Applied Anatomy of the Ear
A Professor Dr Haider Alsarhan
THE EXTERNAL EAR
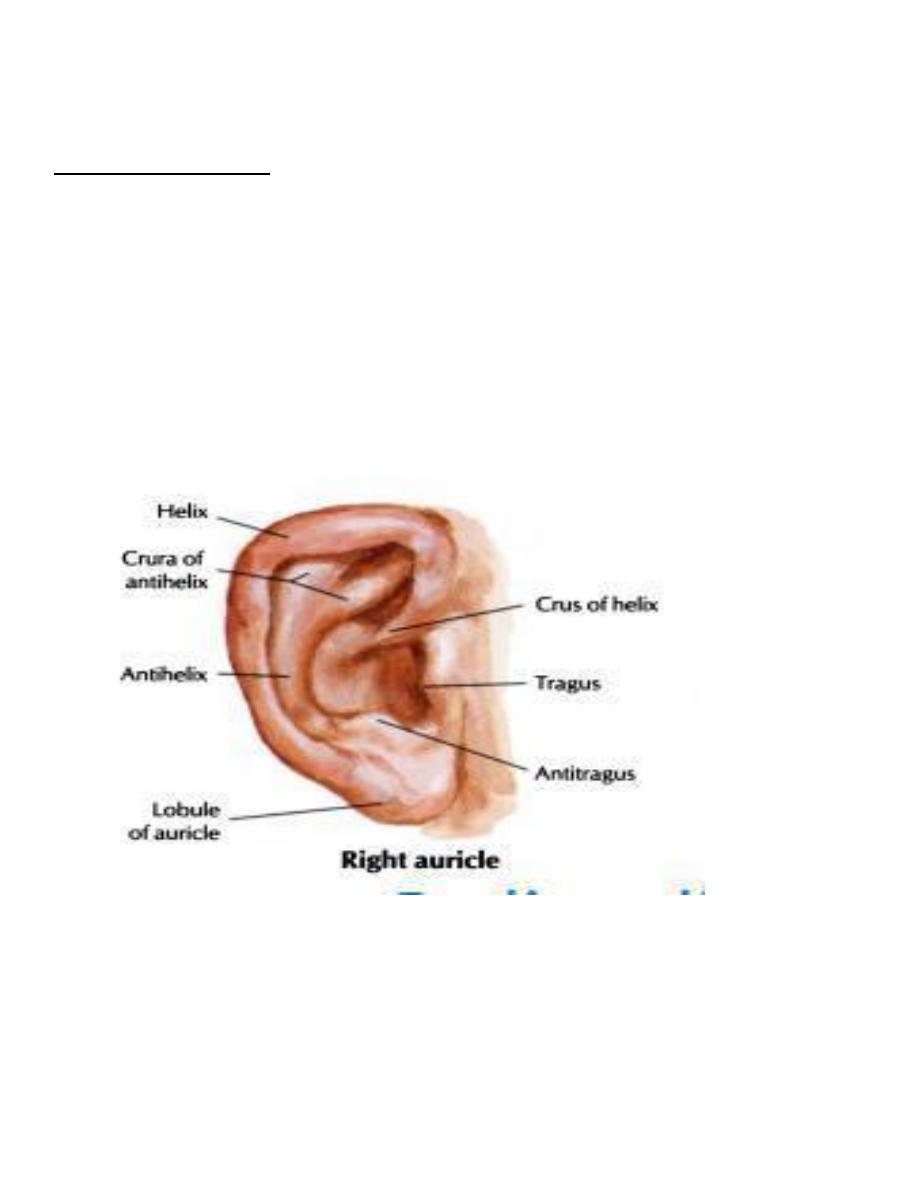
(A) The Auricle: helix, crus of helix, tragus, lobule, antihelix, triangular
fossa, antitragus, concha, External auditory Canal opening
(B)
The External Auditory Canal (EAC): 2.5 cm
1-Outer 1/3: Cartilaginous: hair follicles, sebaceous glands, cerumen glands
The wax: is hydrophobic, acidic & with antibacterial properties,
the epithelium of the EAC has the capacity to migrate.
2- Inner 2/3: Bony
THE TYMPANIC MEMBRANE (TM)
Three Layers;
1.outer : epithelial
2. middle : fibrous
3.inner: mucosal
The tympanic membrane is attached to the temporal bone by the Annulus fibrousus
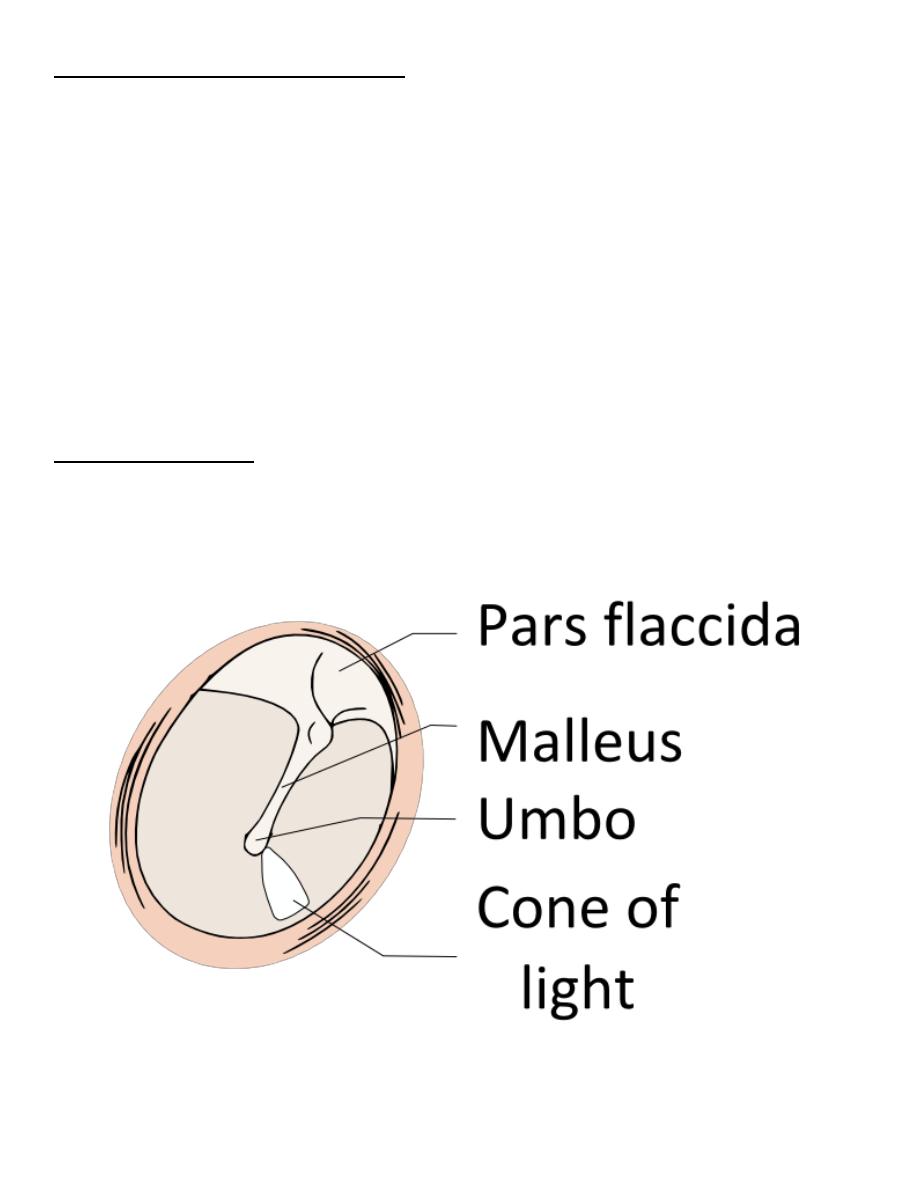
The Tympanic Membrane is divided into two parts:
1. Pars Tensa ( which consist of the 3 layers)
2. Pars Faccida ( in which the mille fibrous layer is deficient)
Landmarks of the TM:
Handle of Malleus (manubrium), Lateral Process of Malleus, Anterior & Posterior
Malleolar Folds, Light Reflex (cone of light).
NERVE SUPPLY OF EXTERNAL EAR:
1. Auriculo-temporal nerve (V3)
2. Greater Auricular (C2, 3)
3. Lesser Occipital (C2 )
4. Arnold`s nerve (X)
5. Facial nerve (sensory twigs)
BLOOD SUPPLY OF EXTERNAL EAR: branches of external carotid artery
Venous drainage: to posterior auricular & superficial temporal veins
Lymphatic drainage: to pre-auricular, infra-auricular & mastoid lymph nodes.
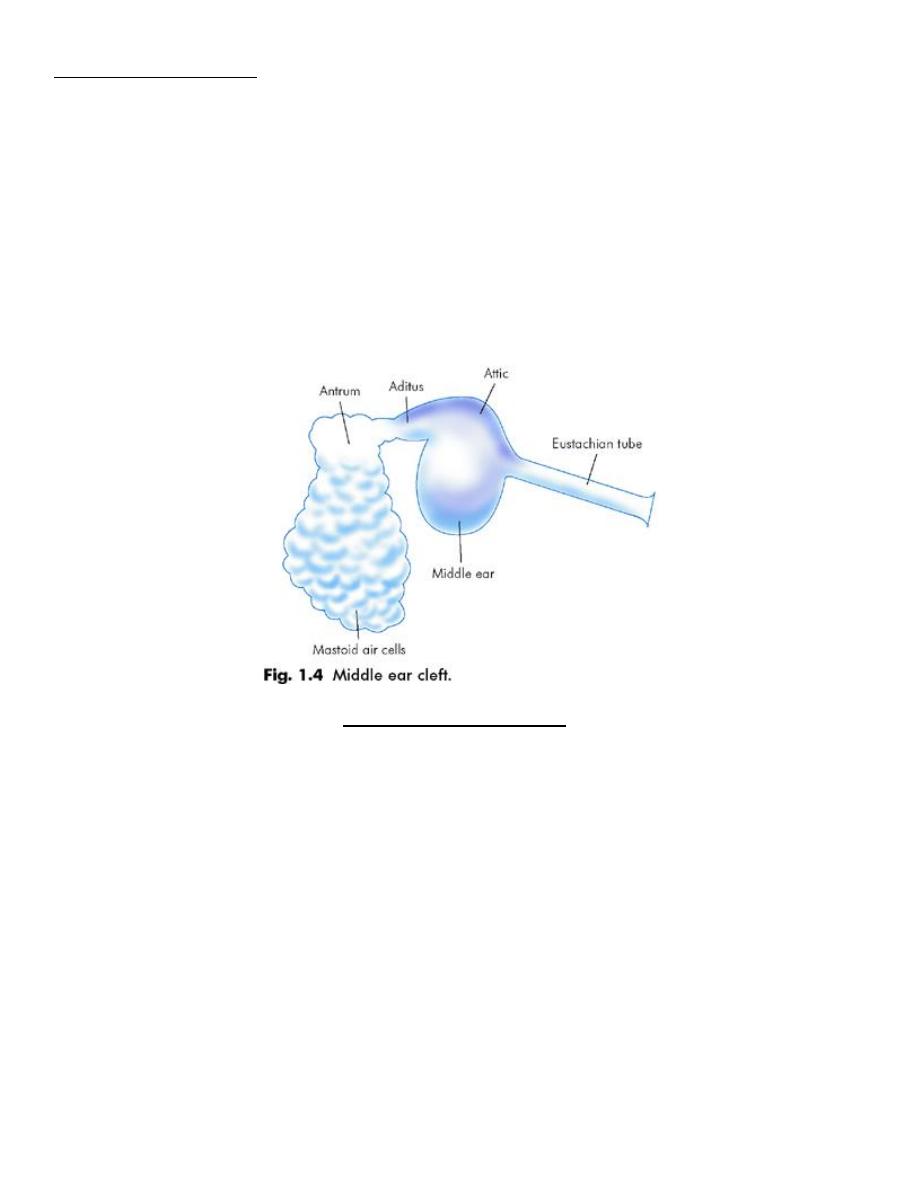
THE MIDDLE EAR CLEFT
Comprises of:
1. Middle Ear Proper
2. Aditus & Mastoid Antrum and Mastoid air cells
3. Eustachian Tube
Upper 1/3: Bony
Lower 2/3: Cartilaginous
THE MIDDLE EAR PROPER:
A box of 6 walls is an air-containing space with bony walls except laterally by TM.
Boundaries:
1. Lateral wall: TM
2. Medial wall: lateral semicircular canal (scc), oval window, promontory, and round
window.
3. Anterior wall: Eustachian tube & canal for tensor tympani muscle
4. Posterior wall: Aditus, pyramid
5. Superior (roof): separate from dura of the middle cranial fossa
6. Inferior (floor): separate from jugular bulb
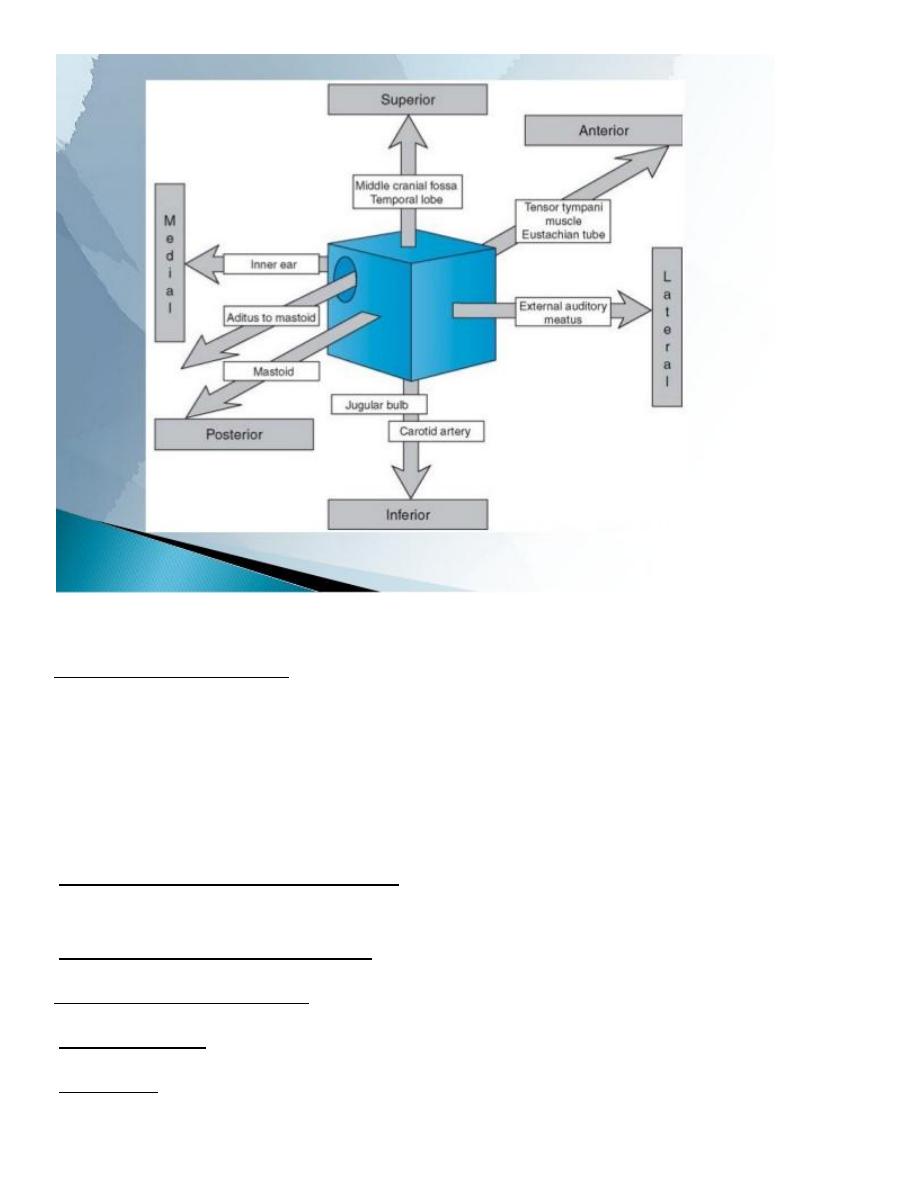
Contents of the Middle Ear:
1. Ossicles: Malleus, Incus and Stapes
2. Middle Ear Muscles: Stapedius( supplied by VII) and Tensor tympani muscles(supplied
by V)
3. Chorda Tympani Nerve
Sensory nerve supply of the middle ear: by Jocobson`s nerve, a branch of IX
(Glossopharyngeal nerve).
Motor supply of middle ear muscles: by V & VII cranial nerves.
Arterial supply of middle ear: from branches of external & internal carotid arteries.
Venous drainage: to pterygoid plexus or superior petrosal sinus.
Lymphatics: Eustachian tube to retropharyngeal lymph node.
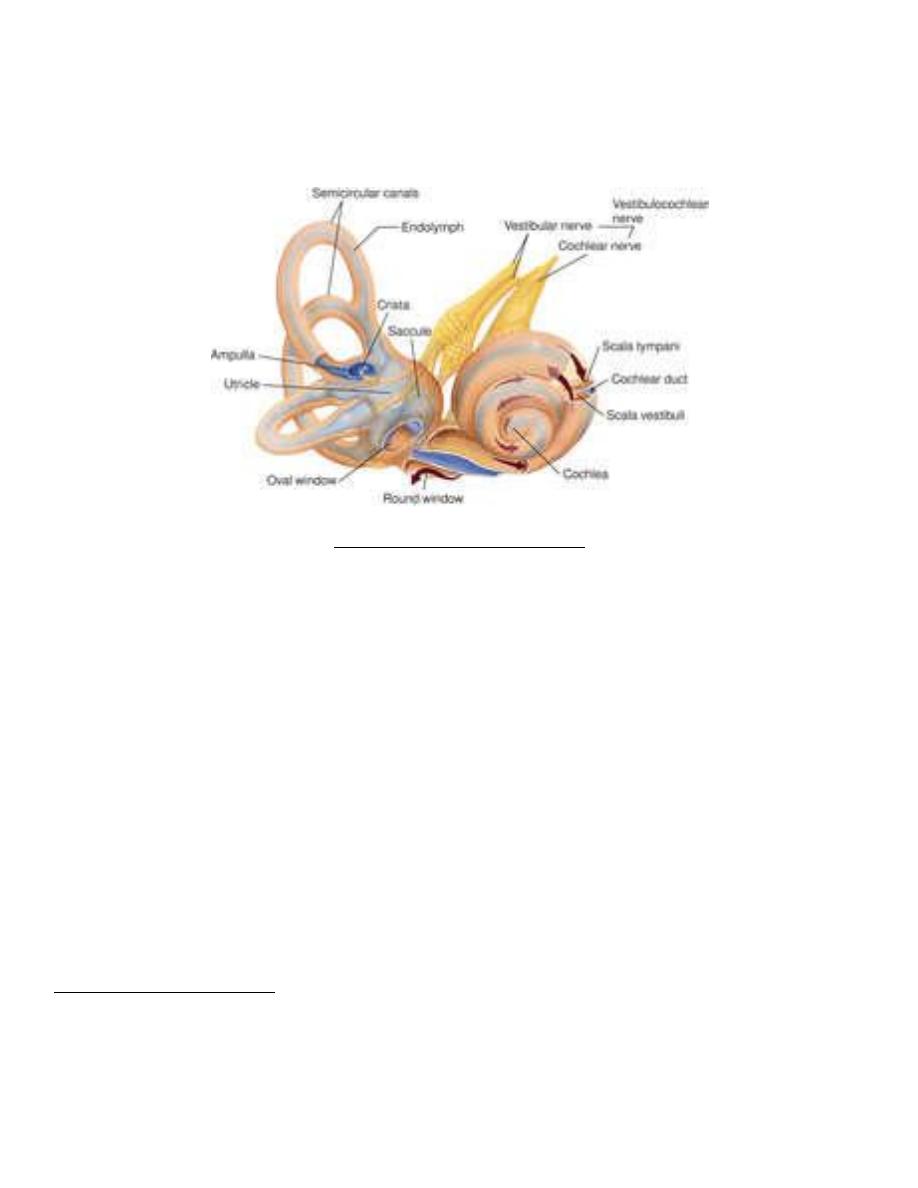
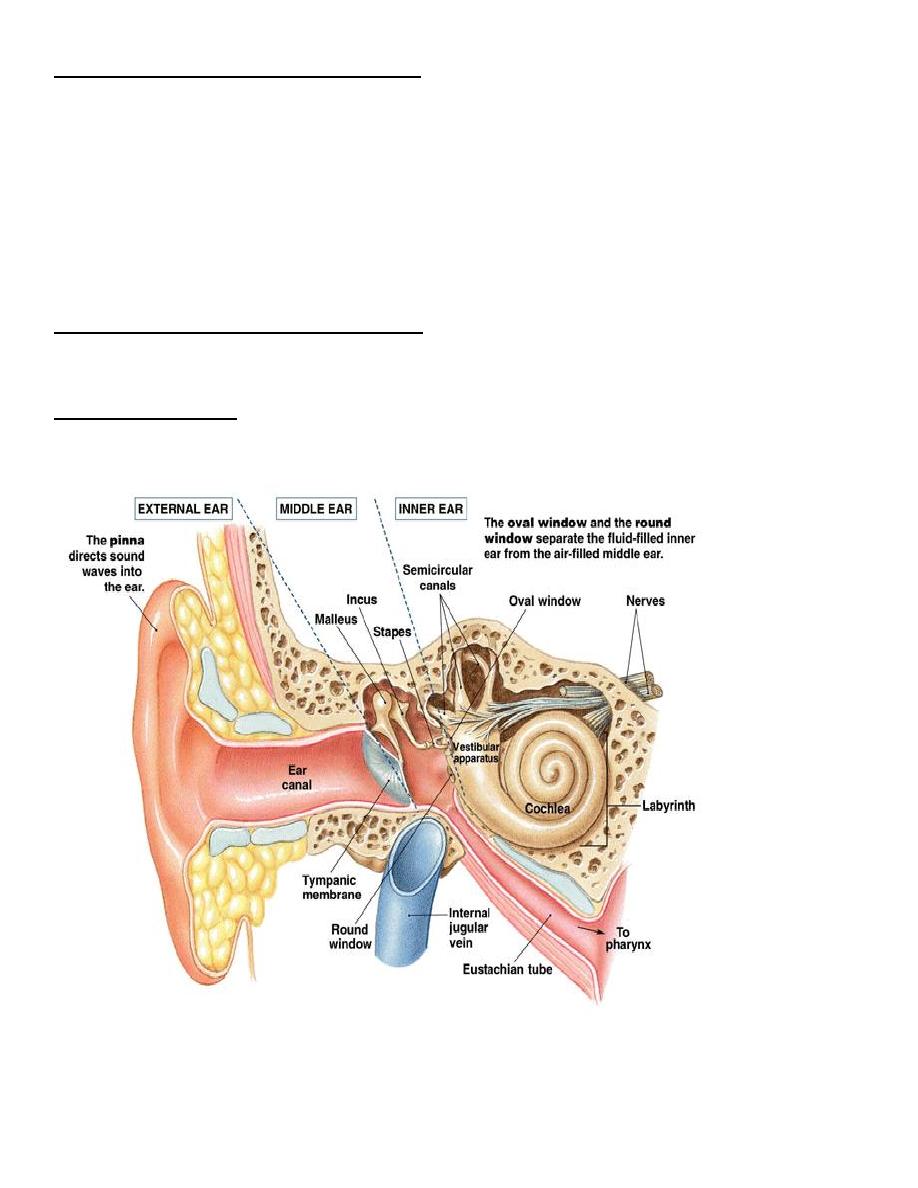
THE INNER EAR (LABYRINTH)
1. Bony Labyrinth (embedded in the Petrous Bone): comprises of
A. Vestibule consist of 3 semicircular canals and the utricle and the saccule
B. Cochlea consist of 2 and a half turns
2. Membranous Labyrinth: comprises of
A. Membranous SCCs ( Crista & Cupula )
B. Utricle & Saccule ( Macula & Otolithic Membrane)
C. Cochlear Duct – triangulal in cross section ( Organ of Corti )
D. Y-shaped Endolymphatic Duct & Sac
E. Ductus Reuniens
Blood Supply of inner ear: internal auditory artery, arise from anterior
Branches of the internal carotid artery
Inferior cerebellar artery
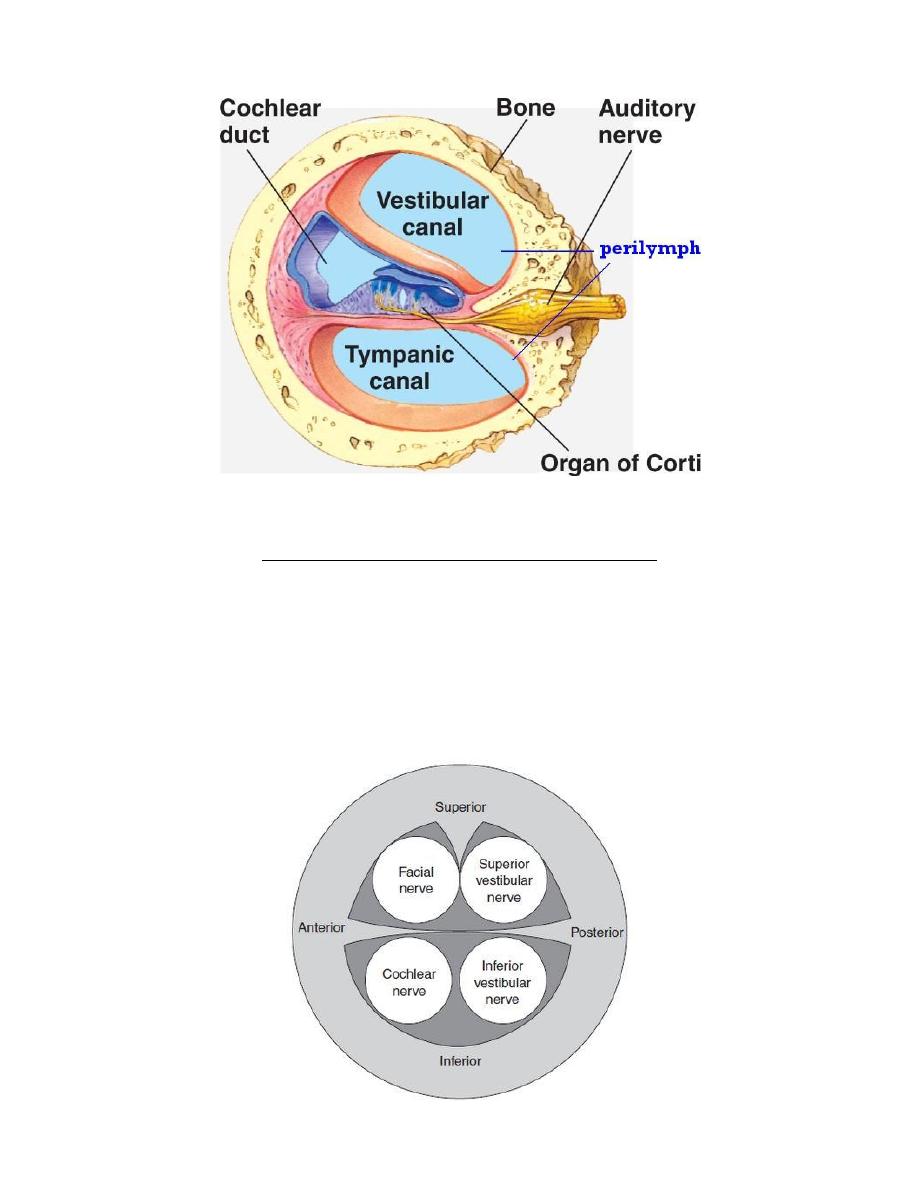
INTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL (IAC) CONTENTS
1. Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve:
Cochlear division and Vestibular division (superior and inferior branches)
2. Facial nerve.
