
-To list extensor muscles of the thigh
-To Define the femoral vessels & nerve & list their
branches
-To localize femoral pulses
-To identify the adductor compartment of the thigh
-To describe the adductor canal, boundaries & contents
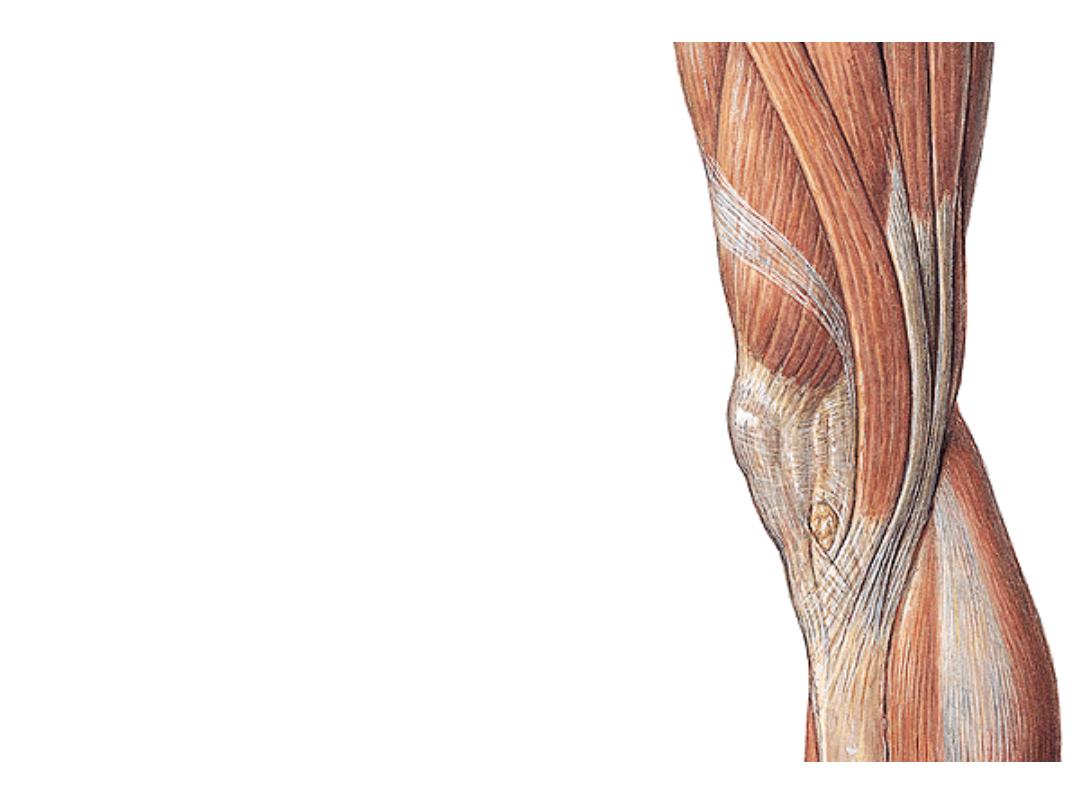
Quadriceps femoris:
-This muscle is formed of 4 heads &
forms the main bulk of the extensor
femoral compartment
-The 4 heads converge into the
upper border of the patella as
quadriceps tendon
-Then leave the patella to the tibial
tuberosity as ligamentum patellae
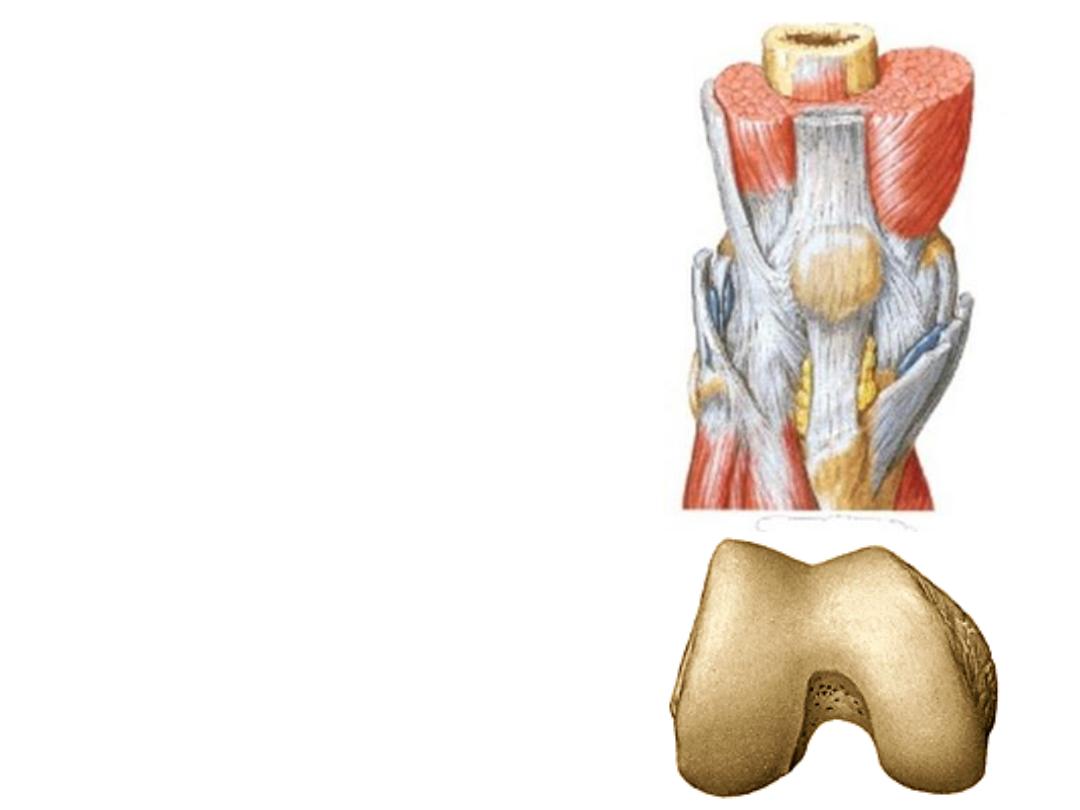
-The pull of QT on the patella is
upward & lateral
-Lateral patellar dislocation is
prevented by:
1- Forward projection of lateral
femoral condyle
2- Pull of lower fibers of vastus
medialis
3- Patellar retinacula
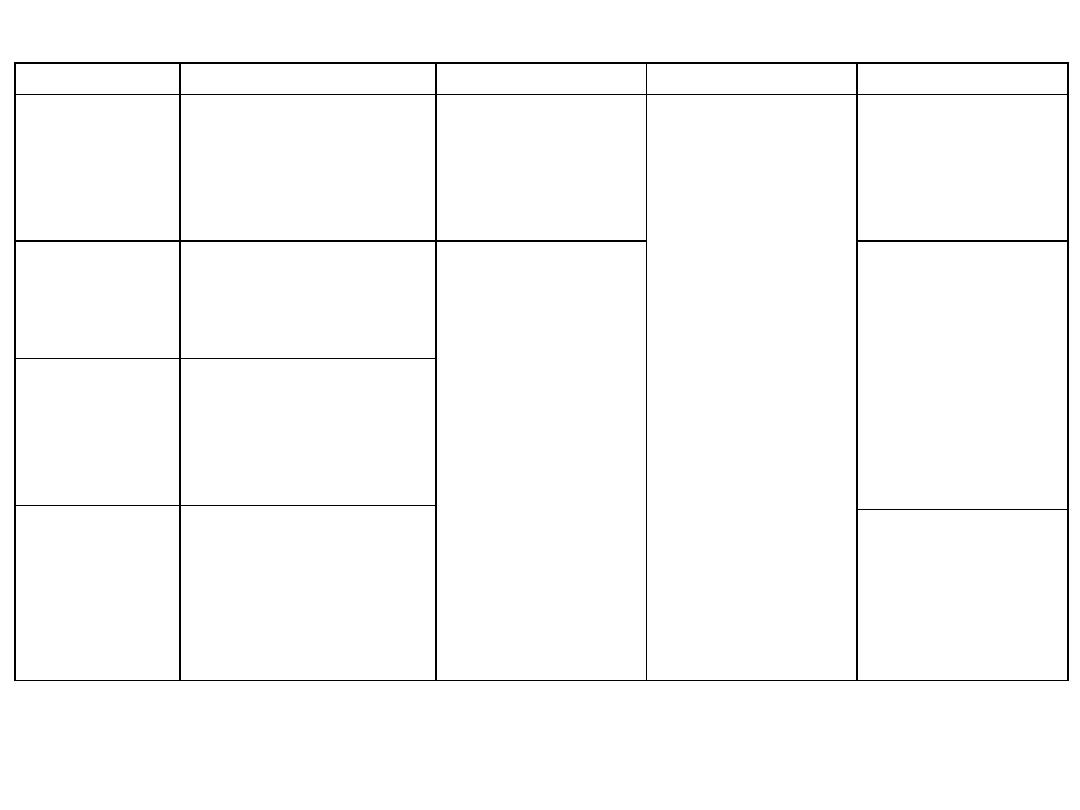
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
Vastus
medialis
-
Medial part of ITL
-
Linea aspera
-
Medial
supracondylar
ridge
Quadriceps
femoris tendon
and medial
border of patella
Femoral nerve
L2,3,4
- Extends the leg
-Lower fibers
prevent lateral
patellar
dislocation
Vastus
intermedius
Anterolateral
surfaces of upper 2/3
of femur
Quadriceps
femoris tendon
Extends the leg at
the knee joint
Vastus
lateralis
-
Lateral part of ITL
-
Linea aspera
Lateral supracondylar
ridge
Rectus
femoris
- Straight head from
the anterior inferior
iliac spine
-Reflected head just
superior to the
acetabulum
Thigh flexor &
knee extensor
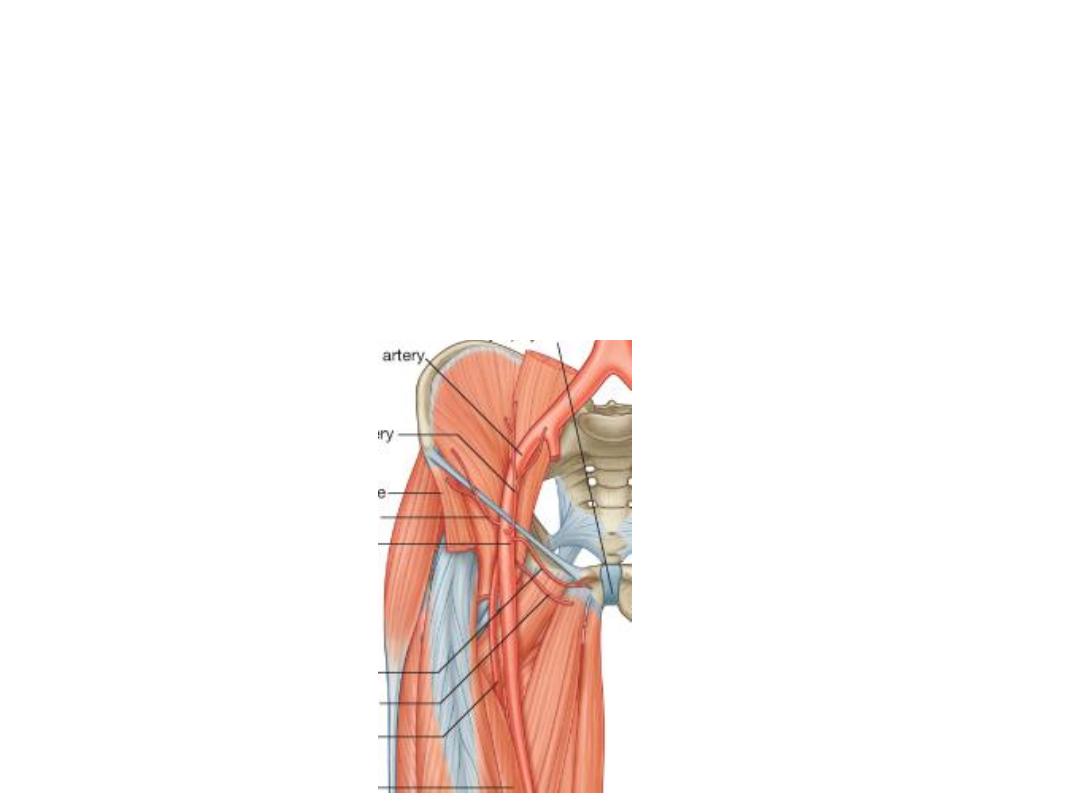
The femora artery:
-It is the continuation of the external iliac artery, after crossing the mid-inguinal
point
-Midinguinal point is the site of femoral pulse
-Midpoint of inguinal ligament is the site of inguinal hernia
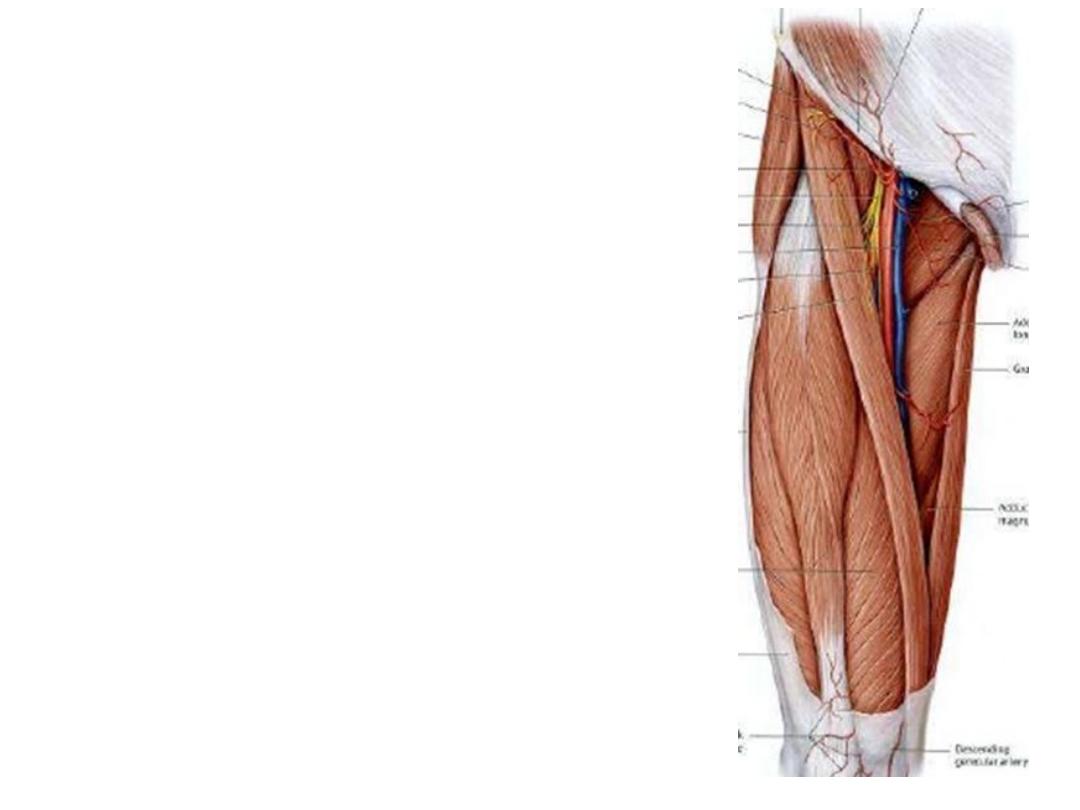
-FA passes in the lateral component of the femoral
sheath between femoral vein & nerve
-Enters the apex of adductor canal
-Leaves the canal by passing through the adductor
hiatus, where it appears in the popliteal fossa as the
popliteal artery
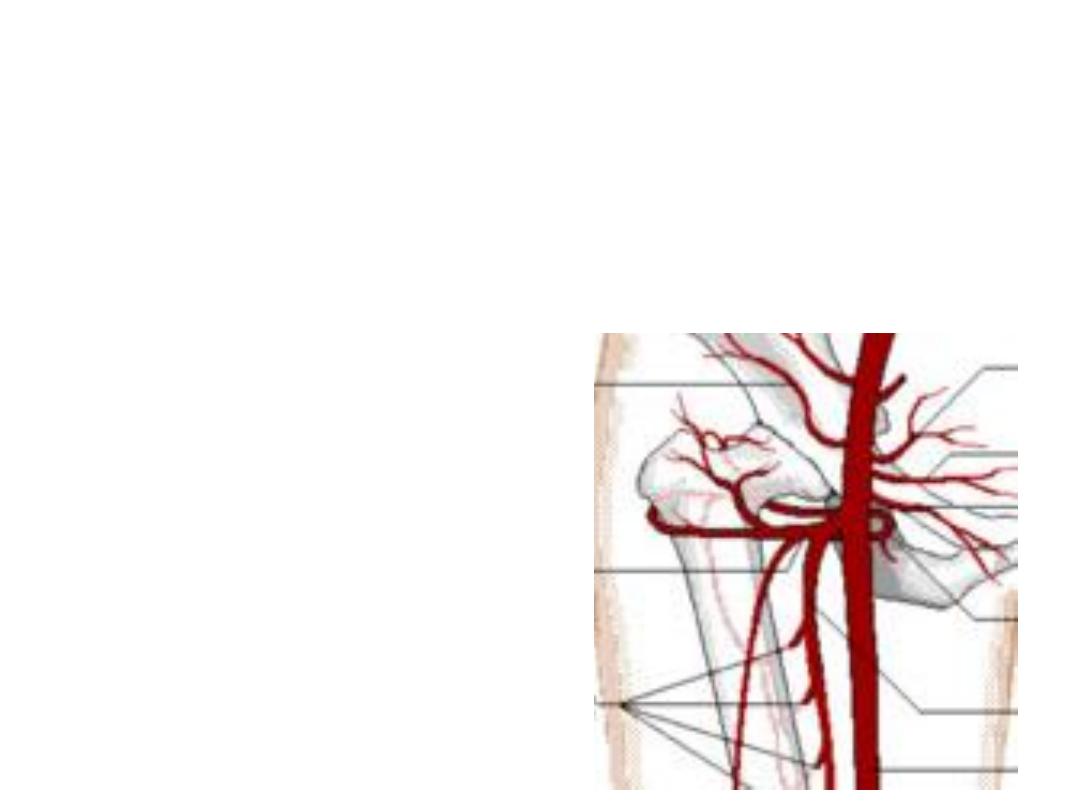
Branches in the thigh:
1- Superficial branches,
given from the proximal part:
a)Superficial circumflex iliac; to the ASIS
b)Superficial epigastric; to the anterior abdominal wall
c)Superficial external pudendal; to external genitalia
d)Deep external pudendal; to external genitalia
Accompanying veins drain to the great saphenous vein
a
b
c
d
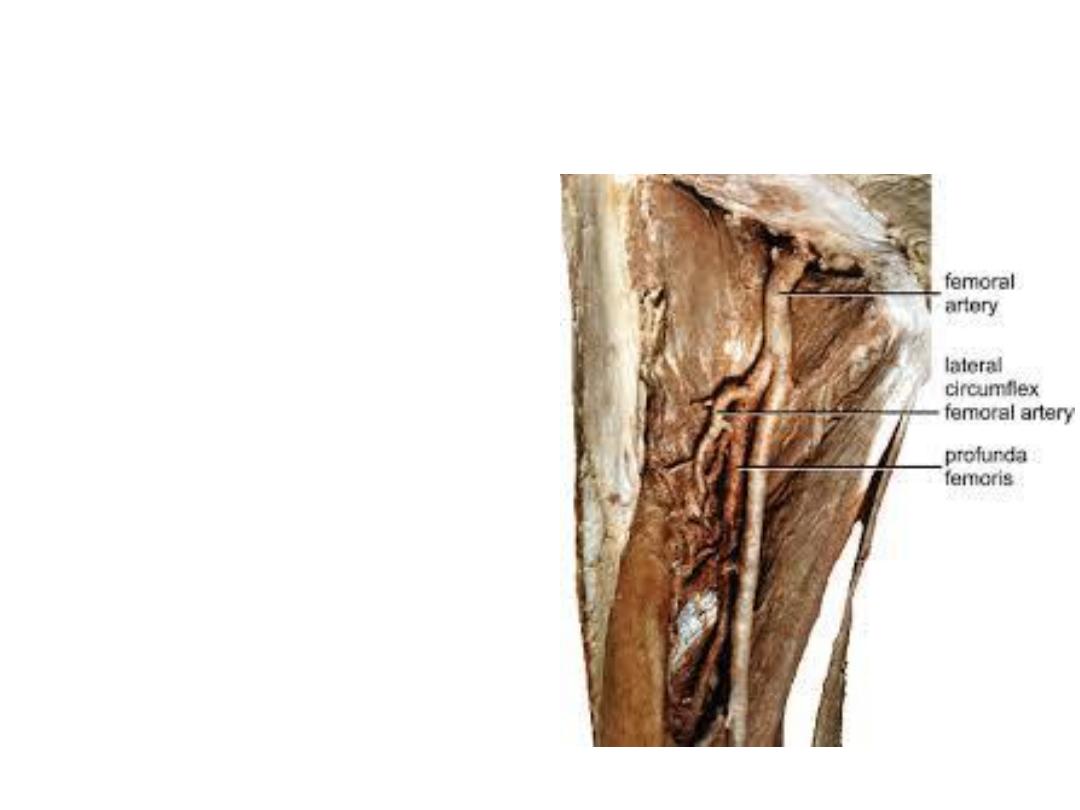
2- Profunda femoris artery (deep artery
of the thigh):
-The largest branch of femoral artery,
arises from its lateral aspect 5 cm
below the inguinal L then goes behind
- Branches;
1- Medial circumflex femoral a.
2- Lateral circumflex femoral a.
3- Muscular arteries
4- Four perforating arteries, the 4
th
is
the continuation of the profunda
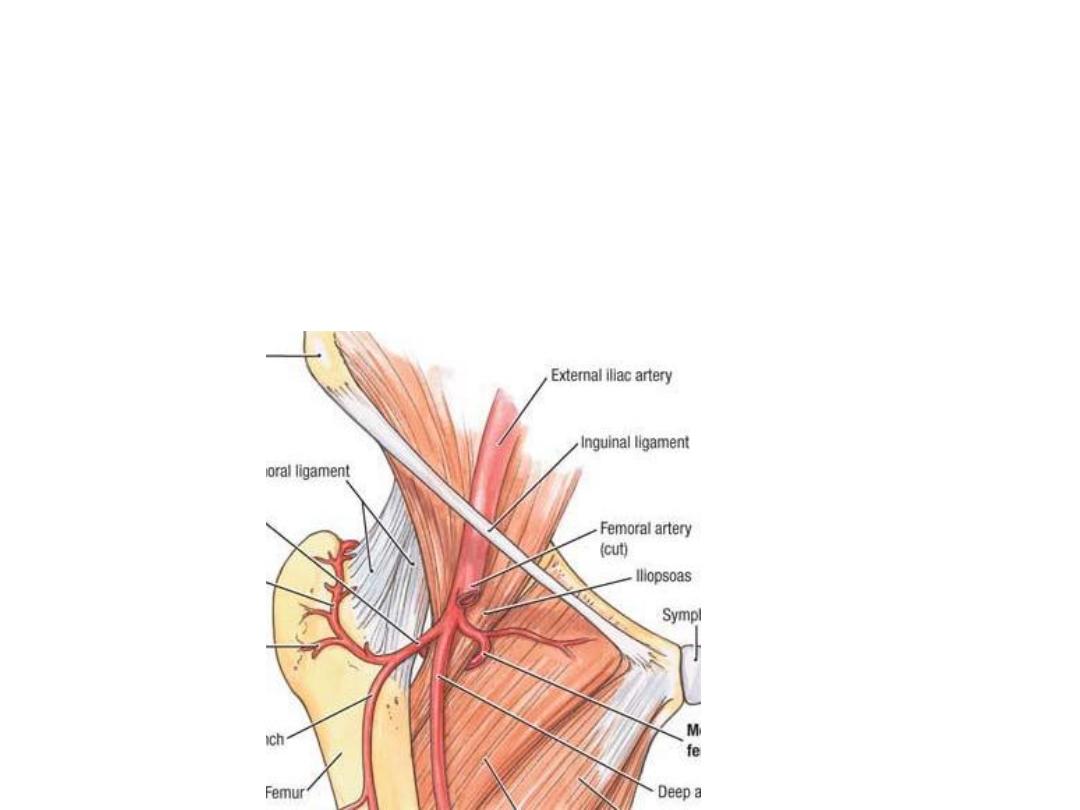
Medial CFA:
Arises from the medial side of profunda
Enters between pectineus & psoas to reach the back of the thigh
Supplies the upper part of adductor compartment, hip joint & back of the thigh
Ends by dividing into ascending & transverse branches, the former goes to the
trochanteric while the latter to the cruciate anastomoses
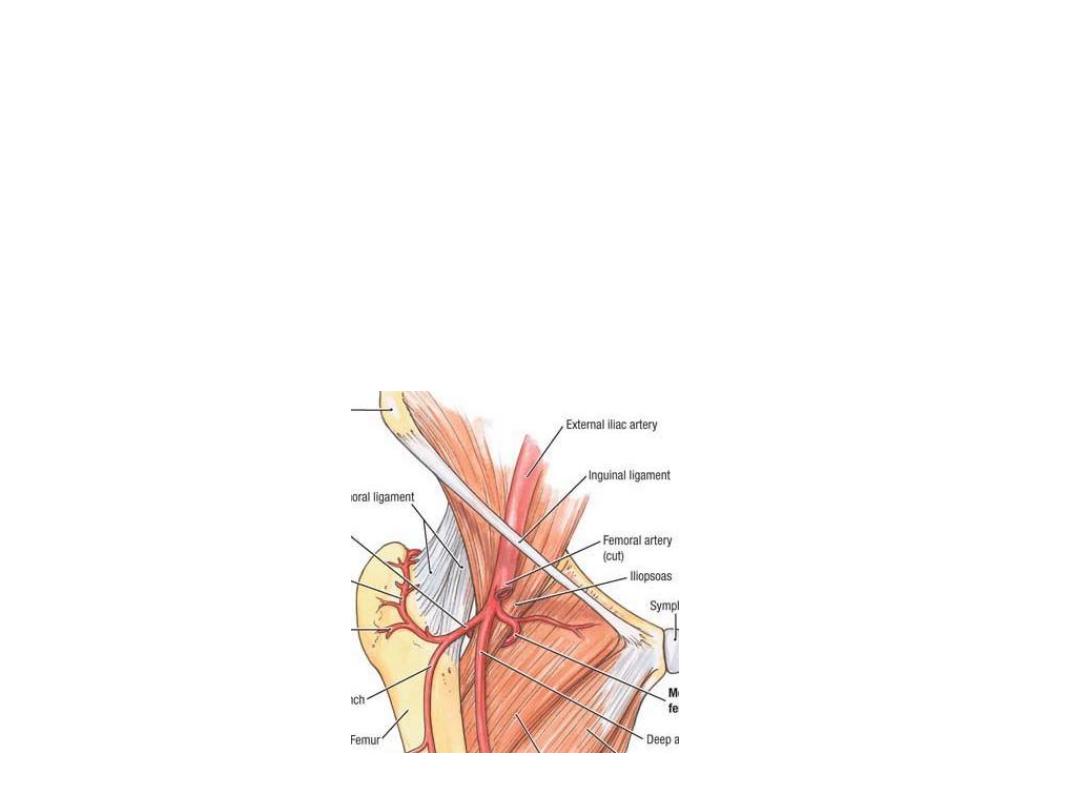
Lateral CFA:
-Goes laterally deep to sartorius & rectus muscles to divide into:
a)Ascending branch to the anastomosis around ASIS & share in the trochanteric
anastomosis
b)Transverse branch to the cruciate anasomosis
c)Descending branch; accompanies nerve to V. lateralis & descends down to
anastomose with arteries around the knee
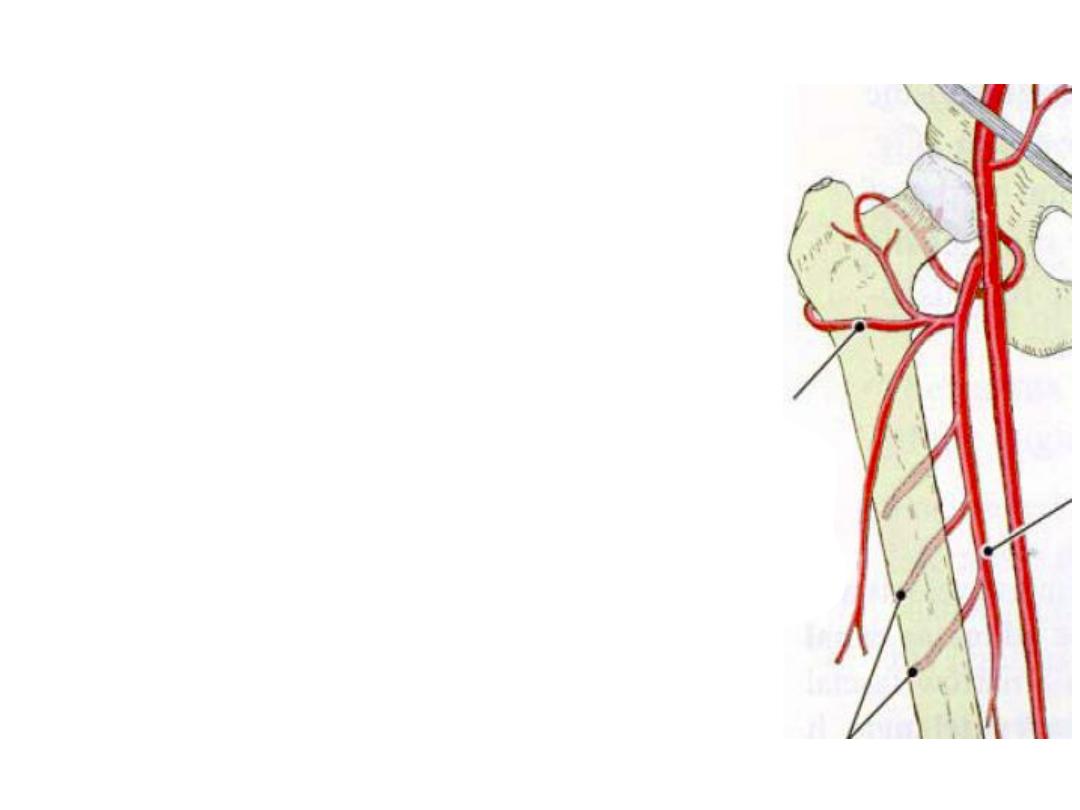
Perforating arteries:
-4 in number, the upper 2 pass through adductor brevis
-They are muscular arteries pierce the adductor mucles &
appear in the hamstring compartment
-The arteries anastomose with each other
-The 1
st
& 4
th
anastomose with adjacent anastomosis
above & below
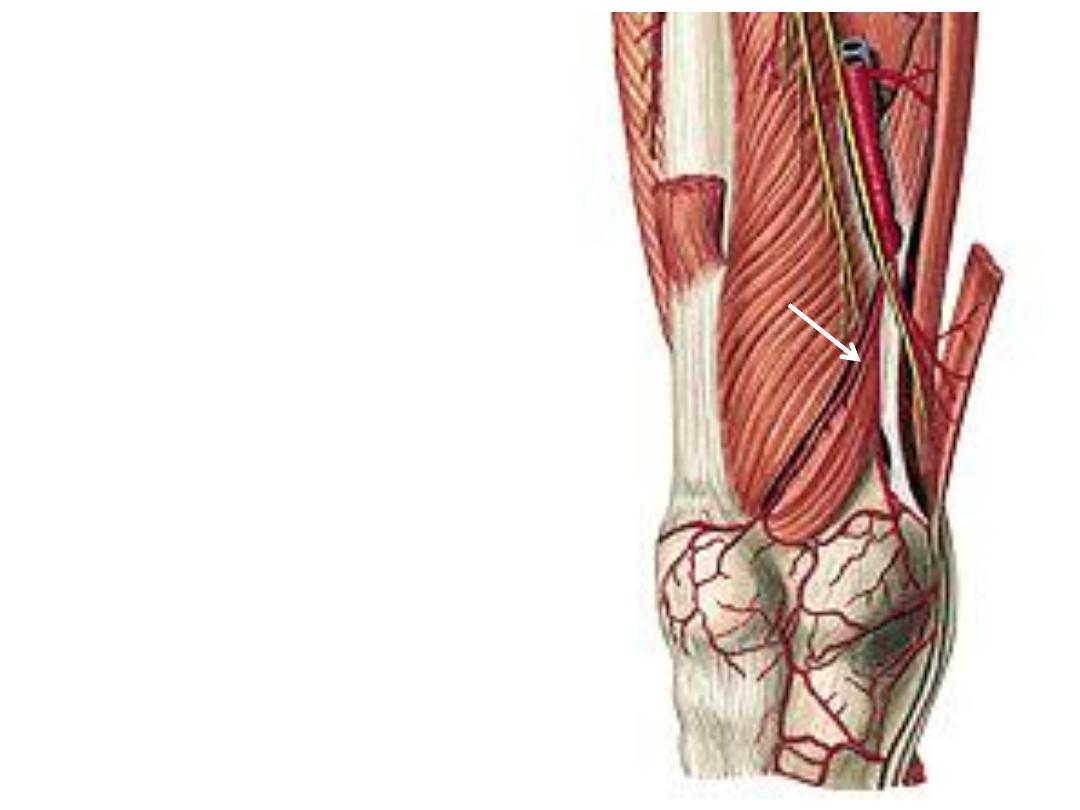
3- Descending genicular a.:
-Given before the femora a. enters the
adductor hiatus
-Divides
into
saphenous
&
genicular
branches
-Saphenous a. accompanies the saphenous
nerve
-Genicular a. share in the anastomosis
around the knee joint
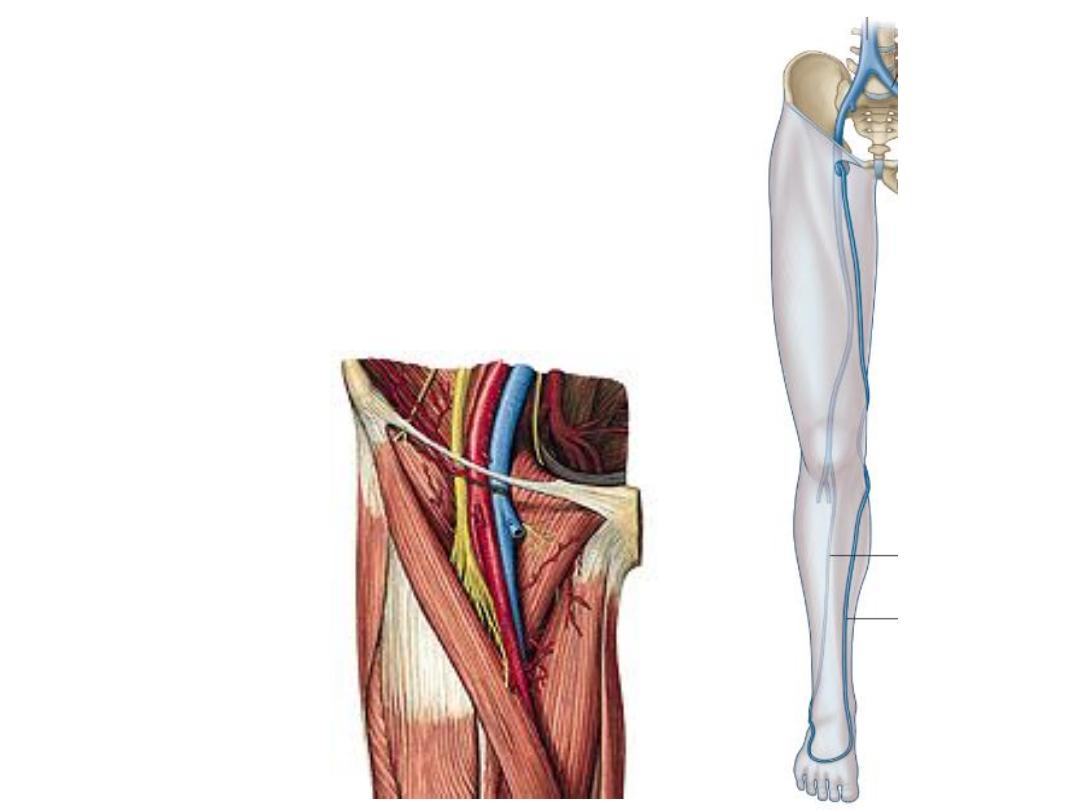
The femoral vein:
-The continuation of the popliteal vein at adductor
hiatus
-Accompanies the femoral artery in the thigh
-Occupies the middle compartment of femoral sheath
-Under the inguinal L, it continue as the external iliac
vein
-It contains 2-3 valves
Tributaries:
1- The great saphenous vein
2- The circumflex veins
3- The deep femoral v. (profunda femoris)
4- perforating veins
5- Venae comitantes of descending genicular
vein
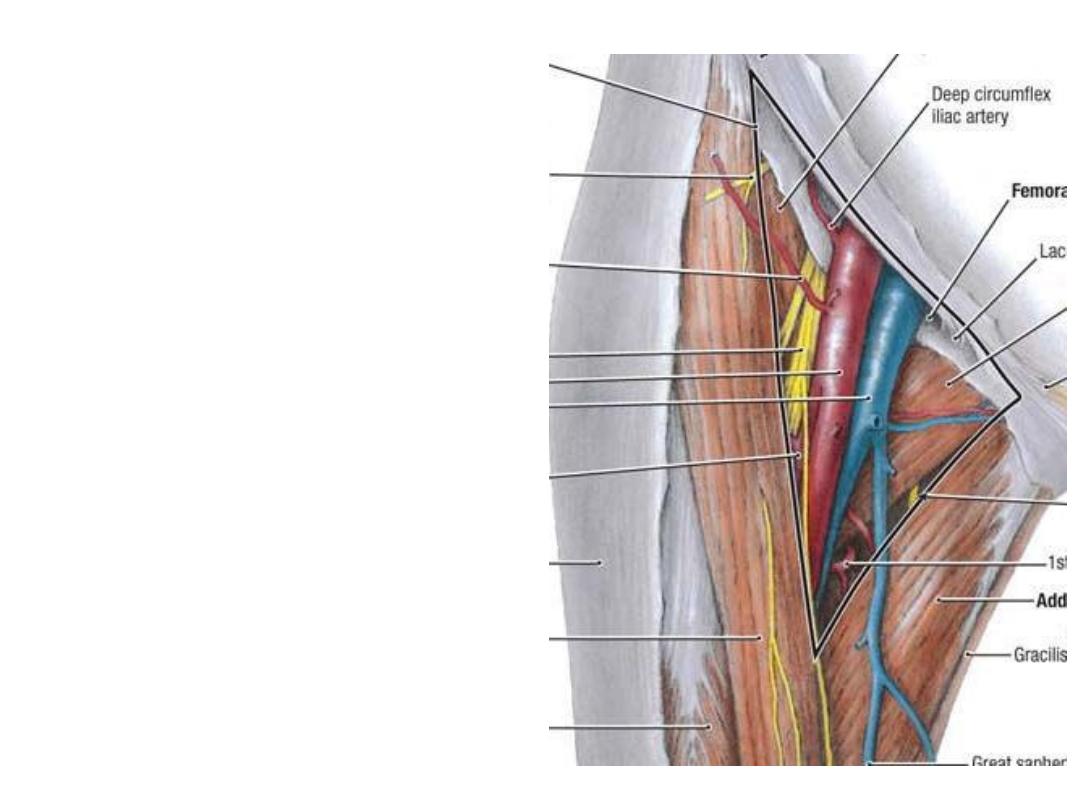
The femoral nerve:
-The largest branch of lumbar plexus,
arises from the posterior divisions of
L2,3,4
-Enters the femoral triangle as a mesh
of fibers lateral to the femoral sheath,
between iliacus & psoas
-The transverse branch of LCFA
passes between the branches dividing
them into anterior & posterior
Cutaneous branches:
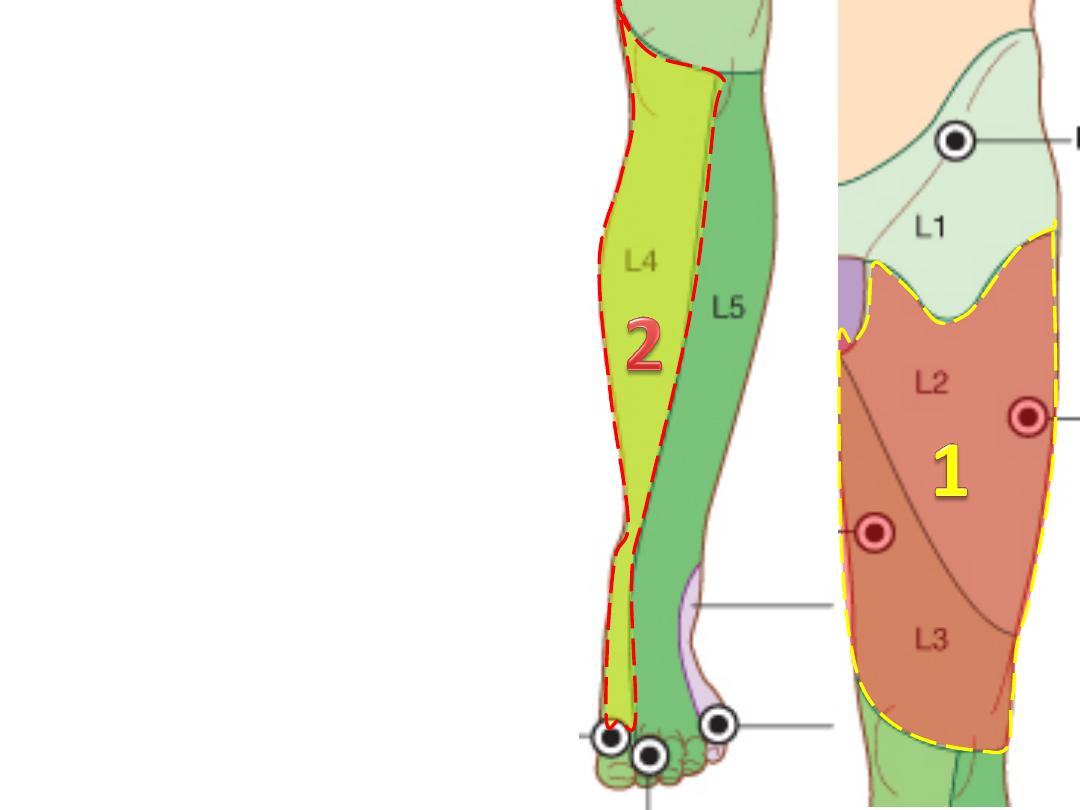
1- Anterior & medial cutaneous nerve
(L2,3);
supplies skin below the
femoral triangle
2- Saphenous nerve (L2,3);
-Accompanies the femoral a. in the
adductor canal
-Emerges
between
sartorius
&
gracilis medial to the knee
-Accompanies the great saphenous
vein down to the ball of the big toe
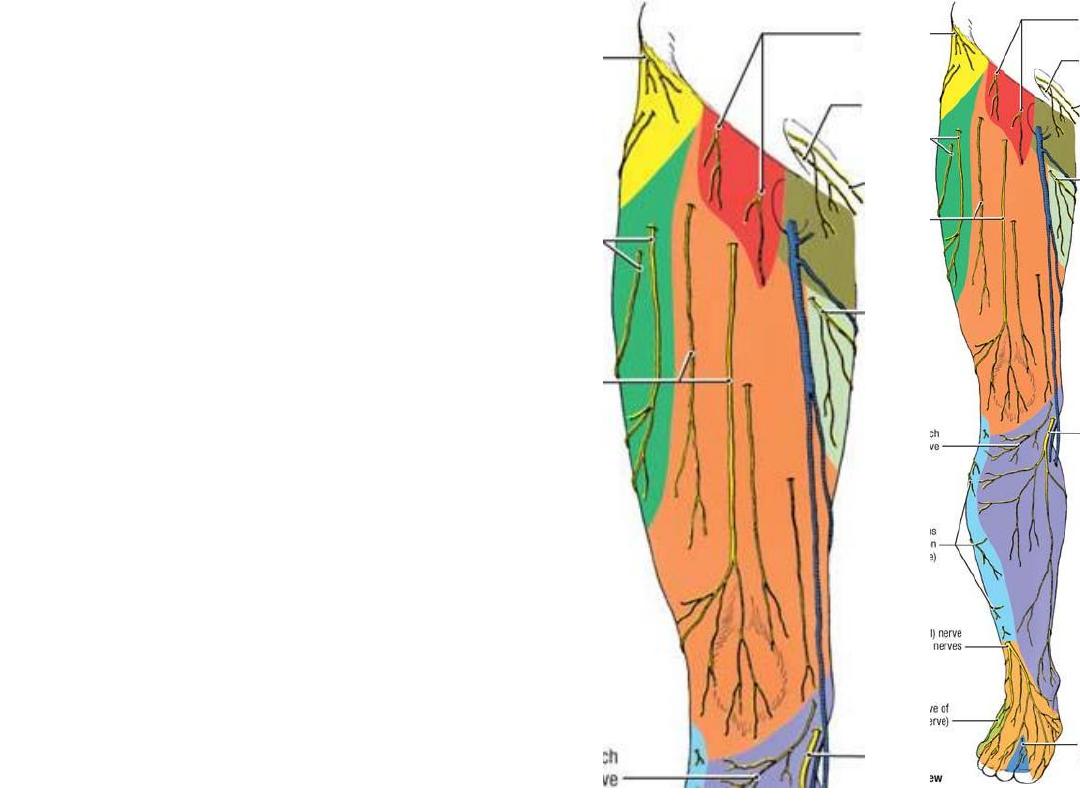
The skin overlying the femoral
triangle is supplied by the
femoral
branch of genitofemoral nerve (L1)
The lateral skin of the thigh is
supplied by the
LCNT (L2,3),
a direct
branch from the lumbar plexus
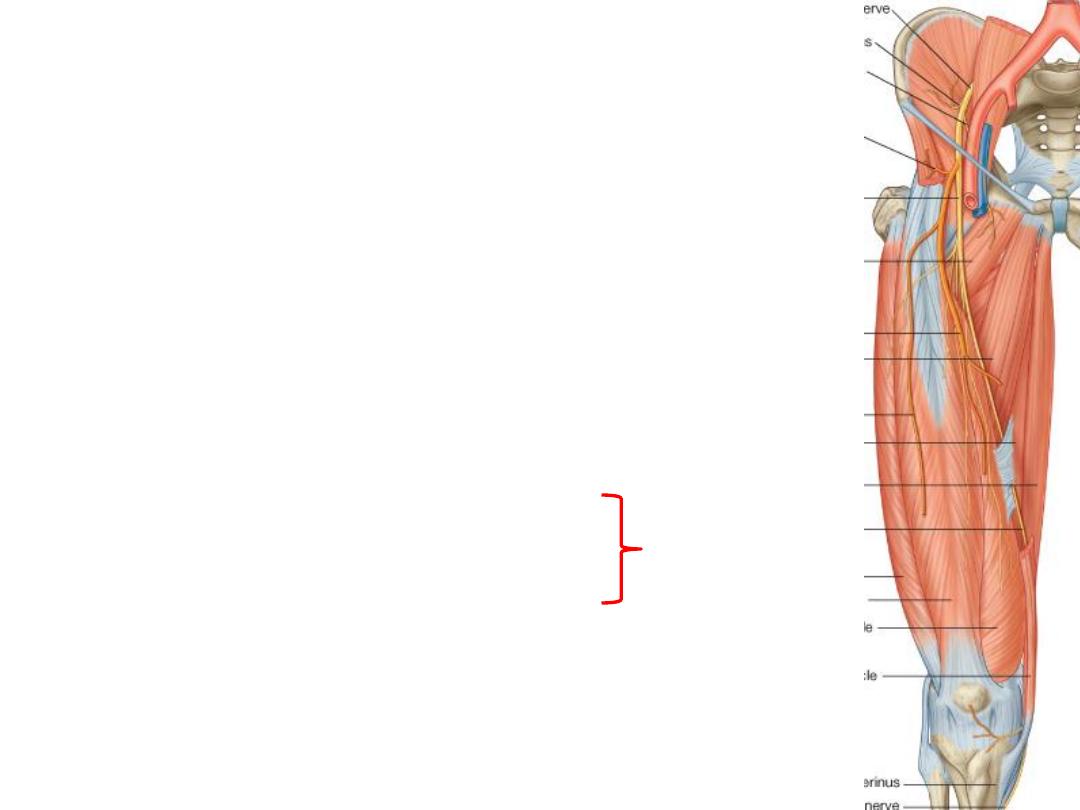
Muscular branches:
1- Nerve to pectineus
2- Nerves to sartorius; 2 in number, one enters each end
of the muscle
3- Nerve to each head of the quadriceps, that of VM is
double, one to each end
4- Nerve to articularis genu
Rectus femoris nerve supplies the hip joint
Vasti nerves supply the knee joint
Hilton law

Femoral nerve
pathology
Motor
(Buckling knee)
Sensory
(Thigh pain)
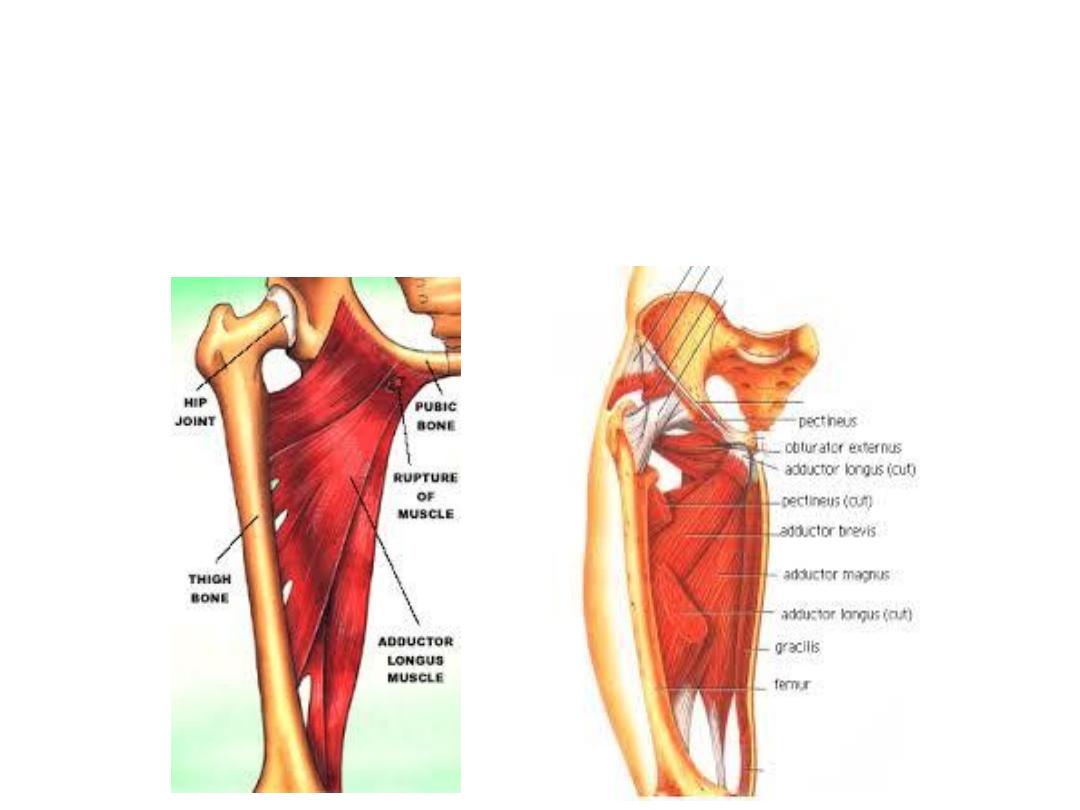
The adductor compartment:
•Lies on the medial aspect of the thigh
•Contains 6 muscles
•The obturator vessels & nerve supply this compartment
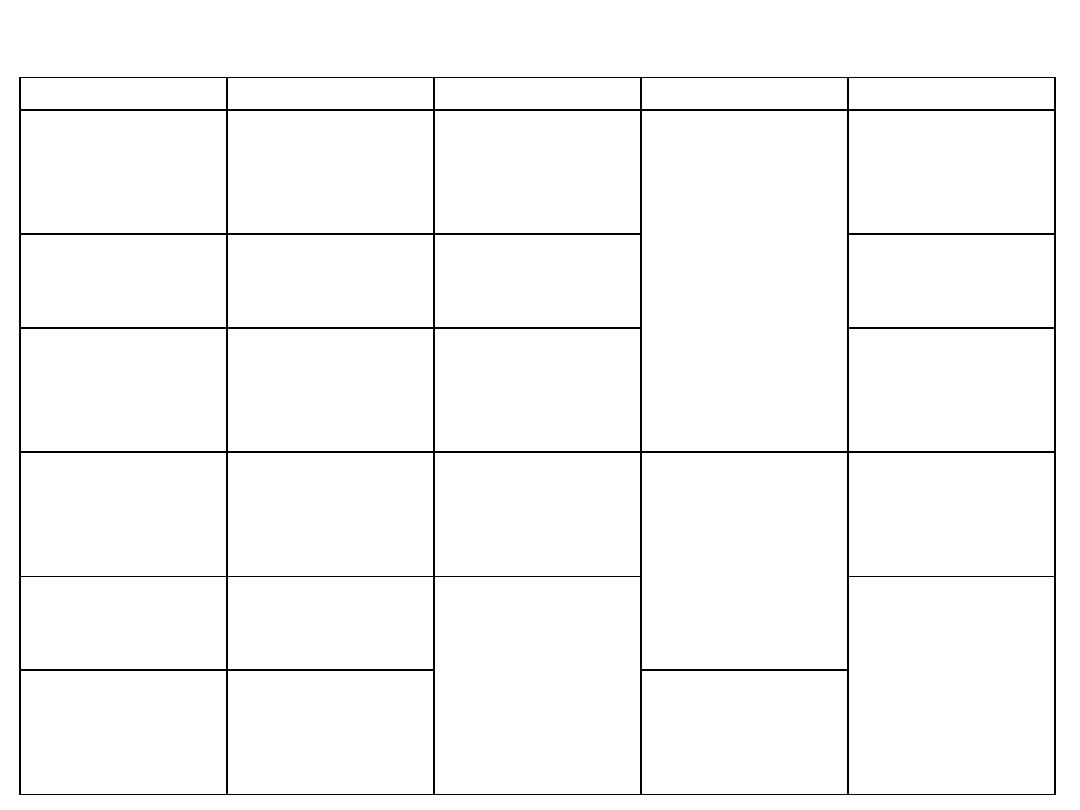
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
Gracilis
-
Body of the
pubis
-
Ischiopubic
ramus
Medial surface
of upper tibia
Obturator nerve
(anterior
division) L2,3,4
-
Hip adductor
-
Knee flexor
Adductor longus
Body of pubis
Linea aspera on
middle one-third
of shaft of femur
Adductor &
medial rotator of
hip
Adductor brevis
-
Body of pubis
-
Inferior pubic
ramus
-
Posterior
surface of
femur
-
Linea aspera
Hip adductor
Obturator
externus
External surface
of obturator
membrane and
adjacent bone
Trochanteric
fossa
Obturator nerve
(posterior
division) L3, 4
Adductor
magnus
Adductor part
ischiopubic
ramus
-
Linea aspera
-
Medial
supracondyla
r line
-
Adductor
tubercle
Adductor &
medial rotator of
hip
Adductor
magnus ischial
part
ischial
tuberosity
Sciatic nerve
(tibial division)
[L2,L3,L4]
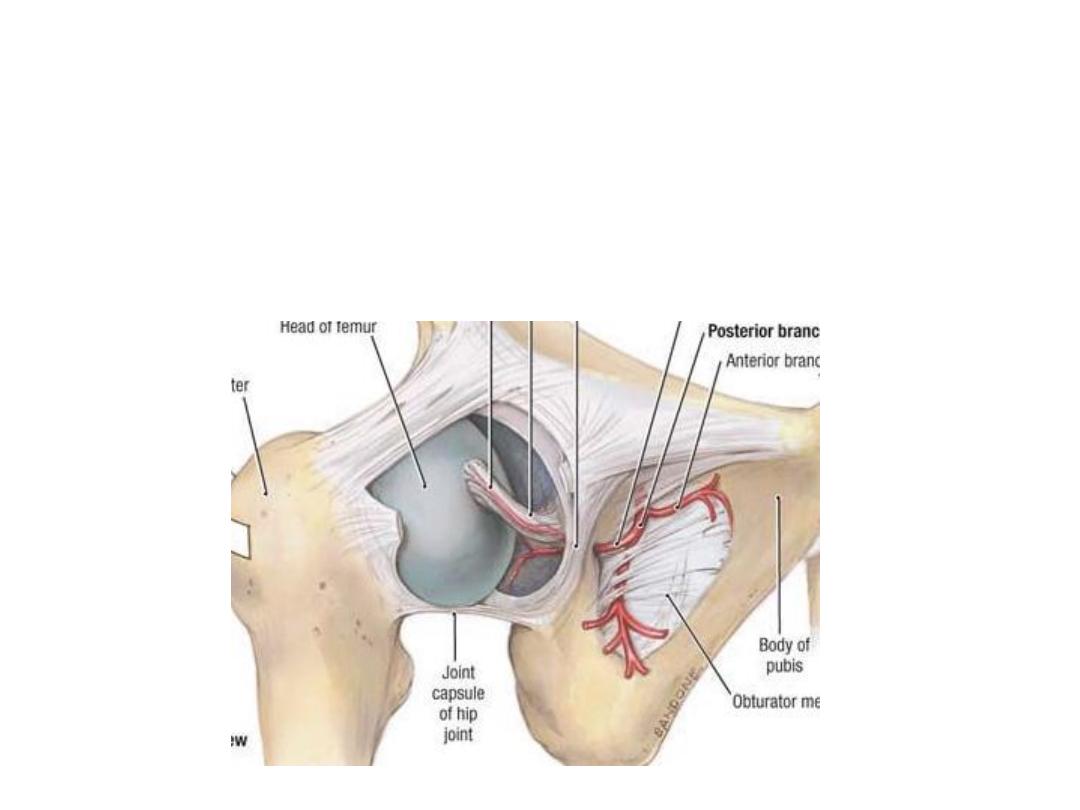
Obturator artery:
-A branch of the internal iliac artery
-Passes through the obturator canal
-Divides into anterior & posterior divisions embracing the obturator
foramen & supplying the upper part of adductor muscles
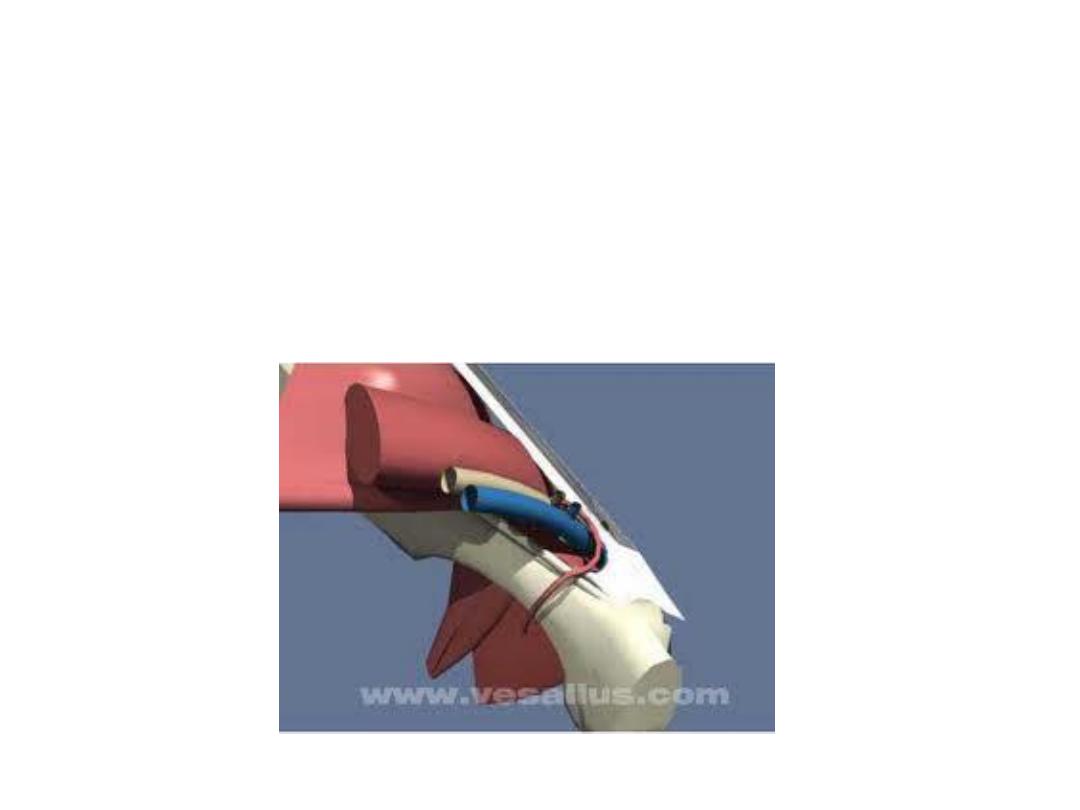
Aberrant obturator artery (30%):
-A branch from the inferior epigastric artery which substitute the
obturator artery
-Descends over the lacunar L medial to the femoral ring
-Endangered in femoral hernia surgery
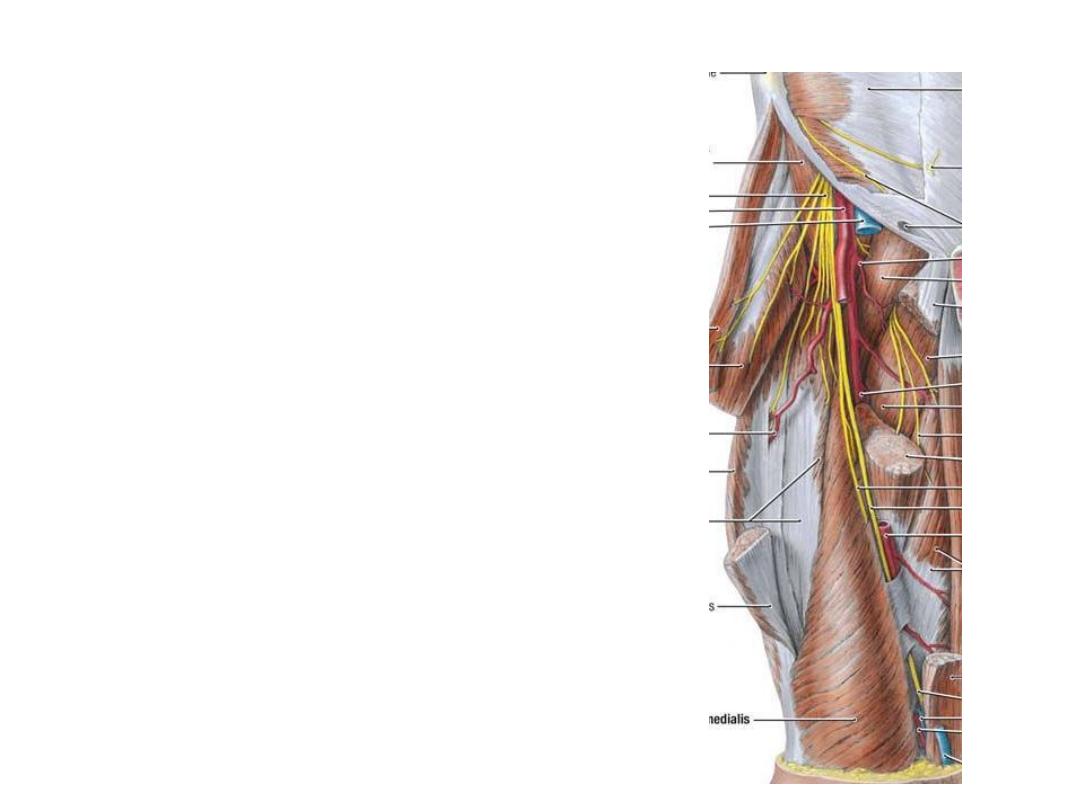
Obturator nerve:
-Arises from the anterior divisions of
lumbar plexus (L2,3,4)
-It has a considerable course in the
pelvis passing close to the ovarian fossa
-Leaves through the obturator canal
-Divides
into
anterior
&
posterior
divisions which override adductor brevis
-Branches:
1- Muscular; to adductor muscles
2- Cutaneous; to the medial aspect of the
thigh
3- Articular; to the hip & knee joints
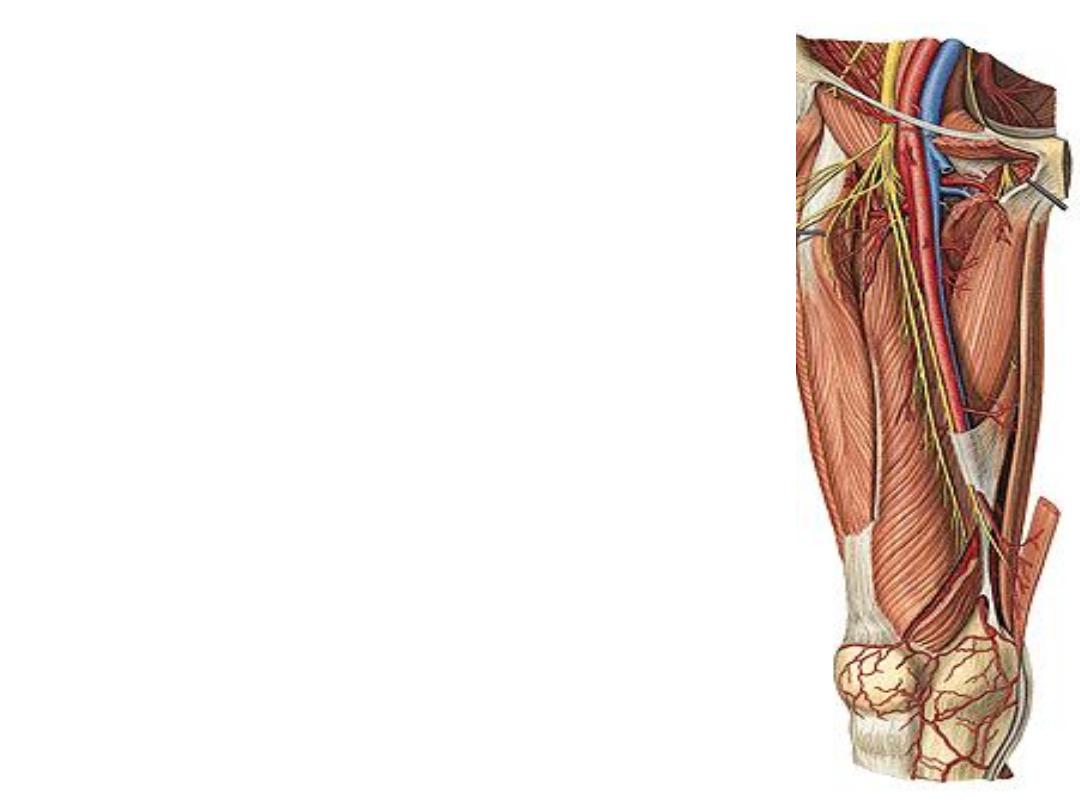
The adductor (subsartorial) canal:
A fascial canal extends between the apex of the femoral
triangle & the adductor hiatus occupying the middle 1/3
of the thigh
Boundaries:
1- adductor longus & magnus posteriorly
2- Vastus medialis laterally
3- Sartorius anteromedially
Contents:
1- Femoral vessels
2- Saphenous nerve
3- Nerve to vastus medialis
