To describe the extensor & peroneal muscles
To define the anterior tibial vessels
To explore the superficial & deep peroneal nerves &
main pathologies affecting them in the region
To describe the dorsum of the foot
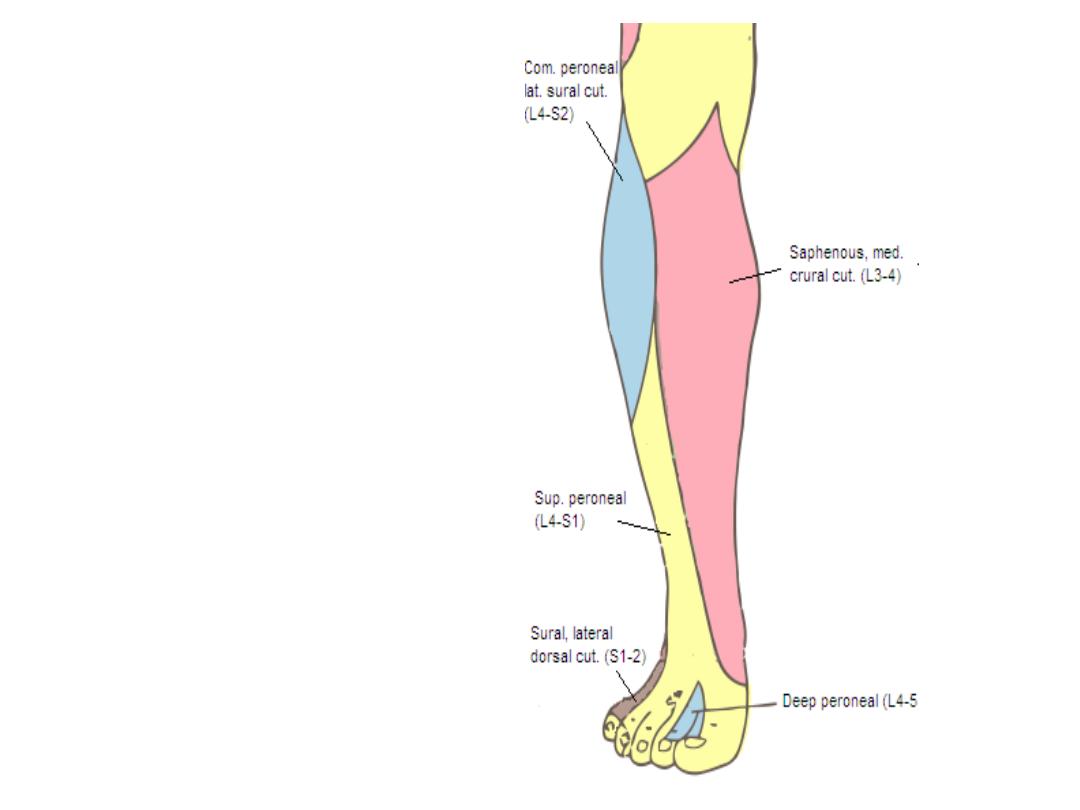
Cutaneous innervation:
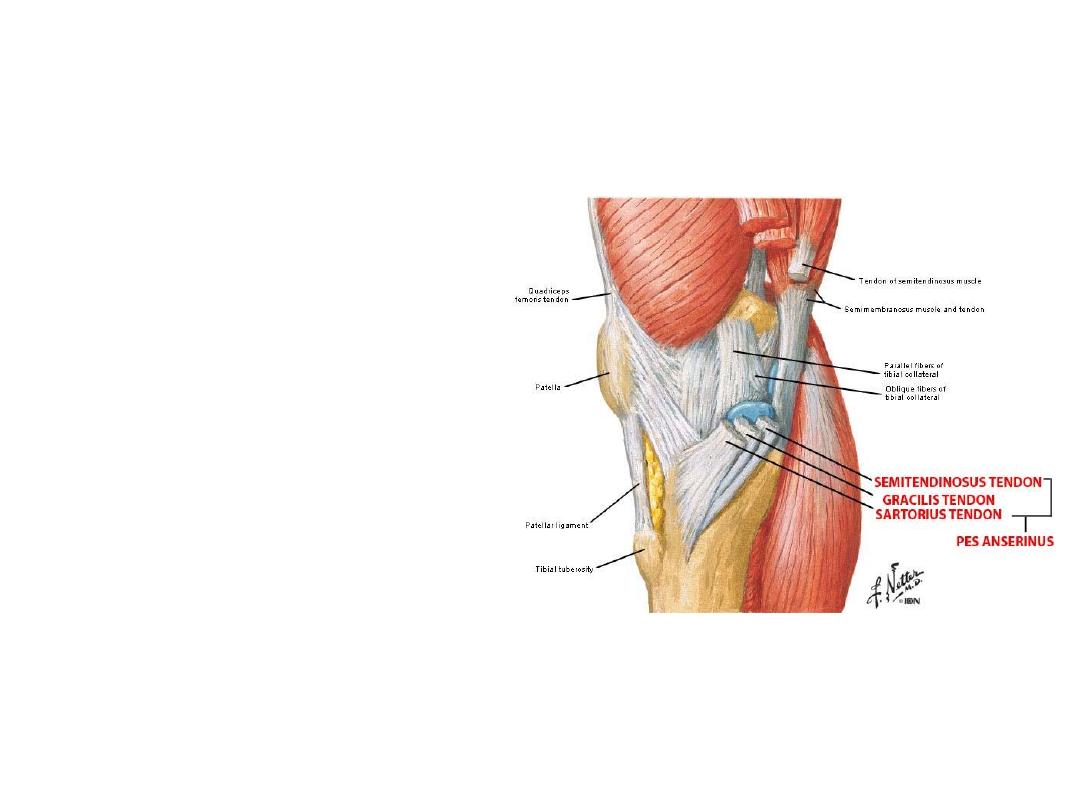
The shin:
- The subcutaneous surface of
the tibia forms the anteromedial
aspect of the leg
- Apart from partial course of the
saphenous
NV,
the
only
important structure here is the
pes anserinus
- Pes anserinus
is the successive
insertions sartorius, gracilis &
semitendinosus
on
the
superomedial part of the tibia
- A
bursa
separates
these
tendons called
bursa anserina
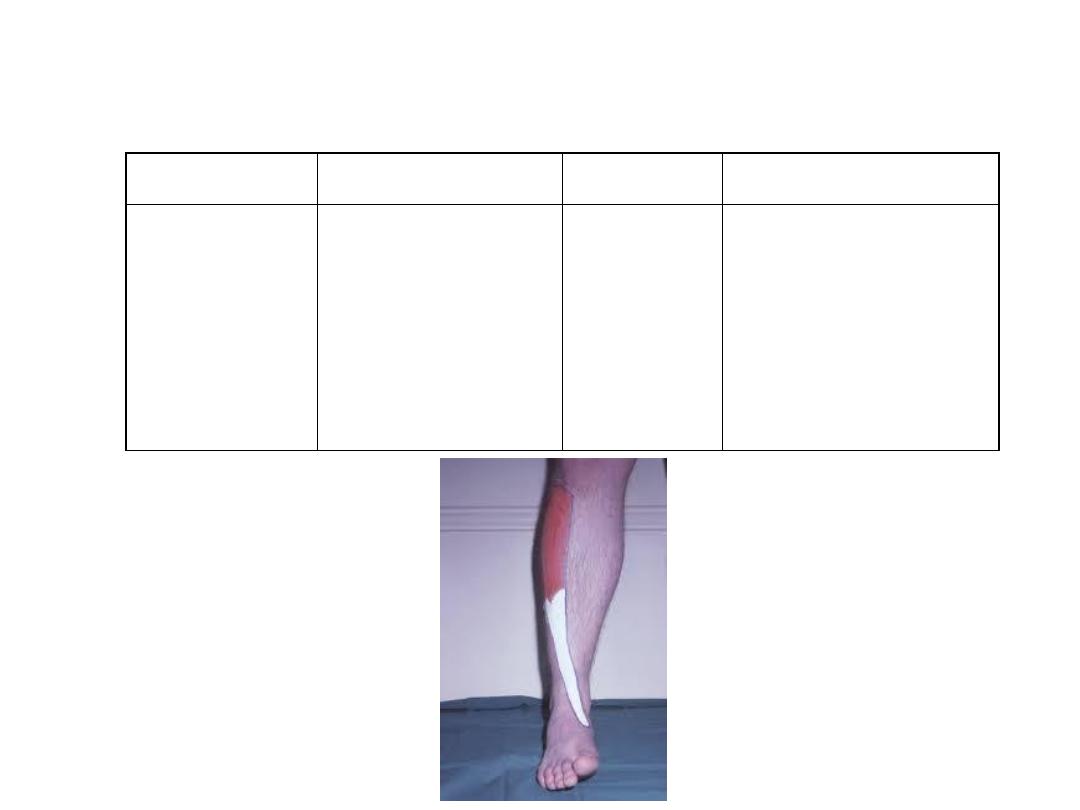
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Lateral
surface of
tibia &
interosseous
membrane
- Inferior
surfaces of
medial
cuneiform
- 1
st
metatarsal
Deep fibular
(peroneal)
nerve L4,5
-Dorsiflexion of foot
-Inversion of foot
-Support of medial
arch
Muscles of the extensor compartment:
Tibialis anterior:
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
- Proximal half of
fibula
- Related surface of
lateral tibial
condyle
Via dorsal
digital
expansions into
distal & middle
phalanges of
lateral four toes
Deep fibular
(peroneal)
nerve L4,5
-Extension of
lateral four toes
and
-Dorsiflexion of
foot
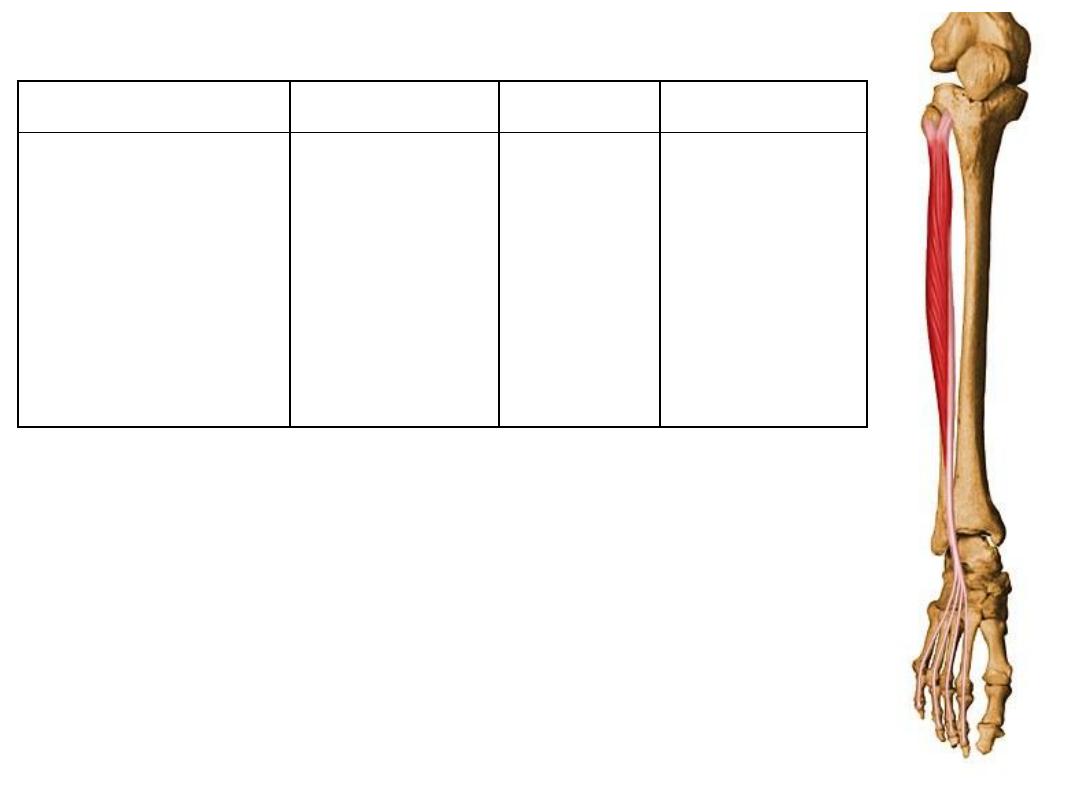
Extensor digitorum longus:
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Middle half of
fibula &
interosseous
membrane
Distal phalanx
of great toe
(via an
extensor hood)
Deep fibular
(peroneal)
nerve L4,5
-Extension of great
toe
-Dorsiflexion of foot
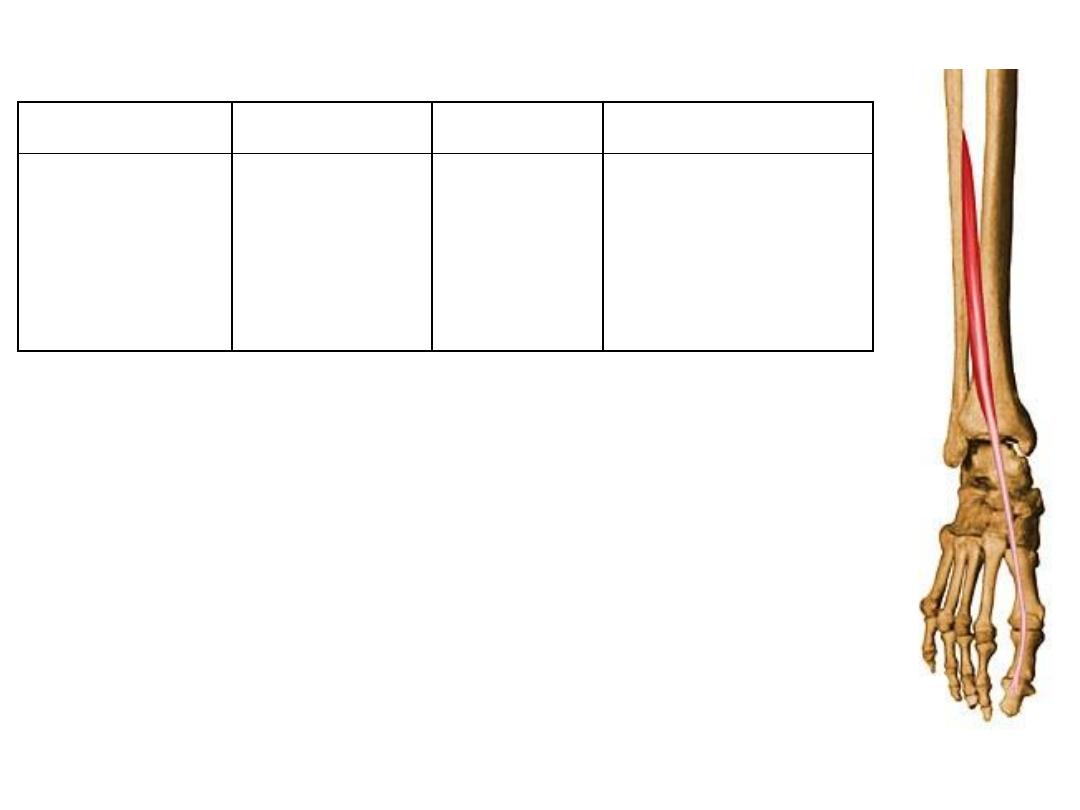
Extensor hallucis longus:
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Distal part of
fibula
Base of 5
th
metatarsal
Deep fibular
(peroneal)
nerve L4,5
- Dorsiflexion
- Eversion
Peronius tertius:
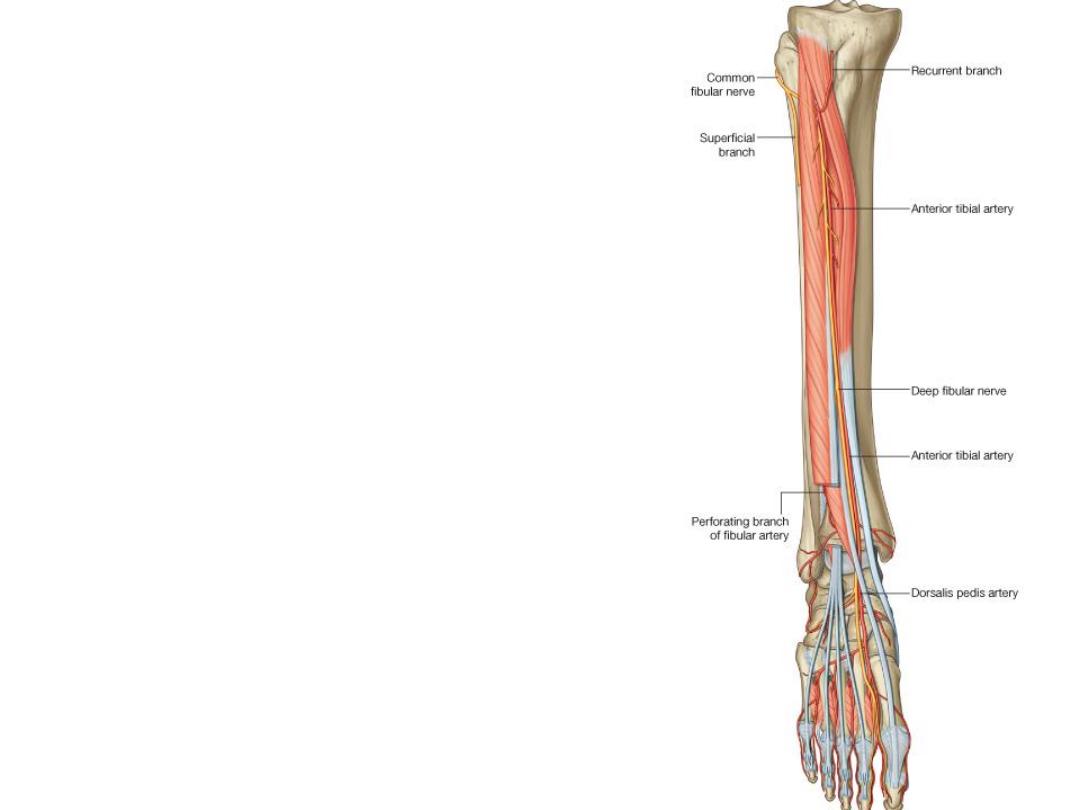
The anterior tibial artery:
-After division of the popliteal artery, the ATA
passes forward through the origin of tibialis
posterior & over the interosseous membrane
to reaches the anterior compartment between
TA & EDL
-When EHL arises, the ATA will lie between it
& TA
-Just above the ankle, EHL crosses medially,
here the artery will lie between the tendons of
the 2 long extensors
-Along its course it is accompanied by 2
veins, & the deep peroneal nerve on its
lateral side
-After crossing below the extensor
retinacula, the artery enters the foot
midway between the 2 malleoli as the
dorsalis pedis artery
Branches:
1- Anterior tibial recurrent a.; shares
in the patellar plexus
2-
Anterior
medial
&
lateral
malleolar; to the ankle & overlying
skin
3- Sometimes the posterior tibial
recurrent
&
circumflex
fibular
arteries arise from it
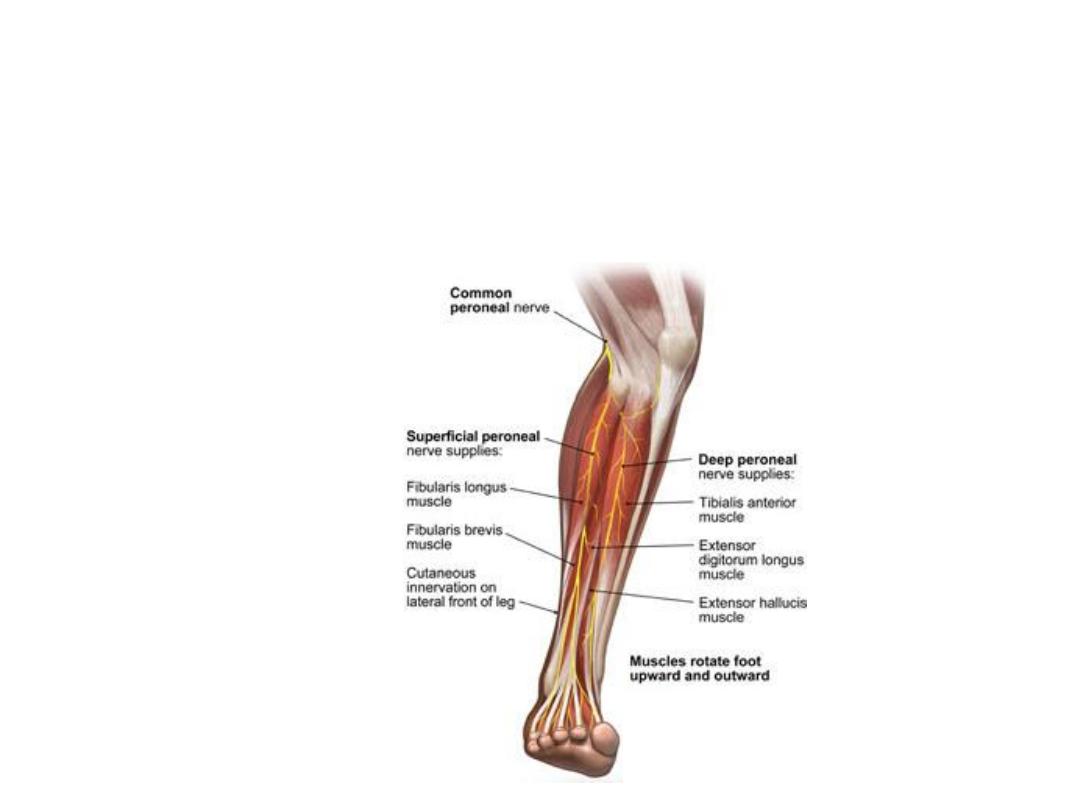
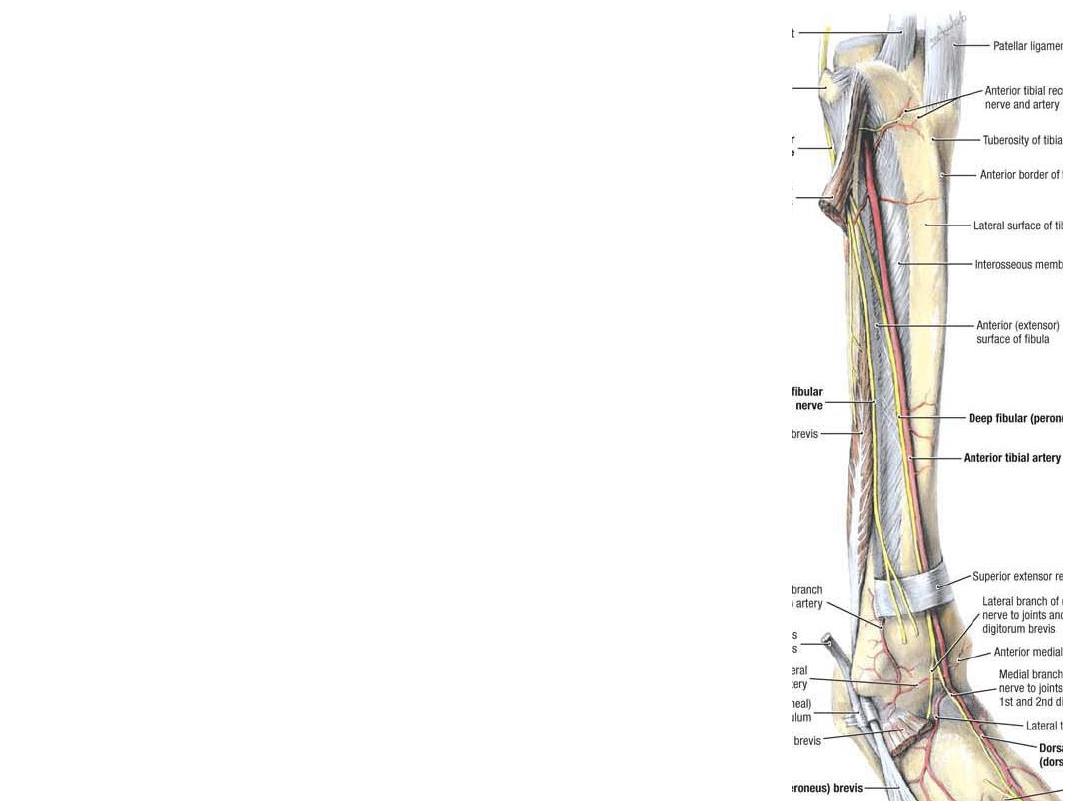
The deep peroneal nerve:
-The common peroneal n. after winding around the fibular neck divides in the
upper part of peroneus longus into superficial & deep peroneal nerves
-The deep peroneal nerve passes medially to the extensor compartment where
it accompanies the ATA
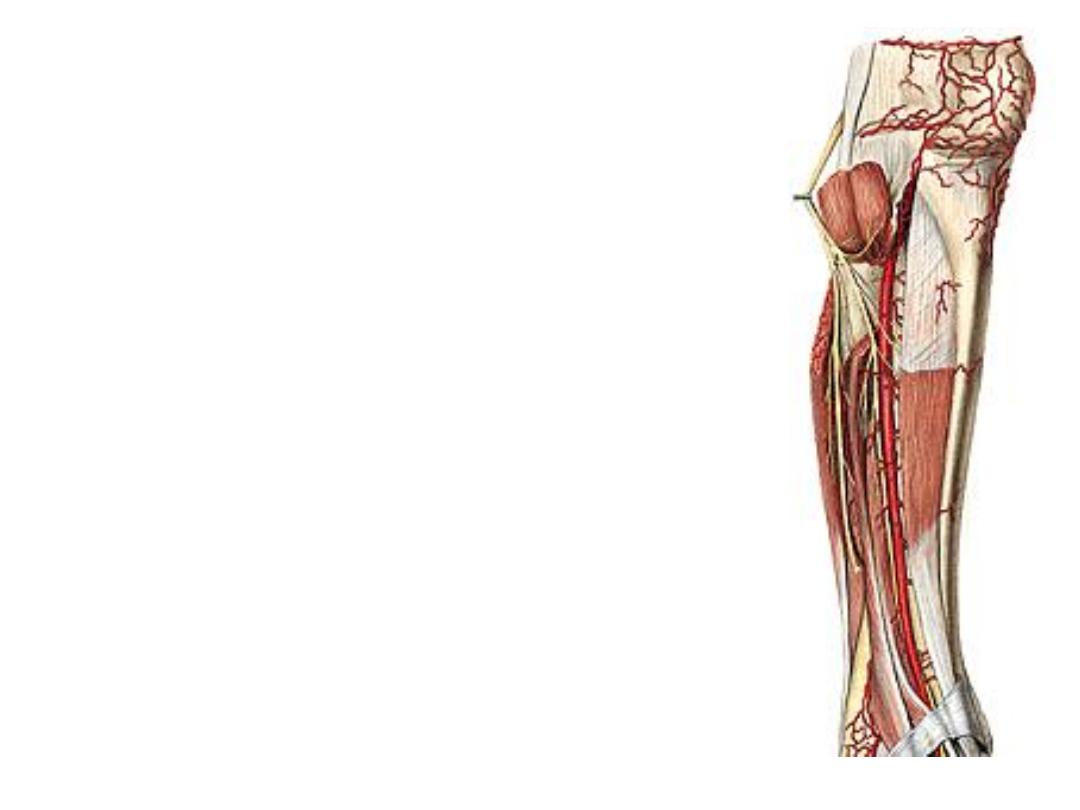
-It supplies all muscles of this
compartment & tibio-fibular joints
-Divide on the dorsum of the foot
into medial & lateral branches
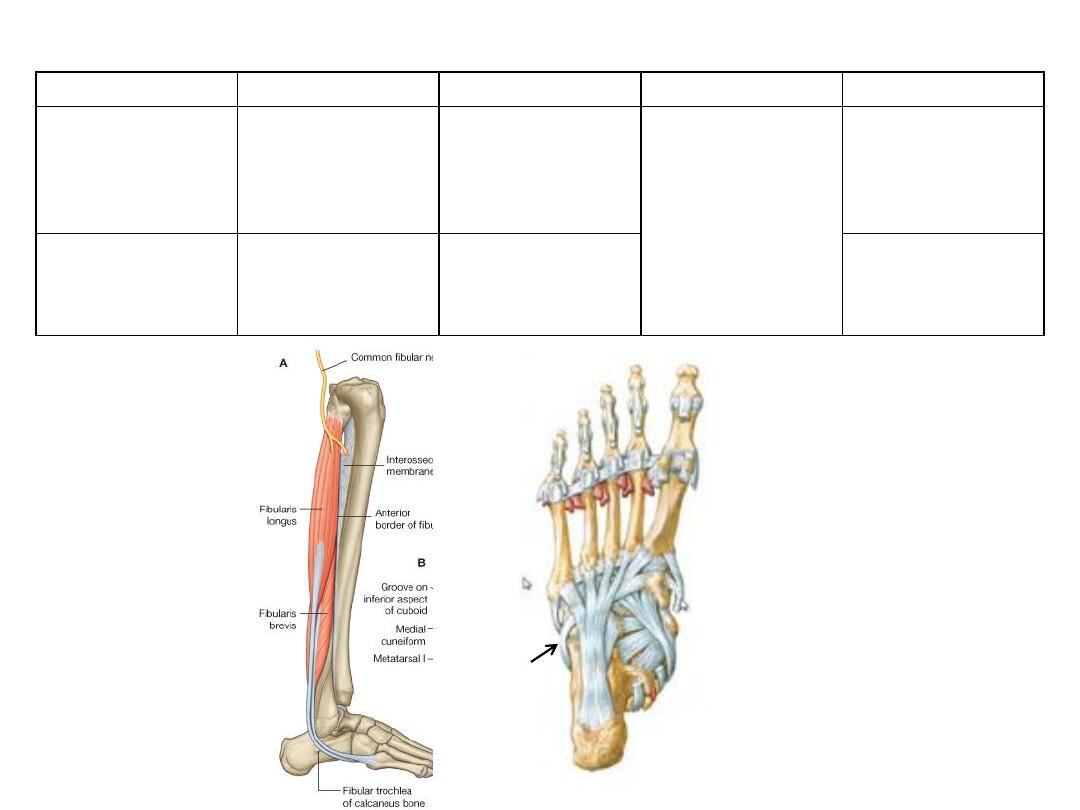
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Fibularis
(peroneus)
longus
-
Upper 2/3 of
fibula
-
Lateral tibial
condyle
-
Undersurface
of medial
cuneiform
-
1
st
metatarsal
Superficial
fibular
(peroneal) nerve
L5-S2
-
Eversion
-
Plantarflexion
-
Supports foot
arches
Fibularis
(peroneus)
brevis
Lower 2/3 of
fibula
Base of 5
th
metatarsal
Eversion of foot
Muscles of the lateral compartment
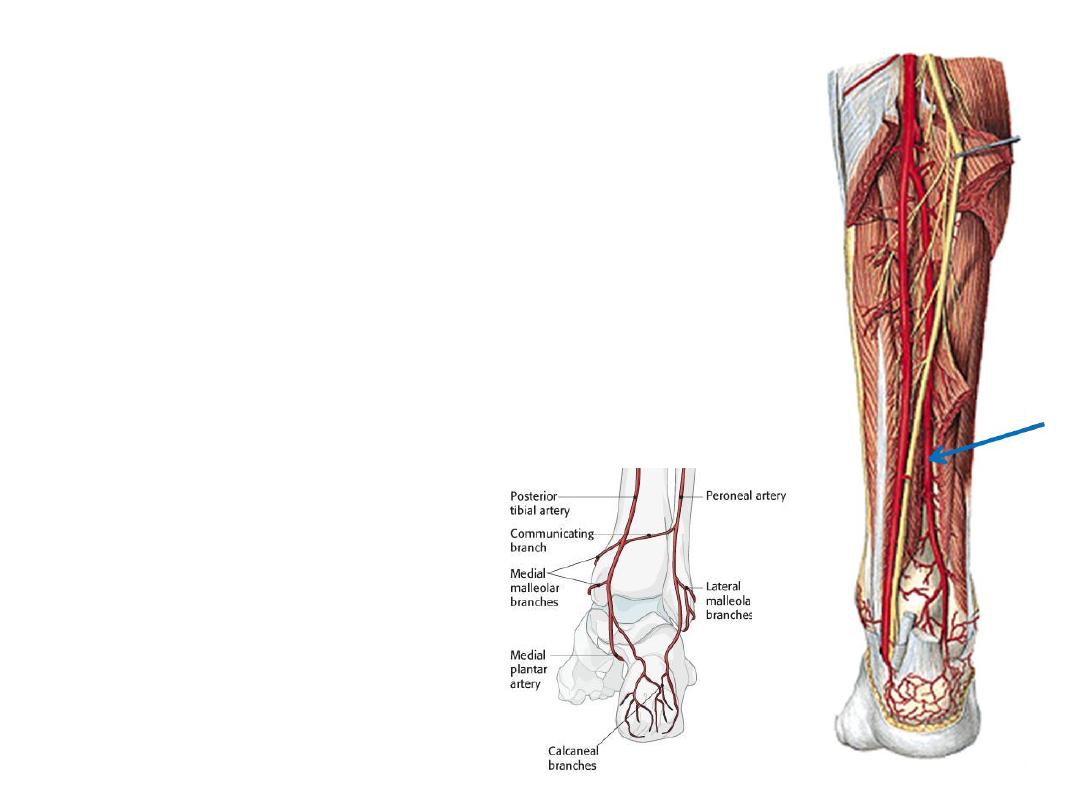
The peroneal artery:
-The principal source of blood to the lateral compartment
-Given from the PTA 2 cm below its origin
-Descends in the posterior compartment of the leg in the
substance of FHL
Branches:
1- Nutrient; to the fibula
2-Perforating branches; given distal to the interosseous
membrane to enter the antreior compartment
3- Lateral malleolar a.; spread on the lateral aspect of the
ankle supplying it & overlying skin
4- Lateral calcaneal branches
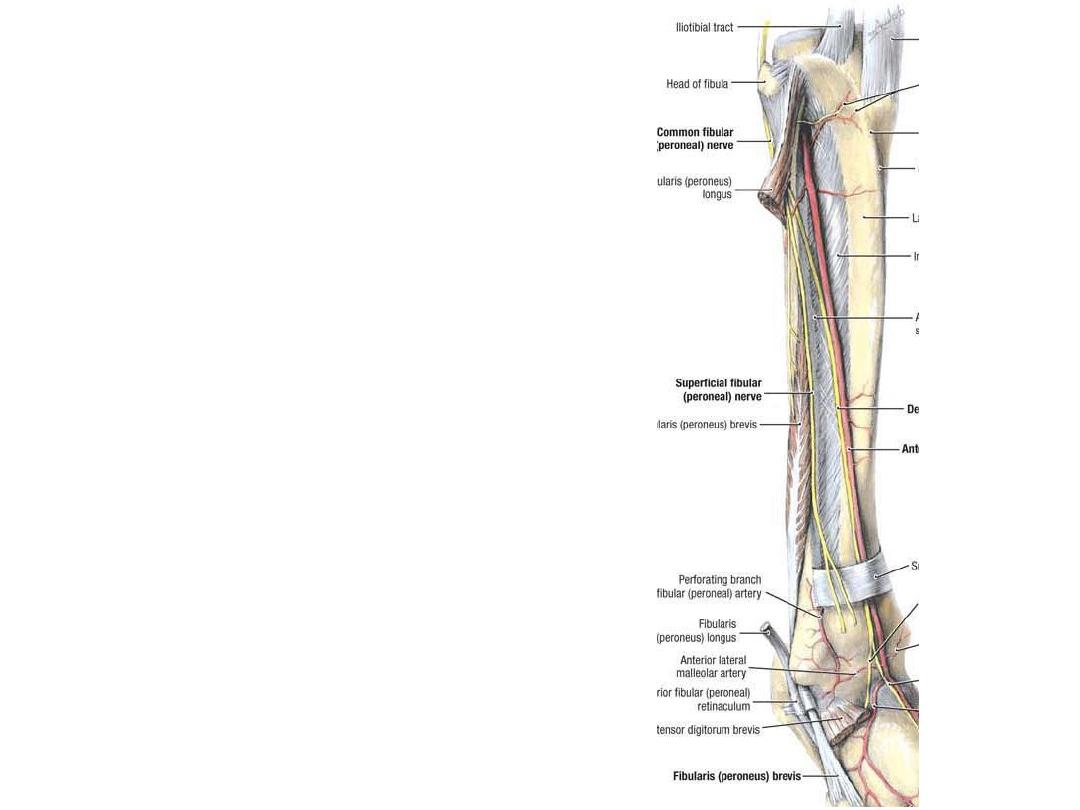
The superficial peroneal nerve:
-Descends in the lateral compartment
of the leg to supply both peronei
-It also supplies skin over the
anterolateral aspect of the leg
-In the lower 1/3 of the leg it pierces
the deep fascia to supply the dorsum
of the foot by medial & lateral
branches
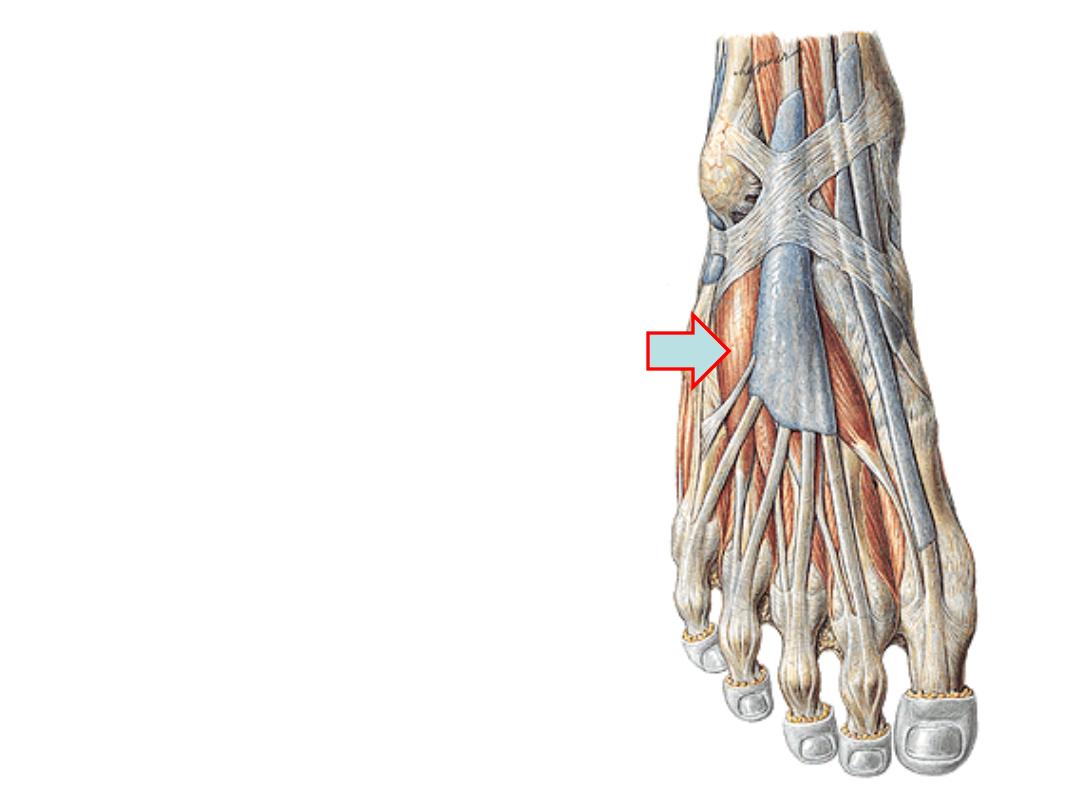
The dorsum of the foot:
Extensor digitorum brevis:
-This thin muscle arises from the extensor
retinacula & calcaneus
-The muscle divides into 4 slips for the
medial 4 toes
-The most medial is called EHB & inserted
into the proximal phalanx of the great toe
-The rest 3 go to the extensor expansion of
the middle 3 toes
-Supplied by the deep peroneal nerve
-Aids
in
extension
of
the
proximal
phalanges
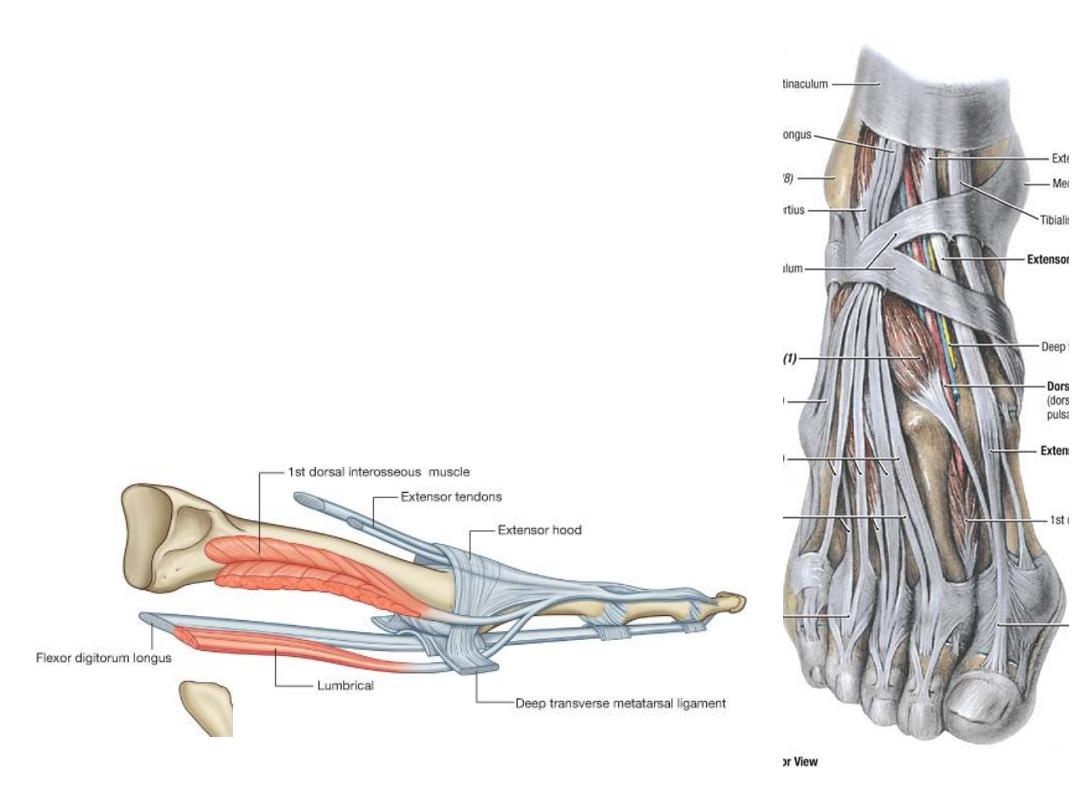
The extensor hoods:
-
Each extensor hood is triangular in shape with the apex
attached to the distal phalanx & the central region attached to
the middle phalanx
-
The corners of the hoods attach mainly to the deep transverse
-
Many of the intrinsic muscles of the foot insert into the free
margin of the hood on each side
-
The attachment of these muscles allows the forces from these
muscles to cause flexion of the MTPJ while at the same time
extending the IPJ
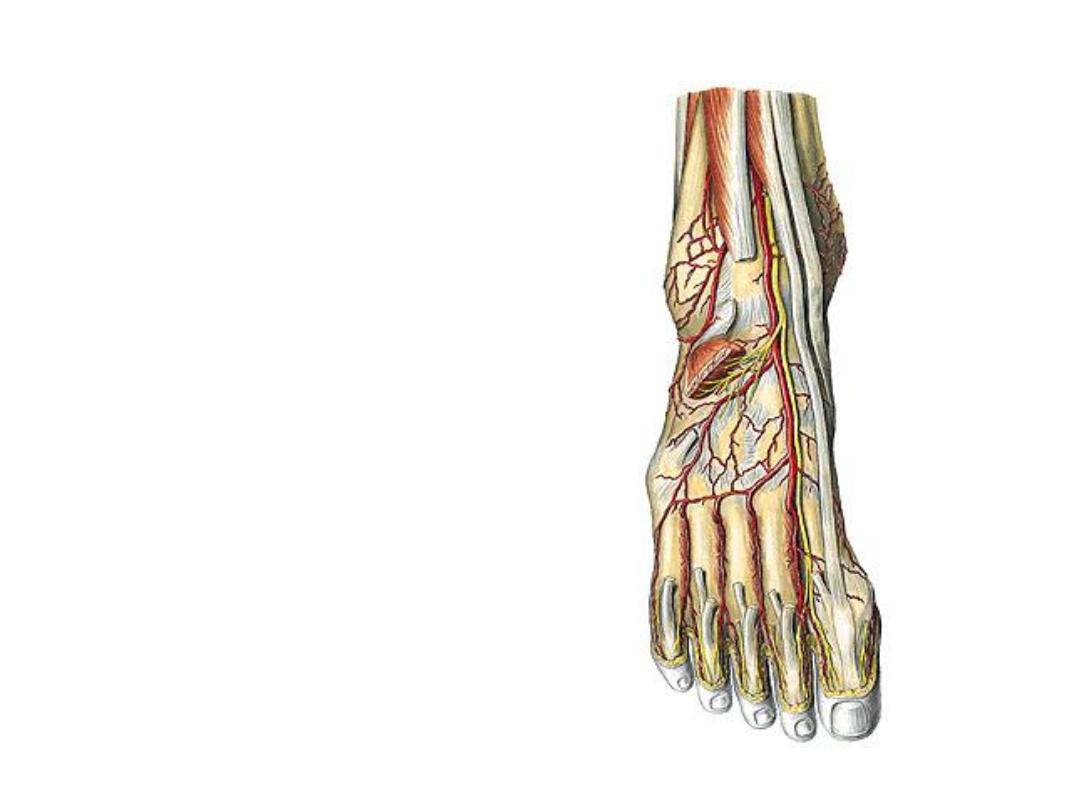
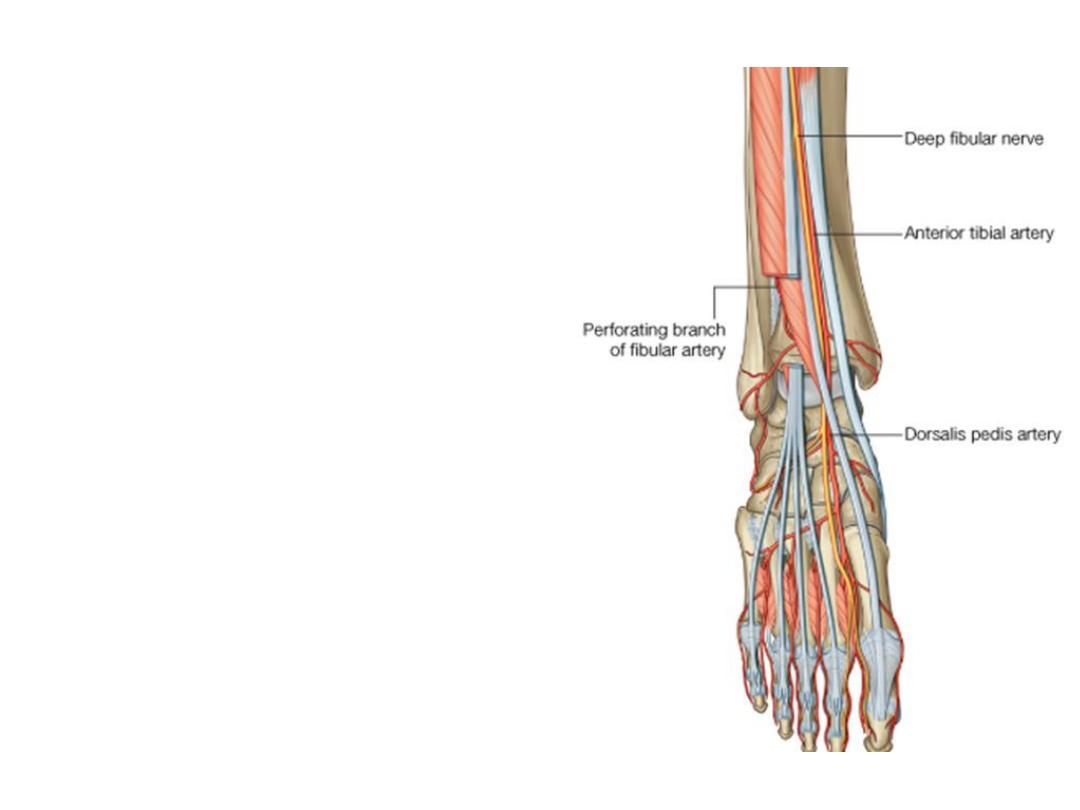
Dorsalis pedis artery:
-The continuation of ATA at the ankle
joint
-The artery lies against bones &
crossed by EHB muscle
-Accompanied by the deep peroneal
nerve
-Dips between the 2 heads of 1
st
dorsal interosseous muscle as the
deep plantar artery to join the deep
plantar arch in the sole
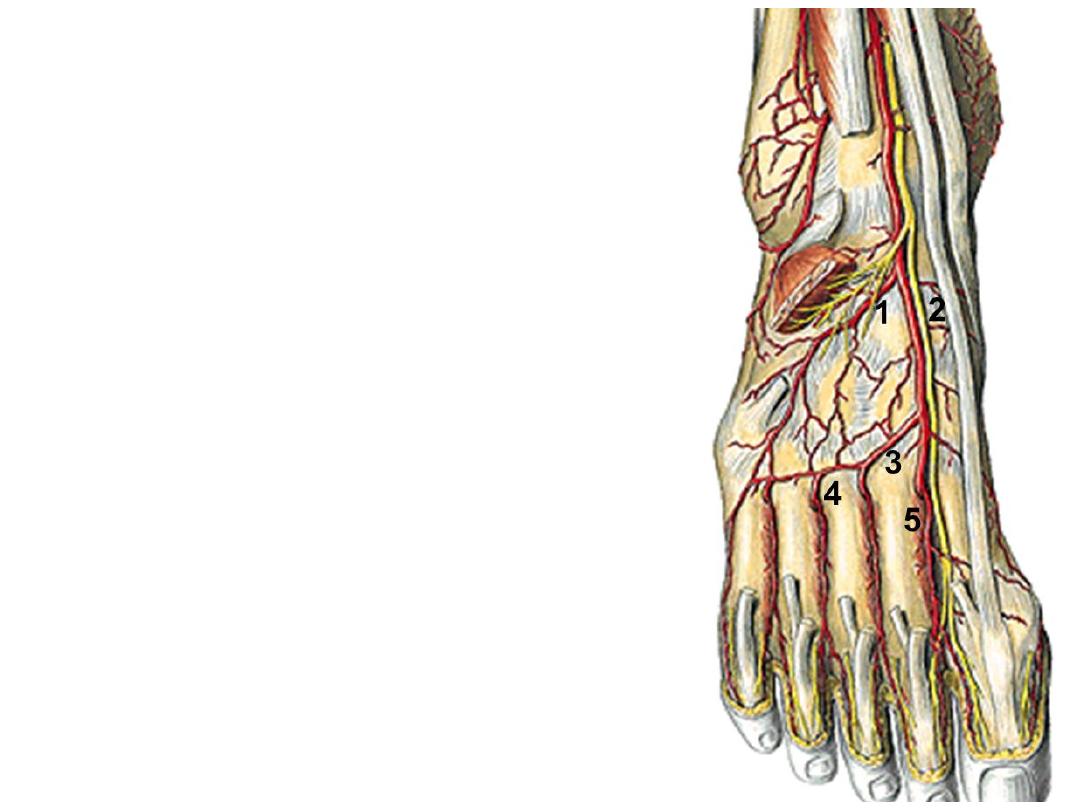
Branches:
1- The lateral tarsal a.; supplies structures in the
region & anastomoses with the lateral malleolar
& arcuate arteries
2- The medial tarsal a.; runs medially to
anastomose with the medial malleolar a.
3- The arcuate a.; arises at the level of the bases
of metatarsal arteries, passes laterally to
anastomose with the lateral tarsal & plantar
arteries
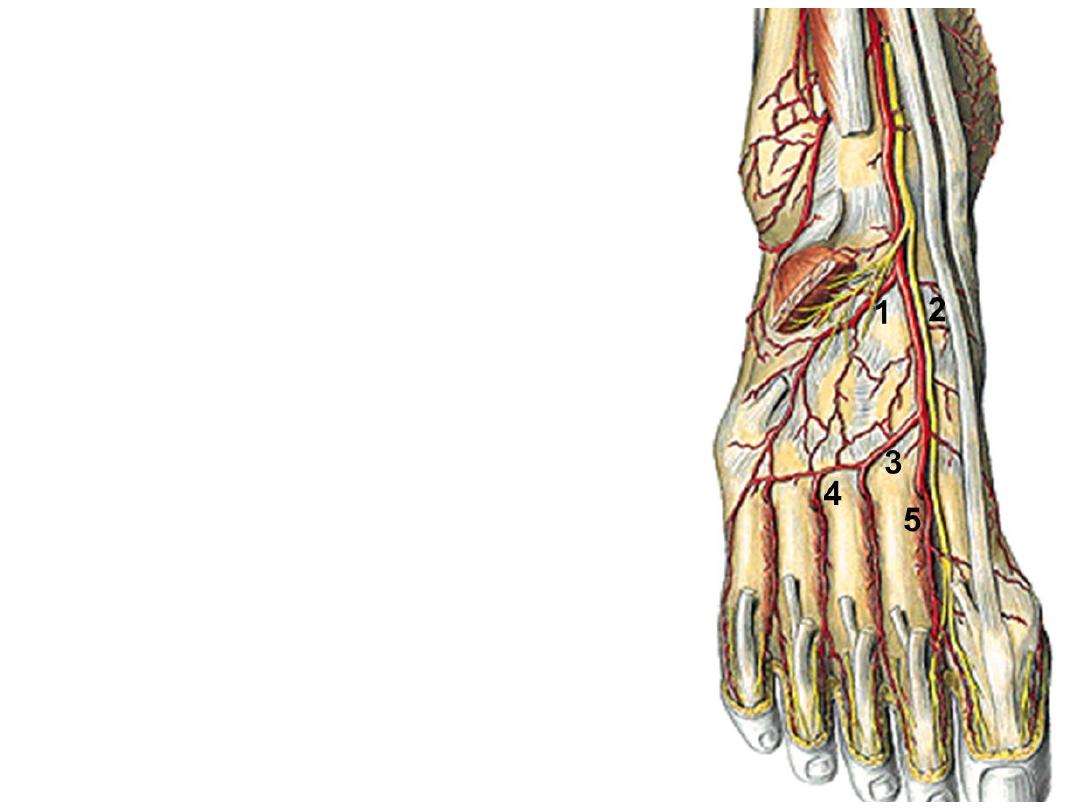
4- Four dorsal metatarsal arteries to the 4
clefts, each divides into 2 dorsal digital
arteries. Each DMA gives a perforating branch
which sinks into the sole between the 2 heads
of origin of dorsal interossei to anastomose in
the foot with plantar arches.
5- First dorsal metatarsal a. passes to the 1
st
web & divides into 2 dorsal digital arteries
6- Deep plantar arteries; is the continuation of
DPA
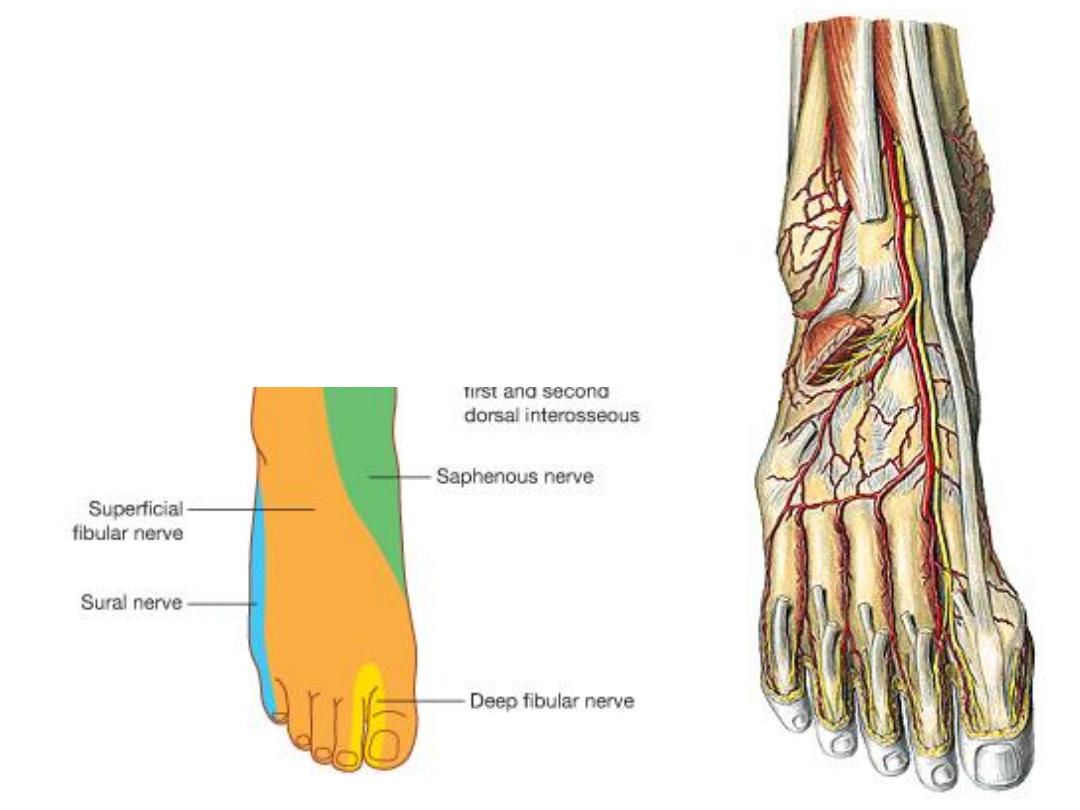
The deep peroneal nerve:
-Lies parallel & lateral to the tendon of EHL
-At the lower border of the inferior ER divides into the
terminal medial & lateral branches
-Lateral branch supplies EDB
-Medial branch supplies the web between 1
st
& 2
nd
digits & the first two dorsal interossei
