
Dr.Muayad j. Al-Haris
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Leg
compartments
anatomy
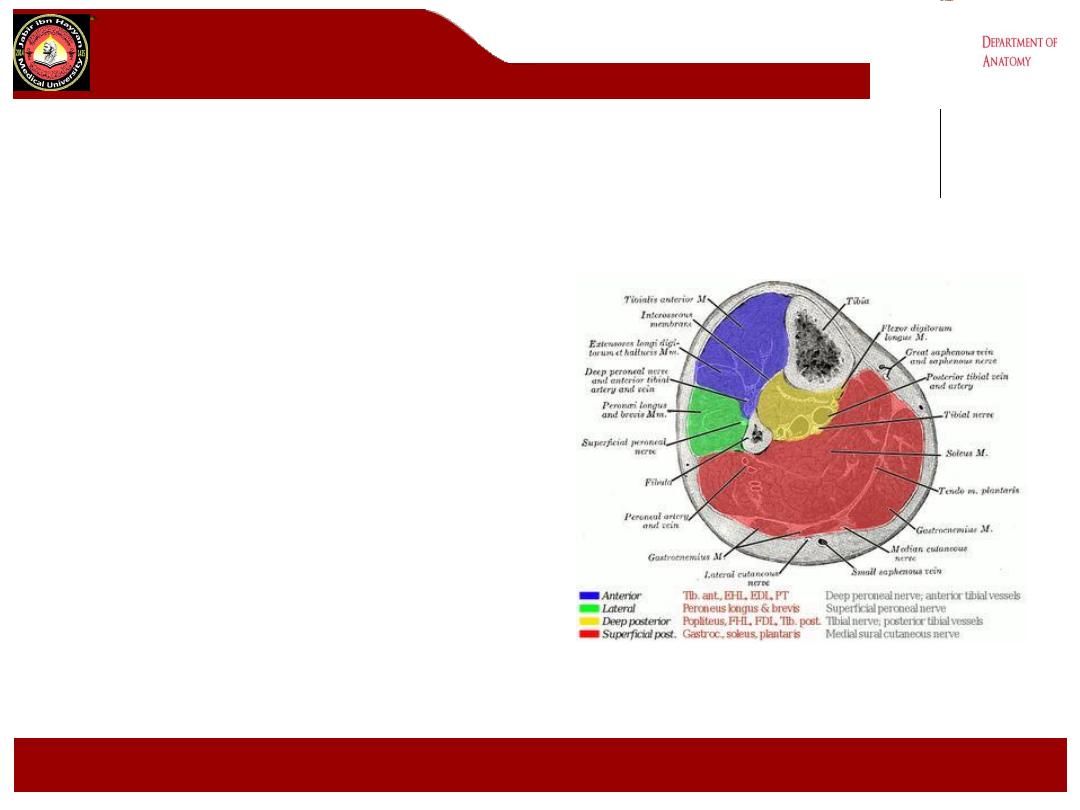
The leg is divided into four osseofascial
compartments by
interosseous membrane of the leg
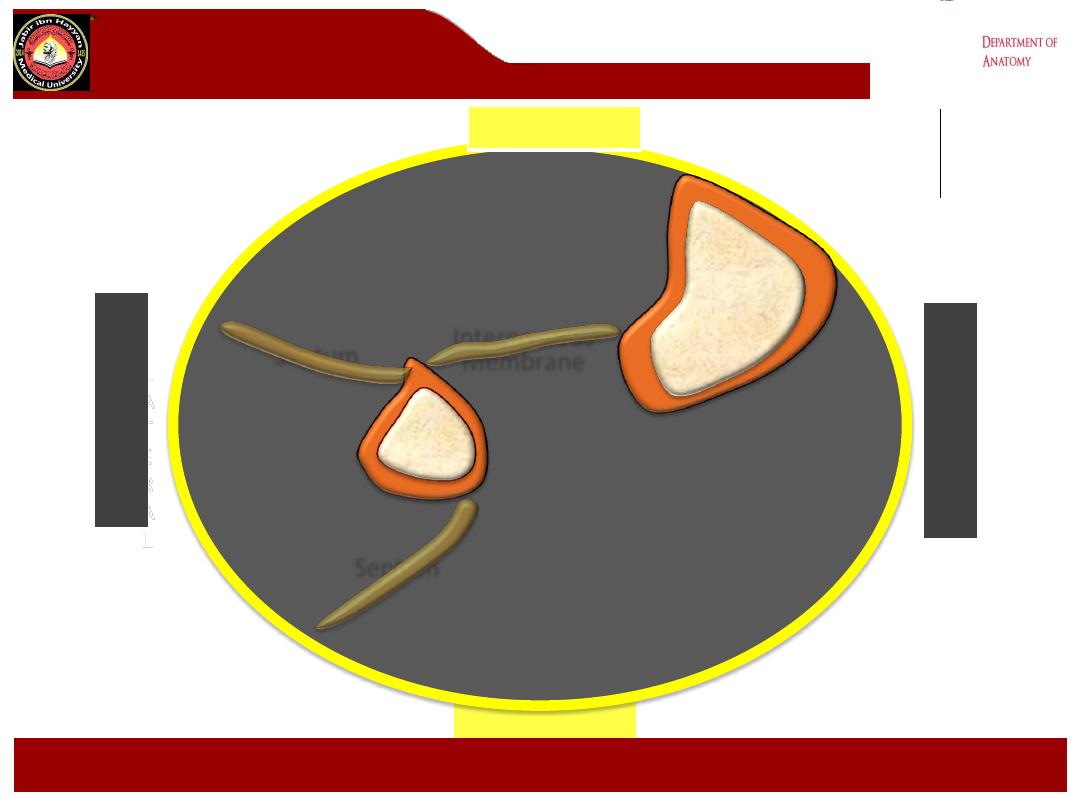
transverse intermuscular septum
anterior intermuscular (crural)
septum
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

The deep fascia (crural fascia)
- The fascia lata of the thigh continuous onto
the leg and called the crural fascia.
- It is connected to the bones by
intermuscular septa, and forms thickened
bands at the ankle called retinacula which act
as a pulley around the tendons of ms.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

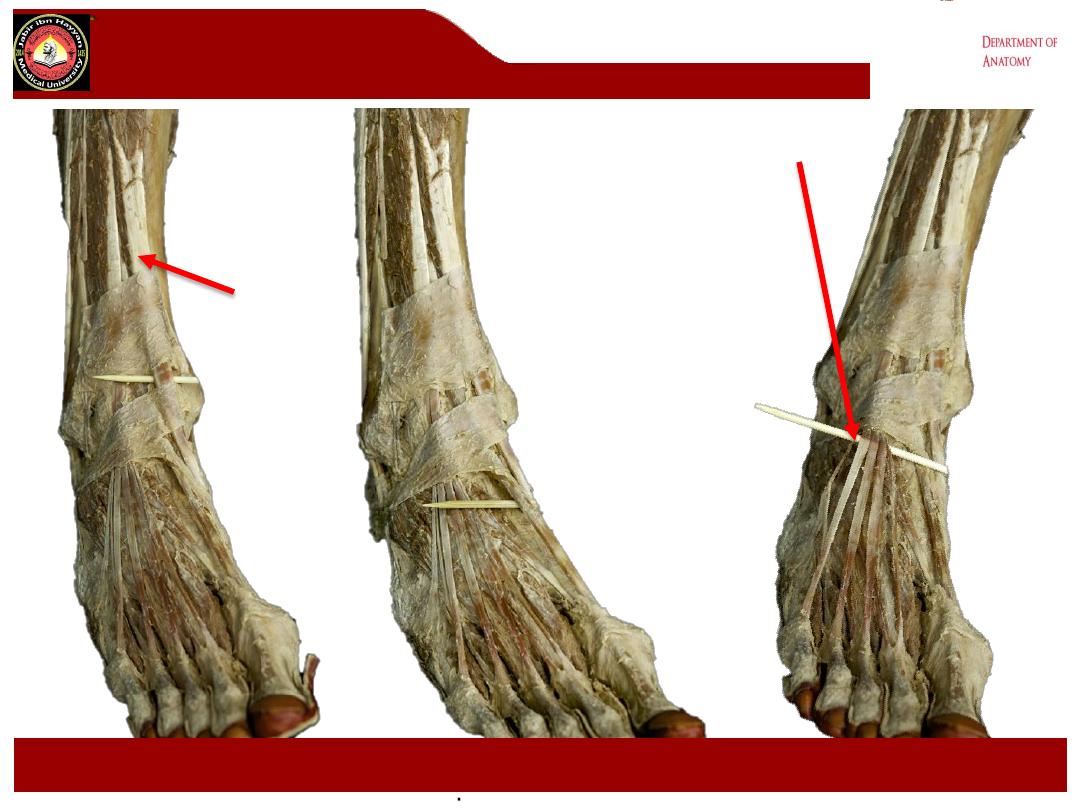
The Retinacula
:
1- Superior extensor retinacula it is broad extends between the fibula
and the medial surface of the tibia.
2- Inferior extensor retinacula is Y shaped.
3- Superior peroneal retinaculum extends from the lateral malleolus
downwards and backwards attached to the lateral surface of the
calcaneum
4- Inferior peroneal retinaculum attached to the lateral surface of the
calcaneum above and below the peroneal muscles.
5- Flexor retinacula extends from the medial malleolus downwards and
backwards to be attached to the medial tubercle of calcaneum
- The dorsum of the foot contains the structures which extend from the
anterior compartment of the leg.
-
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
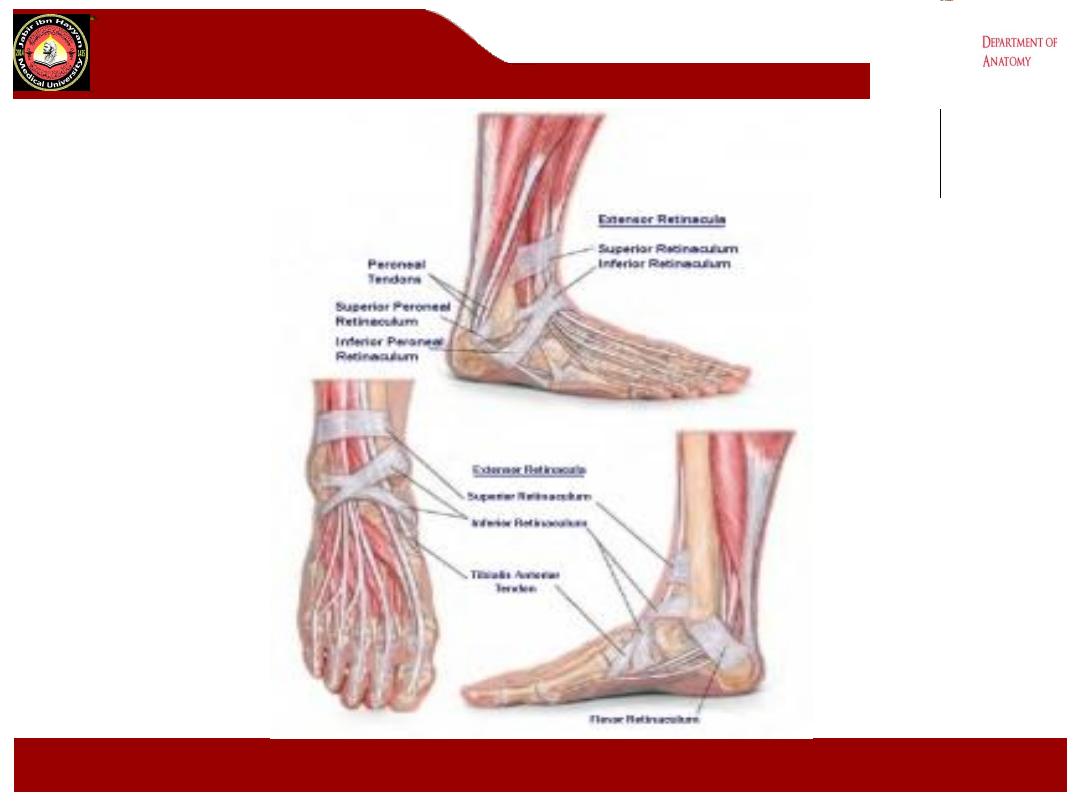
The Retinacula:
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

Intermuscular septa:
-
These are extensions from the deep fascia of the leg to the tibia and
fibula so that it separate the leg into 3 compartments. These septa are:
-
1- The interosseous membrane between the tibia and fibula separate the
anterior and posterior compartments.
2- Anterior intermuscular septa attached to the anterior border of the fibula
separate the anterior and lateral compartments.
3- The posterior septa attached to the posterior border of the fibula
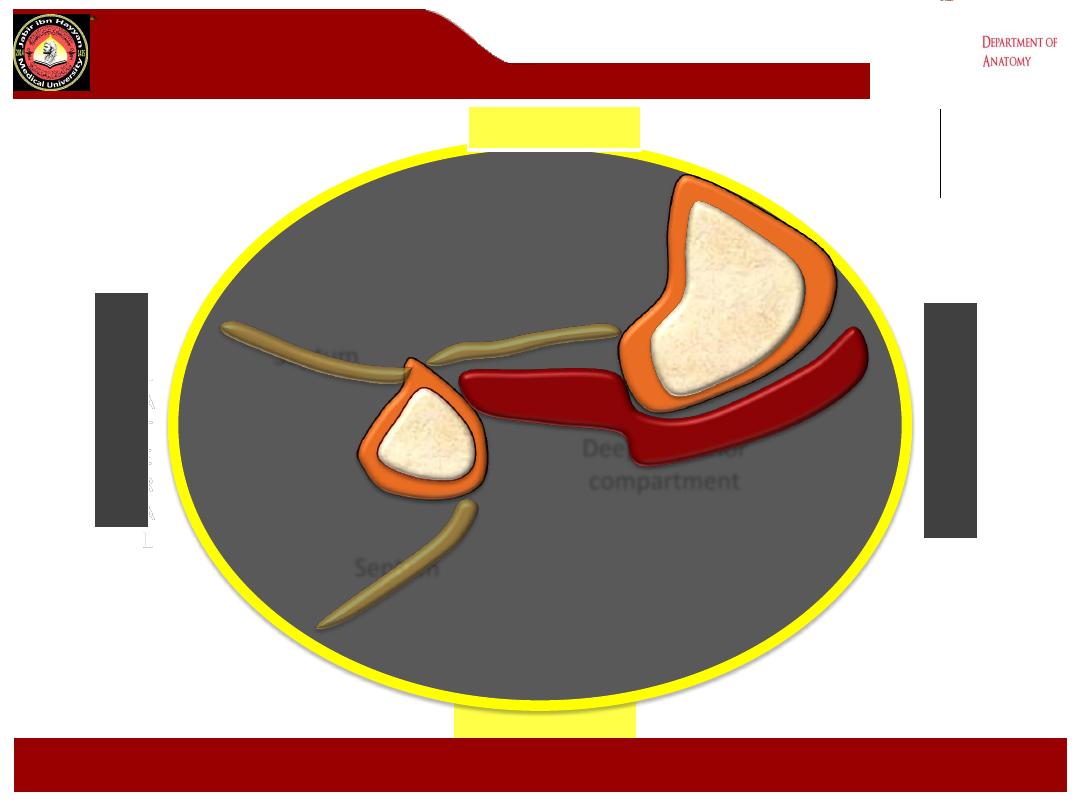
separate the posterior and lateral compartments. From the posterior septa
a broad transverse intermuscular septa separating the superficial and
deep groups of calf muscles.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
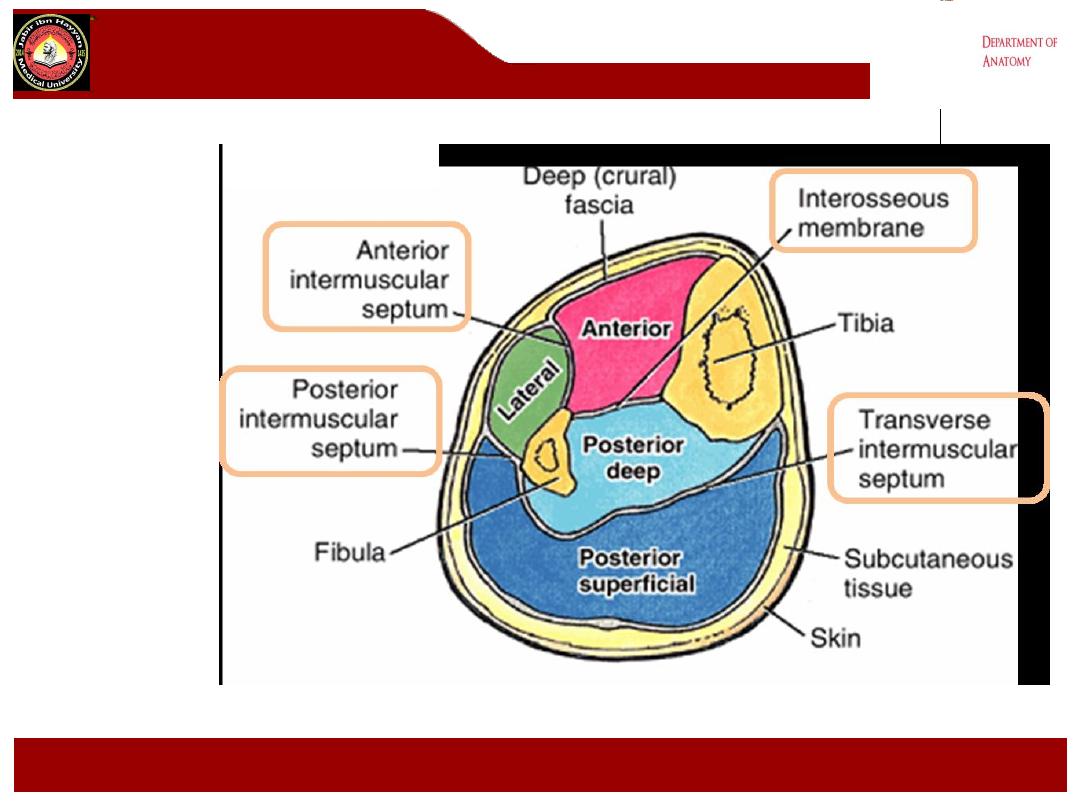
Intermuscular
septa:
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compartment Contents
•Anterior compartment
• muscular
• tibialis anterior
• extensor hallucis longus
• extensor digitorum longus
• peroneus tertius
• neurovascular
• deep peroneal nerve
• anterior tibial vessels
•Lateral compartment
• muscular
• peroneus longus
• peroneus brevis
• neurovascular
• superficial peroneal nerve

Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compartment Contents
•Superficial posterior compartment
• muscular
• gastrocnemius
• plantaris
• soleus
• neurovascular
• sural nerve
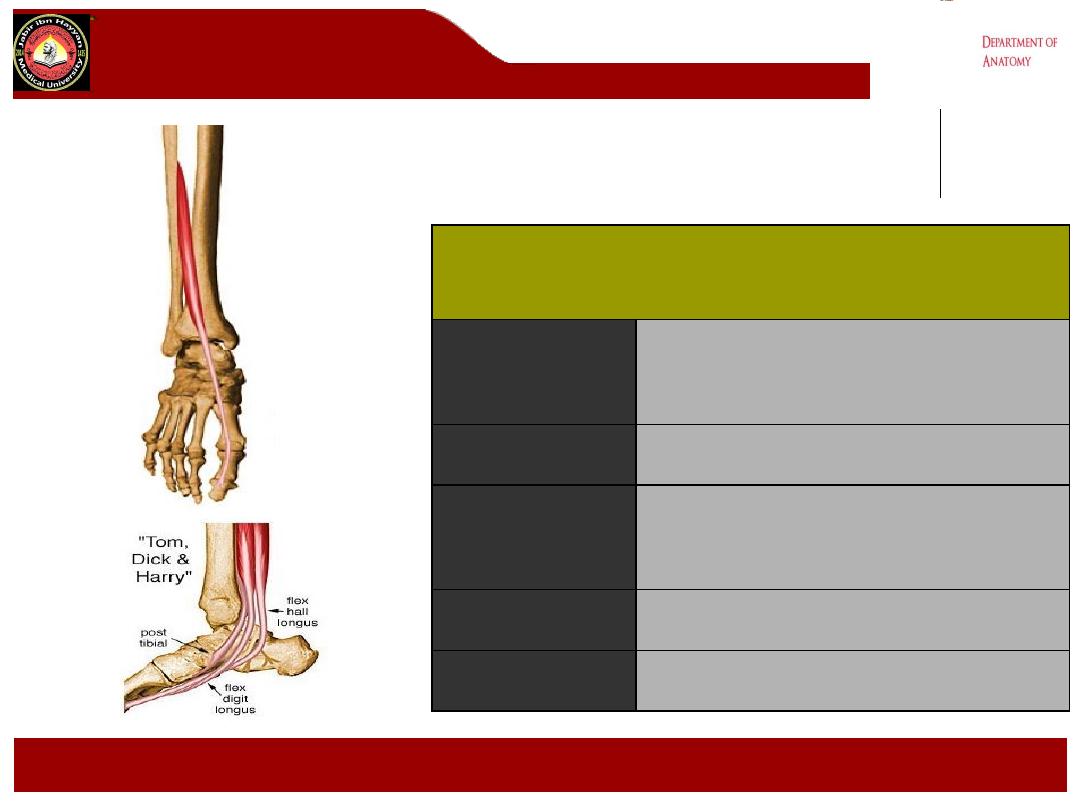
•Deep posterior compartment
• muscular
• tibialis posterior
• flexor hallucis longus
• flexor digitorum longus
• popliteus
• neurovascular
• tibial nerve
• posterior tibial vessels
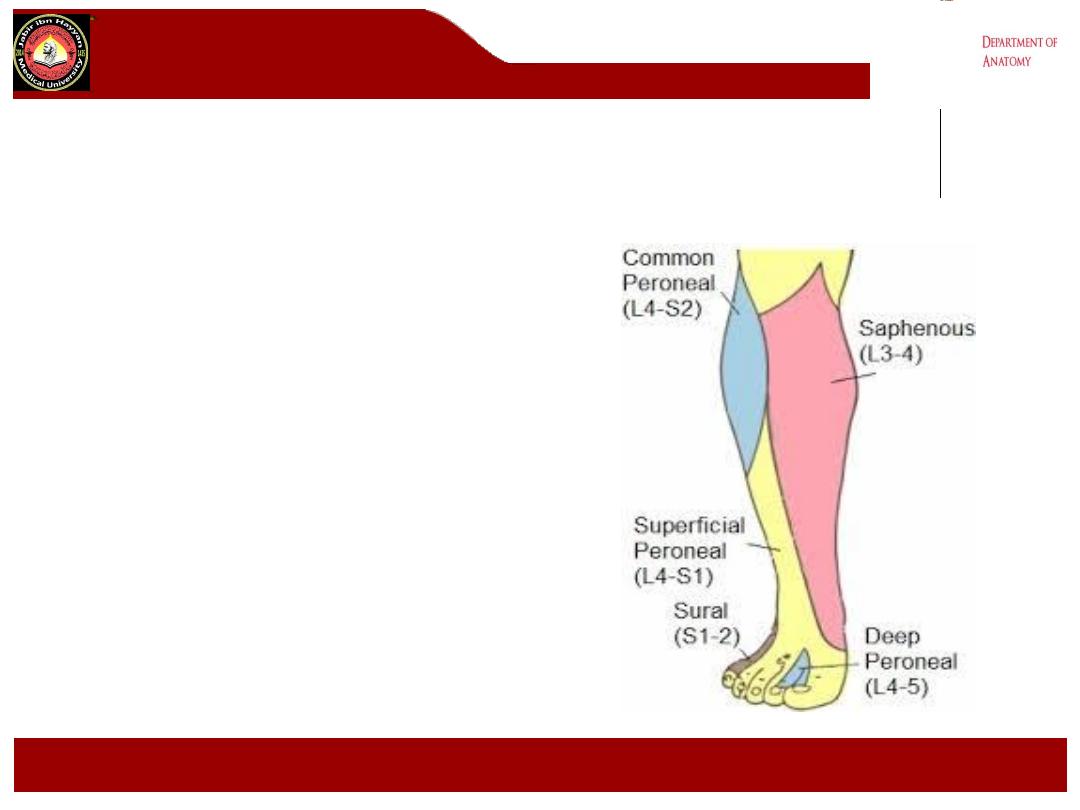
cutaneous innervation of leg
front of the leg
Medial side:
•
.
Saphenous nerve: branch of
femoral nerve
Lateral side:
•
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf :
branch of the common peroneal
nerve ,supplies the skin on the
upper part
•
Superficial peroneal nerve:branch of
the common peroneal nerve
,supplies the skin of the lower part
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

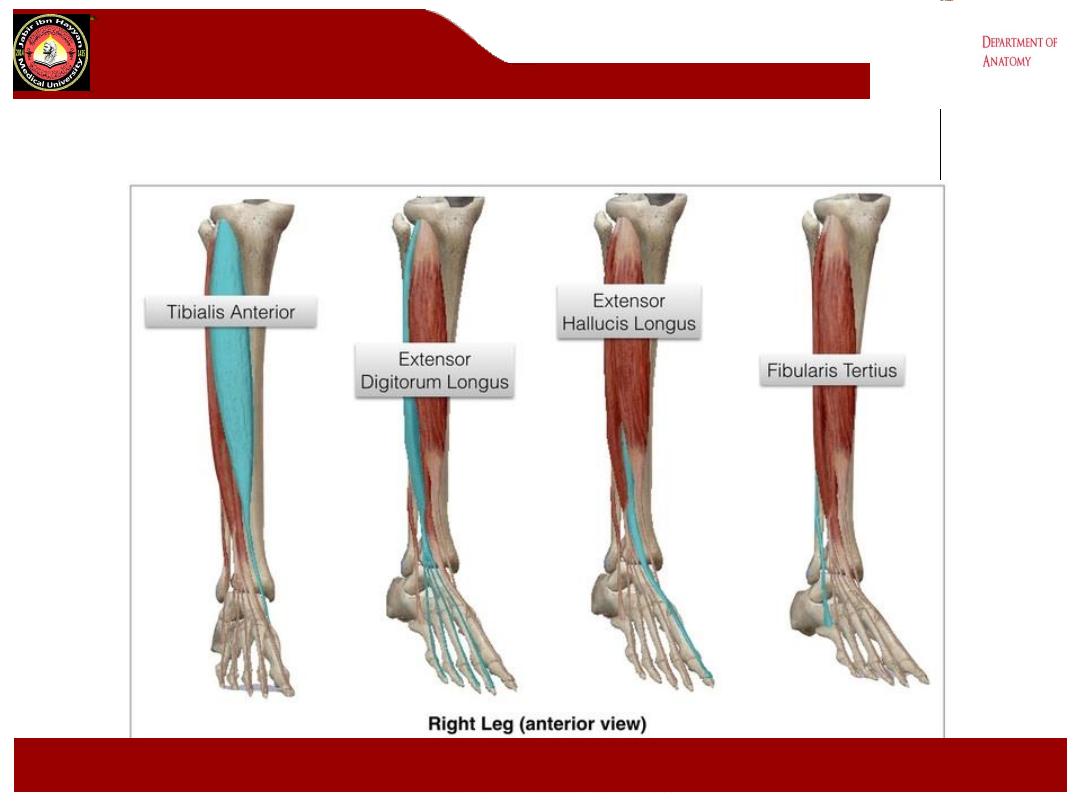
The anterior compartment of the leg contains
extensor muscles that dorsiflex the ankle joint
There are four muscles
•
Tibialis Anterior – also inverts the foot
•
Extensor Digitorum Longus
•
Extensor Hallucis Longus
•
Peroneus Tertius – also known as Fibularis
Tertius
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
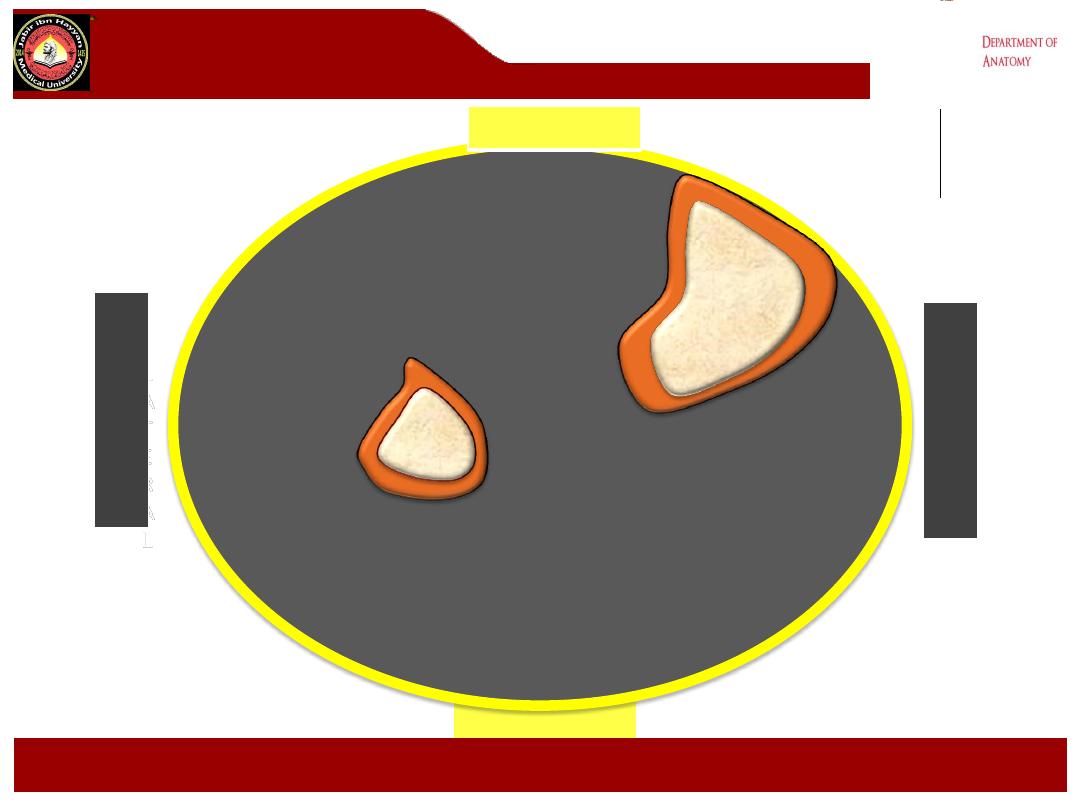
Tibia
Fibula
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Interosseous
Membrane
Septum
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
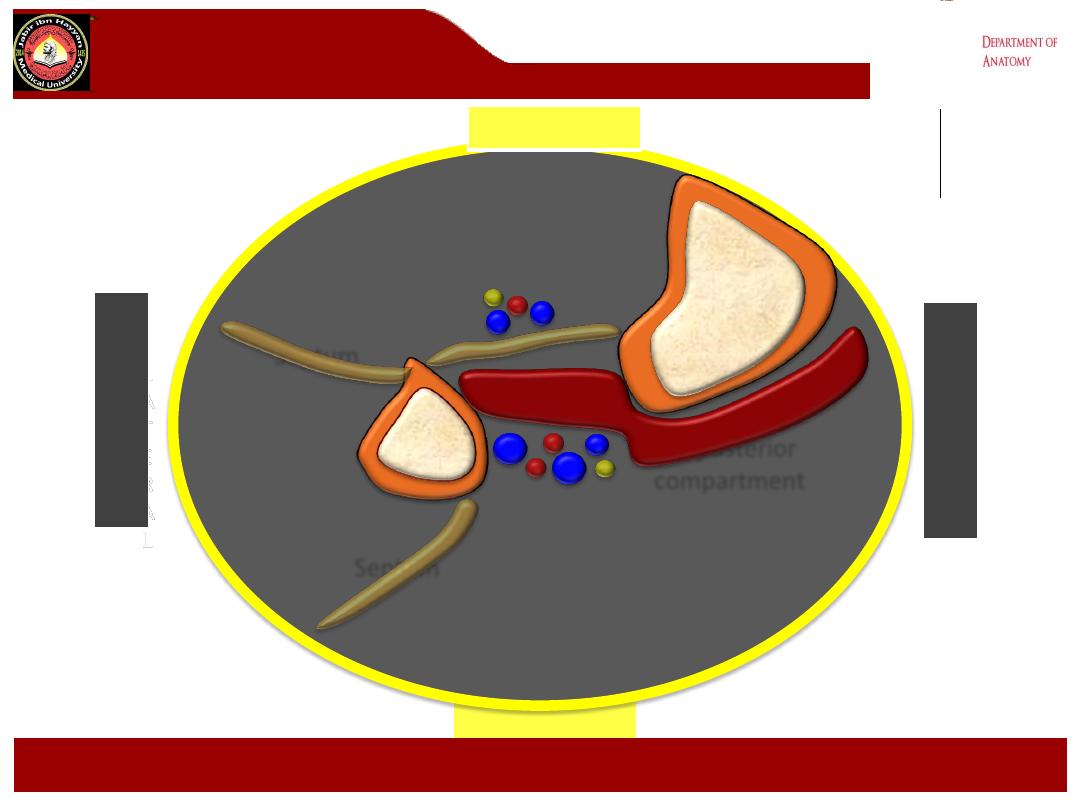
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
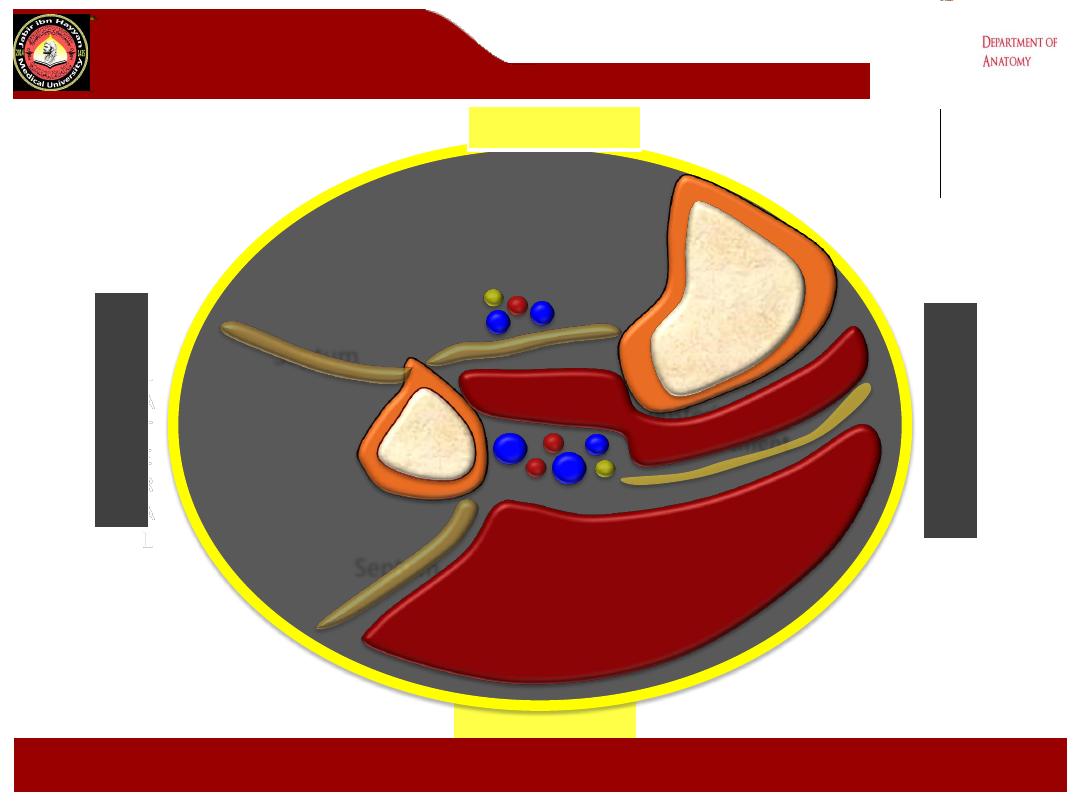
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
Superficial posterior
compartment
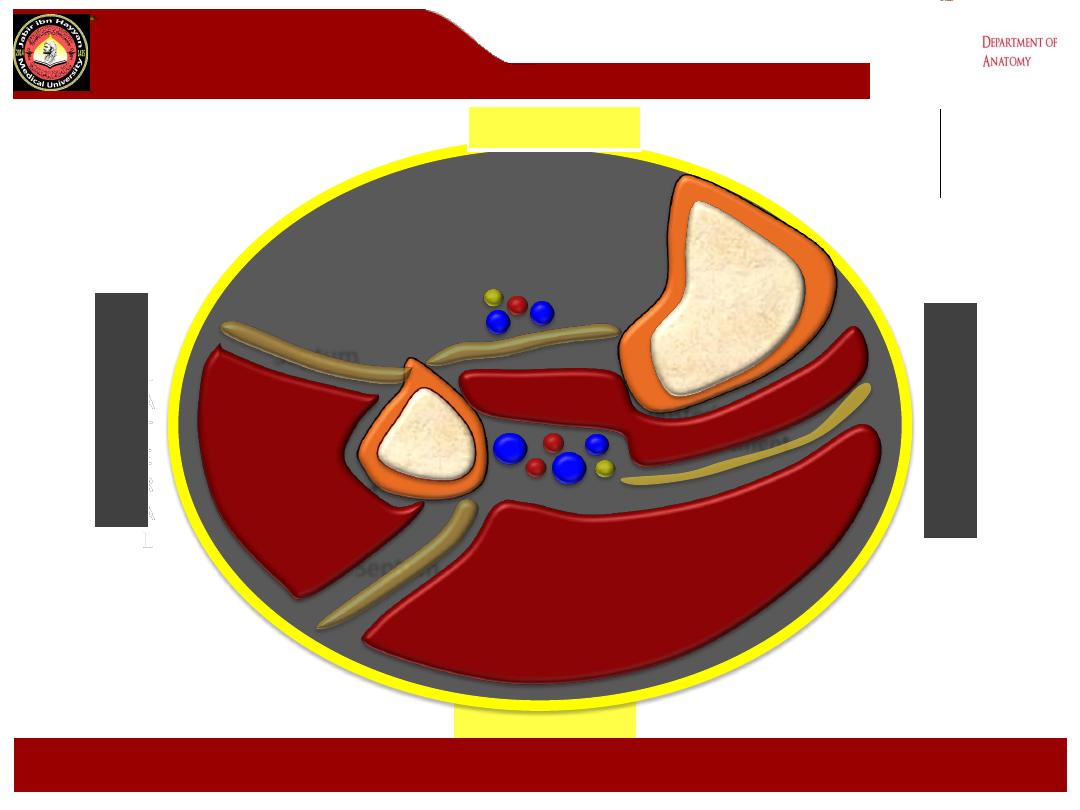
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
Superficial posterior
compartment
Lateral
compartment
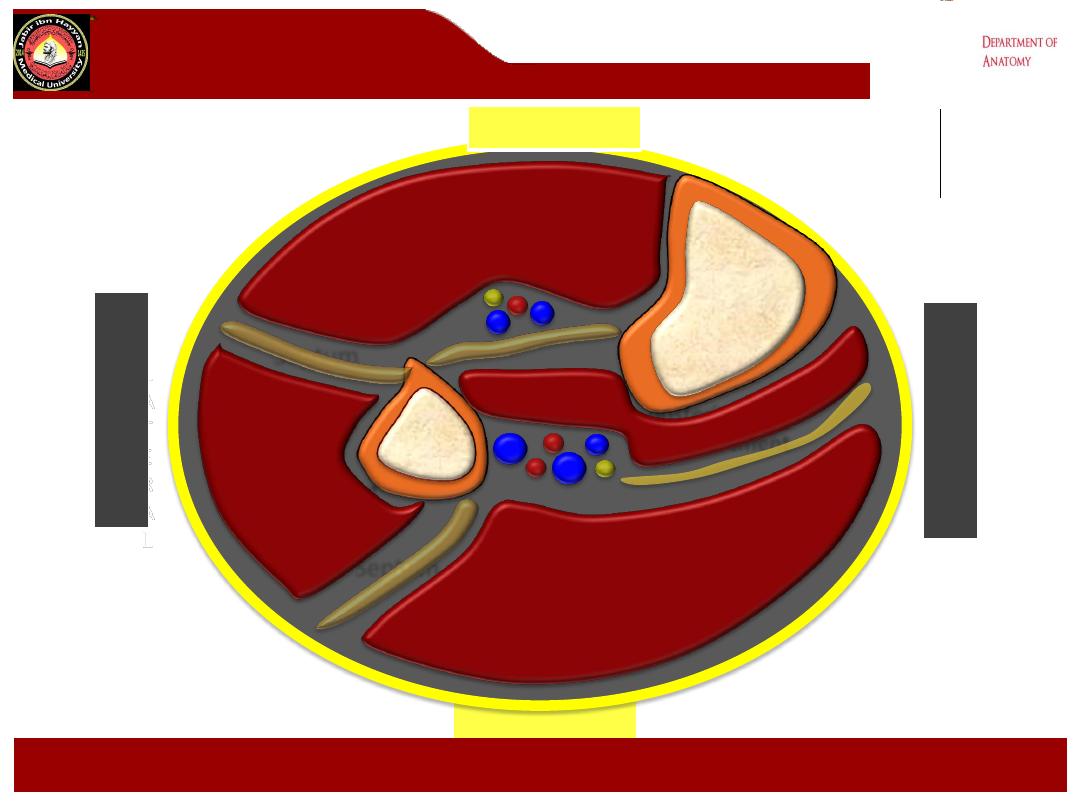
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
Superficial posterior
compartment
Lateral
compartment
Anterior compartment
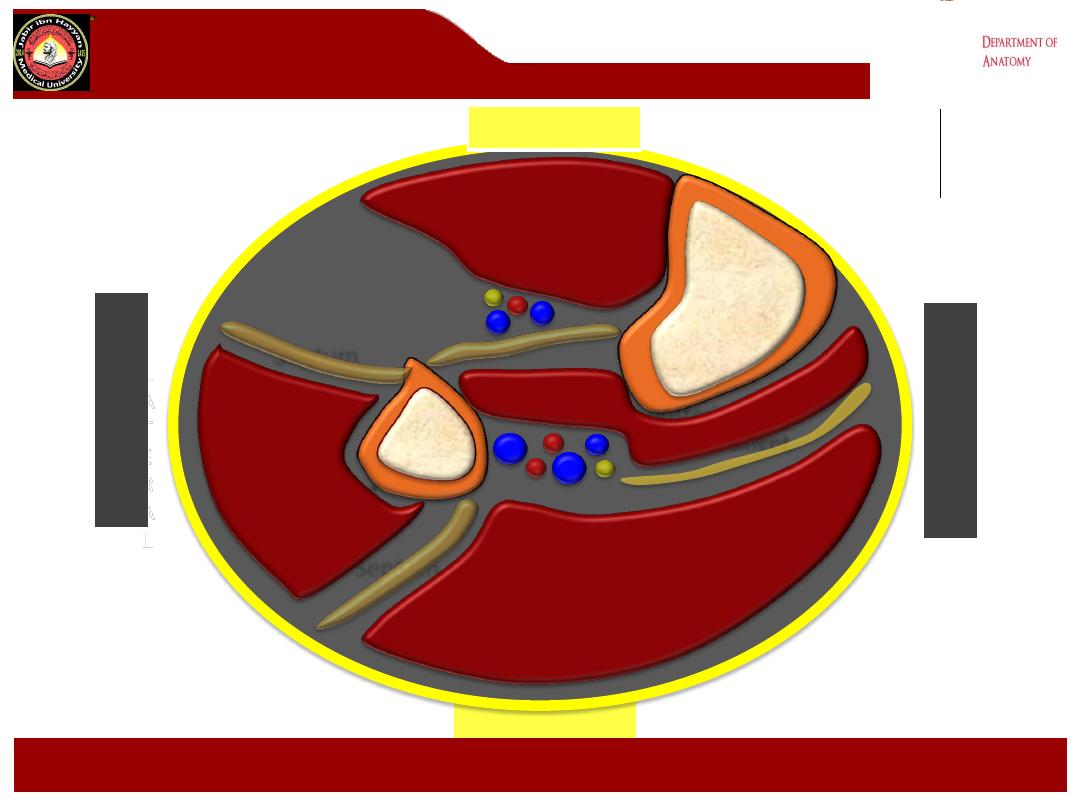
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
Superficial posterior
compartment
Lateral
compartment
Tibialis Anterior
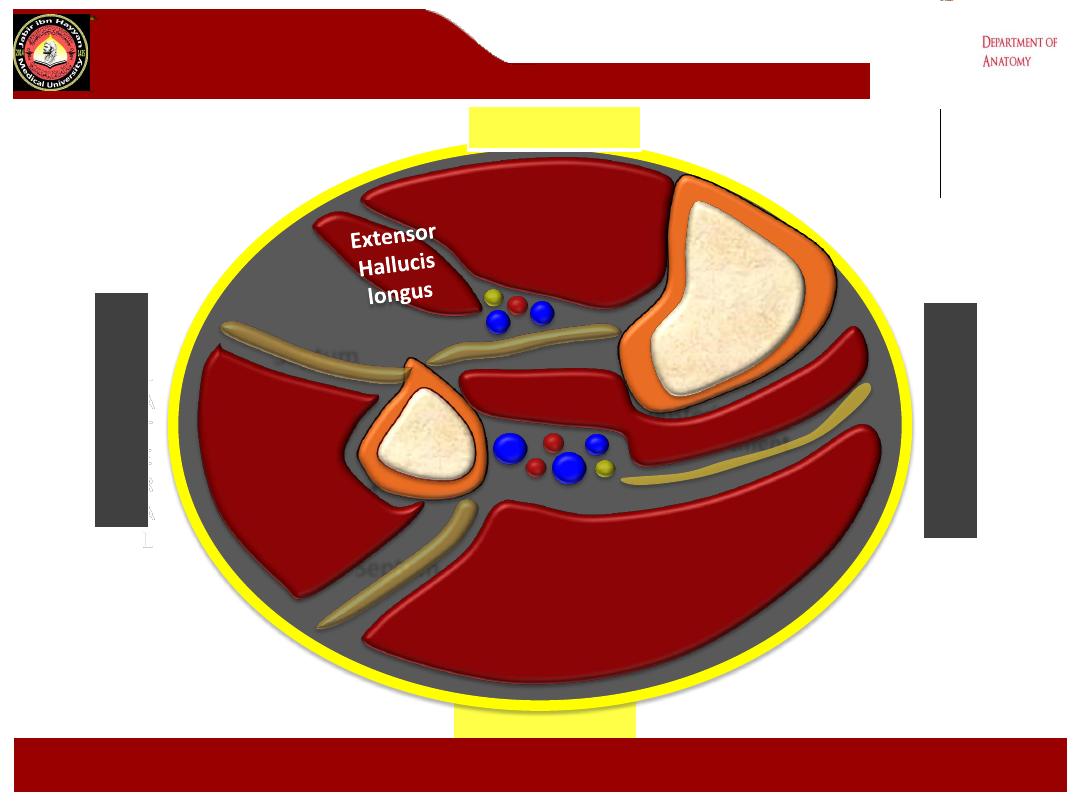
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
Superficial posterior
compartment
Lateral
compartment
Tibialis Anterior
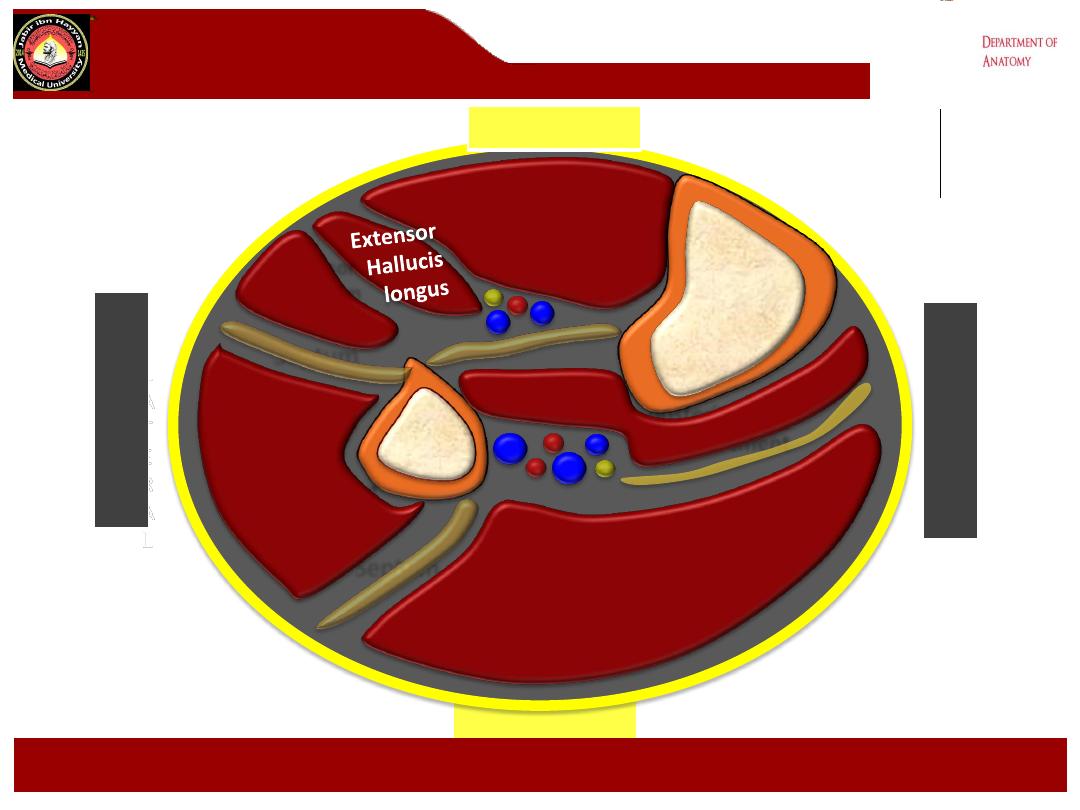
POSTERIOR
Cross section of leg
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
L
A
T
E
R
A
L
M
E
D
I
A
L
ANTERIOR
Tibia
Fibula
Septum
Septum
Deep posterior
compartment
Superficial posterior
compartment
Lateral
compartment
Tibialis Anterior
Extensor
Digitorum
longus
extensor digitorum longus
extensor hallucis
longus
Tibialis
anterior
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Tibialis Anterior
Origin
Lateral condyle of tibia, proximal 2/3rds
lateral surface tibia, interosseous
membrane
Insertion
Medial and plantar surfaces of medial
cuneiform and base of first metatarsal
Action
Dorsiflexor of ankle, invertor of foot
Nerve Supply
Deep peroneal nerve (L4, L5)
Blood Supply
Anterior tibial artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
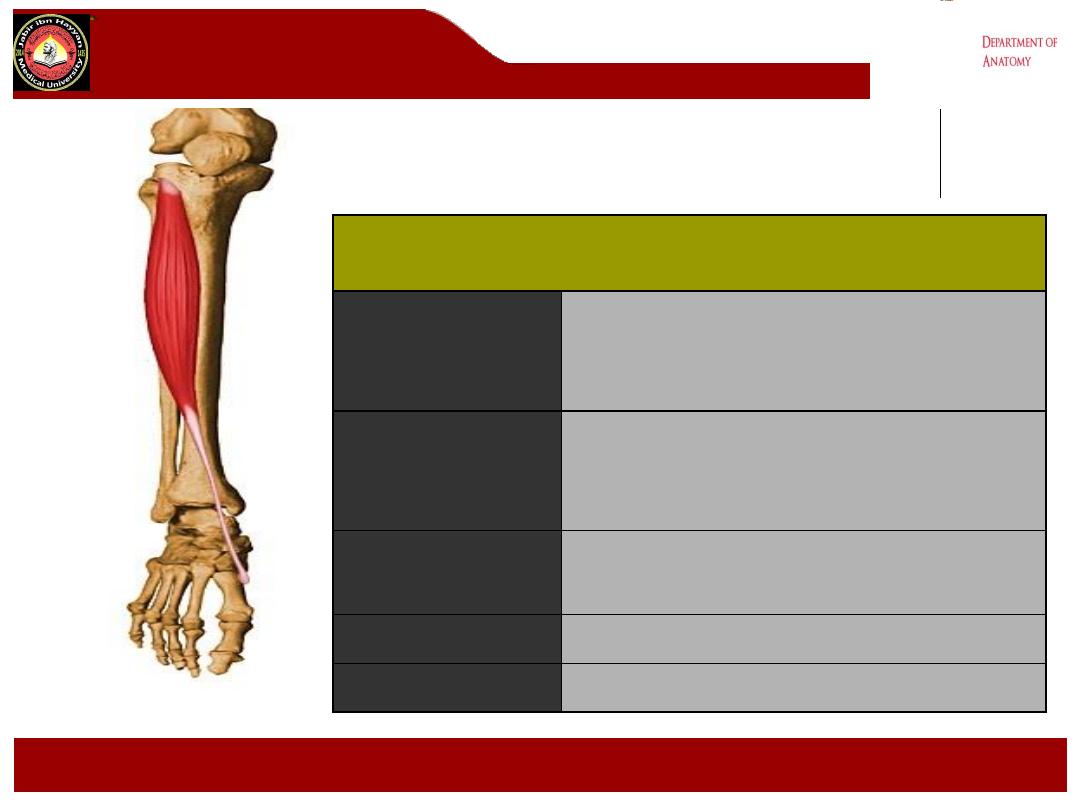
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Origin
Head of fibula, upper 2/3 anterior
fibular shaft, interosseous
membrane
Insertion
Splits into 4 tendons distally; these
insert onto dorsum of middle and
distal phalanges of toes 2-5. Part of
extensor expansion complex
Action
Extends toes 2 - 5 and dorsiflexes
ankle
Nerve Supply
Deep peroneal nerve (L5, S1)
Blood Supply
Anterior tibial artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
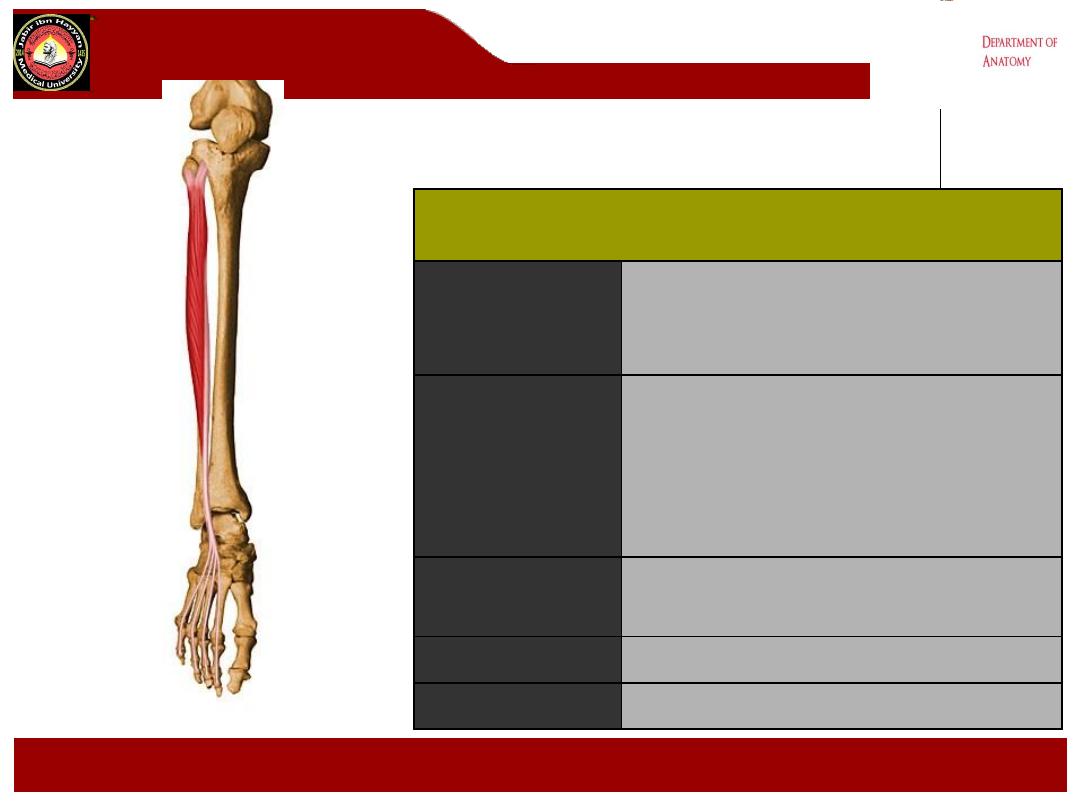
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Origin
Anterior surface of the fibula,
interosseous membrane
Insertion
Base of distal phalanx great toe
Action
Extends great toe and dorsiflexes
ankle
Nerve Supply
Deep peroneal nerve (L5, S1)
Blood Supply
Anterior tibial artery
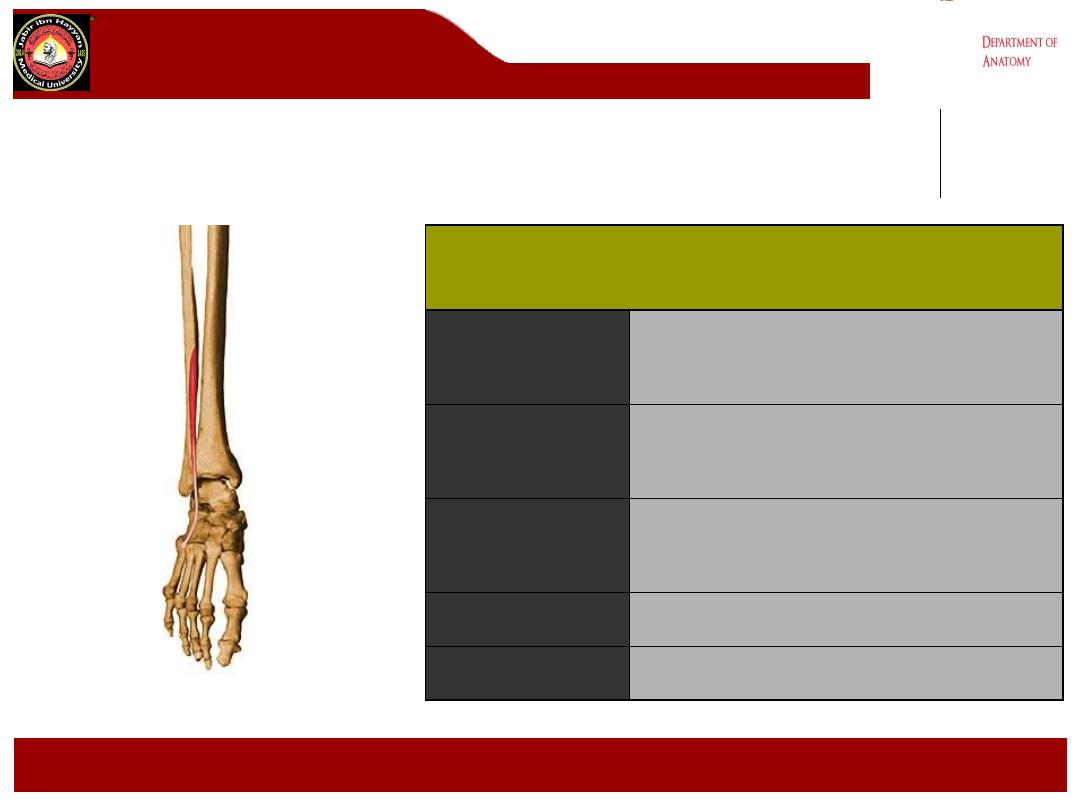
peroneus Tertius
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
peroneus Tertius
Origin
Distal 1/3
rd
anterior surface of fibula
Insertion
Base of dorsal aspect 5
th
metatarsal
Action
Dorsiflexes foot;
everts foot weakly
Nerve Supply
Deep peroneal nerve (L5, S1)
Blood Supply
Anterior tibial artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
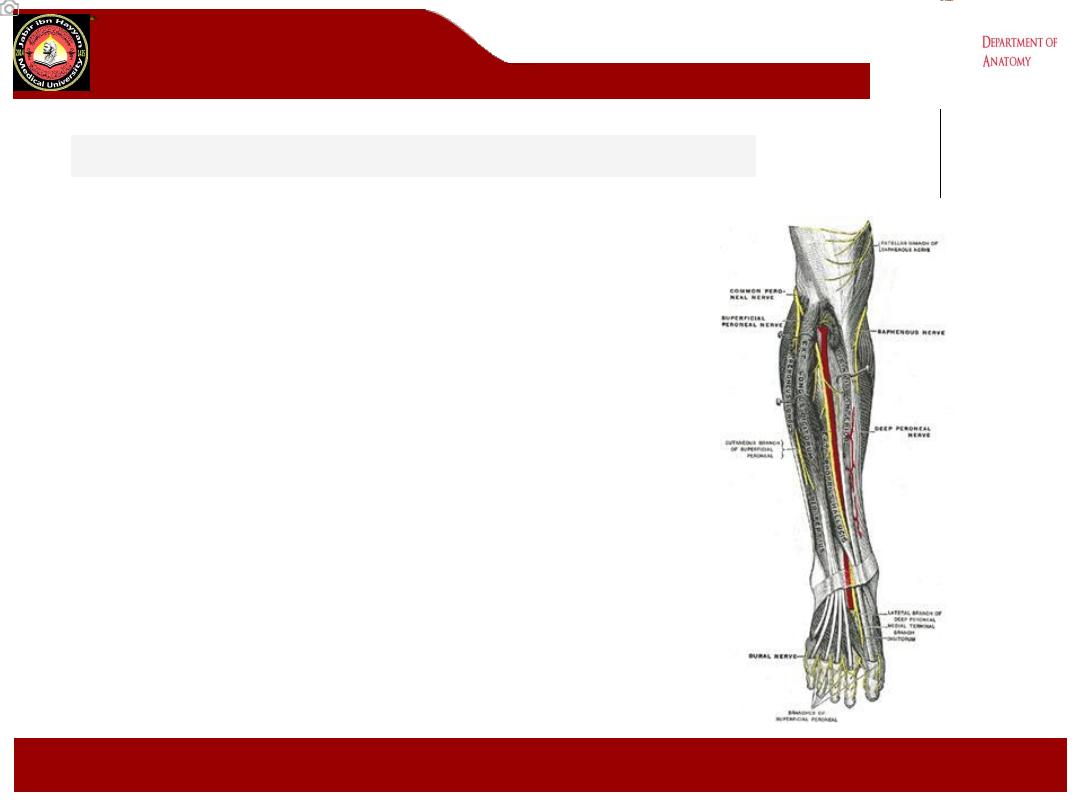
Innervation
•Motor
• leg
• tibialis anterior
• extensor digitorum longus
• peroneus tertius
• extensor hallucis longus
• foot
• lateral terminal branch: extensor digitorum
brevis and extensor hallucis brevis
•Sensory
• articular branch to the ankle joint
• medial terminal branch:
1st dorsal webspace
•Reflex
• none

.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Origin : is derived from the common peroneal nerve, which is made of the
dorsal branches of L4 and L5
Course
•Bifurcation of the common peroneal nerve
• It arises in the substance of peroneus longus muscle on the lateral side
of the neck of fibula
•Interosseous membrane
• The nerve enters the anterior compartment by piercing the anterior
fascial septum. It passes deep to extensor digitorum longus along
anterior surface of interosseous membrane
•Crosses anterior tibial artery
• runs initially lateral to the anterior tibial artery, then anterior , and finally
lateral .the nerve passes behind extensor retinacula.
•Terminal branches
• lateral terminal branch
• medial terminal branch
Clinically
:
Damage to this nerve results in foot drop

.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
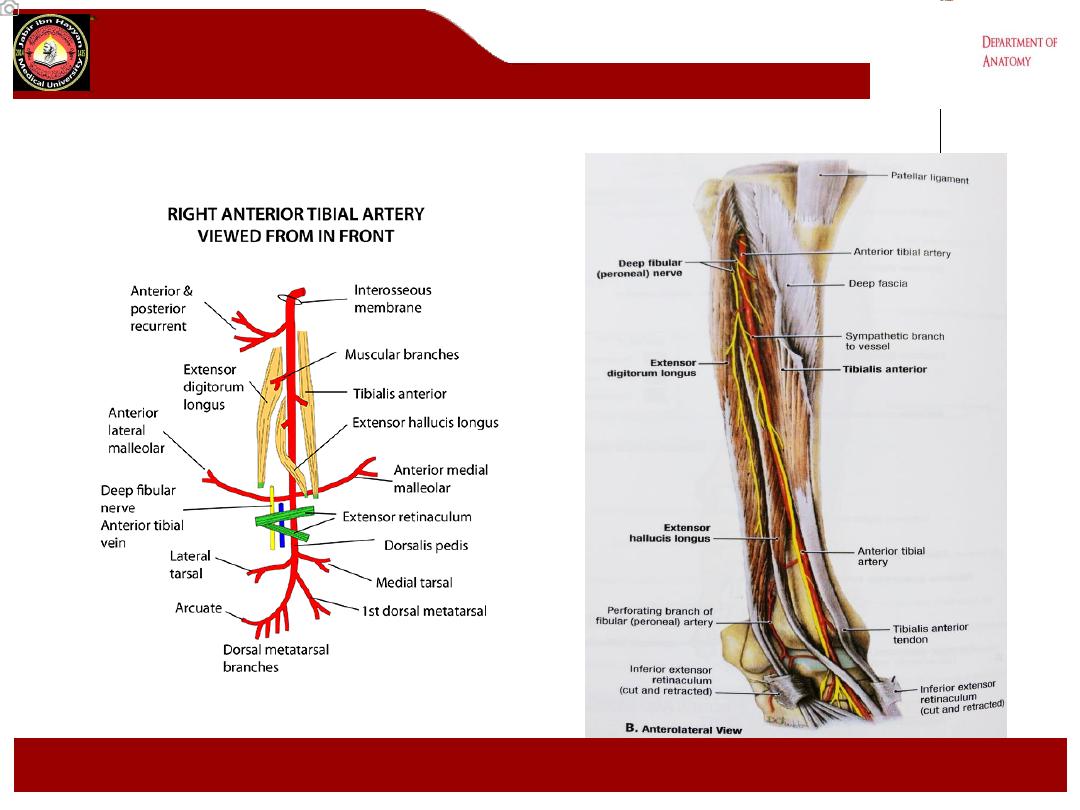
Anterior tibial artery
1- Arises from the popliteal artery at the lower border of the popliteus m.
2- it passes forwards above the upper border of the interosseous membrane
close to the neck of the fibula
3- then descends forward on the membrane with the deep peroneal nerve
passing behind the superior extensor retinaculum.
4- The tendon of extensor hallucis m. lies on its medial side and the deep
peroneal nerve and tendons of extensor digitorum m. on its lateral side.
5- It ends in the front of the ankle joint by becoming the dorsalis pedis artery
midway between the malleoli.
Branches:
1- muscular branches to the muscles of the anterior compartment.
2- Anterior tibial recurrent artery passes upwards to the knee joint.
3- Medial and lateral malleolar arteries to the lateral and medial malleoli,
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

Thank you
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
