Diseases of the parathyroid glands and abnormalities in calcium metabolism
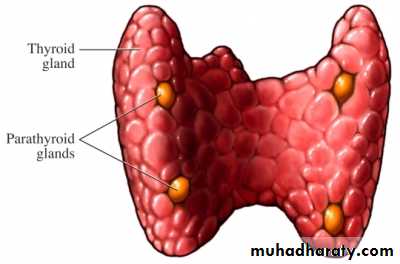
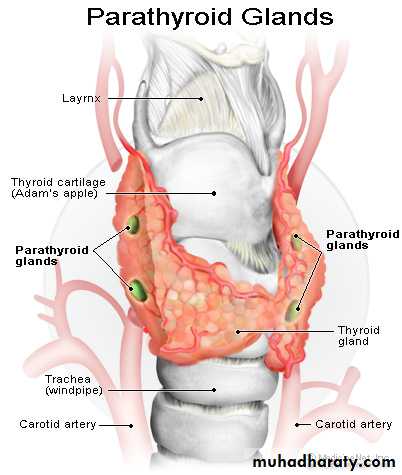
parathyroid glandsparathyroid glands
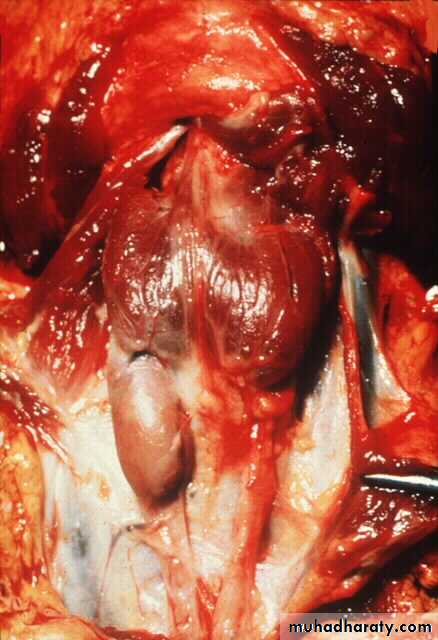
Four parathyroid glands located behind the thyroid lobes secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) .PTH is secreted from the chief cells of the parathyroid glands in response to a fall in plasma ionized calcium concentration.
Function of parathyroid glands
PTH has a direct effect that promotes reabsorption of calcium from renal tubules and resorption of calcium from bone.It indirectly increases calcium absorption from food by enhancing renal conversion of 25(OH) vitamin D to 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D; the active vitamin D metabolite.
In combination, these effects result in a rise in serum calcium.
calcium metabolism
• Around 99% of total body calcium is in bone, which is in a dynamic equilibrium with serum calcium through a process of resorption and deposition.• Calcium in serum exists as:
• 50% ionized (Ca2+)
• 10% non ionized or complexed with organic acids
• 40% protein bound, mainly to albumin.
• Most labs measure total calcium in serum, which should be corrected if the serum albumin is low, by adjusting the value of calcium upward by 0.1 mmol/L (0.4 mg/dl) for each 5 gm/L reduction in albumin below 40 gm/L.
Hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia is one of the most common biochemical abnormalities, commonly detected in asymptomatic patients. If symptoms are present, they may include:
Polyuria, polydypsia and renal colic
Anorexia, nausea, dyspepsia, constipation and peptic ulceration
Lethargy, drowsiness, impaired cognition and depression
Causes of hypercalcaemia
• Hyperparathyroidism (primary or tertiary)• Hypercalcaemia of malignancy
• Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia (FHH)
• Elevated 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D (hypervitaminosis D and sarcoidosis)
• Drugs (thiazide and lithium)
• Other endocrine disorders (thyrotoxicosis and adrenal insufficiency)
• Paget's disease of bone.
Hyperparathyroidism
There are three categories of hyperparathyroidism: primary, secondary and tertiary.Primary hyperparathyroidism is characterized by autonomous secretion of PTH; usually from parathyroid adenoma (90%)
Secondary hyperparathyroidism represents a compensatory increase in PTH secretion from hyperplasia of all parathyroid tissue in response to prolonged hypocalcaemia caused by diseases like chronic renal failure, malabsorption or osteomalacia.
In a very small proportion of cases of secondary hyperparathyroidism, continuous stimulation of the parathyroids results in adenoma formation and autonomous PTH secretion with resultant hypercalcaemia (tertiary hyperparathyroidism).
Primary hyperparathyroidism
It is 2 – 3 times more common in females
90% of patients are more than 50 years of age.
The disease also occurs in two autosomal dominant disorders called multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes (MEN 1 and 2).
MEN1 is characterized by primary hyperparathyroidism, pituitary tumour and pancreatic neuro-endocrine tumour (e.g. insulinoma or gastrinoma).
MEN2 is the association of primary hyperparathyroidism with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid and pheochromocytoma.
Clinical features of primary hyperparathyroidism
About 50% of patients are asymptomatic, and discovered accidentally after finding hypercalcaemia on routine testing.Symptomatic patients:
present insidiously with chronic symptoms of hypercalcaemia, or
manifest late with renal or bone disease (bones, stones and abdominal groans).
Clinical features of primary hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroid bone disease:Now rare due to early diagnosis and treatment
Caused by prolonged sustained effect of PTH on bone, resulting in increased osteoclastic activity and extensive bone remodeling with associated osteoblastic activity and fibrous tissue repair (osteitis fibrosa).
The patient may present with bone pain and tenderness, fracture and deformity.
Chondrocalcinosis is due to deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals within articular cartilage (typically the menisci of the knees), with consequent degenerative arthritis and episodes of pseudogout.
Clinical features of primary hyperparathyroidism
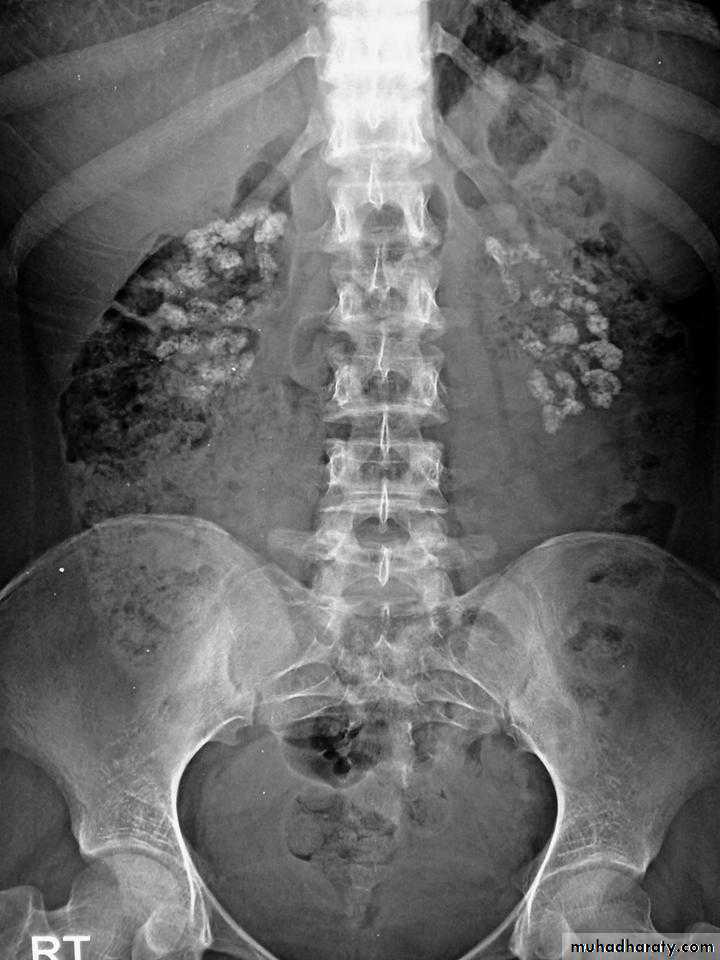
Renal disease:Nephrocalcinosis: calcification of the renal parenchyma.
Renal calculi are other important manifestation of primary hyperparathyroidism. 5% of first stone formers and 15% of recurrent stone formers have primary hyperparathyroidism.
Hypertension is more common in hyperparathyroidism.
Parathyroid tumours are almost never palpable.
Primary hyperparathyroidism(Radiological features)
Characteristic changes on plane X ray are:
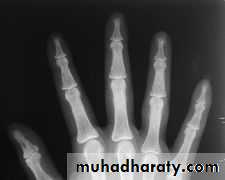
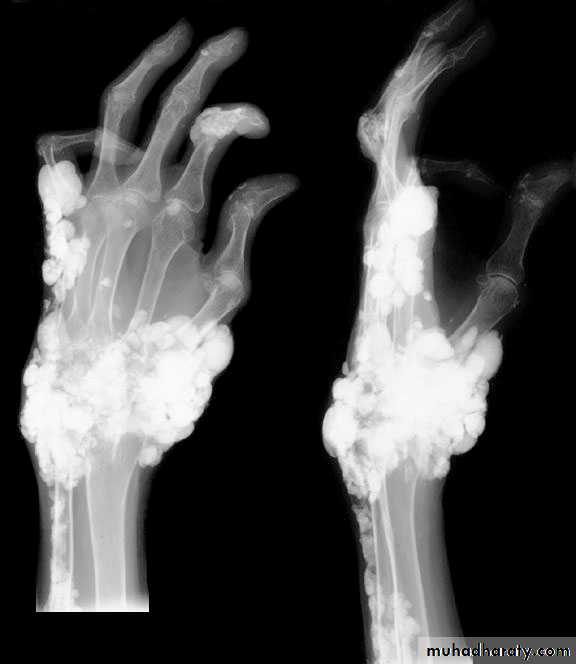
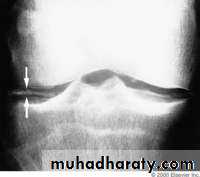
Demineralization, subperiosteal erosion and resorption of terminal phalanges
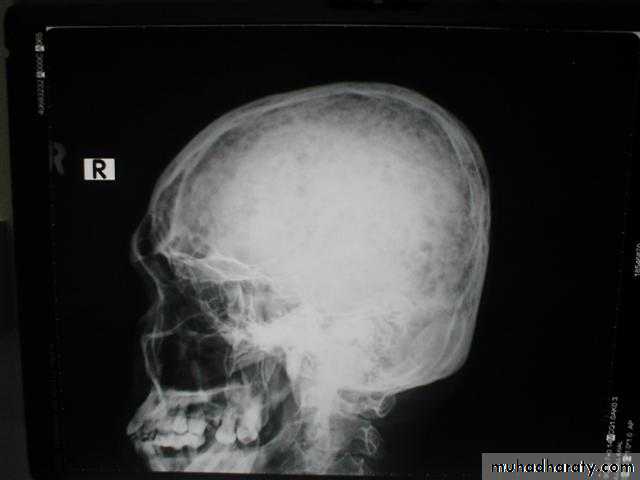
Pepper pot appearance of the lateral X ray of the skull
Scattered opacities within the renal outline (nephrocalcinosis)
renal stones
Soft tissue calcification affecting arterial walls, hands or cornea
Chondrocalcinosis
Very early changes of reduced bone mineral density is only evident on DEXA (deep energy X ray absorptiometry) scanning
Hypercalcaemia of malignant disease
Common causes are lung, breast and renal carcinoma, and multiple myelomaHypercalcaemia can occur as a result of direct bone involvement or ectopic tumour production of a paratharmone – related peptide (PTHrP).
The duration of symptoms of hypercalcaemia is characteristically short and renal stone formation is consequently rare.
The main problem is dehydration due to the diuretic effect of elevated urinary calcium
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia (FHH)
A rare autosomal dominant disorder, characterized by reduced ability of the parathyroid glands to sense ionized calciumAs a result, higher than normal calcium level is required to suppress PTH secretion.
The minor elevation of PTH may result in a misdiagnosis of hyperparathyroidism and unnecessary surgery.
The presence of family history of hypercalcaemia and low urinary calcium excretion should help to make the proper diagnosis.
Investigations of patients with hypercalcaemia
• PTH
• Urinary
• calcium
• Serum
• phosphate
• Serum
• calcium
• N or
•
•
•
• Primary hyperparathyroidism
•
•
•
•
• Secondary hyperparathyroidism
•
•
•
•
• Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
•
•
•
•
• Malignant hypercalcaemia
• N or
•
•
•
• FHH
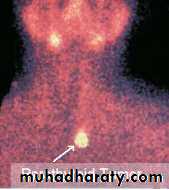
Localization of parathyroid tumours
If primary hyperparathyroidism is confirmed biochemically, pre-operative localization of the adenoma is not necessary, as surgeons are able to locate the adenoma in 90% of cases.
However, there is a trend toward performing 99mTc-sestamibi scanning prior to surgery.
Unsuccessful surgical exploration can be helped by the same scanning or by CT or selective neck vein sampling for PTH.
Management of hypercalcaemia
Severe hypercalcaemia associated with malignancy or other causes is treated as an emergency with normal saline hydration (4 – 6 litres).Bisphosphanates (like pamidronate 90 mg I.V. over 4 hours) cause a fall which is maximum after 2 – 3 days and sustained for weeks. This can be followed by oral bisphosphanate.
In a very ill patient, normal saline hydration can be can be supplemented with frusemide, corticosteroid (prednisolone 40 mg / day), calcitonin, or dialysis.
Management of primary hyperparathyroidism
• Surgical excision of a solitary parathyroid adenoma or debulking of hyperplastic glands is the long term treatment of first choice.• Post-operative hypocalcaemia can occur transiently after surgery, until suppressed parathyroid tissues recover.
• Indication for surgery:
• patients younger than 50 years
• very high serum calcium (more than 3 mmol/L)
• documented complications, such as renal stones, renal impairment, osteopenia or peptic ulceration.
• When surgery is not indicated, patients can receive:
• the bisphosphanate alendronte 10 mg daily as long term therapy to prevent osteoporosis.
• calcimimetics (like cinocalcet) are recently introduced drugs which can reduce PTH secretion by increasing sensitivity of the parathyroids to ionized calcium.
Hypocalcaemia
Before diagnosing hypocalcaemia, the reported serum calcium should be corrected for albumin. Hypoalbuminaemia reduces total serum calcium without affecting the ionized calcium; the biologically active fraction.Conversely, symptoms of hypocalcaemia may occur in patients with alkalosis (commonly due to hyperventilation or repeated vomiting) in the presence of normal serum calcium, because alkalotic serum increases albumin binding and reduces ionized calcium.
Causes of hypocalcaemia
True hypocalcaemia occurs in the following conditions:Vitamin D deficiency
Chronic renal failure
Hypoparathyroidism
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Acute pancreatitis
Hypomagnesaemia
Causes of hypocalcaemia
Vitamin D deficiency can be nutritional or caused by lack of sun exposure or malabsorption, where hypocalcaemia is associated with hypophosphataemia, raised alkaline phosphatase and secondary hyperparathyroidism.Chronic renal failure is an important cause. Hypocalcaemia is accompanied by hyperphosphataemia (because of phosphate retention), high alkaline phosphatase and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Hypomagnesaemia reduces PTH secretion and induces tissue resistance to its effect.
Hypoparathyroidism
In hypoparathyroidism, low serum calcium is associated with high phosphate and low PTH.
Post-thyroidectomy hypoparathyroidism: The most common cause of hypoparathyroidism is damage to the parathyroid glands (or their blood supply) during thyroid surgery (transient in 10% of cases and permanent in 1% of them).
Primary hypoparathyroidism: congenital or inherited.
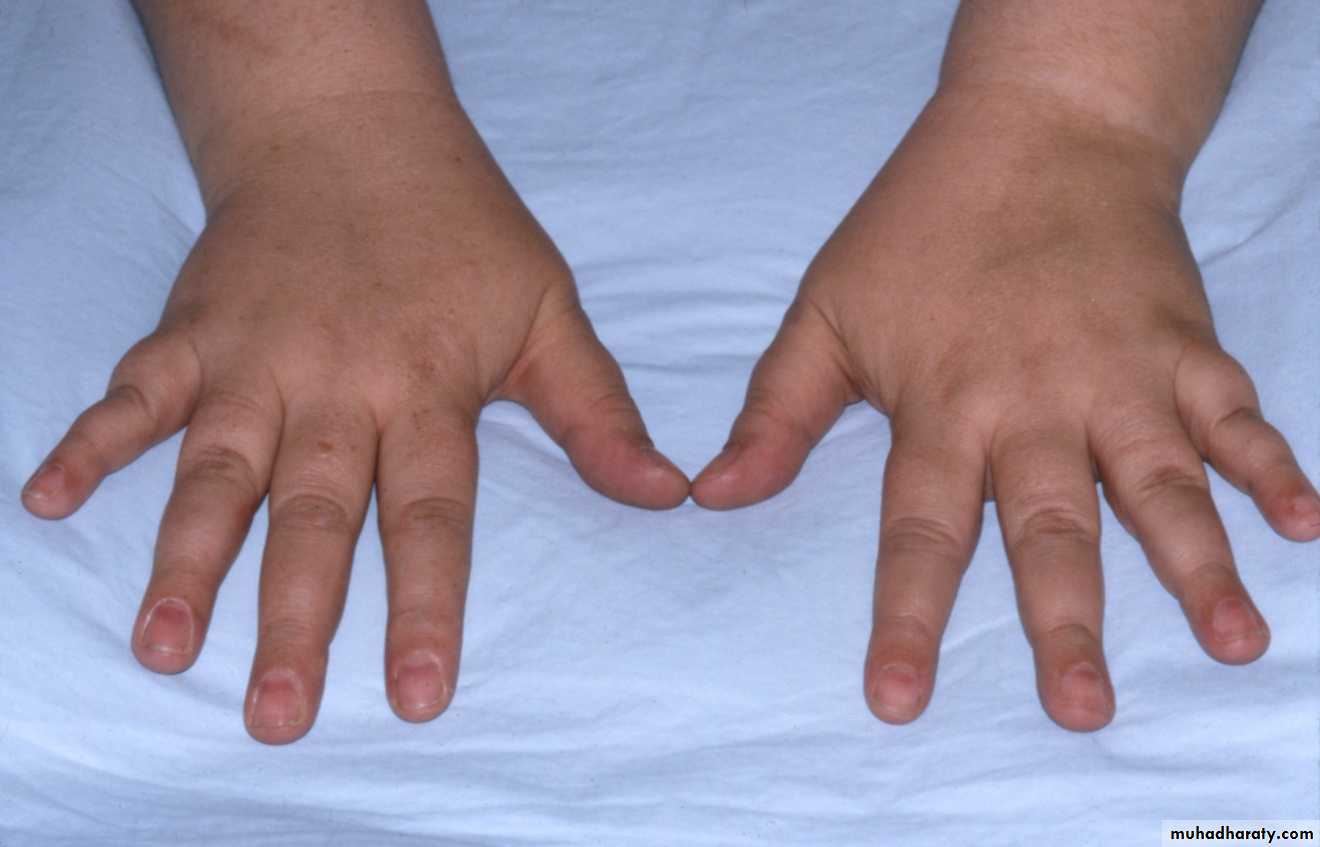
Pseudohypoparathyroidism have tissue resistance to the effect of PTH, consequently PTH is markedly elevated. The disease is hereditary, and characterized by a unique phenotype of obesity, short stature, round face and short 4th metacarpals and metatarsals.
Pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism is used to describe patients with these clinical features in whom serum calcium and PTH are normal.
Clinical features of hypocalcaemia
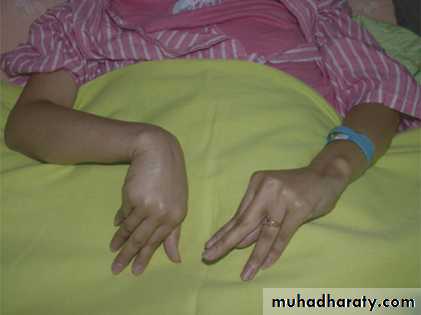
Tetany is the clinical syndrome of increased excitability of peripheral nerves caused by low ionized calcium. In the absence of alkalosis, tetany occurs in adults when serum calcium below 2 mmol/L.Tetany is manifested by:
Tingling in the hands, feet and around the mouth.
Carpal spasm
Pedal spasm
Strider
Convulsions
Clinical features of hypocalcaemia
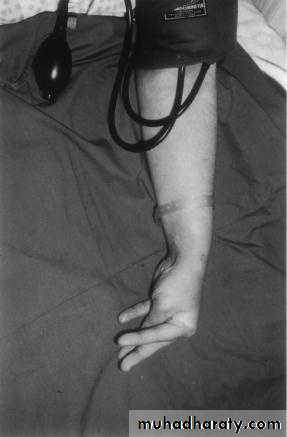
Latent tetany may be present when signs of overt tetany are lackingTrousseau's sign; inflation of a sphygmomanometer cuff on the upper arm to more than the systolic blood pressure is followed by carpal spasm within 3 minutes.
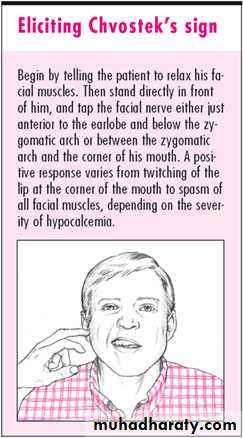
Chvostek's sign is less specific; tapping over facial nerve branches as they emerge from the parotid gland produces tingling of facial muscles.
Latent tetany
Clinical features of hypocalcaemia
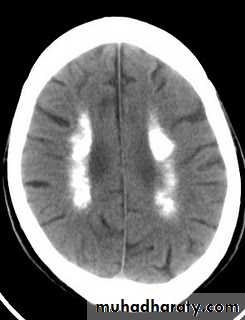
Because of associated hyperphosphataemia, patients with hypoparathyroidism may develop calcification of the basal ganglia, grand mal seizure, psychosis and cataract.Management of hypocalcaemia
If tetany is caused by alkalosis with normal serum calcium, the condition can be rapidly controlled by rebreathing expired air in a paper bag (to increase PaCO2).Hypocalcaemia can be immediately corrected by slow IV injection of 20 ml of 10% solution of calcium gluconate. An additional IM injection of 10 ml may also be given for a more prolonged effect.
IV magnesium may be required to correct associated hypomagnesaemia.
Treatment of Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism are treated with oral calcium salts and vitamin D analogues; either 1 (OH) vitamin D (alfacacidol) or 1,25(OH)2 (calcitriol).
The therapy needs careful monitoring to avoid hypercalcaemia and its consequences.