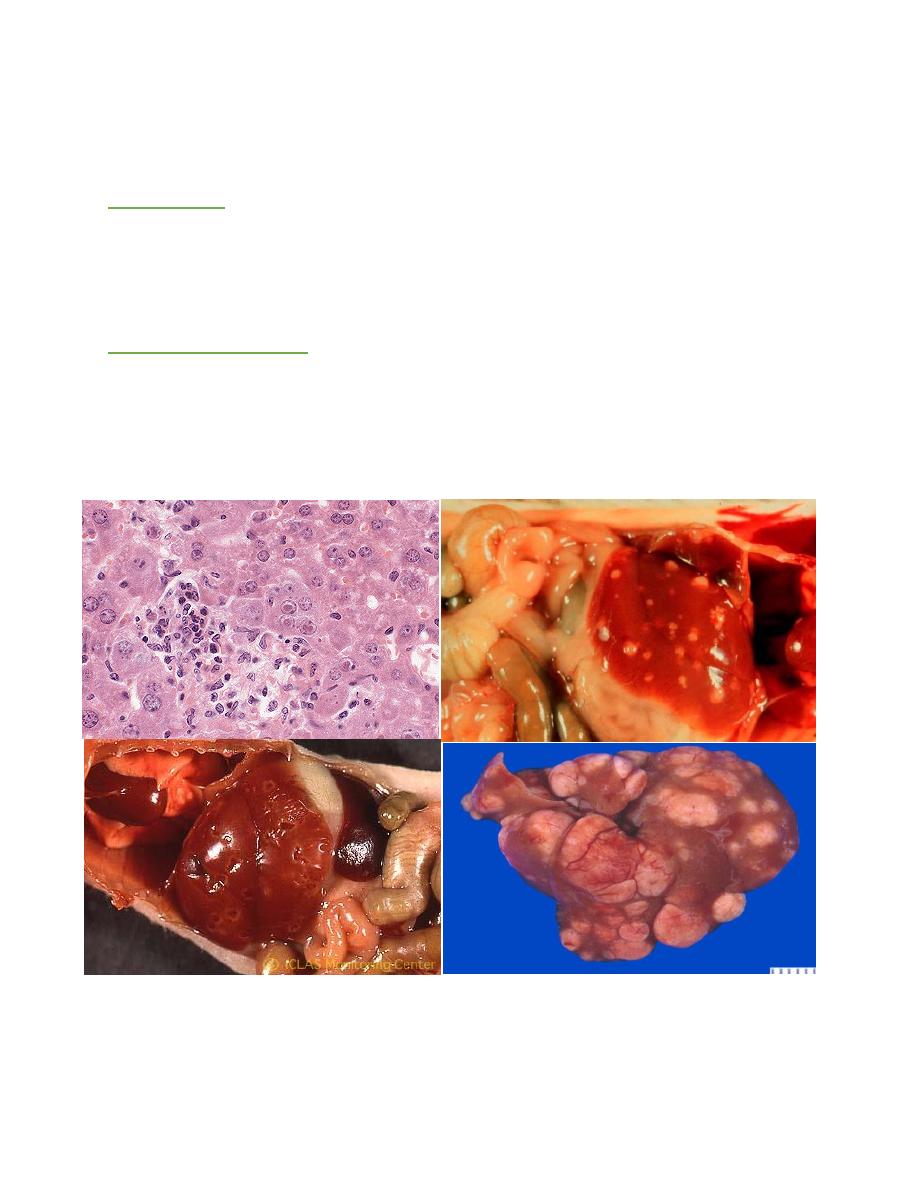
MOUSE HEPATITIS VIRUS INFECTION
MHV belongs to the order
Nidovirales
, family
Coronaviridae
, genus
Coronavirus
. Its official name is Murine Hepatitis Virus (MHV), but mouse hepatitis
virus is more generally accepted.
P.M. Finding
Hepatic nodular hyperplasia with parenchymal collapse and fibrosis. Foci of
splenic necrosis, with splenomegaly due to extramedullary hematopoiesis. With time
there is developing of nodule about 2-5 mm in diameter present in liver only started
as drop in liver tissue.
Differential Diagnosis:
1- T.B.
2- Nocardial Diseases.
3- Actinomyces.
4-Actinobacillus.
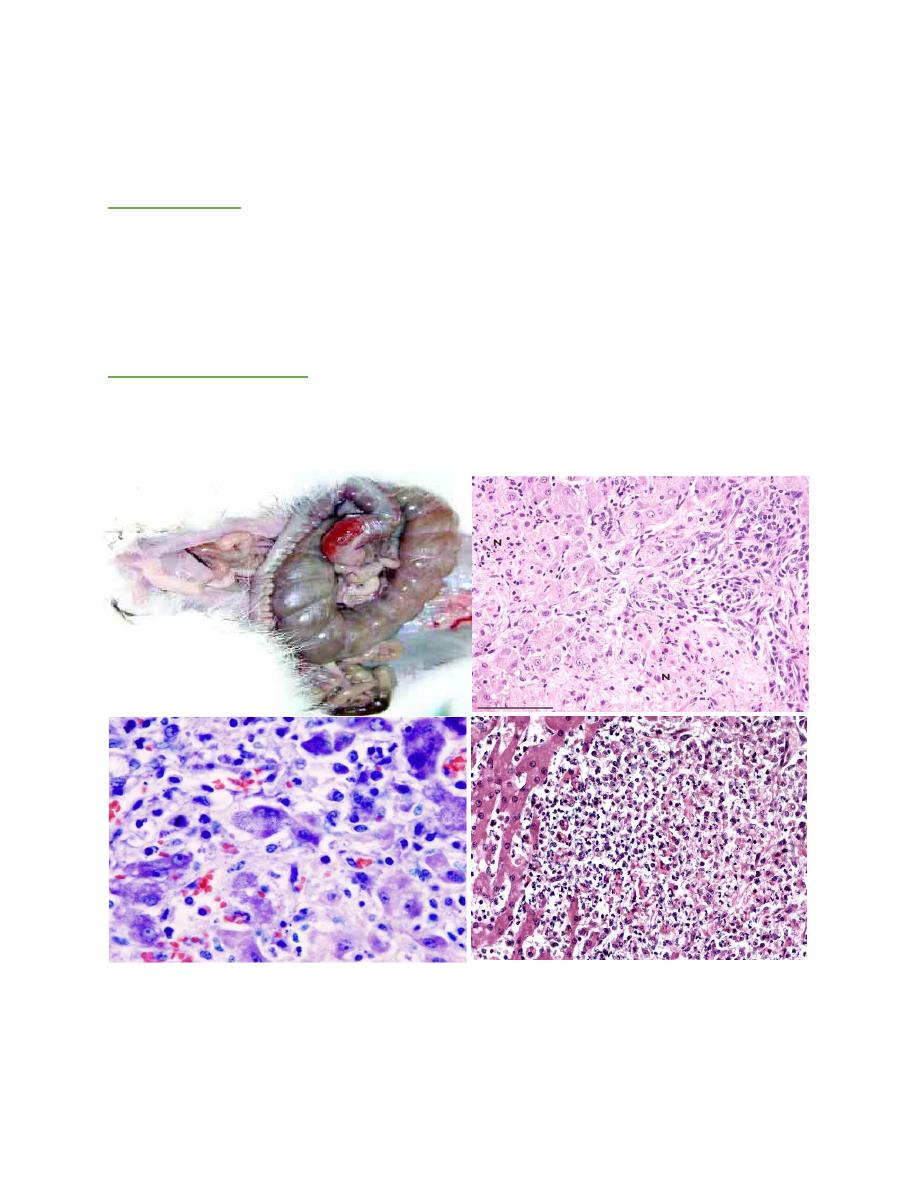
TYZZER’S DISEASE
Tyzzer’s disease was first recognized and characterized by Ernest Tyzzer in
1917. He described an epizootic that decimated a colony of Japanese waltzing mice
caused by
Clostridium piliforme
Infection.
P.M. Findings:
The primary lesion arises in the mucosa of the intestine, with grossly visible
reddening of the ileum and cecum. Microscopically, foci of degeneration,
inflammation, edema, and necrosis are evident in the intestinal mucosa and
muscularis. Clusters of organisms are apparent in enterocytes but also in the smooth
muscle and neurons of Auerbach’s plexus.
Differential Diagnosis:
1- E. coli Infection.
2- Aflatoxicosis.
3- Heavy metal toxicity.
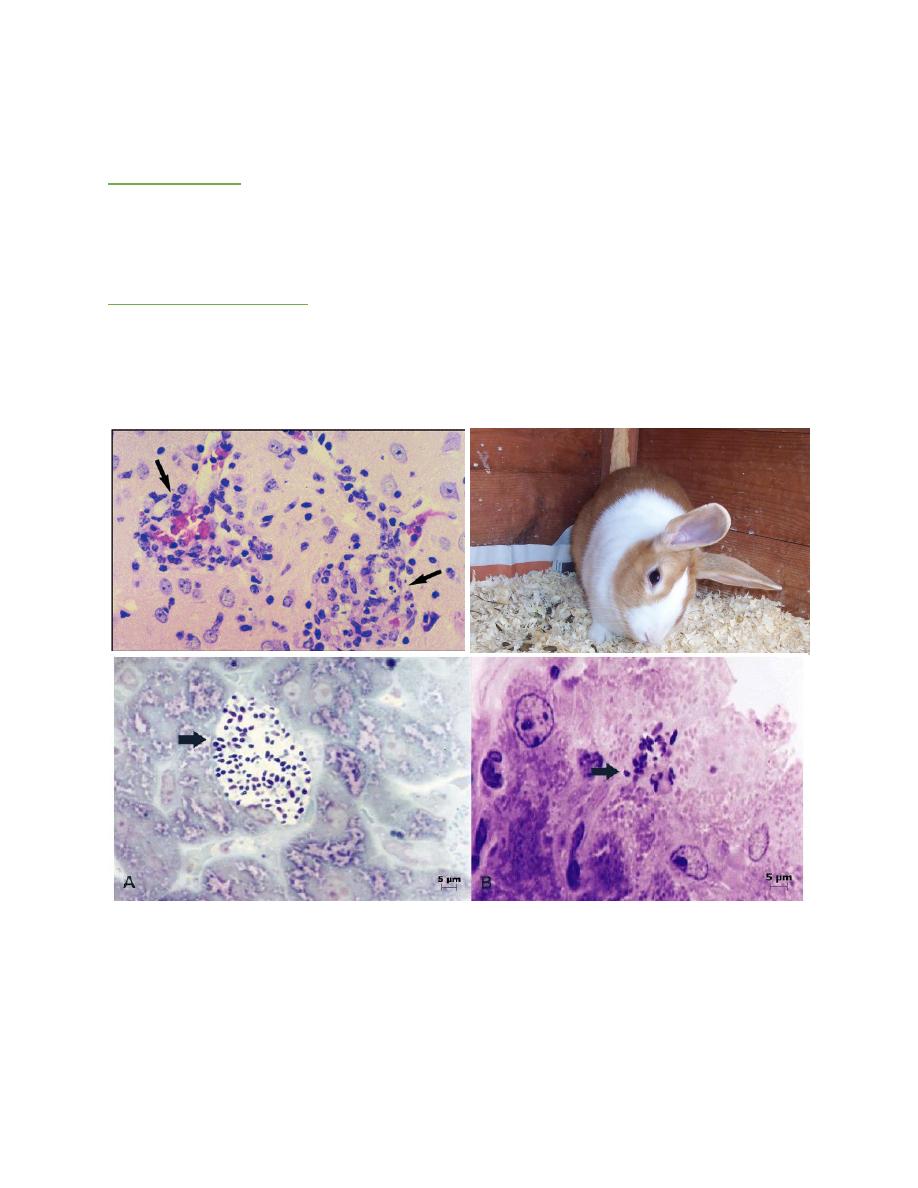
MICROSPORIDIOSIS
Caused by
Encephalitozoon cuniucli
a fungal disease characterized by
diarrhea with encephalitis.
P.M. Findings:
There is sever hemorrhagic enteritis with enlargement of liver and spleen with
watery diarrhea. There is encephalitis with congestion of meninges which associated
by torticollis of head.
Differential Diagnosis:
1- Coccidiosis.
2- Listeriosis.
3- Leptospirosis.
4- Cryptosporidiosis.
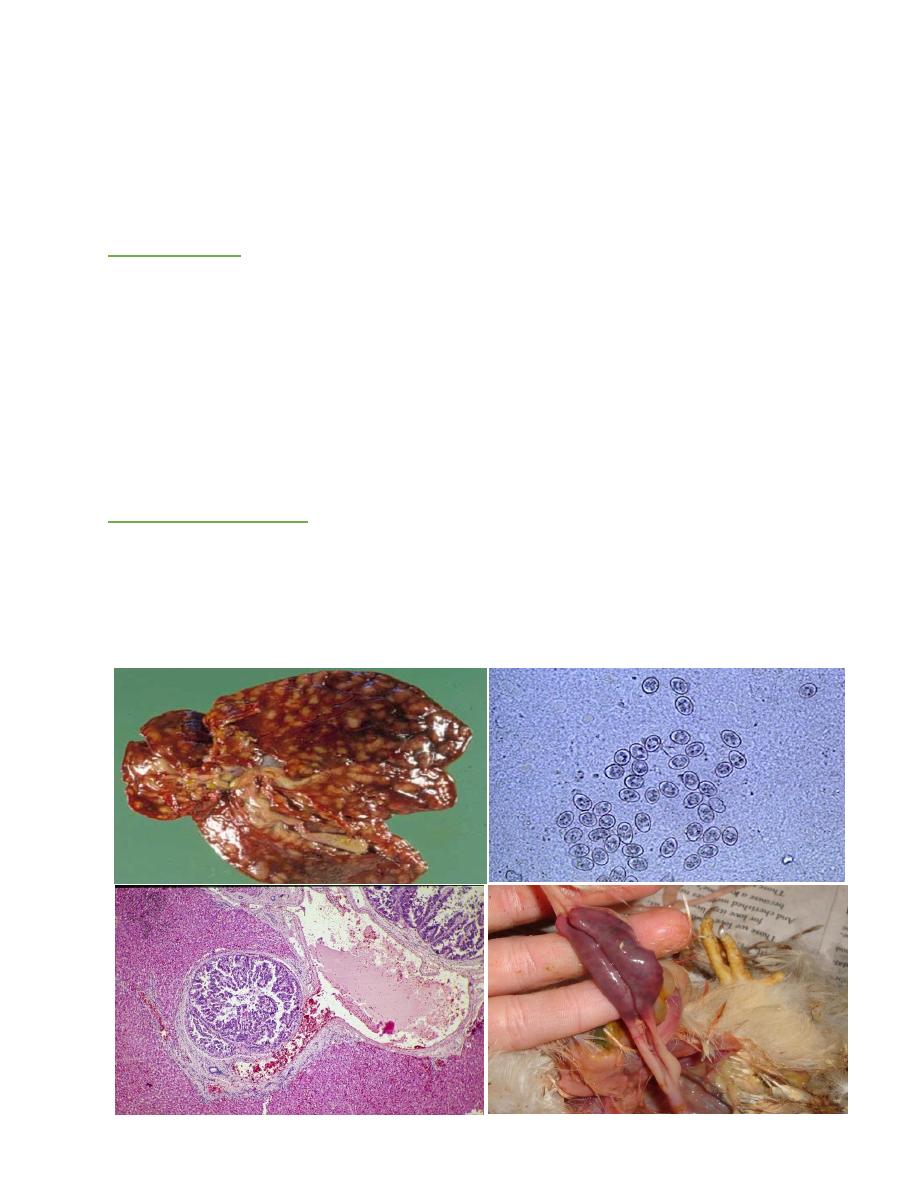
COCCIDIOSIS
Coccidiosis remains a major disease problem in commercial rabbit flocks, the
species of
Eimeria
associated with rabbit infection:
E. intestinalis
and
E.
flavescens
are considered the most pathogenic;
E. magna
,
E. irresidua
, and
E. piriformis
moderately pathogenic;
E. perforans
,
E. neoleporis
, and
E. media
the least pathogenic.
P.M. Findings:
At necropsy, the perineal region and belly are frequently smeared with watery
dark green to brown feces. The cecum and colon contain dark green to brown watery,
foul-smelling material. The liver is mostly affected show many nodular lesion as
white to yellow tubercles.
The location of microscopic changes concentrated in the caudal half of the
small intestine and in the cecum. In acute coccidiosis, there is destruction of
enterocytes, villous atrophy in affected areas of small intestine, and marked
leukocytic infiltration, heterophils predominating. Gametocytes and oocysts are
usually evident in the intestinal mucosa in affected areas
Differential Diagnosis:
1- Giardiasis.
2- Cryptosporidiosis.
3- E. coli infection.
4- Microsporidiosis.
5- T.B.
