Psychological Bases of Behaviorpart 1: Psychoanalytic theory
د.ثراء الجوديPsychoanalytic theory is based on Freud’s concept that behavior is determined by forces derived from unconscious mental processes.
Psychoanalysis and related therapies (eg. Psychodynamic psychotherapy) are psychotherapeutic treatments based on this .concept
To explain his ideas, Freud developed, early in his career, the topographic theory of the mind
and, later in his career, the structural theory
Topographic theory of the mind
In the topographic theory, the mind contains three levels: The unconscious, preconscious, and conscious.1. The unconscious mind contains repressed thoughts and feelings that are not available to
the conscious mind, and uses primary process thinking.Topographic theory of the mind
Primary process: is a type of thinking associated with primitive drives, wish fulfillment, and pleasure seeking, and has no logic or concept of time, focuses on immediate gratification.Primary process thinking is seen in young children and psychotic adults. It manifest itself during dreaming.
Dreams: represent gratification of unconscious
instinctive impulses and wish fulfillment.
Freud))“Dream is the royal road to the unconscious”
Topographic theory of the mind
2. The preconscious mind contains memories that, while not immediately available, can be accessed easily.3. The conscious mind contains thoughts that a person is currently aware of.
It operates in close conjunction with the preconscious mind but does not have access to the unconsciousmind.
The conscious mind uses secondary process thinking (logical, mature, time oriented) and can delay gratification.
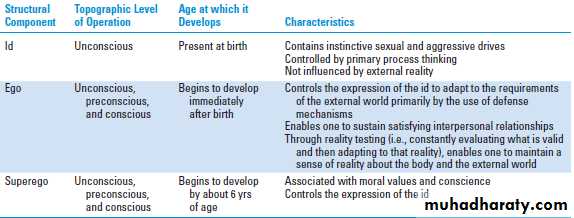
Structural theory of the mind
In the structural theory, the mind contains three parts: The id, the ego, and the superego.Structural theory of the mind
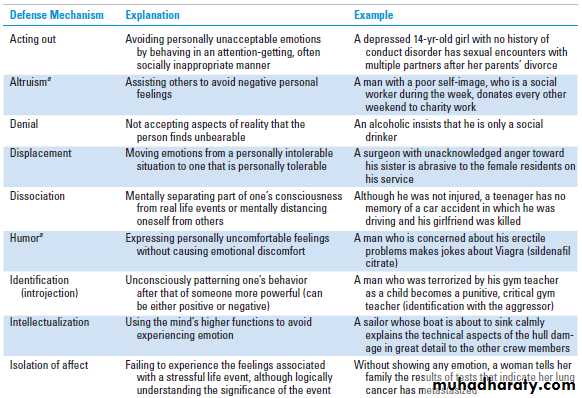
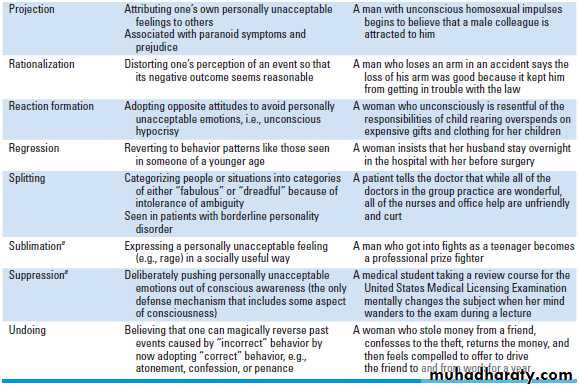
DEFENSE MECHANISMSDefinition:
Defense mechanisms are unconscious mental techniques used by the ego to keep conflicts out of the conscious mind, thus decreasing anxiety and maintaining a person’s sense of safety, equilibrium, and self-esteem.
They can be useful in helping people deal with
difficult life situations such as medical illness, but, when used to excess, can become a barrier to seeking care or adhering to treatment recommendations.DEFENSE MECHANISMS
Specific defense mechanisms1. Some defense mechanisms are immature (i.e., they are manifestations of childlike or disturbed behavior).
2. Mature defense mechanisms (e.g., altruism, humor, sublimation, and suppression), when used in moderation, directly help the patient or others.
3. Repression, pushing unacceptable emotions into the unconscious, is the basic defense mechanism on which all others are based.
TRANSFERENCE REACTIONS
DefinitionTransference and countertransference are unconscious mental attitudes based on important past personal relationships (e.g., with parents).
These phenomena increase emotionality and may thus alter judgment and behavior in patients’ relationships with their doctors (transference) and doctors’ relationships with their patients (countertransference).
TRANSFERENCE REACTIONS
Transference1. In positive transference, the patient has confidence in the doctor. If intense, the patient
may over-idealize the doctor or develop sexual feelings toward the doctor.
2. In negative transference, the patient may become resentful or angry toward the doctor if
the patient’s desires and expectations are not realized. This may lead to poor adherence
to medical advice.
TRANSFERENCE REACTIONS
In countertransference, feelings about a patient who reminds the doctor of a close friend orrelative can interfere with the doctor’s medical judgment.
Review questions
1. When a 27-year-old patient who had a contentious relationship with his father joins a new health insurance plan, he must change from his primary care physician, a young man, to a new physician, a middle-aged man. On his first visit to the new doctor, the patient seems annoyed with everything the doctor says and states, "You are an old man with old-fashioned ideas; you just want to control my life." This patient's behavior is most closely related to which of the following?(A) Positive transference
(B) Negative transference
(C) Countertransference
(D) Dislike of the doctor
(E) Fear of the doctor
Review questions
2. A physician becomes very angry with a patient when the patient does not take his medication. The patient reminds the doctor of her rebellious son.This physician's intense reaction to the patient's behavior is most likely to be a result of
(A) positive transference
(B) negative transference(C) countertransference
(D) dislike of the patient
(E) Fear of the patient