RADIOLOGY BONE DISEASE
Imaging techniqueI.plain bone radiograph :
Radiological X.ray sings of bone disease :
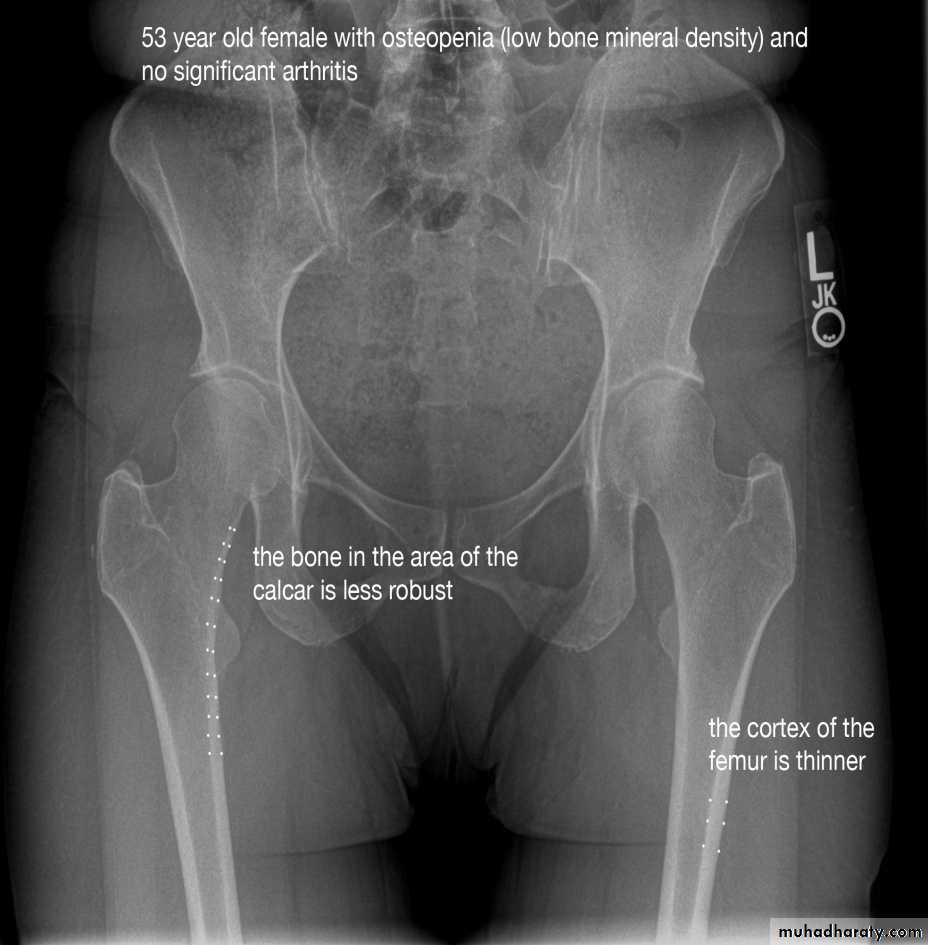
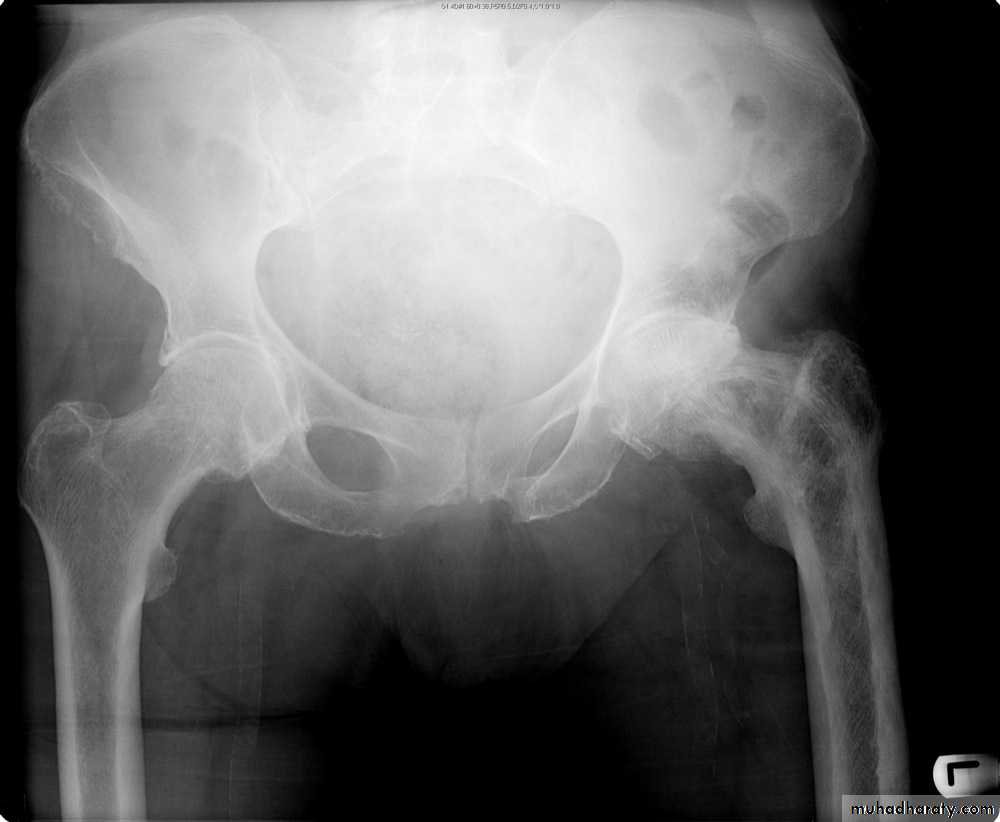
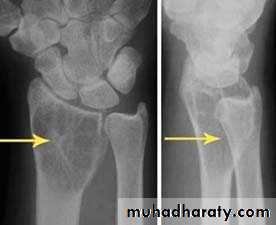
1.decrease in bone density , it can be focal or generalized
2-increase bone density ( sclerosis ) can also be focal or generalized
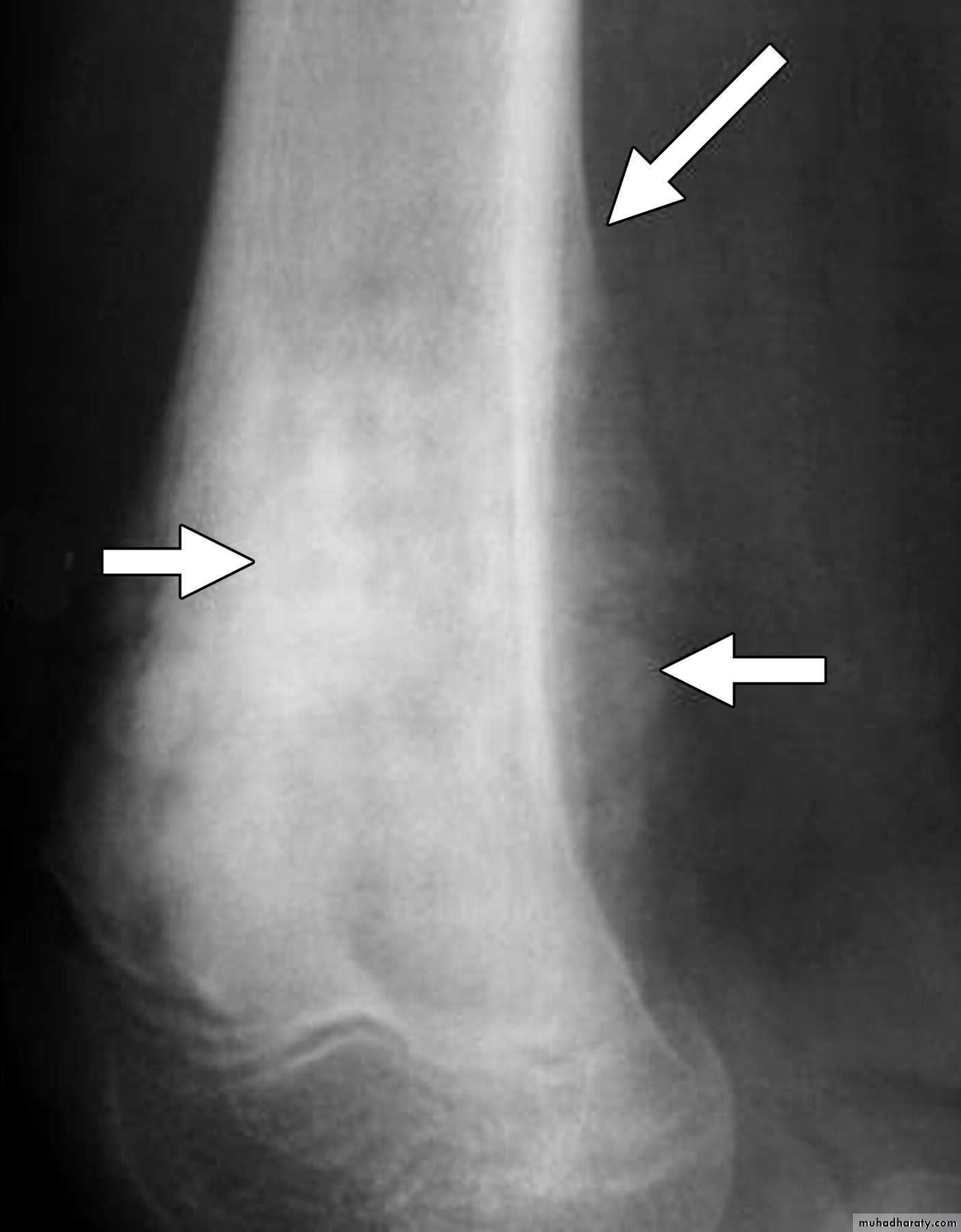
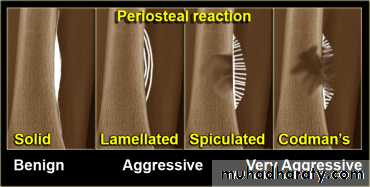
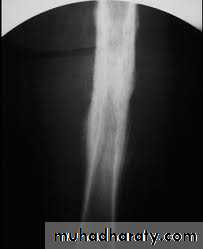
3-periosteal reaction
4- cortical thickening
5. alteration in trabecular pattern
6- alteration in the shape of bone e.g acromegaly
7- alteration in bone ageII. U/S in musculoskeletal disease
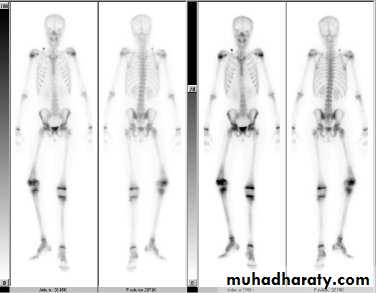
III. radionuclide bone scanning
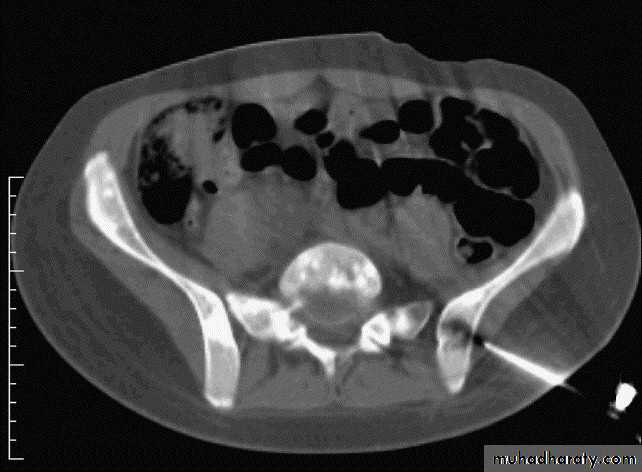
IV. computed tomography in bone disease (CT scan ) :
1.Demonestrating abnormality in the pelvis and spine2.Demonstrating the extent & characterization of bone tumour in selected cases to complement MRI
3.As gide of bone biopsy
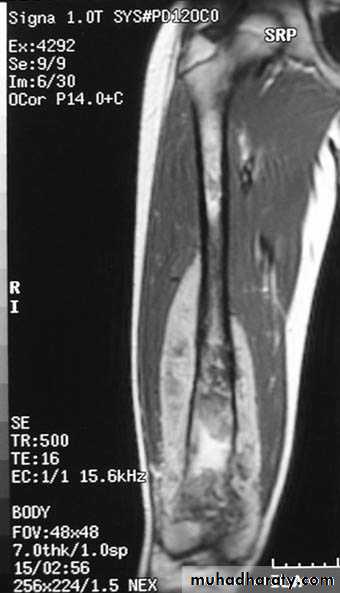
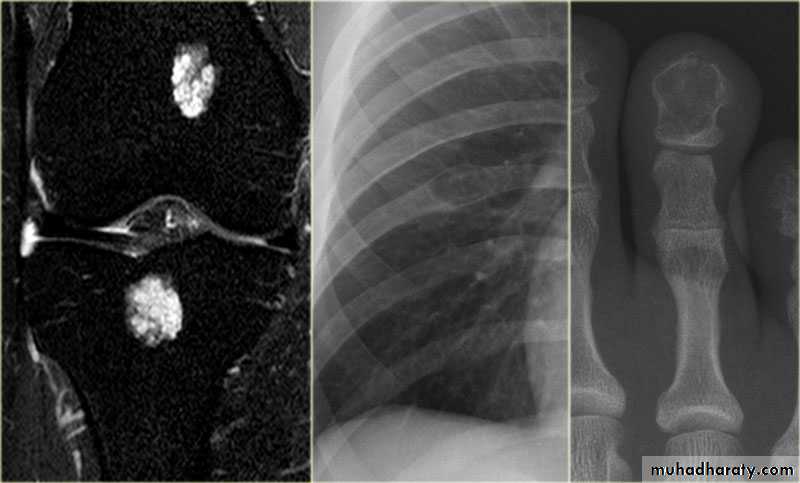
V.MRI (magnetic resonance imaging in bone disease ):
.demonstrate disc herniation and spinal cord or nerve root compression. to diagnose bone metastasis
.show extent of primary bone tumor & demonstrate myloma & lymphoma
. image soft tissue mass
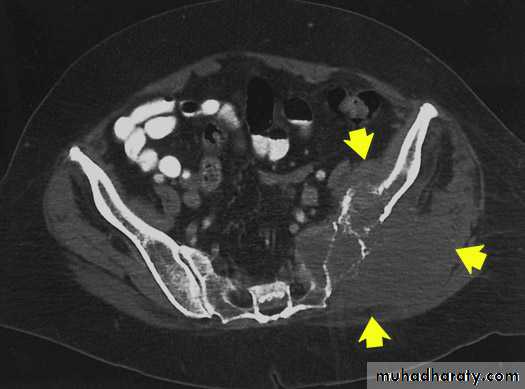
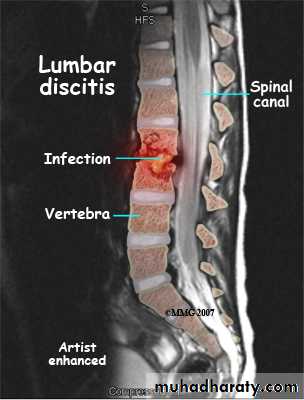
. to diagnose osteomylitis & show any soft tissue abnormality
. to diagnose a vascular necrosis & other joint pathology .
Bone diseases
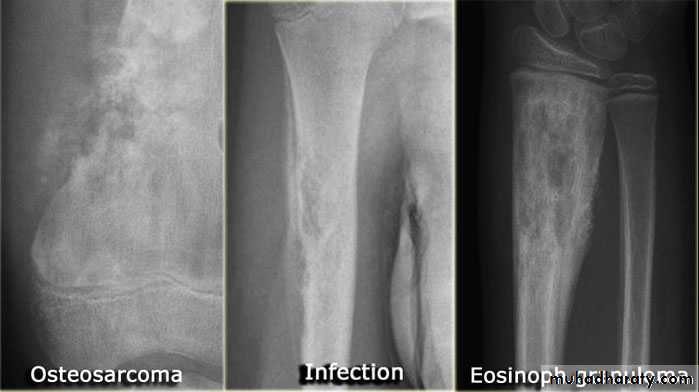
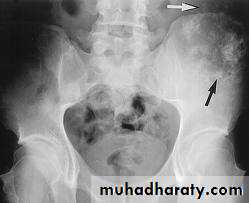
Solitary bone lesion are usually one of the following.bone tumor: malignant ( primary or secondary ) , benign
. osteomyelitis
. bone cyst, fibrous dysplasia or other non –neoplastic defects of bone
. condition of uncertain nature such as langerhans histiocystosis
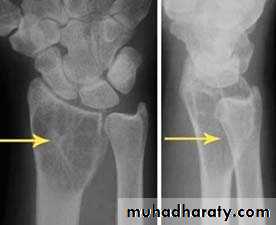
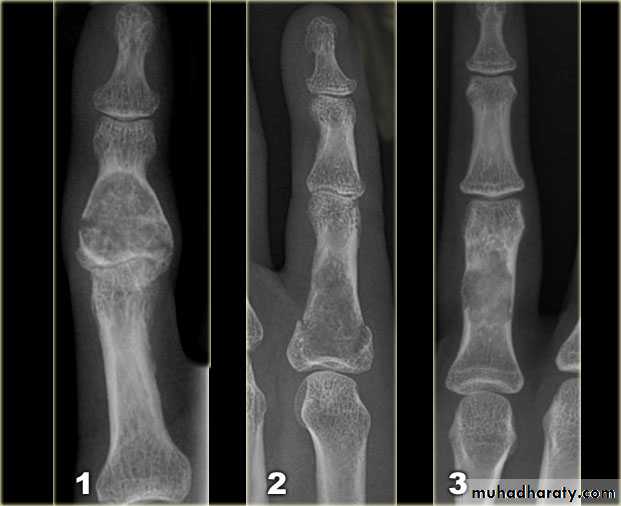
the initial radiological decision is usually to try &decide whether the solitary lesion is benign or its aggressive by looking for the following features on plain radiographs & CT :
1.Zone of transition
2.The adjacent cortex
3.Expansion
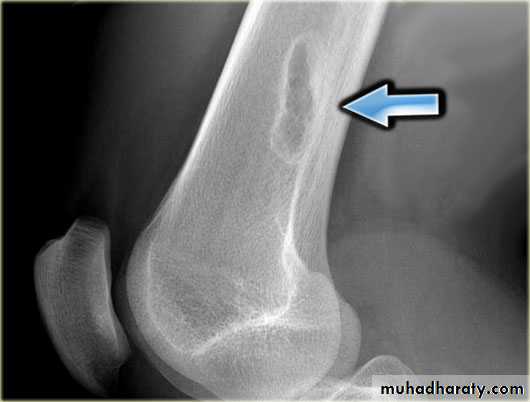
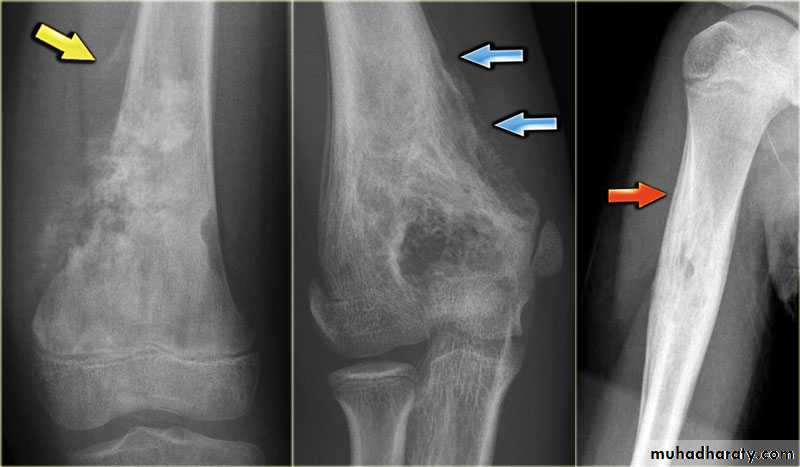
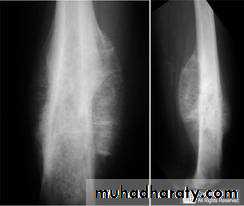
4.Periosteal reaction
the causes of localized peiosteal reactions adjacent to a lytic or sclerotic lesions are :
.Osteomyelitis.Malignant bone tumour , particularly Ewing sarcoma & osteosarcoma
.Occasionally metastasis , particularly neuroblastoma
.Langerhans histiocytosis
.Trauma
5. Calcific densities within the lesion
6. Soft tissue swelling
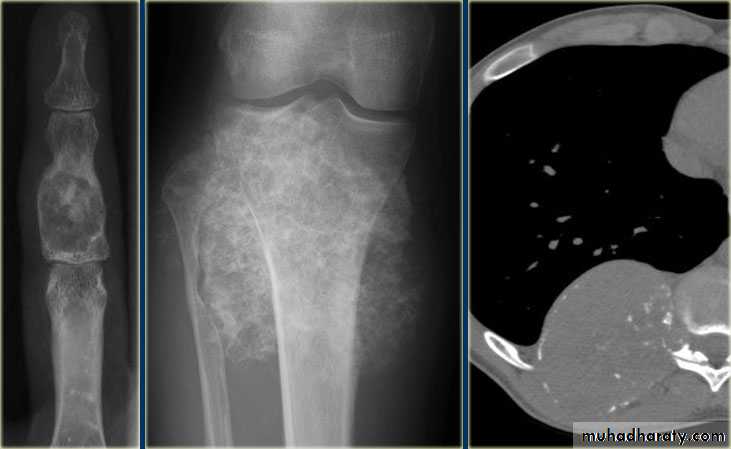
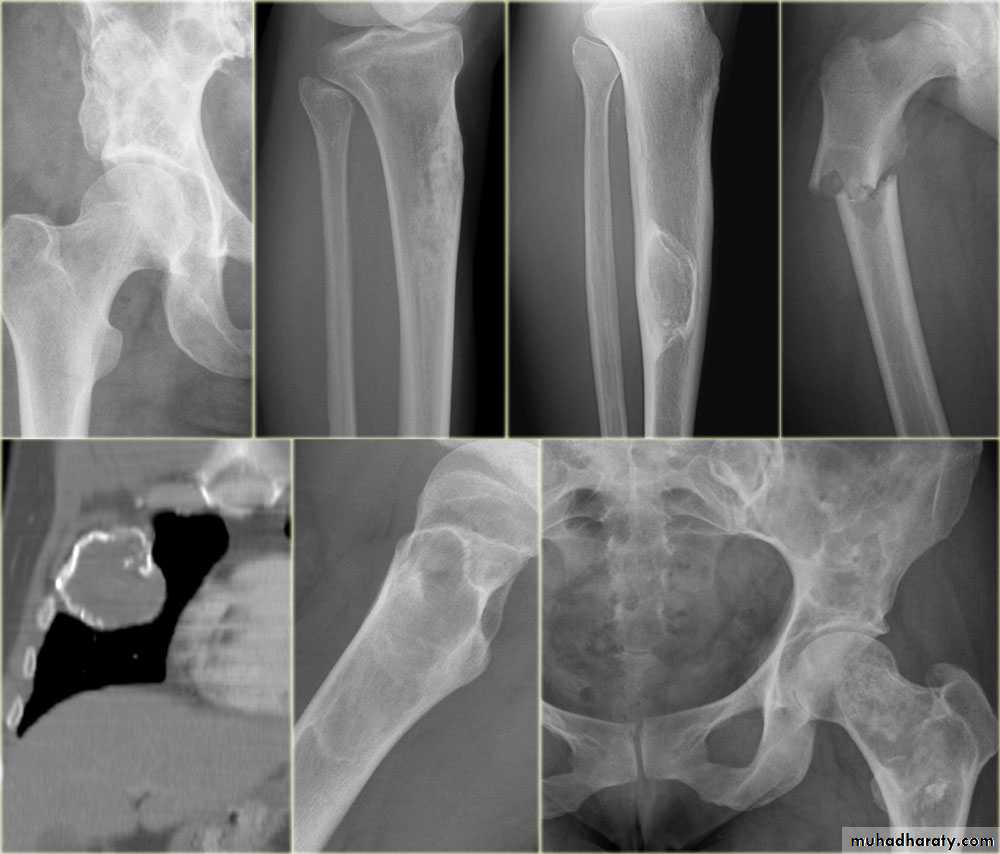
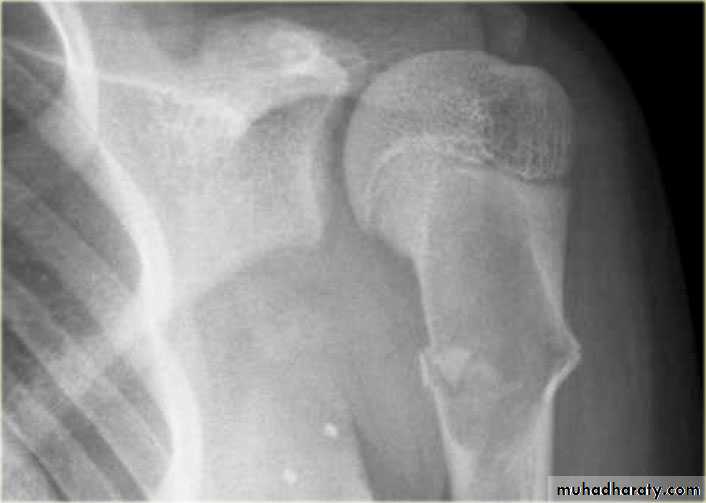
7.Site:The site of a lesion is most important as certain lesions tend to occur at certain sites.Bone tumours
Primary malignant tumoursOsteosarcoma ( osteogenic sarcoma )
Chondrosarcoma :
Ewing sarcoma
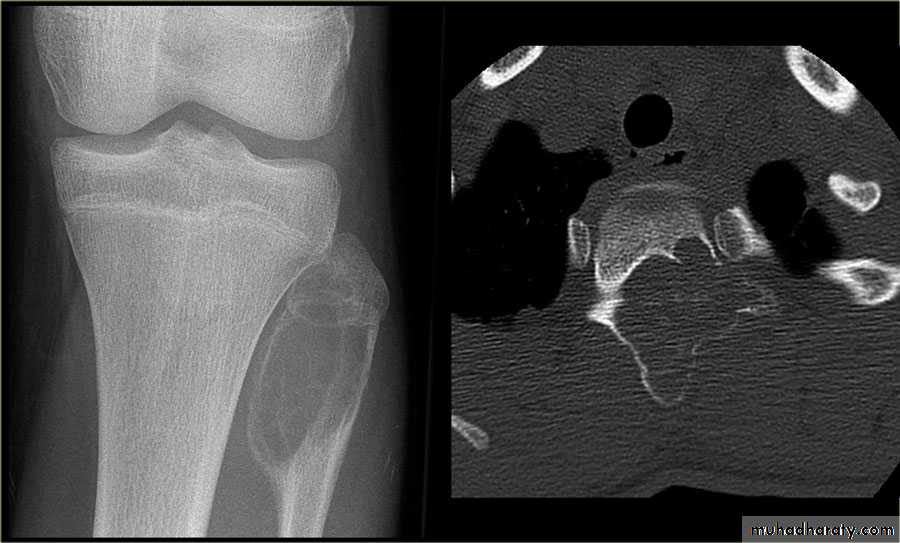
Giant cell tumour
Benign tumour & tumour like condition
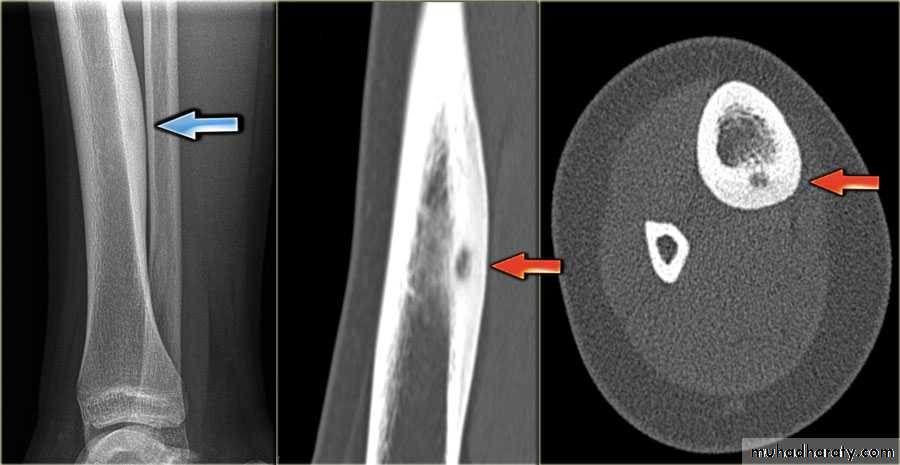
Enchondromas :Fibrous cortical defects ( non ossifying fibromas )
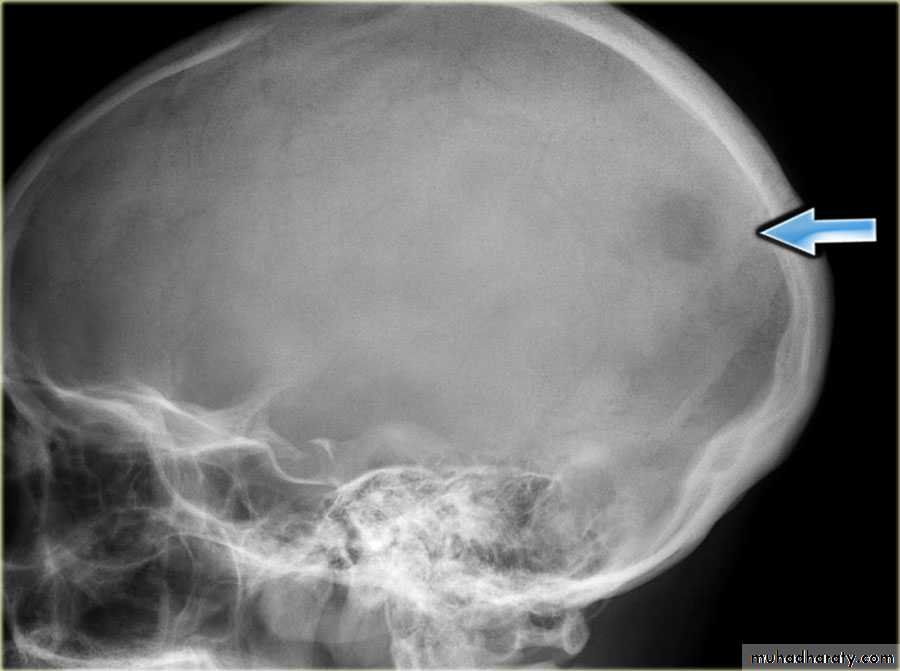
Fibrous dysplasia :