1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-7
د
.
مثنى
8/3/2017
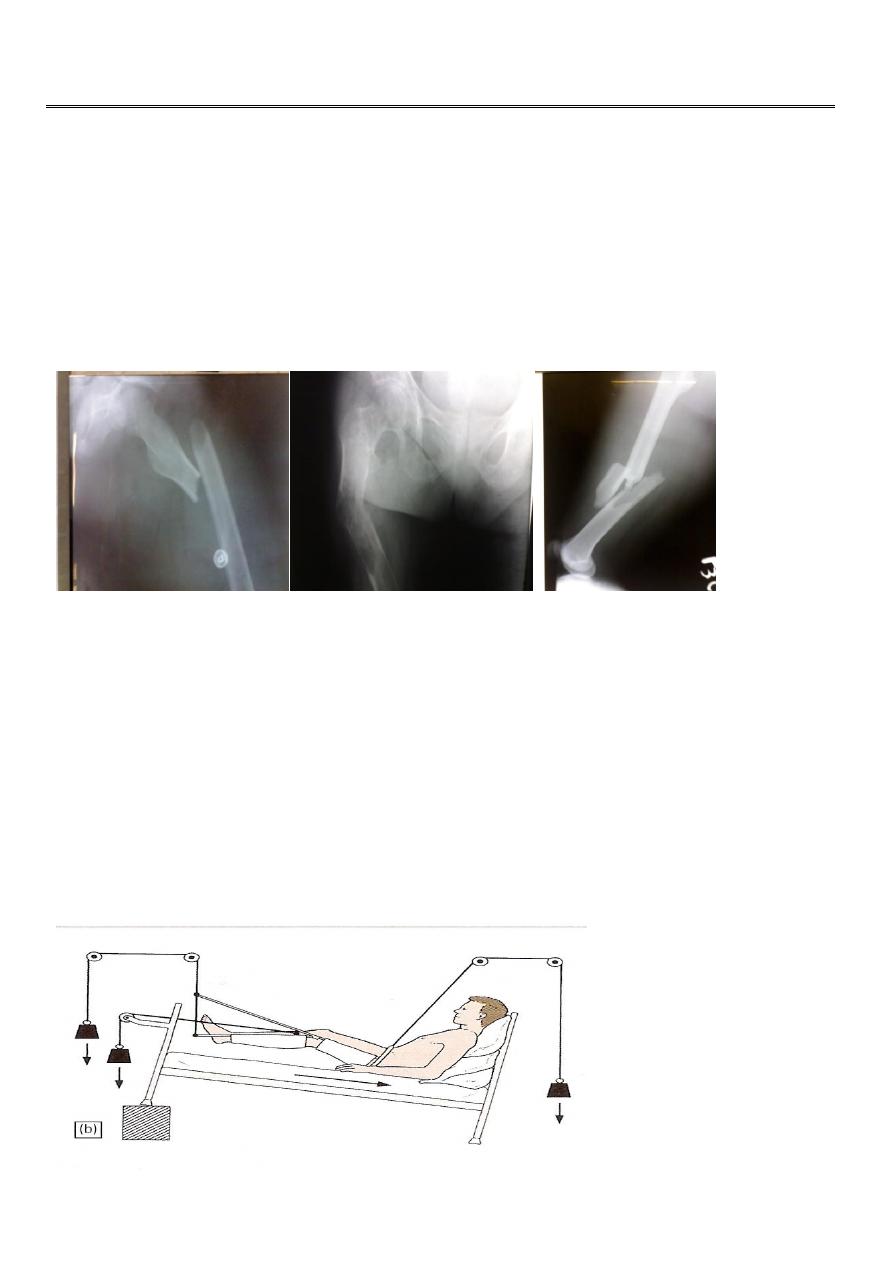
Femoral shaft fractures
Important notes:
Femur is well padded in muscles.
Great force is needed to fracture the bone in a young adult.
Fragments are displaced by muscle pull which makes closed reduction difficult.
In elderly it is a pathological fracture until proved otherwise.
In children think of physical abuse.
X-ray:
Usually there is some comminution.
X-ray of the pelvis and the knee to avoid missing injuries.
Treatment:
Remember the risk of systemic complications:
Bleeding and shock.
DVT and pulmonary embolism.
Fat embolism.
Etc….
Early stabilization
Splintage or tracion to reduce and hold the fracture in a reasonable alignment to
reduce further tissue damage and bleeding, e.g. Thomas splint.
Traction
Indications:
1-Contraindication to anesthesia.
2-Lack of skills and facility for surgical therapy.
2
Contraindications to traction:
1- Elderly.
2- Pathological fracture.
3- Multiple injuries.
Drawbacks of traction
Prolonged bed rest (10-14 wks) with its attendant problems:
DVT.
UTI.
Bed sores.
Pneumonia.
Joint stiffness.
Malunion.
Skin problems (irritation, blistering, necrosis,…)
Neurovascular complications.
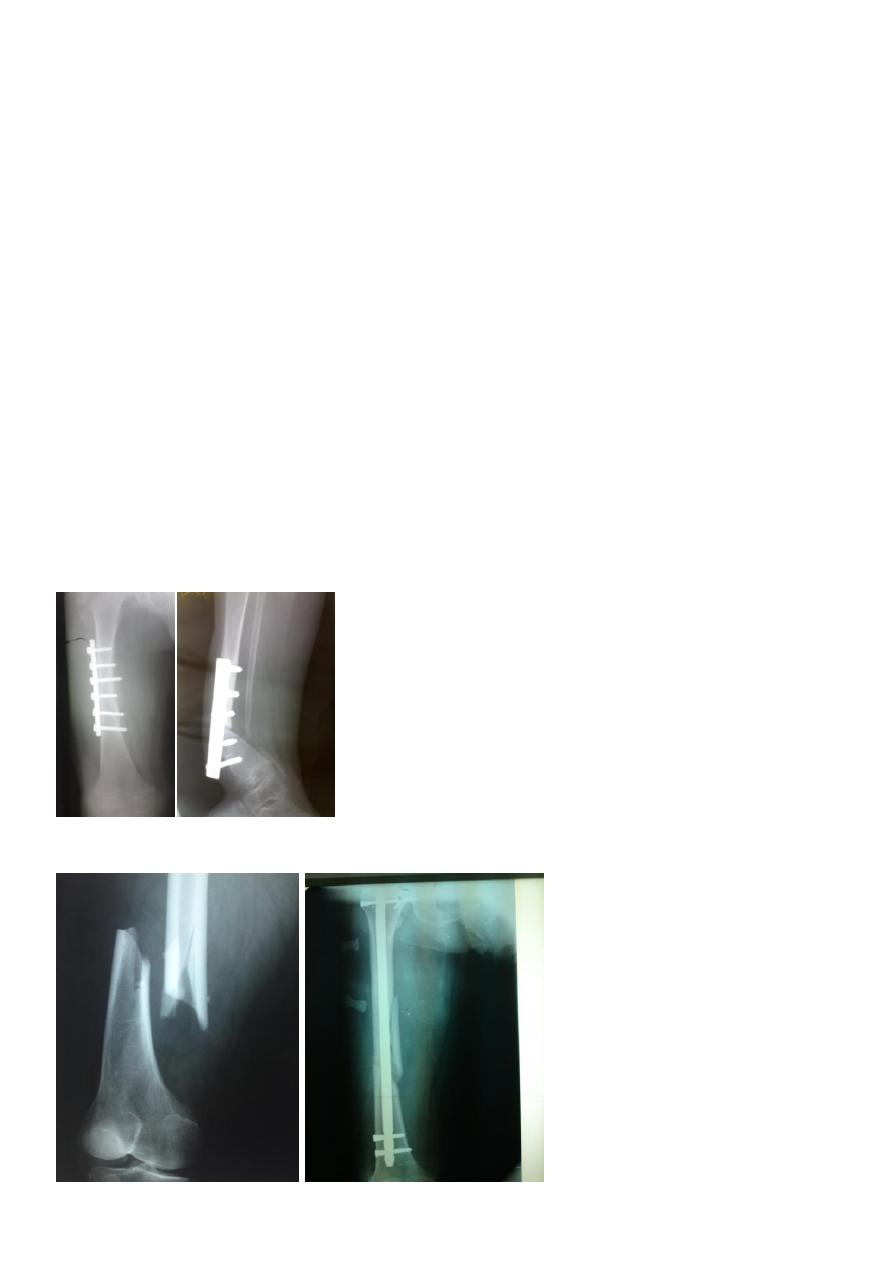
Open reduction and plating
Out of favor because of high rate of complications e.g. implant failure, infection…
Indications:
Shaft and neck fractures.
Vascular injury.
Implant failure
Intramedullary nail with interlocking screws is the method of choice
3
External fixation
Indications:
Open injuries.
Multiple injuries to reduce operating time.
Bone transport for bone loss.
In adolescents.
Femoral fractures in children
Infants: 1-2 wks traction then hip spica for 3-4 wks. (Gallows traction)
Children <10 years: traction 2-4 wks then spica for 6 wks.
Teenagers: traction then spica or plate and screws.
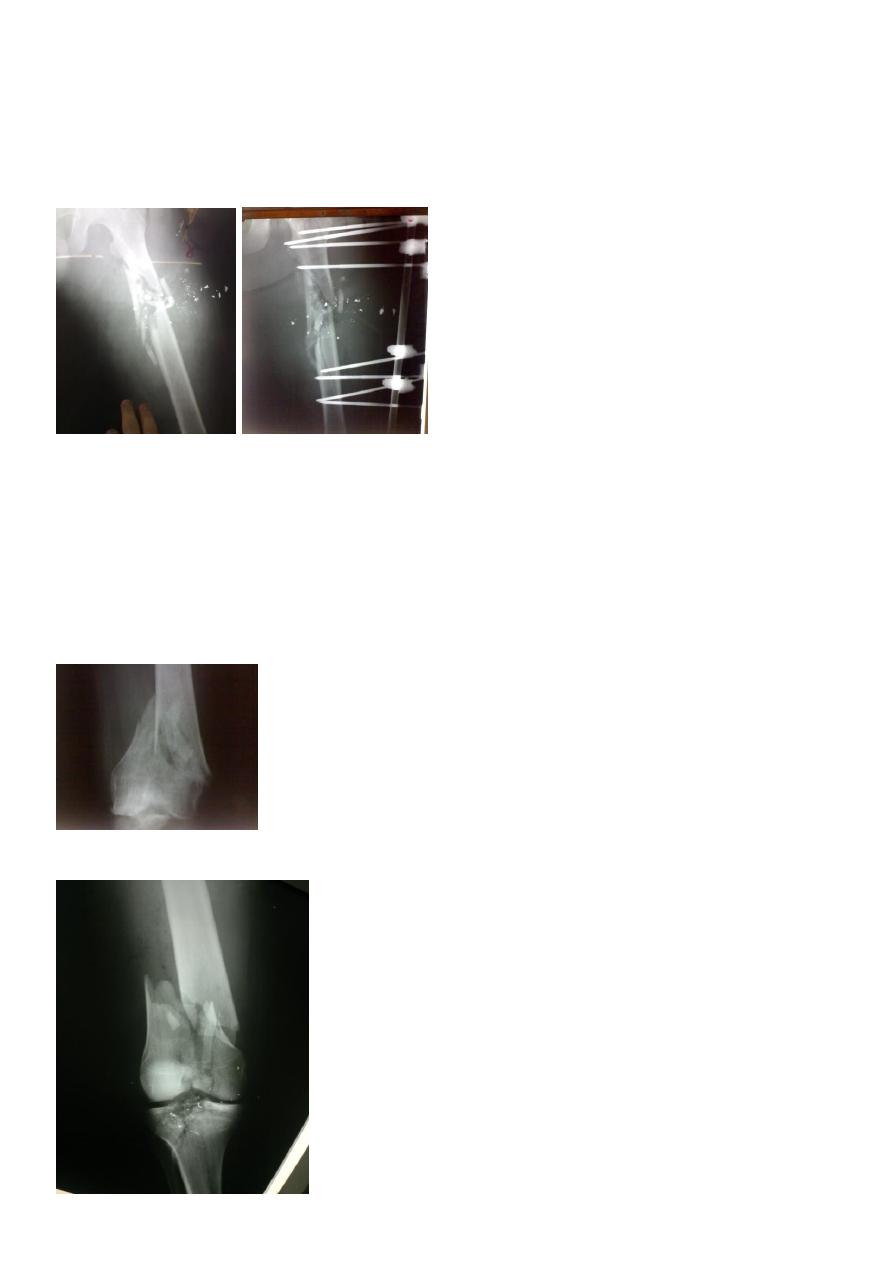
Supracondylar fractures of femur
In young adults after high energy injury.
In elderly osteoporotic after trivial injury.
Intercondylar extension may occur.
Supracondylar fracture with intercondylar extension
4
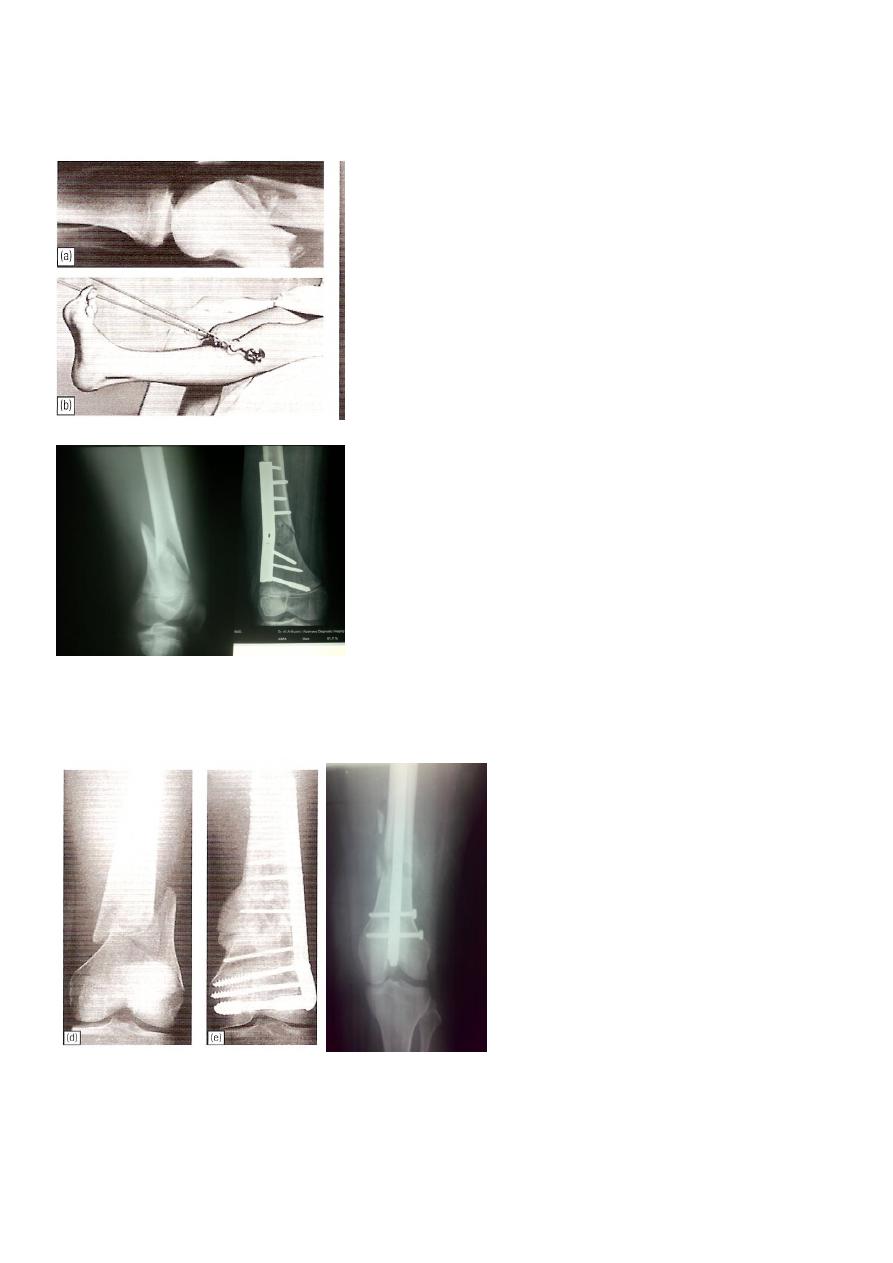
Supracondylar fracture femur
In children and adolescents- usually Salter-Harris II injury.
Distal fragment tilted backward by gastrocnemius muscle.
Check distal pulses.
Supracondylar fracture-child
Treatment
Slightly displaced #s- skeletal traction through proximal tibia.
If closed reduction fails- ORIF.
Locked intramedullary nail is the fixation of choice.
Complications
Joint stiffness- of knee is almost inevitable.
Non-union.
Osteoarthritis of knee joint; when the fracture extends into articular surface.
5
Condylar fractures
Fracture of one or both condyles with or without supracondylar fracture.
Doughy swelling of the knee due to hemarthrosis.
Treatment:
Aspirate hemarthosis.
Displaced articular fracture demands ORIF.
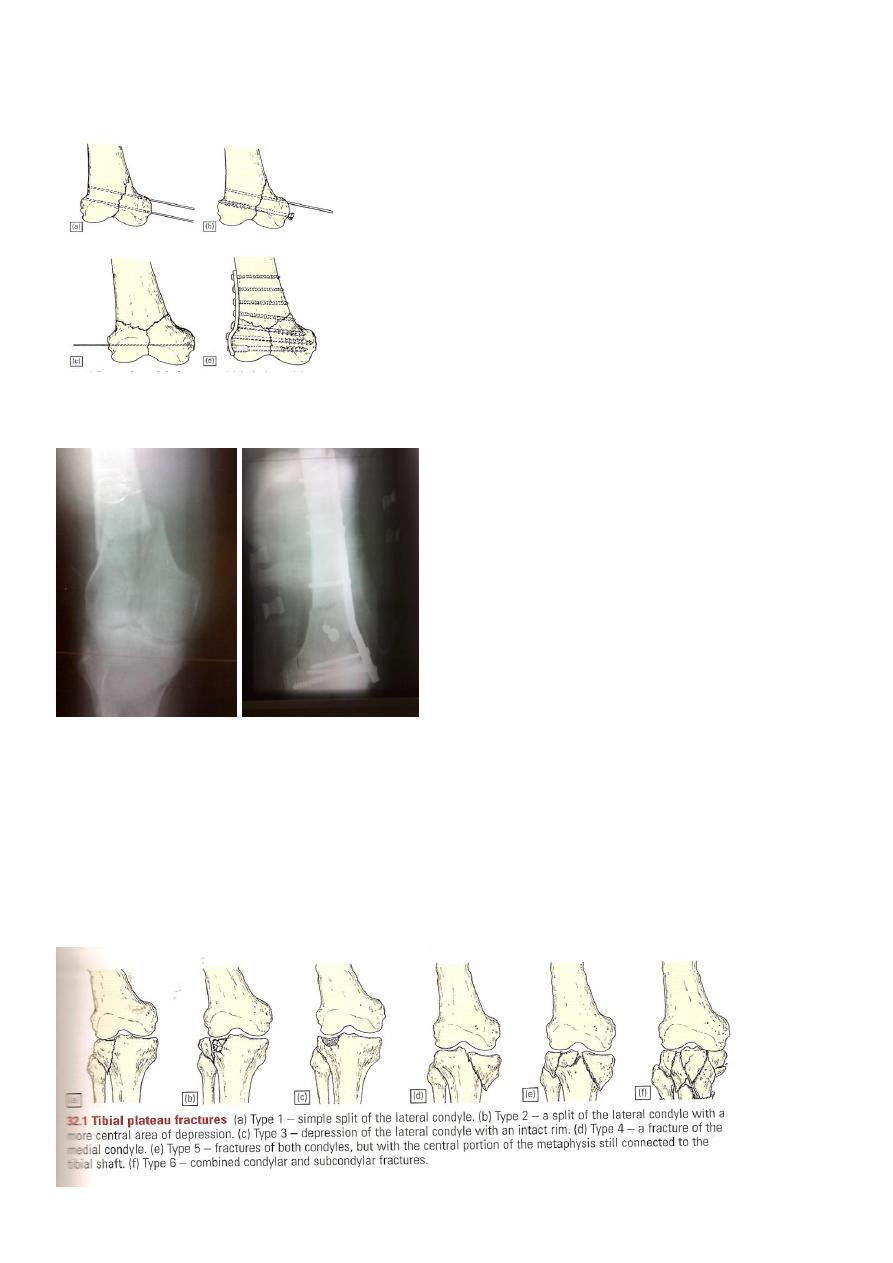
Tibial plateau fractures
Mechanism: medial or lateral bending force with axial loads, e.g. bumper fracture.
Doughy swelling of hemarthrosis.
Diffuse tenderness.
May be associated with knee ligament injury (collateral ligament, cruciate ligament).
X-ray:
One or both condyles may fracture with varying degrees of comminution.
C-T:
scan in complex fractures.
6
Treatment
Aspirate hemarthrosis.
Minimally displaced fractures: compression bandage, gradual exercise,then
functional brace and gradual exercise after 3 wks.
Displaced and/ or comminuted lateral or medial tibial condyle fracture
Treatment:
ORIF.
Associated ligament injury repaired.
Bicondylar fracture: needs ORIF with plate and screws or external fixation.
Complications
Compartment syndrome.
Joint stiffness.
Knee instability.
Deformity: genu varum or genu valgum.
Secondary osteoarthritis.
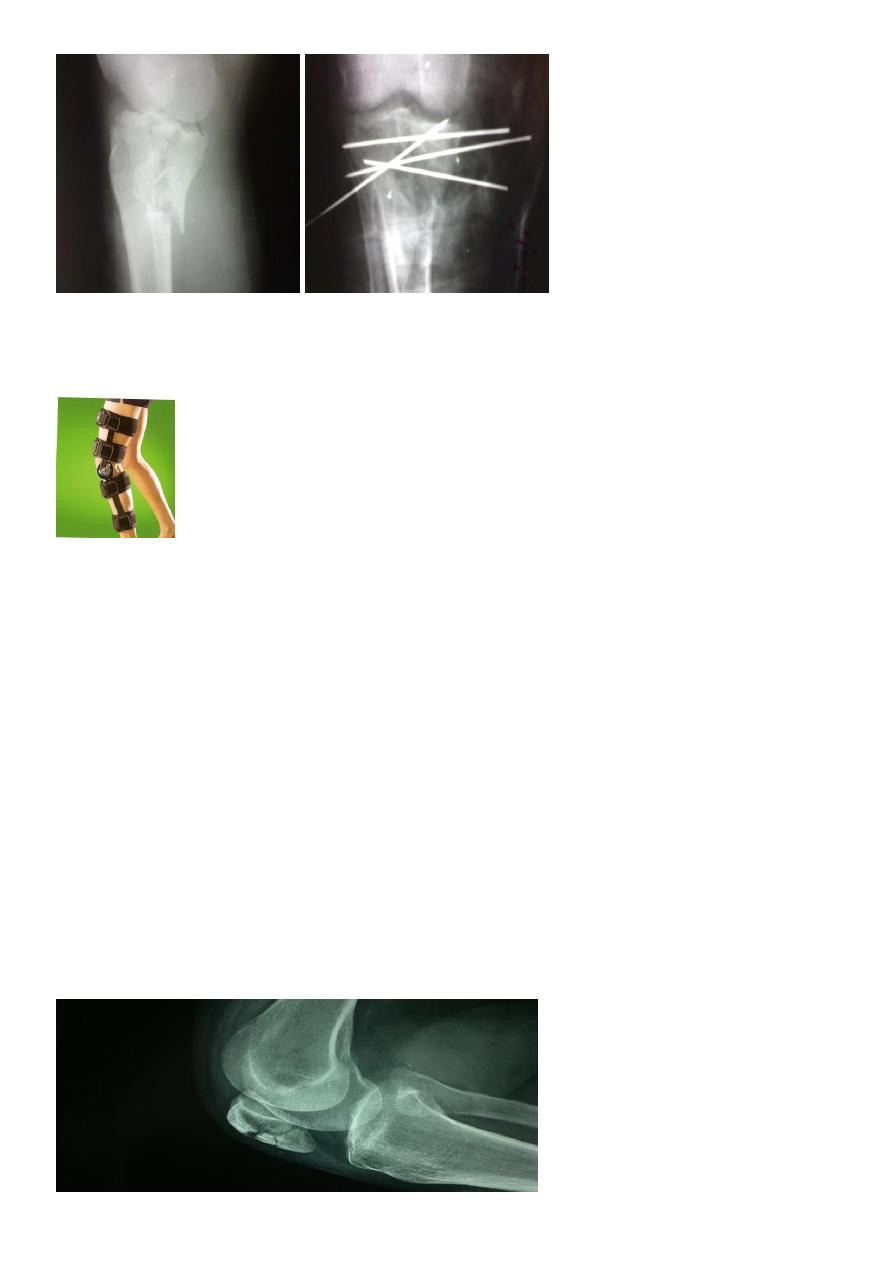
Patella fractures
3 types
Undisplaced crack.
Stellate comminuted fracture- direct blow on front of knee.
Transverse fracture with a gap- indirect traction force.
Quadriceps mechanism usually lost.
Undisplaced crack
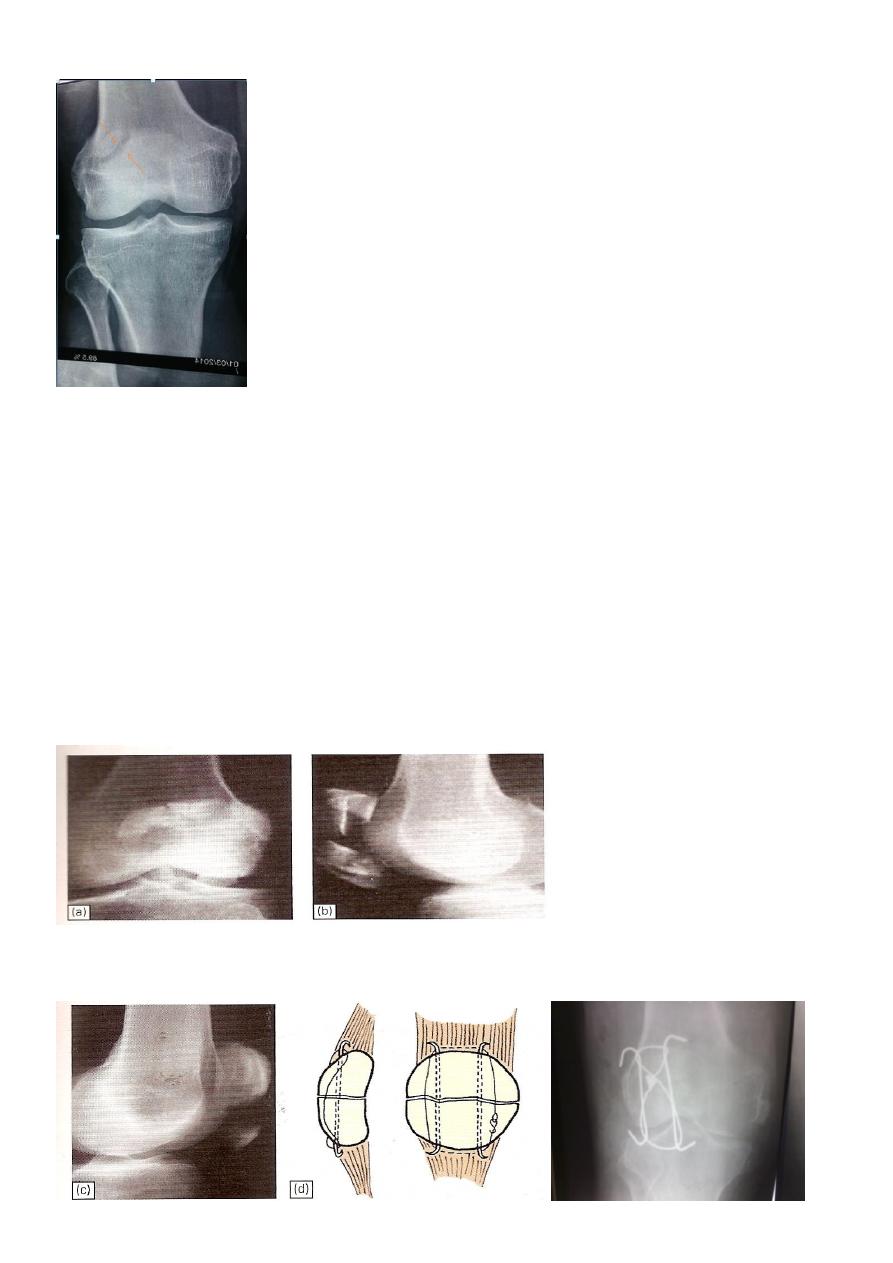
7
congenital Bipartate patella
Clinical assessment
Degree of hemarthrosis.
Ability to extend the knee (integrity of quadriceps mechanism).
Differential diagnosis: congenital bipartate patella.
Treatment
Undisplaced or minimally displaced crack:
Aspirate hemarthrosis.
POP cylinder for 4-6 wks.
Quadirceps exercise.
Comminuted (stellate) fractures:
Extensor expansion is intact.
Undersurface of patella irregular- may damage patellofemoral joint.
Patellectomy.
Displaced transverse fractures:
Knee extension is impossible.
Initial fixation by tension wire with backslab.
8
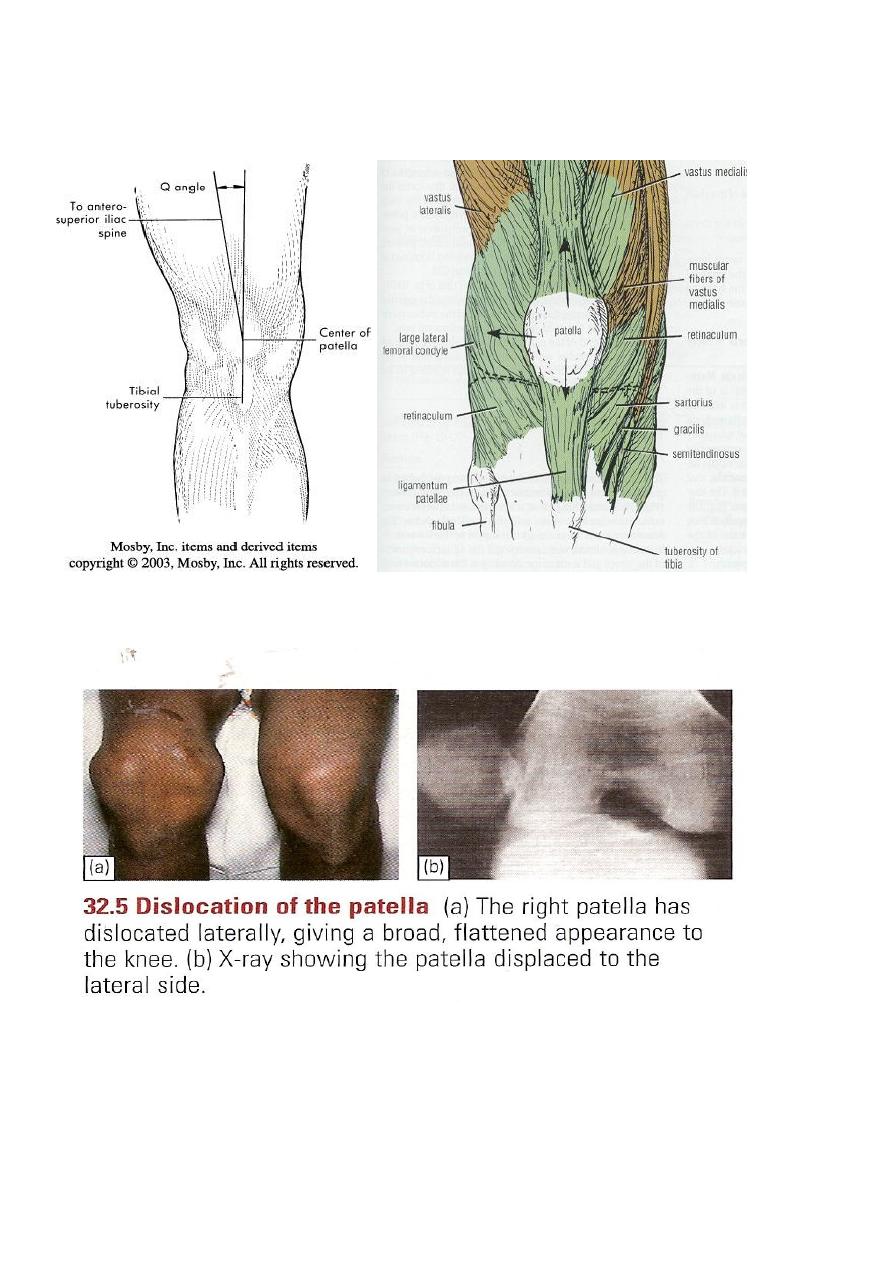
Dislocation of patella
Knee is normally in valgus- quadriceps tend to pull the patella laterally.
Sudden severe quadriceps contraction with the knee stretched in valgus lead to lateral
dislocation of the patella.
Clinical features
First time dislocation; tearing sensation, patient collapse on the ground.
Patella may remain dislocated or springs back into position spontaneuously.
Treatment
Reduction with or without anesthesia
Backslab for 3 weeks
Recurrent dislocation occur in patients with small high patella and excessive
genu valgum and joint laxity
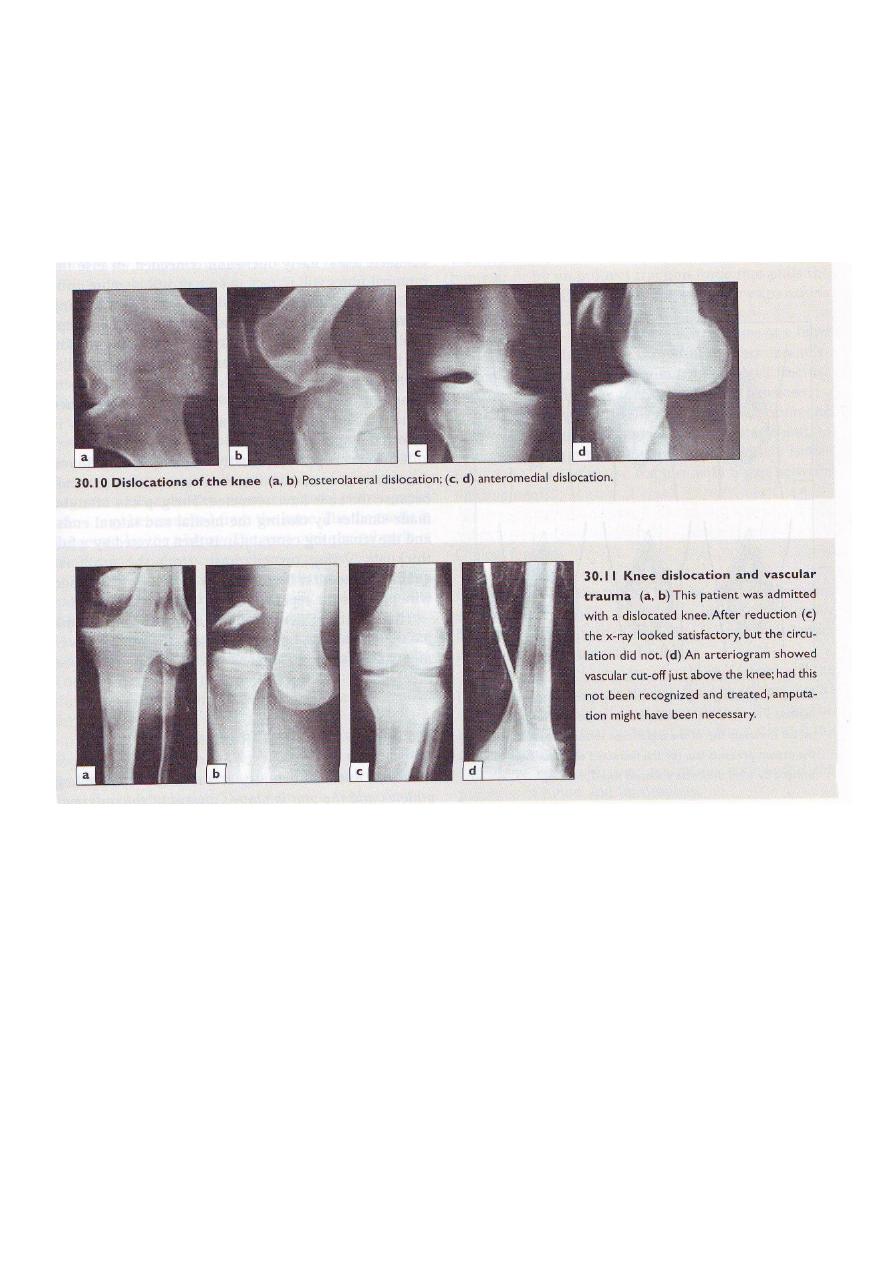
9
Dislocation of the knee
Considerable violence is required e.g. RTA
ACL, PCL & one or both collaterals are usually torn.
Clinical features:
Swelling, bruising and deformity
Exam distal neurovascular integrity
Treatment: reduction under anesthesia and backslab.
Early detection and treatment of compartment syndrome and vascular inj.
