MALE INFERTILITY
INFERTILITYThe inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting couple to achieve pregnancy in one year
EPIDEMIOLOGY
25% of couples don’t achieve pregnancy within one year, 15% of them seek medical treatment.The chance of normal couples conceiving is estimated to be:
20% per month
75% by 6 months
90% by 1 year
EPIDEMIOLOGY
20% of infertility cases are due to male factors & 30-40%of them due to both male & female factors.
Fertility rates are at their peak in men & women at age 24 years,beyond that age,they decline in both sexes.
25-35% of infertility couples will conceive at sometime by intercourse alone.
Goals of evaluation of infertile men
• Identification of reversible disorders.• Identification of irreversible conditions.
• Identification of chromosomal & genetic abnormalities that may affect the offspring.
• Identification of idiopathic cases.
Prognostic factors
• Duration of infertility.• Primary or secondary infertility.
• Results of seminal fluid analysis(SFA).
• Age & fertility state of female partner.
Evaluation of infertile male
History.Physical examination.
SFA.
Adjunctive laboratory investigations.
Radiologic investigations.
Testicular biopsy.
History
Physical examination
Abnormal secondary sexual characters.Gynecomastia.
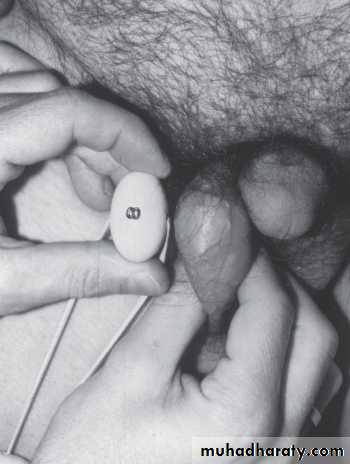
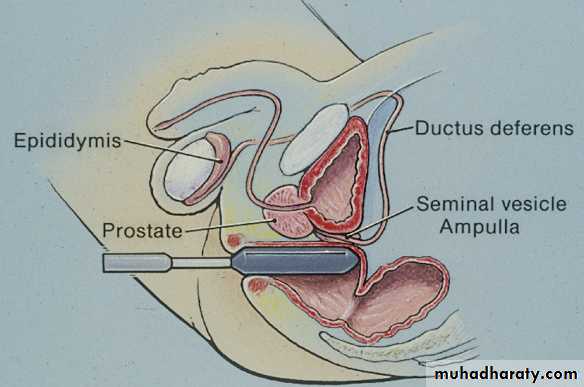
Genital examination:
Penis
Scrotum
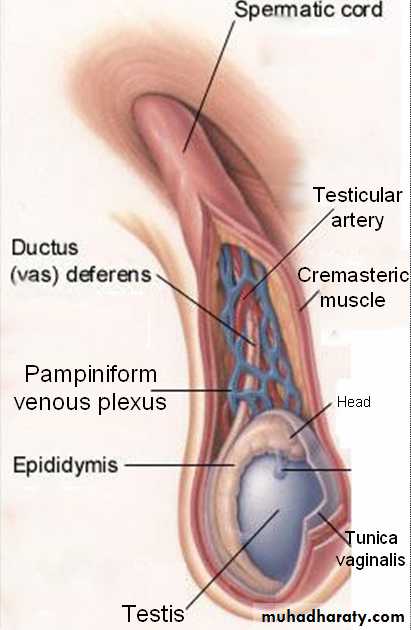
Spermatic cord.
DRE.
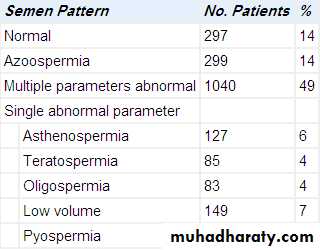
Seminal fluid analysis(SFA)
2 0r 3 samples examined over a period of several weeks for more accuracy.Sample collection.
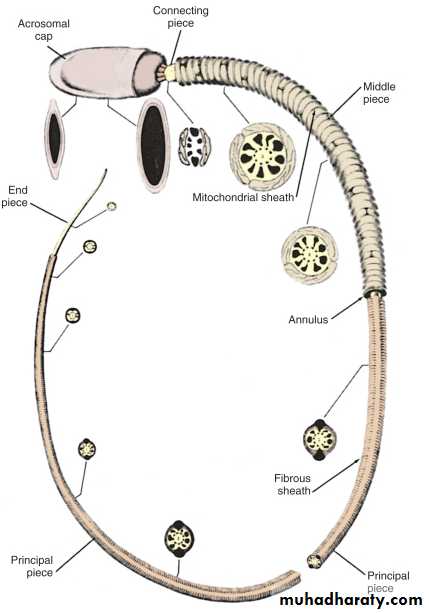
Sperm morphology
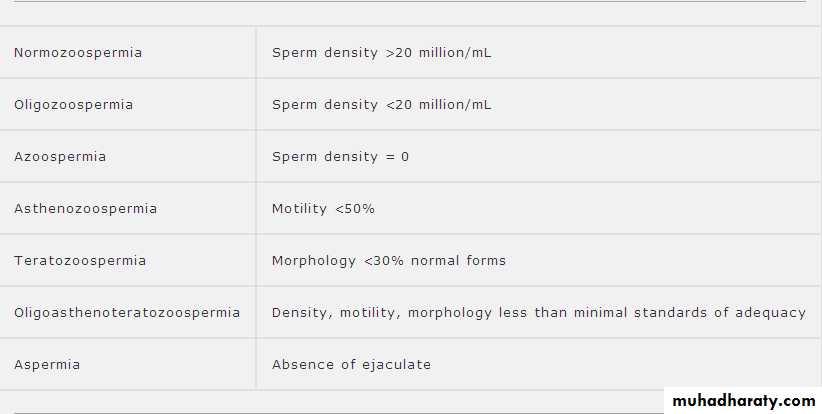
SFA nomenclature
Adunctive laboratory tests
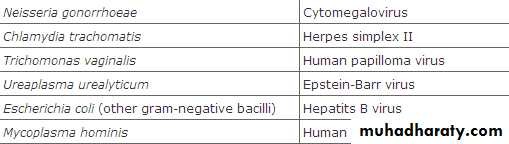
Semen cultureFor pyospermia (3-23% of infertility case).
Immature germ cells vs. leukocytes ??Indications :
1.History of genital infection.
2.Presence of > 1000 pathogenic bacteria/ml.
3.Presence of >10⁶ WBC/ml.
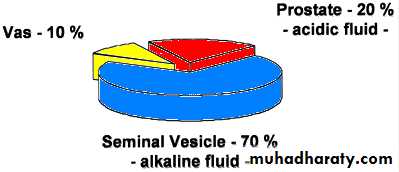
Semen fructose
Indicated in seminal fluid with low ejaculate volume, acidic PH & no sperms.Absent in seminal vesicle agenesis or obstruction.
Post ejaculate urinalysis
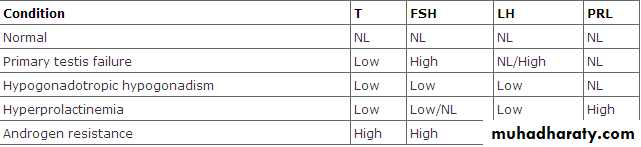
For suspected retrograde ejaculation.Hormonal tests
Less than 3% of infertile men have hormonal etiology.Used to evaluate the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis.
Testosterone,LH,FSH &prolactin are the main hormones.
Indications of hormonal evaluation:
1.Sperm density< 10x10^6/ml
2.Impaired sexual function.
3.Findings suggestive of a specific endocrinopathy.
Antispermantibody(ASA) test
These antibodies occur if the blood-testis barrier is broken(by testicular trauma or torsion or by vasectomy).Indirect Ab. or direct Ab.
Commonly measured by mixed agglutination reaction.
ASA are detected in 10% of infertile men vs. 2% of fertile men.
Indications:
1.Sperm agglutination or clumping by SFA.2.+ve postcoital test(PCT).
3.Low sperm motility with history of testicular injury or surgery.
4.Unexplained infertility.
Chromatin/DNA integrity testing.
Electron microscopy
For ultrastructural defects in sperms.
Indicated if sperm motility < 5-10 % with good viability of sperms.Sperm function tests
1.Sperm-cervical mucus interactionIndicted in:
1.Hyperviscous semen.
2.Low volume semen with normal sperm count.
3.Suspected cervical mucus abnormalities.
4.Unexplained infertility.
2.Sperm viability assay (hyposmotic swelling test)
Used if sperm motility<5-10%.3.Sperm penetration assay
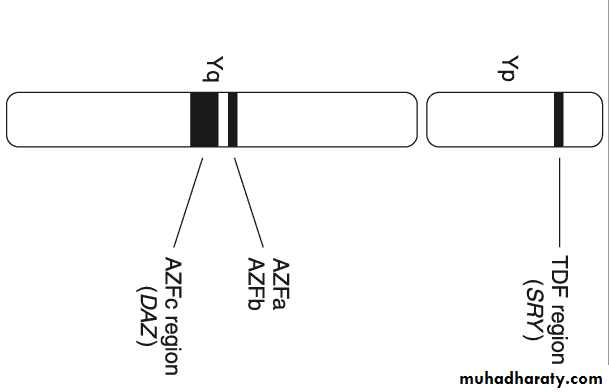
Genetic (chromosomal) testsIndicated in azospermia or severe oligospermia.
5.8%of infertile men have genetic defects.
The defects are either:
Numerical (e.g. klinefilter syndrome).
Structural (e.g. CFTRG mutations).
The defects are in the sex chromosomes or autosomes.
Y chromosomes microdeletions ( AZFc is the most common).
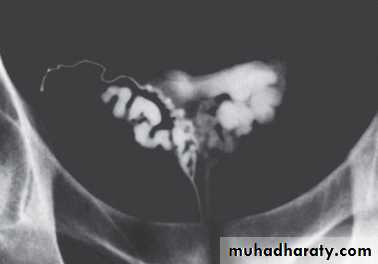
Radiologic investigations
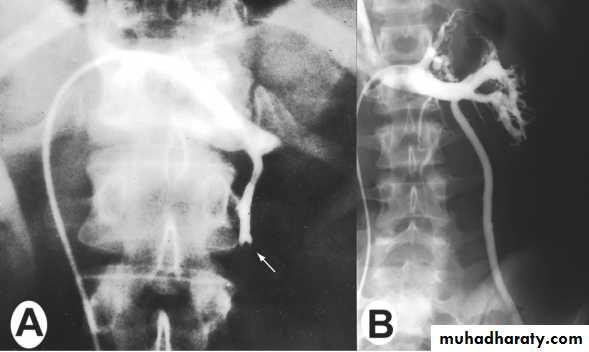
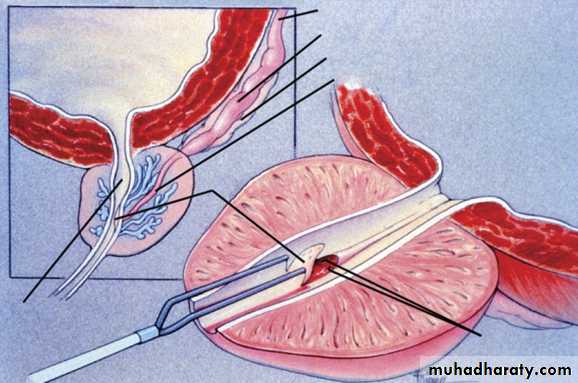
VasographyUsed to assess the patency of the vas, seminal vesicles & ejaculatory duct & to aspirate vasal fluid.
The best timing of it is prior to vasal reconstructive surgery.
Indicated in :
• Azospermia with normal testicular biopsy.
• Severe oligospermia
• Venography
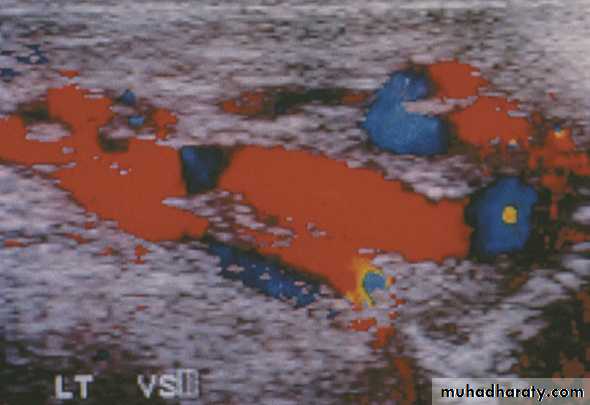
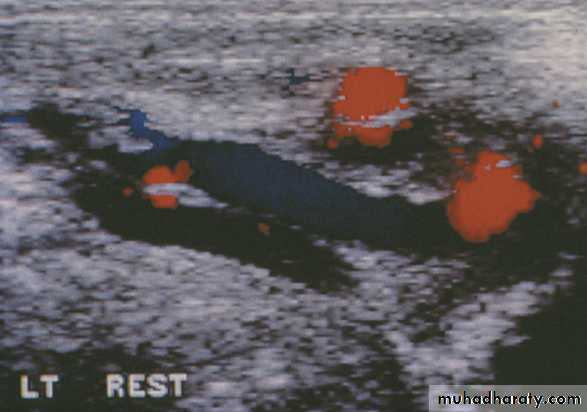
• The best tool to diagnose varicocele & to treat it by embolization (via femoral or internal iliac veins).• Ultrasonography (US)
• Scrotal US: for varicocele or testiculr tumors.
• Abdominal US: to detect renal agenesis (in 80% of pt. with unilateral CAVD).
•
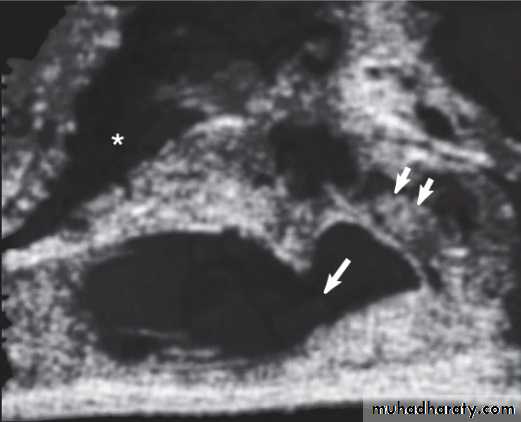
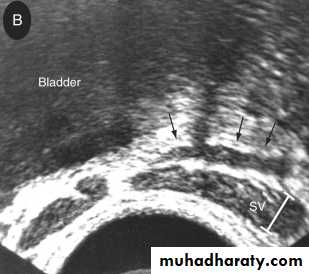
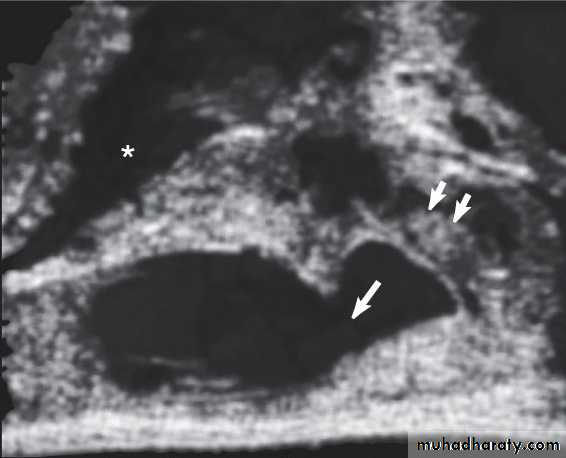
3.Transrectal U.S.(T.R.U.S.)
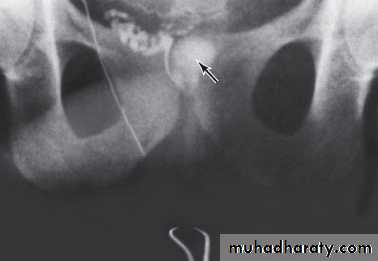
To assess the prostate,seminal vesicles,ejaculatory duct &vas.Indicated in azospermia with suspected ejaculatory duct obstruction.
Equivocal TRUS findings in suspected ejaculatory duct obstruction can be confirmed by seminal vesicle aspiration.
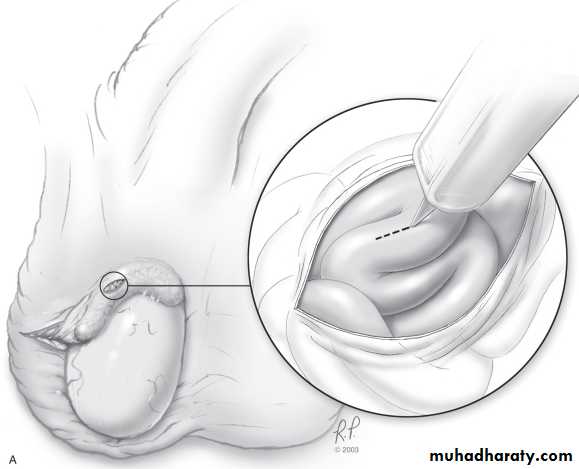
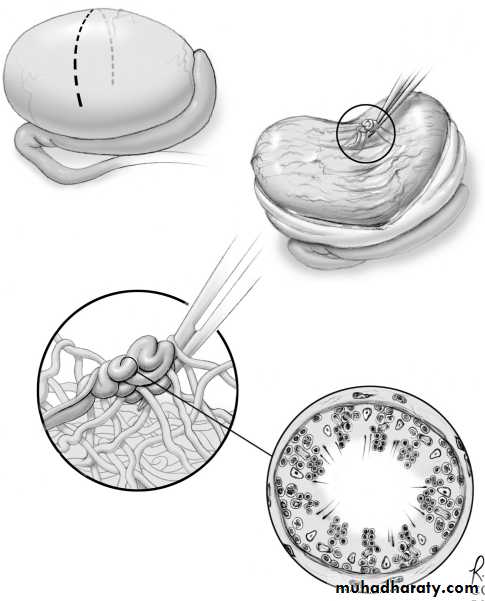
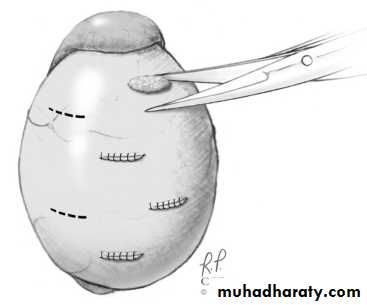
Testicular biopsy
Eitherdiagnostic( to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive azospermia in pt.with normal testicular size & normal FSH level).
Or
theraputic (to harvest sperms for IVF or for cryopreservation).
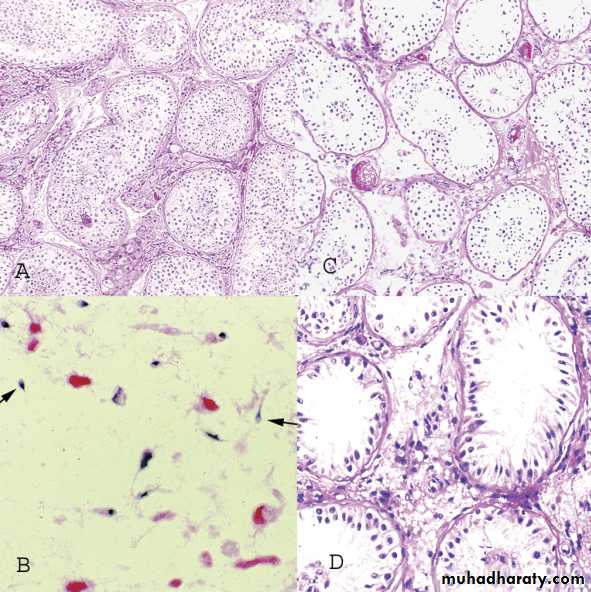
• Histological forms seen in testis biopsy
• 1.Normal testis.
• 2.hypospermatogenesis.
• 3.Maturation arrest.
• 4.Germ cell aplasia(Sertoli cell only syndrome).
• 5.End stage testis(sclerotic testis).
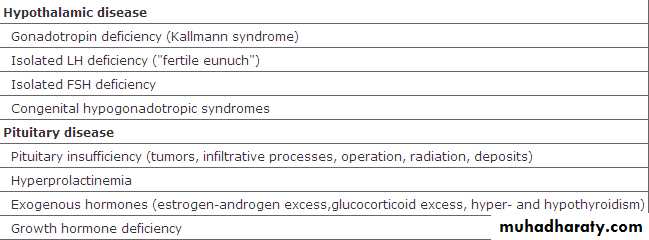
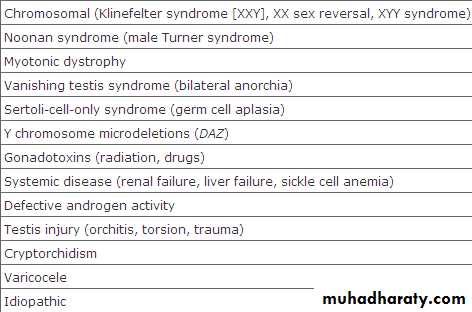
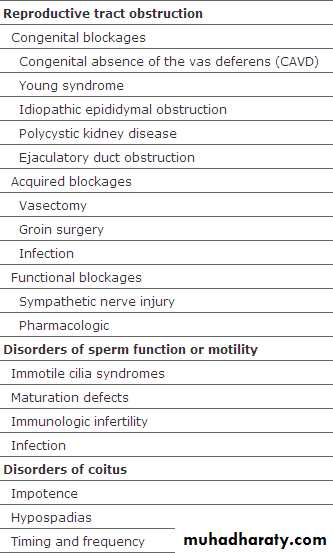
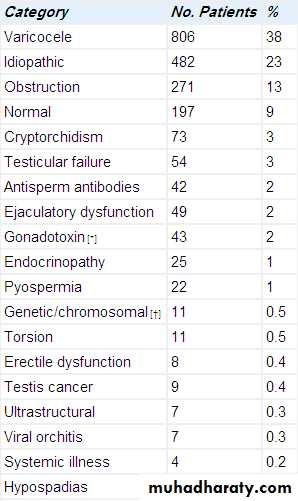
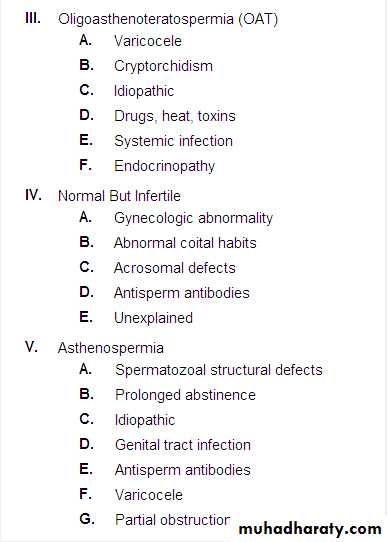
Causes of male infertility
Causes of male infertility
Causes of male infertility
varicocele
Abnormally dilated testicular veins within the spermatic cord.Clinical vs. subclinical varicocele.
Affects 15%of normal adolescents vs. 20-40% of infertile men.90% left sided-10% bilateral.
The most common surgically correctable cause of infertility.
Why it occur?
MULTIFACTORIALAnatomic variations.
Raised Hydrostatic pressure.
Raised Testicular temperature.
Reflux of renal &adrenal metabolites from renal vein.
ALLreduced testicular size,sperm motility & count infertility.
Diagnosed:
*clinically
*SFA.
*doppler scrotal U.S.
Treatment
surgical
1.embolization.
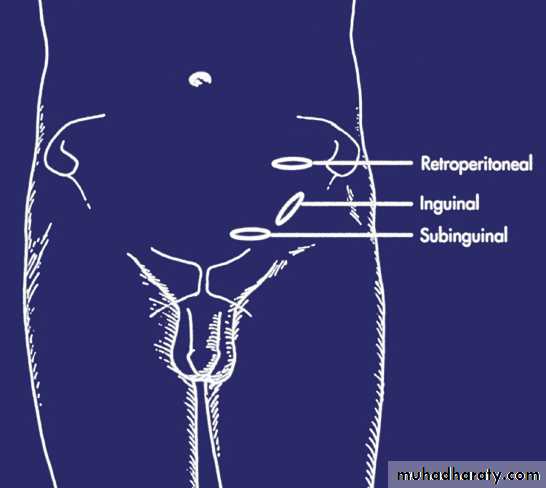
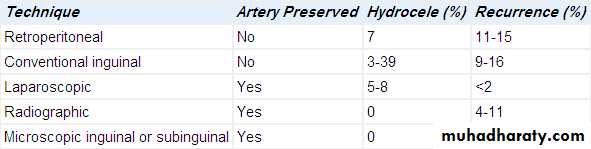
2.ligation of dilated testicular veins:
*retroperitoneal
*inguinal
*subinguinal
*laparoscopic
This Rx. Improve seminal parameters in 70% of pt. & improve conception rate in 40-50% of couples.
For whom to do surgery?
clinical varicocele.
abnormal SFA or infertility.
affected testicular growth especially adolescents.
Treatment of male infertility
It is better to improve male/female fertility & to allow natural conception
If this is not successful, assissted reproductive techniques(ART) are used.
Types:
medical Rx.
surgical Rx.
ART.
Medical Rx.
1. Life style modifications.2. Hormonal Rx.
Gonadotropins(LH/FSH)
*Used for hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism.
* Formulae: HCG, HMG or recombinent FSH.
GnRH
uesed only for hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism with intact pituitary function.
Testosterone Rx.
different formulae are used to induce virilisation in pt. with primary or secondary testicular failure.excess testosterone is a male contraceptive.
Antiprolactinaemic drugs
For hyperprolactinaemia.
Treatment of thyroid disorders, estrogen excess & corticosteroid excess.
Corticosteroids
*used for immunologic infertility( it accounts for 10% of infertility cases).
*It achieves pregnancy rate = 30-40%.
3. Treatment of pyospermia
*proper antibiotics
*antioxidants.
*frequent ejaculation.
4. Empirical medical Rx.
*for idiopathic infertility(25% of *infertility cases).
*Not proven effective.
*Includes clomiphen citrate, tamoxifen & GnRH/gonadoropins
5. Other drugs
kallikreins,antioxidants,zinc,arginine& L-carnitine.6. Growth hormones
For oligospermia(under investigations).
Surgical treatment
1. Varicocele Rx.Ligation of dilated testicular veins to eliminate retrograde reflux of venous blood via gonadal veins.
Types of surgery:
*percutaneous embolization.
*surgical ligation via:
-retroperitoneal
-inguinal
-subinguinal
-laparoscopic routes.
Improved seminal parameters in 70% of pt.
Improved pregnancy rate in 40-50% of pt.Complications:
1. recurrence 2. hydrocele
3. vasal injury 4. testicular atrophy.
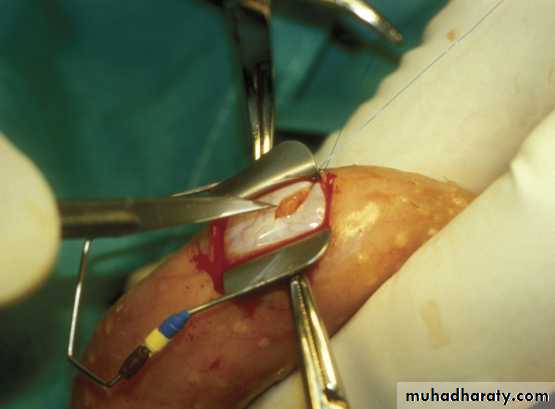
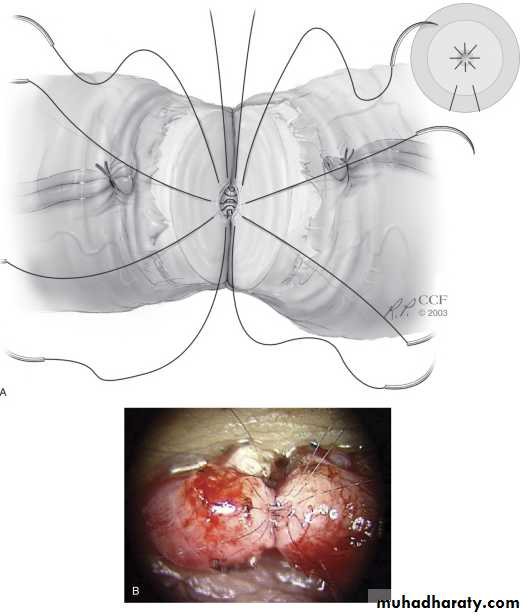
2. Repair of vasal or epididymal obstruction.
Vasovasostomy*indicated for vasectomy reversal.
*Complications
1.testicular atrophy 2. hematoma
3.recurrence(3-12%).
*patency & pregnancy rate:
Vaso-epididymostomy
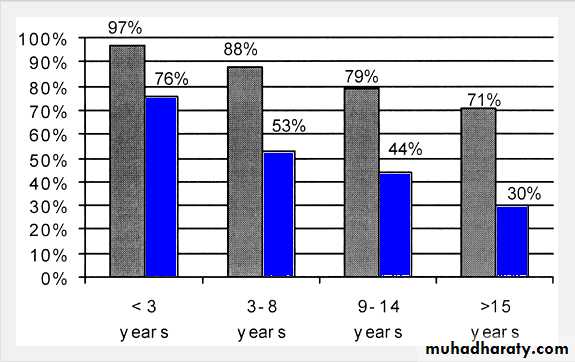
indicated inreversal of vasectomy for >15 years(if vasovasostomy failed).
epididymal obsruction.
Patency rate: 30-65%.
Pregnancy rate: 20-40%.
3. Rx. Of ejaculatory duct obstruction
Ejaculatory duct obsruction accounts for 1-5% of infertility cases.Treated by transurethral ejaculatory duct resectionn(TUEDR).
Patency rate: 65-70%.
Pregnancy rate: 20-30%.
4. orchidopexy.
5. Surgical Rx. Of pituitary tumors.6. Rx. Of ejaculatory dysfunction
a. Retrograde ejaculation(RGE)treated by alfa-agonists or TCA or sperm retrieval for IVF.
b. Anejaculation
absent seminal emission.mostly caused by spinal cord injury& retroperitoneal lymph nodes dissection & sometimes psychologic.
Treated by penile vibratory stimulation or electroejaculation.
The semen obtained is used for IVF.
Success rate: 75%.
7. Rx. Of anatomic,congenital & organic causes of male infertility
Hypospadias repair.Plication of peyronies disease.
Rx. Of erectile dysfunction.
Assissted reproductive technologies(ART)
Intrauterine insemination(IUI).In vitro fertilization(IVF).
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection(ICSI).
Gamete intrafallopian transfer(GIFT)
-zygote intrafallopian trasnfer(ZIFT)
-tubal embryo transfer(TET)
Intrauterine insemination
(IUI)*Indicated in:
-male factor infertility.-unexplained infertility.
-cervical mucus or anatomic abnormalities that interfere with sperm deposition at the cervical os.
*Office procedure, no anasthesia.
*Success rate: 15-20%.
*Complications
1.Uterine cramps 2.pelvic infections.
3.Multiple gestations.
IVF
It includes harvesting the oocyte & sperm in order to incubate them for fertilization then transferring the embryo to the uterine cavity.
Pregnancy rate: 20-30% per cycle.
Costs: 12000-15000 $ per cycle.
Indications:
failed medical or surgical Rx. or IUI.CBAVD.
severe oligospermia.
cryopreserved sperms.
azospermia( obstructive or non).
few viable sperms in the ejaculate.
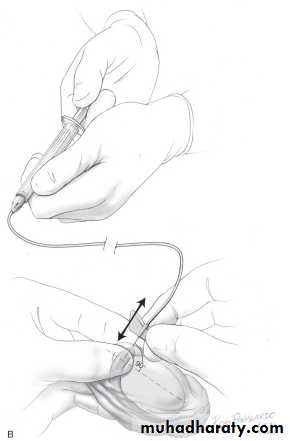
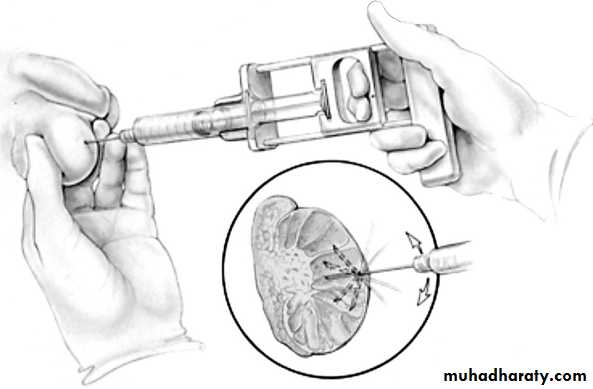
Sperms are retrieved for IVF by:
percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA)
microsurgical epididymal sperm aspiration(MESA).
Testicular sperm aspiration(TESA).
Testicular sperm extraction(TESE).
-microsurgical.-nonmicrosurgical
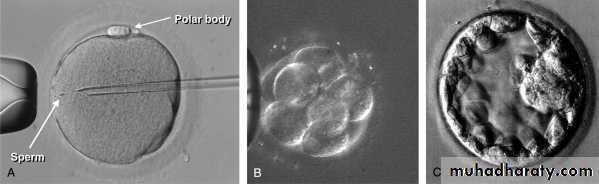
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection(ICSI)
A special micromanipulation of the sperm into the cytoplasm of a harvested oocyte.Useful in severe oligosprmia,azospermia & ultrasructural sperms defects.
Conception rate: 50% per cycle.
Varicocele repair,vasovasostomy or vasoepididymostomy are more cost effective with a better pregnancy rate than IVF/ICSI.
MOST COUPLES PREFER,
NATURAL FOODS,NATURAL FIBERS,
AND
NATURALLY CONCEIVED BABIES