Dr. Nawal Pediatrics
1
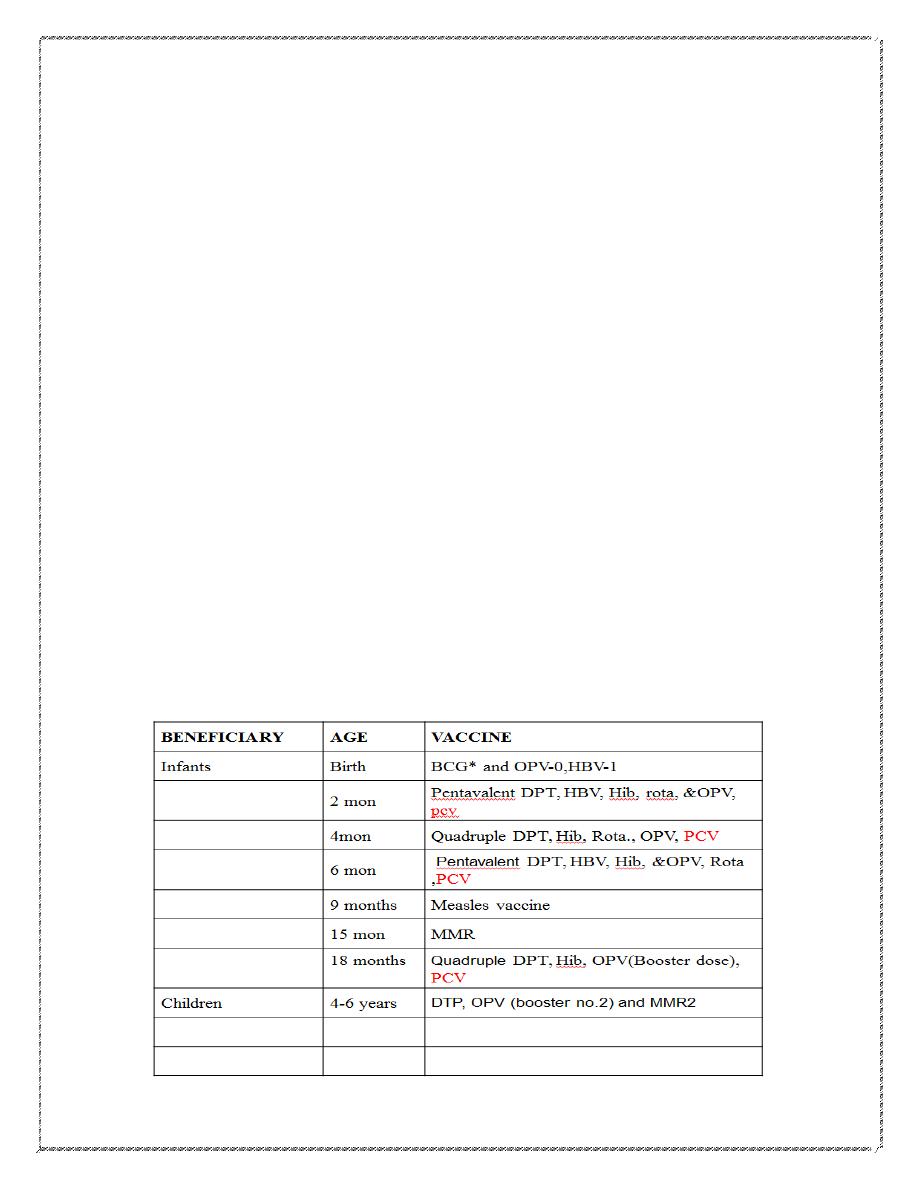
Immunization
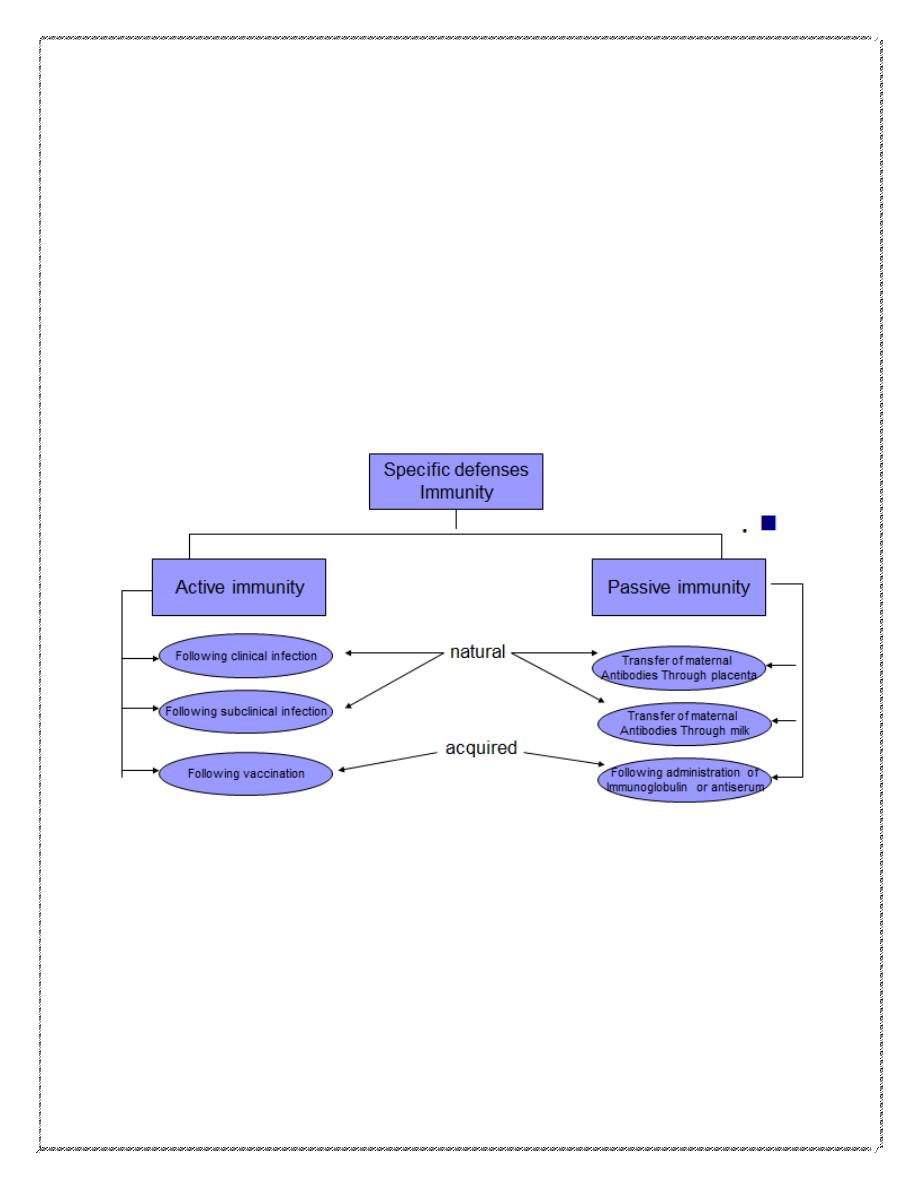
Immunity
o B cell( humeral)
o Tcell (cellular)
o complement
Definition
Immunization is the process of inducing immunity against a specific disease
1- Passive Immunity
1- administration of preformed antibodies to induce transient protection against an infectious agent.
2- naturally through transplacental transfer of antibodies during gestation. Maternally derived antibodies
can provide protection during an infant's first months of life. Protection for some diseases may persist
for as long as a year after birth.
Dr. Nawal Pediatrics
2
The major indications for passive immunity protection to
(1) immunodeficient children with B-lymphocyte defects who have difficulties in making antibodies.
(2) persons exposed to infectious diseases or who are at imminent risk of exposure where there is not
adequate time for them to develop an active immune response to a vaccine.
(3) persons with an infectious disease as part of specific therapy for that disease, Rabies, tetanus,
hepatitis
2- Active Immunization
Vaccines are defined as whole or parts of microorganisms administered to prevent an infectious disease.
Vaccines can consist
1- whole inactivated microorganisms (polio and hepatitis A).
2- parts of the organism (acellular pertussis, human papillomavirus [HPV], and HepB).
3- polysaccharide capsules (pneumococcal and meningococcal polysaccharide vaccines).
4- polysaccharide capsules conjugated to protein carriers (Hib, pneumococcal, meningococcal conjugate
vaccines),
5- live attenuated microorganisms (BCG, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, rotavirus, and live
attenuated influenza vaccines, polio).
6- toxoids (tetanus and diphtheria) . A toxoid is a modified bacterial toxin that is made nontoxic but is
still able to induce an active immune response against the toxin.

Dr. Nawal Pediatrics
3
Precautions and Contraindications
A contraindication means the vaccine should not be administered under any circumstances.
A generic contraindication for all vaccines is anaphylaxis to a prior dose & Anaphylactic
hypersensitivity to vaccine constituents (egg proteins for vaccines grown in eggs; gelatin, a stabilizer in
many vaccines; and antimicrobia agent if essential, desensitizing protocols
.
*Live attenuated vaccines generally are contraindicated in immunocompromised persons; except MMR,
which may be given to a child with HIV infection (asymptomatic or symptomatic without evidence of
severe immunosuppression
*Recent blood product
*Preterm--- same except HBV wt more than 2 kg
*Steroid
*Moderate – sever illness until recovery
Vaccine Reactions
1- Common/ minor reactions.
Local reactions (pain , swelling , redness),
systemic symptoms – result as a part of immune response.
fever
Other reactions – result as a part of the components in the vaccine (viz. Aluminum adjuvant, stabilizers
or preservatives ).
2- Rare Vaccine Reactions
rare & more serious reactions (like anaphylaxis , encephalopathy, Febrile seizures , thrombocytopenia
not lead to long term problems.
BCG : Suppurative lymphadenitis, Osteitis, Disseminated infection(immunosupp).
Hep-B : Anaphylaxis

Dr. Nawal Pediatrics
4
Measles/MMR : Febrile seizures , thrombocytopenia, anaphylaxis, encephalopathy
OPV : Vaccine associated paralytic poliomyelitis
Tetanus : Brachial neuritis, Anaphylaxis
Pertussis : Persistent inconsolable screaming (>3hrs) , seizures , anaphylaxis , encephalopathy
Reactions Due to Hypersensitivity
Contain traces of antibiotics to which some individuals are sensitive.
ANAPHYLAXIS: is a severe reaction of rapid onset , characterized by circulatory collapse.
SKIN (erythema , urticaria , angioedema)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (dry cough , cyanosis , respiratory distress)
GIT (abdominal cramps)
CVS (tachycardia , hypotension)
CNS (loss of consciousness)
BCG VACCINE;
The live attenuated strain of M. bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) .
Intradermal, Lt upper arm.
Swelling within 2 wks, papule, ulcer, heal within 12wks, flat scar
Not protect from primary infection . prevent disseminated TB
Sabin's polio vaccine Oral live-attenuated vaccine
Contains 3 serotypes of vaccine virus
Shed in stool for up to 6 weeks.
Paralysis rare
Local & systemic protection

Dr. Nawal Pediatrics
5
MMR vaccine:
highly effective vaccine, SC in two doses
rubella portion to protect against congenital rubella
side effects 5-12 days following immunization.
Fever and rash .
Transient arthritis.
Thrombocytopenia (rare)
Encephalopathy (very rare)
Arranged by: Mustafa Hürmüzlü
