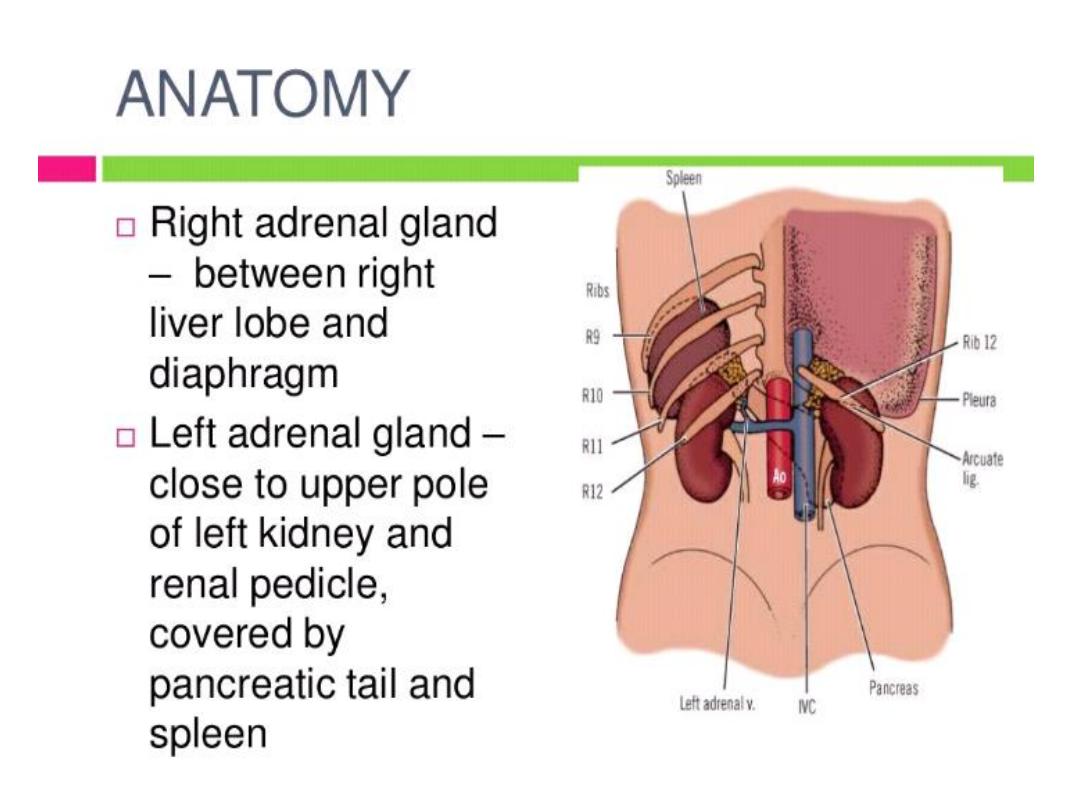
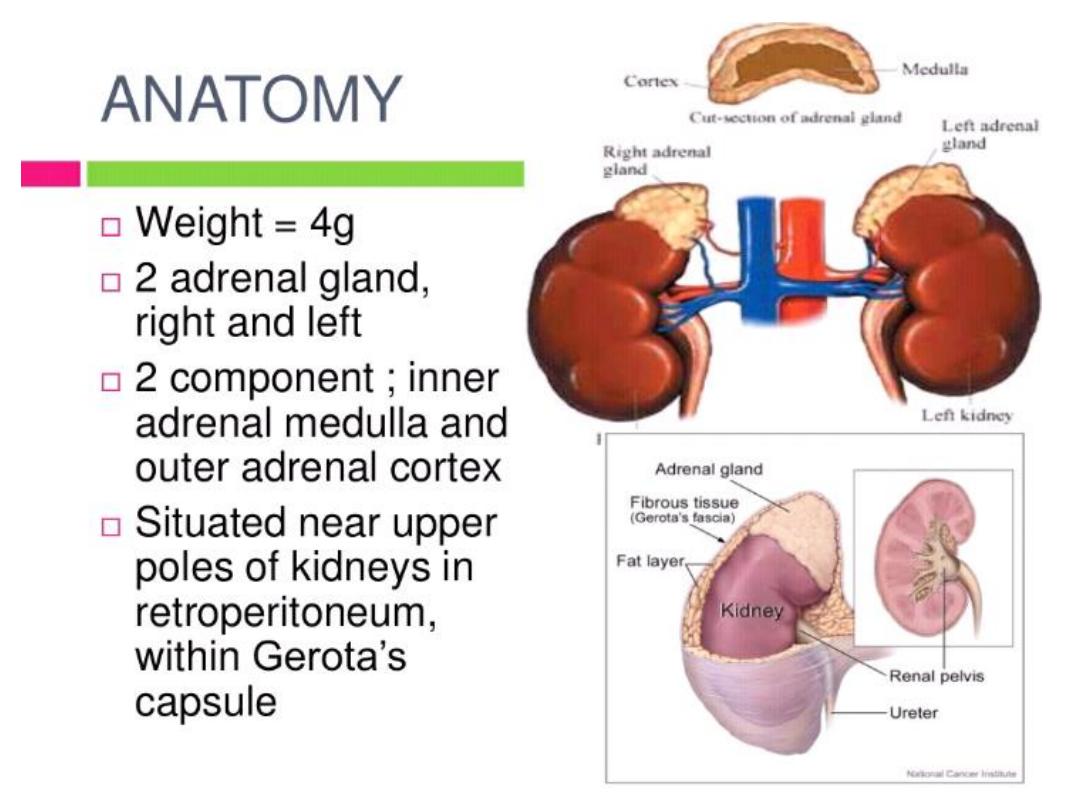
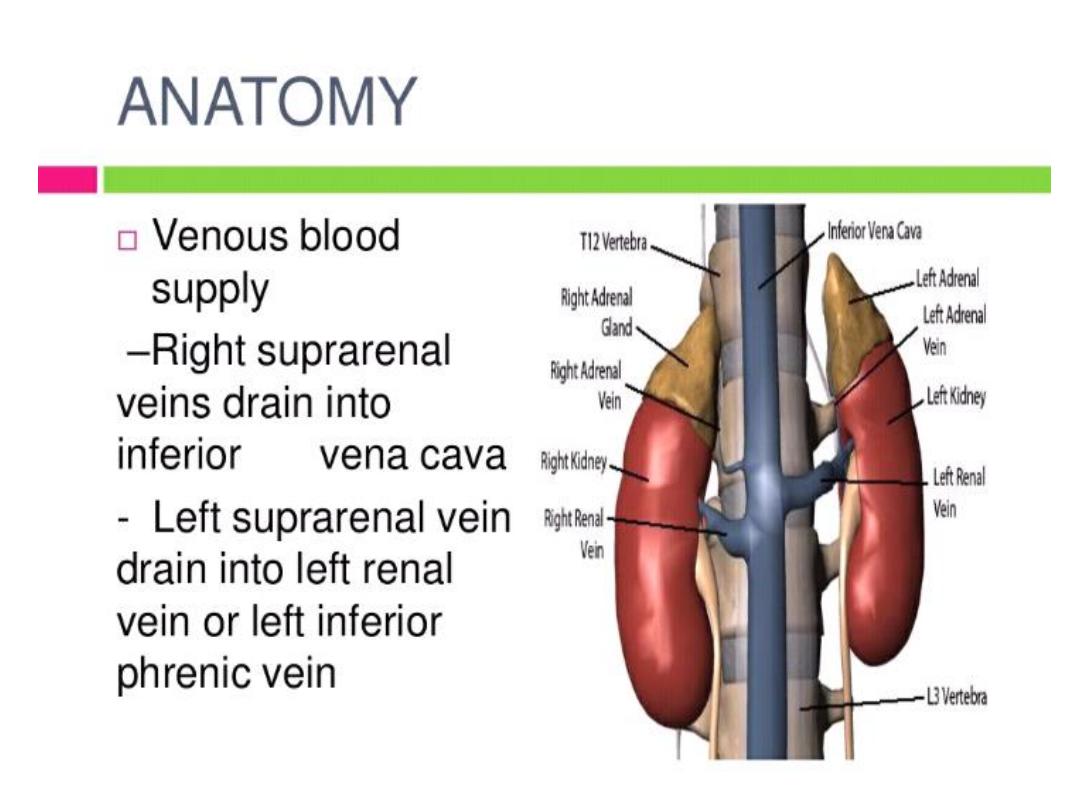
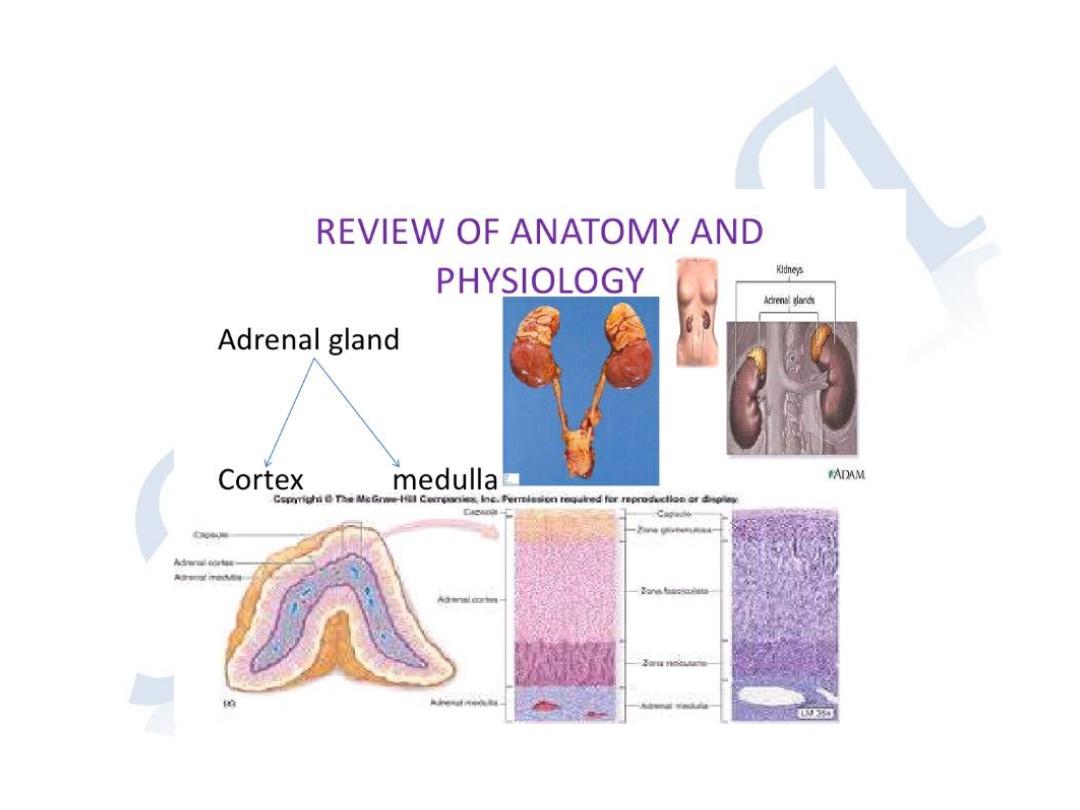
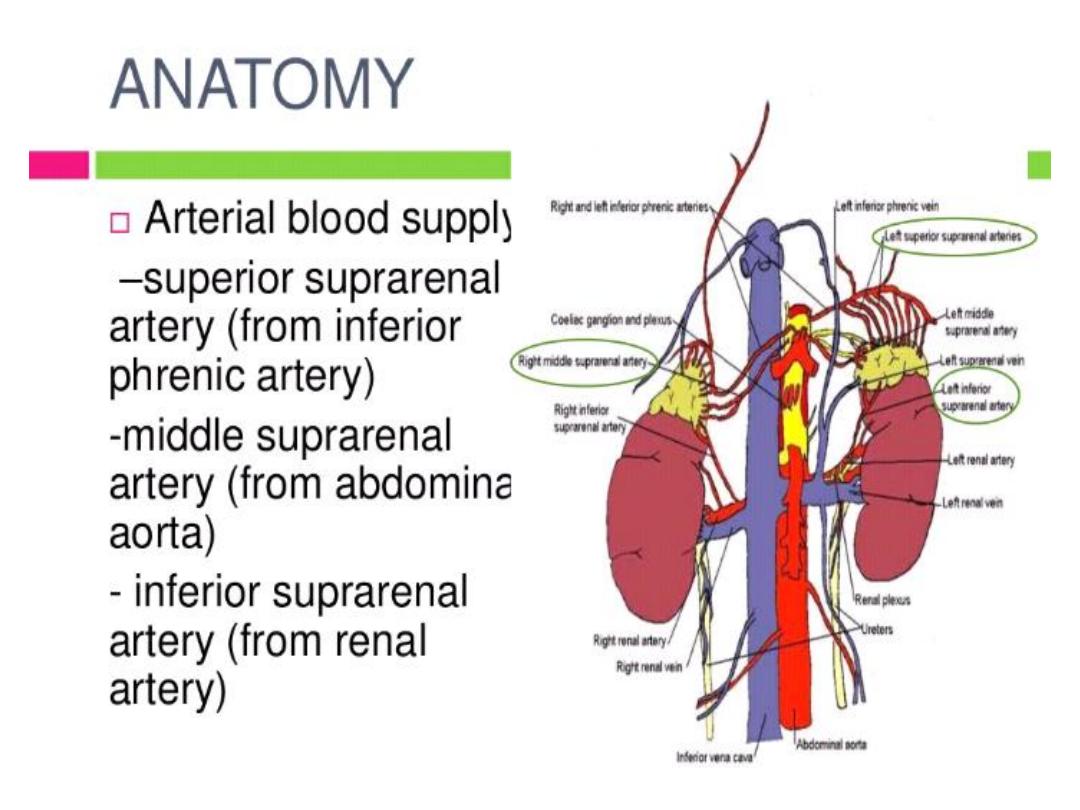
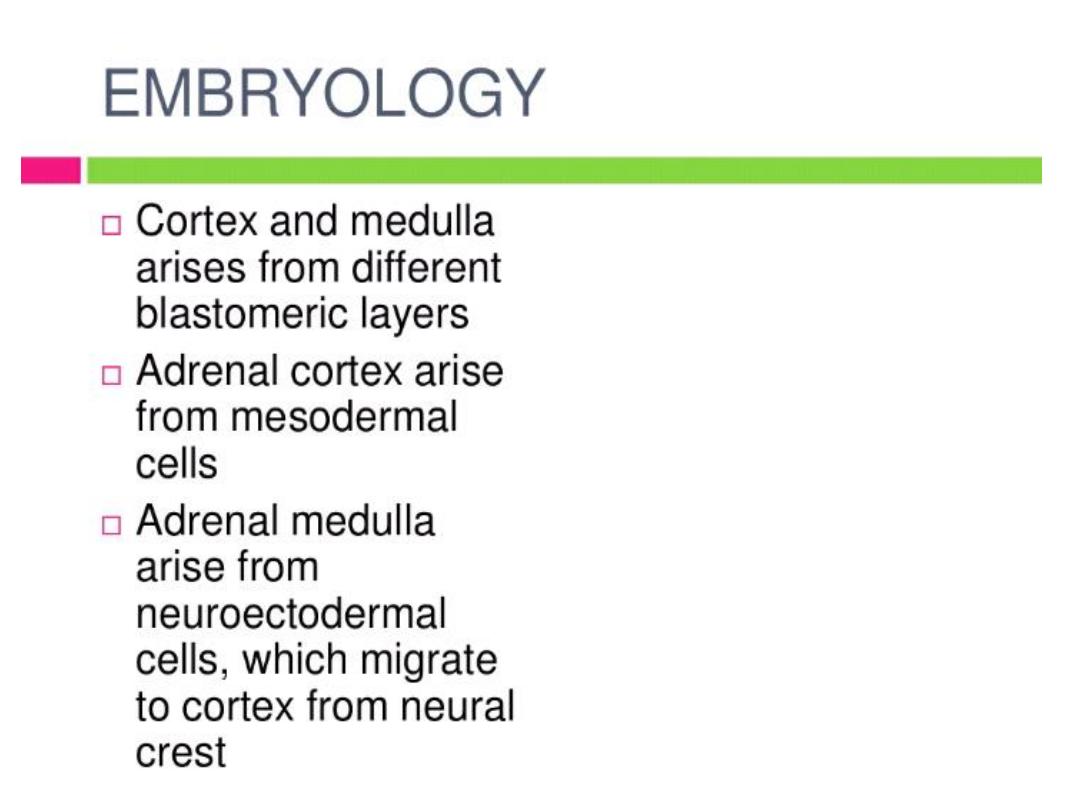
ADRENAL GLANDS
DR. Zaeem f. dahla
General surgeon MD


INCIDENTALOMA
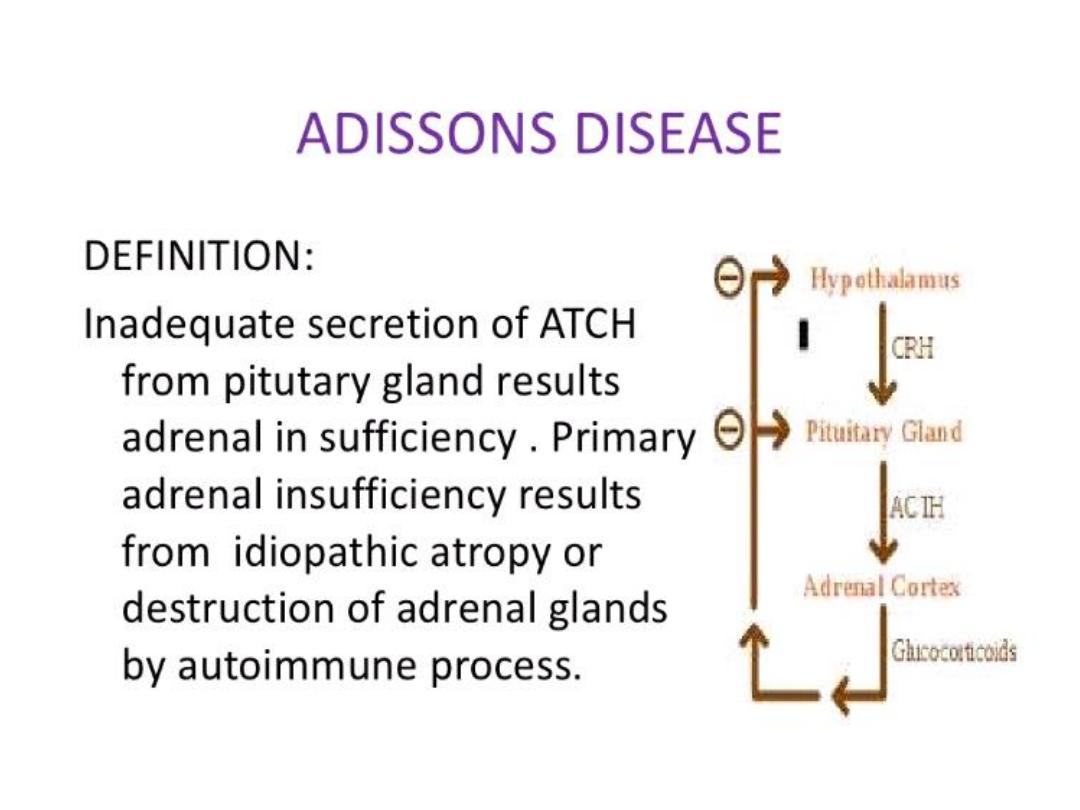
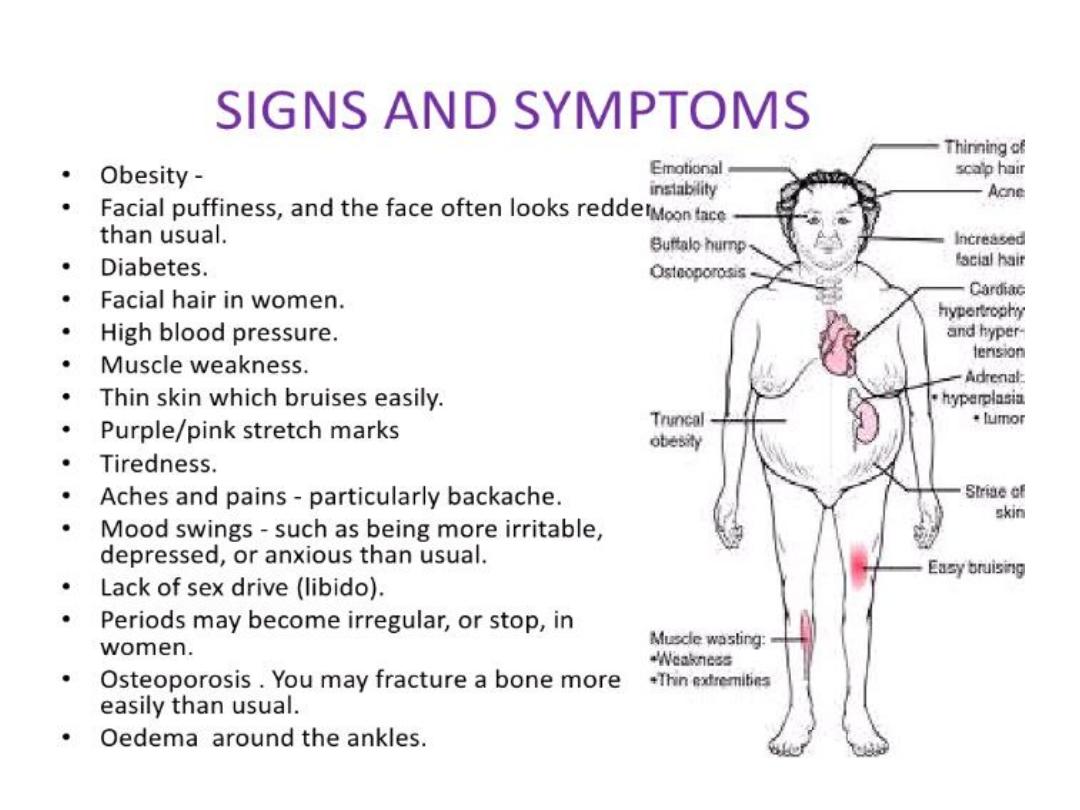
• DEFINITION
; a clinically unapparent mass detected
incidentally by imaging studies conducted for other reasons.
• Incidence;1.4%--8.7% increase with age.
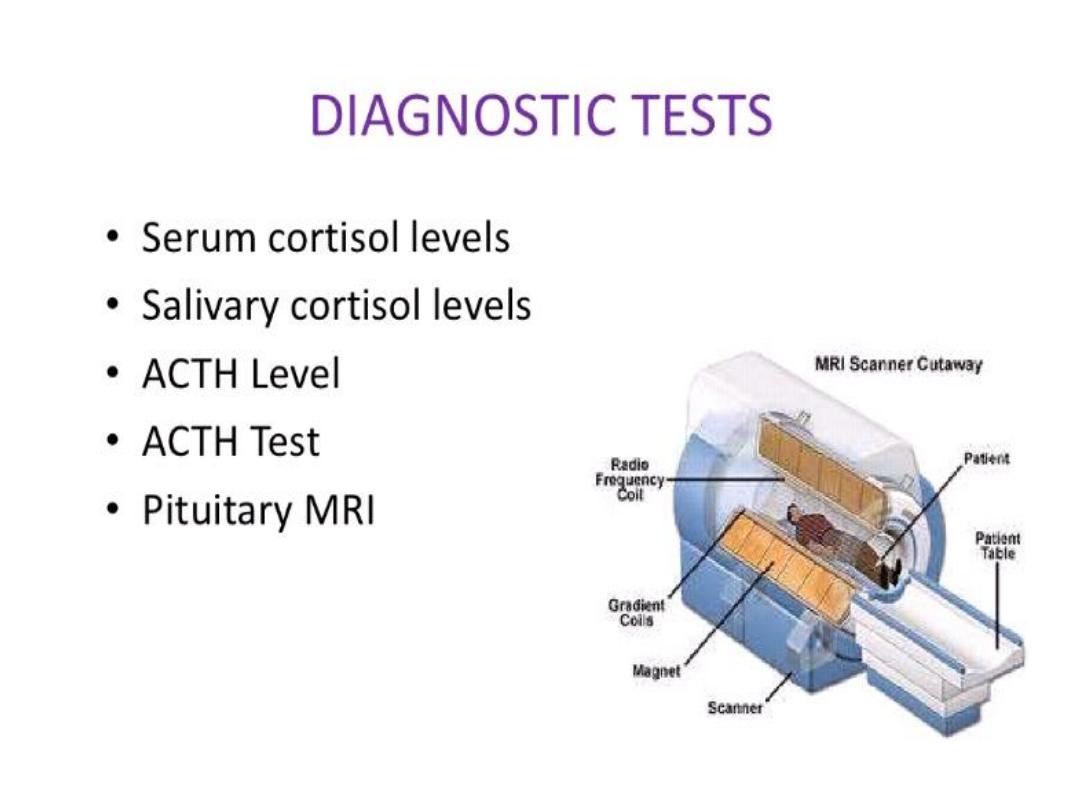
• DIAGNOSIS
;
• Hormone evaluation; morning and mid night plasma cortisol
measurements.
• 1 mg dexamethasone suppression test.
• 24 h urinary cortisol level.
• 24 hs urine cortisol metabolite.
• S k , aldosterone , renin activity.
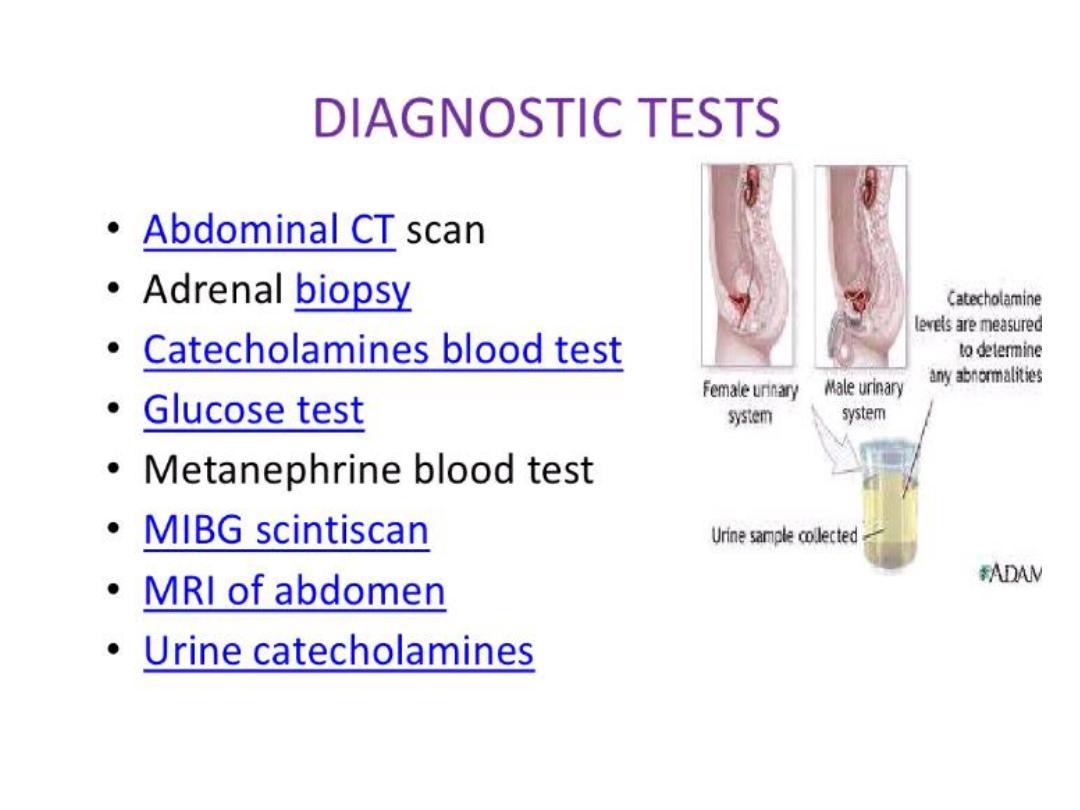
• CT,MRI.
• Adrenal gland biopsy.


INVESTIGATION
• When incident Loma identified , good
informative history and physical examination
,should be done.
• Occult endocrine disease my be detected.
• Biochmemical work up should be done.
• Hormonal evaluation should be done.

Hormonal evaluation
• Morning and mid night cortisol level.
• 1 mg dexamethasone suppression test.
• 24h urinary cortisol excretion.
• 12-24 h metanephrines & plasma
metanephrines level.
• Serum plasma aldosterone ,plasma Renin.
• DHEAS , testosterone , or 17 hydroxyestradiol
(virilizing or feminizing tumors).
• Imaging technique CT,MRI.

TREATMENT
• Non-functioning mass <4 cm , smaller tumor
that increase in size---resection.
• Non-functioning tumor less than 4 cm ,
followed up for 6,12,24 months.

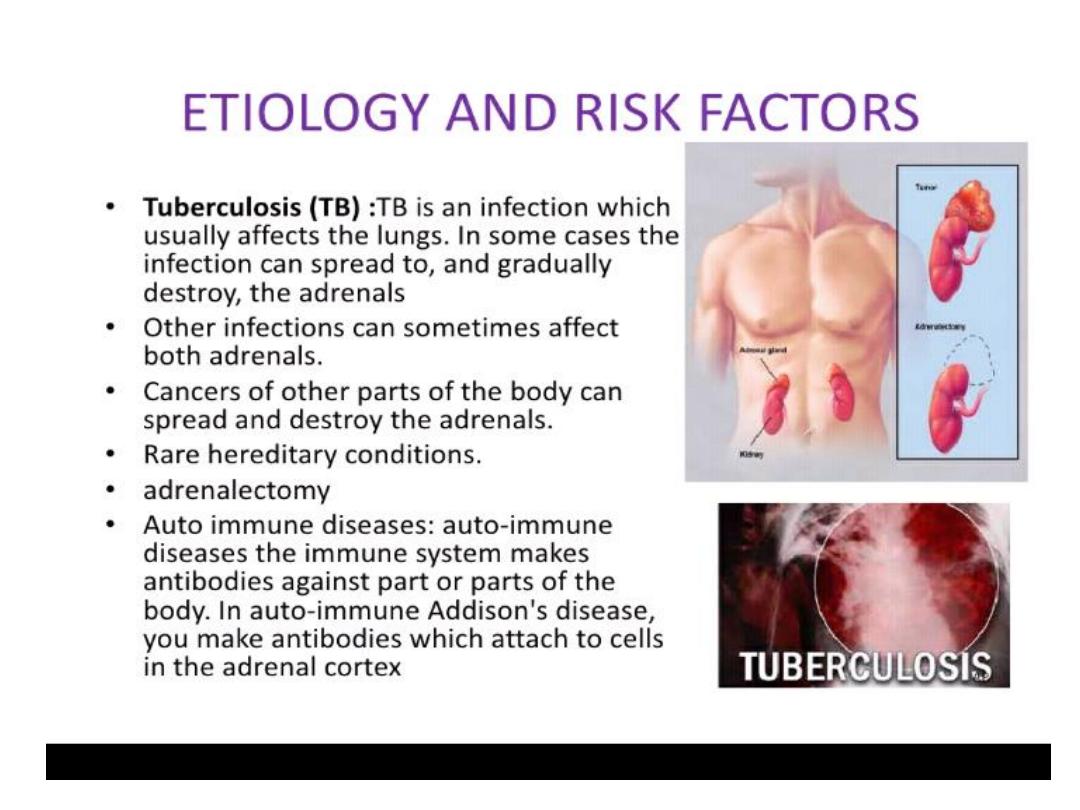
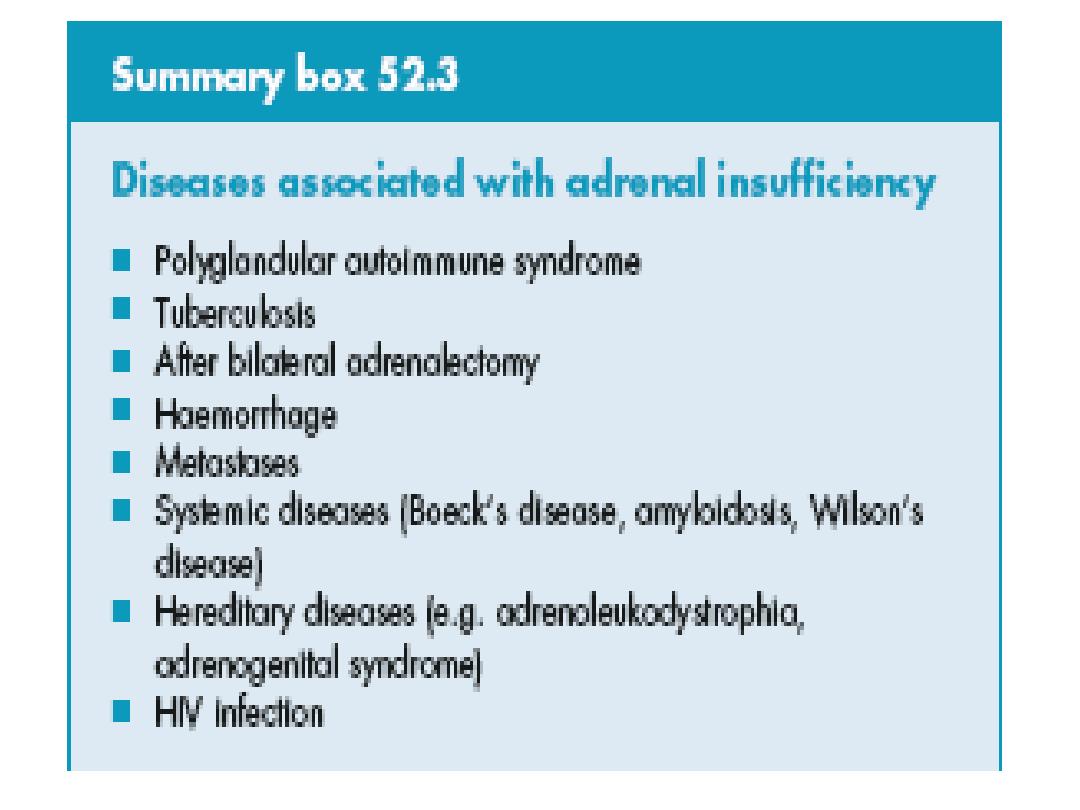
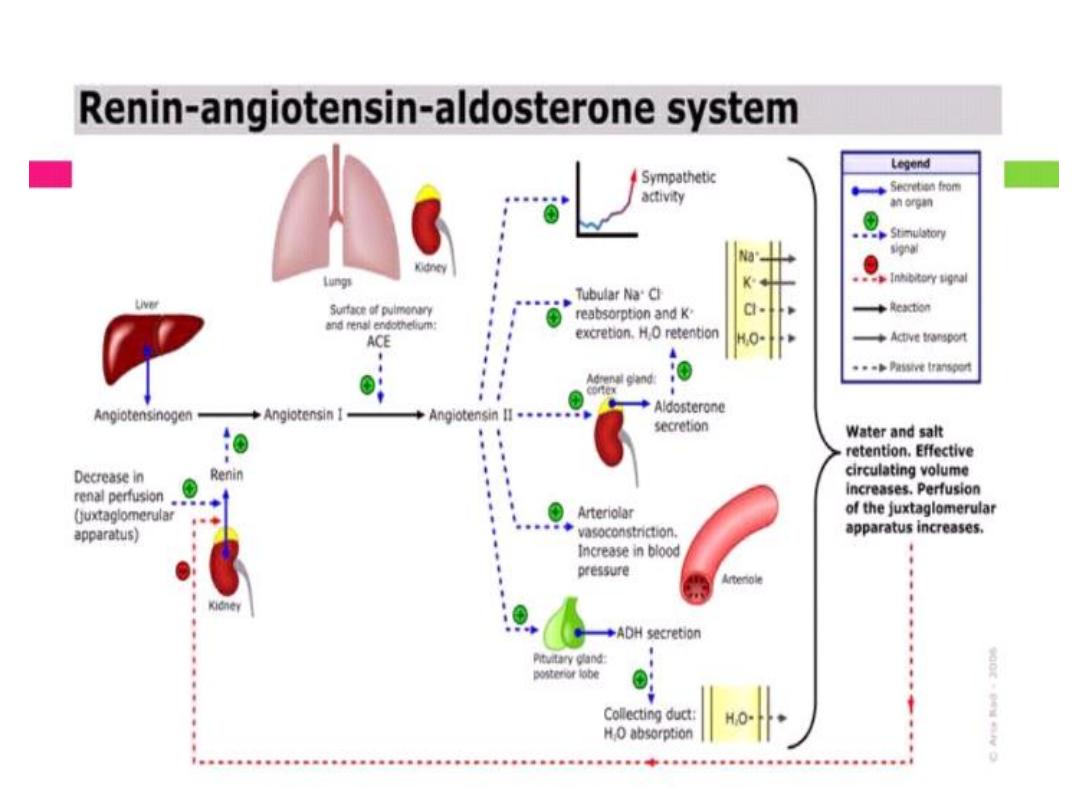
PRIMARY HYPERALDOSTERONISM(CONN”S
(
SYNDROME
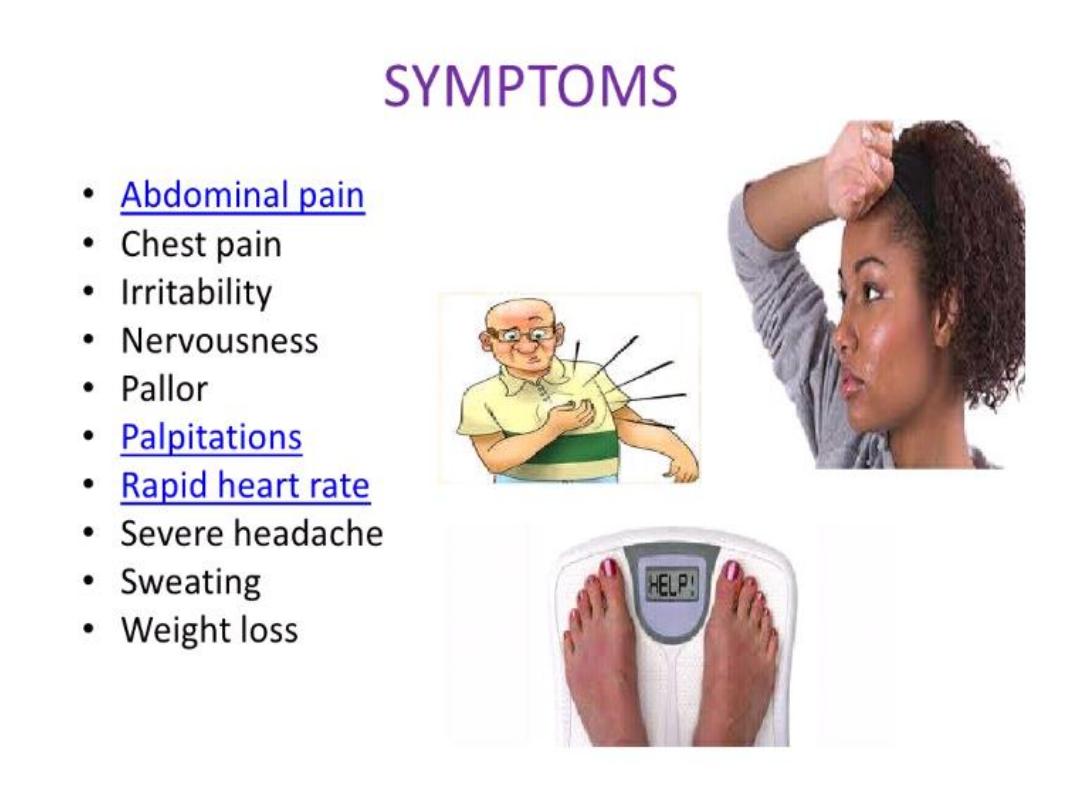
• Hypertension , hypokalemia , hyper secretion
of aldosterone.
• Hypertensive patient with hypokalemia 2%.
• Hypertensive patient with normal potassium
12%.

Primary hyper aldosteronsim(PHA)
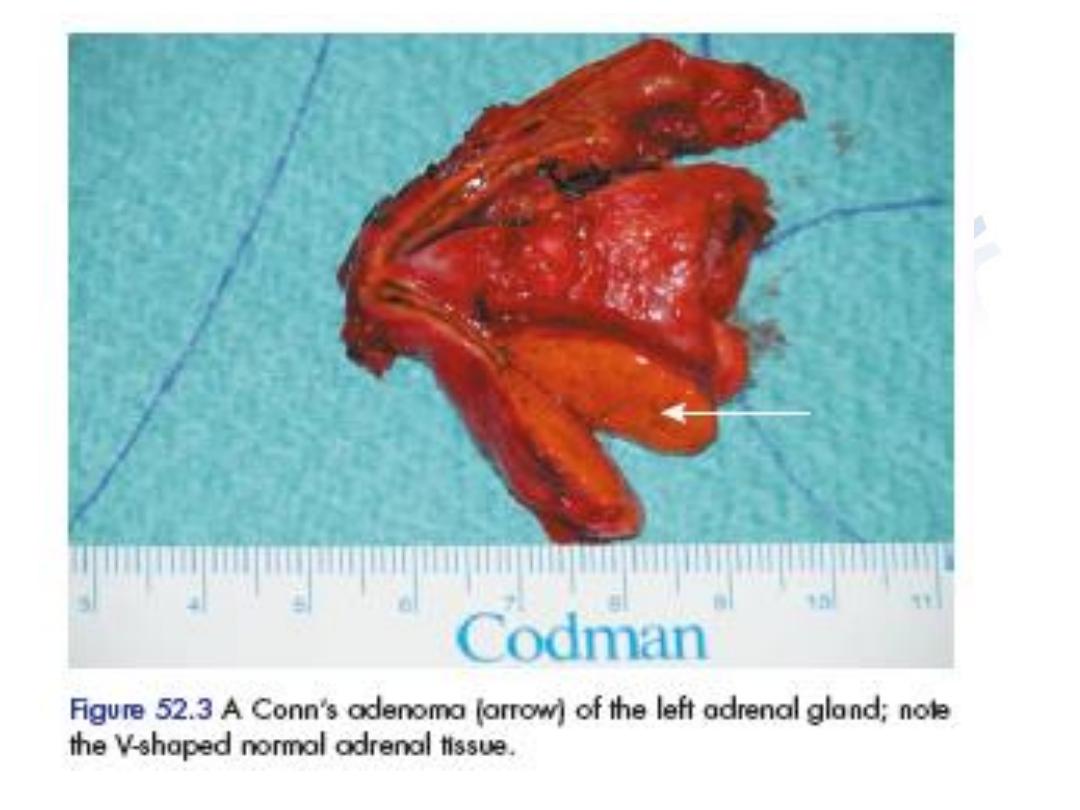
• Pathology:
• Most unilateral adrenocortical
adenoma(conns syndrome)
• 20-40% bilateral adrenal hyperplasia.
• Rare;carcinma

Clinical features
• Age;30-50 ys with female predominance.
• Hypertension.
• Headache.
• Muscles weakness.
• Cramps
• Intermittent paralysis
• Polyuria
• Polydipsia
• Nocturia

DIAGNOSIS
• Biochemical test ; Asses potassium
,aldosterone, level to plasma renin activity.
• MRI,CT, to distinguish unilateral from bilateral.
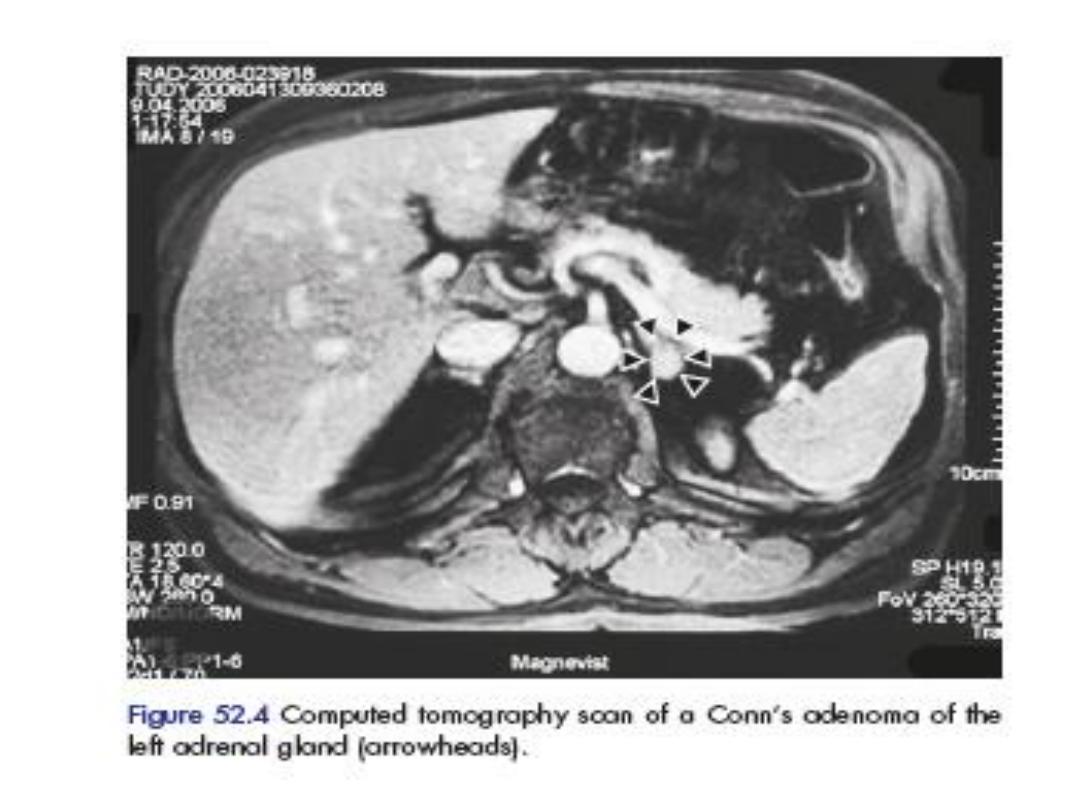
• Conns adenoma usually measure 1-2 cm.
• Selective adrenal vein catheterization ,for
sample taken,Aldosterone & cortisol ratio
.differentiate unilateral from bilateral active
gland.

TREATMENT
• Frist line of treatment with bilateral
hyperplasia is medical= spironolactone.
• Antihypertensive medication.
• Lap . surgical resection for disease gland.