
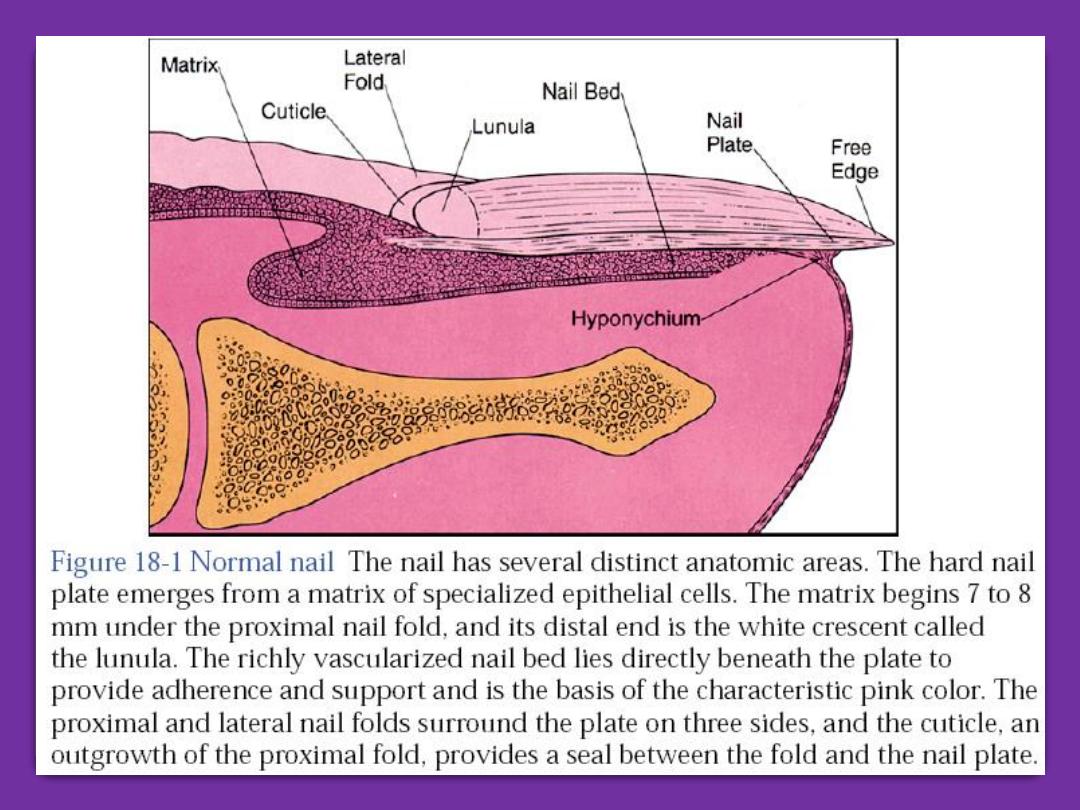
Nail Diseases
By
Dr. Salam Altemimi

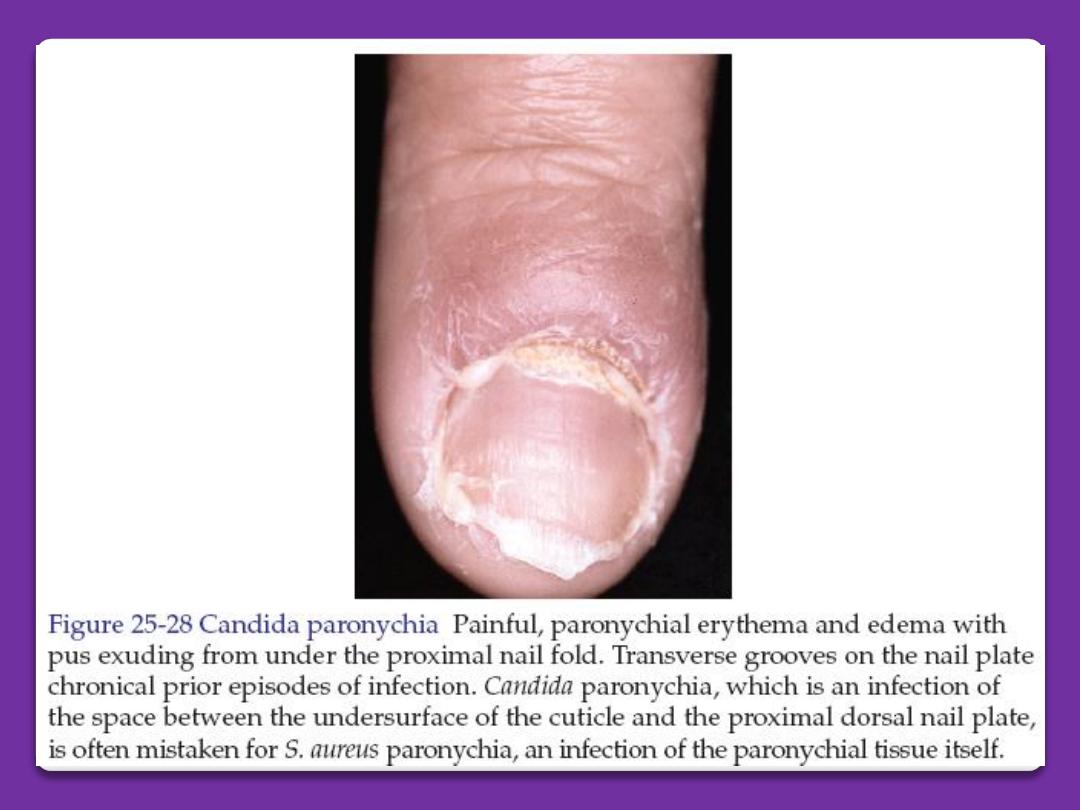
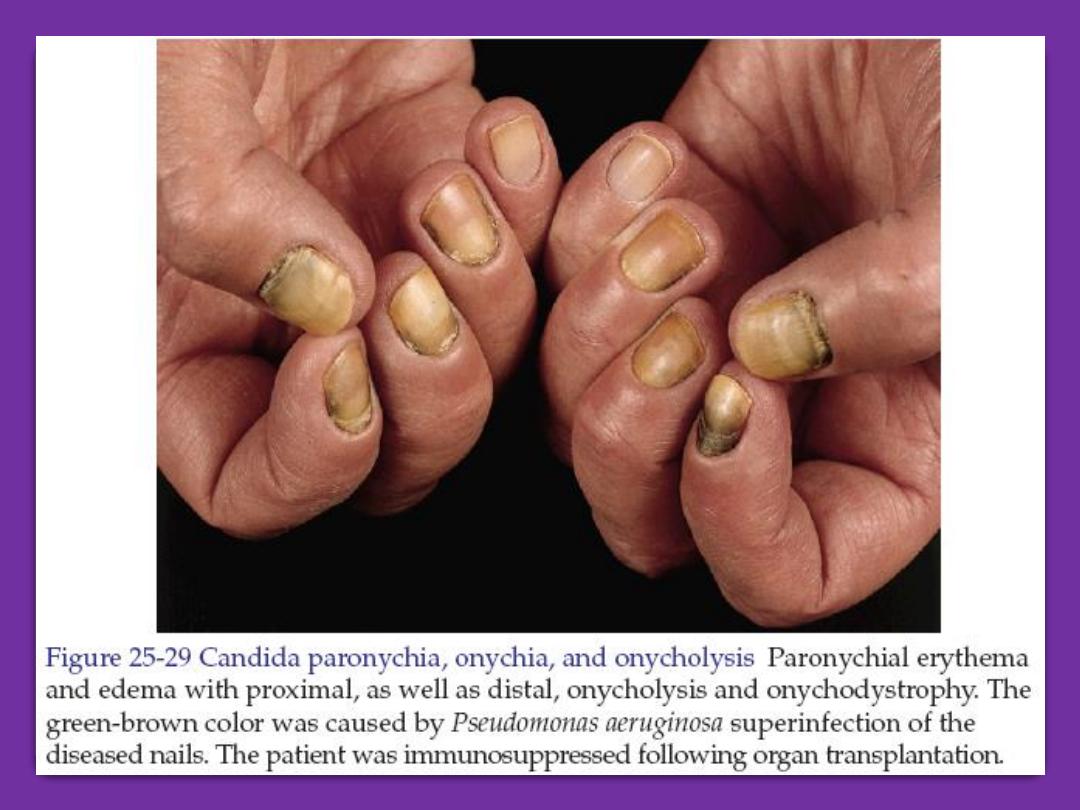
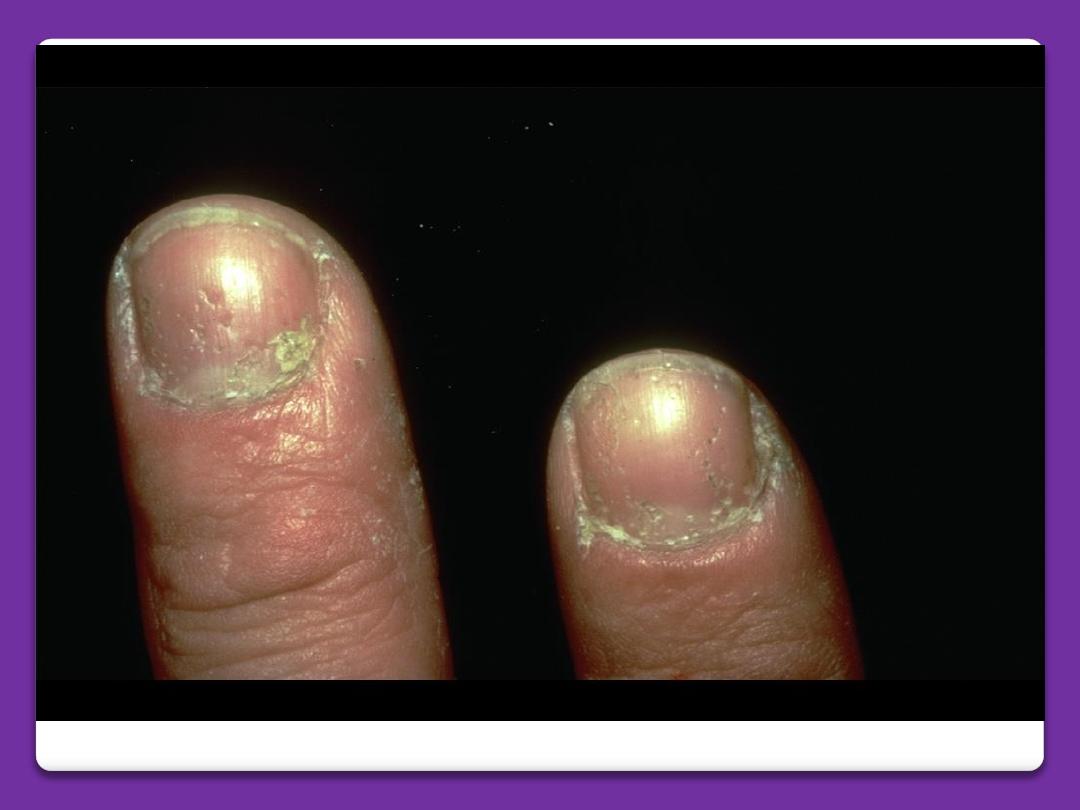
Chronic paronychia
Is infection of the nail fold and matrix by
candida albicans. There is glazed and red
swelling of the nail fold with loss of the cuticle.
There is mild to moderate pain. Occasional
bead of pus comes out from under the nail fold.
Ridging and furrowing of nail plate may occur
due to damage of the matrix. Dark brown
pigmentation of nail plate occurs in direct
invasion by monilia. The disease is occupational
of housewives due to wetness, which lead to
maceration of the cuticle then the entrance of
the microorganism.
Differential diagnosis: acute paronychia is
bacterial infection of the nail fold. There is
bright red swelling of the nail fold. The
inflammation is more severe, the condition
is more painful.
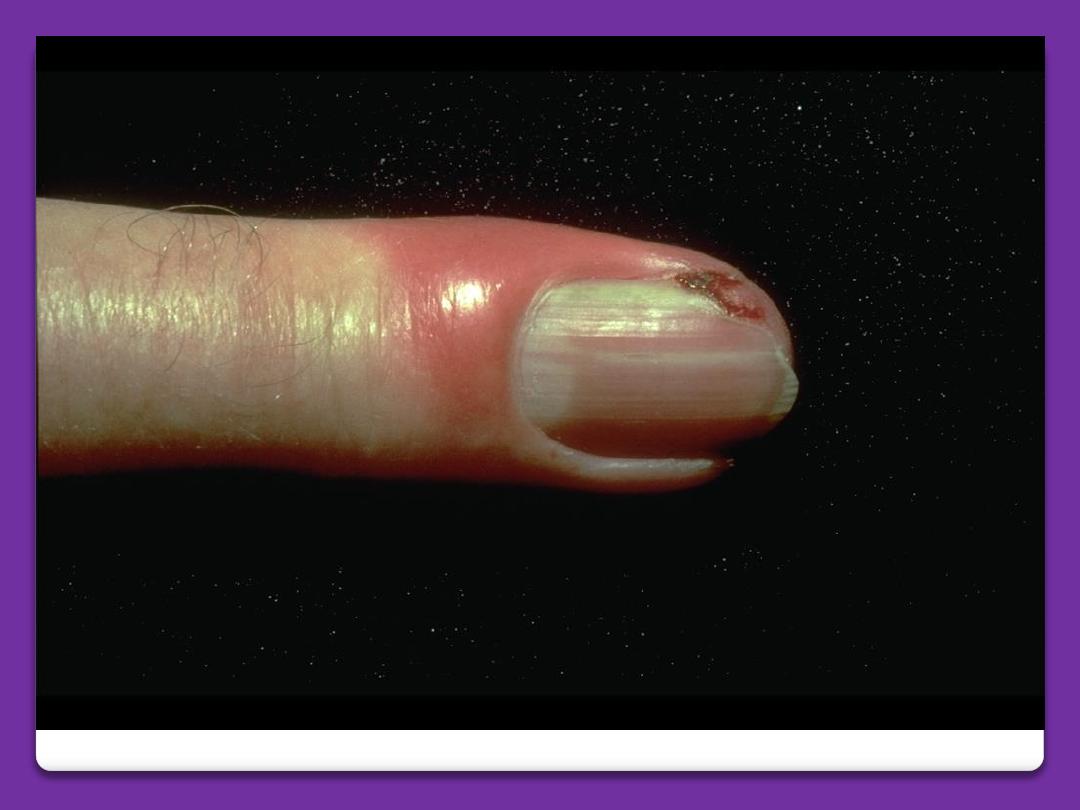
Acute paronychia

Treatment of Acute paronychia
Incision to evacuate the pus.
Oral antistaphylococcal antibiotics e.g.
cephalexin 250 mg four times daily for 7
days.

Treatment of chronic paronychia
Maintain dryness.
Topical clotrimazol cream.
Oral choice is fluconazole 150 mg per
week for 4 weeks.

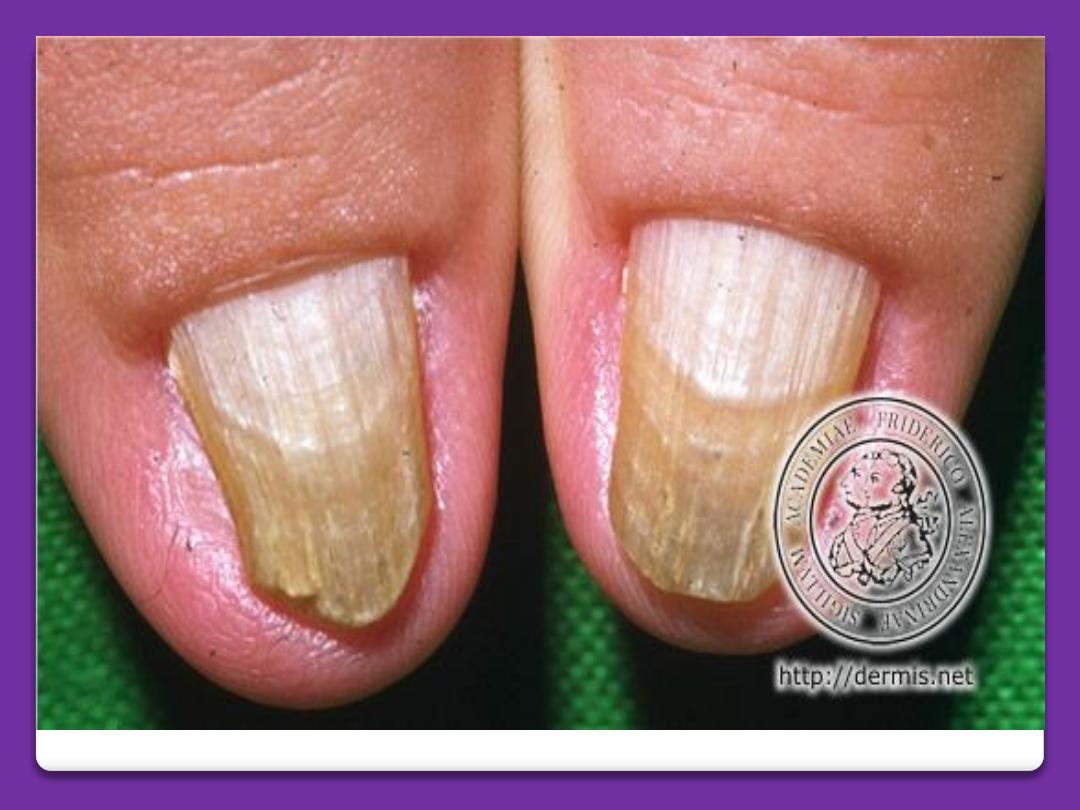
Tinea unguium
(onychomycosis)
It is the dermatophyte (ringworm)
infection of the nails. Commonly caused
by trichophyton and epidermophyton. The
affected nail is roughing, opaque and
friable. It has an accumulation of
keratinous debris under it. The diagnosis
can be confirmed by shaving of the nails
to find fungus on 20% KOH microscopic
exam. Also culture on Sabouraud medium
can be performed.
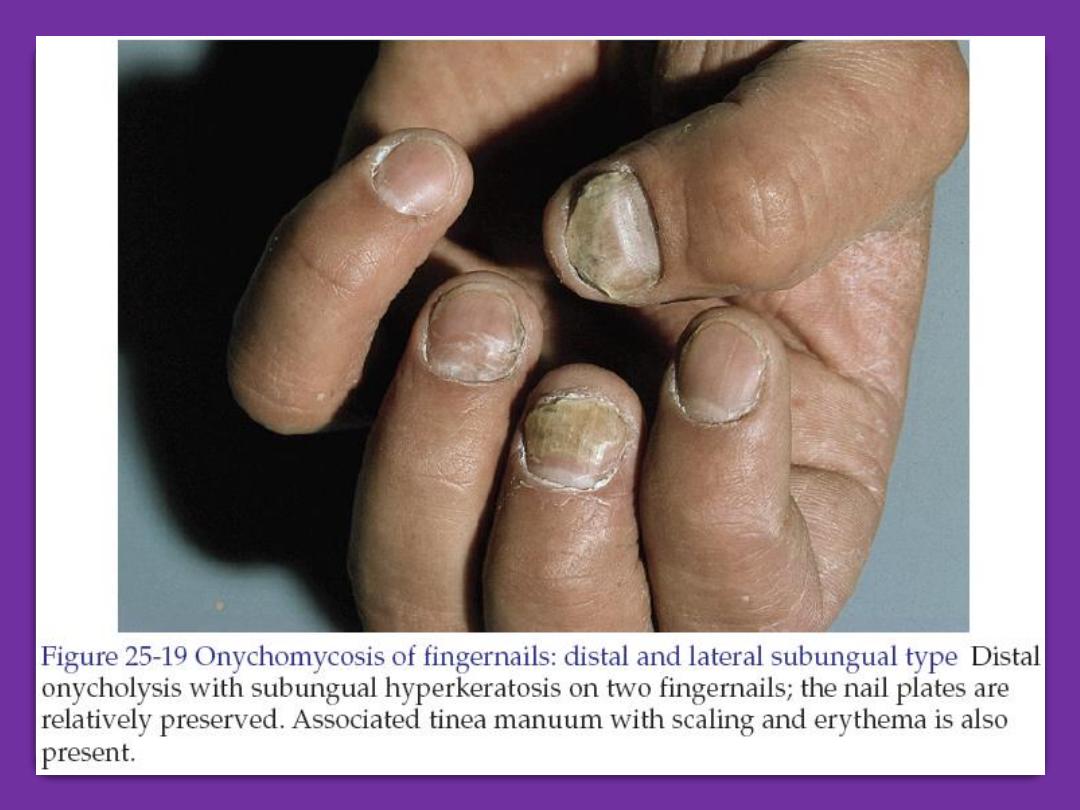
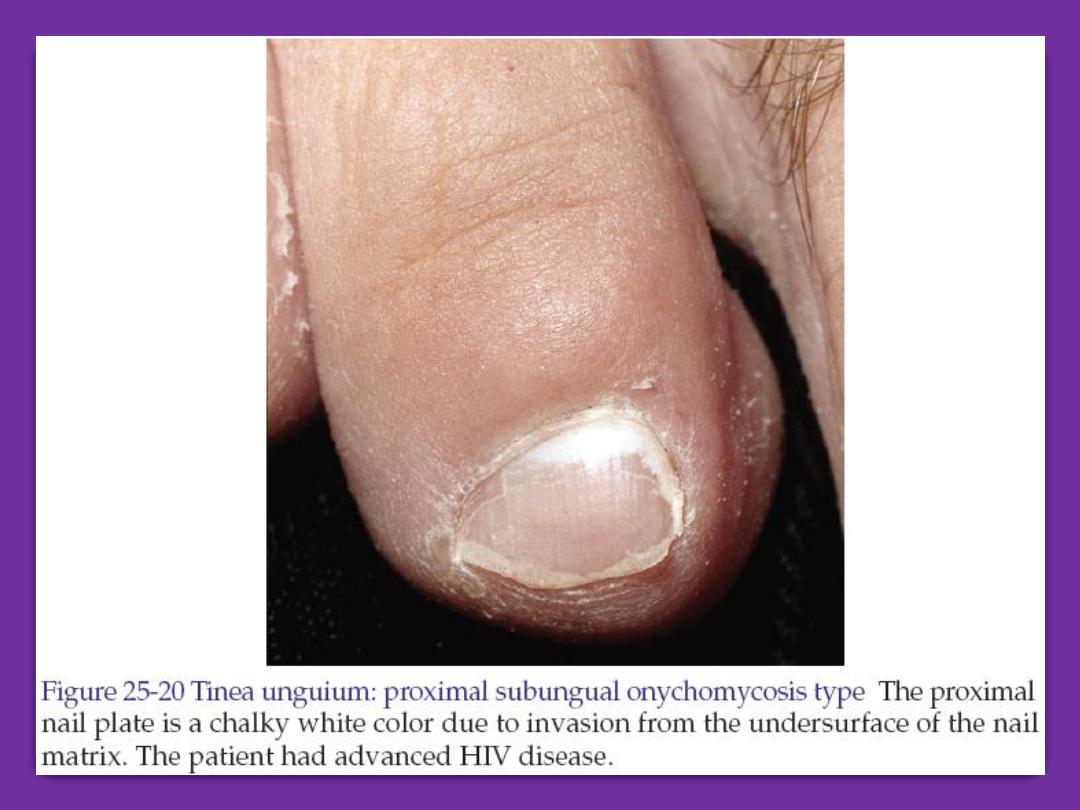
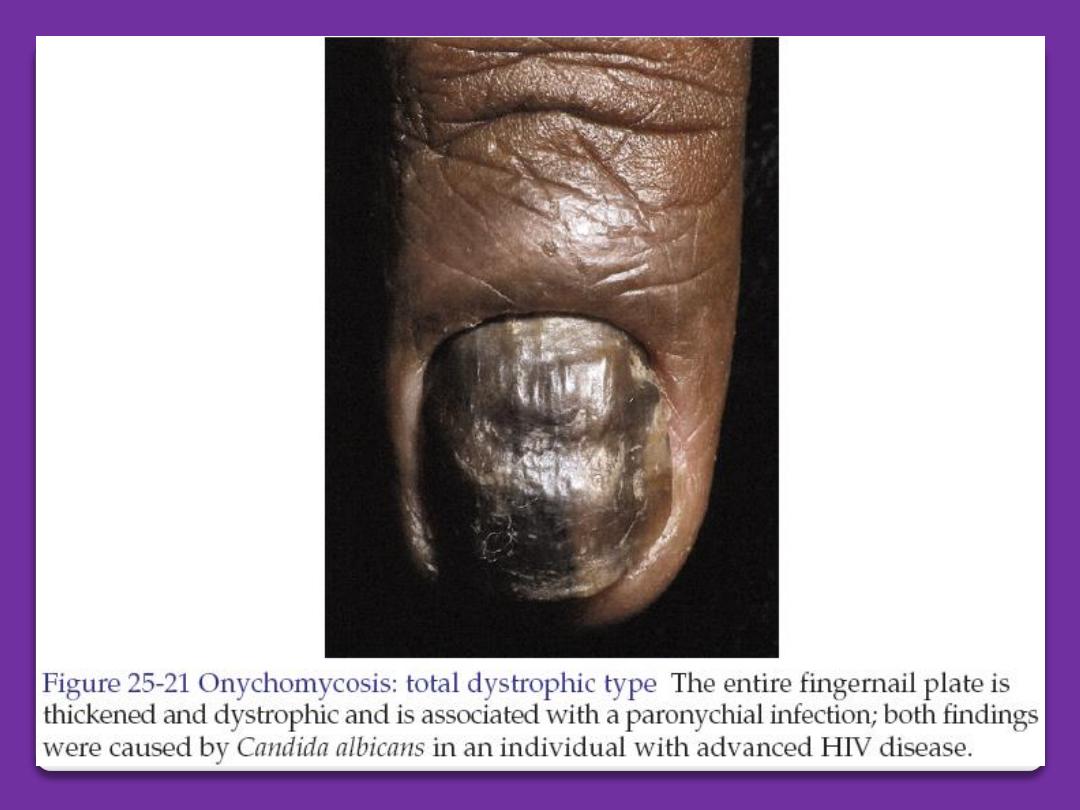
Tinea unguium

Treatment of tinea unguium
The treatment of choice is oral
terbinafine 250mg daily for 6 weeks in
fingernail infections and for 12 weeks in
toenail infections.
Fluconazole 150 mg once a week for 9
months.
Itraconazole (100 mg capsule) given in
pulse therapy. The pulse consists of 2
capsules twice daily for 1 week followed
by 3 weeks of drug free interval. Two to 3
pulses is given for fingernail infections
and 3-4 pulses for toenail infections.

Dermatosis associated with
nail involvement
1.
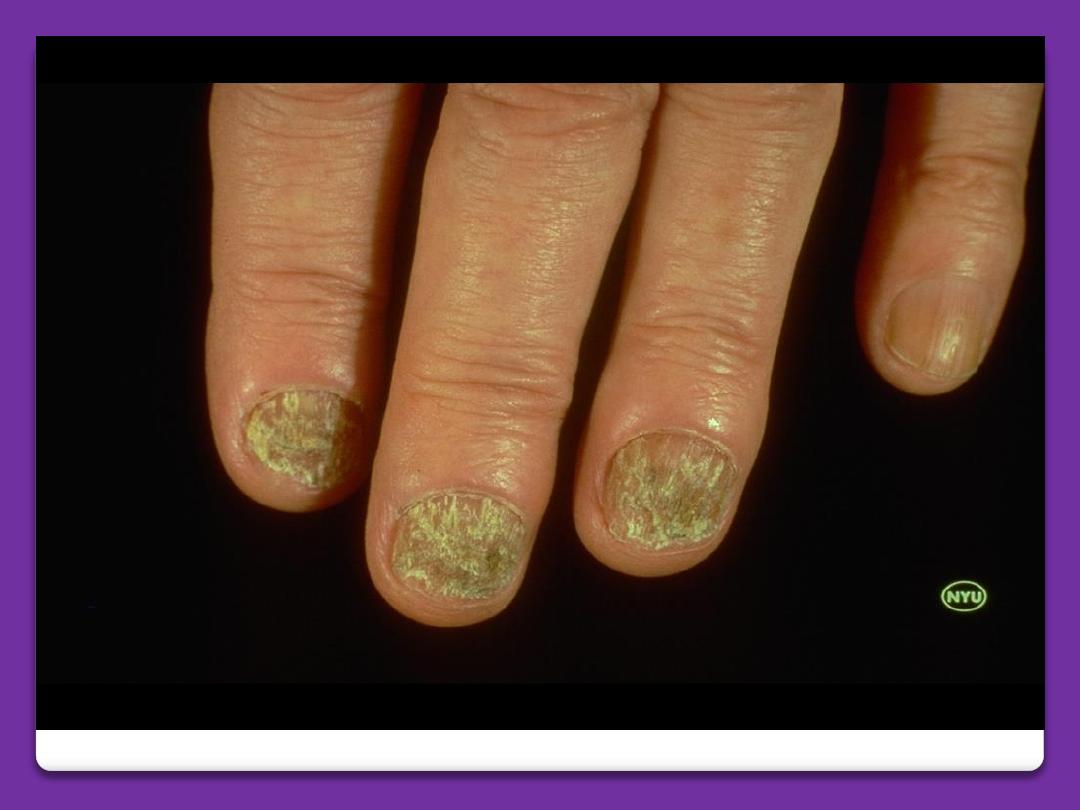
Psoriasis
◦
Pitting
◦
Onycholysis
◦
Discoloration
◦
Subungual thickening
◦
Malformed nails
◦
Splinter hemorrhages
Psoriasis of the nails

Dermatosis associated with
nail involvement
2.
Lichen planus
◦
Longitudinal grooving and ridging
◦
Pterygium
Lichen planus of the nails
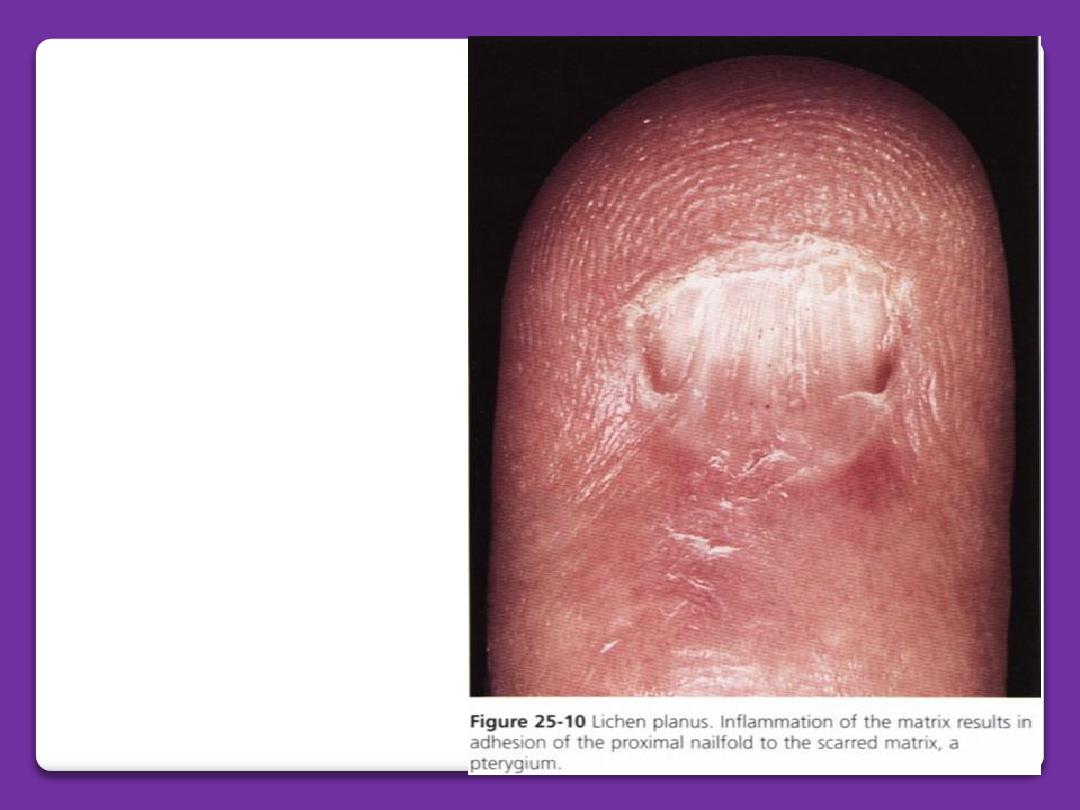
Lichen planus of the nail
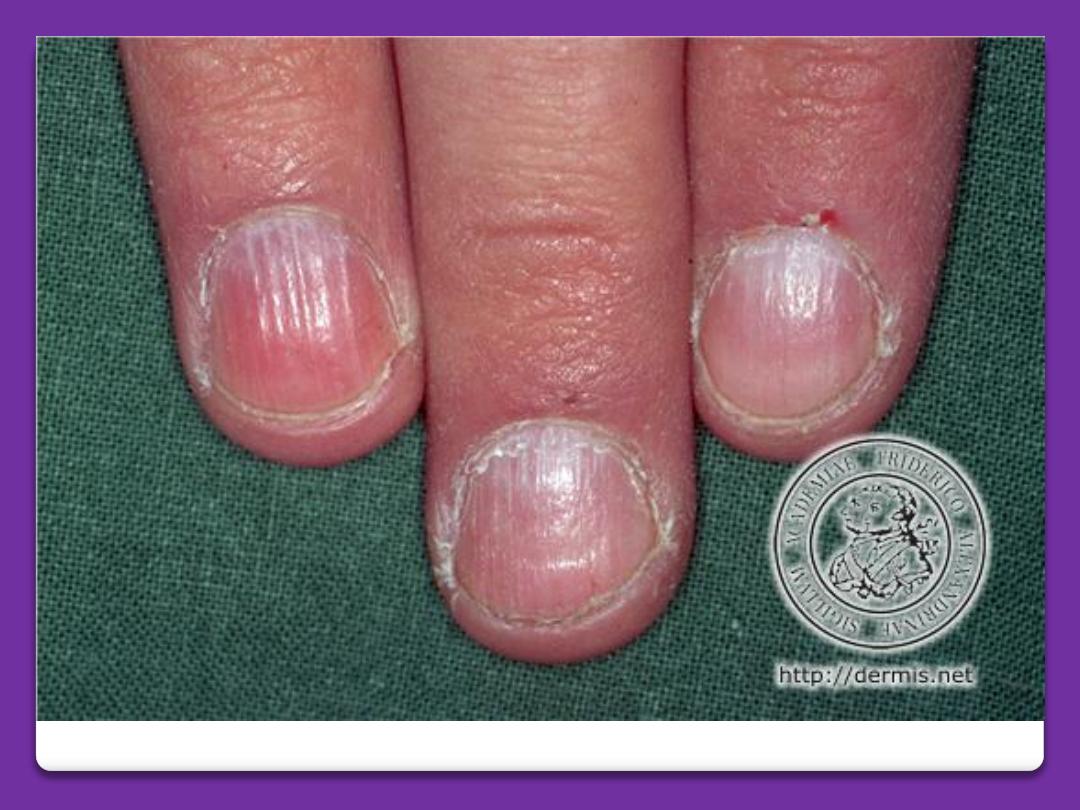
Alopecia areata-nails

3.
Alopecia areata
◦
Pitting
4.
Norwegian scabies
◦
Nail plate dystrophy
5.
Eczema and dermatitis
◦
Ridging, thickening and discoloration
6.
Paronychia
◦
Ridging, thickening and discoloration
Dermatosis associated with
nail involvement

Onycholysis
It is the separation of the nail plate from
the nail bed at distal and lateral margins.
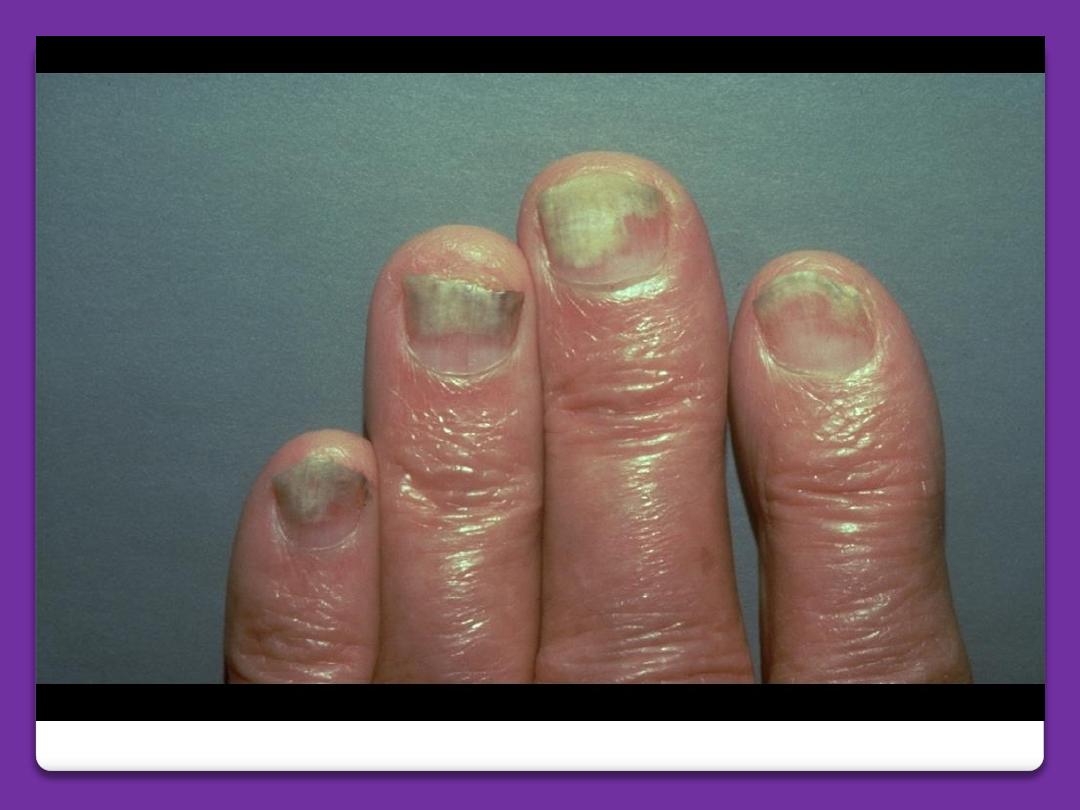
Onycholysis (from psoriasis)

Etiology of onycholysis
Idiopathic
Secondary
1.
Dermatosis: psoriasis, fungal infections.
2.
General medical conditions: like
hyperthyroidism, Raynaud’s phenomenon.
3.
Trauma: like typing, long nails.
4.
Drugs: photo-onycholysis occurs with
tetracycline or psoralin.

Nail pitting
It is a tiny, punched out or ices pick
depressions of the nail plate. Common
causes are psoriasis, alopecia areata, and
sometimes a normal variant.

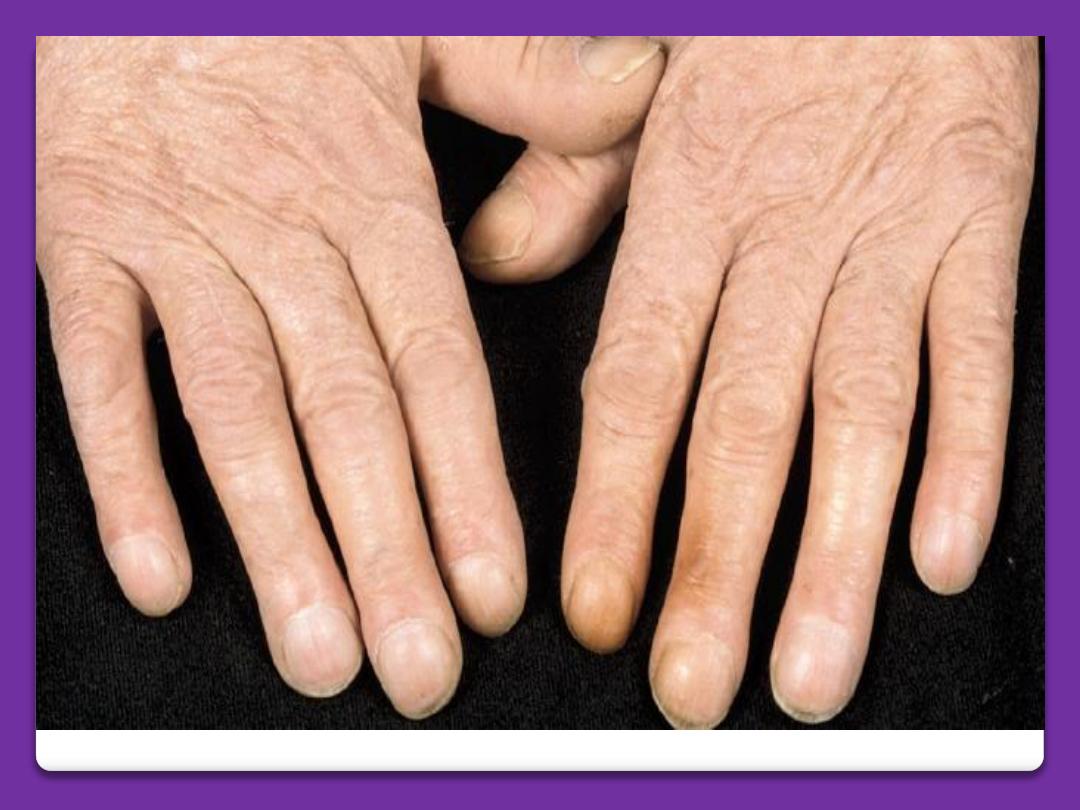
Koilonychia
The nail is flat or concave has spoon-
shape. It is often thin and brittle. The
condition associated with hypochromic
iron deficiency anemia.
Koilonychia

Finger clubbing
It is increase in the size and curvature of
nail plate with loss of the angle between the
nail plate and the posterior nail fold. It is
associated with many diseases e.g.
carcinoma of the bronchus, heart diseases.
Finger clubbing

Ingrown toenail
It is the soft tissue of the side of the nail
(lateral nail fold) is penetrated by the
edge of the nail plate, resulting in pain,
sepsis and later the formation of the
granulation tissue. The great toe is often
affected. The cause is compression of the
toe by ill-fitting footwear and cutting of
the toenail in a half-circle instead of
straight across.
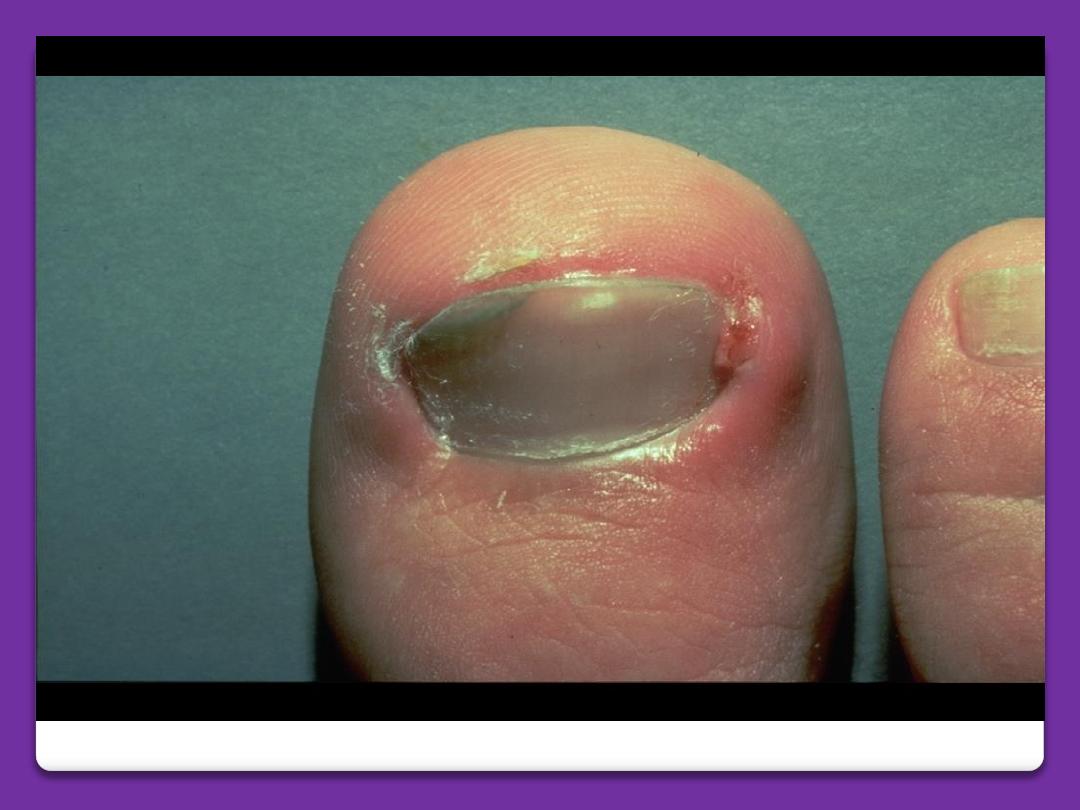
Ingrowing toenail

Treatment of ingrown toenail
Wearing wide and pliable shoes.
Antibiotics.
Cauterization of granulation tissues by
silver nitrate sticks.
If yet no benefit, avulsion of nail plate or
removal part of it in continuing cellulitis.

Good luck
