Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses
IMCISpecific objectives of the current lecture
At the end of this lecture you will be able to:• Enumerate most common causes o underfives death in developing countries.
• Define IMCI.
• Identify objectives of IMCI.
• Discuss elements of IMCI.
• Draw charts show summary of IMCI for children 2months-5 years and 1 week to 2 months.
IMCI
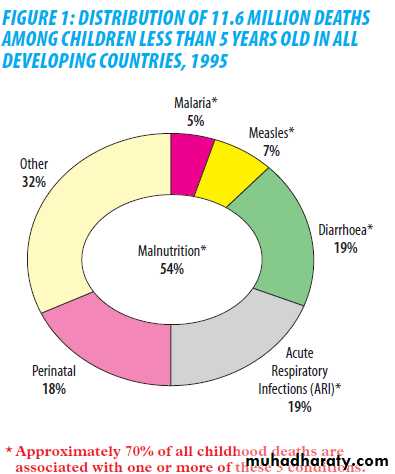
Altogether more than 10 million children die each year in developing countries before they reach their fifth birthday.Seven in ten of these deaths are due to
acute respiratory infections (mostly pneumonia),diarrhea,
measles,
malaria, or
malnutrition; and often
to a combination of these conditions
IMCI
Every day, millions of parents take children with potentially fatal illnesses to first-level health facilities such as clinics, health centers and outpatient departments of hospitals.IMCI
In some countries, three in four episodes of childhood illness are caused by one of these five conditions. And most sick children present with signs and symptoms related to more than one.IMCI
This overlap means that a single diagnosis may not be possible or appropriate, and that treatment may be complicated by the need to combine therapy for several conditions.IMCI
Surveys of the management of sick children at these facilities reveal that many are not properly assessed and treated and that their parents are poorly advised.IMCI
At this level, in most developing countries,Diagnostic supports such as radiology and laboratory services are minimal or non-existent;
drugs and equipment are scarce;
combined with an irregular flow of patients,
IMCI
Health care providers at primary health care centers have few opportunities to practice complicated clinical procedures.
Instead, they must often rely on history and signs and symptoms to determine a course of management that makes the best use of available resources.
IMCI
WHO and UNICEF developed a strategy known as Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI).The strategy combines Improved management of childhood illness with aspects of
nutrition,
immunization, and
other important disease prevention
In addition to health promotion elements.
IMCI
The objectives of IMCI are to:• reduce deaths, frequency and severity of illness and disability, and
• contribute to improved growth and development.
IMCI
Integrated case management relies on:Case detection using simple clinical signs and treatment.
Few clinical signs as possible are used.
The signs are based on expert clinical opinion and research results, and strike a careful balance between sensitivity and specificity of the signs and symptoms.
IMCI
Sensitivity and specificity measure the diagnostic performance of a clinical sign compared with that of the gold standard, which by definition has a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 100%.IMCI
Sensitivity measures the proportion or percentage of those with the disease who are correctly identified by the sign. In other words, it measures how sensitive the sign is in detecting the disease.
Sensitivity = true positives / [true positives + false negatives]
IMCI
Specificity measures the proportion of those without the disease who are correctly called free of the disease by using the sign.Specificity = true negatives / [true negatives + false positives
IMCI
IMCI allows a health care provider to determineIf a child should be urgently referred to another health facility
Or
If the child can be treated at the first-level facility (e.g. with oral antibiotic, antimaiarial, ORS, etc.)
Or
If the child can be safely managed at home.
The core of the IMCI strategy
The core of the IMCI strategy is focus on the most important causes of death:Diarrhea
ARI
Malaria
Measles
Malnutrition
IMCI
The complete IMCI case management process involves the following elements:IMCI
First assesses the child by• Identifying any danger signs,
• Asking about the four main symptoms in all children (cough or difficult breathing, diarrhea, fever, and ear problem), Carrying out further assessment if a main symptom is reported, and
• Reviewing the nutritional and immunization status in all children.
IMCI
Then classifies the child's illnesses.
Each illness is classified according to whether it requires:
• - urgent referral;
• - specific medical treatment and advice; or
• - simple advice on home management.
IMCI
After classification, specific treatments are identified.If the child has to be referred urgently to a hospital, give only essential treatment before departure. Since most children have more than one illness.
IMCI
Practical treatment instructions are carried out, includingTeach the mother how to administer oral drugs,
To increase fluid intake during diarrhea and to treat local infections at home.
The mother is advised on the signs which indicate that the child should immediately be brought back to the clinic and when to return for routine follow-up.
IMCI
Feeding is assessed and counseling of mothers on feeding problems is provided.Follow-up instructions for various conditions are given when the child returns to the clinic.
If necessary, reassess the child for new problems.