
TUTORIALS
Prof. Dr. Basil
2016-2017
IV
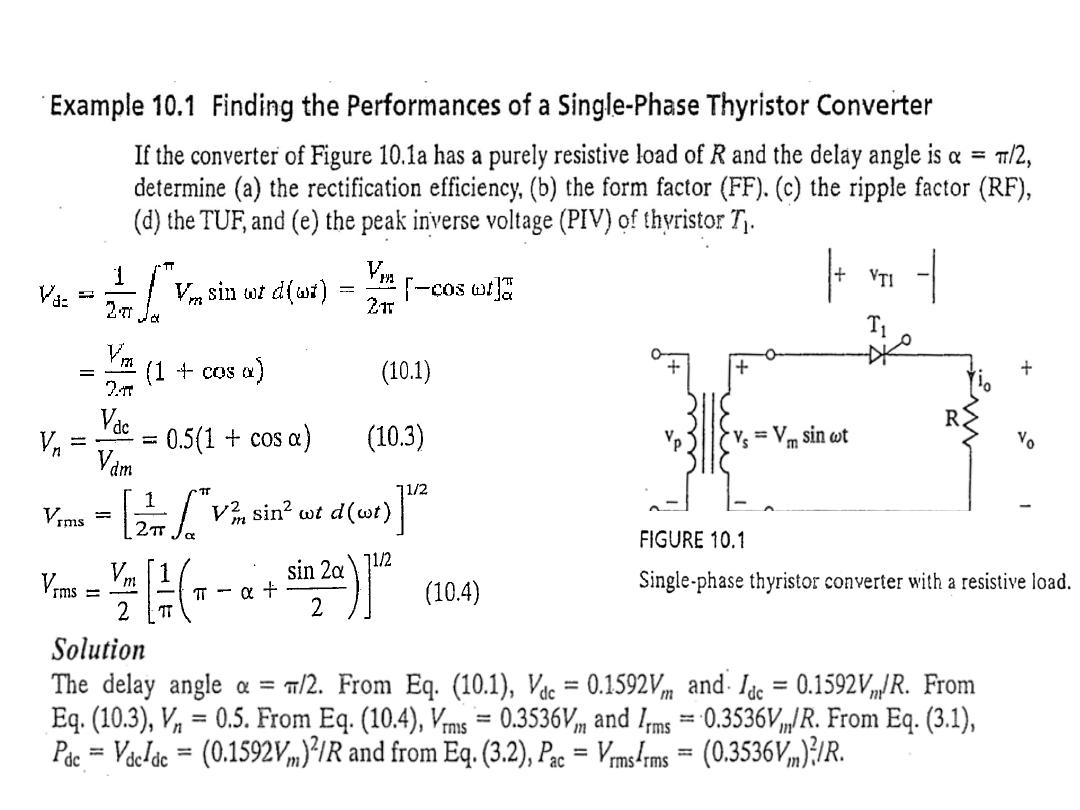
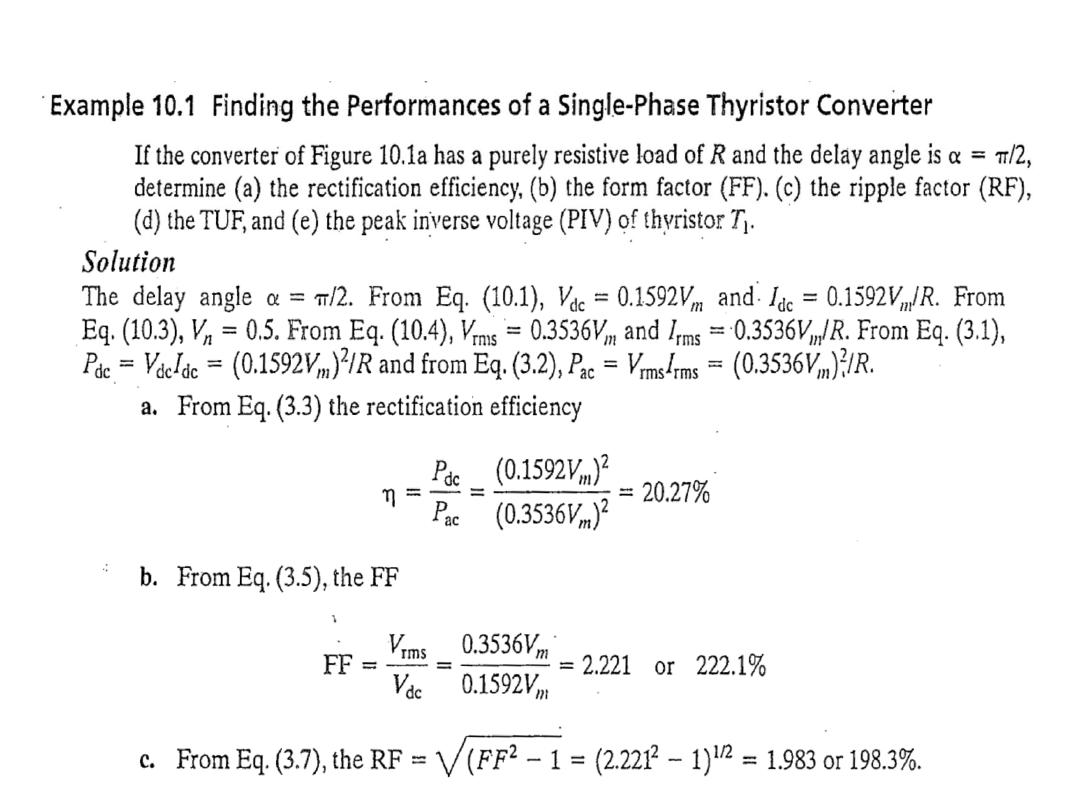
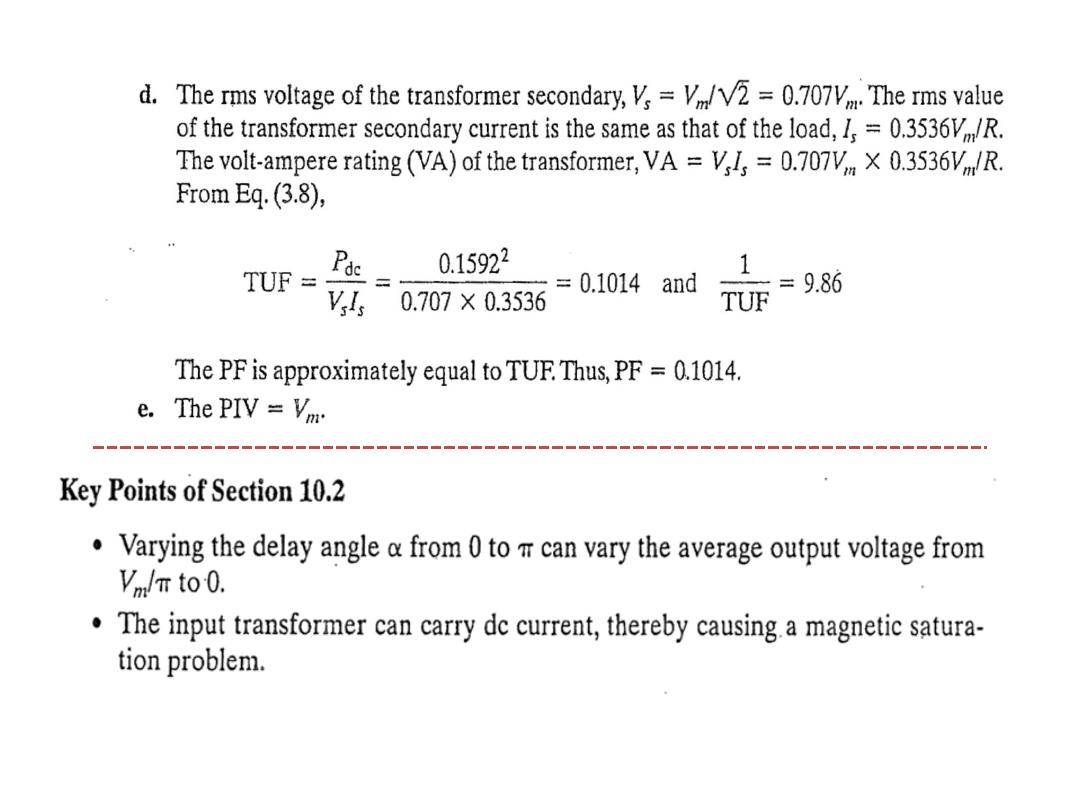
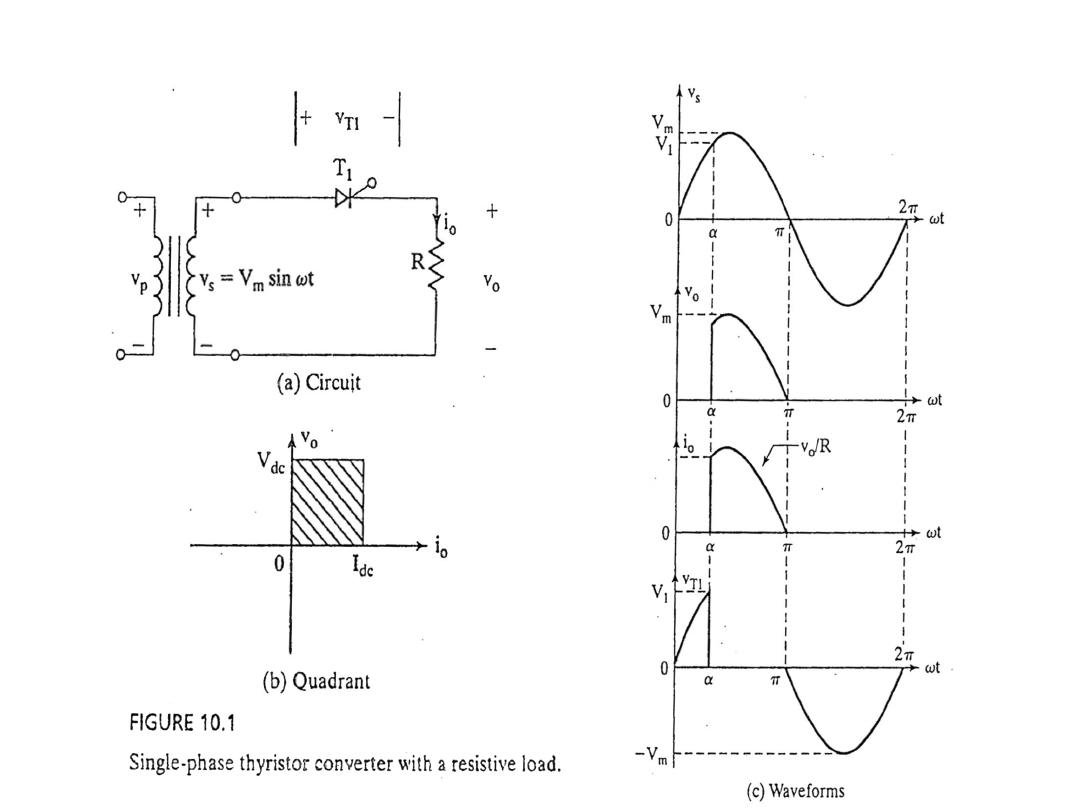
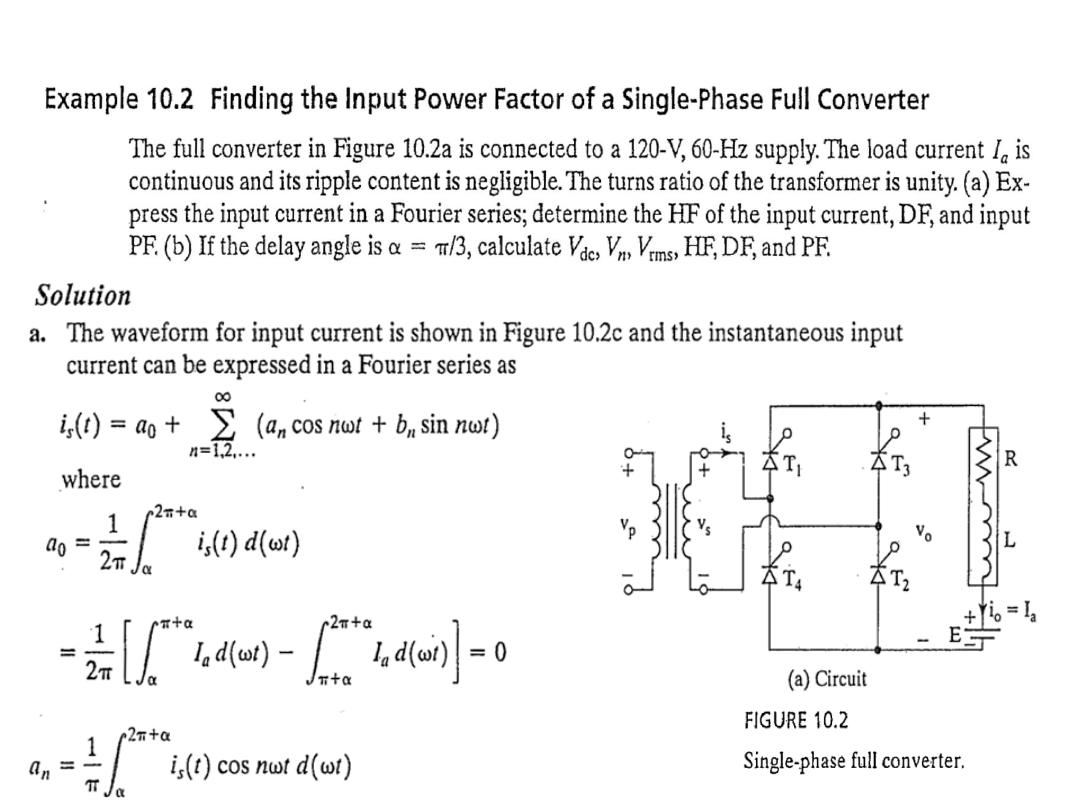

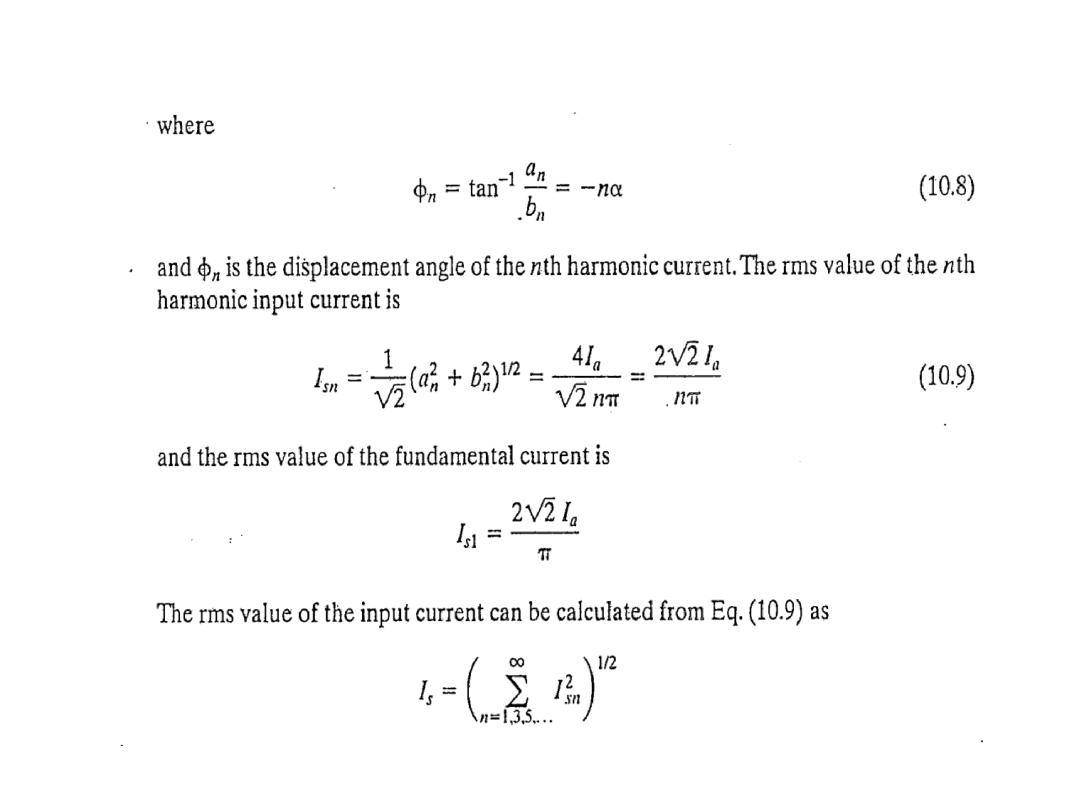
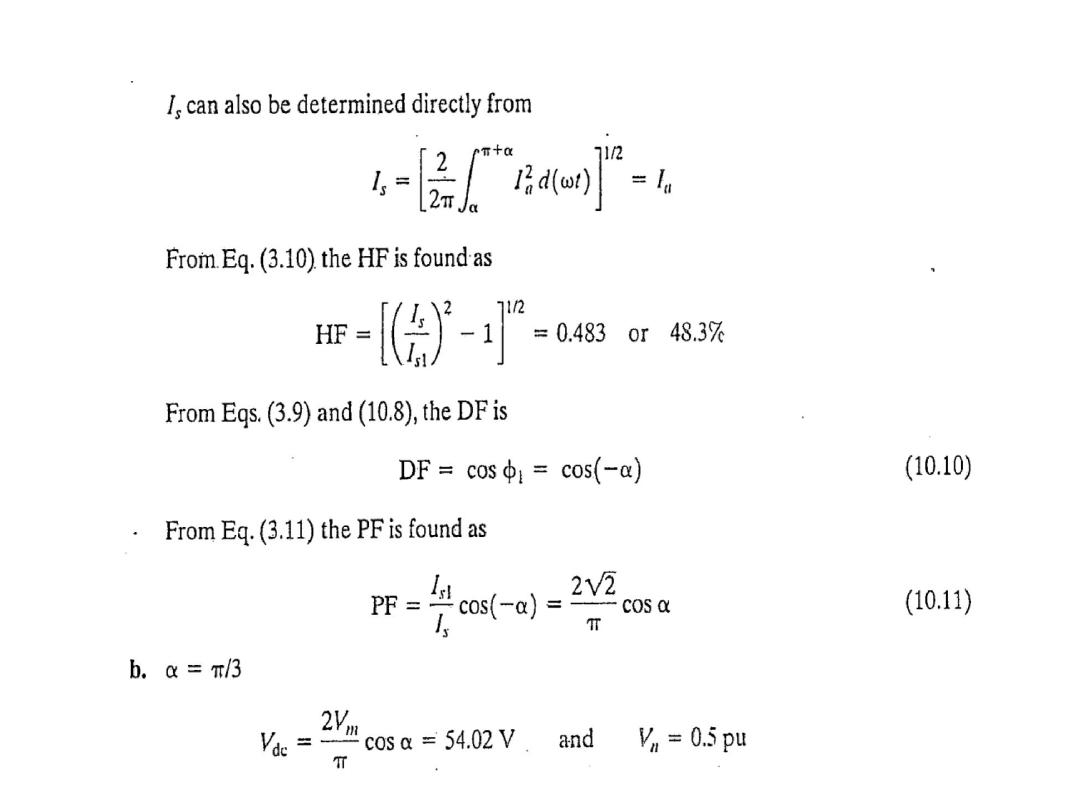
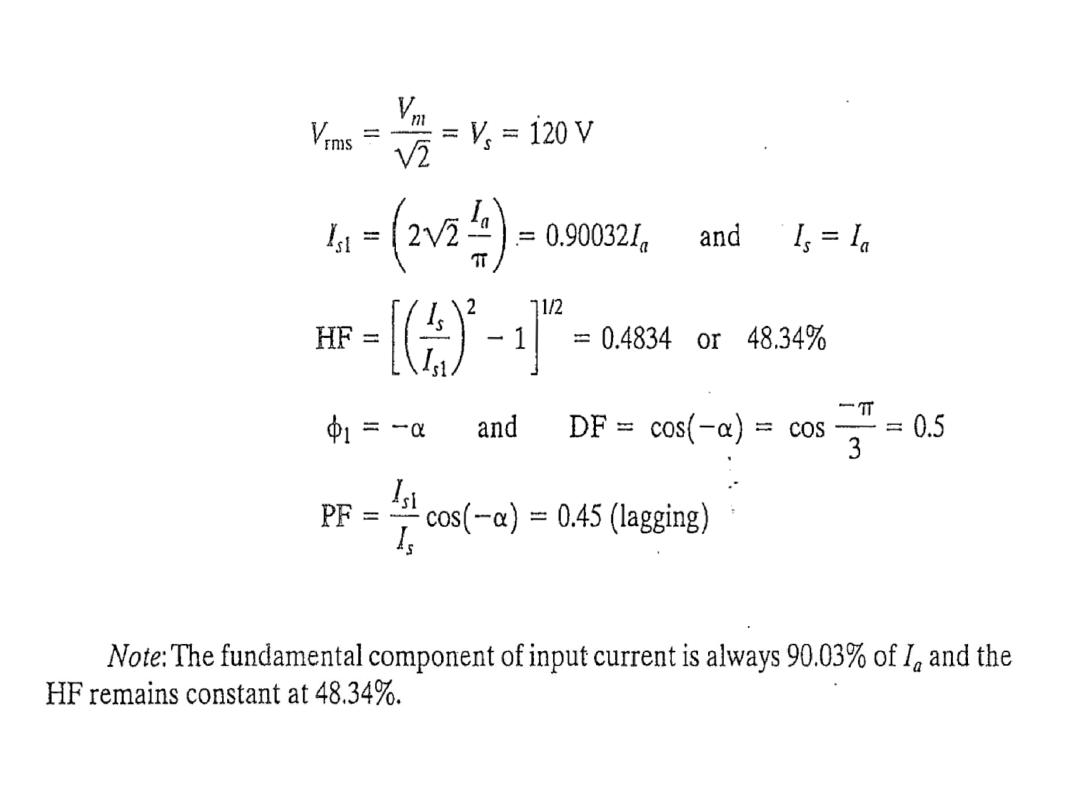
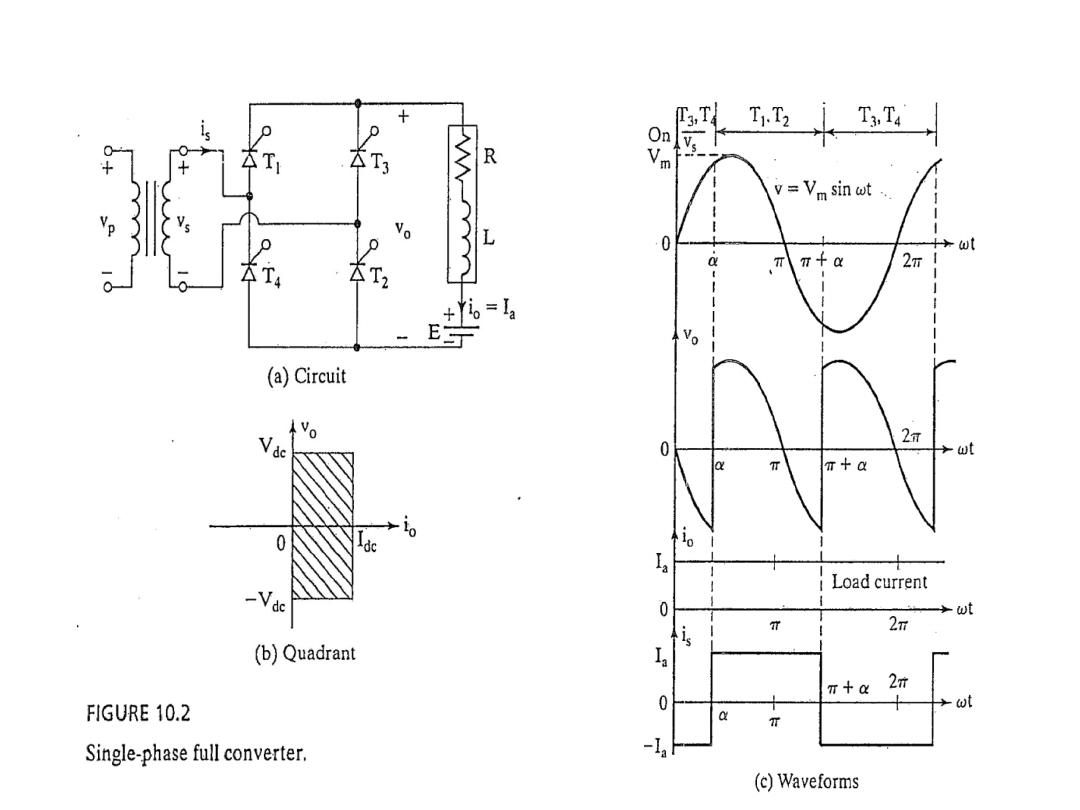

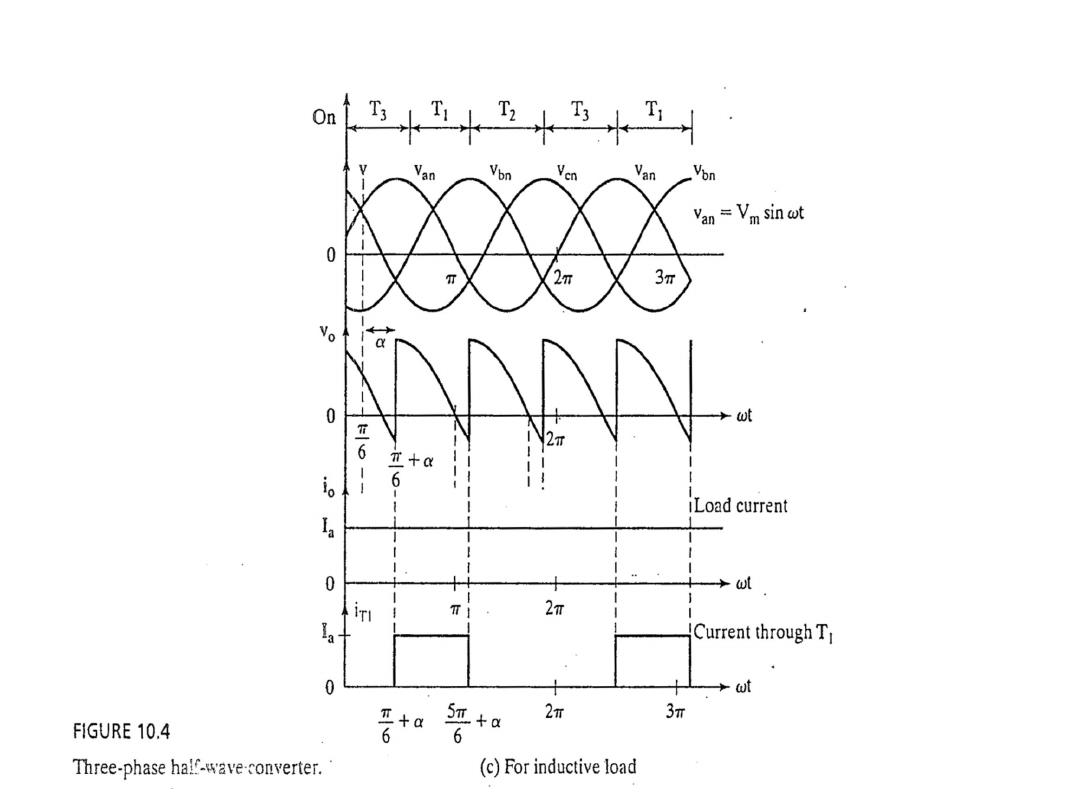
The average output voltage derivation as a function of firing angle for highly inductive load
:
The average output voltage derivation as a function of firing angle for resistive load :
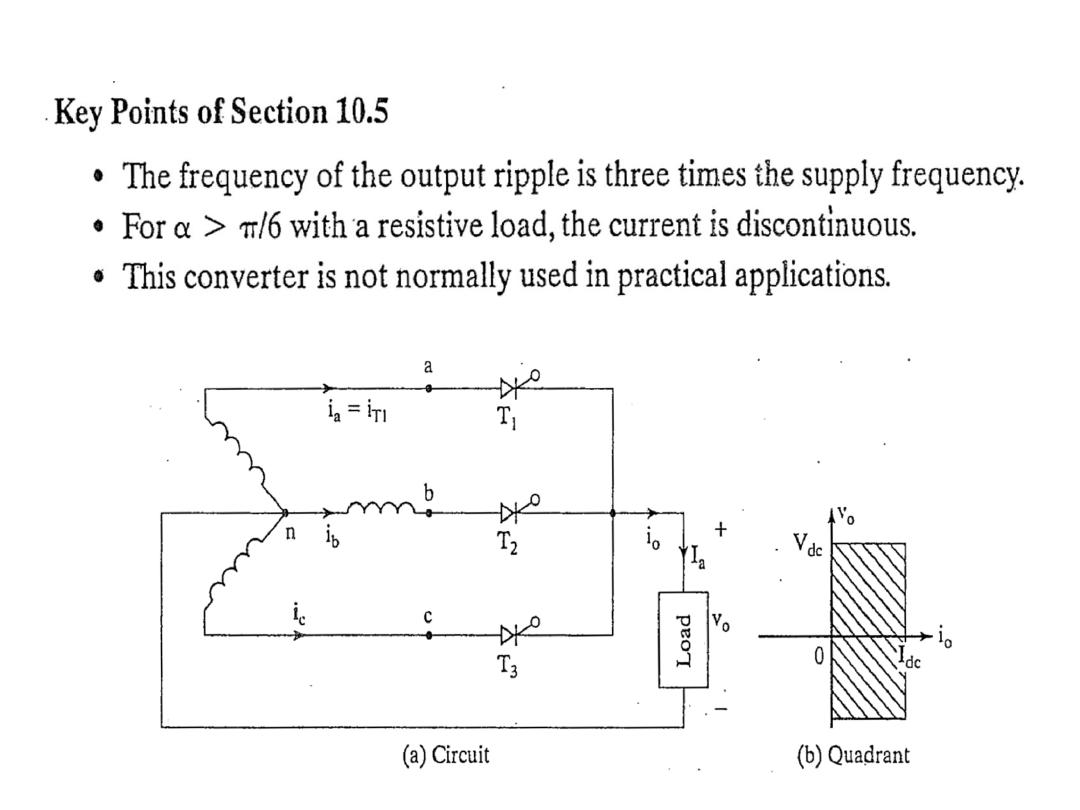
Where : α ≤ π/6
The average output voltage derivation as a function of firing angle for resistive load :
Where : α ≥ π/6
10.22
10.19
10.19
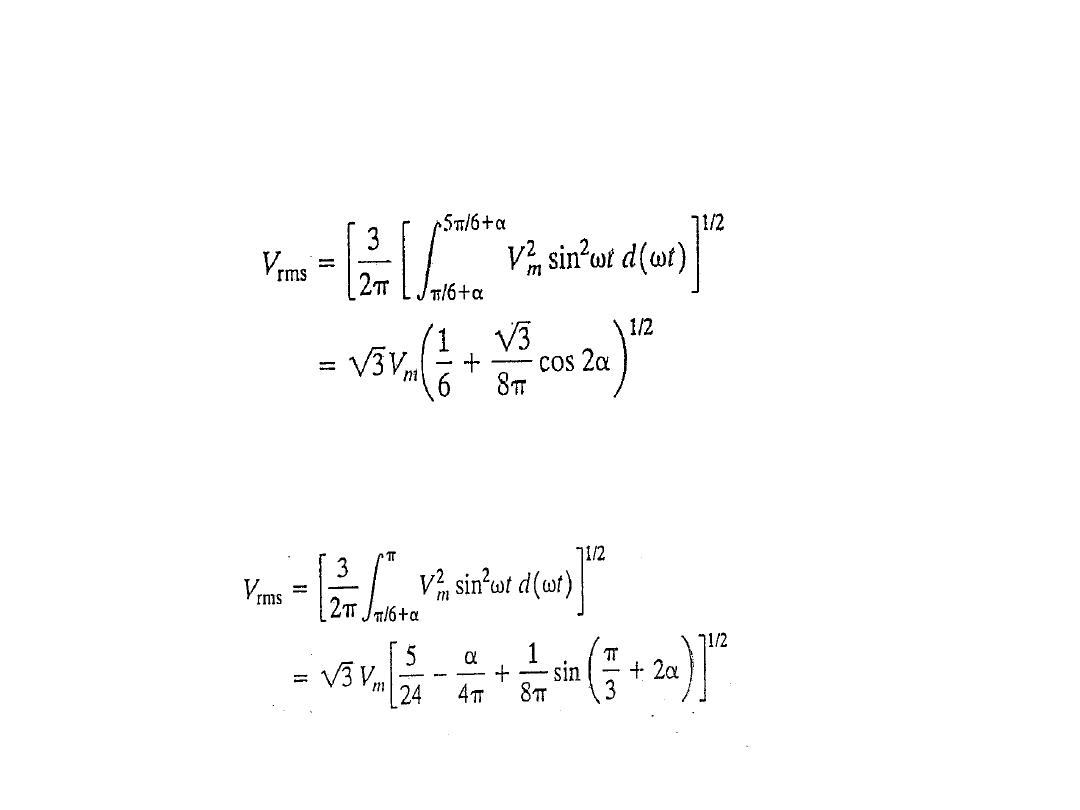
The rms output voltage derivation as a function of firing angle for highly inductive
load
(and also for resistive load with α ≤ π/6)
:
The rms output voltage derivation as a function of firing angle for resistive load with
firing angle range α ≥ π/6
10.21
10.24

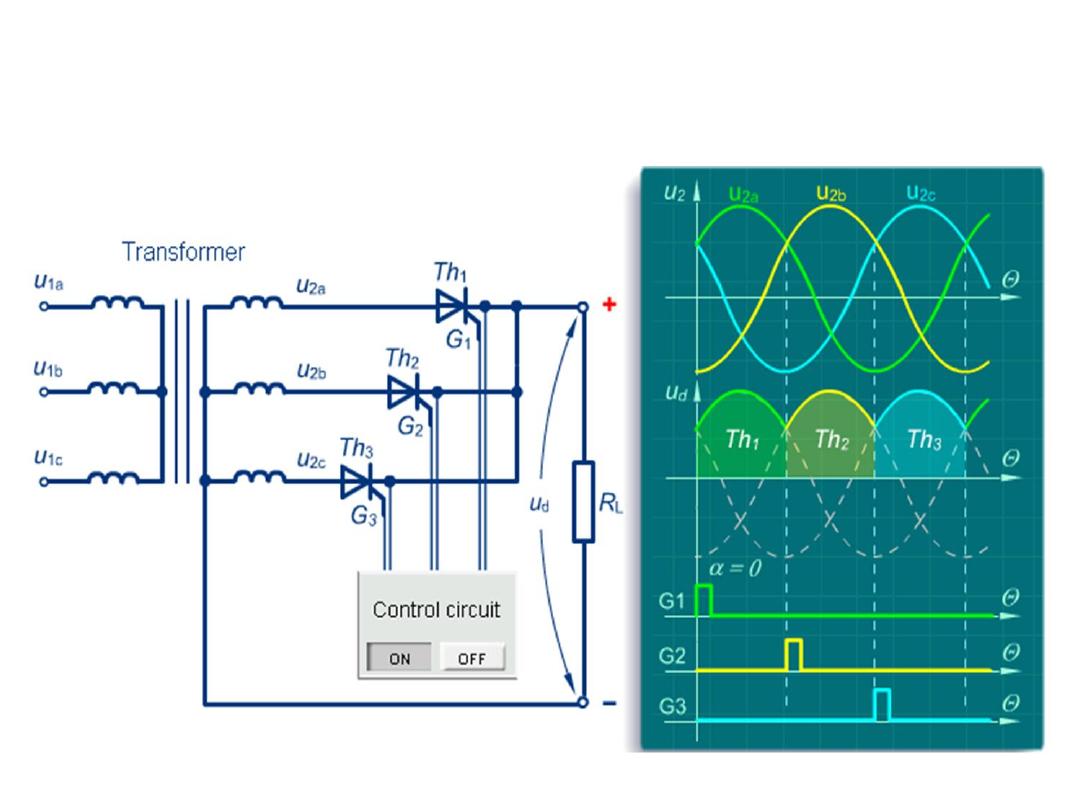
Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Rectifier
With Resistive Load at α = 0
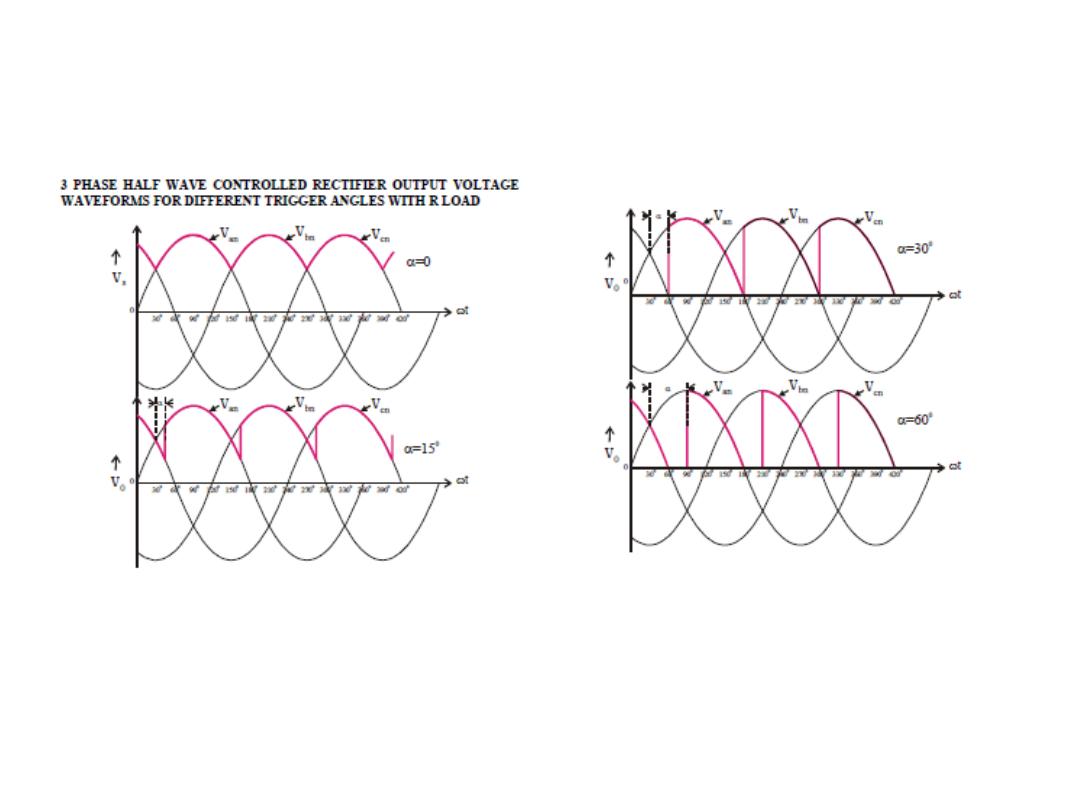
Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Rectifier
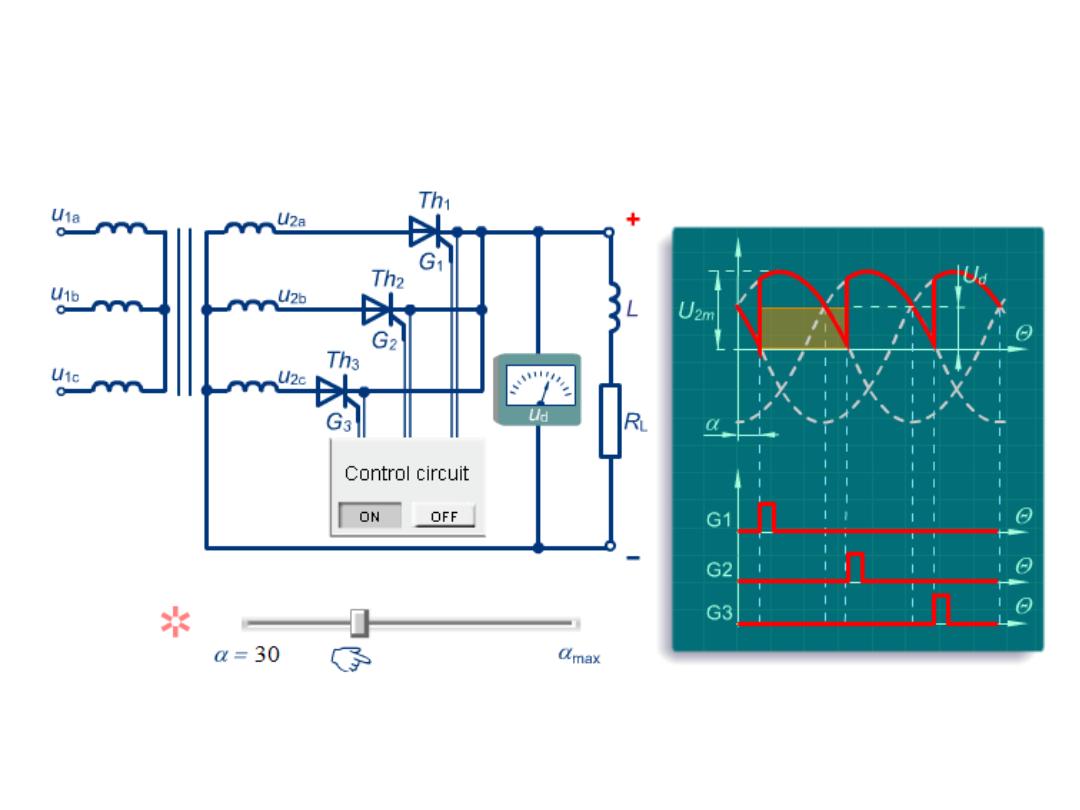
With Inductive (or resistive α ≤ 30) Load for α = 30
Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Rectifier
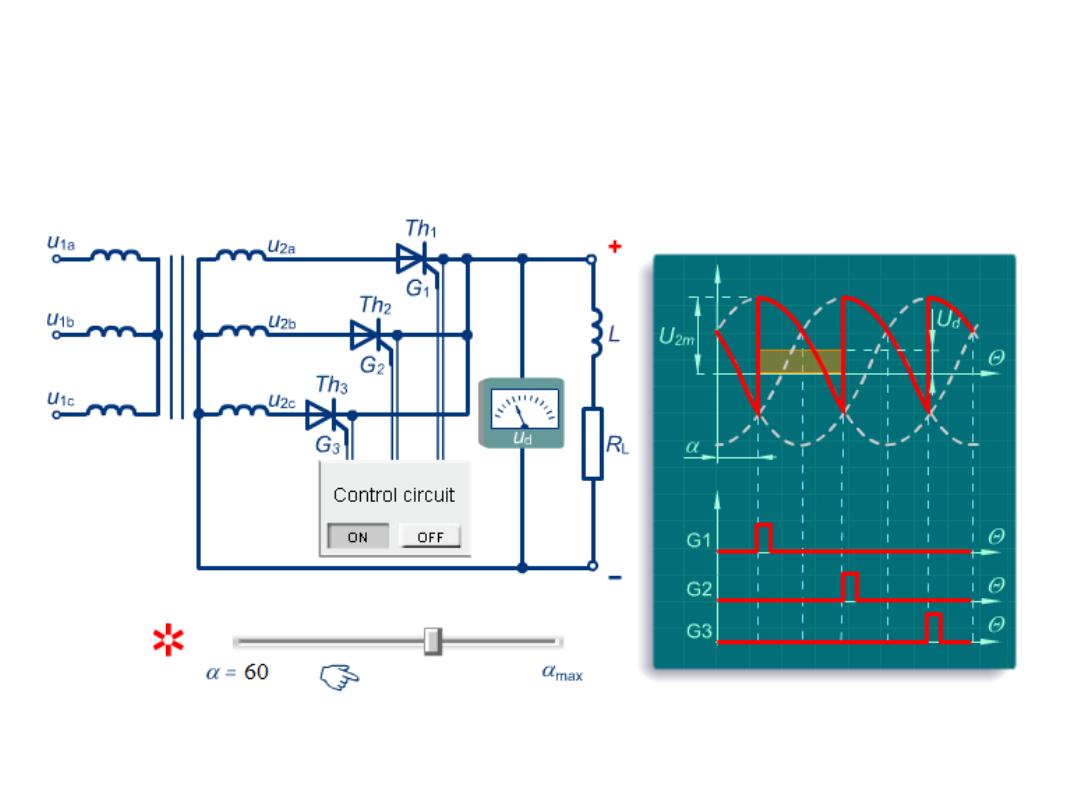
With Inductive Load for α = 60
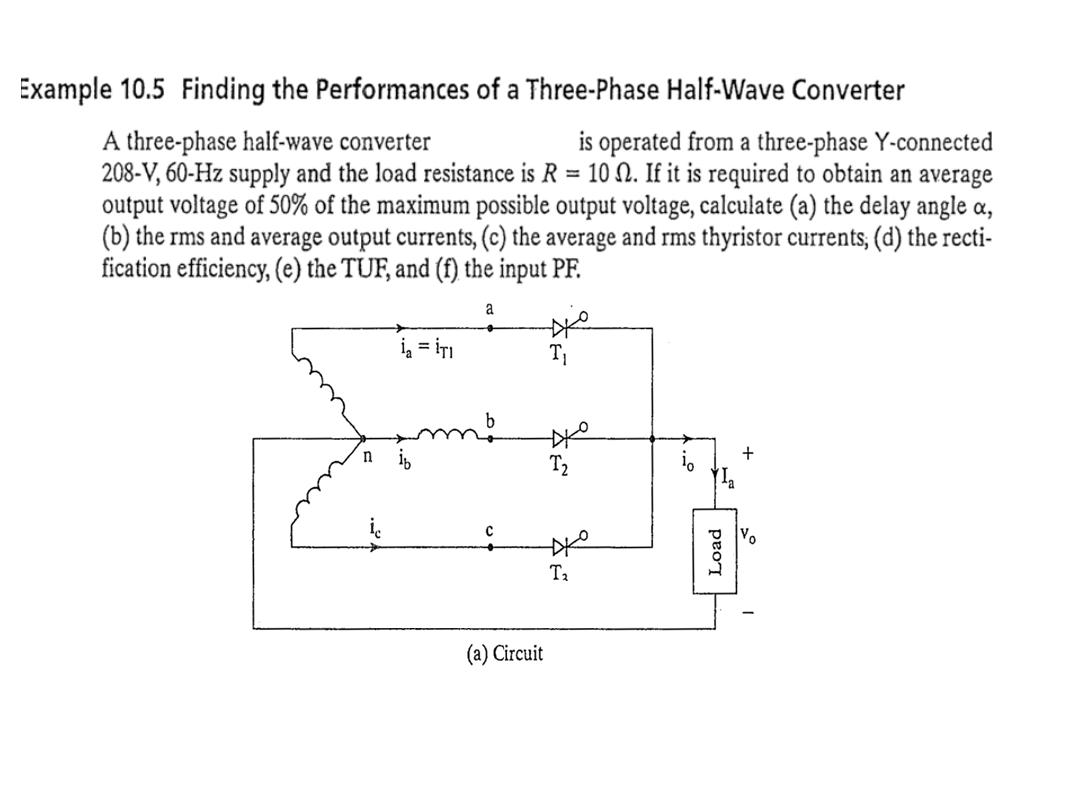
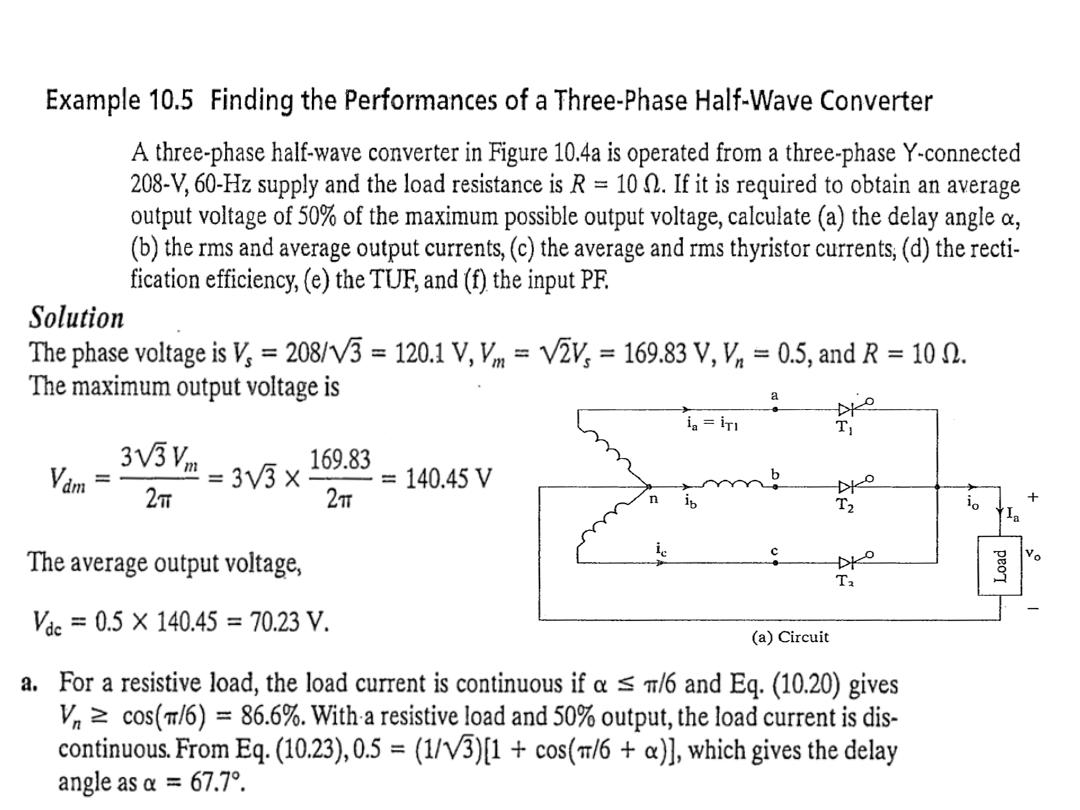
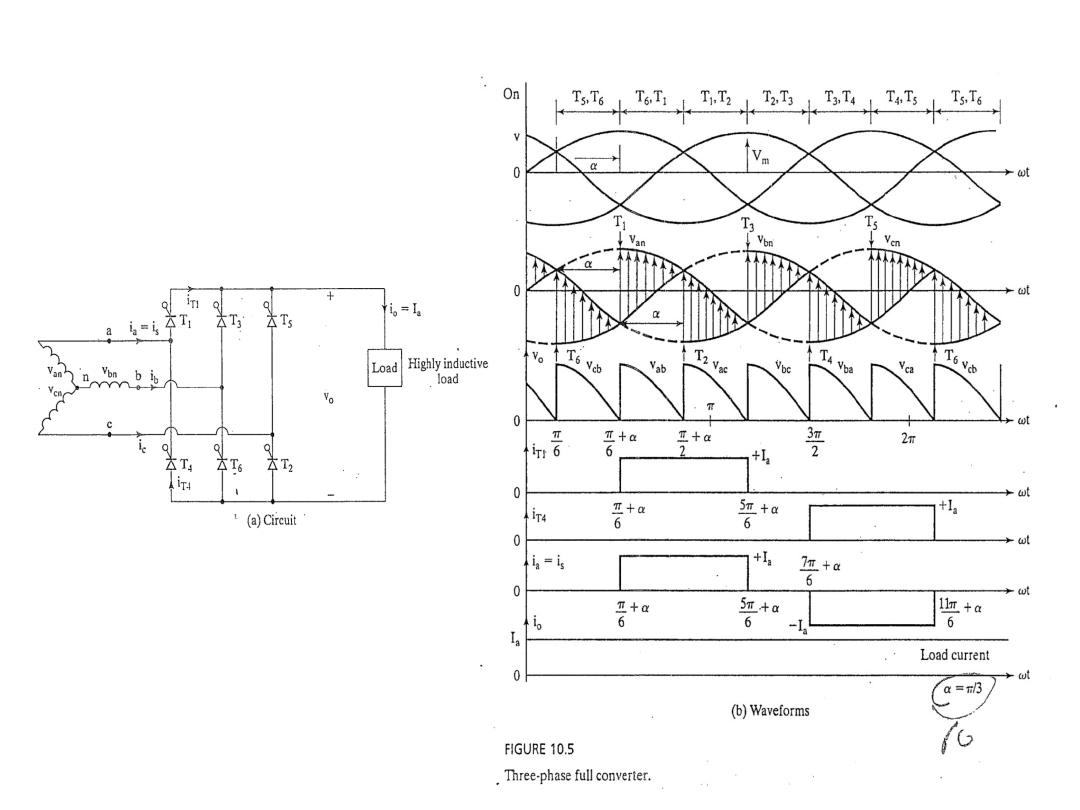
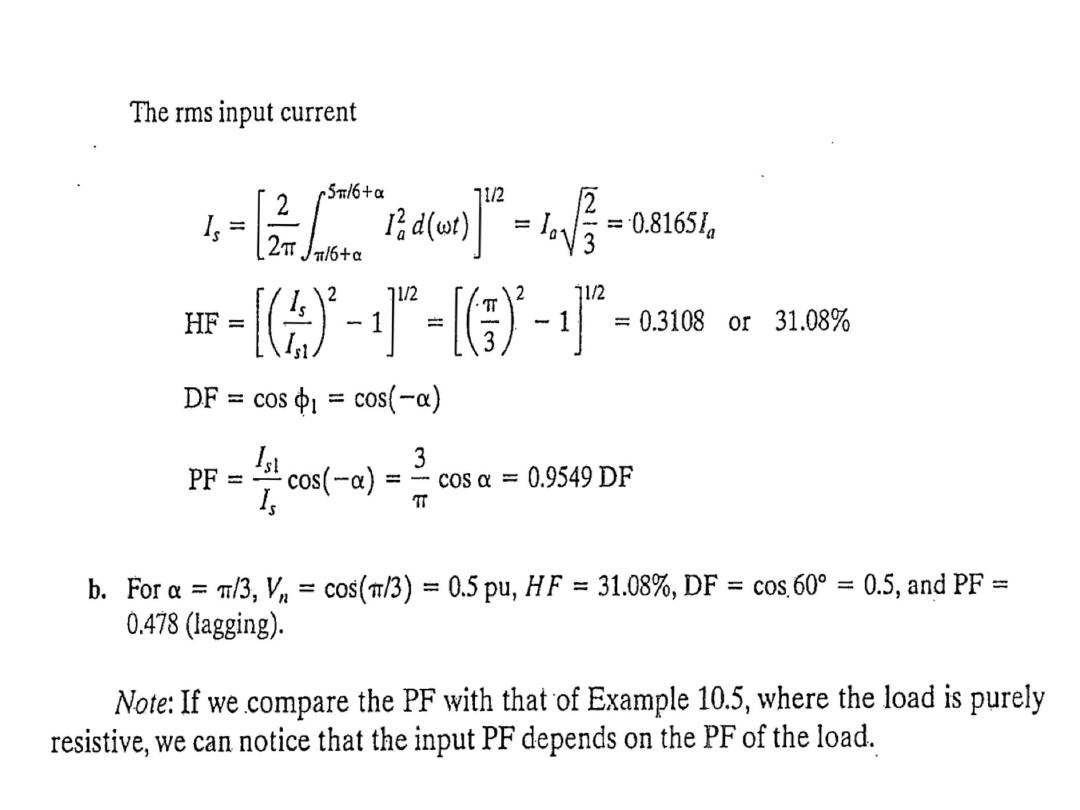
Example 10.6
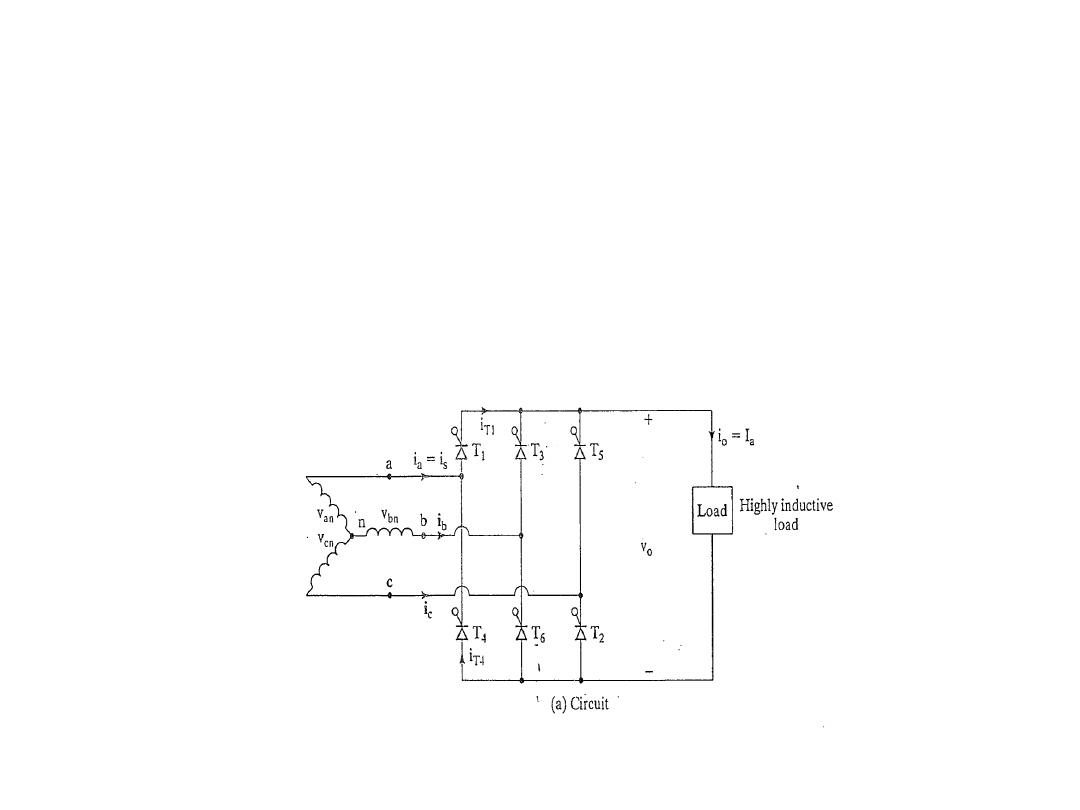
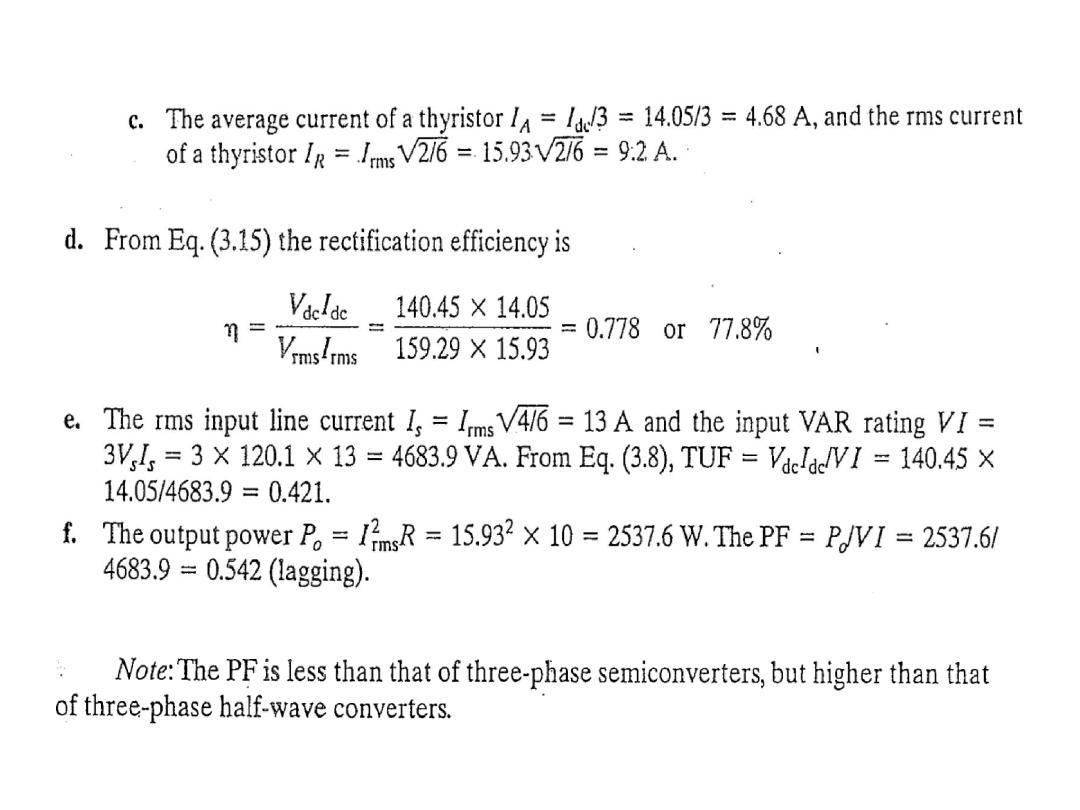
A three-phase full-wave converter is operated from three phase
star connected 208 V, 60 Hz, supply and the load is R= 10 Ω. If it
is required to obtain an the average output voltage of 50% of the
maximum possible average output voltage , calculate : (a) the delay
angle α, (b) the rms and average output currents, (c) the average
and rms thyristor currents, (d) the rectification efficiency, (e) the
transformer utilization factor, and (f) the input power factor.
Figure 10.5 a Three- phase full converter.






THE END
