١
Fifth stage
Pediatrics
Lec-
Dr.Athal
4/2017
HUMAN GENETICS
Genetic Disorders
Common, with 2-4% of live-born babies having a significant congenital
malformation and about 5% a genetic disorder.
30-50% of hospitalized children have congenital anomalies or genetic
disorders.
Categories of Genetic Disorders
1. Single gene mutations,(Mendelian disorders)- 6%
2. Chromosomal disorders. (7.5%)
3. Multifactorially inherited conditions. (20%)
4. Disorders that show an unusual pattern of inheritance. (2-3%)
5. Teratogenically caused conditions. (6%)
Single Gene Disorders
Disorders with these patterns of inheritance, described by Mendel in 1865, are
rare individually, but collectively they represent an important contribution to
childhood disease.
The
hallmark
of a single-gene disorder is that the phenotype is overwhelmingly
determined by changes that affect an individual gene (quantity or function.)
The phenotypes associated with single-gene disorders can vary from one
patient to another based on the severity of the change affecting the gene and
additional modifications caused by genetic, environmental, and/or stochastic
factors. This feature of genetic disease is termed
variable expressivity
.
Variable Expressivity:
AD disorders show variability in symptoms expressed in different individuals
carrying the same mutated gene. Some individuals have only mild clinical
symptoms, whereas others have more severe disease.
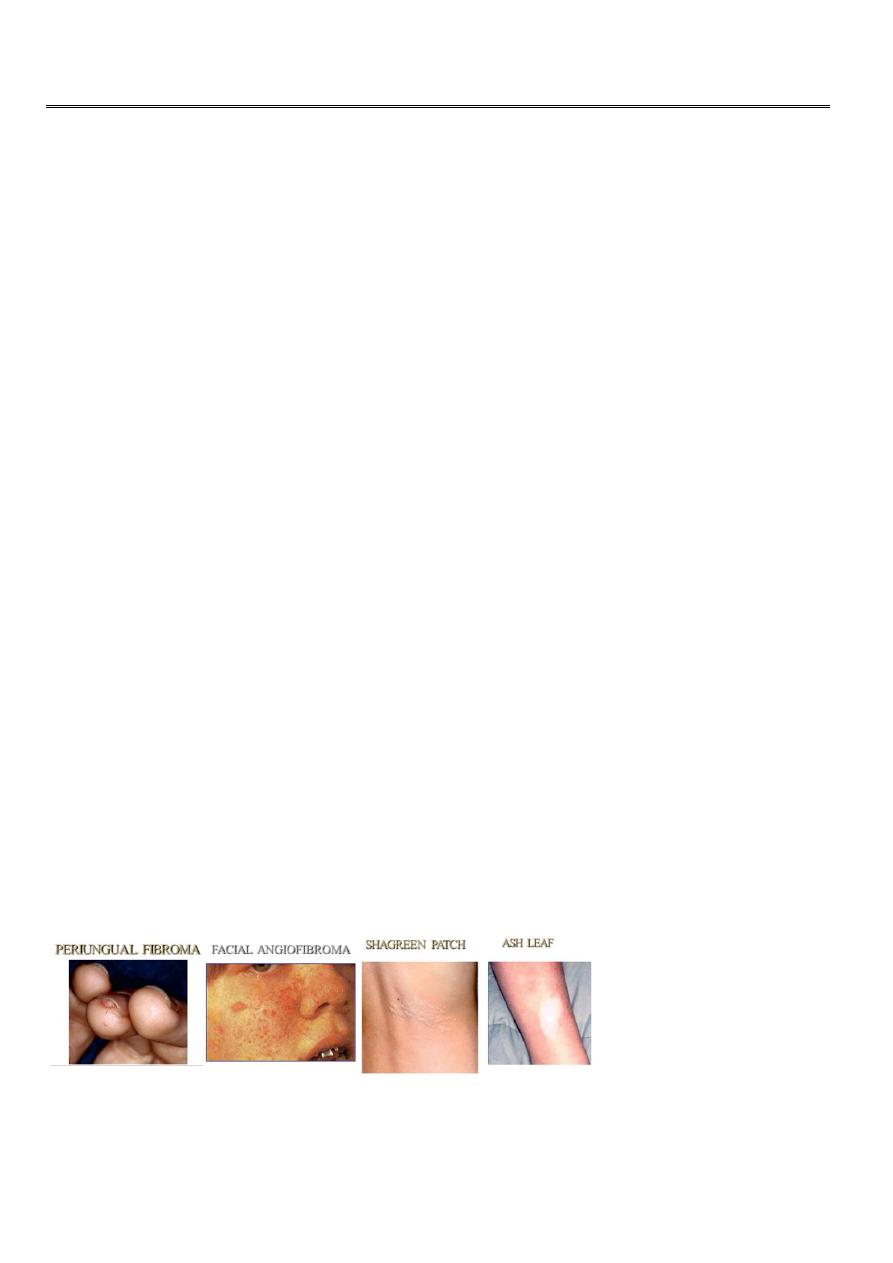
For example, a parent with
tuberous sclerosis
may have mild skin
abnormalities only, but his or her affected child may have, in addition, epilepsy
and learning difficulties.
Patterns Of Inheritance:
Autosomal Dominant.
Autosomal Recessive.
X-Linked Recessive.
X-Linked Dominant.
٢
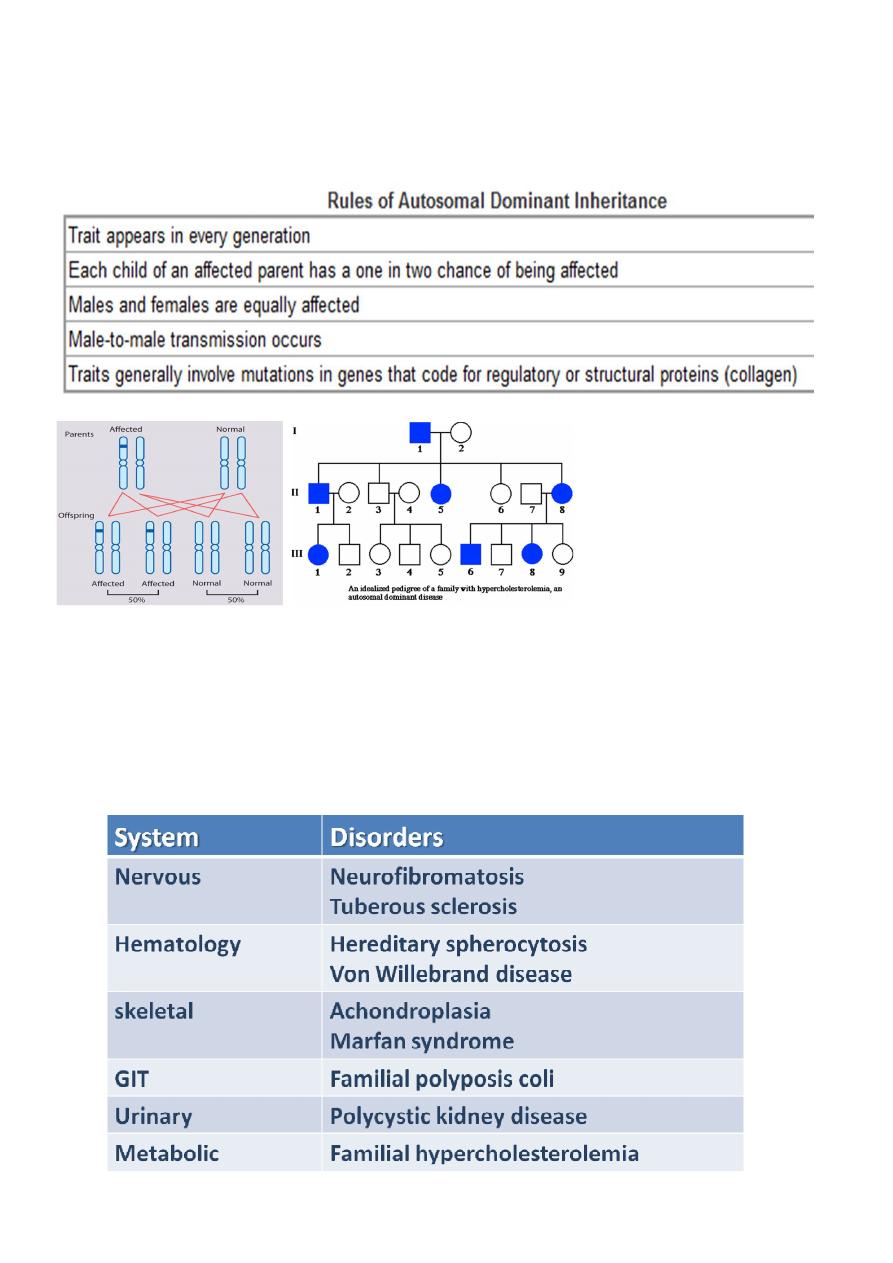
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
This is the most common mode of Mendelian inheritance.
Single copy of a gene bearing mutation (one of the autosomes;
chromosomes 1–22) is sufficient to cause disease, that is usually manifest in
heterozygous state.
Spontaneous Mutation:
AD disorders sometimes appear in a child of unaffected parents because of a
spontaneous mutation ”a new mutation in one of the gametes leading to the
conception of the affected person”.
This is the most common reason for absence of a family history in dominant
disorders, e.g. >80% of individuals with achondroplasia have normal parents.
E.g. of some AD inheritance
٣
Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is the most common skeletal dysplasia in humans.
The bony abnormalities in achondroplasia lead to short stature,
macrocephaly, a flat midface with a prominent forehead, and
rhizomelic shortening of the limbs.
_______________________________________________________________
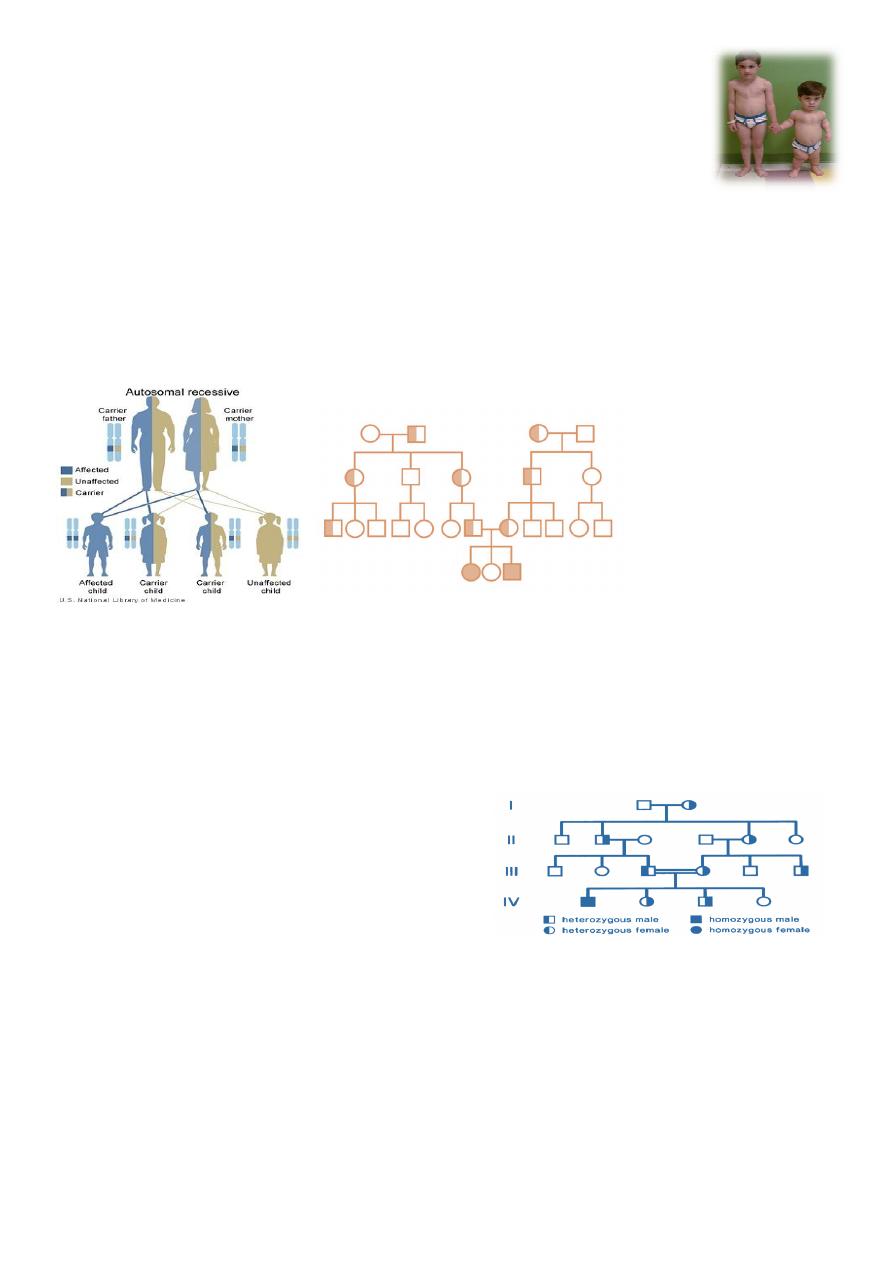
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Disorders that are inherited in an AR manner manifest only when both copies
of a gene pair located on an autosome chromosome have a mutation.
Affected children usually are born to unaffected parents, each of whom carries
one copy of the mutation. If both members of a couple are carriers (or
heterozygotes) for this mutation, each of their offspring has a 25% chance of
being affected
Consanguinity:
It is thought that we all carry at least one abnormal recessive gene. Fortunately,
our partners usually carry a different one.
Marrying a cousin or other relative increases the chance of both partners carrying
the same abnormal autosomal recessive gene, inherited from a common ancestor.
A couple who are cousins therefore have an increase in the risk of having a child
with a recessive disorder.
pedigree of autosomal recessive inheritance
consanguineous marriage
Rules of AR inheritance:
1. Affected individual are homozygous for the abnormal gene, each parent is a
heterozygous carrier.
2. 1 in 4 risk of having an affected child for 2 carrier parents.
3. All offspring of affected individuals will be carriers.
4. Males and females are likely to be affected equally.
5. Risk of AR disorder increased by consanguinity and withen specific racial groups.
6. Often affect metabolic pathways (enzymopathy) and associated with serious illness
and shorten life span
٤
E.g. of some AR inheritance
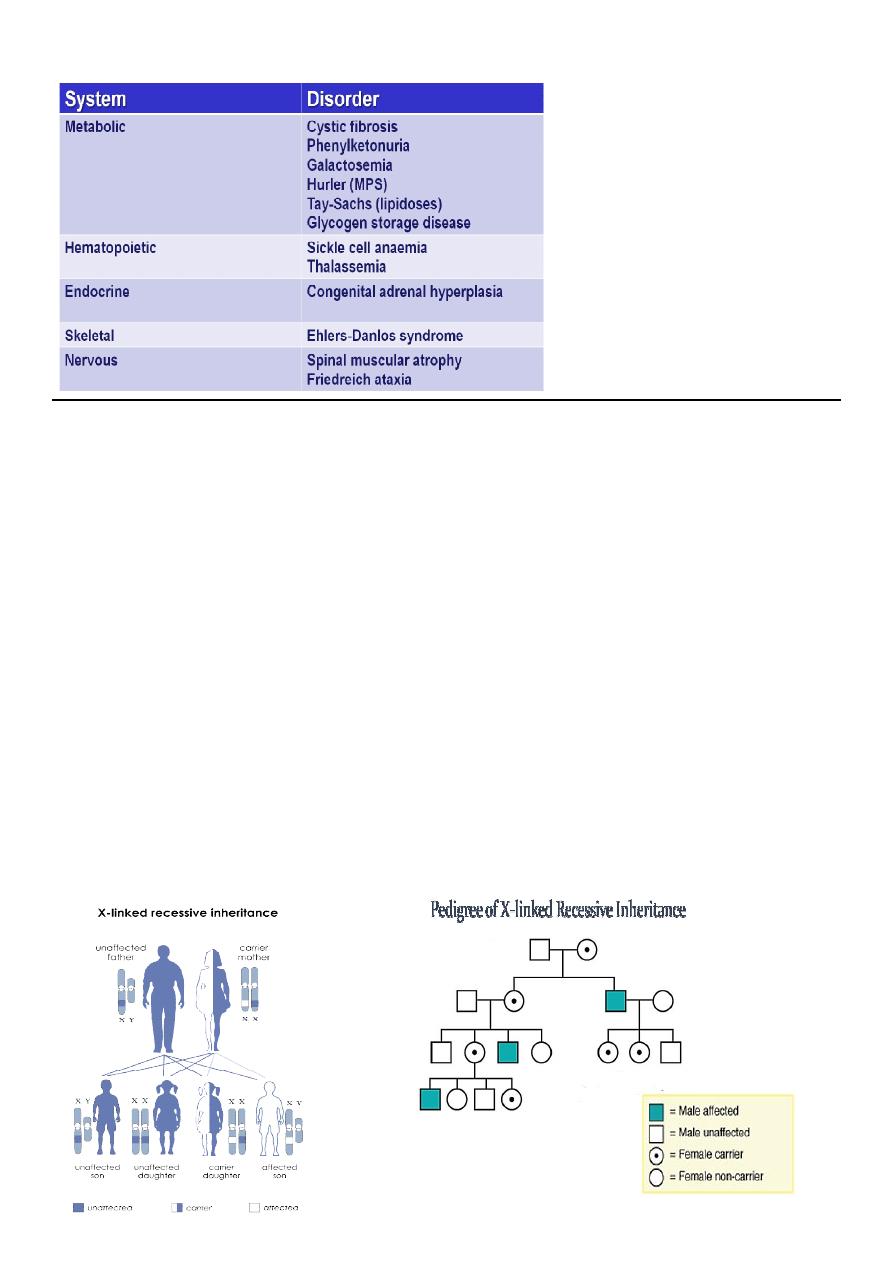
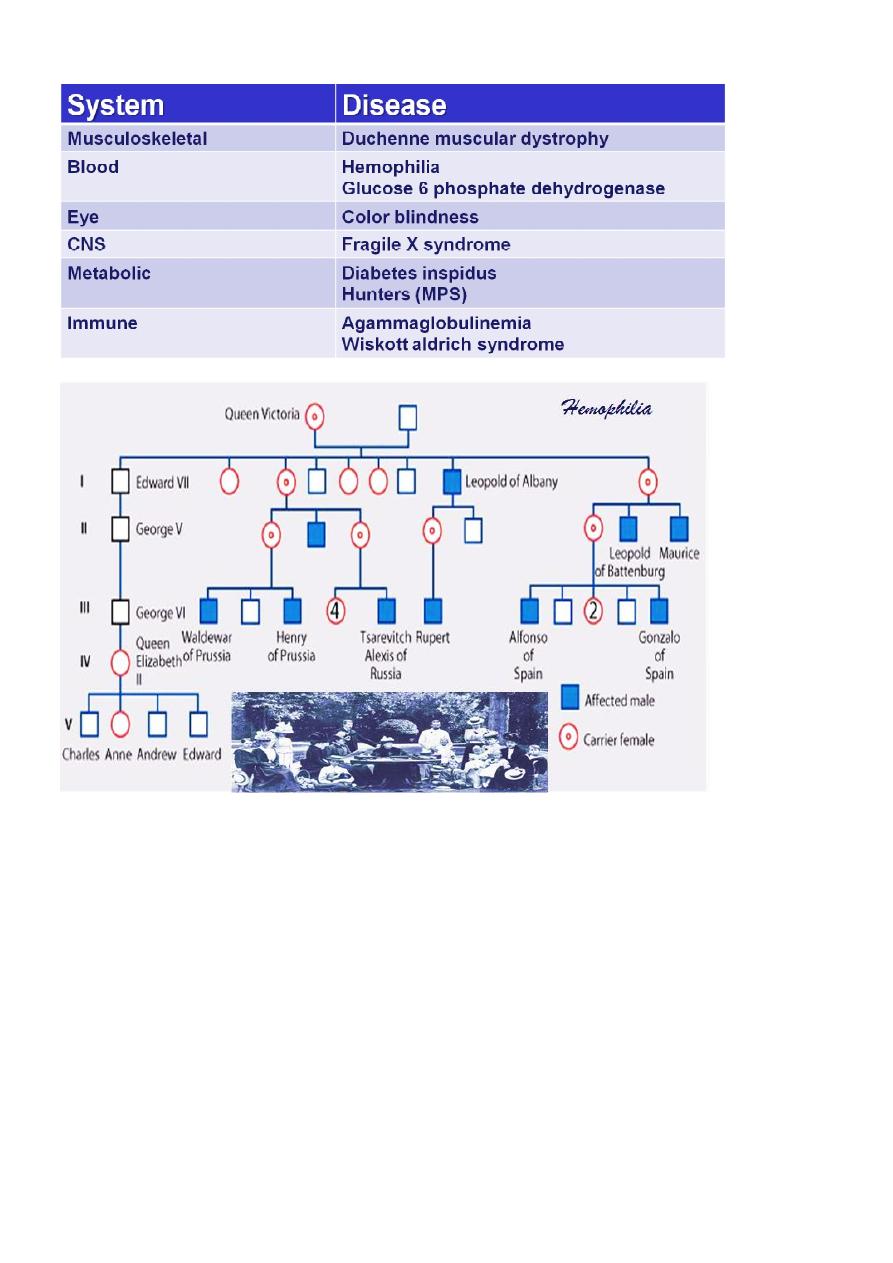
X-linked recessive inheritance
More than 1000 genes have been identified on the X chromosome,
whereas only about 200 are believed to be present on the Y
chromosome.
Rules of XR inheritance:
1. Males are more commonly and more severely affected than females.
2. Female carriers are generally unaffected, or if affected, they are affected
more mildly than males.
3. Female carriers have a 25% risk for having an affected son, a 25% risk
for a carrier daughter, and a 50% chance of having a child that does not
inherit the mutated X-linked gene.
4. Trait is transmitted from affected males to all of their daughters; it is
never transmitted father to son because they pass their X chromosome
to all of their daughters and their Y chromosome to all of their sons.
5. Male-to-male transmission excludes X-linkage but is seen with
autosomal dominant and Y-linked inheritance.
6. Family history may be negative - new mutations and gonadal mosaicism.
7. Identifying female carriers is important to be able to provide genetic
counselling.
٥
E.g. of some XR inheritance
