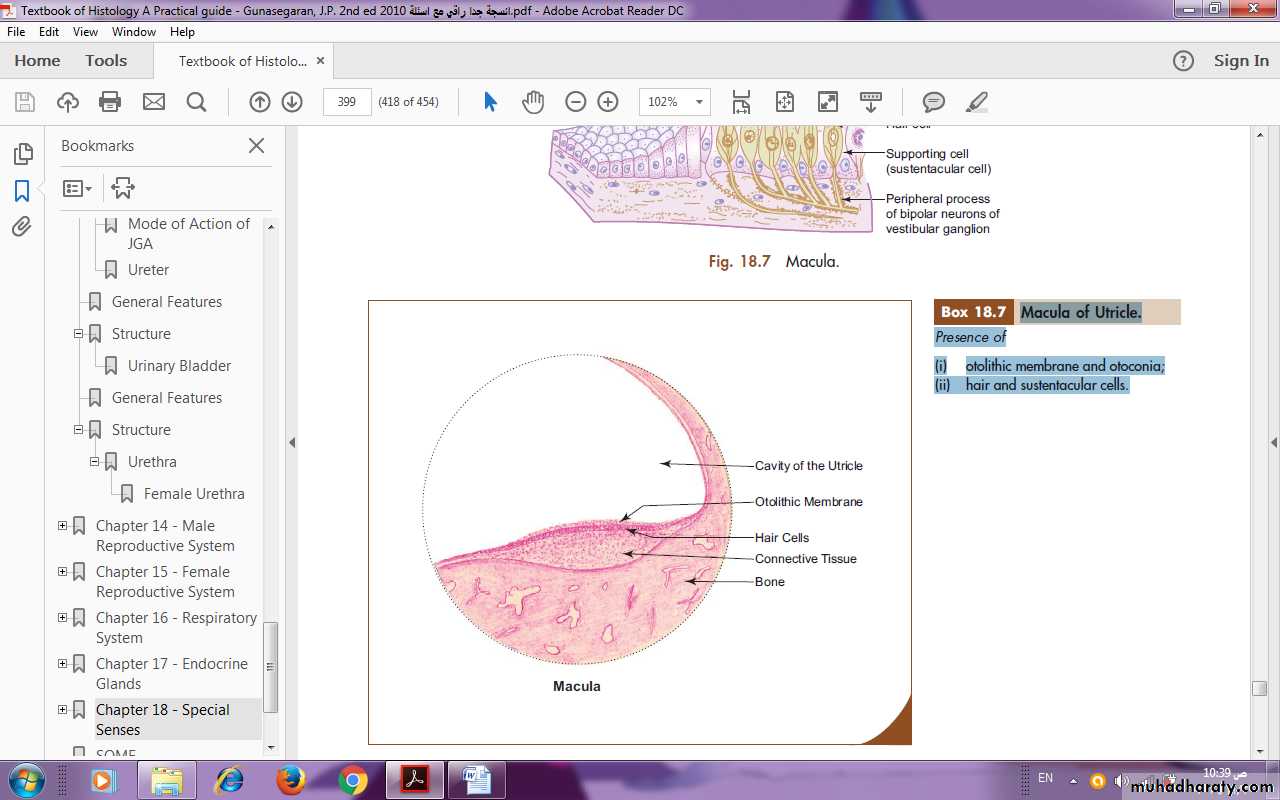
Macula of Utricle.
Presence of:Otolithic membrane and otoconia;
Hair and sustentacular cells.
2. Semicircular ducts
Semicircular ducts are three in number, small in size and found within the semicircular canals.These ducts have the same confi guration as the semicircular canals. Sensory receptors are found in the ampullae of semicircular ducts as transverse thickening called crista ampullaris.
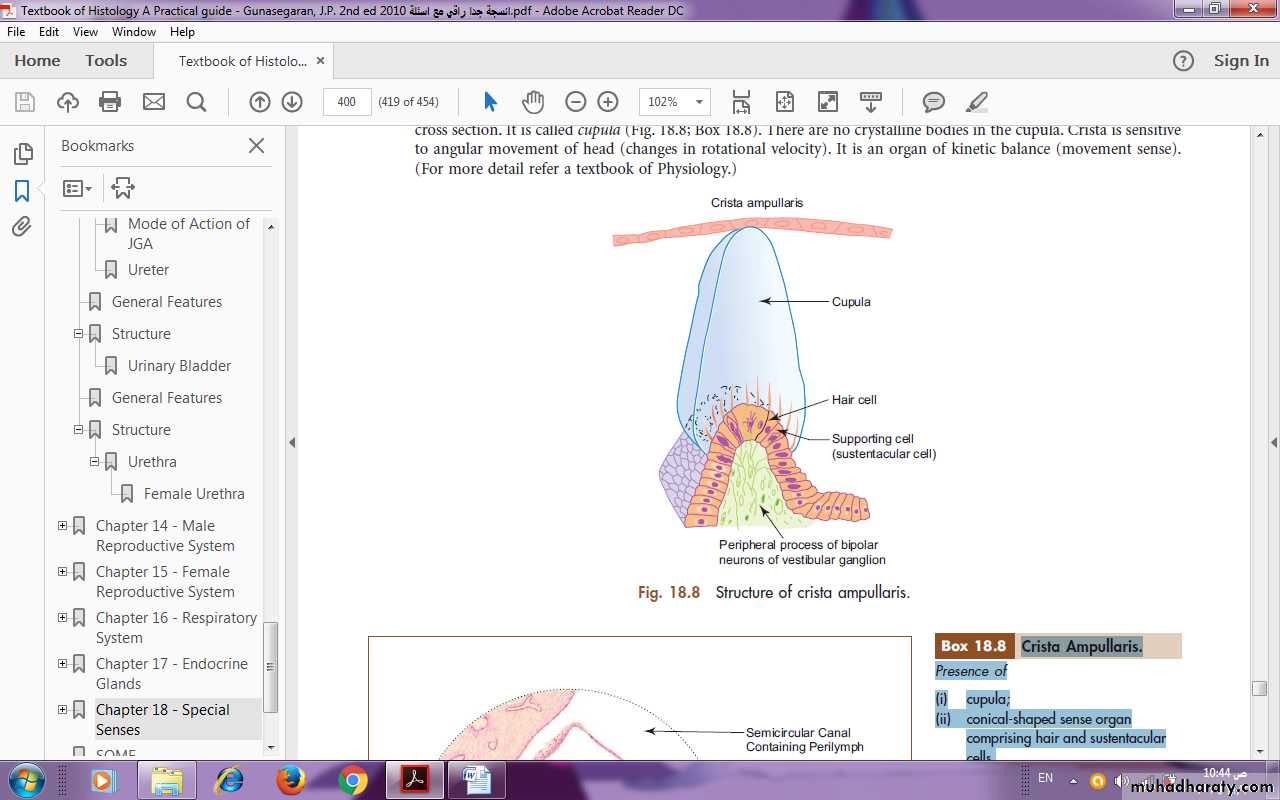
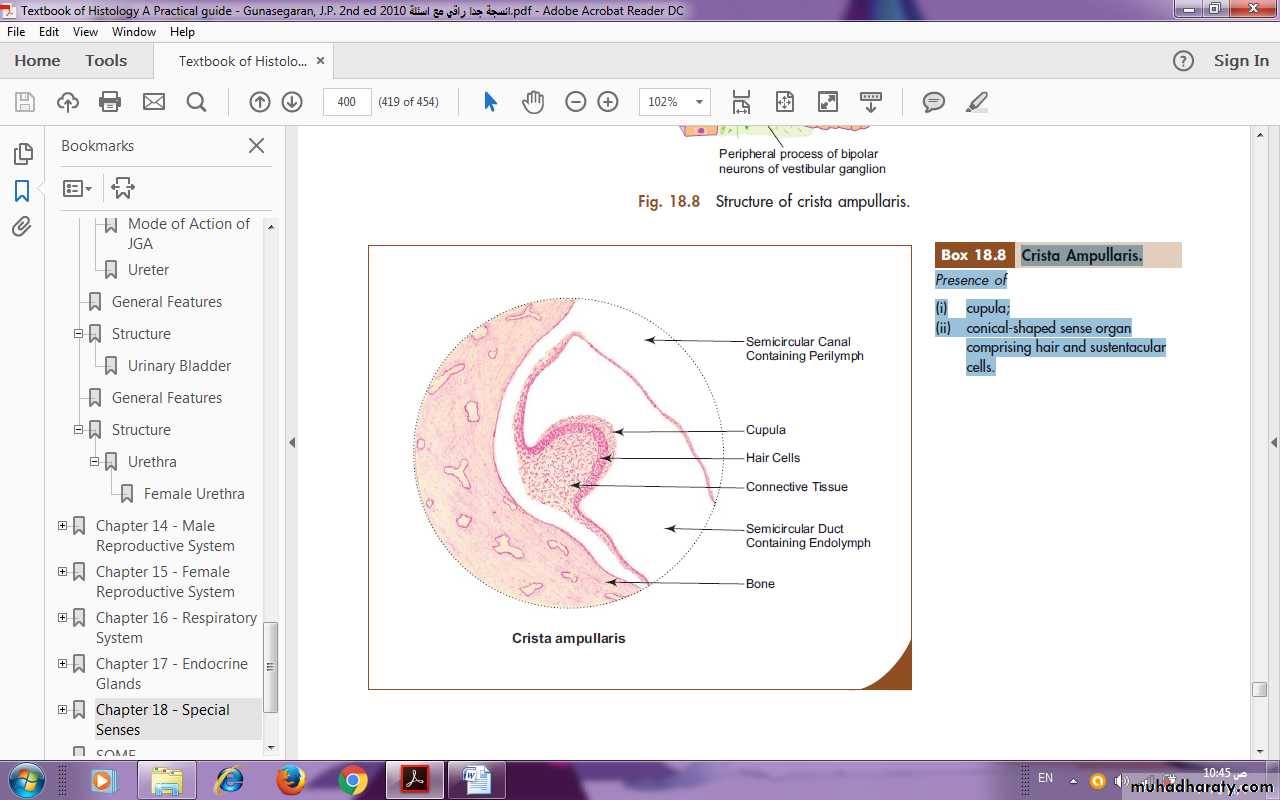
Crista ampullaris is similar in structure to macula, but the glycoprotein layer is very thick and conical in shape in cross section. It is called cupula (Fig.). There are no crystalline bodies in the cupula. Crista is sensitive to angular movement of head (changes in rotational velocity). It is an organ of kinetic balance (movement sense).
fig. : structure of crista aampullaris
Crista Ampullaris.
Presence of:Cupula;
Conical-shaped sense organ comprising hair and sustentacular cells.
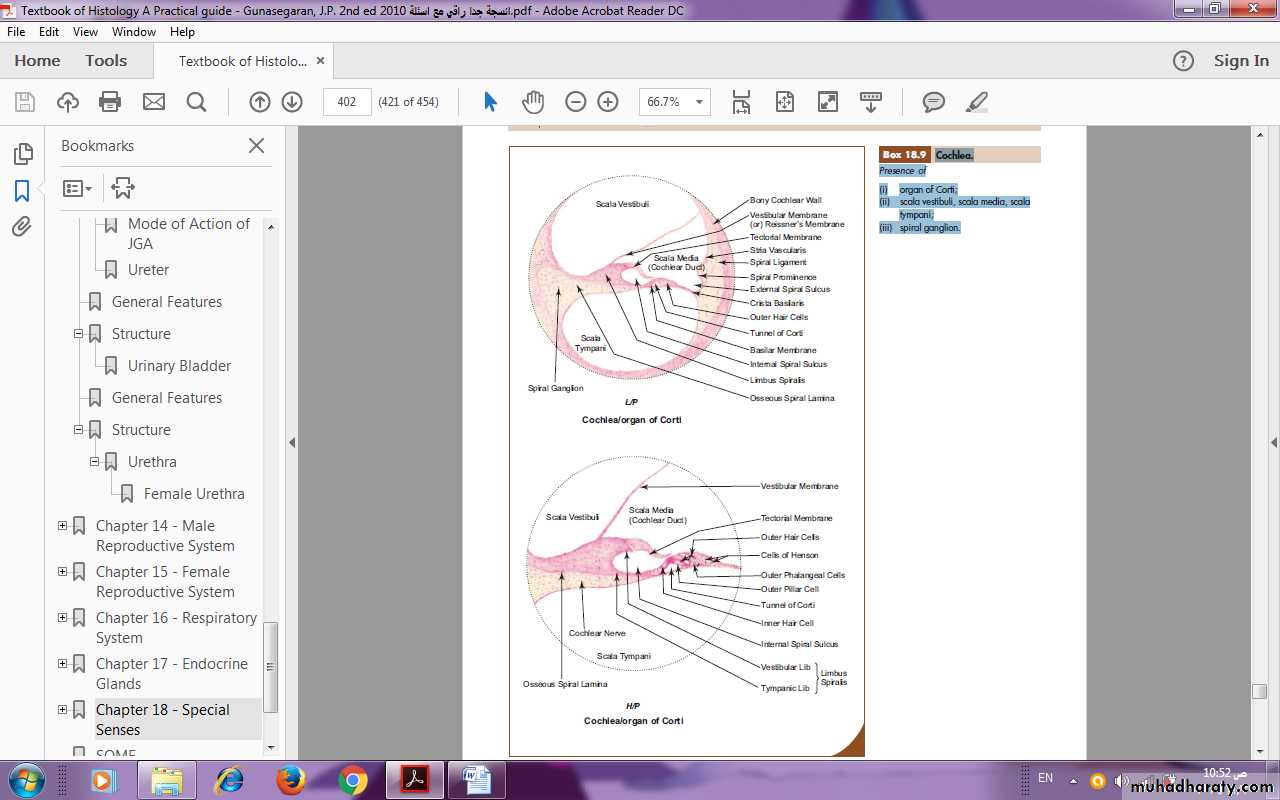
3. Cochlear duct
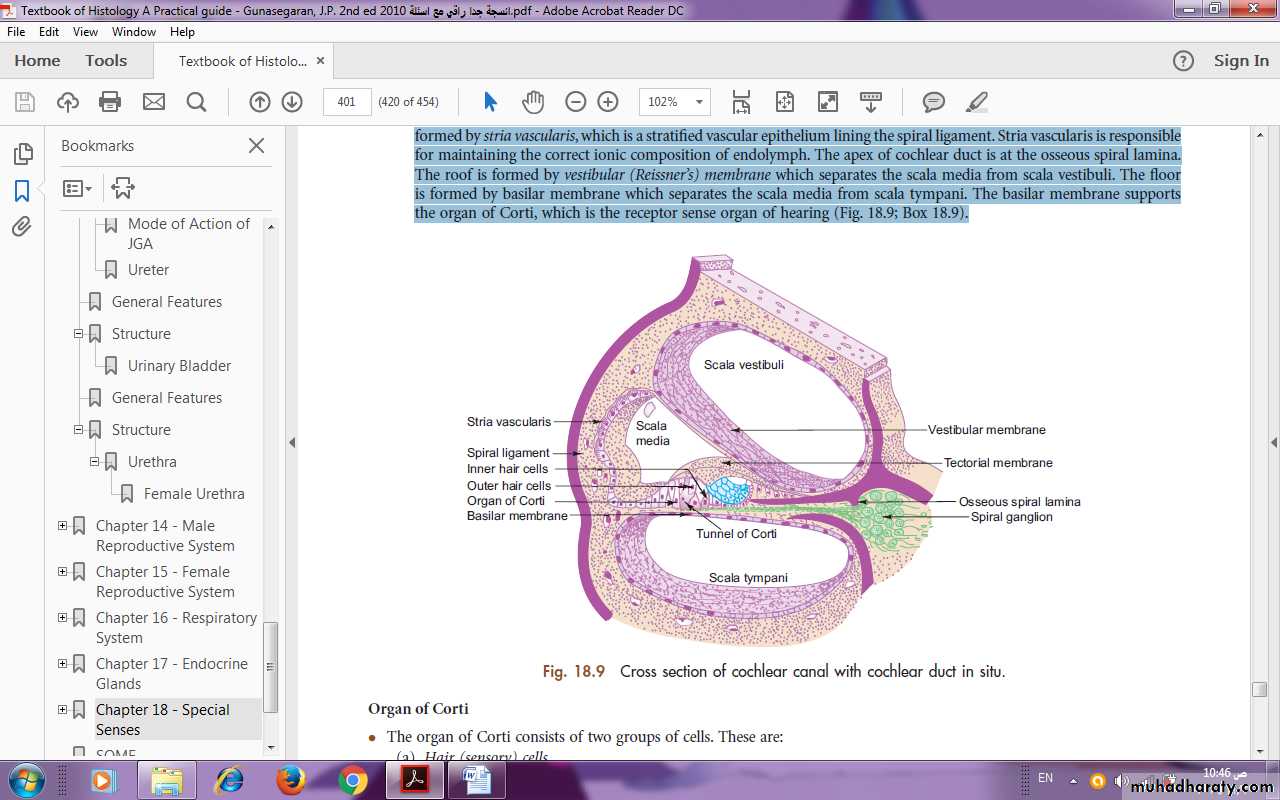
Cochlear duct (scala media) lies within the bony cochlear canal and is triangular in cross section. The base (outer wall) is formed by stria vascularis, which is a stratifi ed vascular epithelium lining the spiral ligament. Stria vascularis is responsible for maintaining the correct ionic composition of endolymph. The apex of cochlear duct is at the osseous spiral lamina.The roof is formed by vestibular (Reissner’s) membrane which separates the scala media from scala vestibuli. The fl oor is formed by basilar membrane which separates the scala media from scala tympani. The basilar membrane supports the organ of Corti, which is the receptor sense organ of hearing (Fig.).
Fig. :cross section of coch lear duct in situe
Organ of CortiThe organ of Corti consists of two groups of cells. These are:
(a) Hair (sensory) cells
Inner hair cells
Outer hair cells
(b) Supporting cells
Inner and outer pillar cells
Inner and outer phalangeal cells
Border cells
Hensen’s cells
In the center of the organ of Corti there is a canal, the tunnel of Corti, bounded by inner and outer rows of pillar cells. The pillar cells are rod-like cells containing tonofi brils.
On the inner aspect of the inner row of pillar cells is a single row of columnar cells, the inner phalangeal cells. They support the bases of inner hair cells, arranged in a single row. The inner hair cells are fl ask-shaped cells. They bear stereocilia (hair) which are arranged in the form of letter ‘U’.
On the outer aspect of the outer row of pillar cells, there are three to fi ve rows of outer phalangeal cells. They support the same number of rows of outer hair cells. Outer hair cells are much taller than the inner hair cells and their hair (stereocilia) are arranged in the form of letter ‘W’.
Both inner and outer hair cells do not reach the basilar membrane and they are supported by the inner and outer phalangeal cells through their apices. The hair cells have no kinocilium and have only stereocilia (hair). The hair project into a gelatinous layer, the tectorial membrane, which overhangs the organ of Corti from the limbus spiralis. The hair cells are innervated by peripheral processes of bipolar neurons whose cell bodies are situated at the base of the osseous spiral lamina as spiral ganglion. Their central processes pass through the modiolus as cochlear nerve.
The organ of Corti is limited internally by the border cells. These are columnar cells arranged in a single row on the inner
aspect of inner phalangeal cells.
Hensen’s cells limit the outer boundary of the organ of Corti. They are arranged in several rows on the outer aspect of the outer phalangeal cells.
Stereocilia are agitated due to vibration of basilar membrane caused by conduction of sound from bone to fluid.
Cochlea.
Presence of:
Organ of Corti;
Scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tympani;
Spiral ganglion.