Genetics: is the study of genes including the structure of genetic materials, information stored in the genes, how the genes are expressed and how the genetic information is transferred, also it is the study of heredity and variation.
Genes: Genes are genetic determinants and they control heredity and determine properties of the organism. The genes are functional units of the chromosomes. Synthesis of protein components and enzymes of a cell is regulated by genes. DNA is responsible for both gene function and replication. By replication heredity or stability of a type is maintained. An organism containing a normal gene is known as 'wild type'. Genes may rarely mutate (change) resulting in heritable variations called mutations. The changed organism is called a mutant.
Genotype. It is the genetic determinant of a cell.
Phenotype. This is the structural and physiological manifestations of the organism due to a particular genotype.
Genome. Genome is the entire set of genes and thus is the totality of genetic information in an organism.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
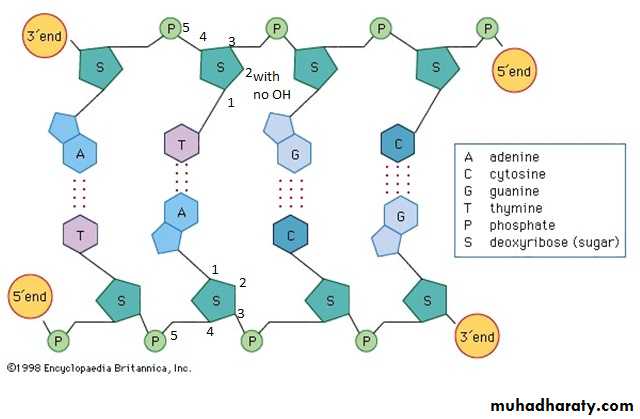
DNAis a very large molecule made up of a long chain of subunits. It is a polymer of two strands of nucleotides with a hydrogen bounded to each other to form a double helix. The sugar is called deoxyribose because there is no hydroxyl (OH) at position 2(just two hydrogen).The phosphate, sugar and one base called a nucleotide, The sugar and base alone are called a nucleoside. The phosphodiesters backbone are held between phosphate group and sugar, the base pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds to form (complementary base pairing).
There are 4 different Nucleotides categorized as either Purines or pyrimidine. These are usually represented by a letter. These Are:
Purines (double ring)
Adenine (A).
Guanine (G)
Pyrimidine (single ring)
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
Complementary base pairs means:
Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) (by 2 hydrogen bonds).
Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to Guanine (G) (by 3 hydrogen bonds).
Each base bind to sugar molecule at 1st carbon atom, the sugar molecule bind to phosphate group at 3' to 5' carbon atom while in opposite direction by 5' to 3' carbon atom to form antiparallel structure.
DNA helix form have grooves :
Minor :in which exposed edge from which C1atom is extended.Major: in which opposites edges of base pairs are extended.
There are 3 major forms of DNA :
B-form : which is most common form of the human cell.
A-form: which is found in low humidity condition such as bacterial spores.
Z-form : which is found in high salt concentration.
RNA molecules
The basic building blocks of RNA are almost the same as those of DNA, except for two differences:
The sugar deoxyribose is not used in the formation of RNA (ribose) that contain an extrahydroxyl ion appended to the ribose ring structure.
Thymine is replaced by another pyrimidine called uracil. i.e. adenine , guanine, cytosine and uracil.
Types of RNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA): RNA copy of the DNA strand to be “read” during translation.
Transfer RNA (tRNA): Carries individual amino acids to site of replication.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) :Attached to ribosome complex, site of protein synthesis.
mRNA synthesis ( gene expression)
DNA contains genes and the genes is a continuous sequences of nucleotides containing a region that code for RNA molecules. The gene have two ends, one is a promoter region and the other is a terminator region. This region of gene use for RNA synthesis in a process of gene expression.
The gene expression or mRNA synthesis are include :
Transcription: is the process in which a gene's DNA sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an RNA molecule.Some genes are transcribed in large quantities because we need large amount of this protein. Some genes are transcribed in small quantities because we need only a small amount of this protein
Transcription can occur in the nucleus where DNA is used as a template to mRNA synthesis. This process can occur by three steps:
Initiation.
The RNA polymerase can bind to the gene sequence by recognize the promoter region of the gene, here the double helix of DNA will be opened or unwind.
Elongation
The complementary base pair up and the RNA polymerase bind the nucleotides from 3' to 5'.
Termination
Once the RNA polymerase reach to the terminator portion of the gene, the mRNA synthesis is completed. The RNA polymerase and mRNA strand will dissociate from each together.
The mRNA strand have two portion , exon (codon) and intron(uncodon) with 5' cap and 3' poly –A tail.The intron portion should be removed by a process of intron splicing by a complex of proteins and RNA molecule called spliceosome, then the exon edges will be bind together to form mature mRNA strand that can be exit from the nucleus through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm where the translation occurs by ribosomes on rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Translation
Initiation
The mRNA strand are arranged as each three nitrogenous base codes,called codon, for single amino acid. In translation the mRNA strand have two portion of codon, one for start and three codon for stop.
Small subunit of ribosome will bind to the start portion and a specific amino acid bring by tRNA to the ribosome-mRNA complex (tRNA + amino acid, called charged tRNA )(tRNA without amino acid called uncharged).
Elongation
Each amino acid have a specific anticodon sequence of tRNA molecules , so the complementary base pair will be occur between codon of mRNA and anticodon of tRNA .After the tRNA bind to the mRNA through small ribosomal subunit, the large ribosomal subunit bind to the mRNA to form a translation complex (mRNA + small and large ribosomal subunit). In the large ribosomal subunit there are three distinct sites, which are, E, P and A sites. The process of protein production will proceed as follows, the tRNA (charged) transfer the amino acid into the A site, the amino acids binds to each other in the P site , the tRNA (uncharged) will exit from E site.
Termination
The formation of a polypeptide will increased until completion , then a release factor will bind to the stop codon and the polypeptide will release from the tRNA at the P site. The ribosomal complex are dissociate and can be reassemble to start again.
The polypeptide now is completed and it may be need for some modification by added some molecules like CHO or lipid, or its shape , all of these will occur inside the Golgi apparatus.
DNA replication
Is the process that take place when cells divide , each new cell gets an exact copy of DNA before cell division occur. This process occur during S phase of the cell cycle phases.
The replication begins with separation of the two DNA strand to form two of parent strand at origin of replication (replication fork).
The scientist have study the DNA replication firstly in the prokaryotes cells.
There are several enzymes involved in this process:
Helicase separate the double helix of DNA and use of stabilizer to held each newly single strand.
DNA gyrase is used to make sure that the double strand area outside of the replication fork do not supercoil.
DNA polymerase used to catalyzed the addition of new nucleotides to growing daughter strand.
Beta clamp and clamp loader held the DNA polymerase in place of DNA.
Primers a short sequences of RNA, have to be paired to the template strands by the enzyme primase.
Both strands start together but one of them start by continuous orientation from 3'-5' this strand called leading strand.
while the other strand start by discontinuous orientation from 5'-3' this strand called lagging strand, in which the replication occur as a segments by forming an okazaki fragments, primase is used to add a primers at the head of 5' end
DNA polymerase III add short sequences of nucleotides to the primer filling in the gap.
DNA polymerase I used to replace the primers of okazaki fragment by DNA nucleotides.
Ligase is used to ensure bonding between the okazaki fragments.
The process will continue until two identical dsDNA strands are completed