1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-6
د
.
مثنى
8/3/2017
LOWER LIMB TRAUMA AND FRACTURES
HIP DISLOCATION
It is of three main types :
1- posterior.
2- anterior.
3- central.
4/5 traumatic dislocation of the hip is of posterior type .
Posterior hip dislocation
It is the commonest type
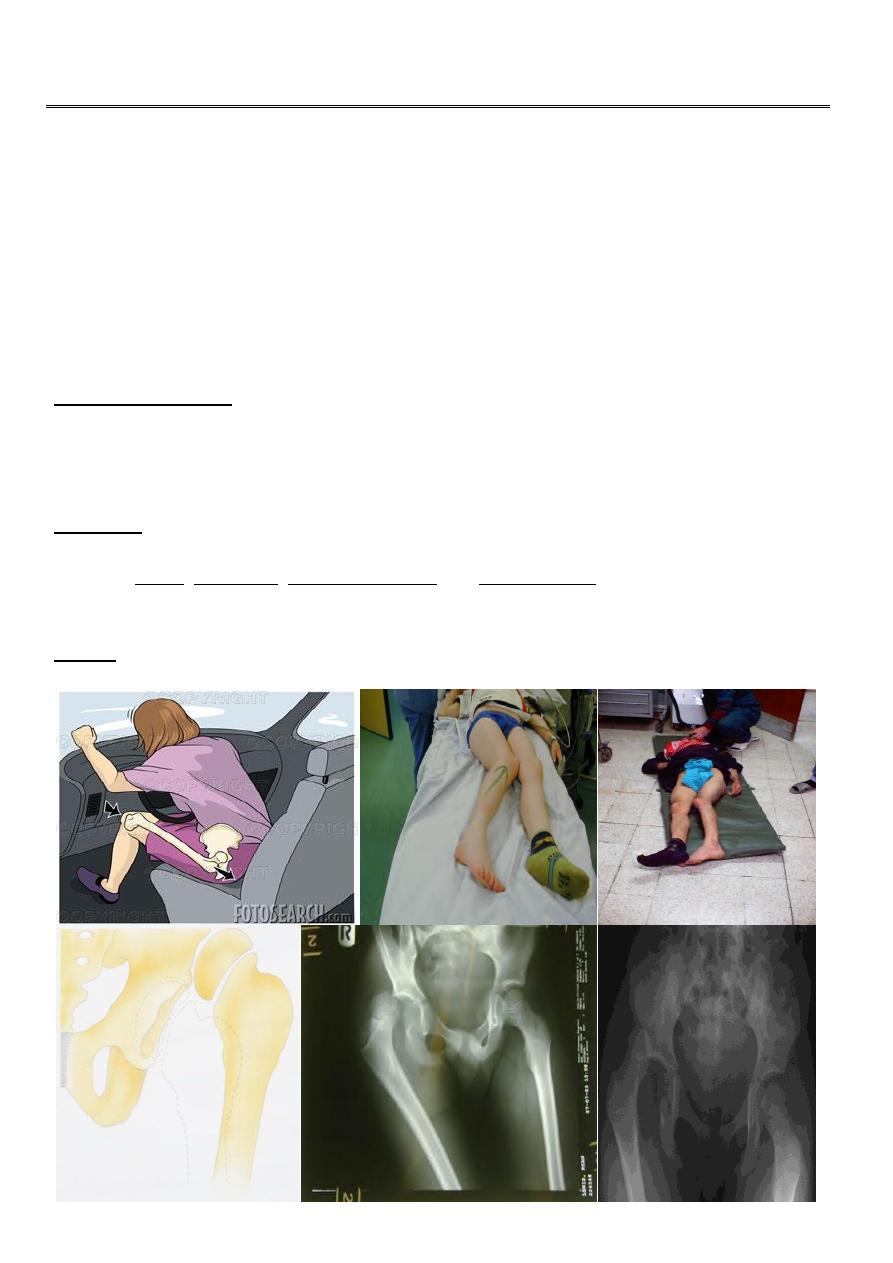
Mechanism of injury :
It occurs in road traffic accident when someone seated in truck or car is thrown foreword
striking the knee against the dashboard . The femur is thrust backward and the femoral
head is forced out of its socket . Often a piece of bone of the acetabulum is sheared off
making it a fracture – dislocation
Clinically :
On examination :
the leg is short ,adducted , internally rotated and slightly flexed .
This injury is easily to be missed when associated with fracture femur .
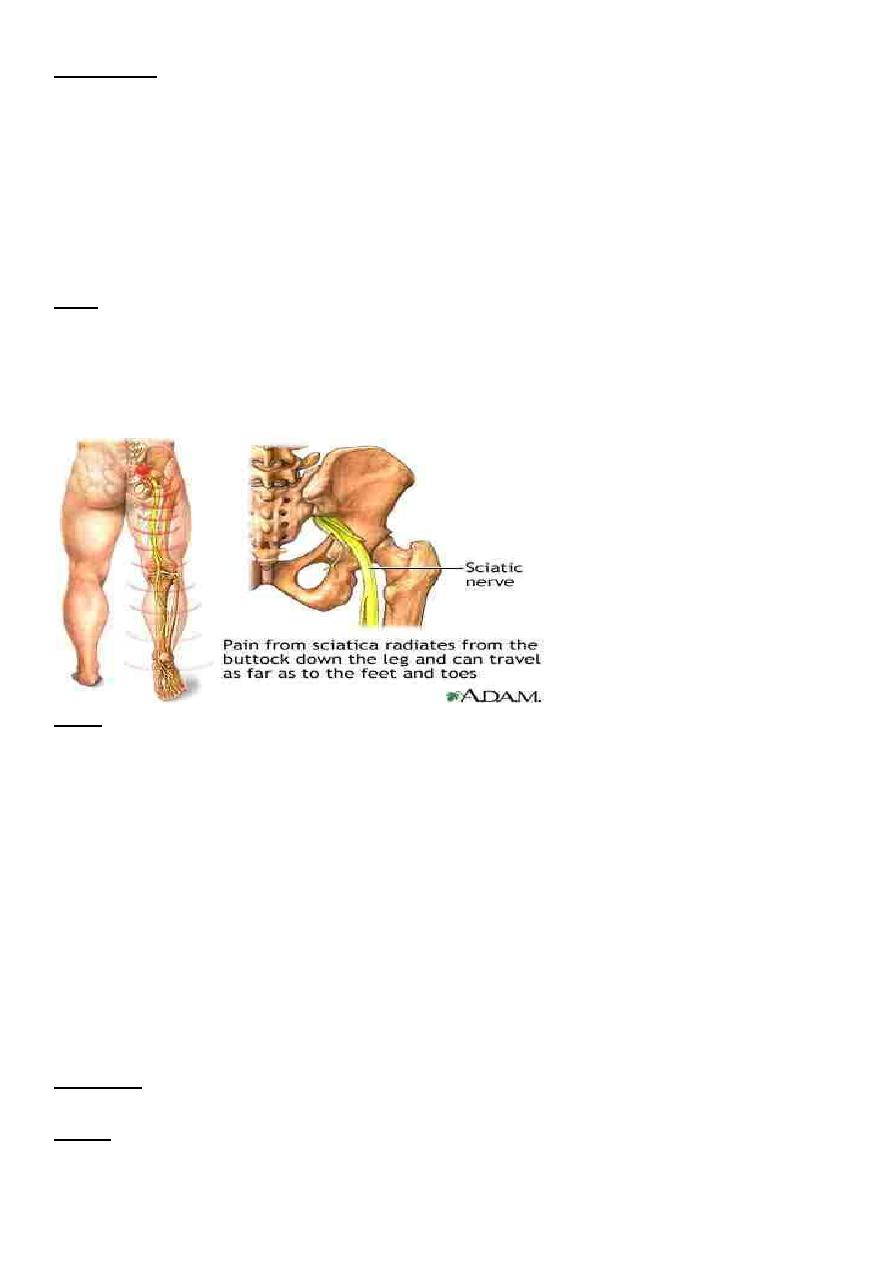
The lower limb should be examined for sciatic nerve injury .
X-ray : AP view : the femoral head is seen out of its socket and above the acetabulum .
There may be associated fracture in the femoral head or in the rim of the acetabulum .
2
Treatment :
Dislocation must be reduced as soon as possible under general anesthesia .
The patient put on ground. The assistant steadies the pelvis , the surgeon start by applying
traction in the line of the femur 90% flexion of both hip and knee , then a clunk terminate
the maneuver . Followed by x-ray checking ; then put the injured limb in rest by applying
skin or more beneficial skeletal traction for 3-6 weeks , the patient is allowed to walk by
crutches ; if there is fracture rim of the acetabulum and the piece is large then internal
fixation is mandatory .
Complication :
Early :
1- sciatic nerve injury : it occurs in 10-20 % of the cases but fortunately it usually recover , if
not , then nerve exploration must be considered.
2- vascular injury : superior gluteal artery .
3- associated fractures : acetabular , femoral head , femoral neck and femoral shaft and
here the dislocation may be missed .
Late :
1- avascular necrosis of the femoral head ,appear in the x-ray as an increase in density of
the femoral head , but it is not seen before 6 weeks and some time up to 2 years .
In early weeks , bone scan and MRI will be helpful in the diagnosis of ischemia .
Treatment of avascular necrosis :
in younger patient treated with realignment osteotomy if it is partial or by arthrodesis of
the hip .
In older patient with acetabular changes then total hip replacement .
2- myositis ossificans.
3- unreduced dislocation
4- secondary osteoarthritis
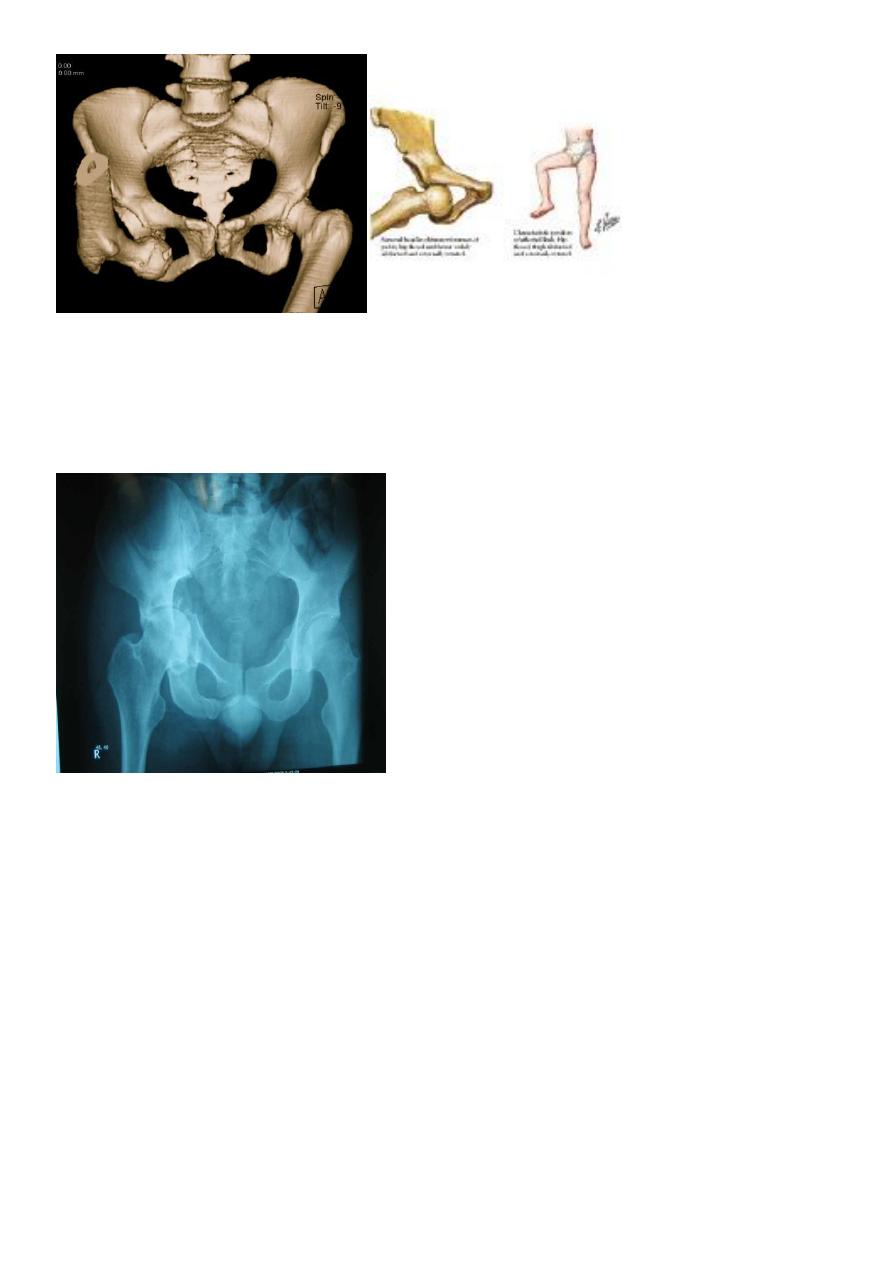
Anterior dislocation of the hip
it is rare .
Clinically : the leg is externally rotated , abducted and slightly flexed , not short .
sometimes the leg is abducted to right angle .
X-ray : AP view , the dislocation is obvious , any doubt is resolved by lateral view .
3
Central dislocation of the hip
fall on the side or blow over the greater trochanter may force the femoral head medially
through the floor of the acetabulum .
Although it is called central dislocation of the hip , it is really a fracture of the floor of the
acetabulum
Fractures of the femoral neck
Neck of the femur is a commonest site of fracture in elderly .
Risk factors :
1- osteoporosis .
2- osteomalascia .
3- diabetes mellitus .
4- stroke (disuse) .
5- weak muscles and poor balance .
6- alcoholism .
7- debilitating diseases .
Generally fracture neck femur is classified in to :
A – intra capsular fracture.
B - extra capsular fracture.
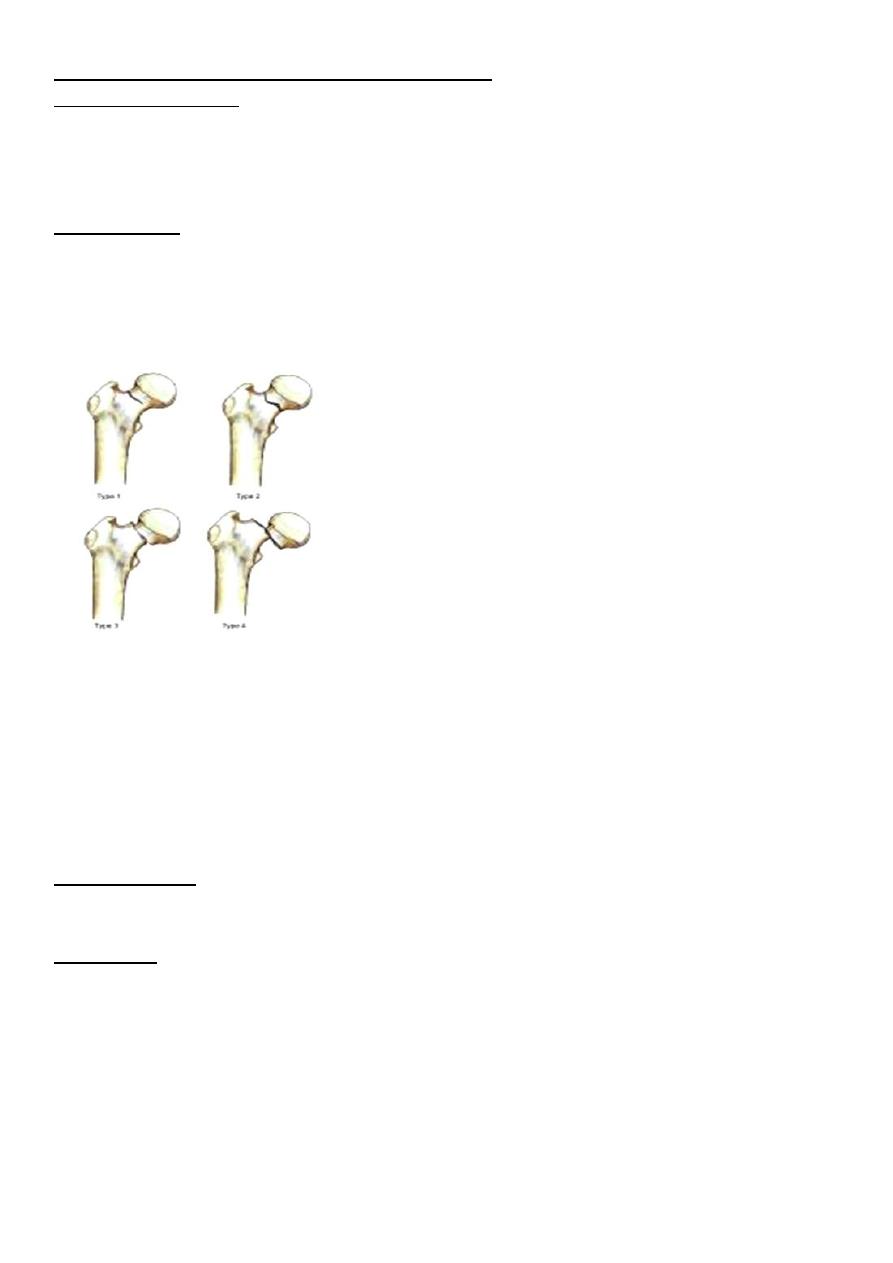
4
A- intracapsular fracture neck of the femur :
Mechanism of injury :
This fracture usually result from a fall directly on to the greater trochanter . In very
osteoporotic patient less forced is required . Sometimes no more than catching a toe in the
carpet and twisting the hip into external rotation .
In young people the cause is mainly car accident or fall from height .
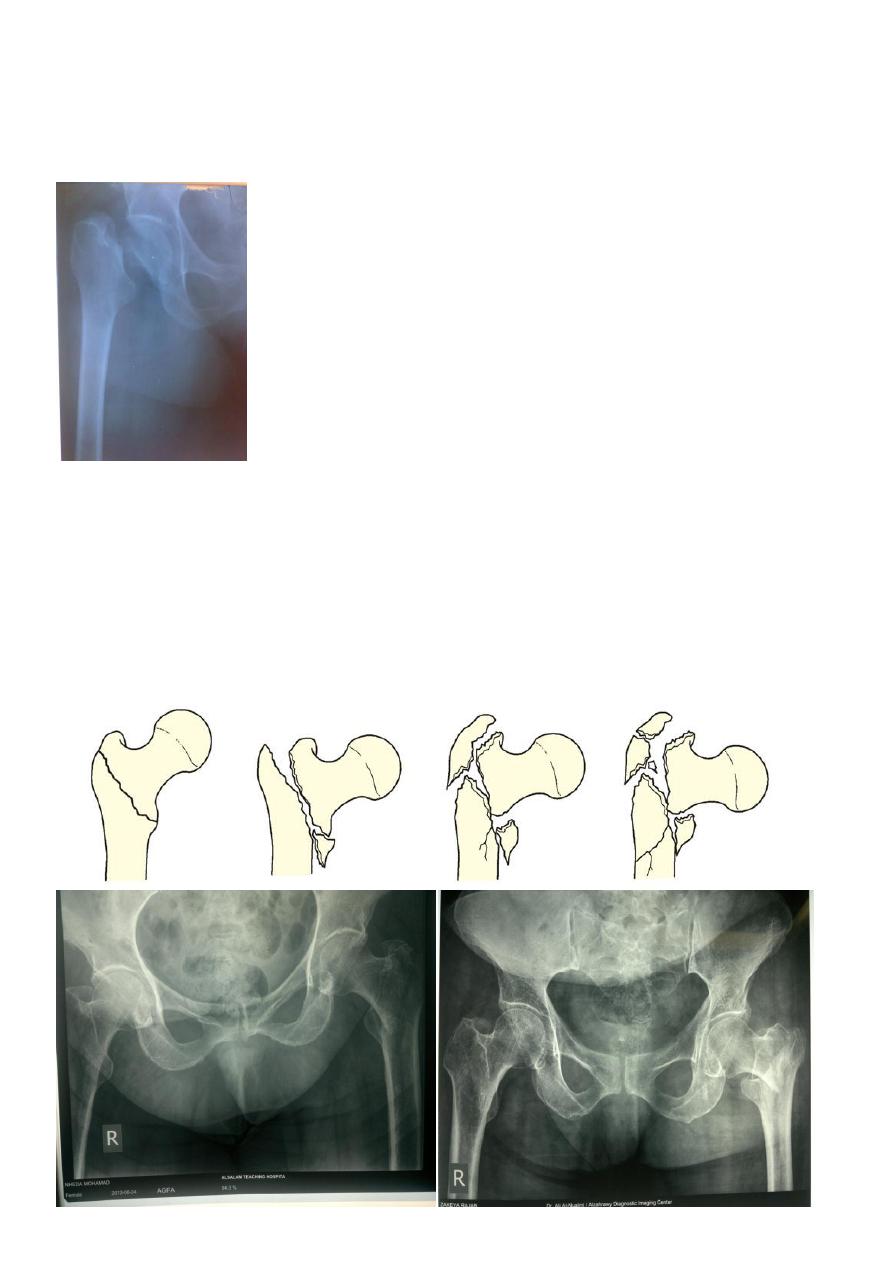
Classification : the most useful classification for intracapsular fracture neck of femur is that
of (Garden classification) which based on the degree of displacement .
Stage one : is incomplete impacted fracture .
Stage two : is complete undisplaced fracture .
Stage three : complete fracture with moderate displacement .
Stage four : is severely displaced fracture .
this fracture is complicated by two main problems which are :
1- ischemia of the head of the femur .
2- tardy union .
The blood supply of the head of the femur are :
1- intramedullary vessels in the femoral neck .
2- capsular vessels ; in the capsule of the joint .
3- the vessel in the ligamentum teres .
The first two vessels are interrupted by the fracture , and the third is present only in 20% of
the elderly .
Clinical feature :
History of fall followed by pain in the hip .
If the fracture is displaced , the limb will be externally rotated ,and short .
Treatment :
The first measure is to apply skin traction to splint the fracture and to control the pain , and
give analgesic for pain relieve .
Operative treatment is always mandatory .
Displaced fracture will not unite without internal fixation .
Old people should be got up and active without delay to avoid pulmonary complication and
bed sore .
The operation should be done as early as possible to avoid risk of complications .
The principle is perfect reduction , secure rigid fixation and early mobilization .
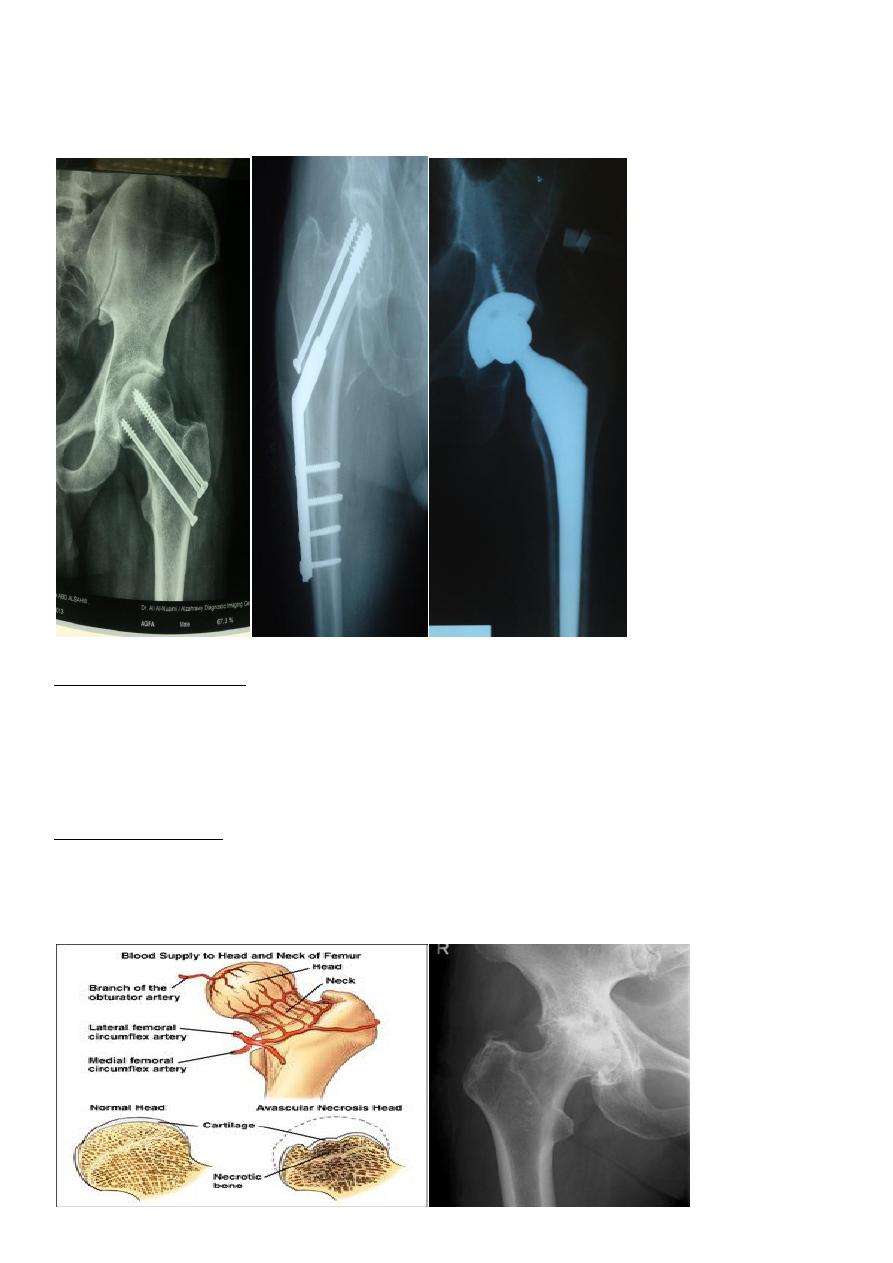
5
the fixation should be done by internal fixators like compression screws , plate and screws ,
dynamic hip screw ……etc .
In patient above 65 years with displaced fracture , partial hip replacement or total hip
replacement.
Complications :
General complication :
Most of these patients are elderly , and they are prone to general complication such as :
1- deep vein thrombosis .
2- pulmonary embolism .
3- pneumonia .
4- bed sore .
Local complication :
1- a vascular necrosis of the femoral head .
Early diagnosis by MRI
few weeks later we can diagnose it by bone scan .
X-ray changes may not show itself for months or even years.
6
Treatment of avascular necrosis :
In patients over 45 years old , the treatment is by total hip replacement .
Below this age , the treatment will be by realignment osteotomy or arthrodesis .
2- non union :
More than 30% of all femoral neck fracture fail to unite , and increase in displaced fracture
3- osteoarthritis of the hip joint .
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head will lead to osteoarthritis later on .
The treatment is by total hip replacement .
Intertrochanteric fractures (Extracapsular)
Common in elderly, osteoporotic people;
most of the patients are women in the 8th decade.
In contrast to intracapsular fractures, extracapsular trochanteric fractures unite quite
easily and seldom cause avascular necrosis.
7
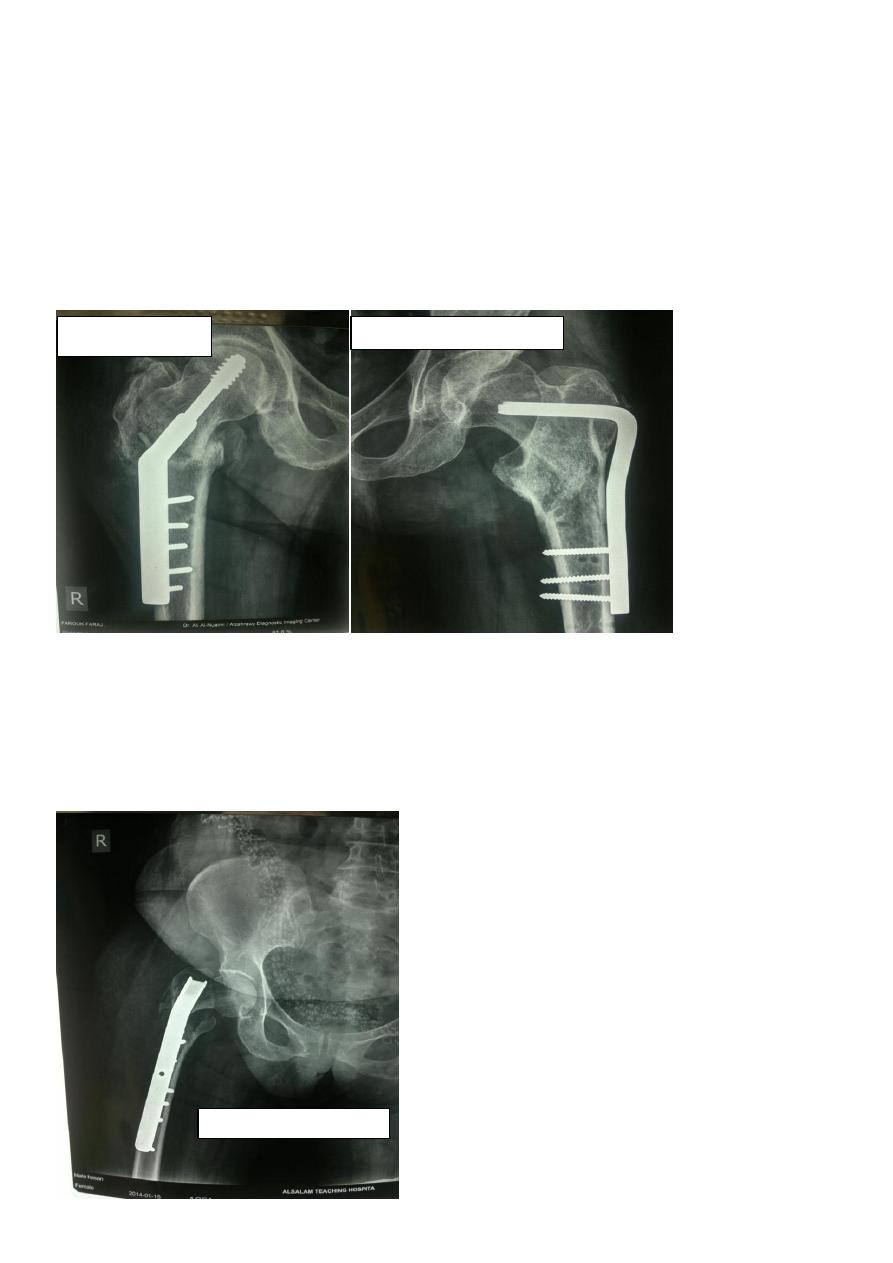
Treatment
Intertrochanteric fractures are almost always treated by early internal fixation
because :
(a) to obtain the best possible position And
(b) to get the patient up and walking as soon as possible and thereby reduce the
complications associated with prolonged recumbency.
The fracture is fixed with an angled device – preferably a sliding screw in conjunction
with a plate (dynamic hip screw) or
intramedullary nail. or
95 degree screw-plate (L-Plate)
Complications
Early complications are the same as with femoral neck fractures
Late Complications:
Failed fixation
Malunion Varus and external rotation deformities
Non-union: Intertrochanteric fractures seldom fail to unite.
Dynamic hip screw
L-plate (fixed angle plate)
Failed internal fixation
