
Viral Skin Diseases
By
Dr. Salam Altemimi

Warts (verrucae)
• Warts are caused by human papillomaviruses
(HPVs).
• The HPVs infect the keratinocytes.
• There are several clinical forms.
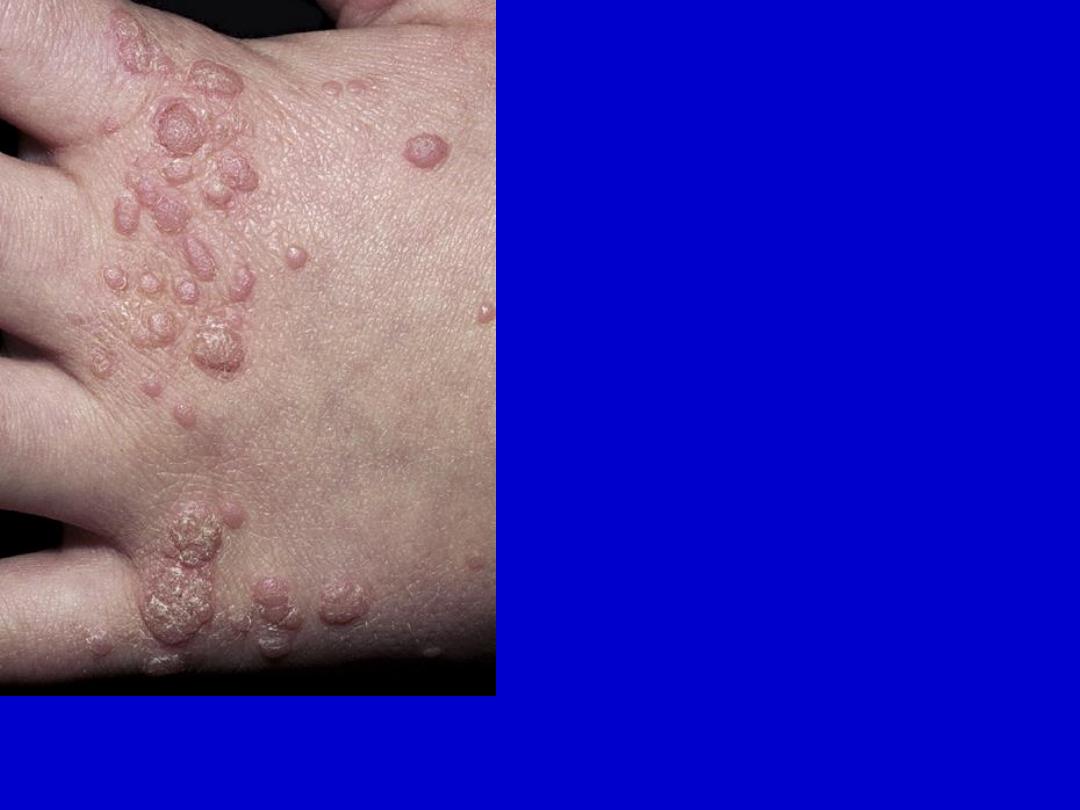
Common warts on the back of the hand. They are dome-shaped, gray-
brown, hyperkeratotic papules with black dots on the surface.
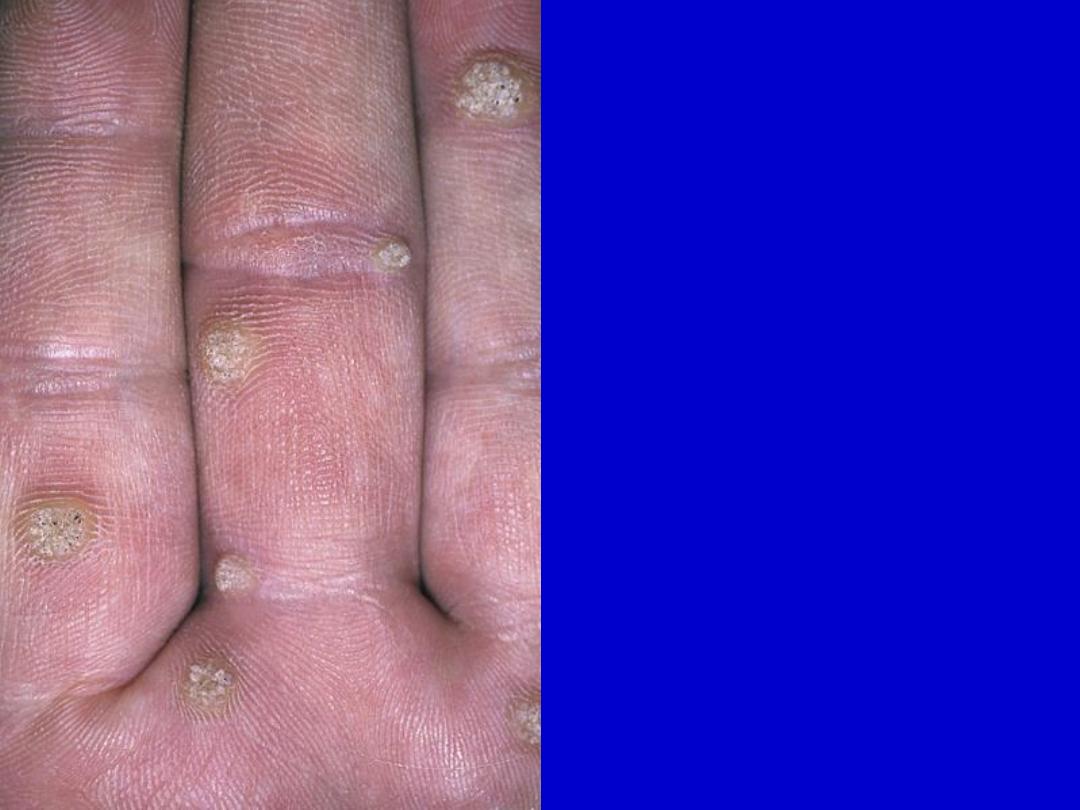
common warts on the palm
with black dots on their
surface.

Treatment options of common warts:
• Topical salicylic acid preparations.
• Liquid nitrogen cryotherapy.
• Very light electrocautery.
• Blunt dissection for resistant or very large
lesions.
• Imiquimod 5% cream.
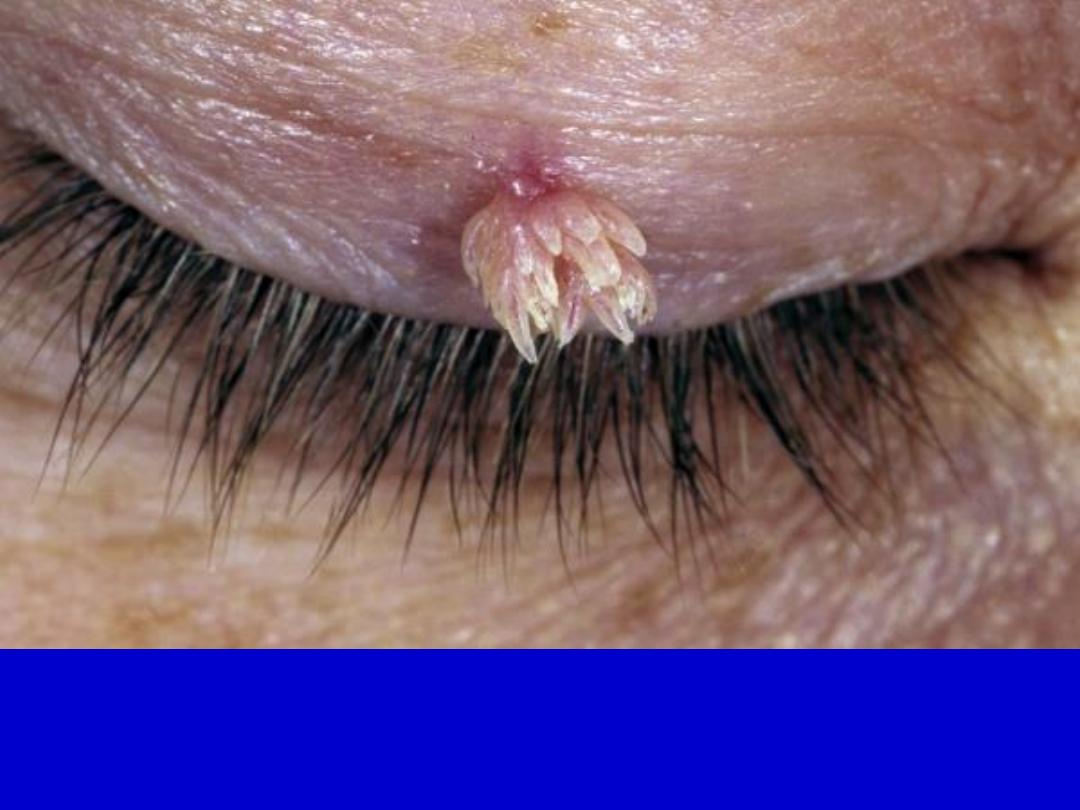
Filiform wart with fingerlike projections. These are most commonly
observed on the face.

Treatment options of filiform warts:
• Curettage.
• Light electrocautery.
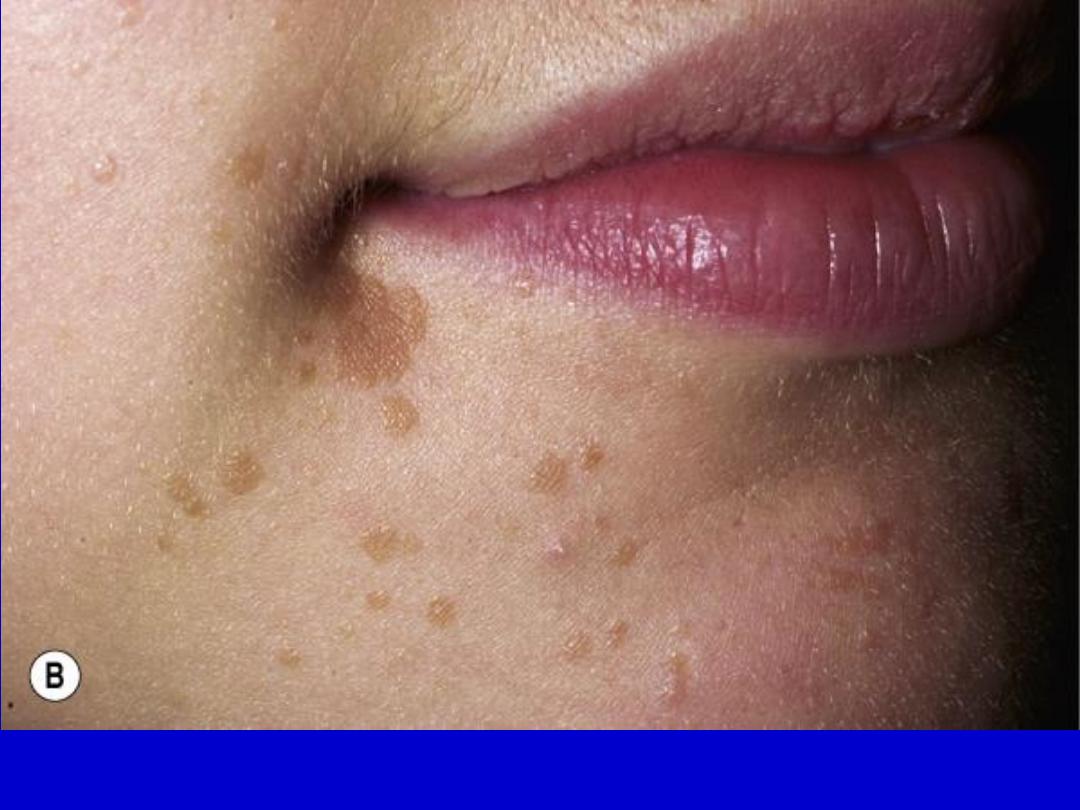
Flat warts (verruca plana) are light brown and slightly elevated, flat-topped
papules that vary in size from 0.1 to 0.5 cm.

Treatment options of flat warts:
• Imiquimod 5% cream.
• Cryotherapy.
• Light touch electrocautery.
• 5-fluorouracil cream.
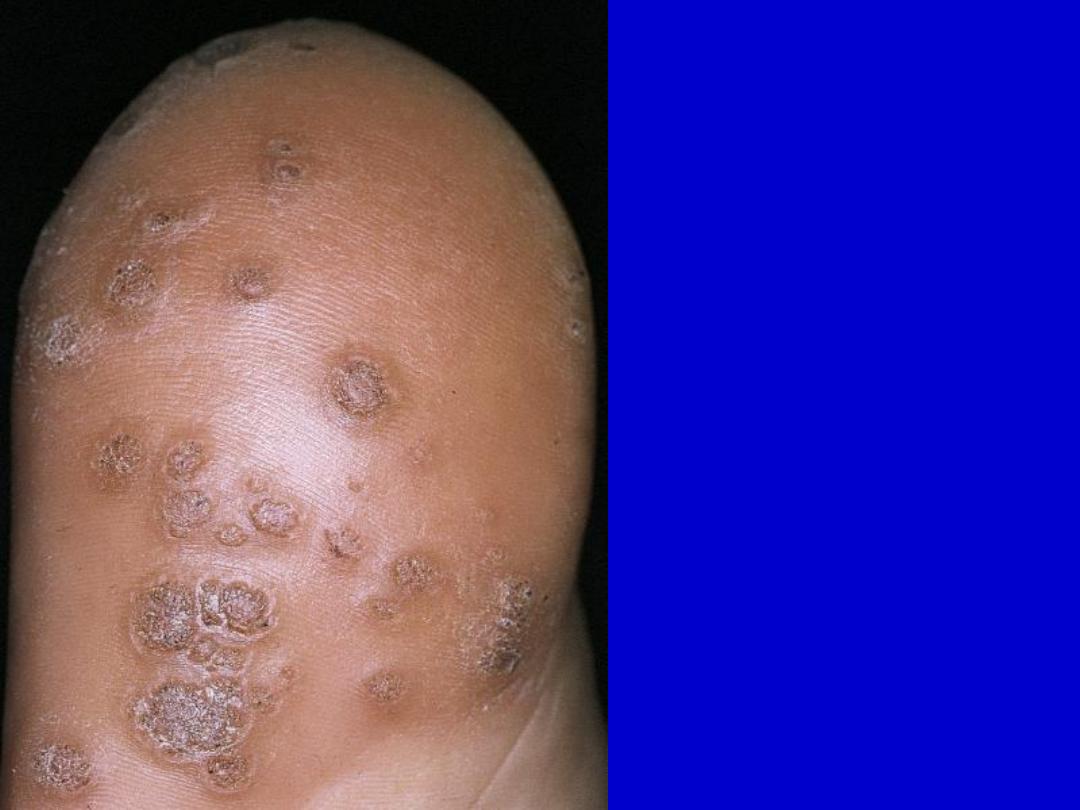
Plantar warts. Warts on
weight-bearing surfaces
accumulate callus and may
become painful.
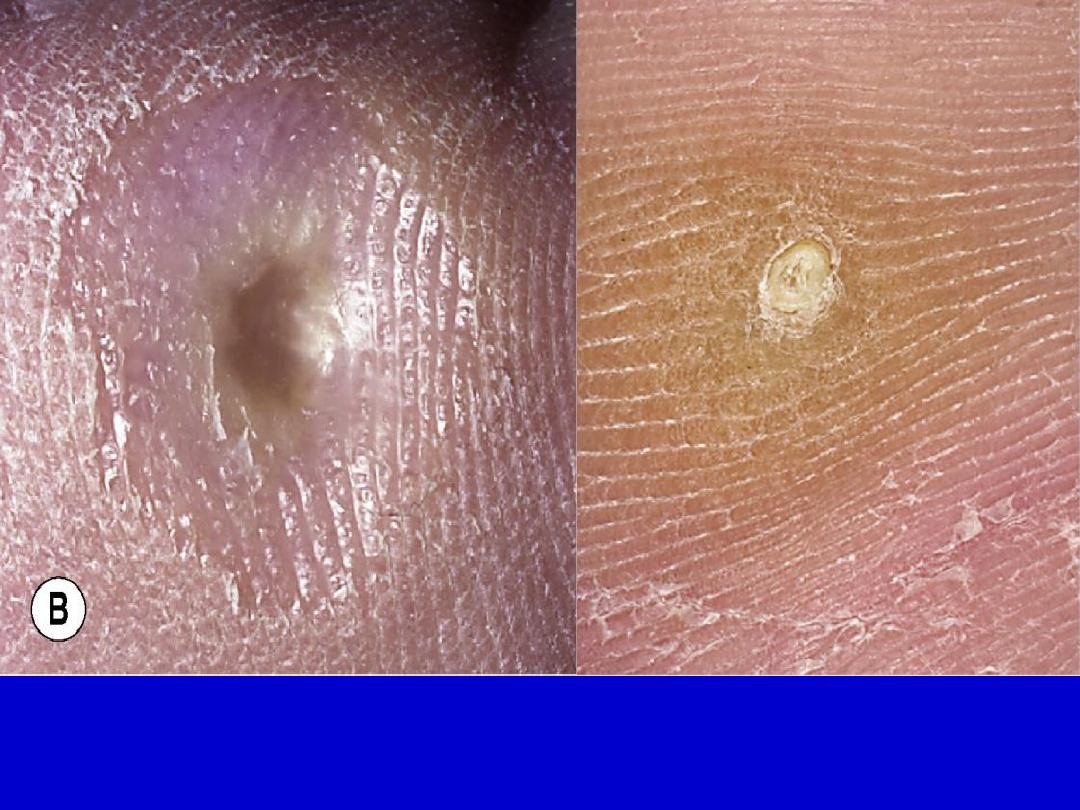
Corns. By paring, translucent white central core is revealed. While
paring a wart lead to bleeding.

Treatment options of planter warts
• Salicylic acid 40% plasters.
• Imiquimod 5% cream.
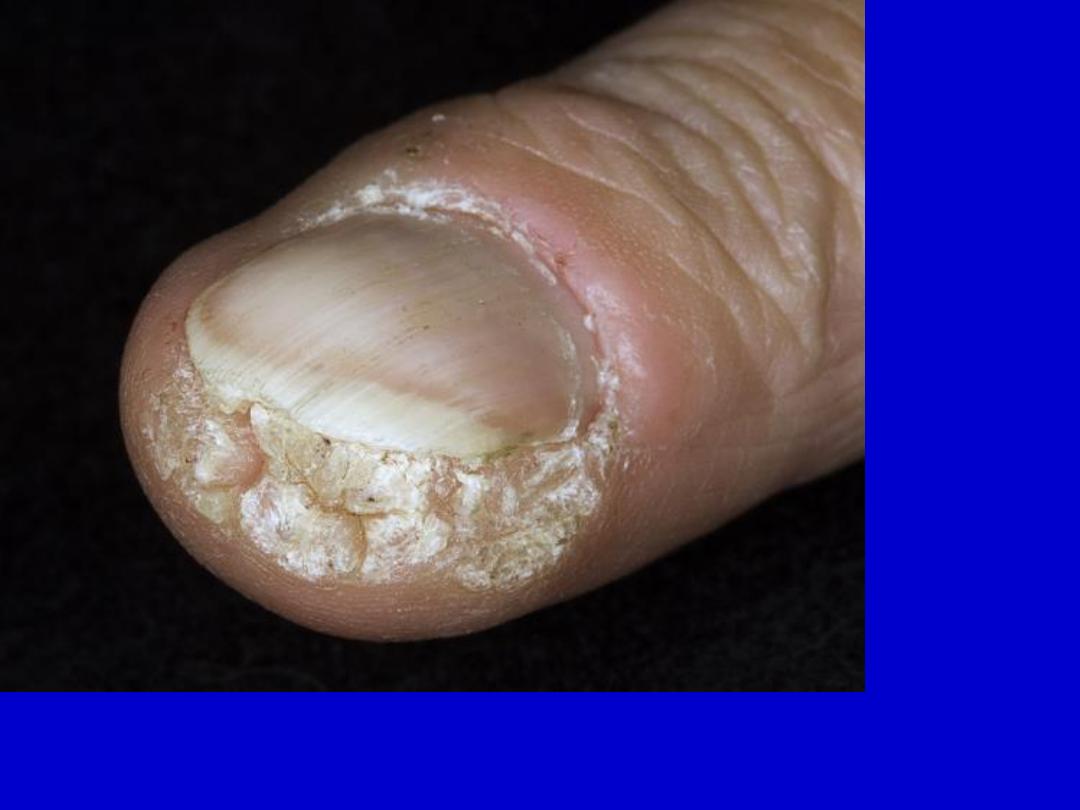
Periungual warts may extend deep under the nail.

Treatment options for periungual warts
• Salicylic acid plasters application.
• Blunt dissection.
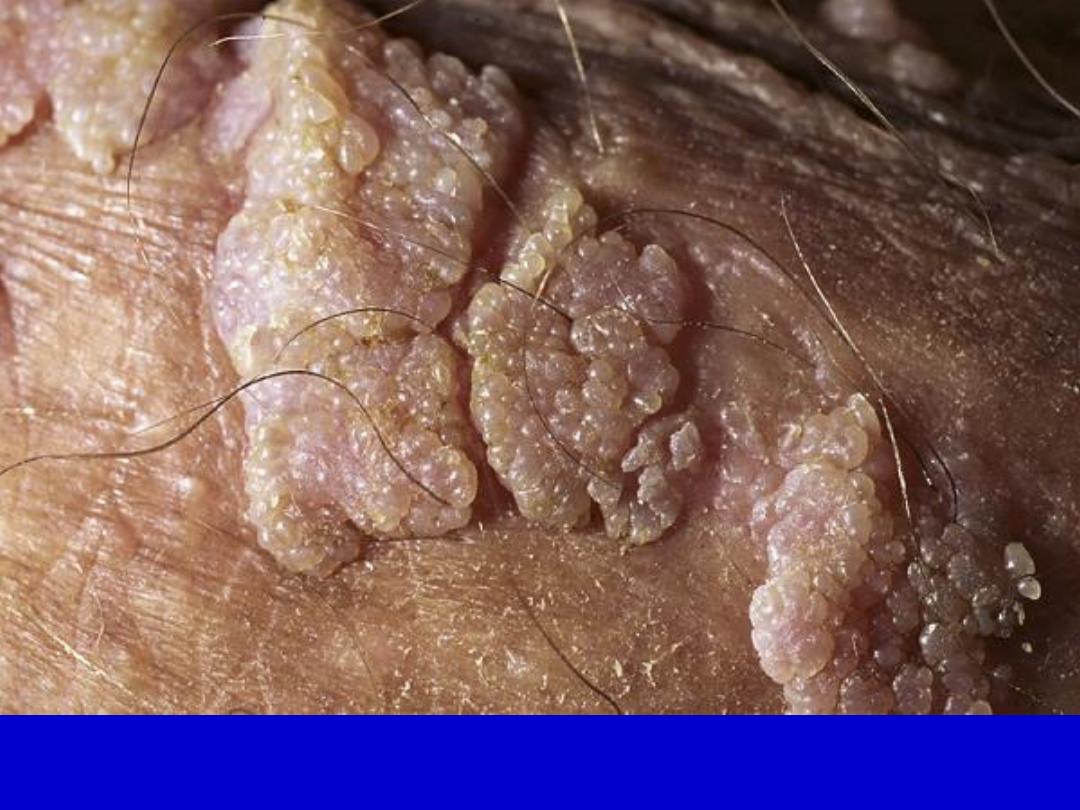
Genital warts (condylomata acuminata). Warts on the shaft of the penis have a
papillomatous surface or projections and a very broad base.
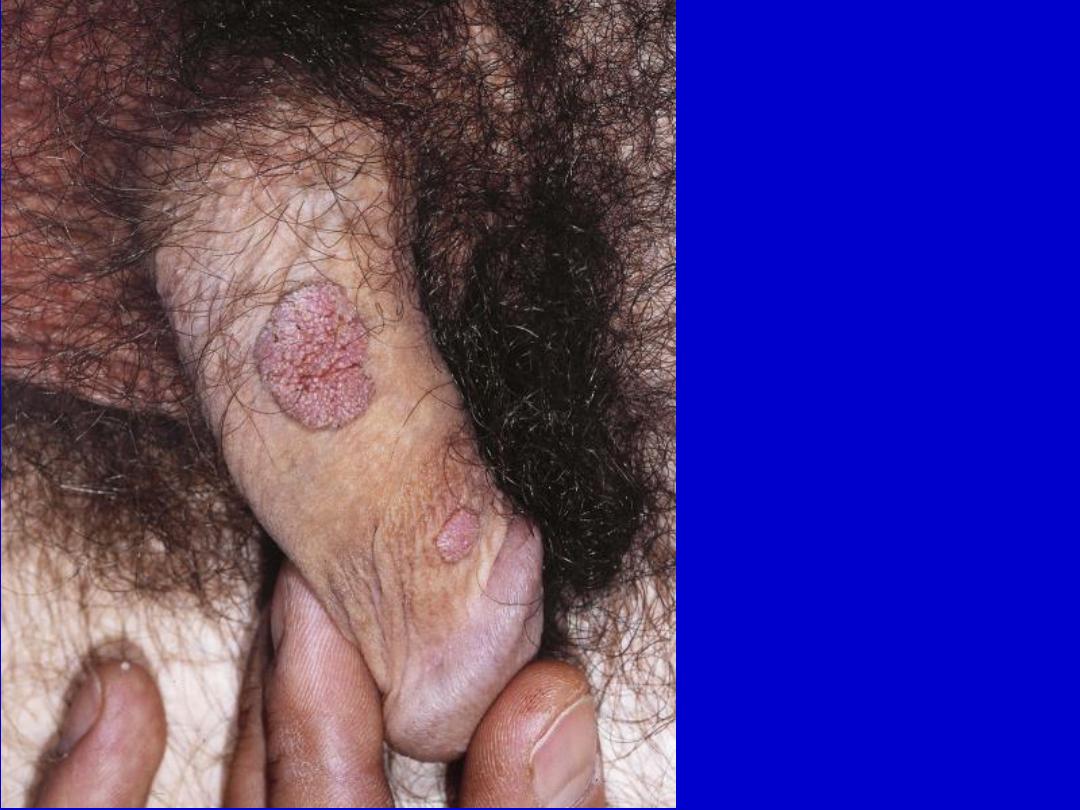
Genital warts. Broad-
based wart on the shaft
of a penis. There are
numerous projections on
the surface.

Treatment options for genital warts:
• Light electrodesiccation.
• Cryotherapy.
• Scissor excision.
• Imiquimod 5% cream.
• Podophyllotoxin gel.
• Trichloroacetic acid solution.
• 5-fluorouracil cream.

Herpes simplex
• Skin infection caused by herpes simplex virus
(HSV).
• HSV infections have two phases: the primary
infection, after which the virus becomes
established in a nerve ganglion; and the secondary
phase, characterized by recurrent disease at the
same site.
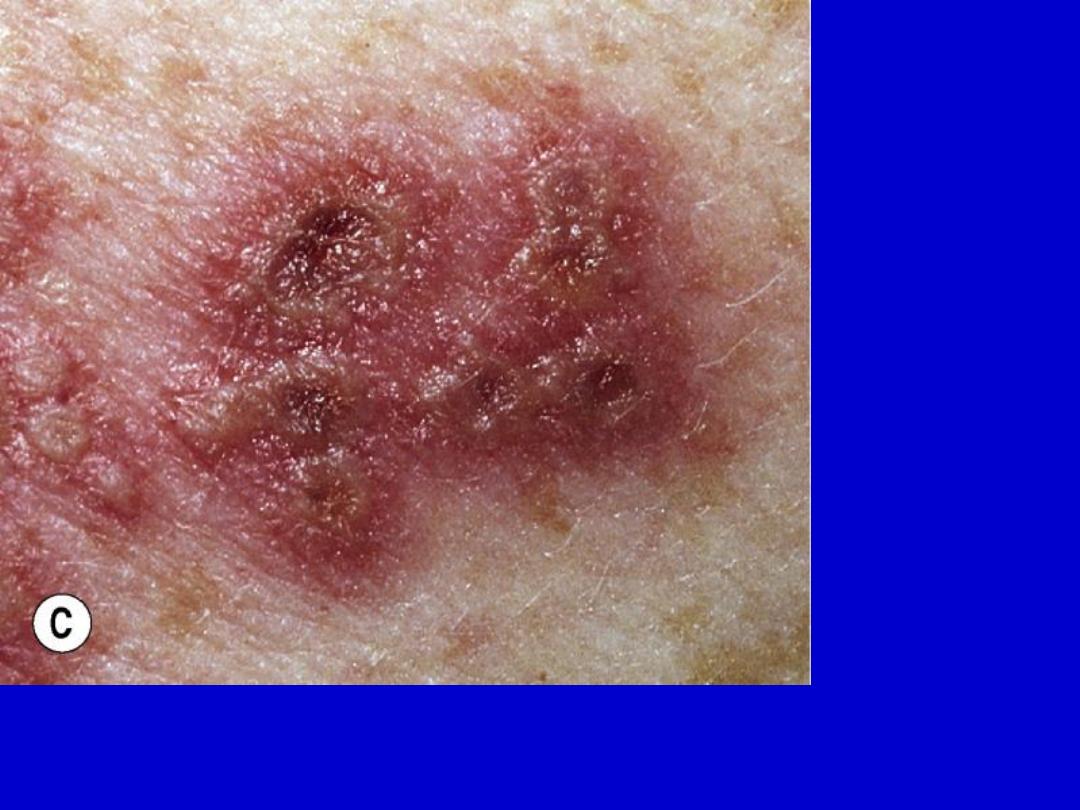
Primary herpes simplex. Vesicles on a red base are the primary lesions. Vesicles
evolve to pustules and become umbilicated. Then, lesions dry and form
discrete crusts.
Vesiculation
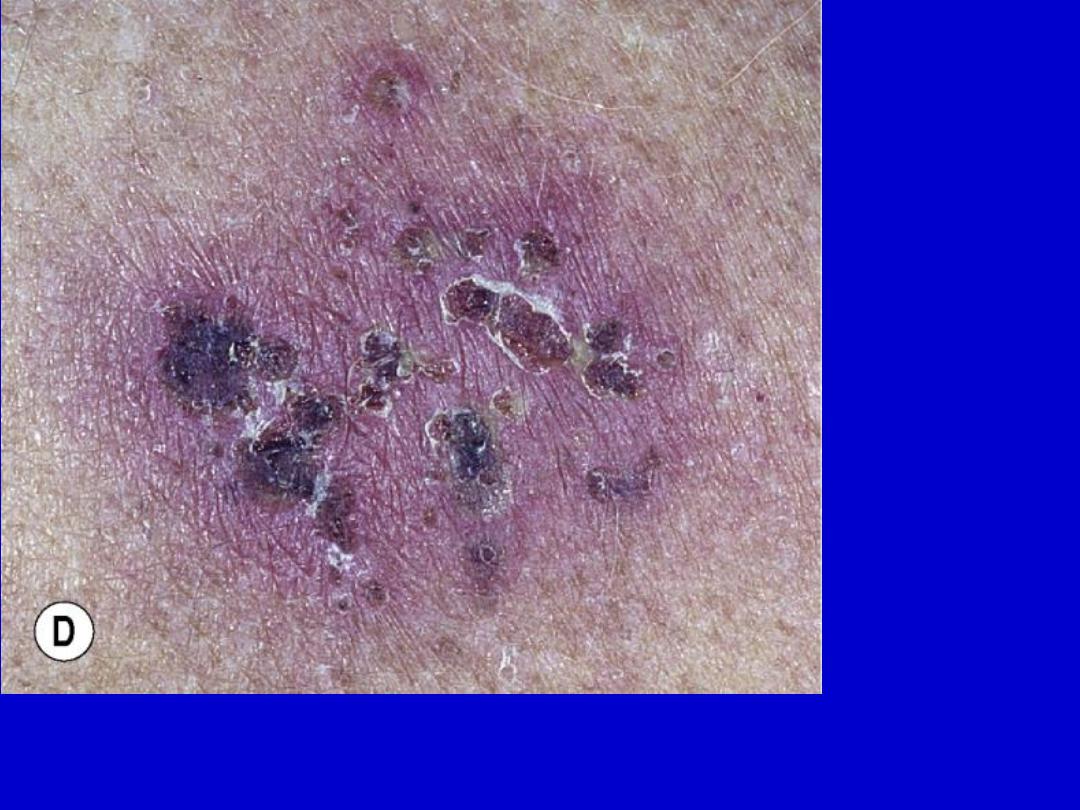
Primary herpes simplex. Vesicles on a red base are the primary lesions. Vesicles
evolve to pustules and become umbilicated. Then, lesions dry and form
discrete crusts.
Crustation
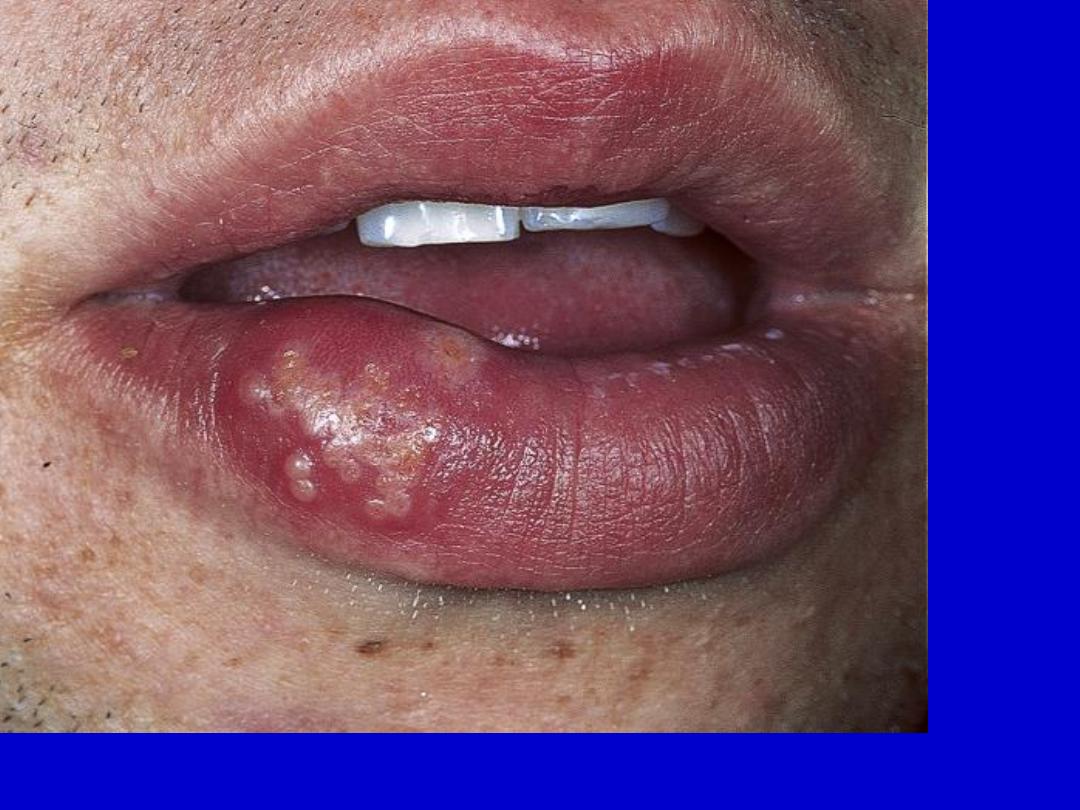
Herpes simplex. A small group of vesicles on an erythematous base are the
initial lesion.
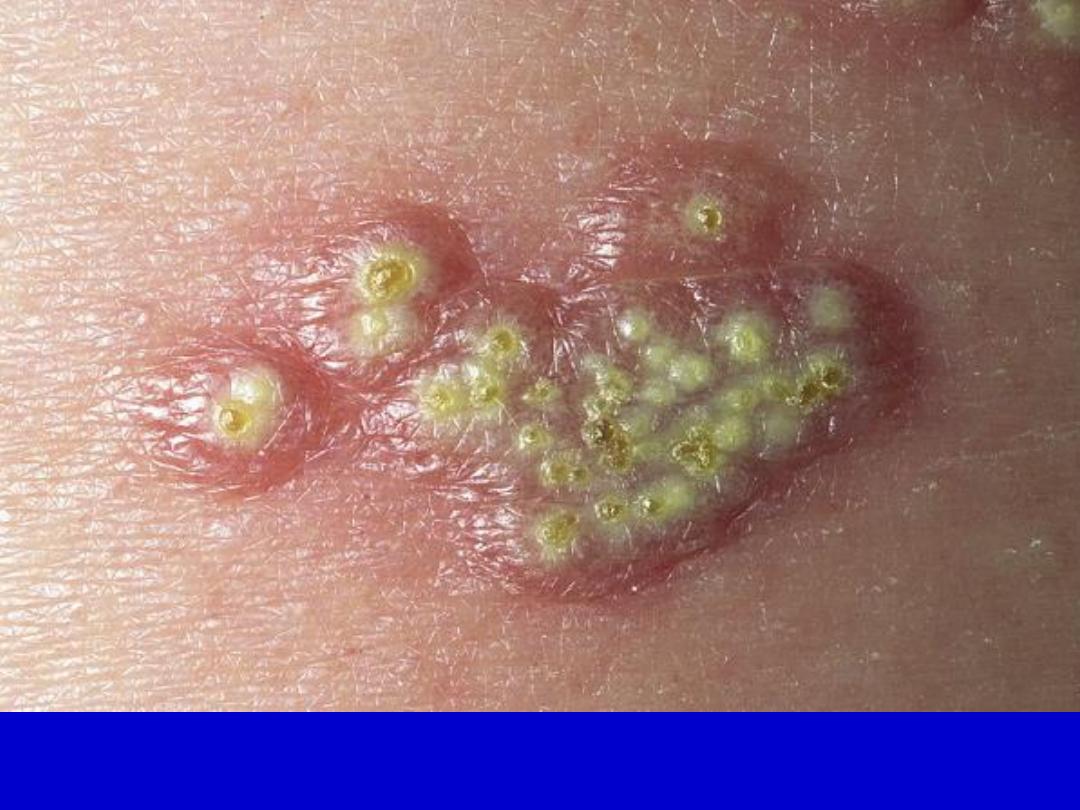
Herpes simplex. The recurrent lesion is a small group of vesicles that, like
primary lesions, evolve to form umbilicated pustules and then crusts.

Treatment of primary and recurrent herpes
simplex is acyclovir 400mg three times daily for
10 days.

Clinical forms of herpes simplex
• Oral labial herpes simplex
• Cutaneous herpes simplex
• Herpetic whitlow
• Eczema herpeticum
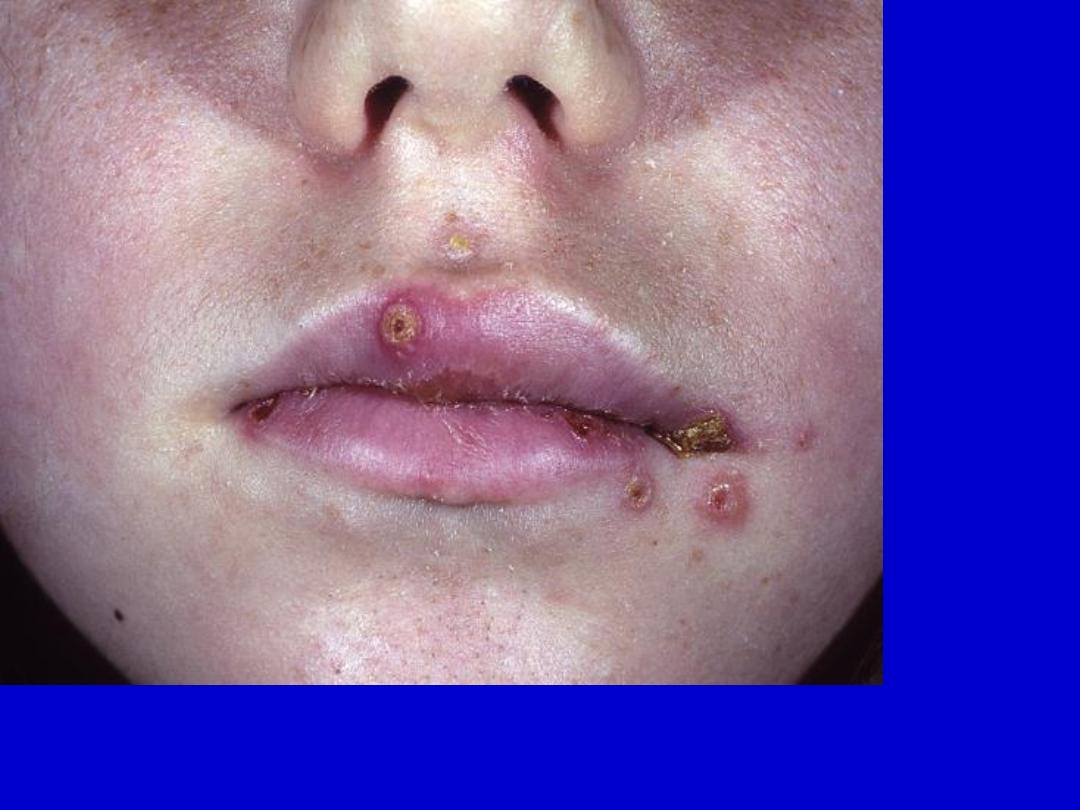
Oral labial herpes simplex (primary infection). The mouth is inflamed, umbilicated
vesicles are widely scattered about the perioral area. Lesions are not grouped as in
recurrent herpes. The patient is febrile.
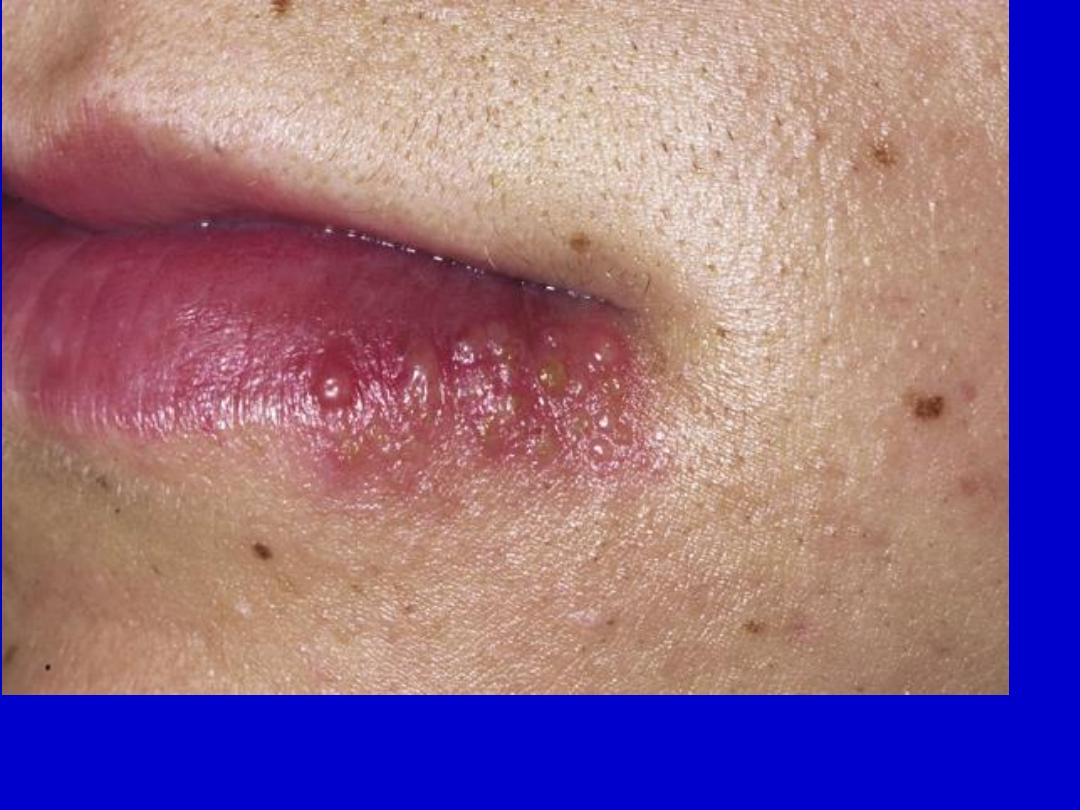
Recurrent herpes labialis. Begins with a prodrome of itching or burning. A
group of vesicles appears on an erythematous base. Previous episodes in the
same area are typical.
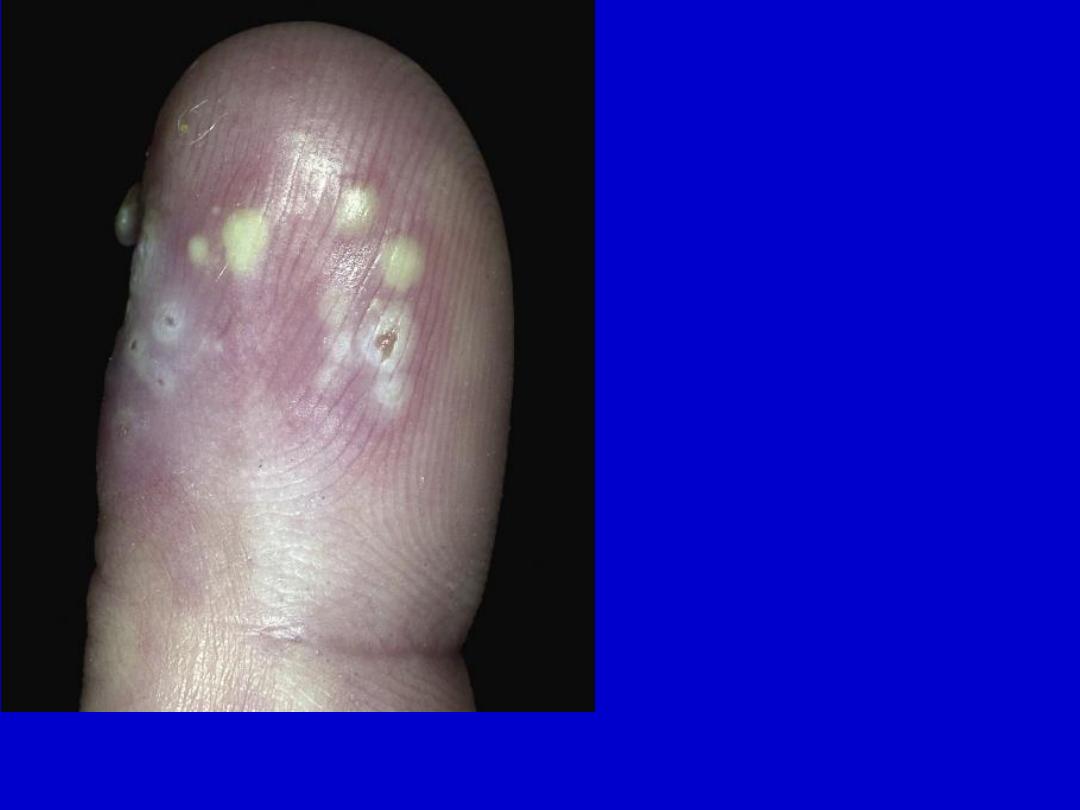
Herpetic whitlow. Grouped pustules may be diagnosed as a bacterial
infection. Recurrence at the same location was the clue to the diagnosis.
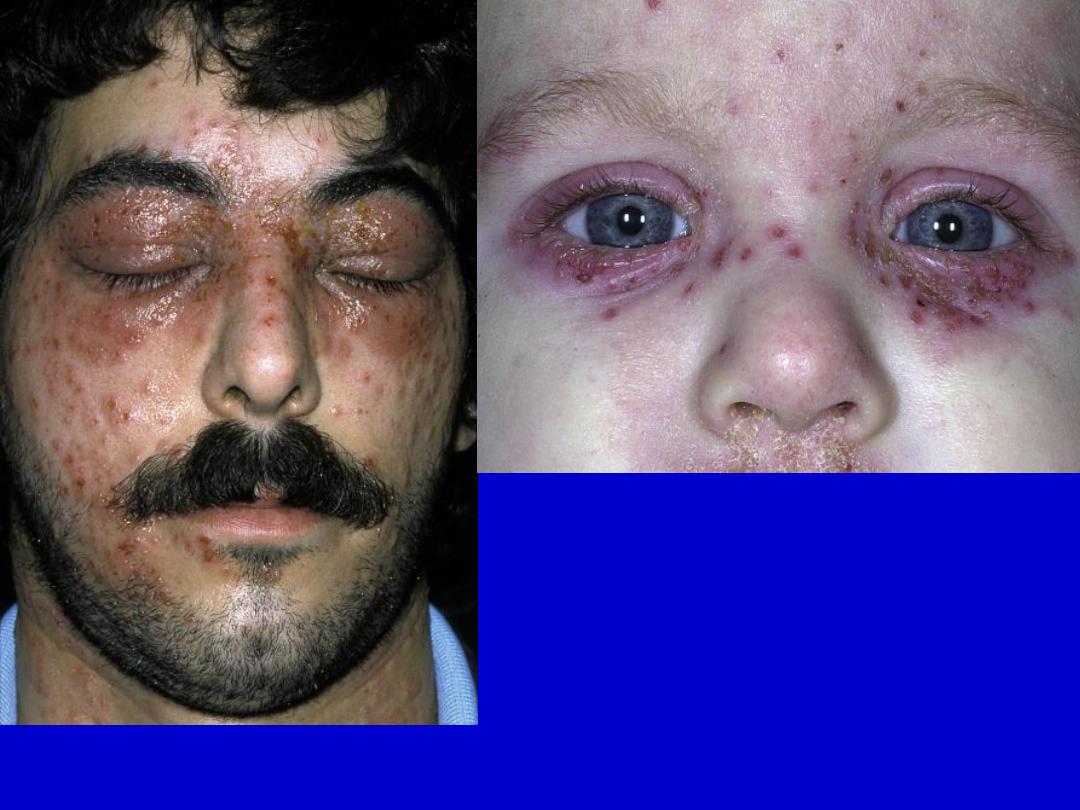
Eczema herpeticum. Numerous lesions spread over the face in these
patients with active atopic dermatitis.

Treatment: Eczema herpeticum of the young infant is
a medical emergency, treated by acyclovir 5-10mg/kg
8 hourly IV. In adult, acyclovir 800mg 3 times daily for
10 days.
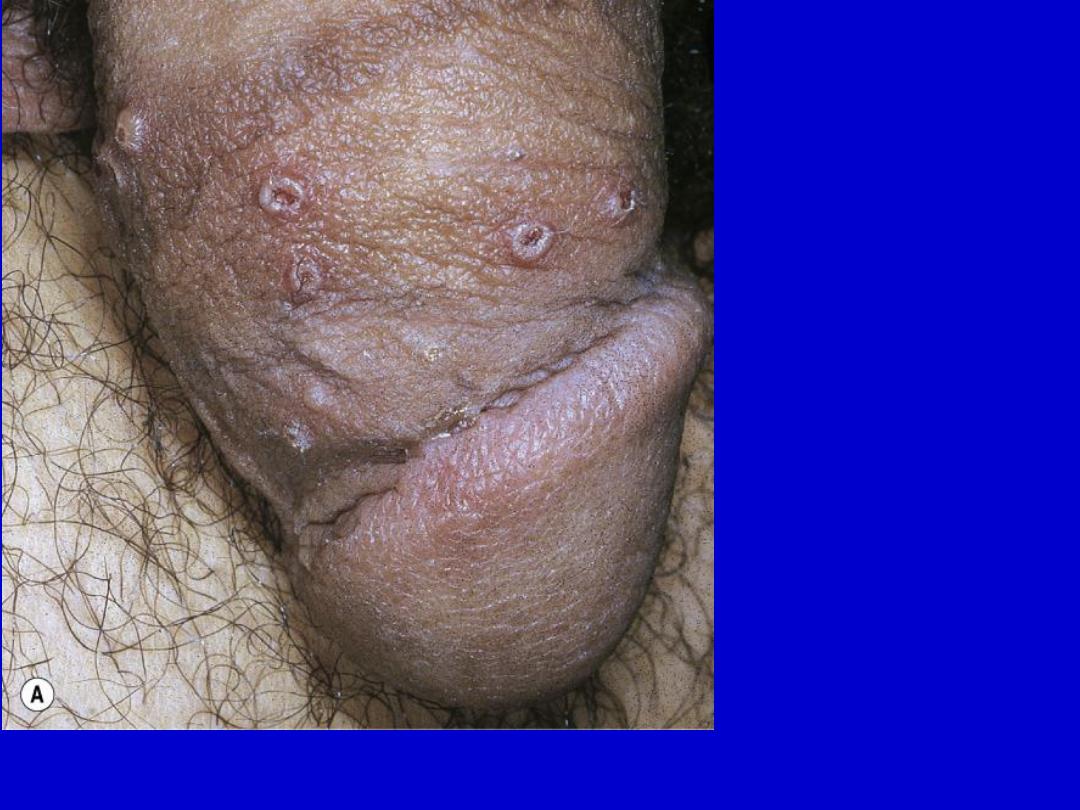
Genital herpes simplex. The primary lesion is a vesicle that rapidly becomes
umbilicated. They are discrete.
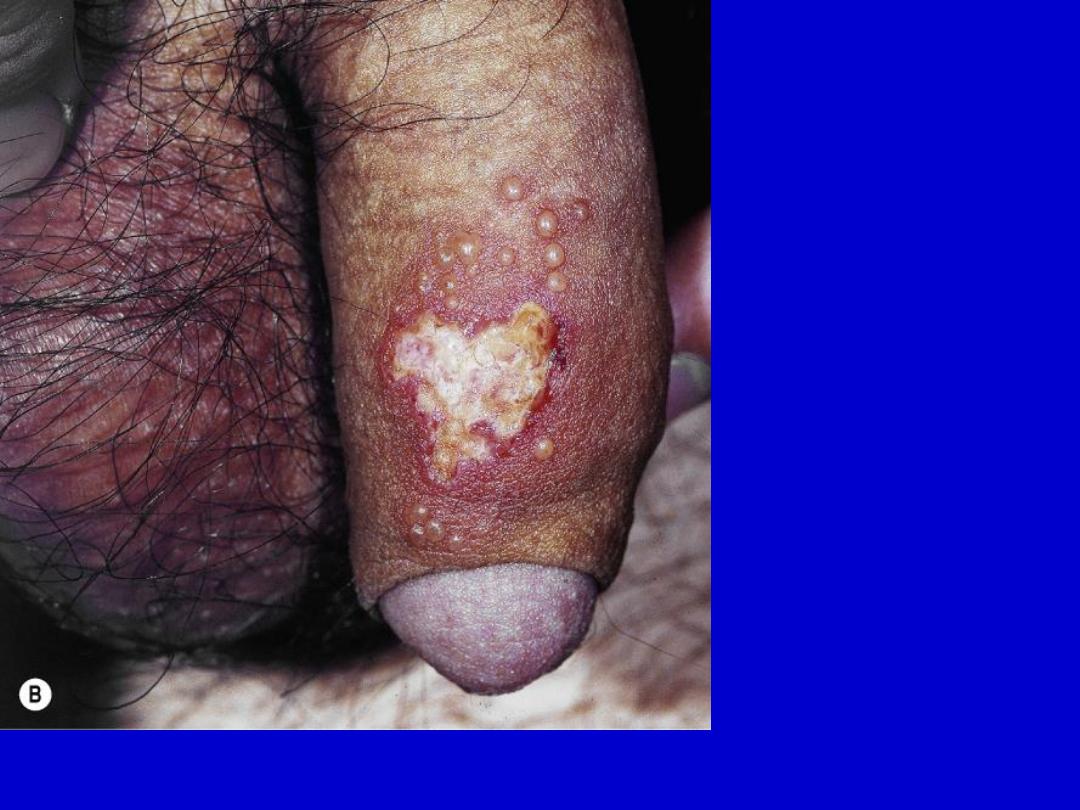
Genital herpes simplex. A group of vesicles has ruptured, leaving an erosion.
Tense vesicles are at the periphery.
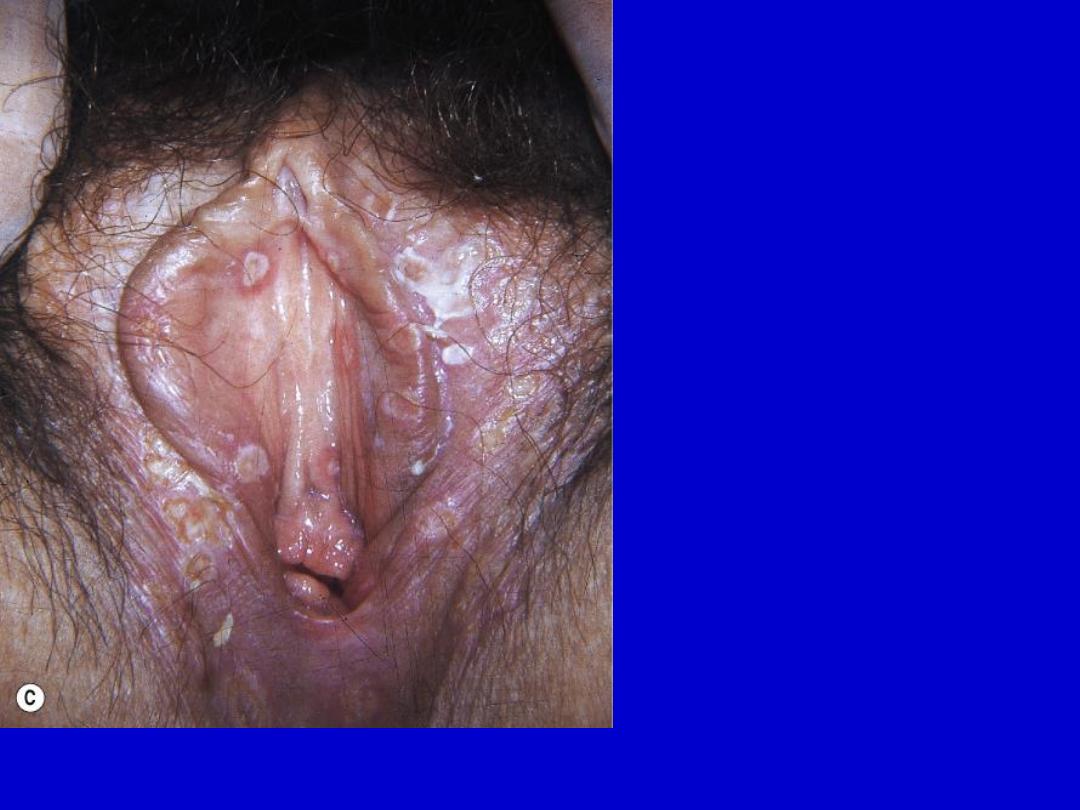
Genital herpes simplex. Scattered erosions covered with exudate.

Treatment of genital herpes simplex:
Acyclovir 400mg 3 times daily for 10 days.
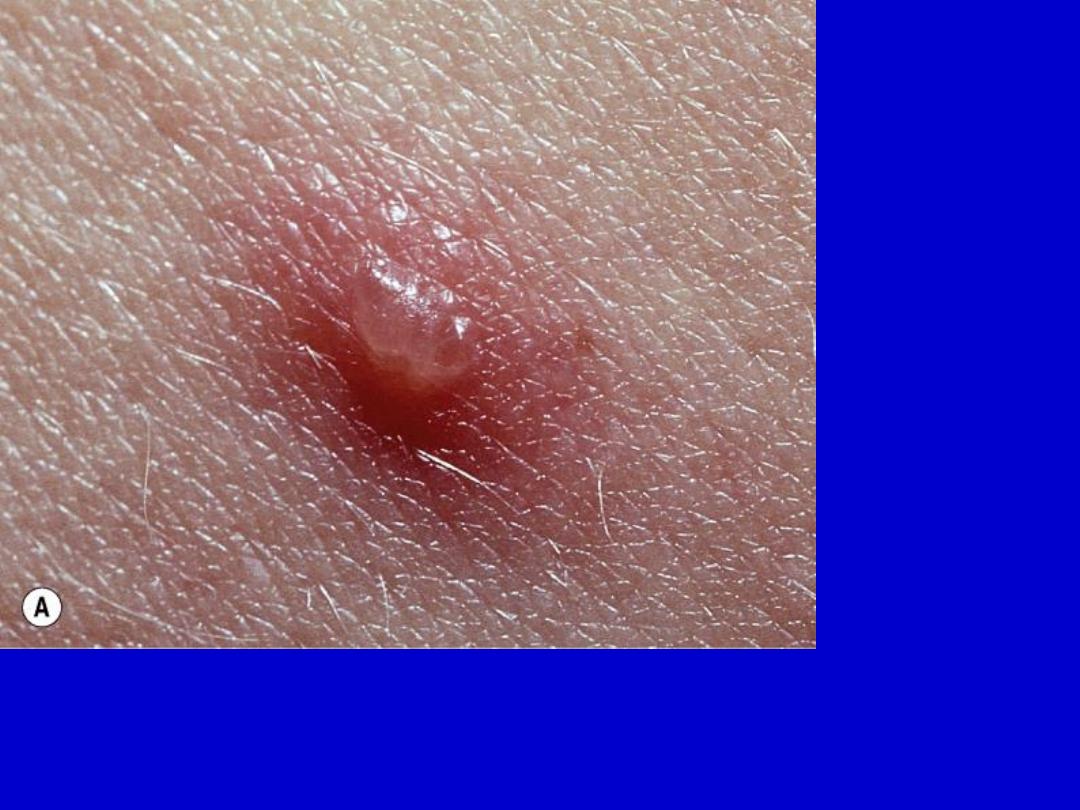
Chickenpox. A. Dewdrop on a rose petal”; a think-walled vesicle with clear
fluid forms on a red base. B. The vesicle becomes cloudy and depressed in the
center (umbilicated), the border is irregular (scalloped). C. A crust forms in the
center and eventually replaces the remaining portion of the vesicle at the
periphery.
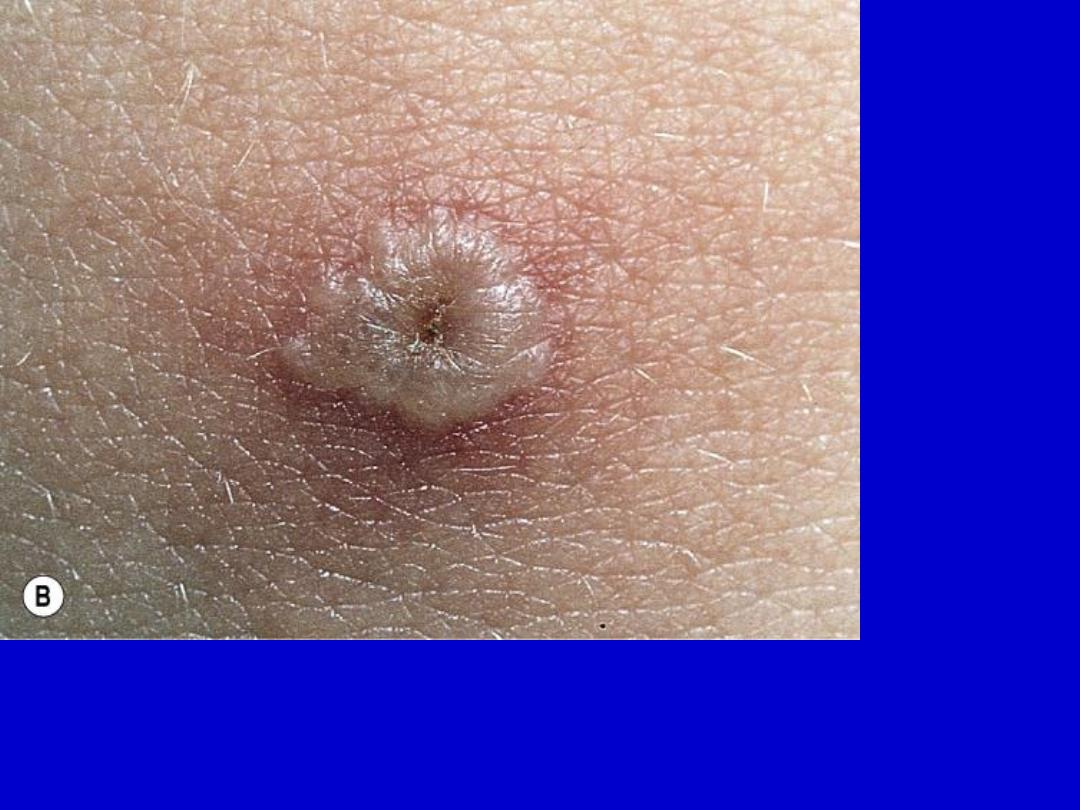
Chickenpox. Dewdrop on a rose petal”; a think-walled vesicle with clear fluid
forms on a red base. B. The vesicle becomes cloudy and depressed in the
center (umbilicated), the border is irregular (scalloped). C. A crust forms in the
center and eventually replaces the remaining portion of the vesicle at the
periphery.
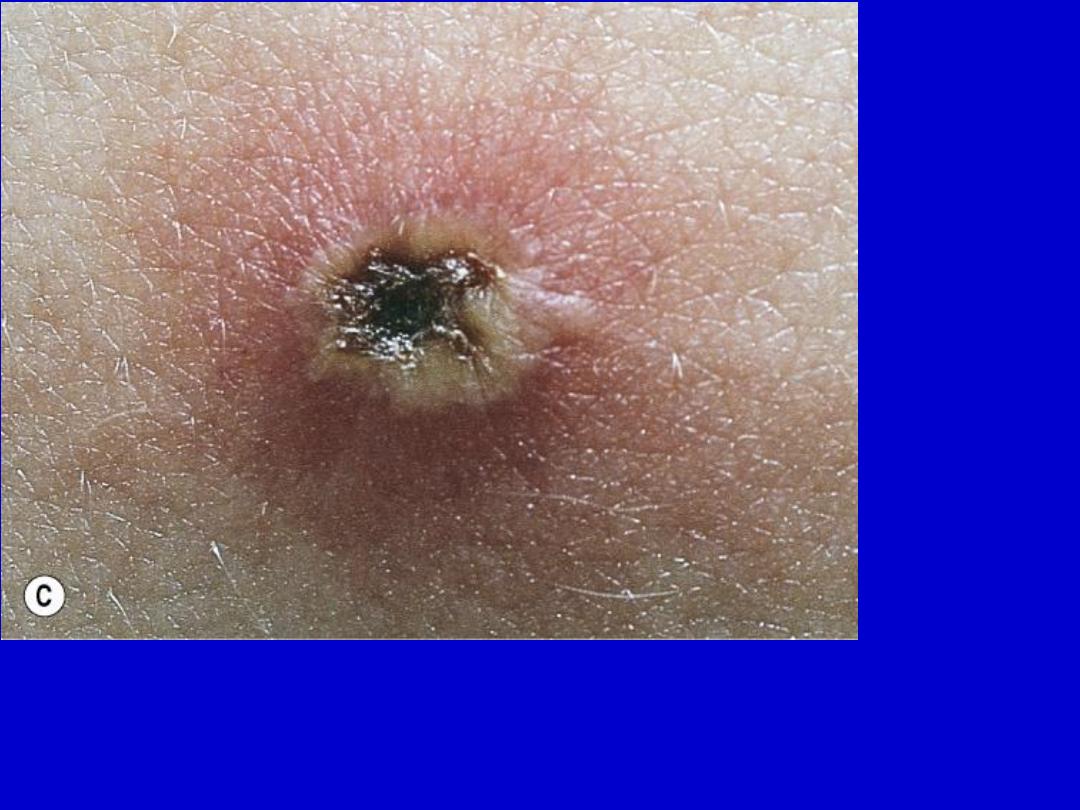
Chickenpox. A. Dewdrop on a rose petal”; a think-walled vesicle with clear fluid
forms on a red base. B. The vesicle becomes cloudy and depressed in the
center (umbilicated), the border is irregular (scalloped). C. A crust forms in the
center and eventually replaces the remaining portion of the vesicle at the
periphery.
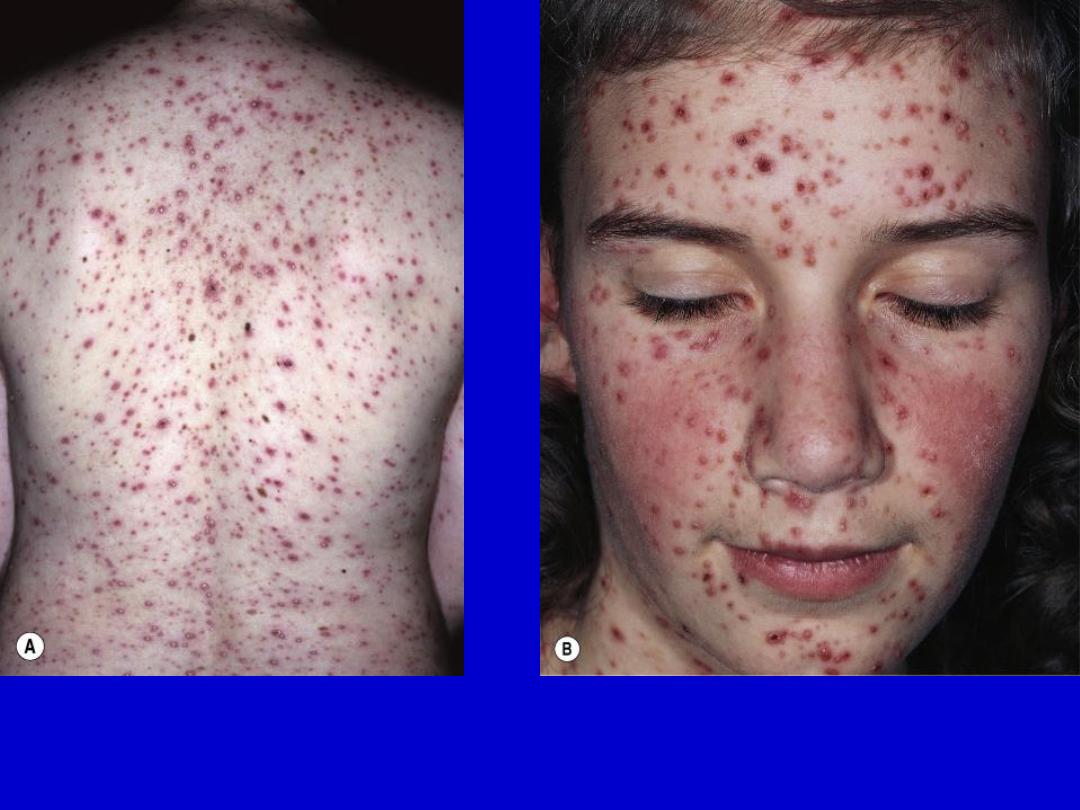
Chickenpox. The disease starts with lesions on the trunk (centripetal
distribution) and then spreads to the face and extremities (centrifugal spread).

The complication of varicella are
• Secondary bacterial infection.
• Encephalitis.
• Reye’s syndrome
• Pneumonia.

Treatment of chickenpox.
• Antipyretic like paracetamol (excluding aspirin
because of its association with Reye’s syndrome).
• Antihistamines like hydroxyzine may help control
excoriation.
• Oral antibiotic active against Streptococcus and
Staphylococcus like cephalexin is indicated for
secondarily infected lesions.
• Adult chickenpox, in addition to above, should be
treated with oral acyclovir 800mg 5 times daily for
7 days.

Herpes zoster
It is caused by varicella-zoster virus.
It is a reactivation process.
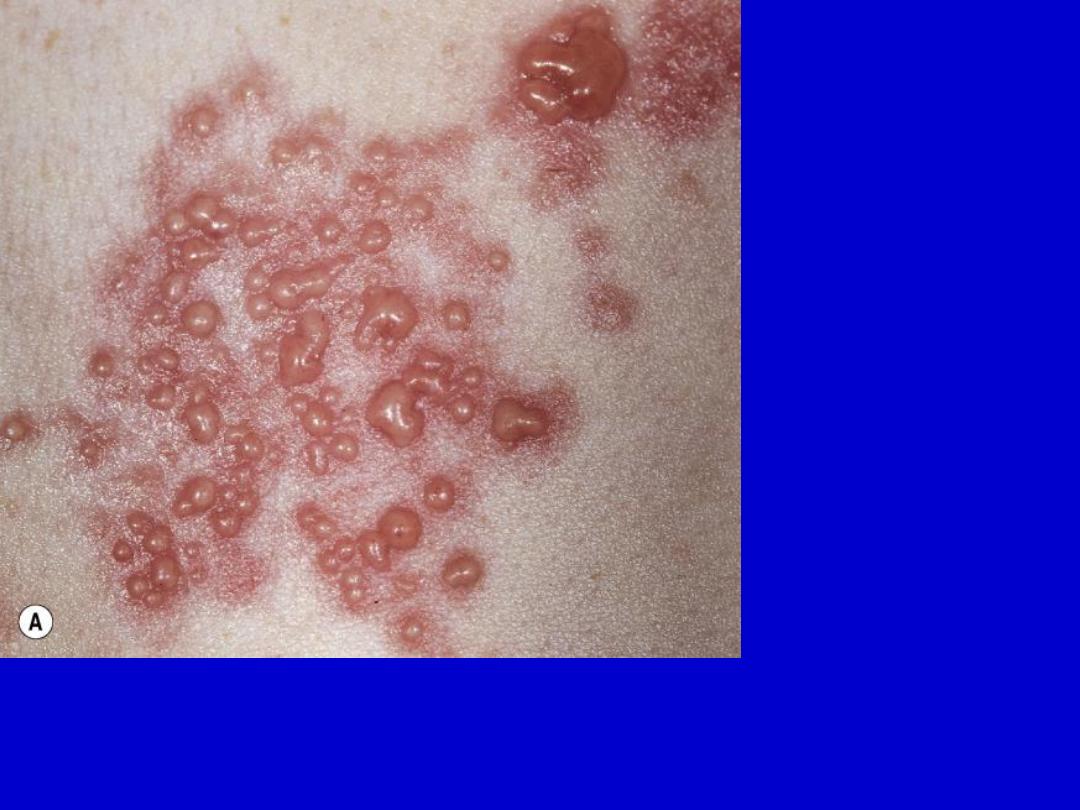
Herpes zoster. A group of vesicles that vary in size. Vesicles of herpes simplex
are of uniform size. Vesicles become umbilicated and then form crusts.
Confluent groups of vesicles in a highly inflamed case. Vesicles evolve to crusts
and may eventually scar if inflammation is intense.
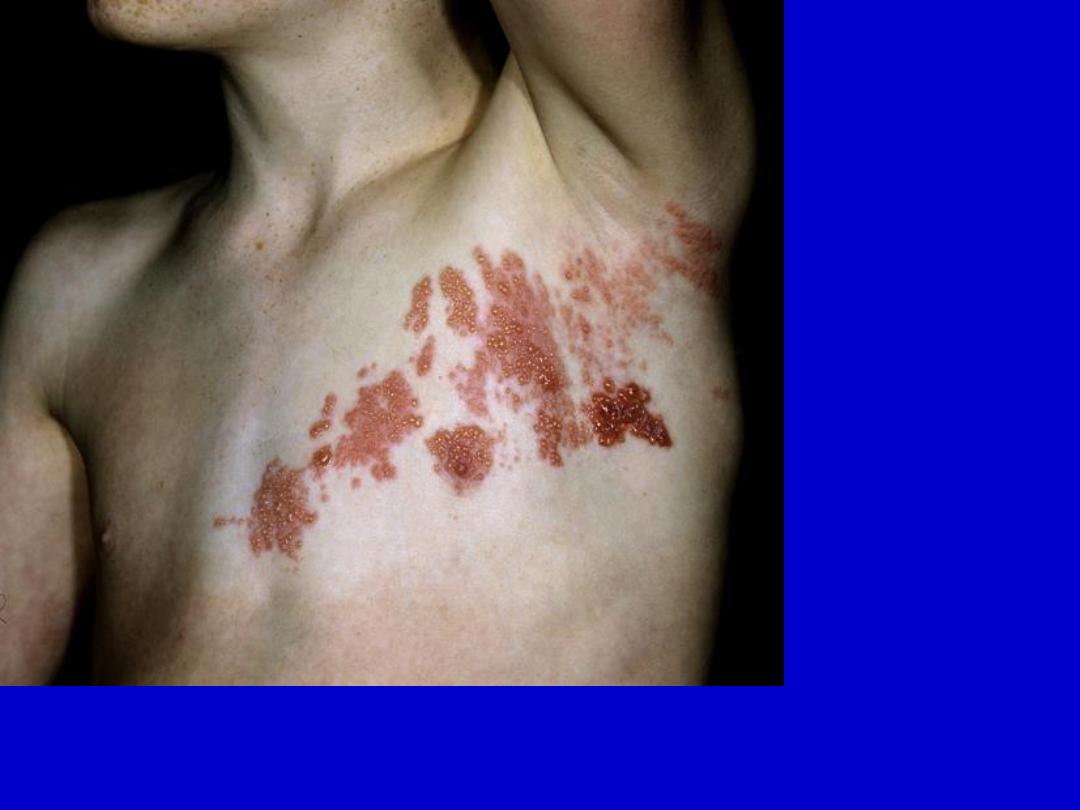
Herpes zoster. Unilateral involvement of thoracic dermatome that does
not cross the medline. Notice the varied size vesicles.
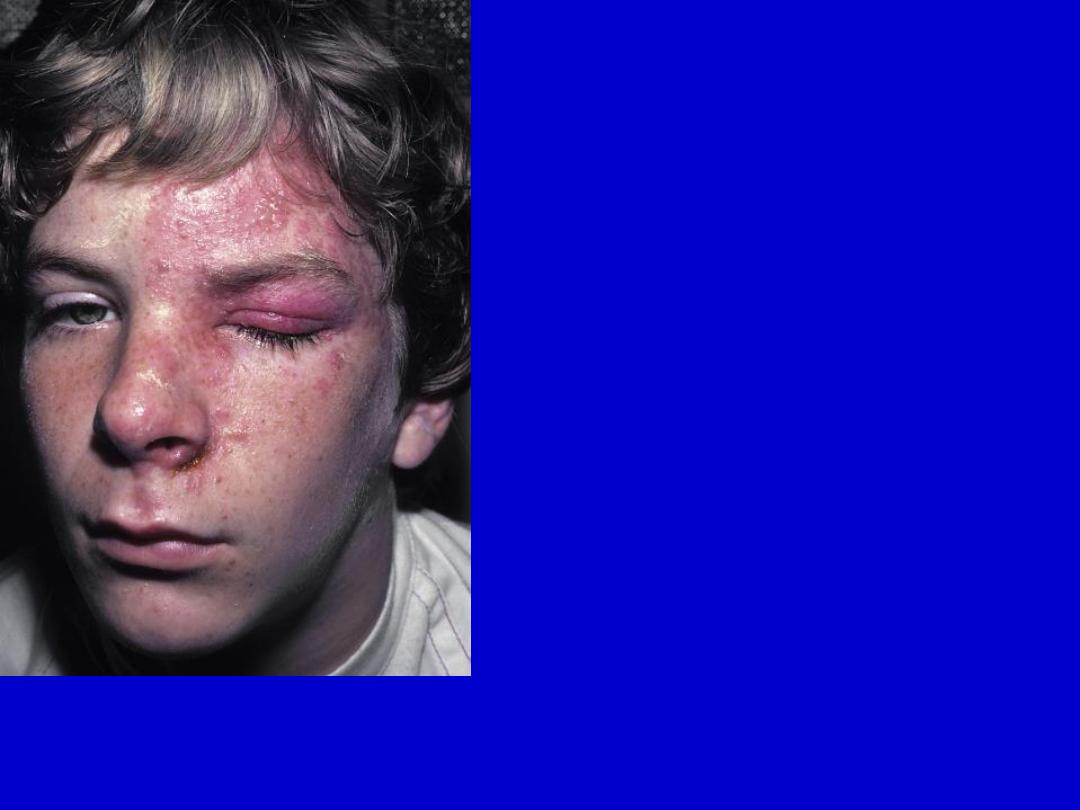
Herpes zoster (ophthalmic zoster). Involvement of the first branch of the fifth
nerve. Vesicles on the side of the nose are associated with the most serious
ocular complications.

Treatment of herpes zoster:
Acyclovir 800mg 5 times daily for 7 days.

Complications of herpes zoster
• Ramsay Hunt syndrome (geniculate ganglion zoster) is
peripheral facial nerve palsy accompanied by a vesicular
rash on the ear (zoster oticus) or in the mouth. It is caused
by zoster of the geniculate ganglion.
• Sacral zoster (S2, S3, or S4 dermatomes). A neurogenic
bladder with urinary hesitancy or urinary retention.
• Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). It is the persistence of pain
in affected dermatome after all lesions of herpes zoster
have healed. PHN occurs especially in patients older than
50 years. Treated by gabapentine.
• Necrosis, infection, and scarring.

Molluscum contagiosum
• It is caused by poxvirus.
• Common sites of involvement are face in children
and pubic area and genitals in adult.
• It spreads via autoinoculation, scratching, or
touching a lesion and fomites. It is STD in adult.
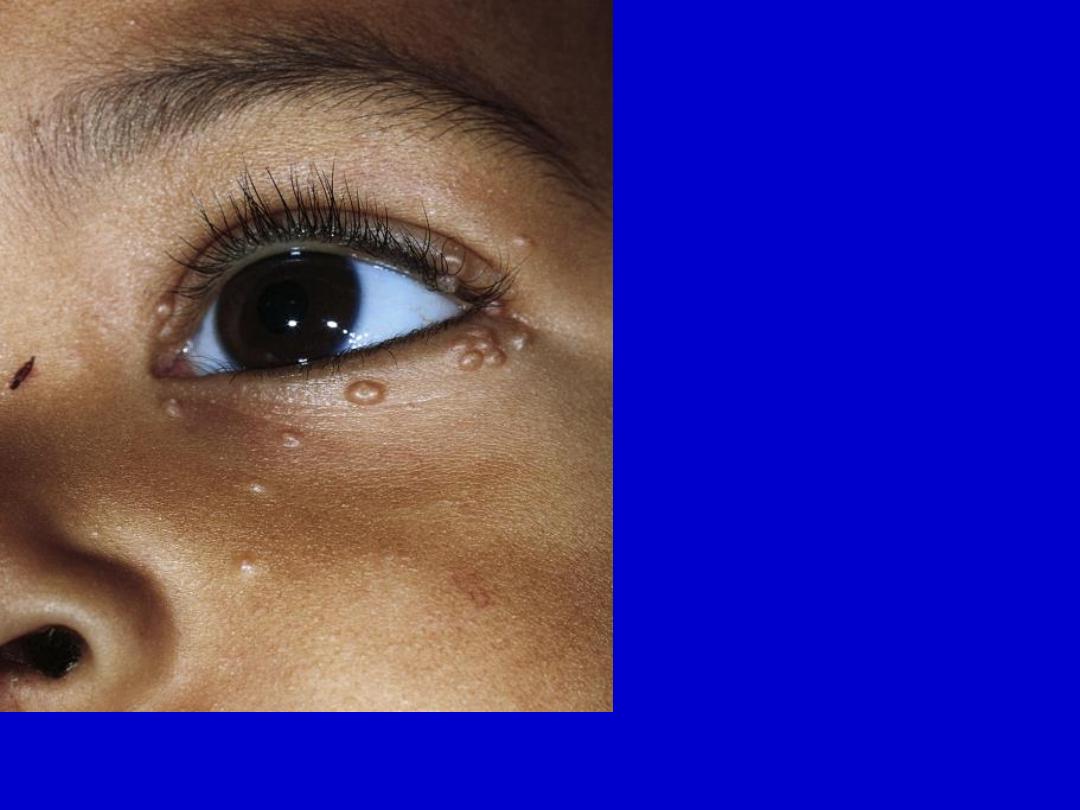
Molluscum contagiosum. Discrete, 2- to 5-mm, slightly umbilicated,
flesh-colored, dome-shaped papules about the eye.
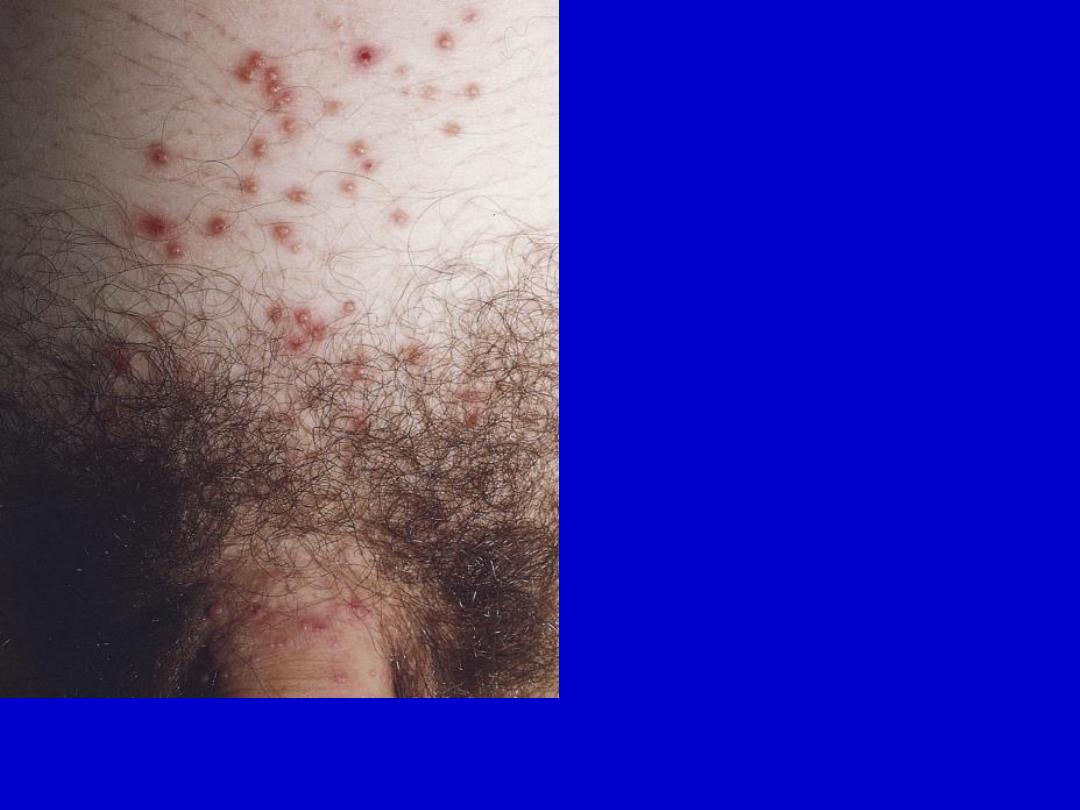
Molluscum contagiosum is a sexually transmitted disease in adults. Discrete, 2-
to 5-mm, slightly umbilicated, flesh-colored, dome-shaped papules in the pubic
area.

Treatment options for molluscum contagiosum.
• Curettage.
• Cryosurgery.
• Topical imiquimod.
• Topical corticosteroids like hydrocortisone
cream are used to treat dermatitis near or
involving the lesions.

Pityriasis rosea
It is a common, benign, usually asymptomatic, self-
limiting skin eruption of unknown etiology. Human
herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) may be involved.
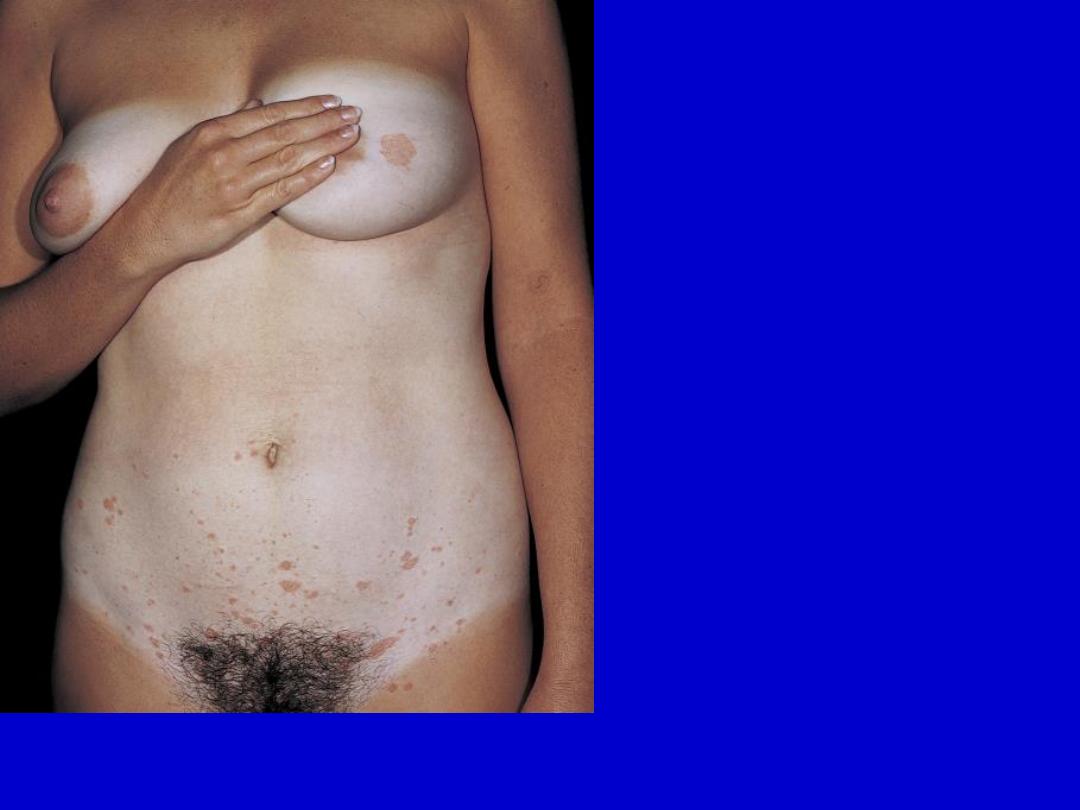
Pityriasis rosea. A herald patch is present on the breast. Subsequent
lesions commonly begin in the lower abdominal region.
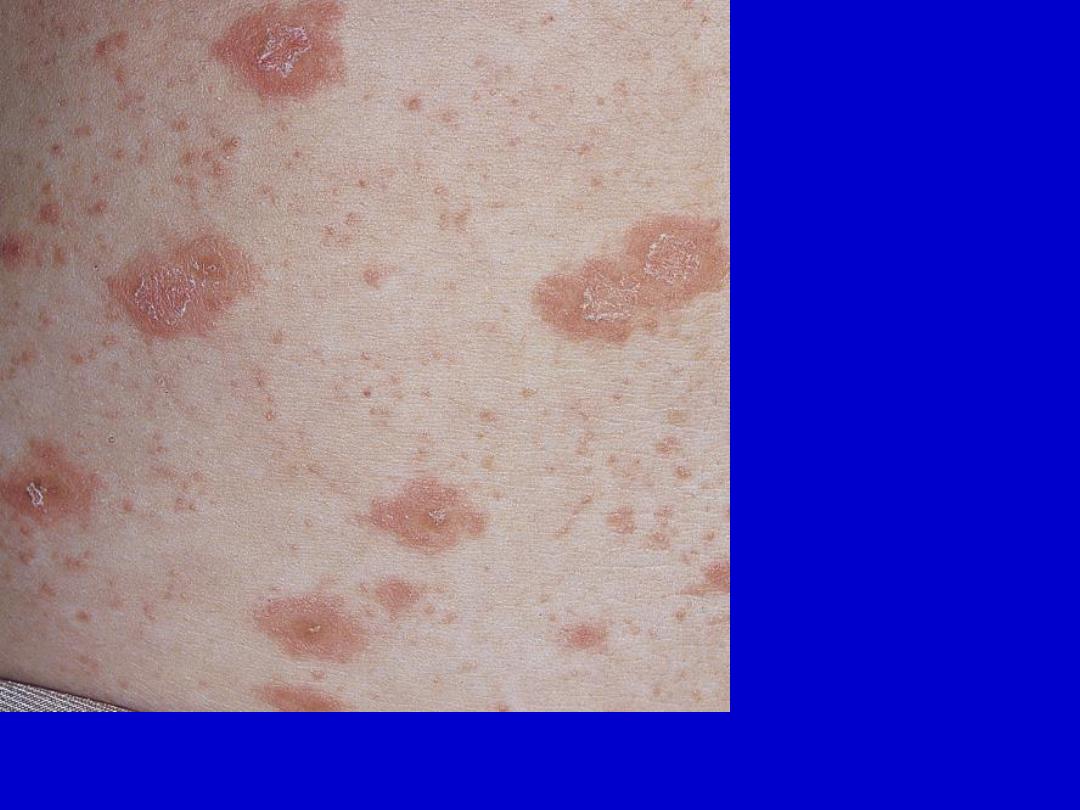
Pityriasis rosea. Both small, oval plaques with colleratte scales and
multiple, small papules are present.
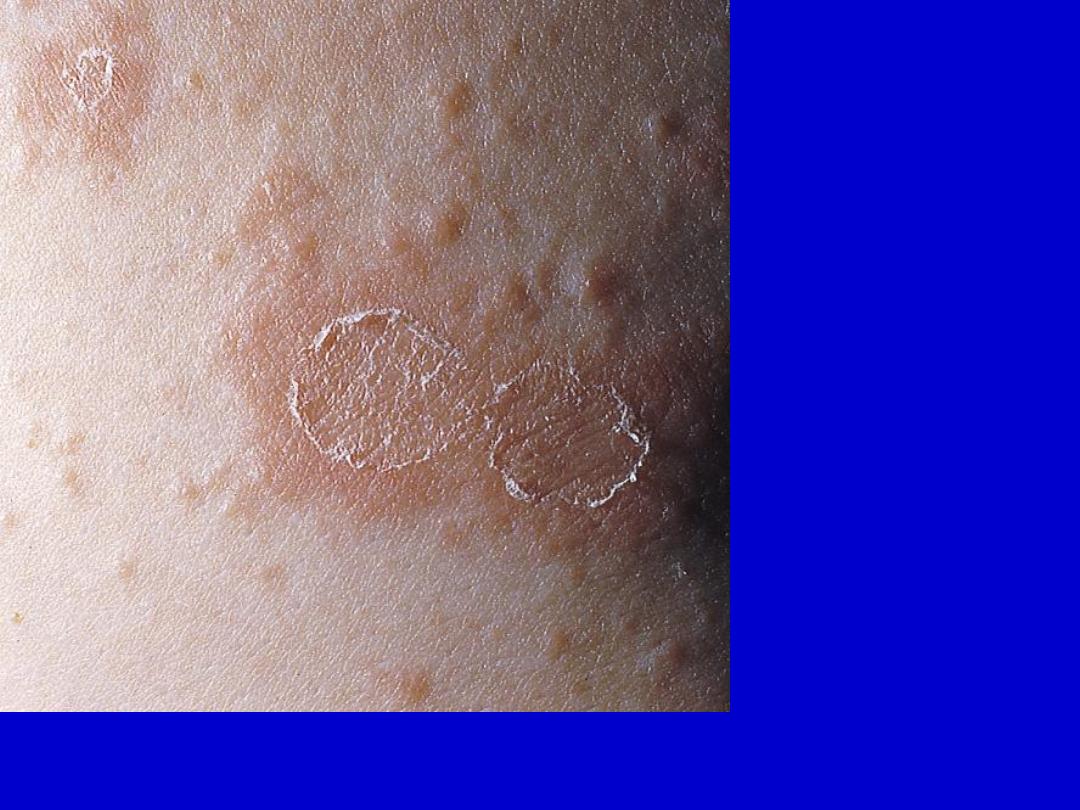
Pityriasis rosea. A ring of tissuelike scale (collarette scale) remains
attached within the border of the plaque.

The differential diagnosis:
• Secondary syphilis.
• Guttate psoriasis.
• Viral exanthems.
• Tinea.
• Nummular eczema.
• Drug eruptions.

Treatment of pityriasis rosea:
• Topical steroids like betamethasone and oral
antihistamines like hydroxyzine may be used for
itching.
• The extensive case with intense itching responds to
a 1- to 2-week course of prednisone (20 mg twice a
day).
• Oral acyclovir (800 mg five times daily) may be of
benefit because of the possible association of the
disease with HHV-6 and HHV-7.

Good Luck
