
INTRODUCTION TO POWER
ELECTRONICS CONVERTERS
AC to DC Converters
Prof. Dr. Basil
2016-2017
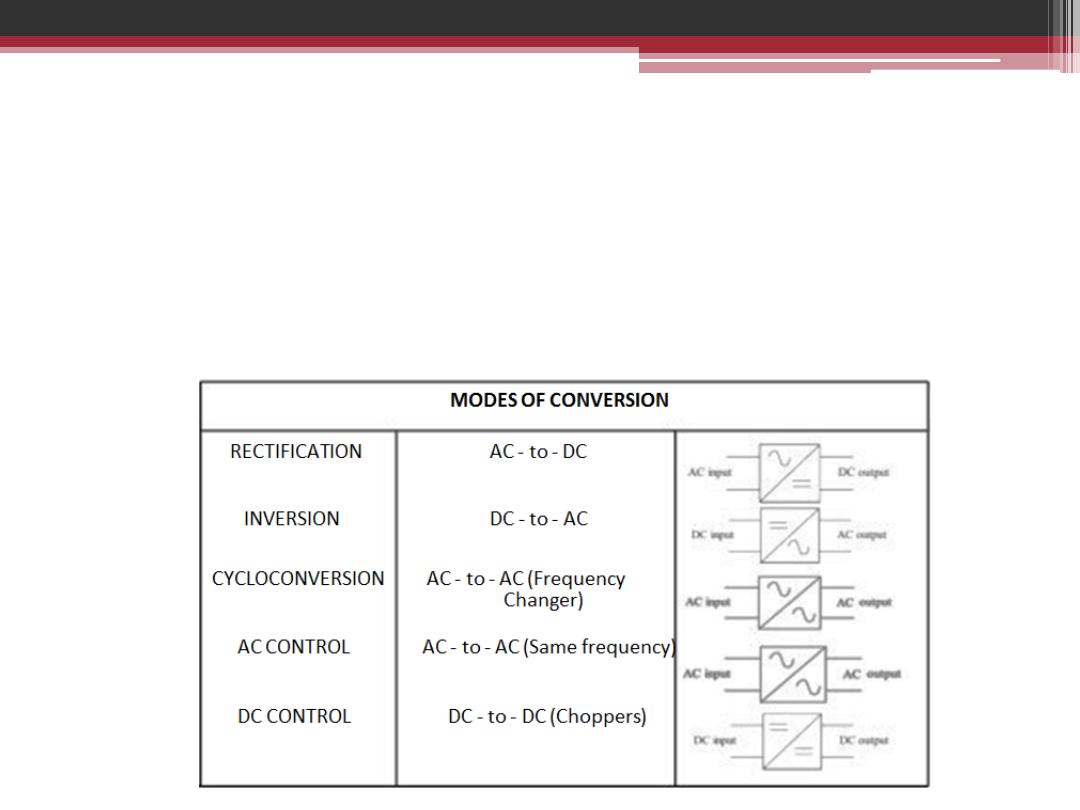
WHAT IS POWER ELECTRONICS?
•
Conversion and control of electrical power by power
semiconductor devices.
•
Definition: To convert i.e. to
process
and
control
the flow of
electric power by supplying voltages and currents in a form that is
optimally suited for
user loads
.
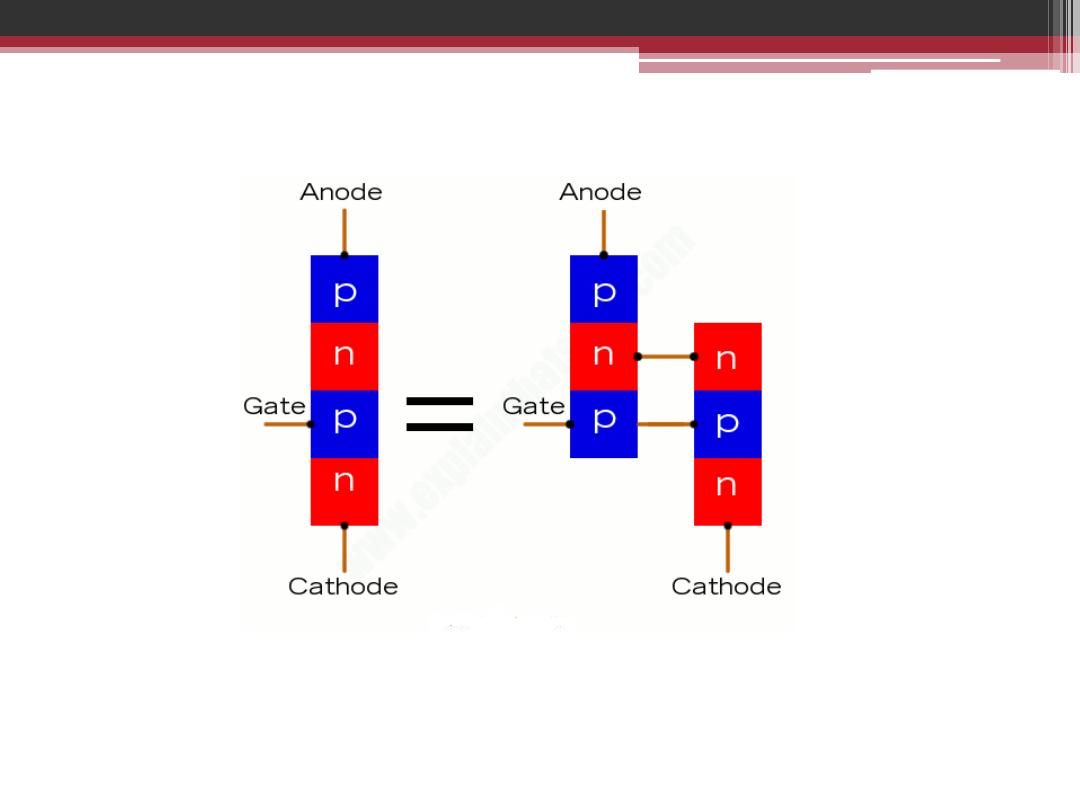
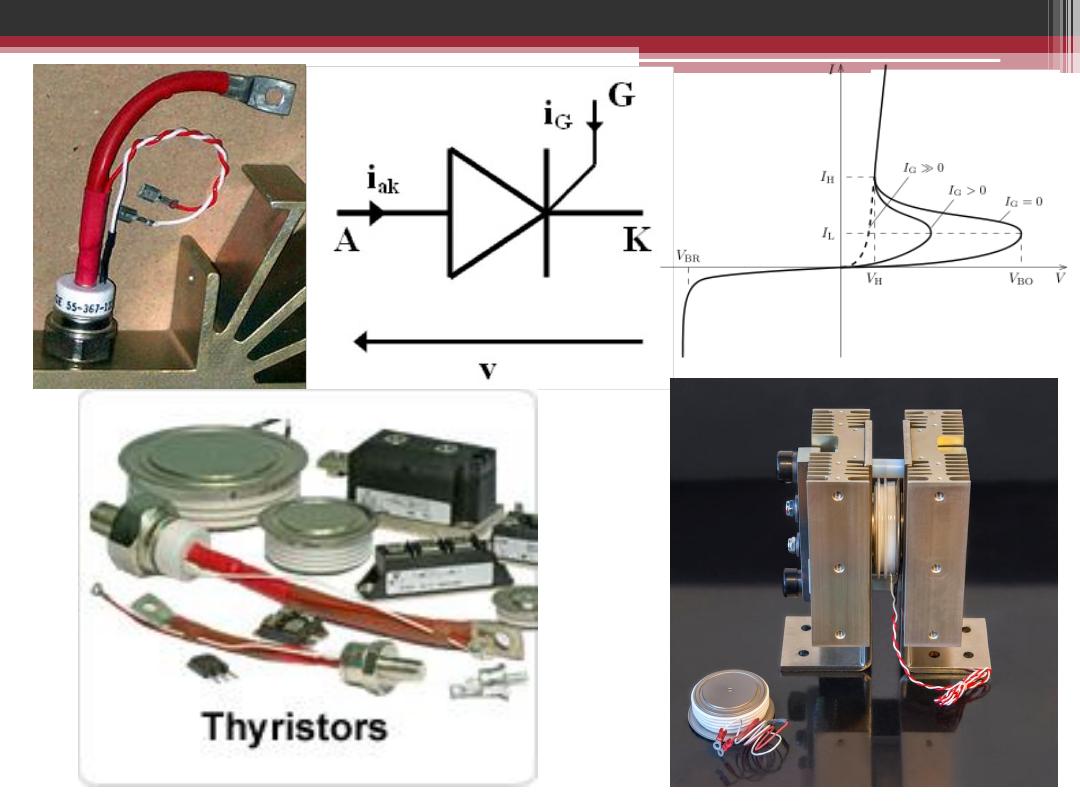
Thyristor is considered as a Power Semiconductor
Device
A thyristor is also like two transistors connected
together, so the output from each one serves as
the input to the other one
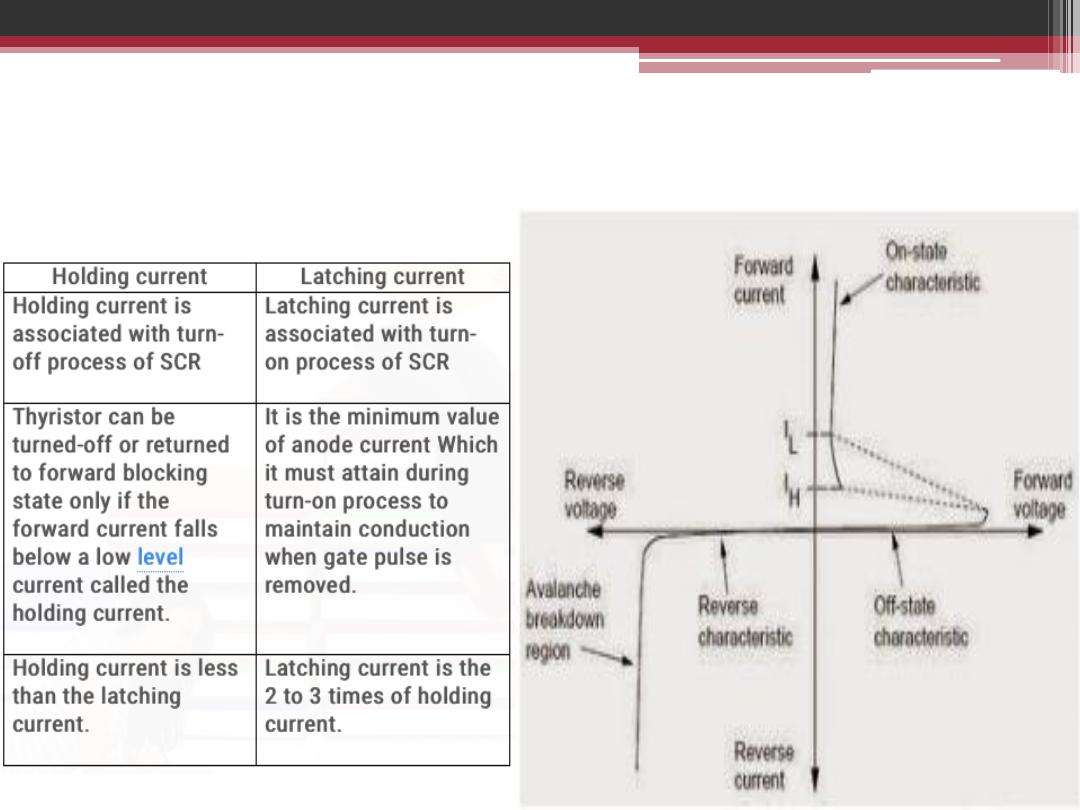
The Difference Between
Holding Current ( I
H
) and Latching Current ( I
L
)

POWER ELECTRONICS
AC to DC Converters
Controlled and Uncontrolled Rectifier
2016-2017
POWER CONVERSION CONCEPT:
EXAMPLE
•
Supply :
50Hz,
240V
RMS
(340V
peak).
Customer need DC voltage for welding
purpose, say.
•
Sine-wave supply gives zero DC
component!
•
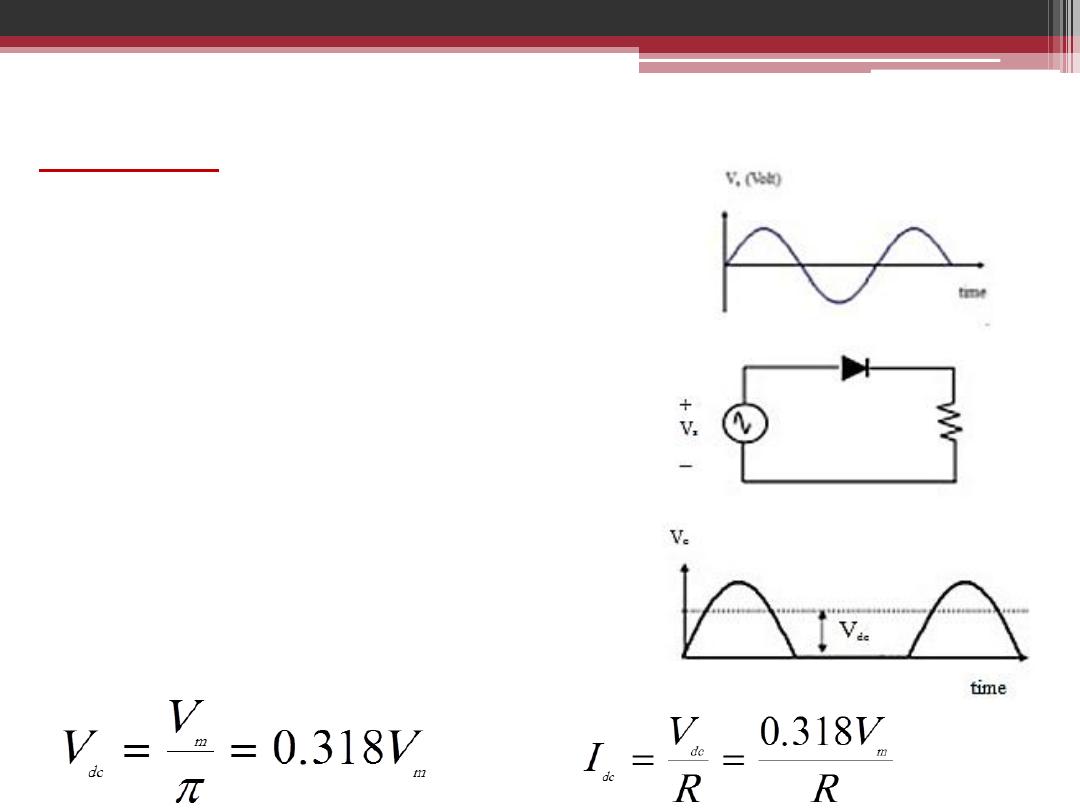
We can use simple half-wave rectifier.
A fixed
•
DC voltage is now obtained. This is a
simple PE system.
Average output voltage:
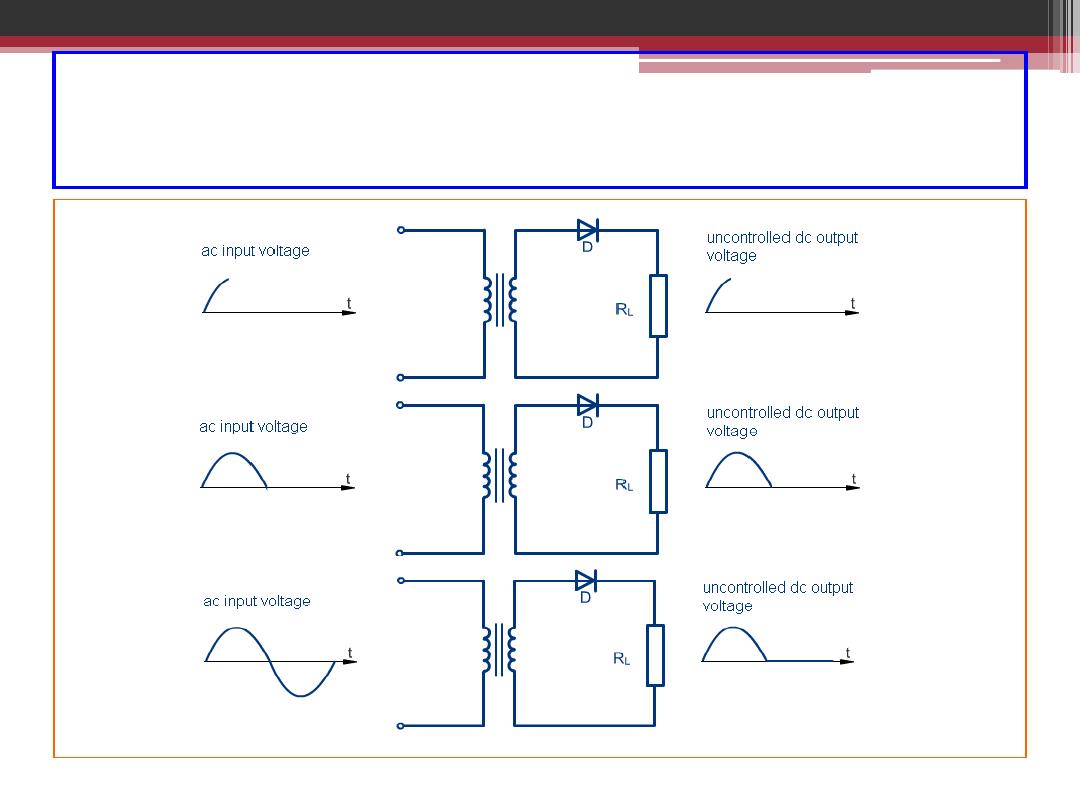
Single Phase Half-Wave Rectifier
•
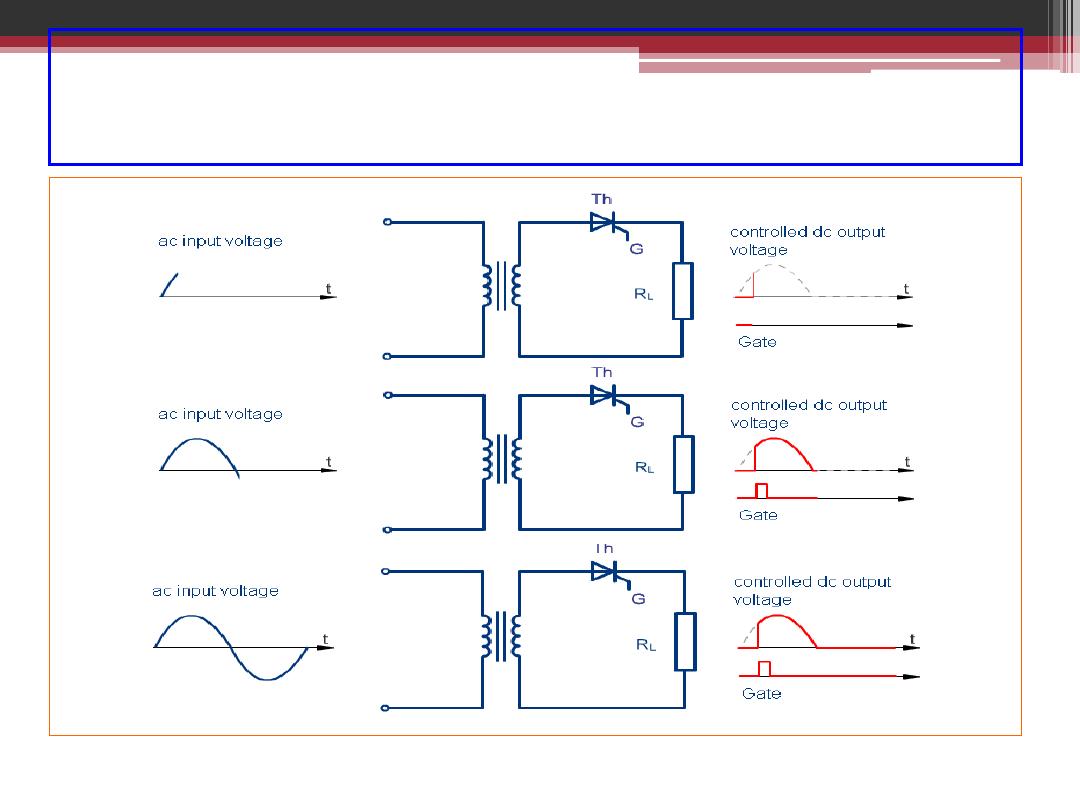
What if customer wants variable DC voltage?
-
More complex circuit using SCR is required.
•
By controlling the firing angle,
, the output DC voltage
(after conversion) can be varied.
•
Obviously this needs electronic circuit to set the firing current
pulses for the SCR.
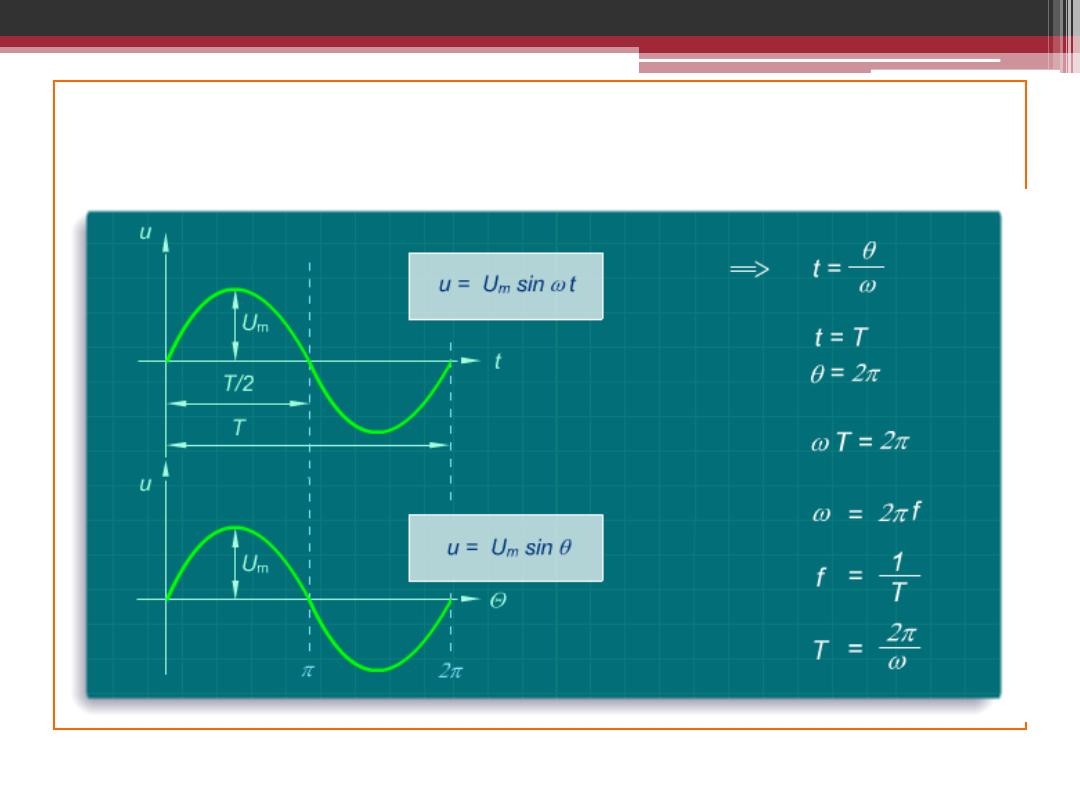
CONVERSION CONCEPT
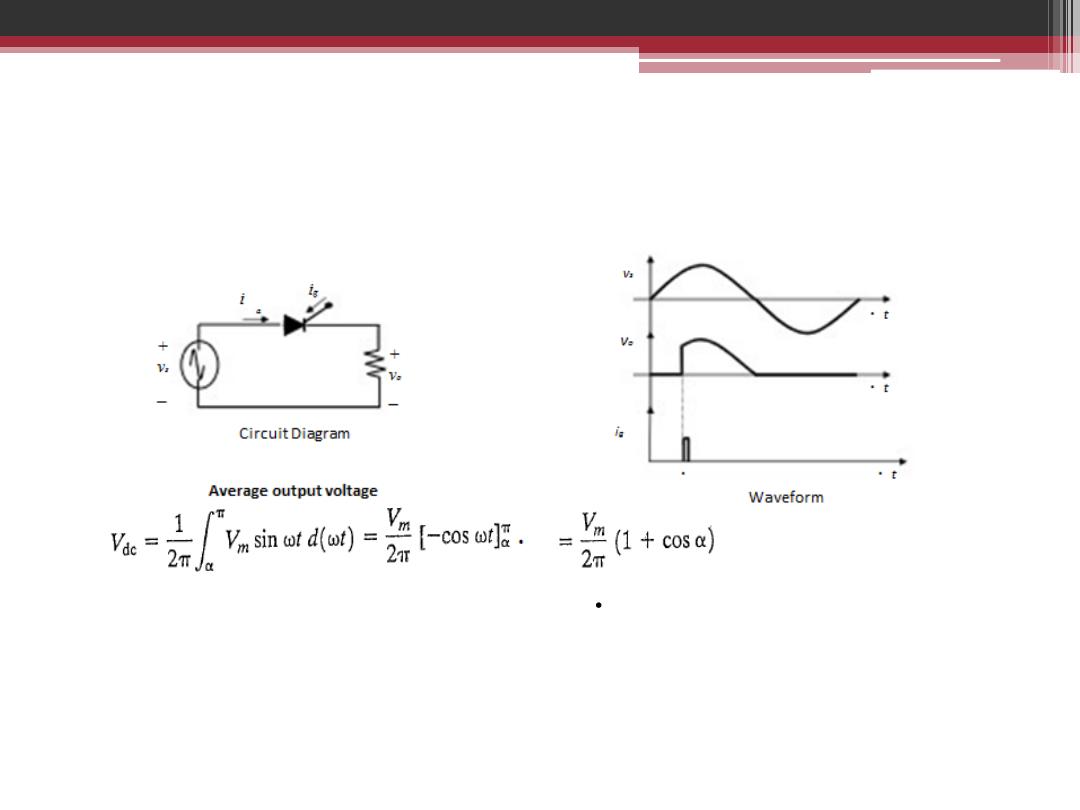
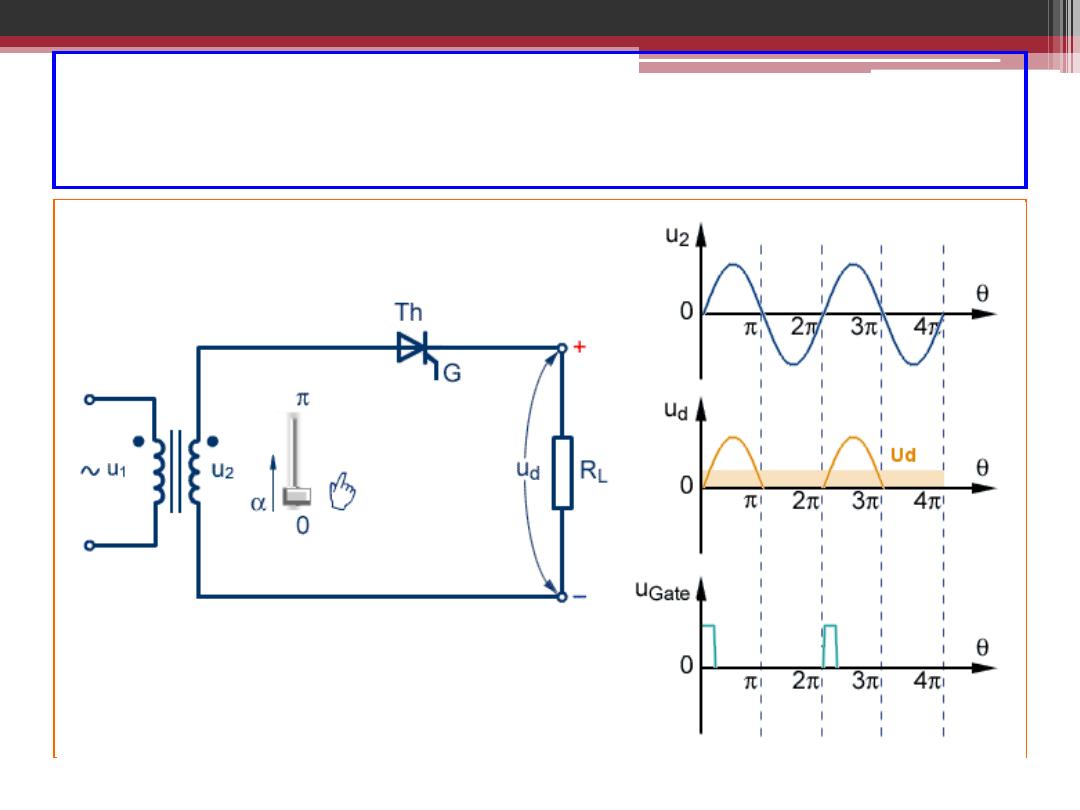
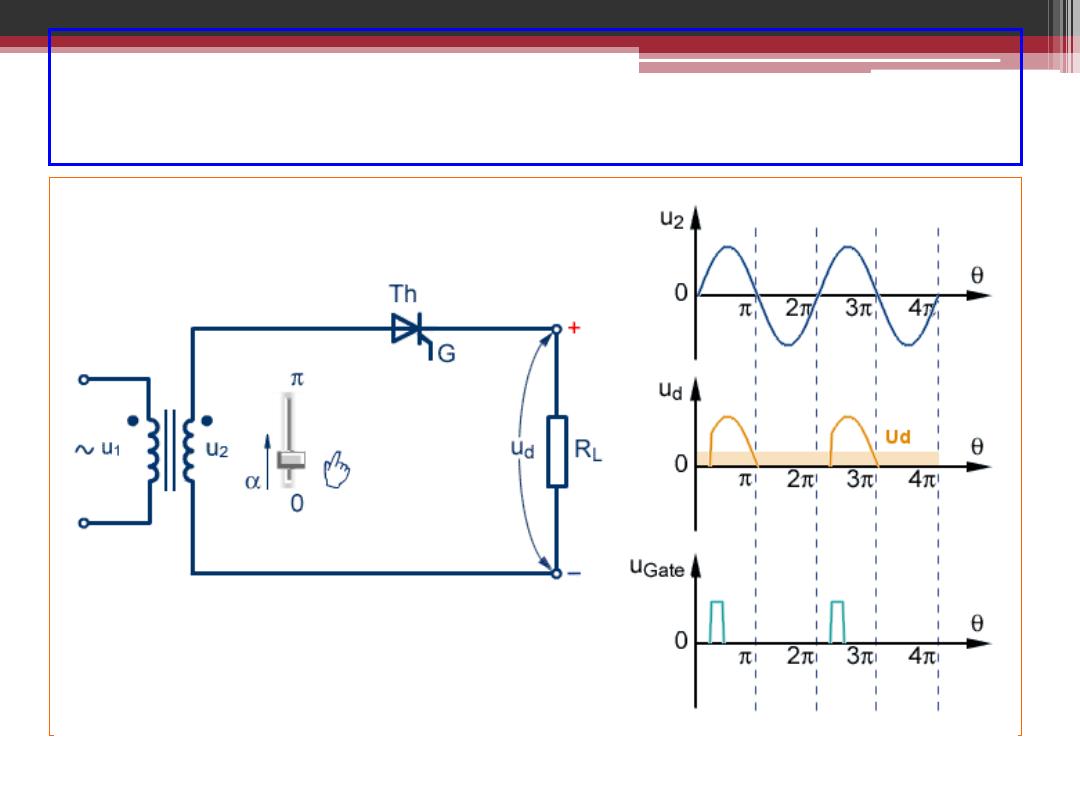
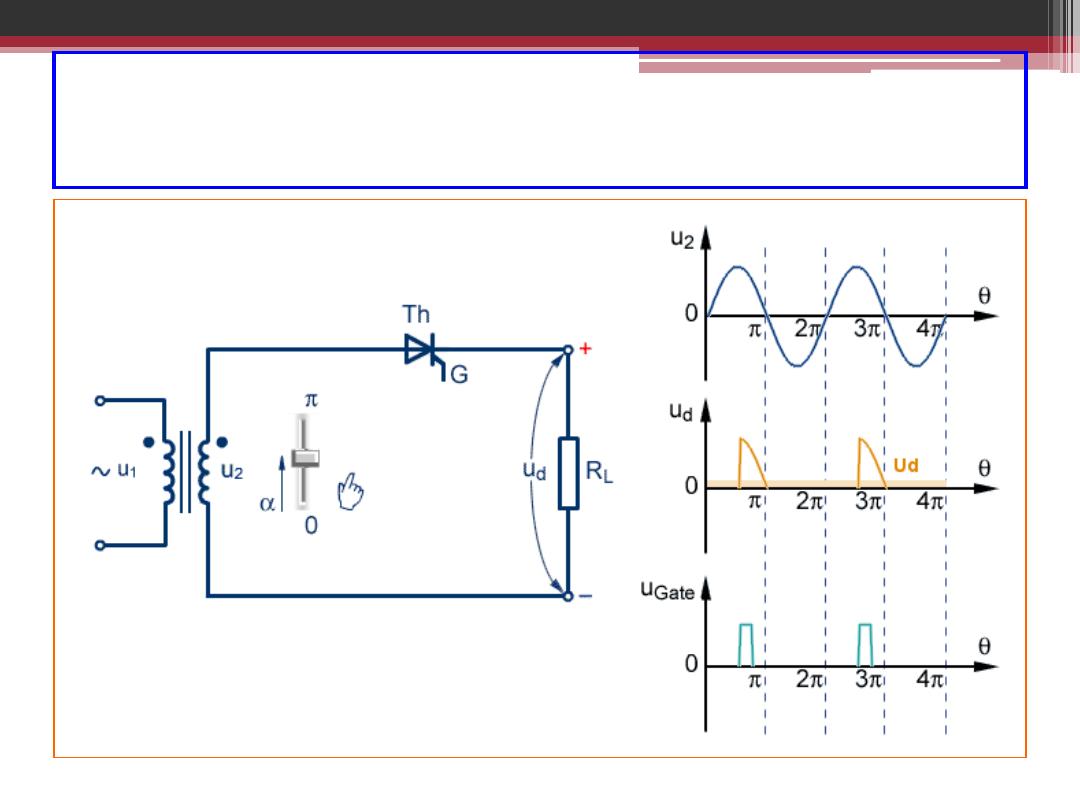
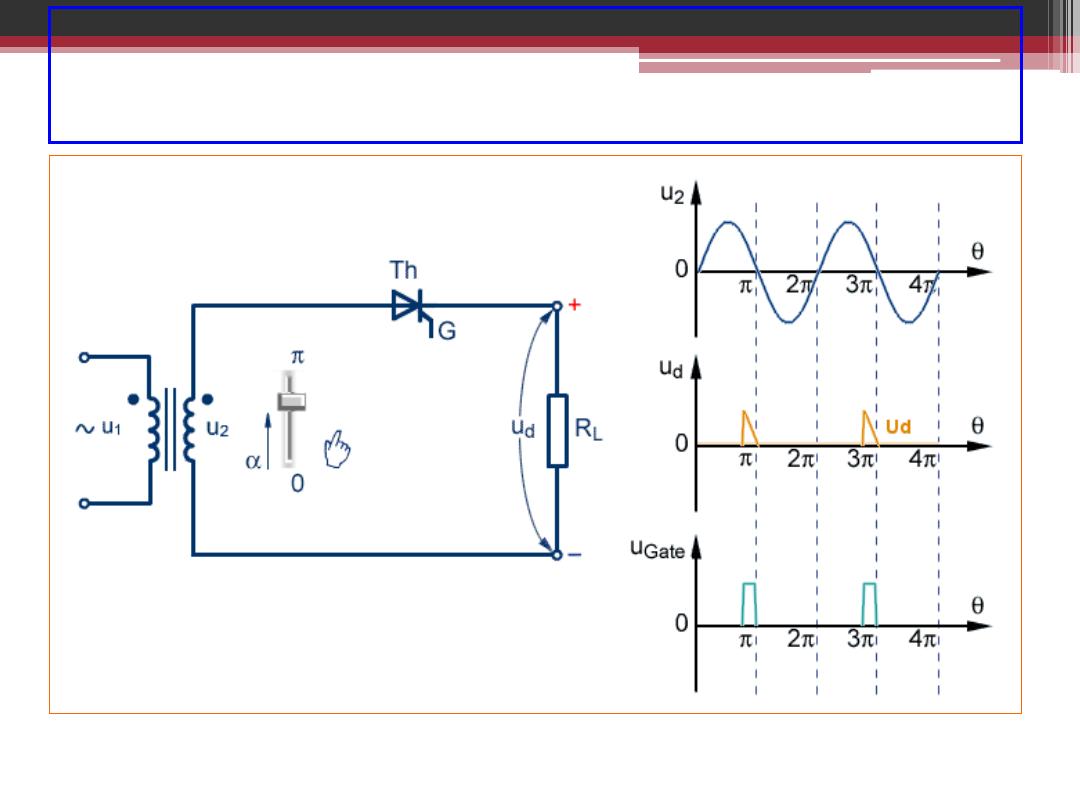
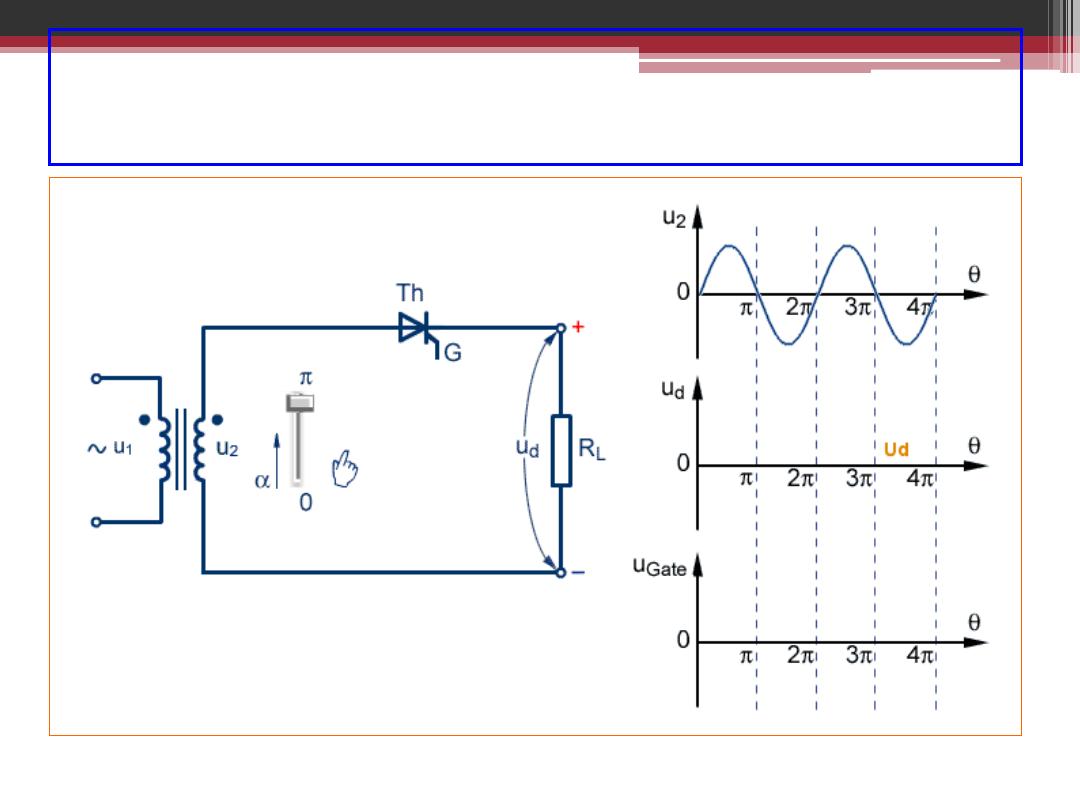
Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier
2016-2017
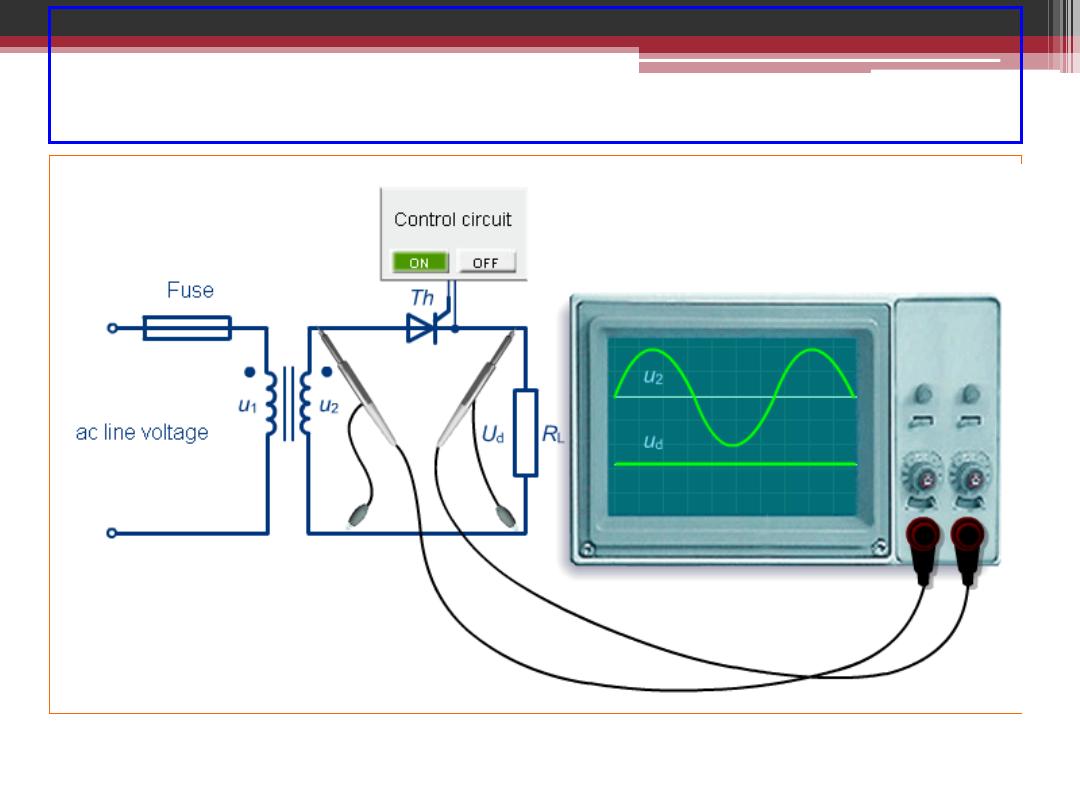
Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier
2016-207
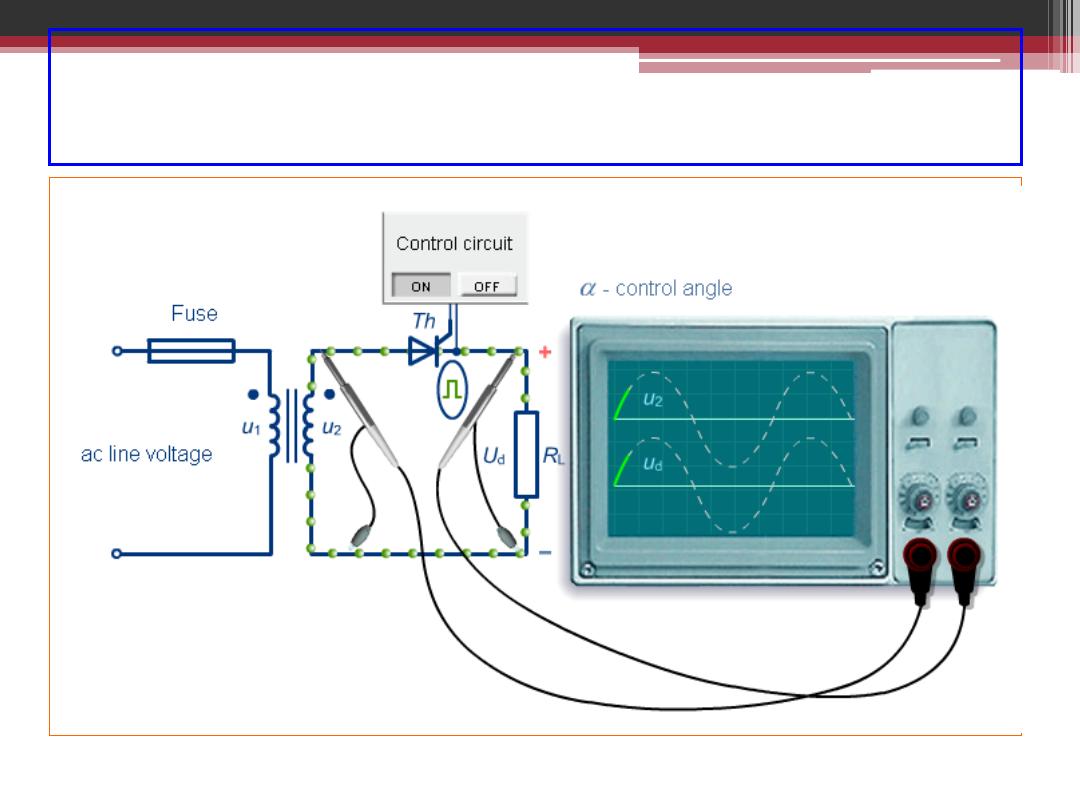
Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier
2016-207
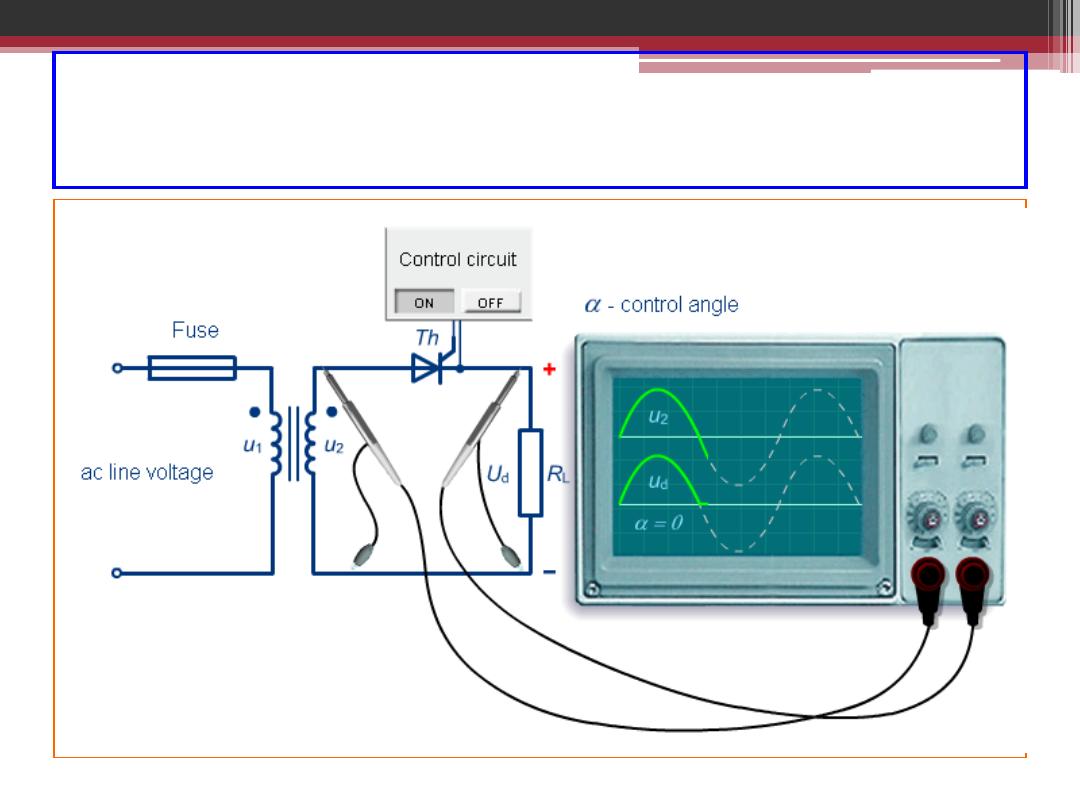
Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier
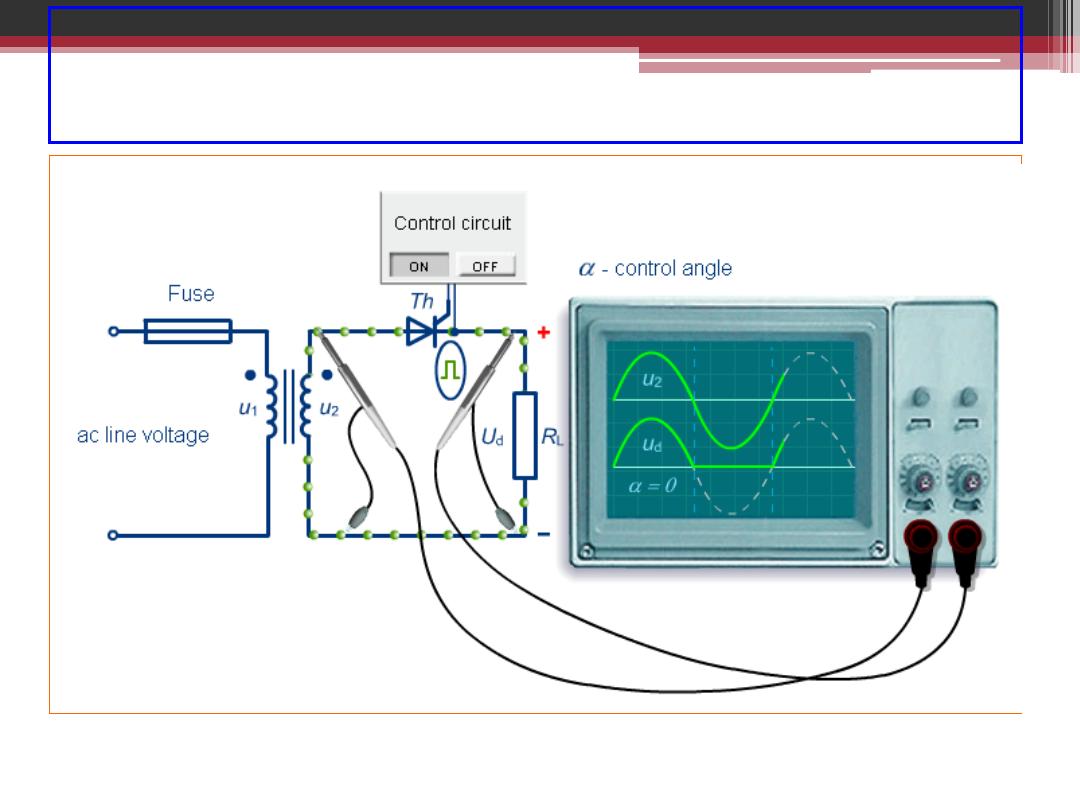
Single Phase Half-Wave Controlled Rectifier
2016-207
Average Rectified Voltage
Average Rectified Voltage
2016-207
Average Rectified Voltage
Average Rectified Voltage
2016-207
Average Rectified Voltage
2016-207
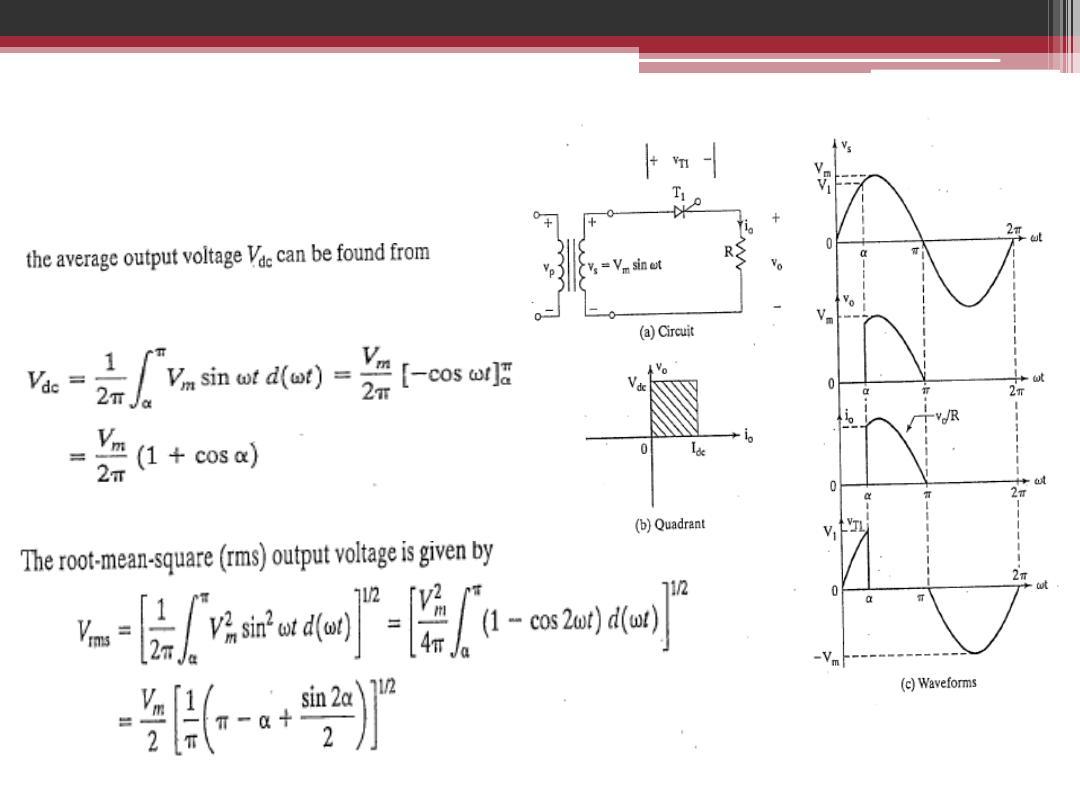
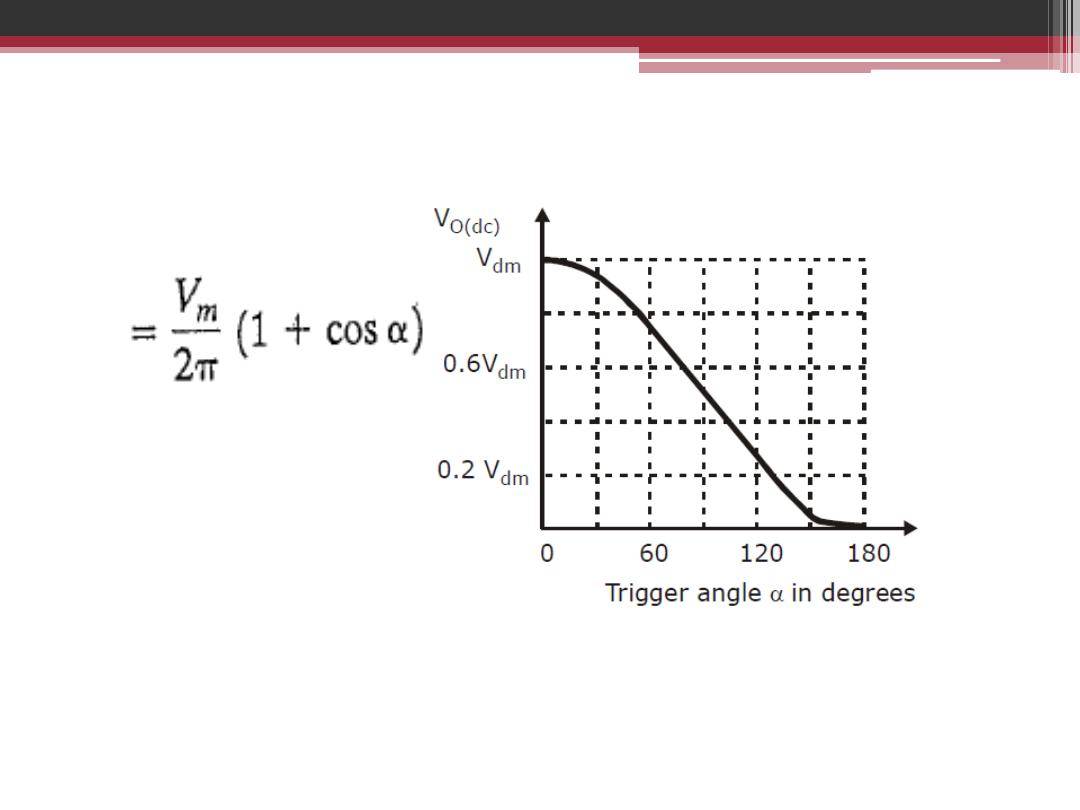
The relation of mean output voltage in terms of firing angle for half-wave
single phase controlled rectifier for pure resistive load
V
dc
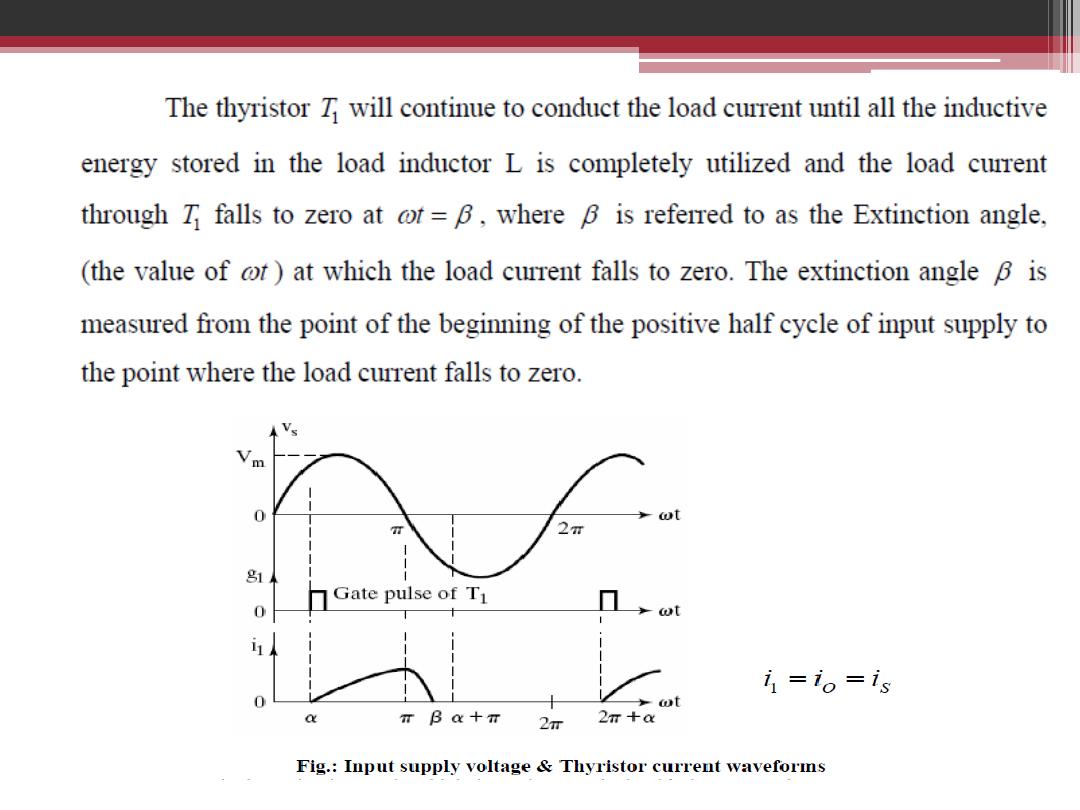


The mean output voltage
The relation of mean output voltage in terms of firing angle for half-wave
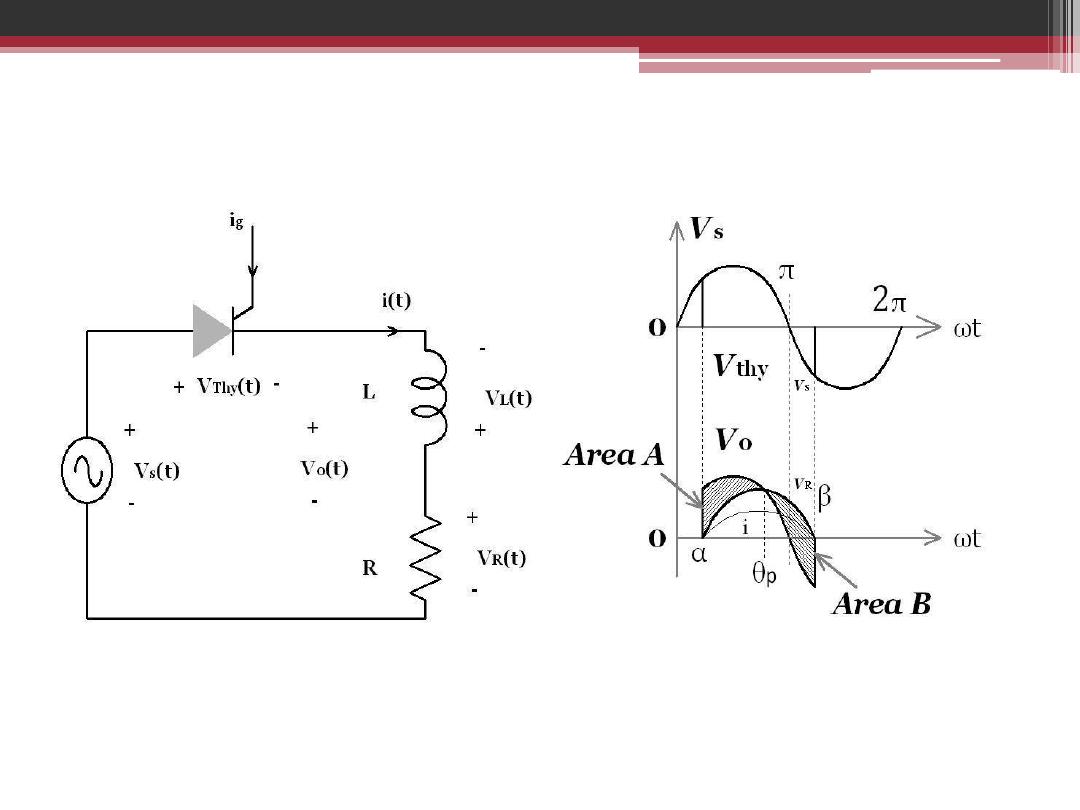
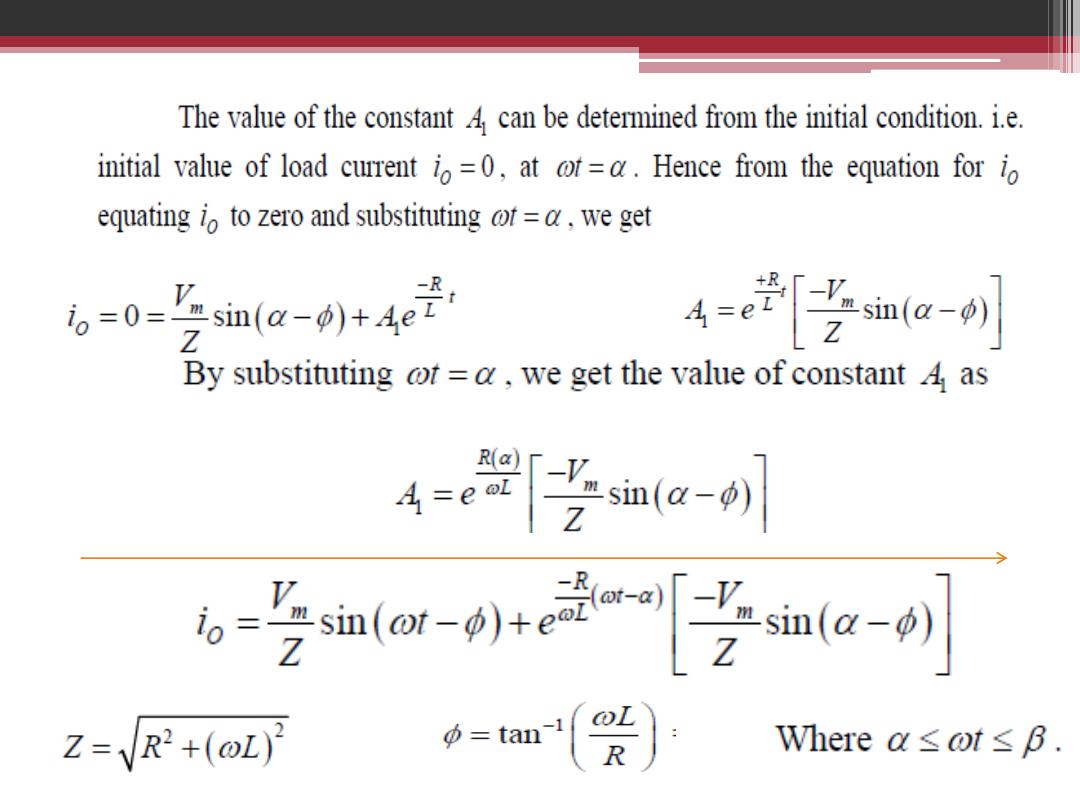
single phase controlled rectifier for R in series with L load.
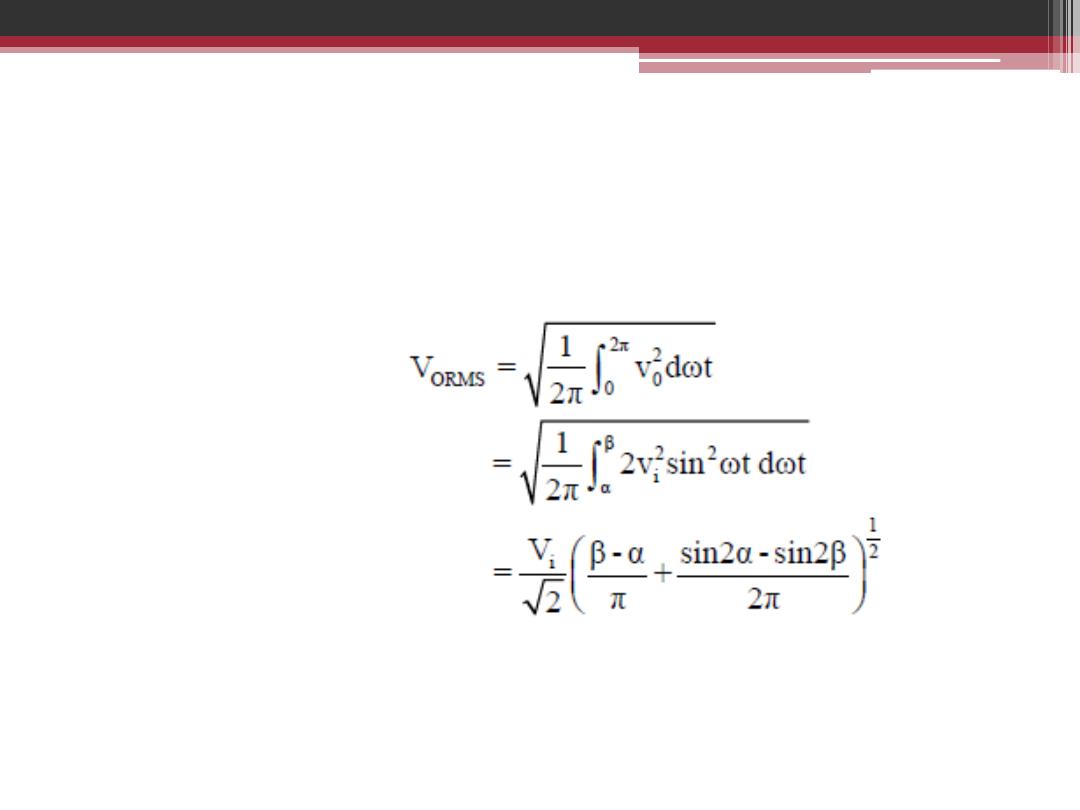
The relation of RMS output voltage in terms of firing angle for half-
wave single phase controlled rectifier for R in series with L load.
The RMS output voltage


POWER ELECTRONICS IN ENERGY
SAVING
ENERGY SCENARIO
•
Need to reduce dependence on fossil fuel.
•
Tap renewable energy resources.
•
About 60% - 65% of generated energy is consumed in electrical
machines -mainly pumps and fans.
•
Variable speed control of electric machines can improve
efficiency by 30% at light load. Light load reduced flux machine
operation can further improve efficiency.
•
Variable speed air-conditioner/heat pump can save energy by
30%.
•
About 20% of generated energy is used in lighting. High
frequency fluorescent lamps are 2-3 times more efficient than
incandescent lamps.

GROWTH OF POWER ELECTRONICS
The rapid growth of PE is due to:
•
Advances in power (semiconductor) switches.
•
Advances in microelectronics (DSP, VLSI, microprocessor/micro
-controller, ASIC).
•
New ideas in control algorithms.
•
Demand for new applications.
PE is an interdisciplinary field:
•
Digital/analogue electronics.
•
Power and energy.
•
Microelectronics.
•
Control system.
•
Computer, simulation and software.
•
Solid-state physics and devices.
•
Packaging.
•
Heat transfer.
