
DIABETES MELLITUS IN PREGNANCY
One of the endocrine disorders affecting pregnancy and its significant hormonal
changes affect carbohydrate metabolism during pregnancy.
Its complicate (3-4 per 1000) pregnancy.
Pathophysiology:
•
D.M is a syndrome in which hereditary. And environmental factors interact leading
to inadequate insulin action.
•
Pregnancy by itself had diabetogenic effects due to action of human placental
lactogen, progesterone and estrogen.
•
In addition to rise in free cortical which leads to ↑ the insulin resistance especially in
third trimester. Diabetes may complicate a pregnancy either because the women
has pre-existing insulin-dependent diabetes before her pregnancy begins or may
develop impaired glucose tolerance during the course of her pregnancy.
Maternal hyperglycemia ===> fetus===> fetal hyperinsulinemia ===> increase
metabolism + (maternal tissue hypoxia & acidemia) ===> increase erythropoietin===>
Erythroblastosis & polycythaemia
Risk factors for the development of diabetes in pregnancy:
•
Family HX.
•
Previous baby > 4.5
•
Previous unexplained still birth.
•
Previous congenital abnormality.
Screening for DM in pregnancy:
•
No single screening test has been shown to be perfect. Urinary glucose unreliable
test and most screening test now rely on blood glucose estimation.
•
Gold stander for screening for gestational diabetes as:
-
50g oral glucose challenge test to all pregnant women at (24-28 week) wont
dietary preparation with 1 hour.
-
Plasma glucose >7.8 mmol/L should have full oral GTT.
-
Timed random blood glucose estimation at booking and at 28 weeks gestation >
6mmol/L fasting state or 2hours after food or >7mmol/L within 2hours of food full
oral GTT should be offered. Always keep blood sugar between (4-6 mmol/L).
Oral GTT:
•
Indications of oral GTT:
1. Family HX of DM in one 1st degree on two second degree relatives.
2. Presence of significant glycosuria.
3. Polyhydramnios.
4. Macrocosmic infant in current pregnancy.
5. Poor obstetric history (death of macrocosmic baby).
6. History of repeated abortion.
7. HX of Dm in previous pregnancy.
8. HX of traumatic delivery.
9. Unexplained IU.D
10. HX of congenital abnormality in previous pregnancy.
11. Obesity >90 Kg.
12. Abnormal screening test.
•
Patients abnormal screening test should be given 3 hours glucose tolerance test, if
1 hour screening test produce plasma glucose >200 mg/dl (11 mmol/L), should
have fasting blood sugar, any patient with abnormal fasting blood sugar 120mg/dl
or more is diabetic and not need 3 hours GTT.
•
Preparation for glucose tolerance (3 hours):
-
Should be instructed to consume daily diet containing 200gm of CHO for at least
3 days before the test to minimize the false positive results.
•
Diabetic defined: As either increases fasting blood sugar >7.8 mmol/L (144 mg/dl)
or > 11 mmol/L (200 mg/dl) following 75g glucose load (after 1-2 hour).
If two or more of values are abnormal it's Diabetic.
Complications:
•
Obstetric complications for gestational Dm:
1. Polyhydroamnios: caused by fetal dieresis due to material hyperglycemia that
lead to fetal hyperglycemia and it is a feature of poorly controlled diabetes.
2. Pre-clampsia.
3. Preterm labour.
4. Repeated UTI.
•
Neonatal complication:
1. Macrocosmic & traumatic delivery leads to brachial nerve injury & birth
asphyxia.
2. R.D.S.
3. Hypoglycemia.
4. Hypo Mg.
5. Poly cythemia.
6. Hyper bilirubinaemia.
7. Complication of prematurity.
•
In post partum period:
1. ↑risk of infection.
2. U.T.I.
3. Wound infection.
4. Thromboembolic ¢.
5. Post partum hemorrhage.
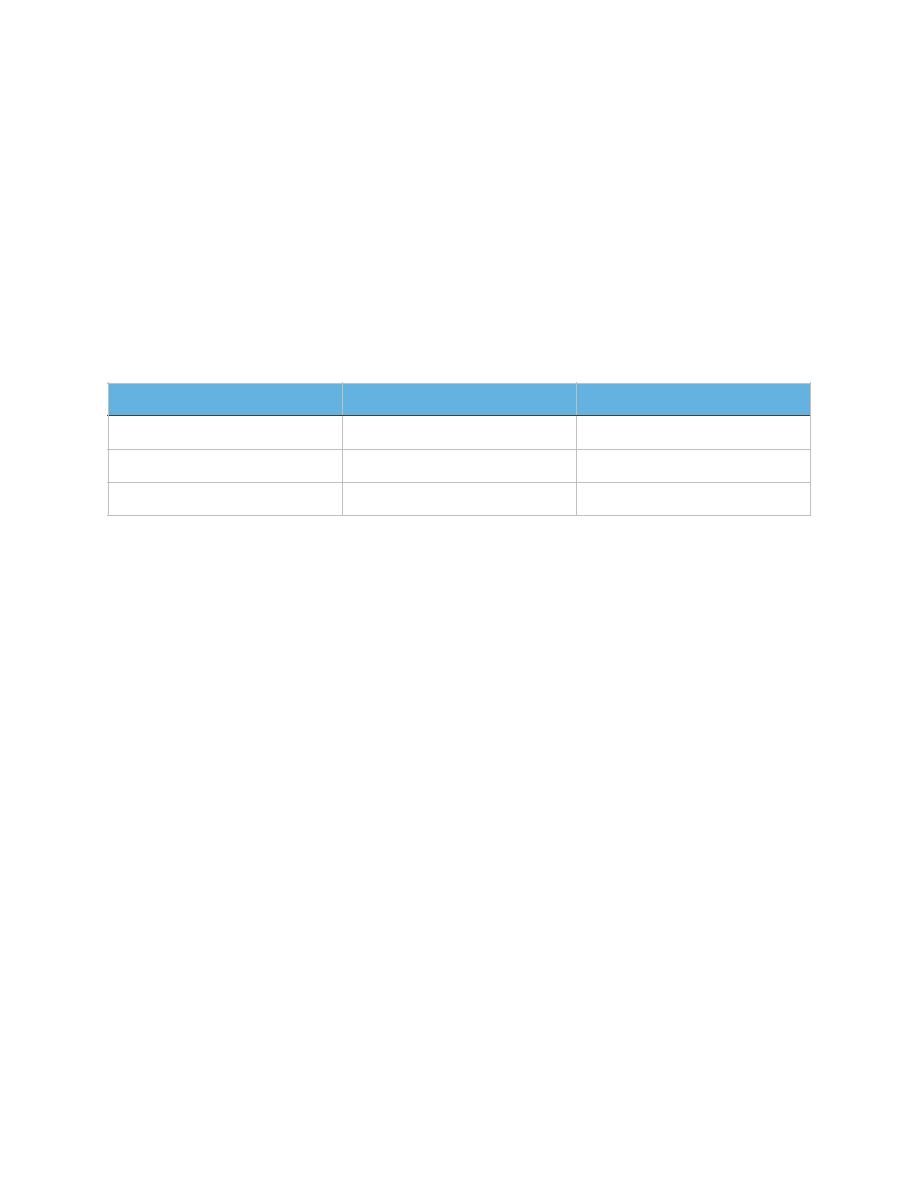
Fasting
96 mg/dl
5.3 mmol/l
1 Hours
172 mg/dl
9.6 mmol/l
2 Hours
156 mg/dl
8.49 mmol/l
3 Hours
131 mg/dl
7.31 mmol/l

•
Complication for already diabetic mother before pregnancy:
1. ↑ risk of vascular complication like Nephropathy & Retinopathy Or may
become worse.
2. More deterioration of hypertension or become more sever and may affect
renal function ended with renal failure.
3. ↑ risk of coronary artery disease.
4. Associated more with congenital abnormalities of fetus like CVS abnormality,
neural tube defect, skeletal, Genitourinary GIT.
5. So that:
-
Gestation DM ===> Macrosomia.
-
In already DM before pregnancy ===> Congenital abnormality.
Antenatal management:
•
Diabetic pregnant woman should be managed in joint clinic with an obstetrician and
physician. Women ώ pre-existing diabetes should be referred directly to this clinic
at booking. The principal of R is to maintain the blood sugar level with mean profile
of less than 6 mmol/L.
•
If the patient on oral hypoglycemia agents must stop it because may cause
neonatal hypoglycemia and risk of IU.GR.
•
In those patient should be controlled in pre-conception period in diabetic clinics.
Most women can continue with their pregnancy insulin regimen.
•
This may involve 3 premeal injections of short acting insulin and single long acting
insulin injection at bed time, also good control of many complication specially
retinopathy & nephropathy. By good assessment of renal function and ↑ B.P
because if end stage renal failure or uncontrollable hypertension pregnancy is CI.
In gestational DM Treatment should be started as:
1. Dietary therapy: ώ appropriate caloric intake high fiber & complex carbohydrates:
a) (50-60) % CHO.
b) 20% Protein.
c) 25% Fat.
2. Insulin therapy: if initial blood glucose > 8 mmol/L or remain above 6 mmol/L in
spite of good diet control its stant single long acting injection at bed time. ώ
frequent measurement of blood sugar (about 4-6 times per day).
3. (Pre-prandial measurement) if blood glucose results during the day remain about
6 mmol/L its necessary to add 1-3 pre-prandial injection of short acting insulin
until keep blood sugar between (4-6) mmol/L.
4. Treatment of any complication like UTI, manila infection, regular check of B.P
and anemia treating on any other type of infection or C.
5. Obstetric MX. early trimester ULS by measurement of CR length to confirm
gestational age, exclude congenital abnormalities especially at 16weeks
deepened on biparietal diameter specially neural tube defects assess ant of CVS
system at (19-20 weeks) by ULS to excludde cardiac defects.
6. Serial measurements of fetal heed &abdominal circumferences to identify growth
of fetal and early detection of macrosomia.

7. Assessment of fetal wedge begs in third trimester by ULS & CTG done weekly or
twice weekly from 36 weeks gestation. Doppler ULS is required if there's element
of IUGR (which occur in Dm associated ώ sever PET).
8. Deal of complication like PET, preterm labour poly hydrations. Tocolytic like
salbutanal are diabetogenic effects and Elena blood sugar. So its C.I prefers
other types like adalate &Mg sulphate.
9. Timing of delivery our aim to achiever vaginal delivery between (38-40 weeks) ώ
optimal diabetic control to reduce the ¢ of premastering and improve the chances
of spontaneous labour.
10. If patient necessity early delivery before 34 weeks due to badly controlled Dm or
other complication start 12mg dose of (Dexamethasone / 12 hours) Interval into
2 doses to improve lung maturity. Delivery after 40weeks ↑risk of macrosomia &
traumatic delivery due to shoulder Dystocia.
MX. of labour: Spontaneous vaginal delivery is a primary goal in the modern MX of
pregnant diabetic women.
Indications of elective C/S:
1. Malpresentations.
2. Fetal weight > 4.5 Kg.
3. Previous scar.
Out time of manage:
1. Adequate analysis because pain ↑ catecholamine release hyperglycemia.
2. Continuous monitoring of HR and uterm contractions.
3. Keep blood sugar during labour between4-6 mmol/L this achieved by
intravenous insulin.
4. Emergency CLS may be needed it true's elements of fetal distress.
5. Start a:b following both emergency & electir CLS to ↓risk of wound infection.
Post natal care: after delivery insulin dose should be halved because rapid ↑in insulin
sensitively occurs after placental separation, encourage breast feeding.
Types of contraception:
1. POP : preferable ώ no effects on CHO metabolism.
2. Progesterone injection → insulin resistance that need ↑insulin dose.
3. Mirena IU.CD prefer.
4. For women complicate her family sterilization.
