…
Chest Investigations
5th year/2017
Dr. Munther MudhafarJaber ibn Hayyan medical university
Investigations
• 1)Conventional chest X ray (CXR )• 2) Computed tomography ( CT scan )
• 3) Biopsy
• Others
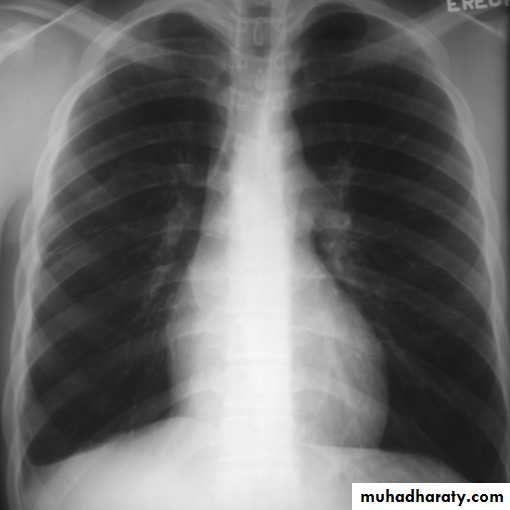
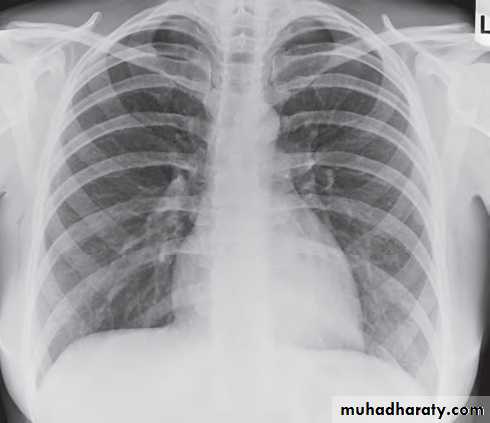
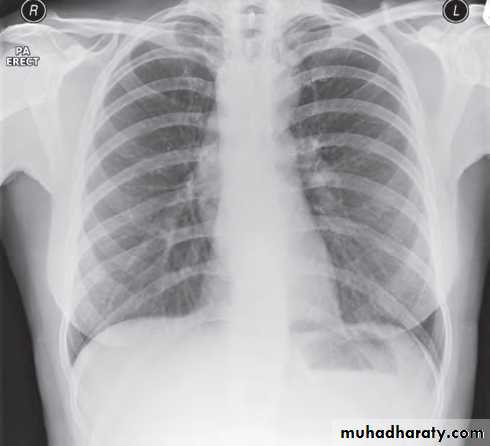
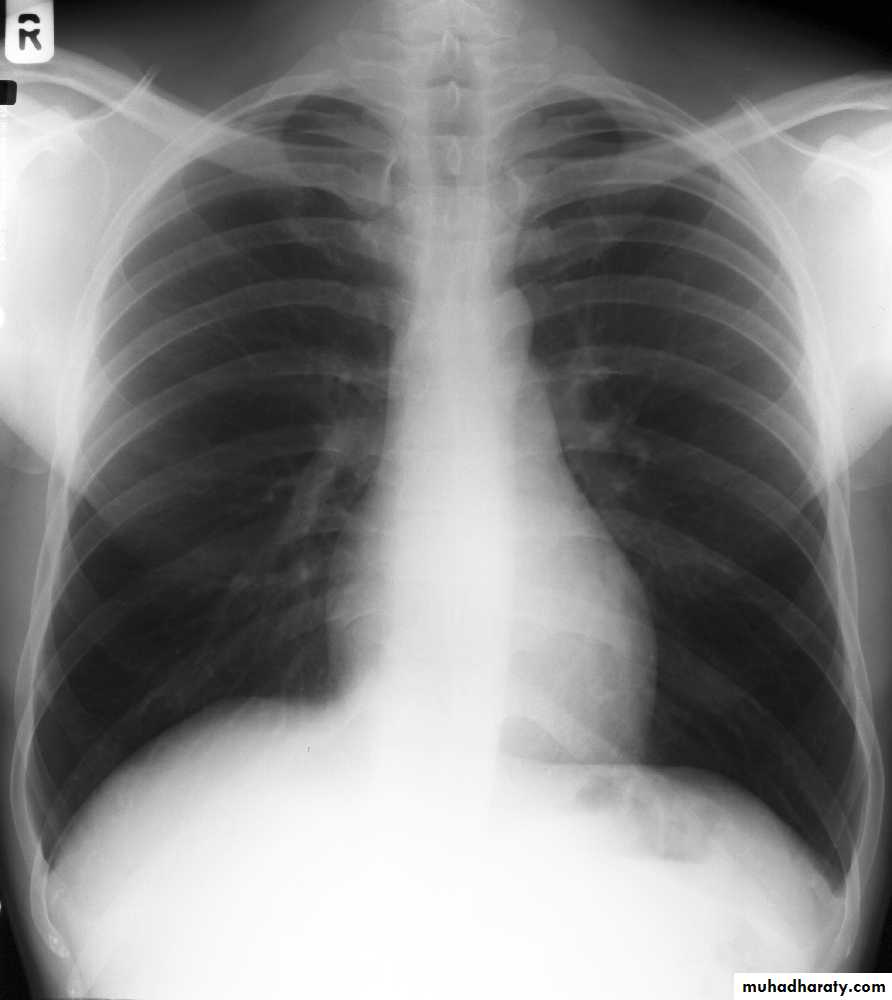
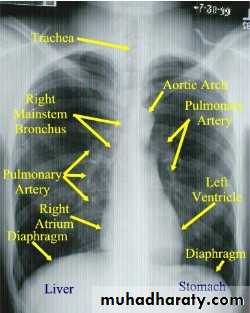
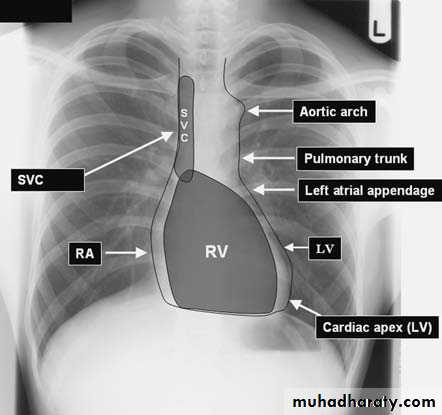
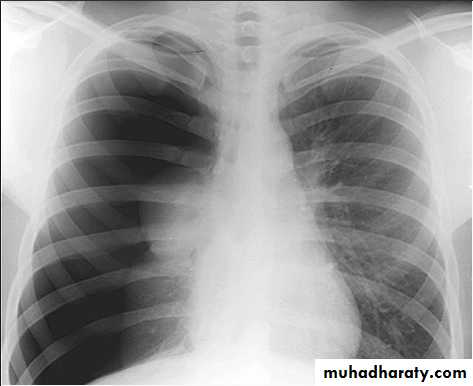
Standard views are the PA & Lateral
PA ( frontal ) VIEW LT. LATERAL VIEW
Other views: AP, oblique, Decubitus, apical, inspiratory, expiratory.
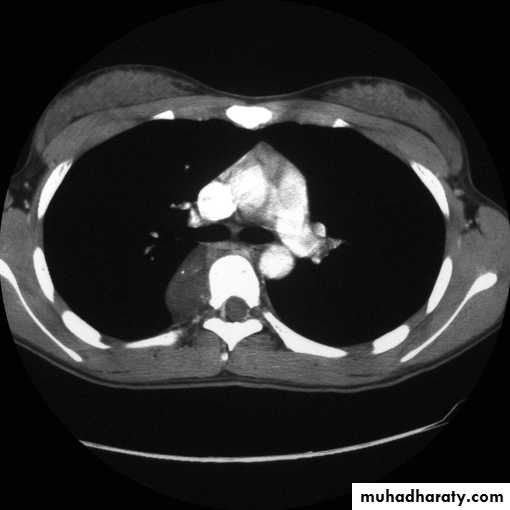
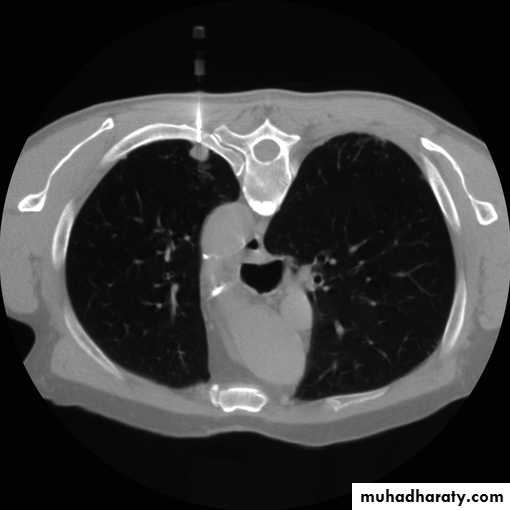
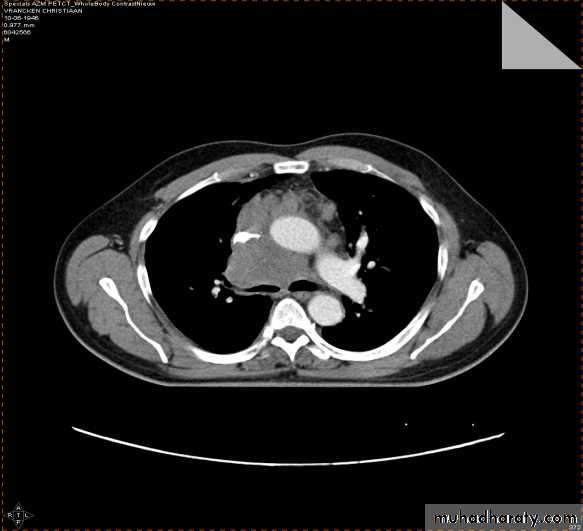
2-CT scan: indications:
• Assessment of trauma and emergency conditions.• assessment of masses( primary & secondary).
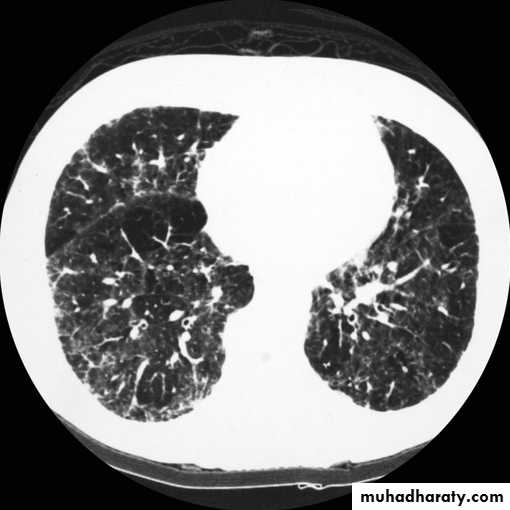
• Diagnosis Of interstitial disease.(HRCT...High resolution CT )
• guided procedures.
• CT angiography in suspected pulmonary embolism.
mediastinal window bone window lung window
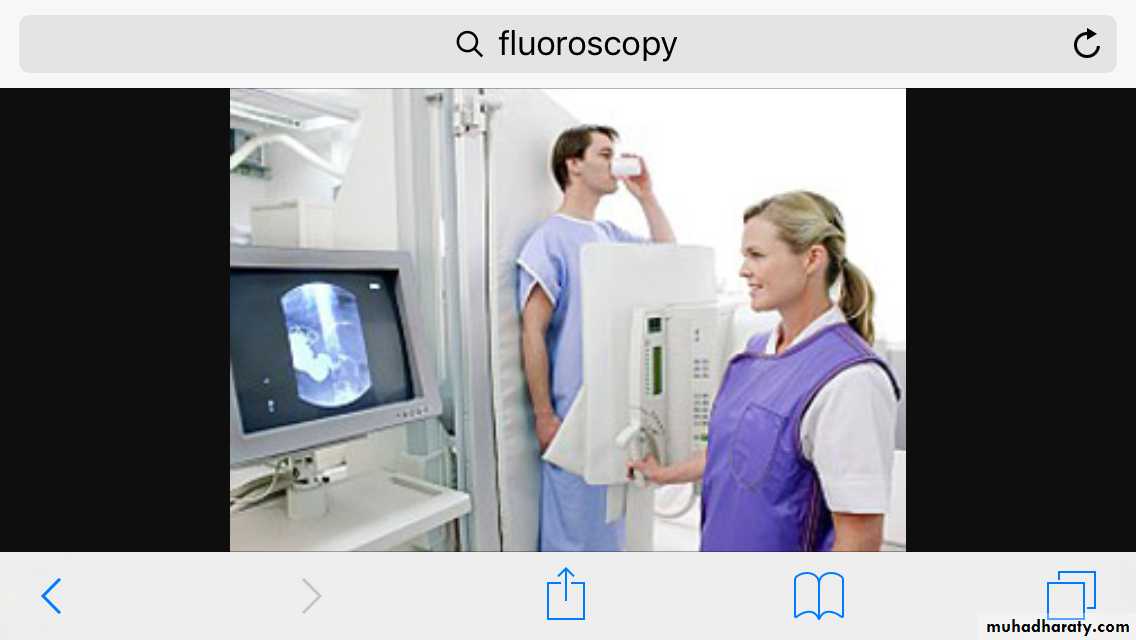
Fluoroscopy
Real time view of moving organsLungs ( at both inspiration &
expiration )
Diaphragmatic movements
Esophageal motility
Any patient position
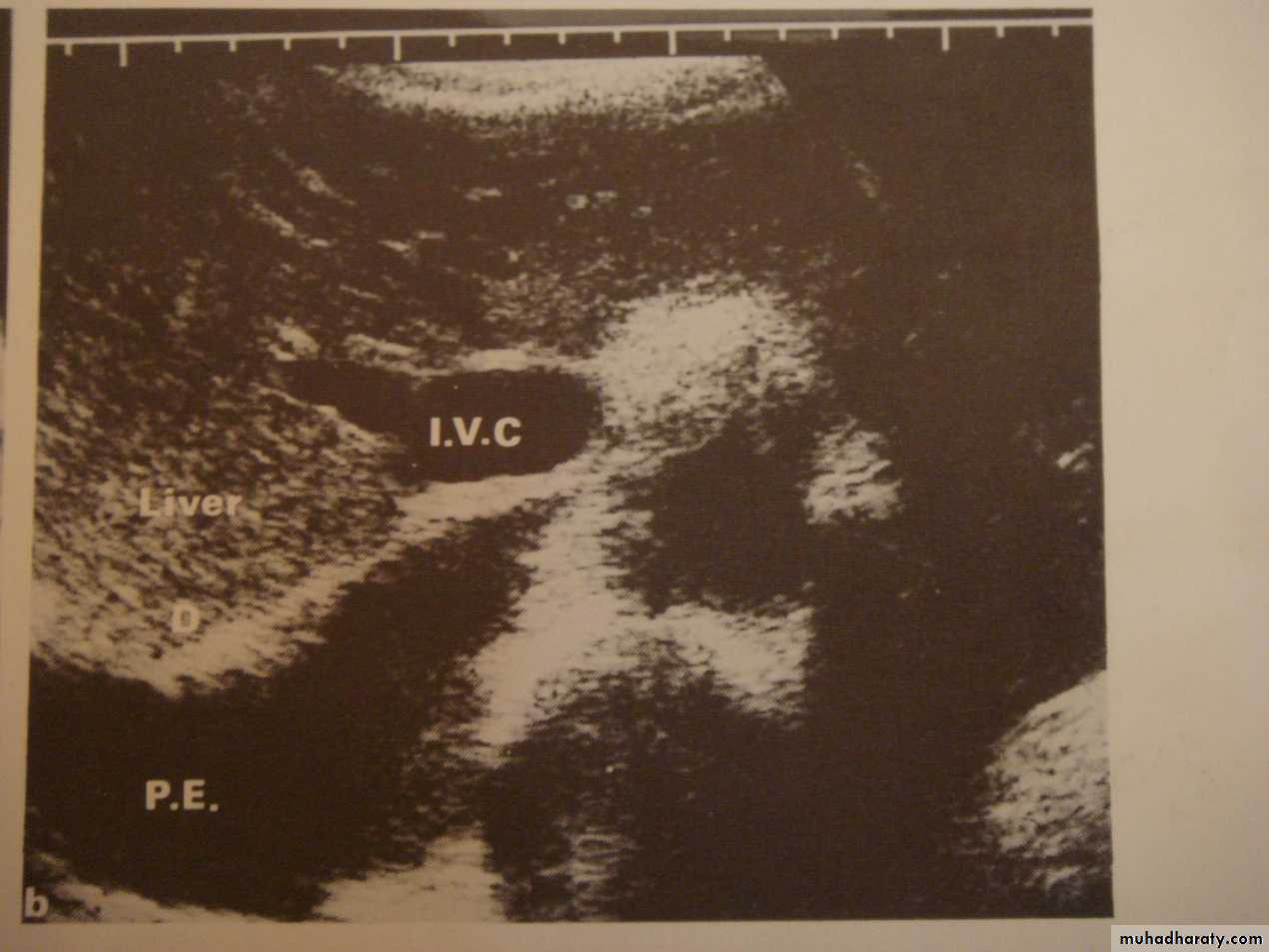
3-US: has limited role in chest imaging due to lungs gases and chest wall bones, but helpful in assessment of pleural effusion, peripheral lung lesions, pleural masses, chest wall masses, diaphragmatic movement, guided procedures and differentiating solid from cystic lesions.
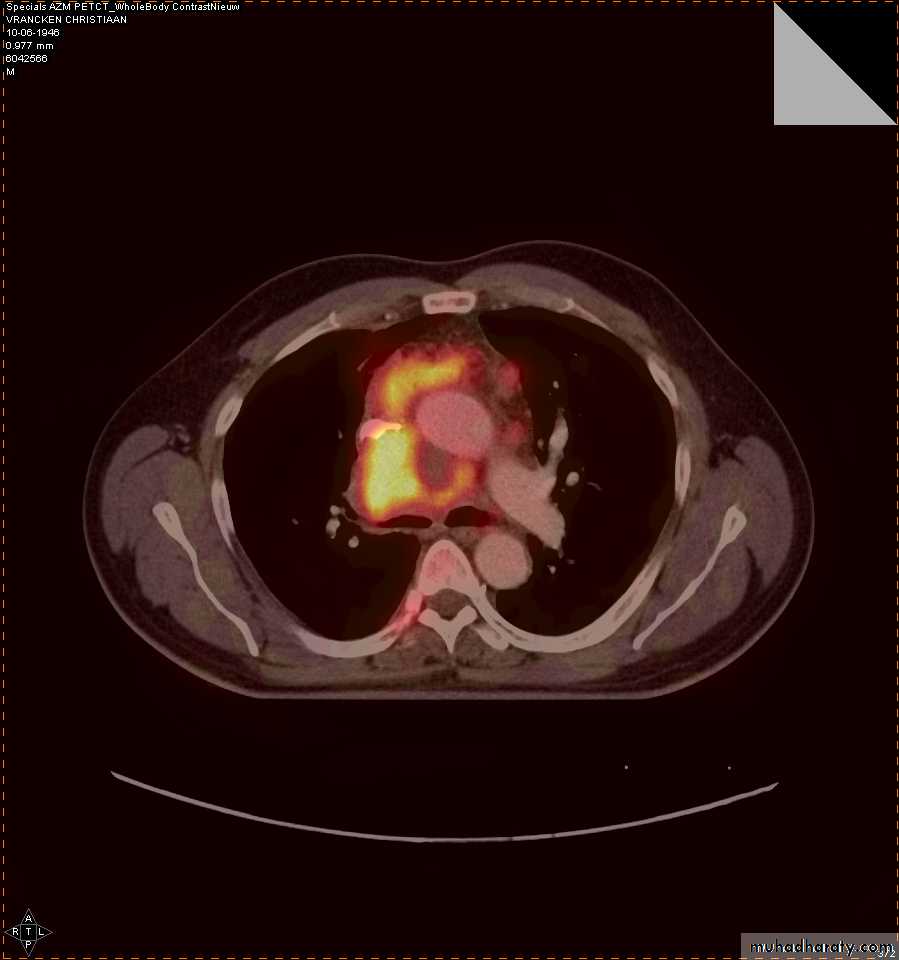
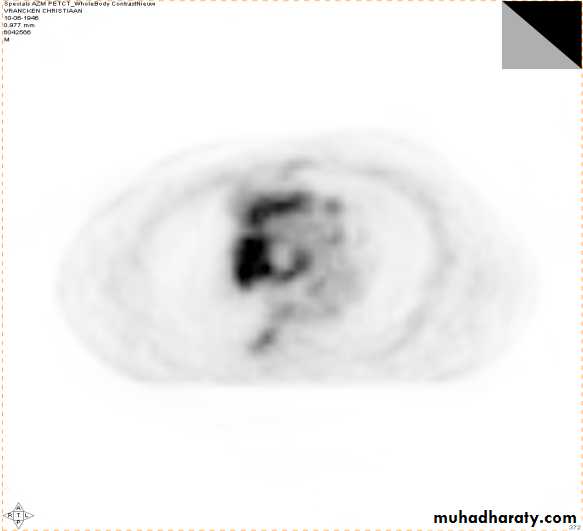
4-PET CT SCAN: its main indication in diagnosis of tumor recurrence after treatment, by demonstrating of increased metabolic level in abnormal tissue. majority of malignant tumors show a greater uptake of the radioactive tracer.
PET
CT
PET/CT
Data UMC Maastricht
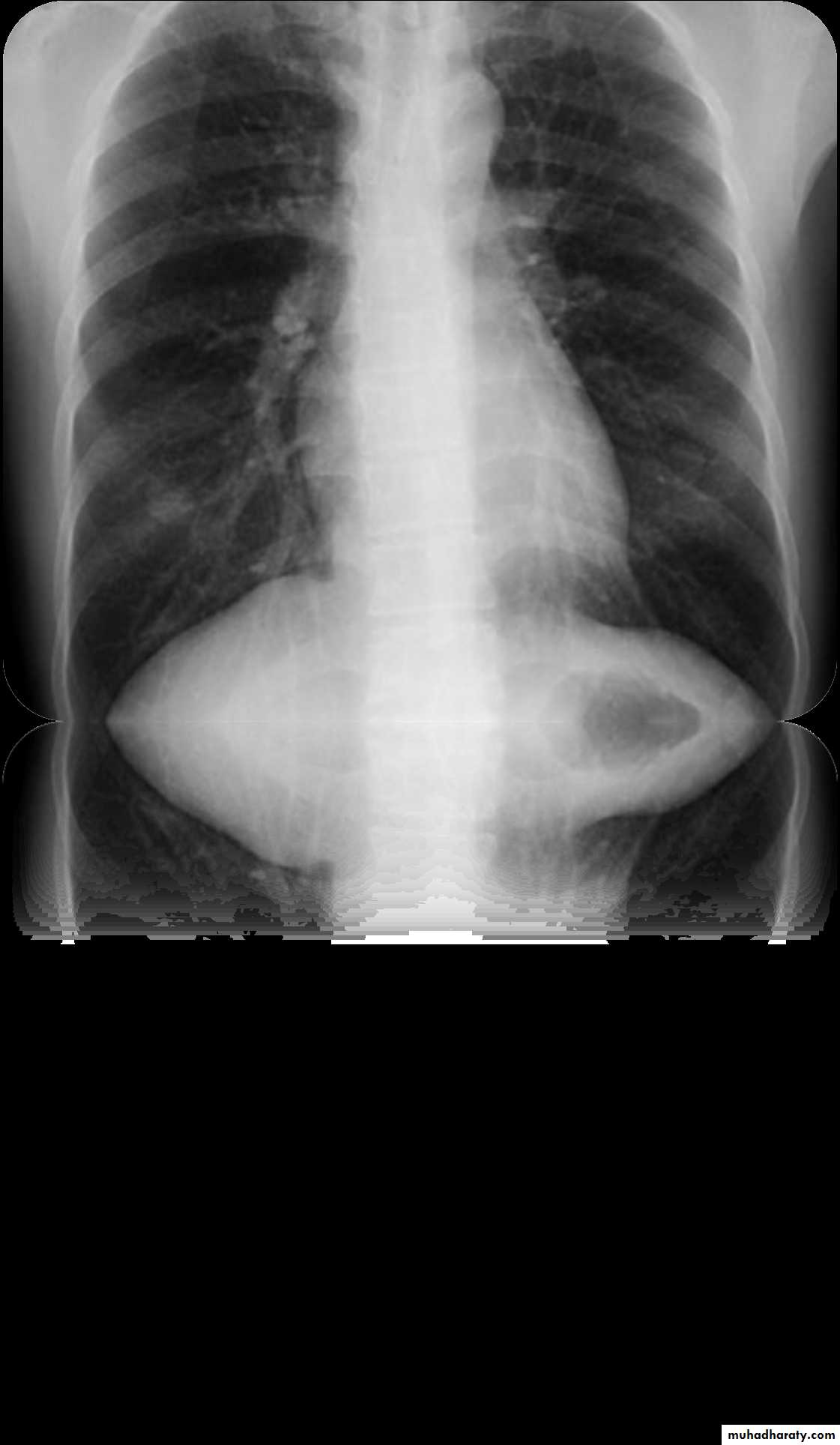
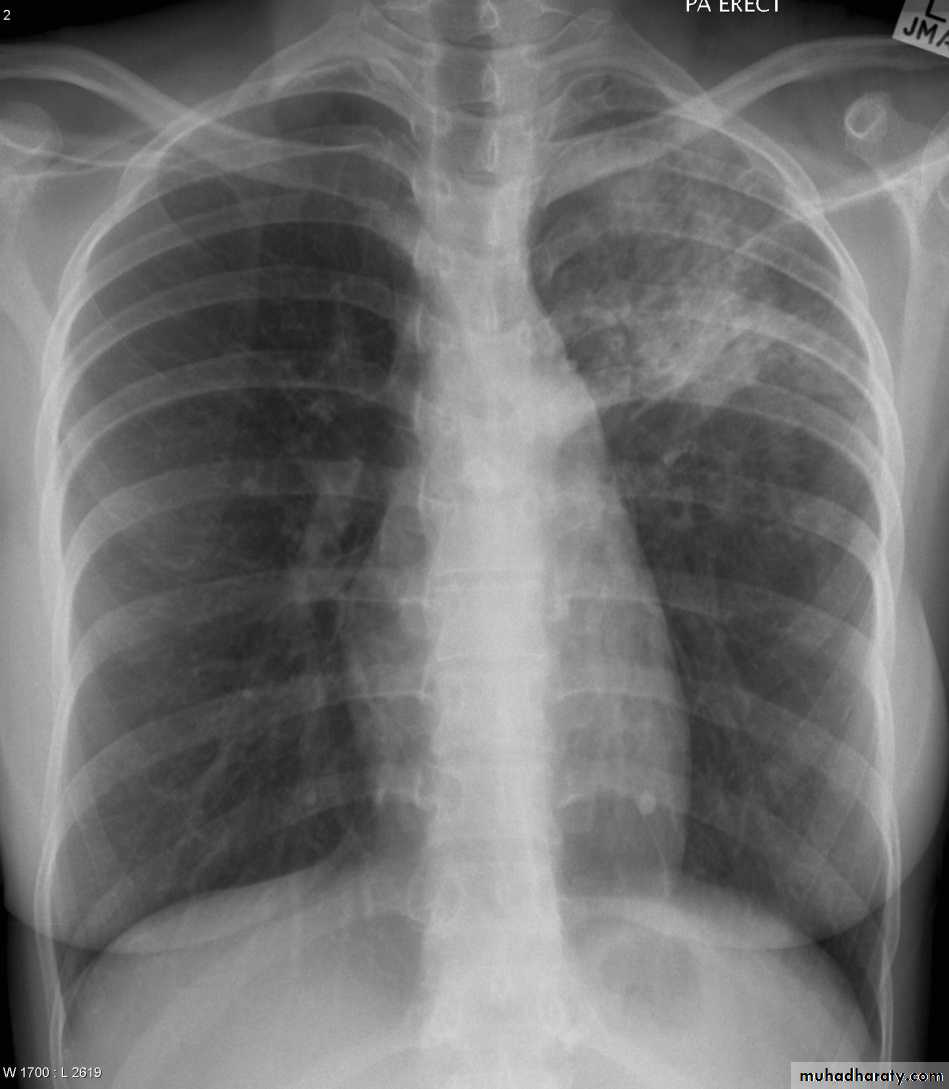
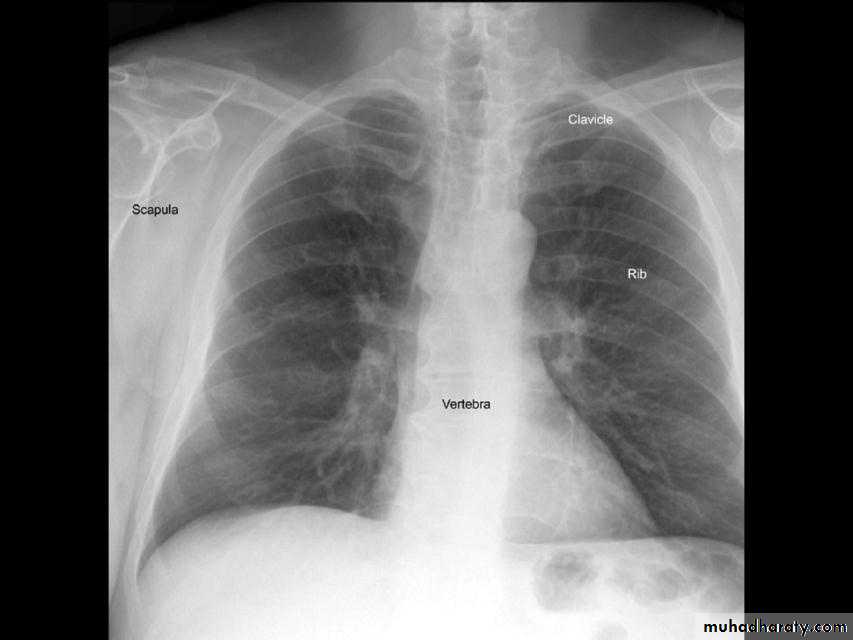
1) CXR
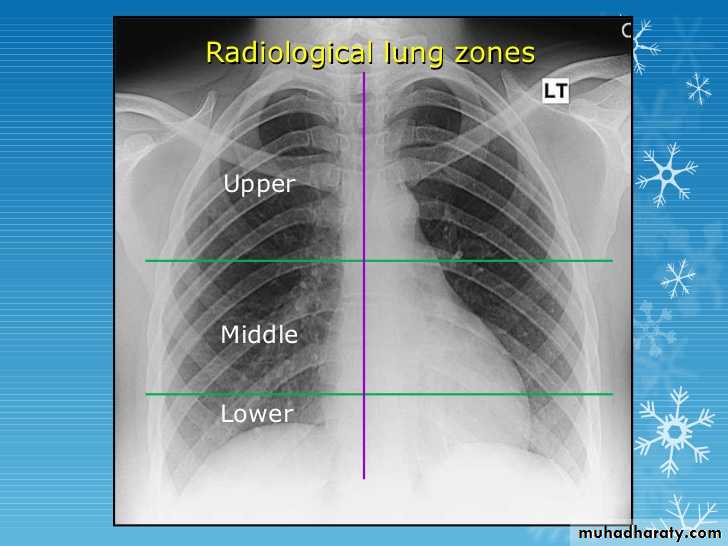
Parts :• 1) Lungs ( Both lung fields )
• 2) Mediastinum
• 3) Chest wall (ribs& soft tissues )
• 4) Diaphragm
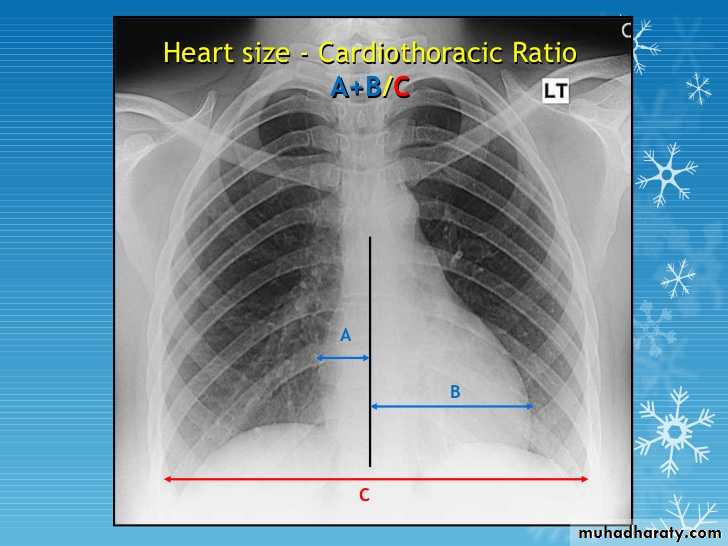
• 5) HilaGood CXR = correct diagnosis
Good CXR
Labeled— Patient’s full )name 1) medico-legal Date of the examinationDirection
Position ( supine or erect )
Radiological center
2)Direction
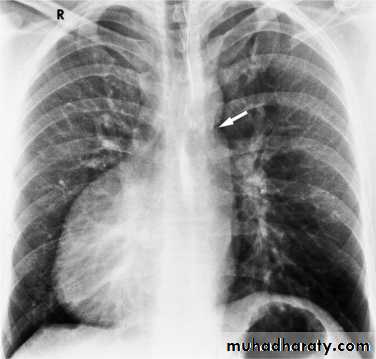
Gastric air bubble on the left & liver on the Rt2/3 of the cardiac shadow lie to the left of midline & one third lie to the Rt
3) PA view( patient facing the cassette )
PA(postero-anterior )
Anterior ends of ribs & clavicles directed downwardAP(infants & bed ridden patients )
anterior ends of ribs & clavicles directed upwardPA VERSUS AP PROJECTION:
Avoid the magnification of the heart.Protect the radio-sensitive organs, lens of the eye, thyroid gland, breast tissue in females and gonads.
Displace the scapula and clavicles away from the lung shadow.
4)Erect position
Erect position mean:PA view
Full inspiration
5)Full inspiration
The diaphragm should be below theanterior end of 6th rib & posterior end of 10th rib .
In expiratory film there is cardiac shadow enlargement , & vascular crowdening
Poor visualization of bases of the lungs1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Inspiration/Expiration
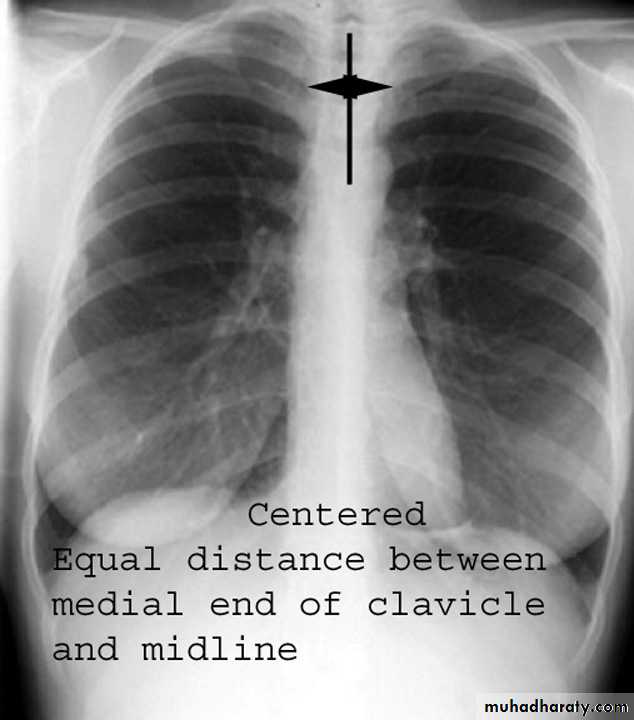
6) Good centering ( not rotated )
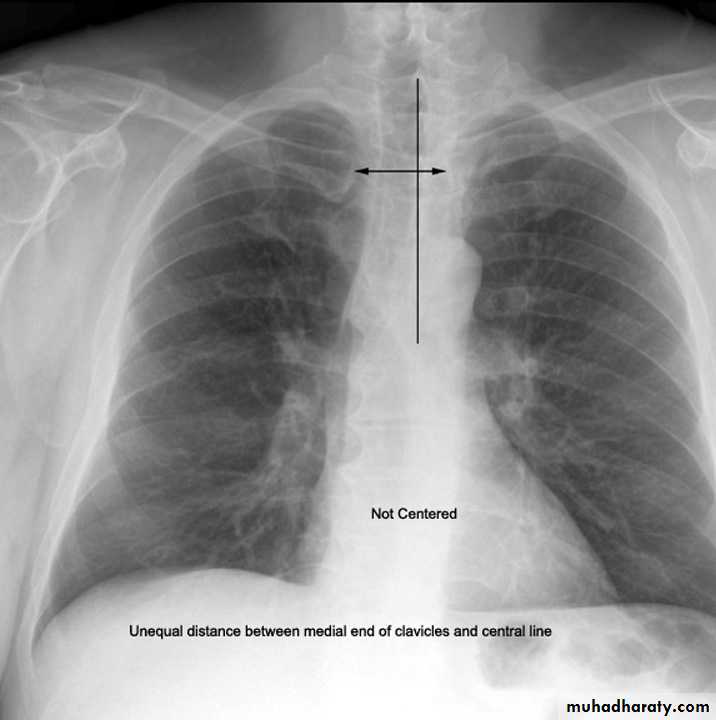
Both medial ends of clavicles are equi-distance from spinous process of adjacent vertebra .In rotated film , one side of the lung appear more opaque than the other with distortion of mediastinal borders.
Rotation .
Rotation of the radiograph is assessed by judging the position of the clavicle heads and the thoracic spinous process.7) Good technique (amount of radiation )
The vertebral bodies are just visible through the cardiac shadow
PenetrationLow KV
High KV
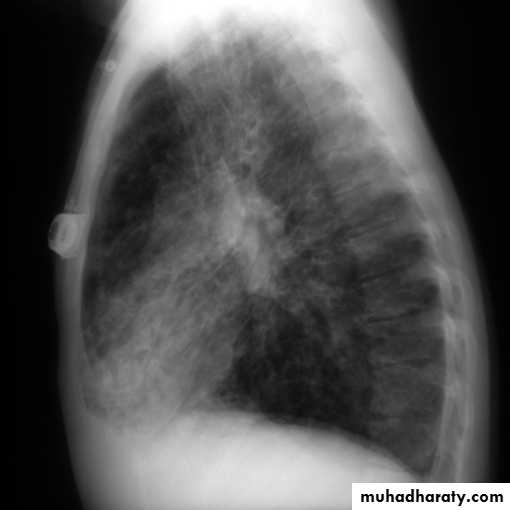
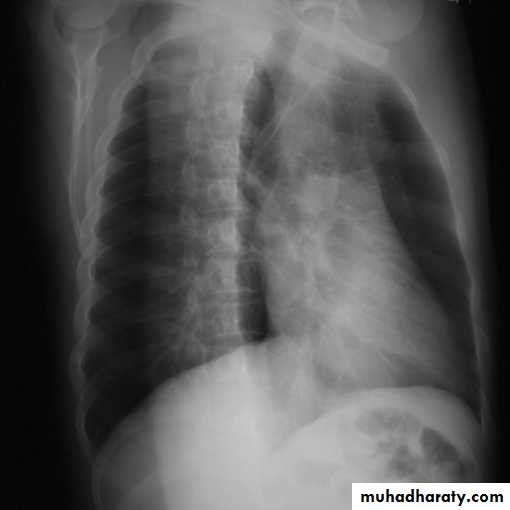
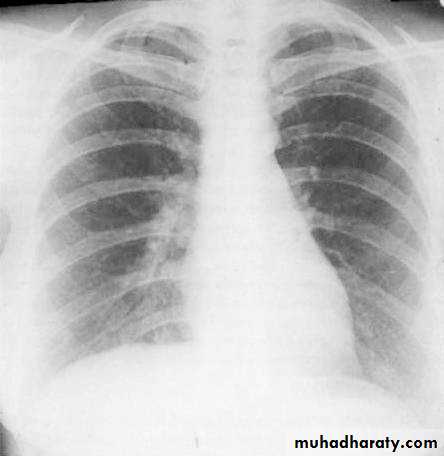
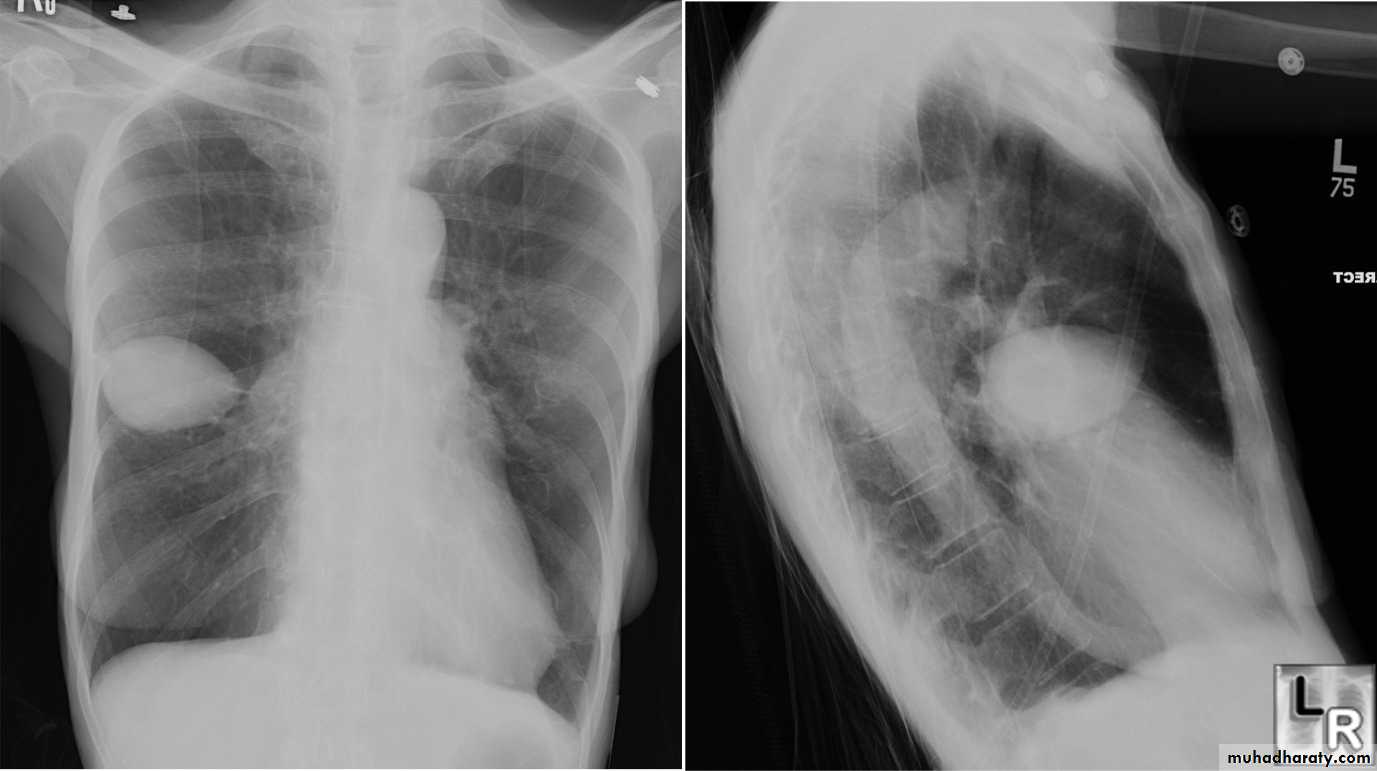
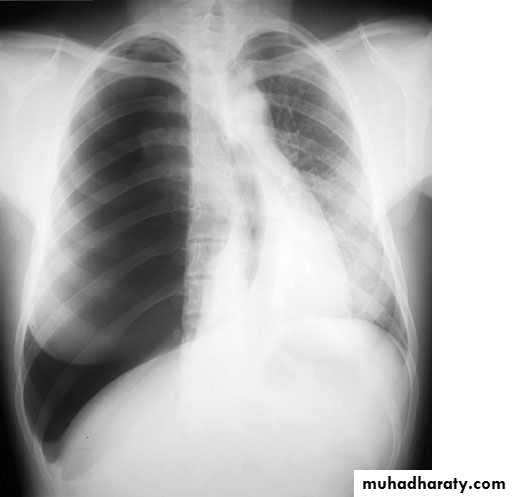
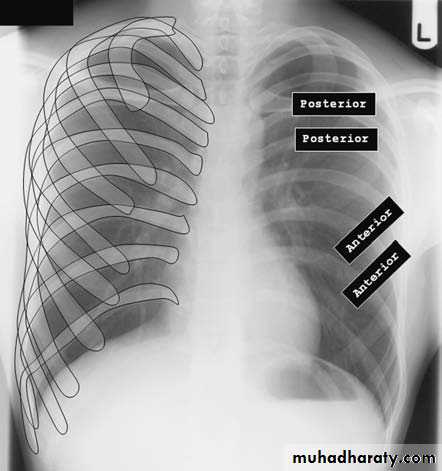
Lateral view
IndicationsAnterior mediastinal mass
Encysted pleural fluids
Posterior basal consolidation
How to read CXR
LungMediastinum
pleura
Diaphragm
Bones &soft tissues
Lungs
apex
Costophrenic angleLungs
Focal lung diseases-nodule
- mass
-cavity
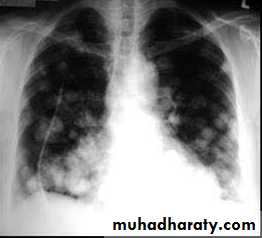
Diffuse lung disease --alveolar ( opacity & consolidation)
--interstitial
Air way diseases –lobar collapse
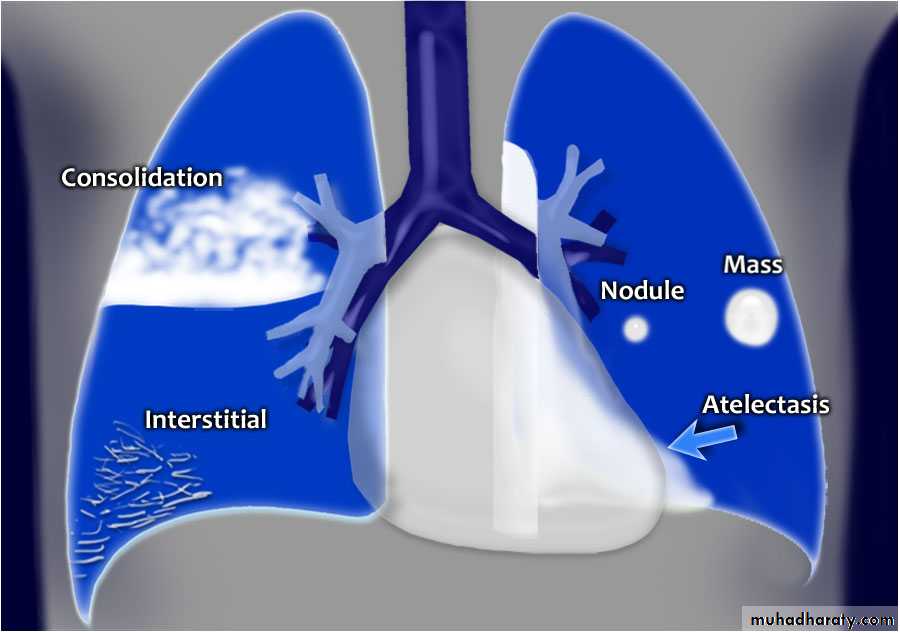
Lung diseases
Focal ( Solitary or multiple )Diffuse ( alveolar or interstitial )
Shadow
Well defined margin-Regular- irregular
Size;
>5mm =miliary
5mm-20mm=nodule
>20mm ( 2cm )= mass ( homogenous or complex)
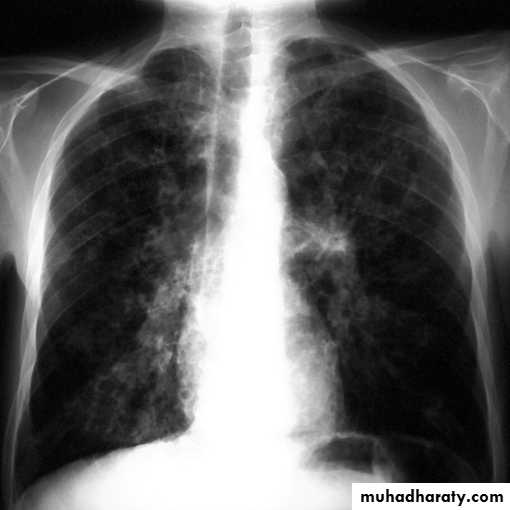
Miliary shadow
1) infection ( TB ,fungal , viral )2)Dust inhalation (workers in dust materials)
3) Metastasis
=2-3mm
After treatment
Miliary TB
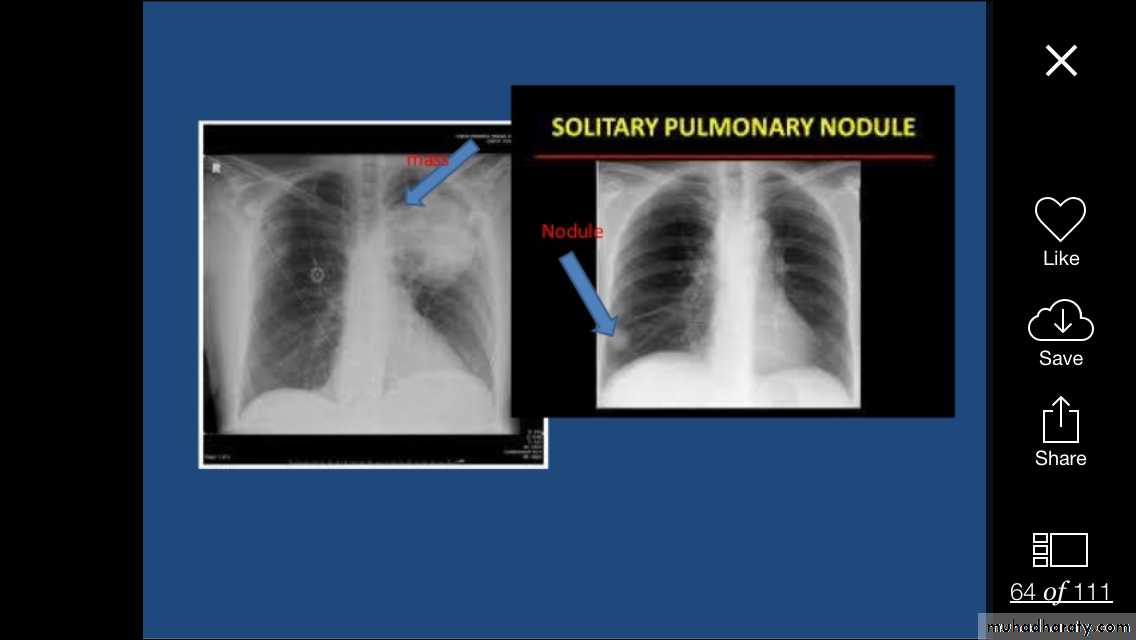
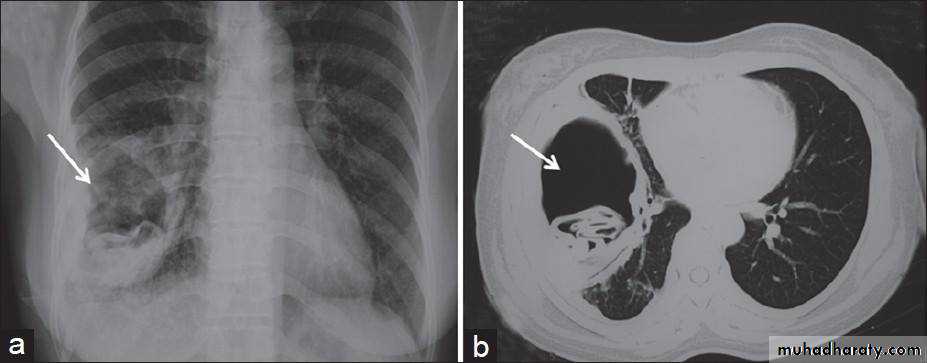
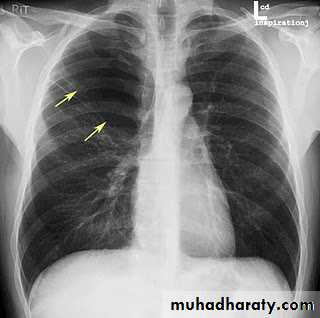
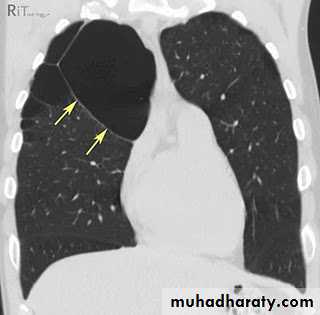
Pulmonary nodule /s1) Bronchogenic CA ( spiculated )
2)Metastasis ( multiple & different size & distribution )
3) Tuberculoma
4) hamartoma
Both are : solitary , peripheral & contain calcification )
5)Hydatid cysts
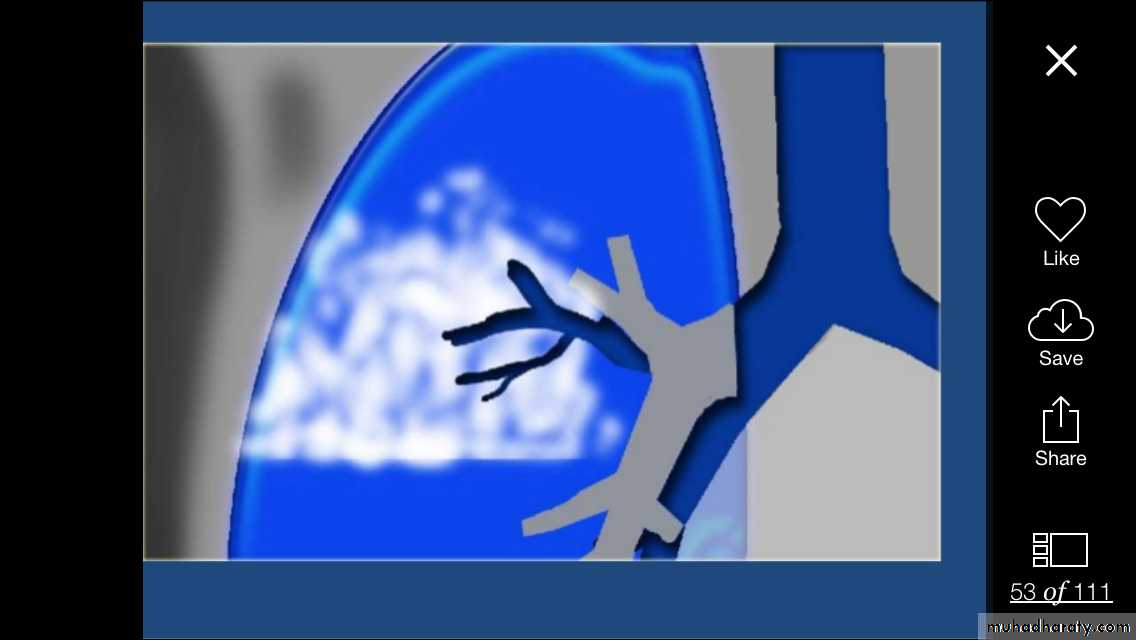
6)AVM (arterio-venous malformations which show feeding vessels
Nipple shadow
Opacity
Ill defined marginIrregular shaped
Homogenous or non homogenous (contain air or calcification )Pulmonary vessels could be traced through it .
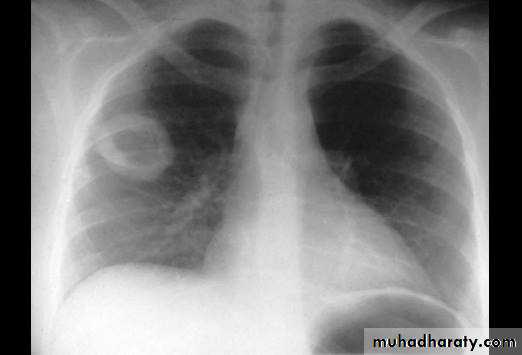
Causes(pneumonia ,pulmonary infarction & pulmonary contusion )Cavity
1/contain air only1)Thin walled-central =pneumatocele
-peripheral = Emphysematous bullae
2)Thick walled-regular= chronic abscess
-irregular =Tumor with central necrosis
2/contain air +fluids :acute abscess
ruptured Hydatid cyst
3/air +nodule :mycetoma( fungus in previous cavity)
Tumor with necrosis
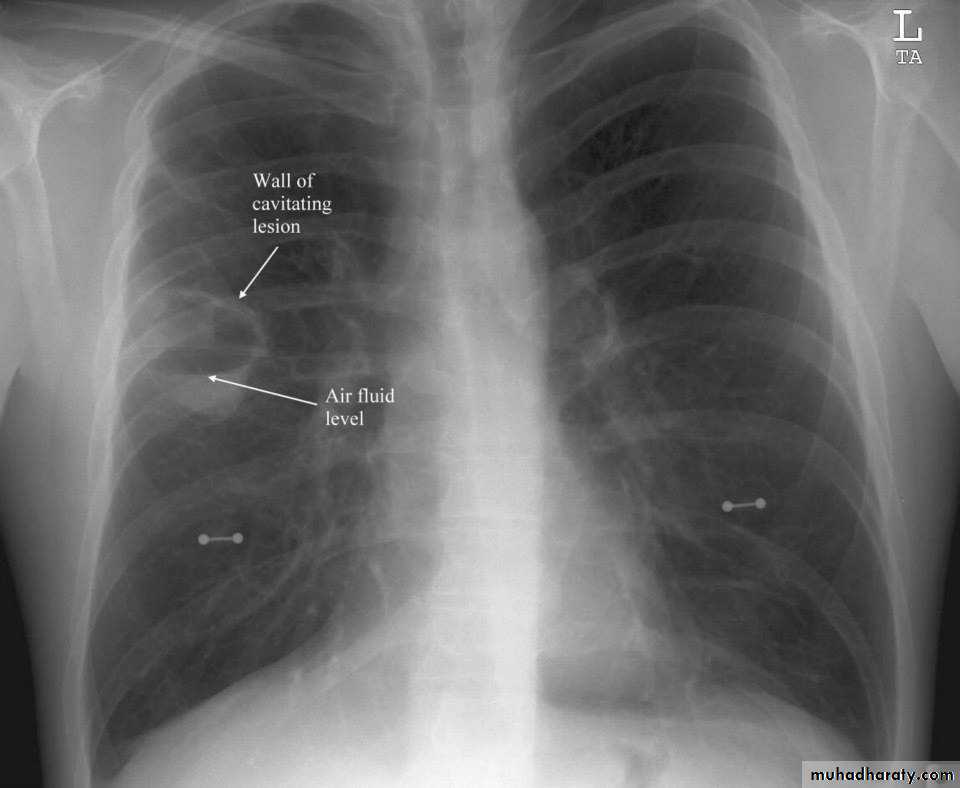
Cavity ( air containing lesion )
Thin walled <3mm
Thick walled >3mm
Cavity with air fluid level
Air fluid level with membrane (ruptured hydatid cyst )
Histology
Diffuse lung disease
AlveolarInterstitial
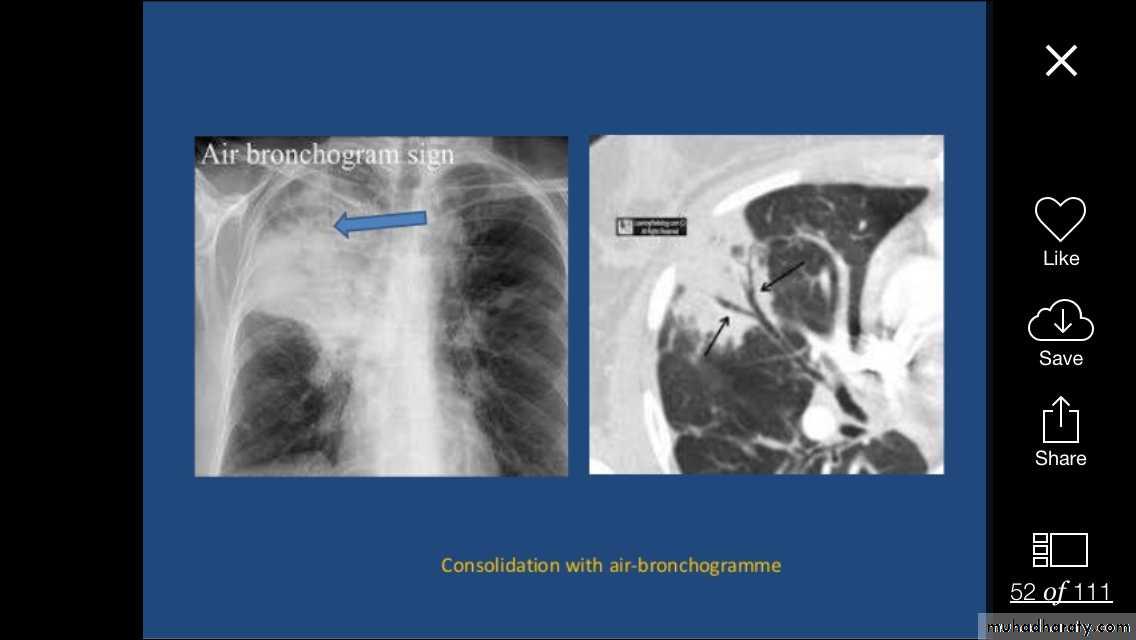
Alveolar shadow (consolidation )
Replacement of air in the alveoli by fluidContain (air bronchogram )
Pneumonia
Pulmunary edemaContusion
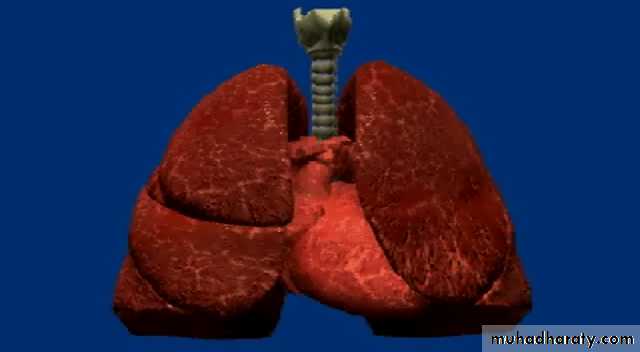
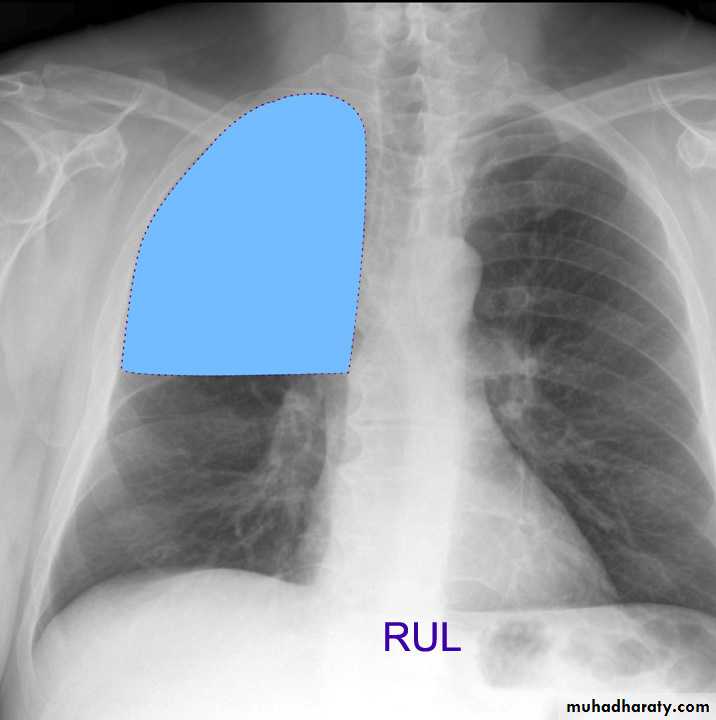
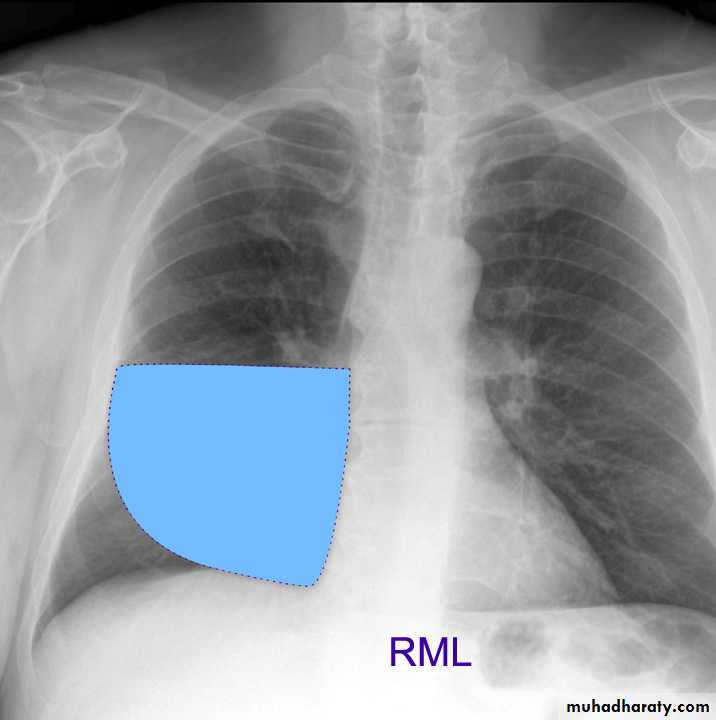
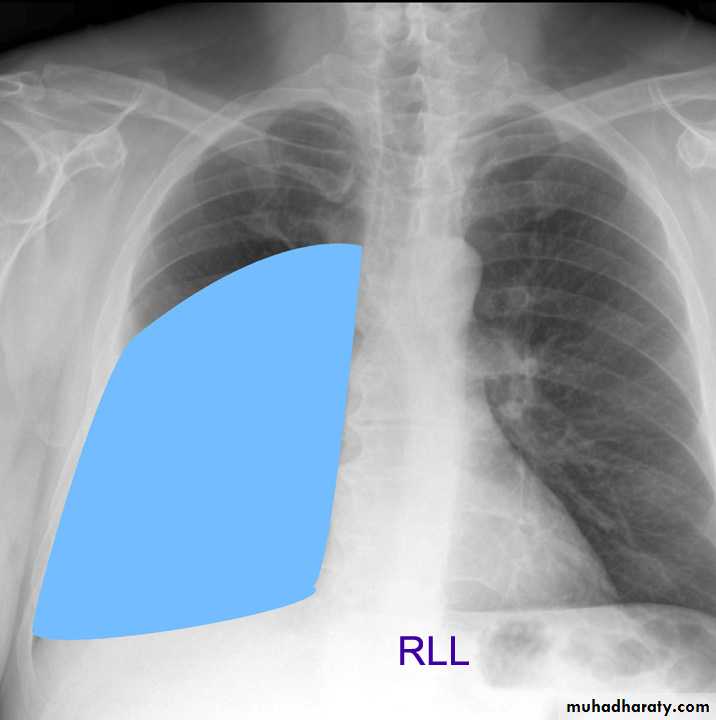
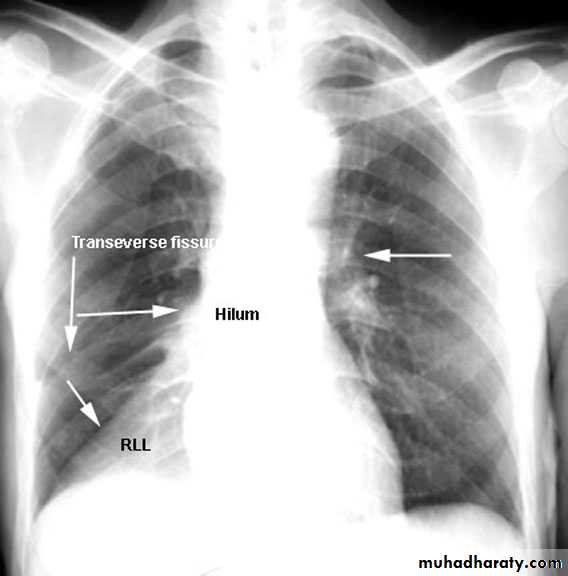
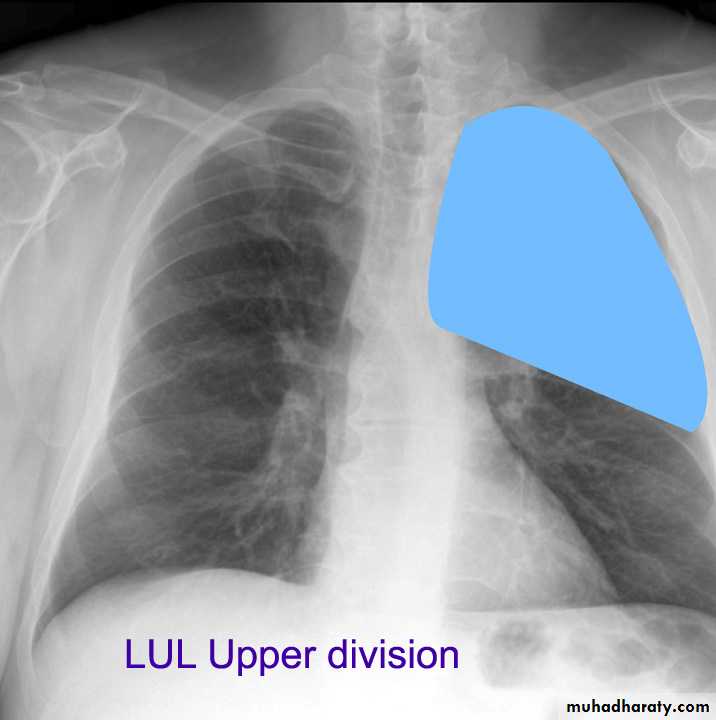
Lung Anatomy
Zonal anatomyLobar anatomy
Rt lung divided to 3 lobes (upper , middle & lower )
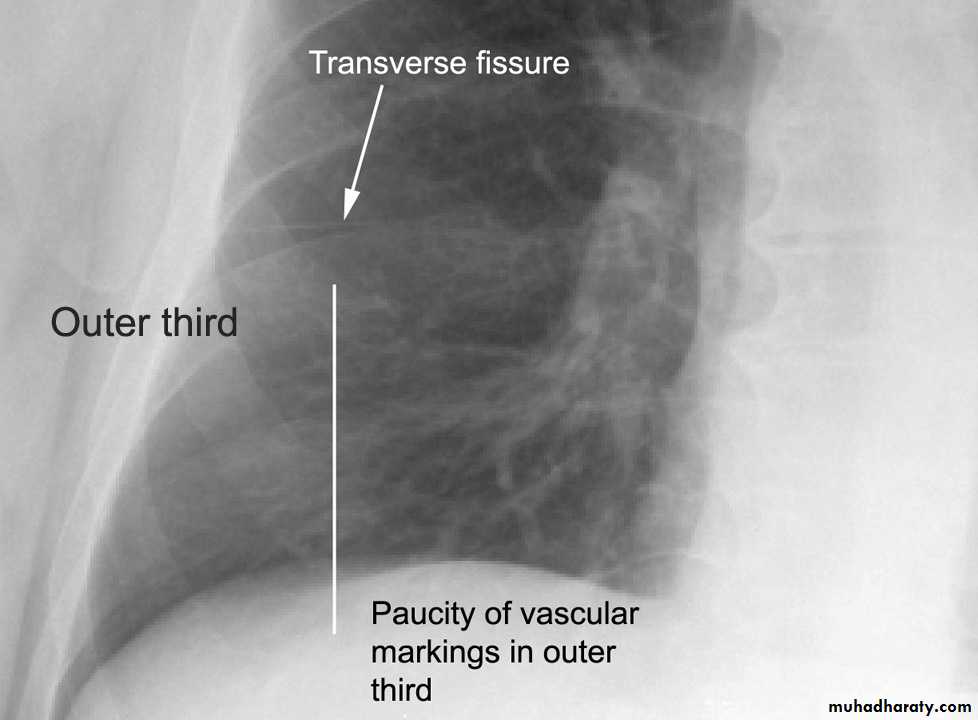
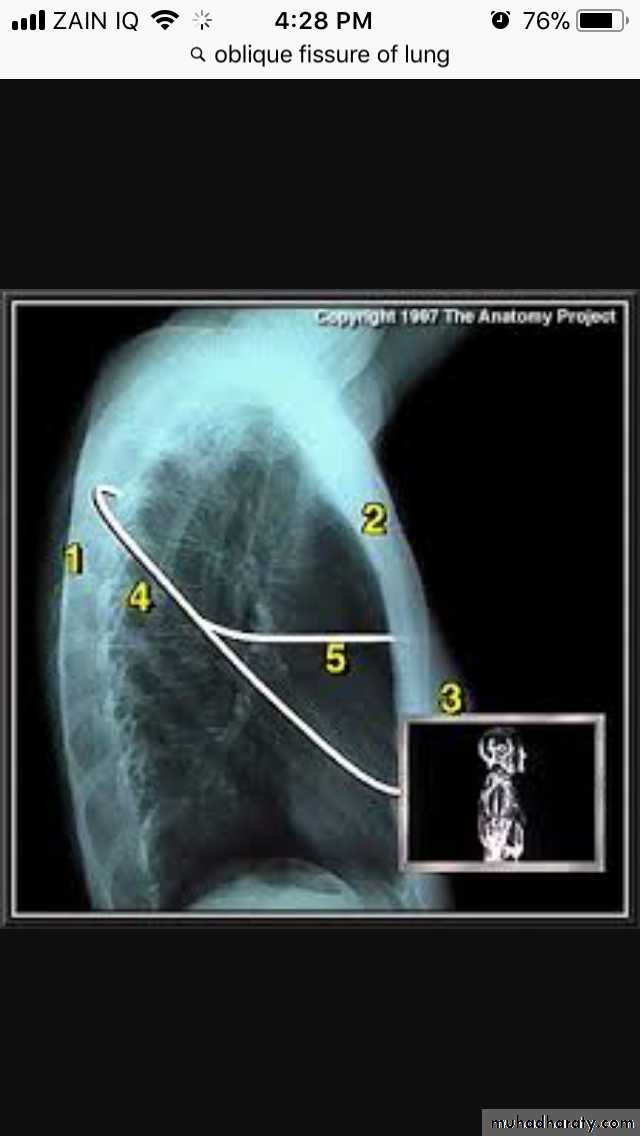
Transverse fissure separate the upper lobe from middle lobeOblique fissure separates the upper & middle from lower lobe .
The left lung subdivided to two lobes by oblique fissure ( upper & lower )
Rt upper lobe
Rt middle lobe
Rt lower lobe
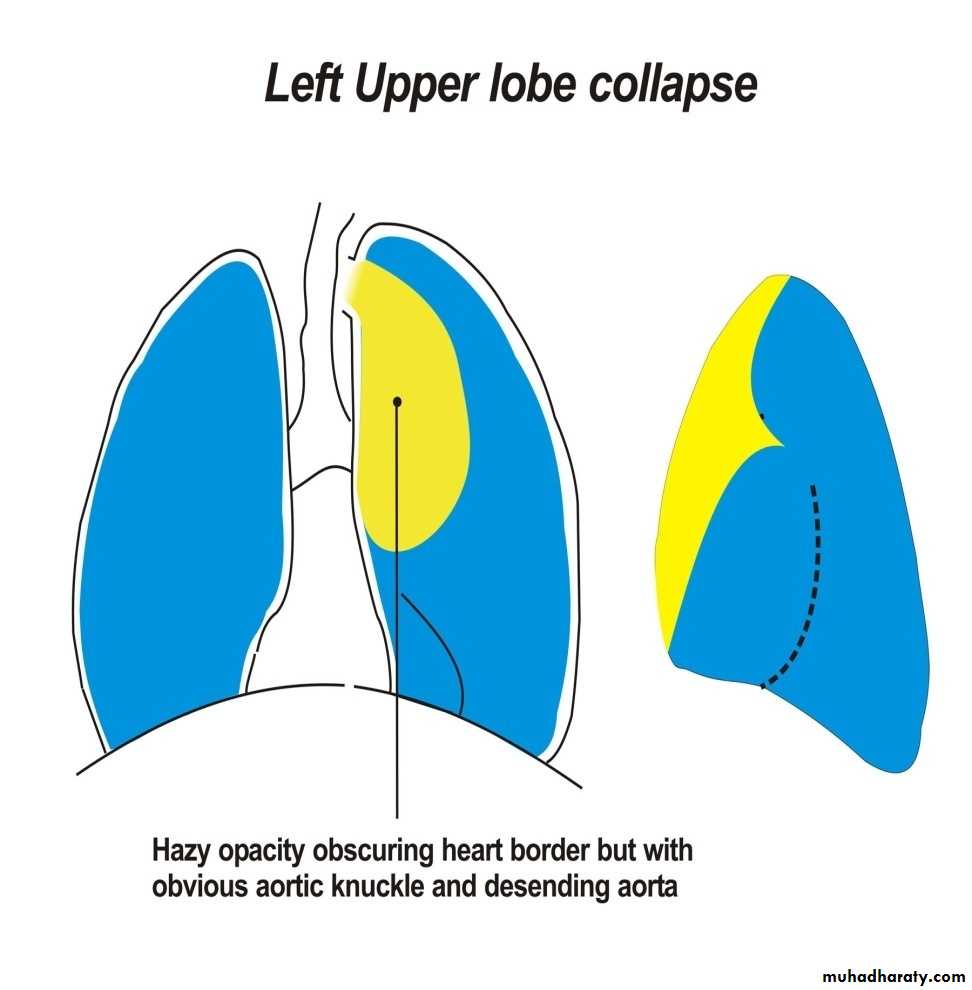
Left upper lobe
LUL collapse
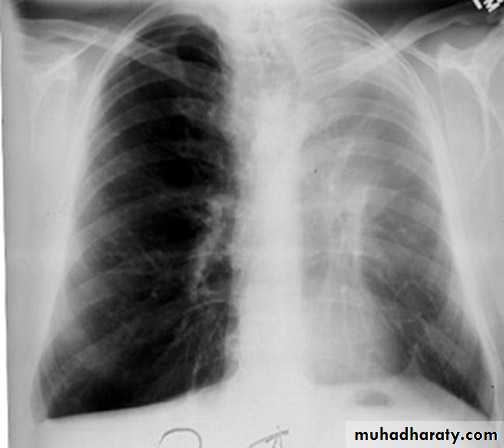
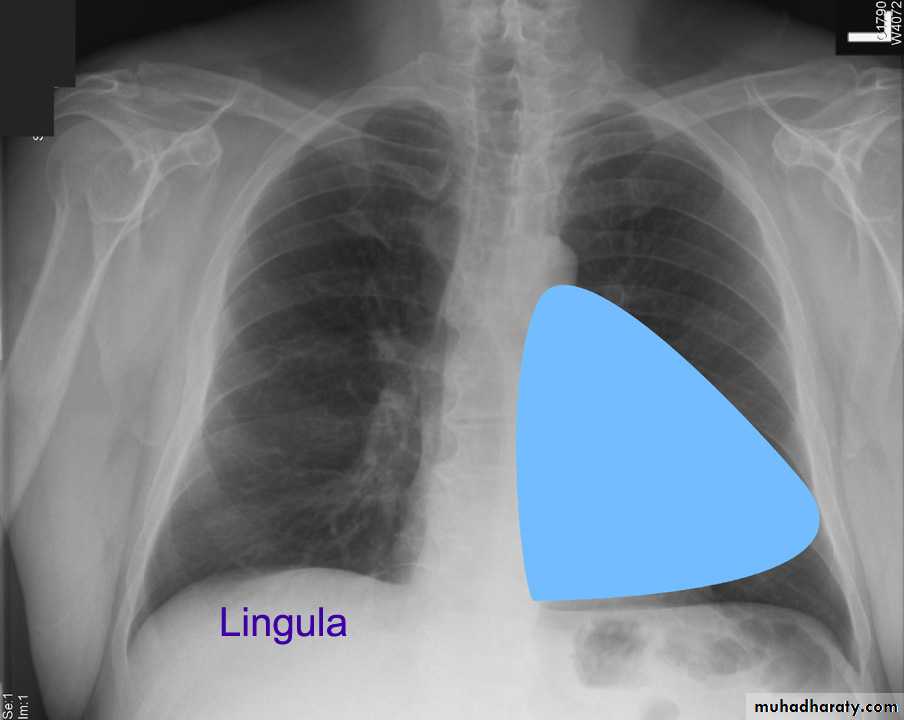
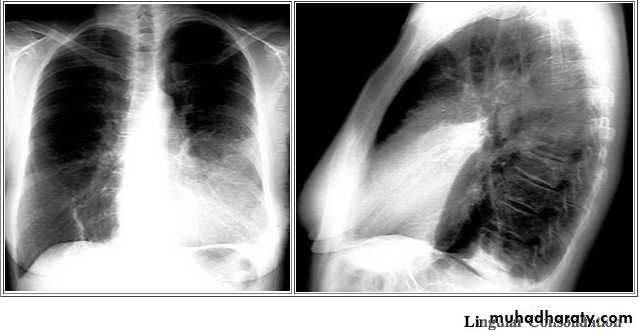
Left lingula
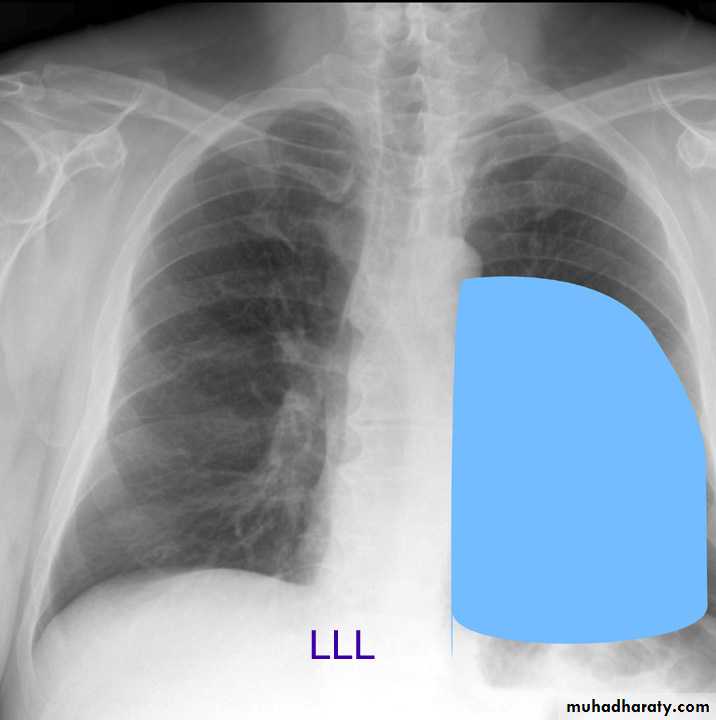
Left lower lobe
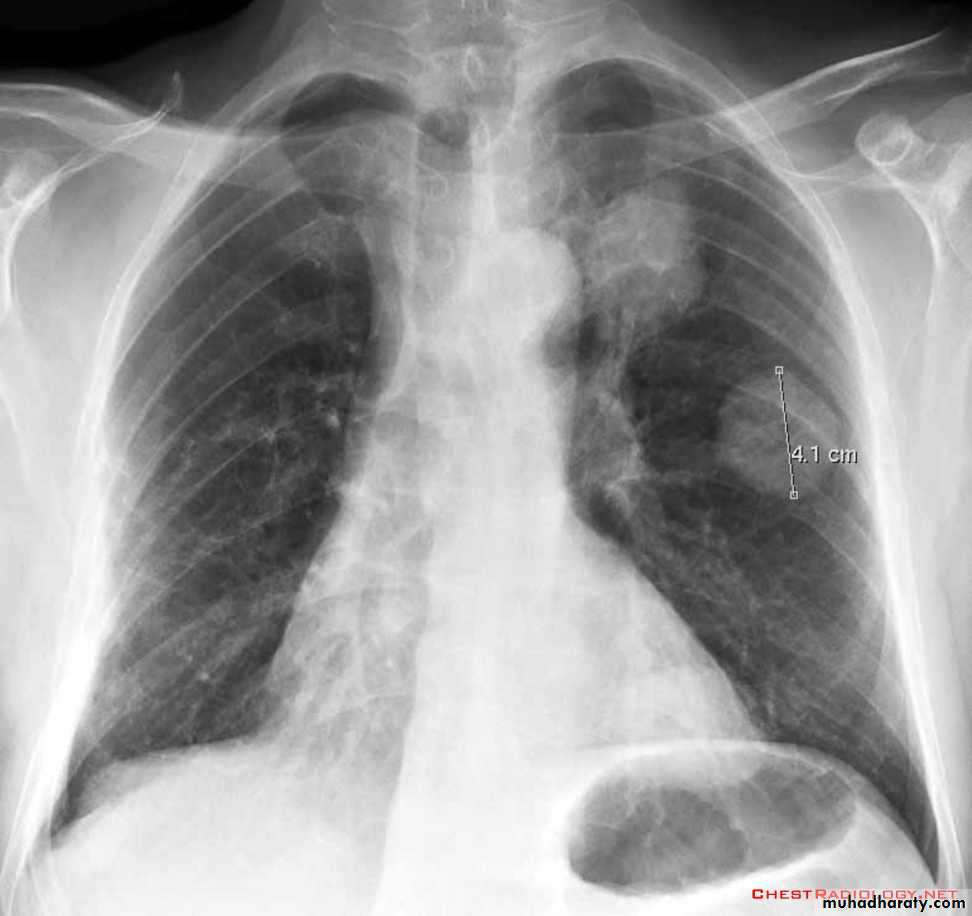
Pulmonary lesion
Mediastinum
Mediastinum
1)Trachea & main bronchi 2) esophagus3)Heart &major vessels
4)LNs
5)Nerves
6) Thymus
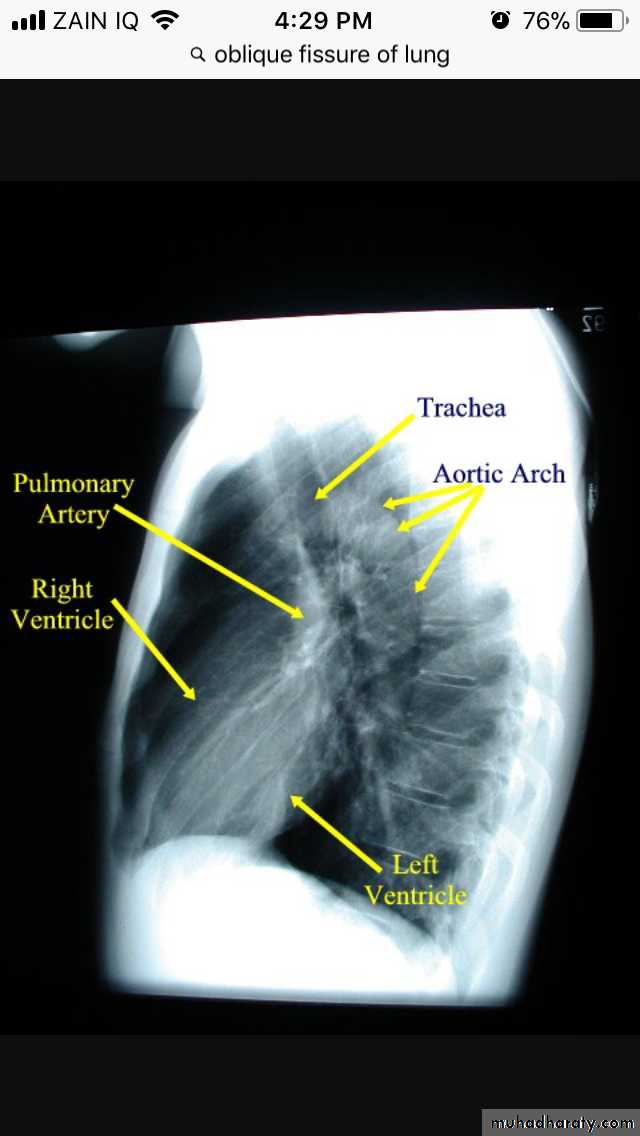
Trachea & main bronchi
سSlightly deviated to the RtTracheal deviation
FB) inhalation )Foreign Body
InspirationExpiration
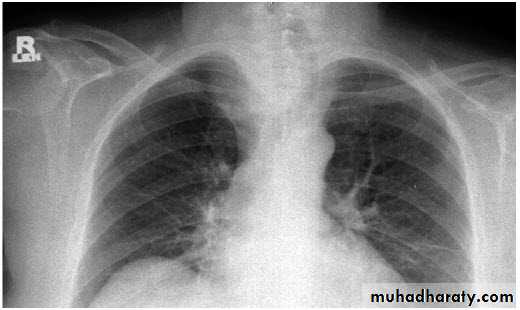
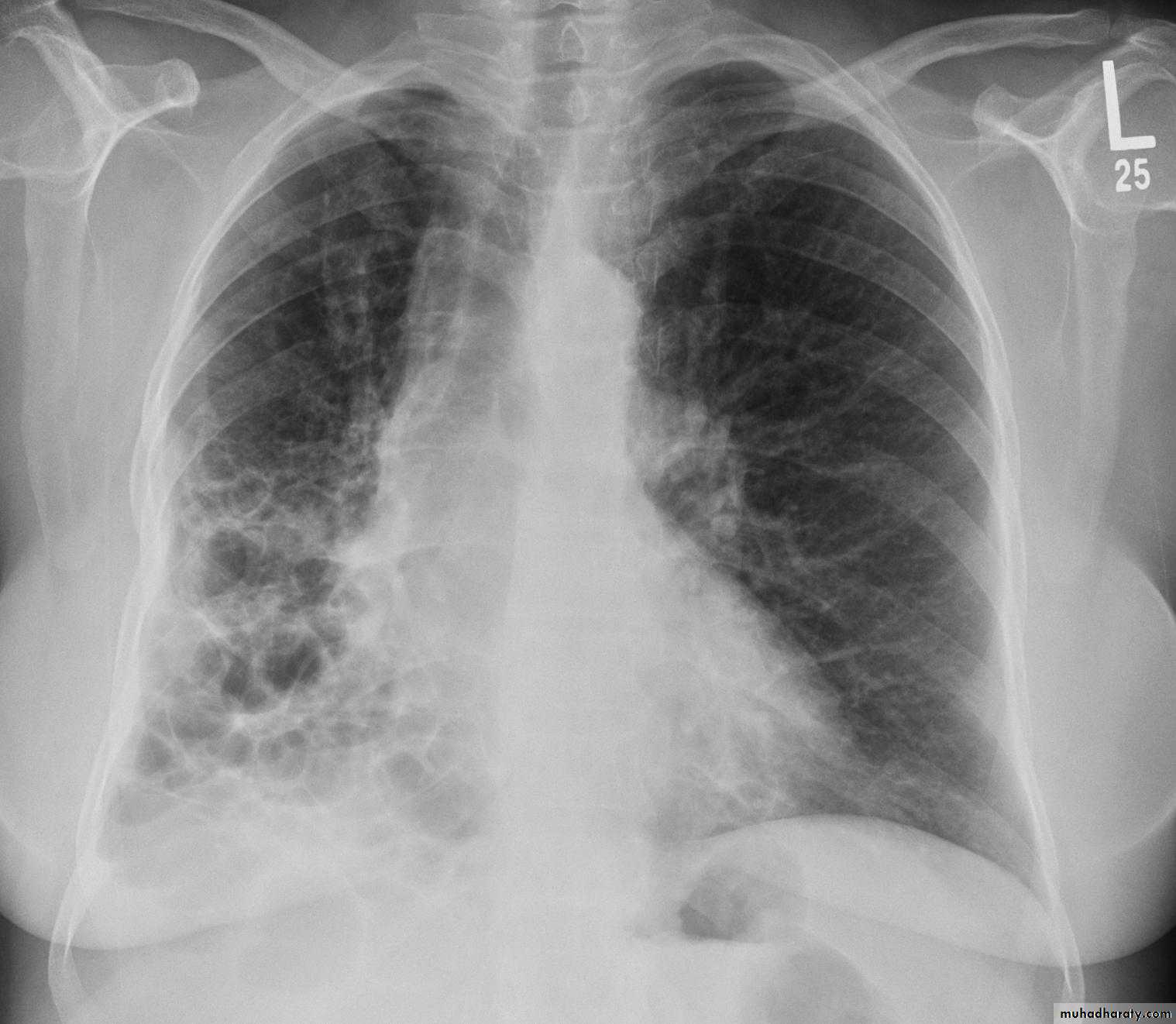
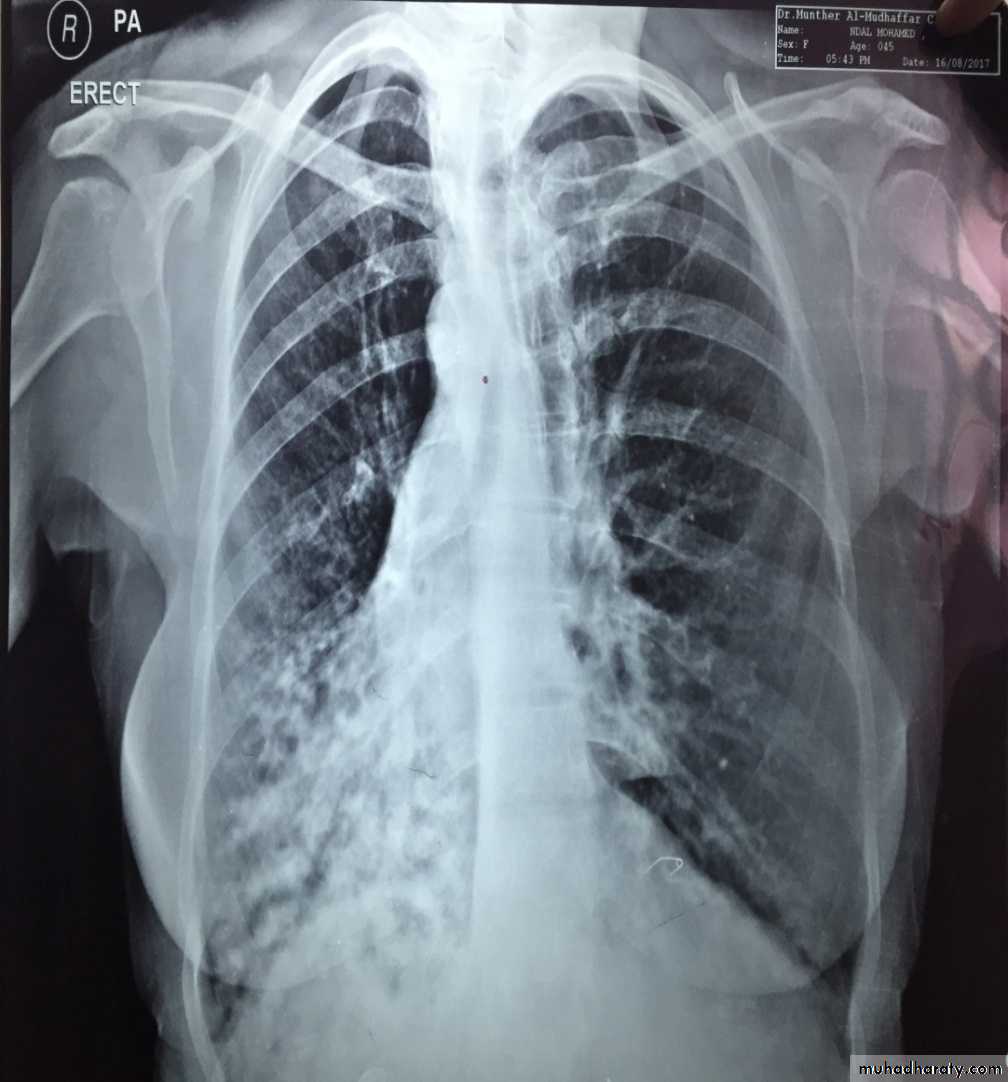
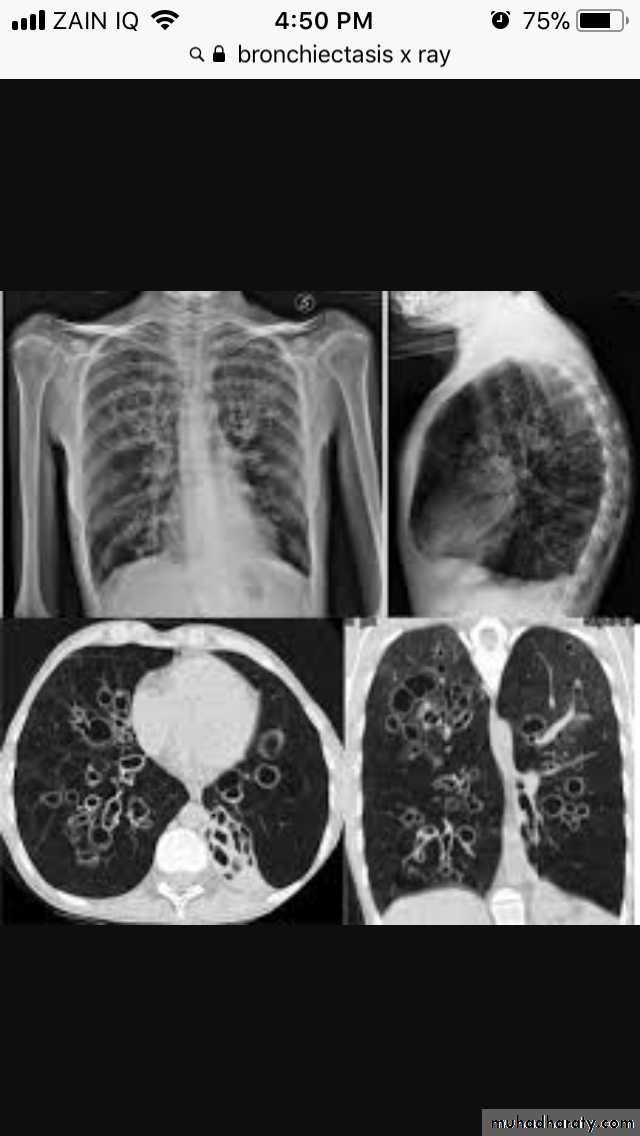
Bronchectasis
Abnormal irreversible dilatation of bronchioles with thickening of their walls . Presented with recurrent pneumonias & haemoptysis ..Types:Cystic
Fusiform
Cylendrical
In which the bronchiole is wider than the near by vascular branch
Causes –infancy & childhood infection
-TB
-pulmonary fibrosis
-cystic fibrosis
-immotile cilia syndromes
Esophagus
Stricture with proximal dilatation with retrocardiac air fluid level .Mediastinal widening
Thymus ( neoborns & infants )Retrosternal goiter
Vascular lesions
Mediasinal LAP
Congenital & acquired cysts
Tumors
Diaphragmatic Hernias
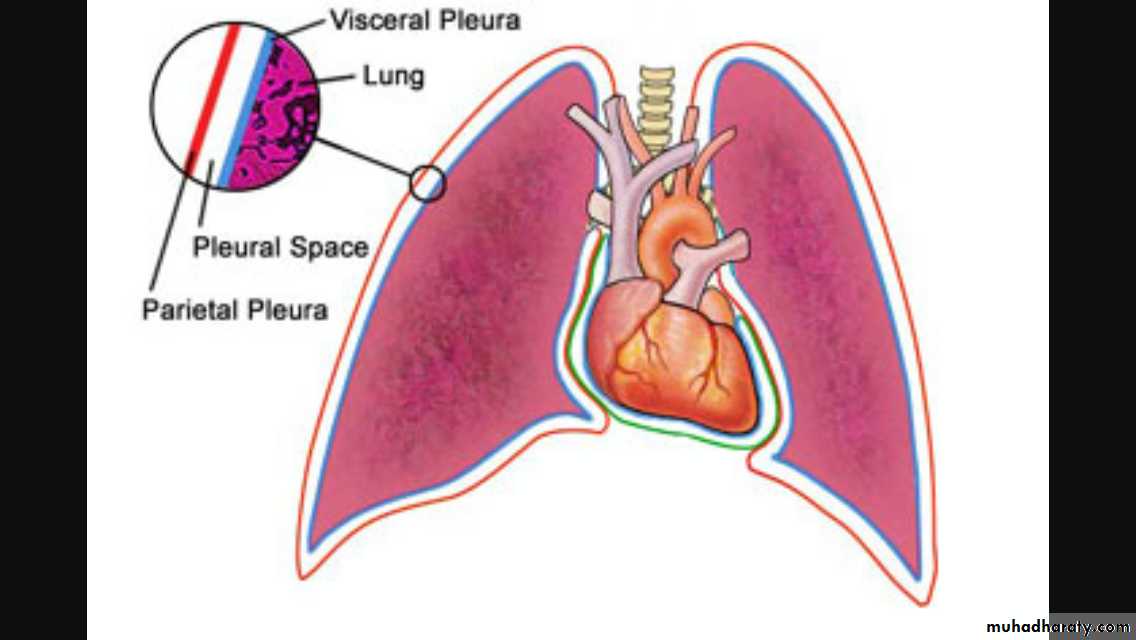
The pleura
pleurapleura is 2 fibrous layers
1st is parietal layer investing the chest wall & diaphragm .
2nd is visceral covering the lung
In between space is invisible & containing scanty lubricating fluids . l
Pleural pathology
1) Pleural effusion : accumulation of fluids in the peritoneal space .2)Pneumothorax : accumulation of air in the pleural space .
3) Pleuricy: infection of the pleura
4)Pleuritis : inflammation of pleura
5) Mesothelioma : primary tumor of the pleura
6)Secondaries
The pleura :
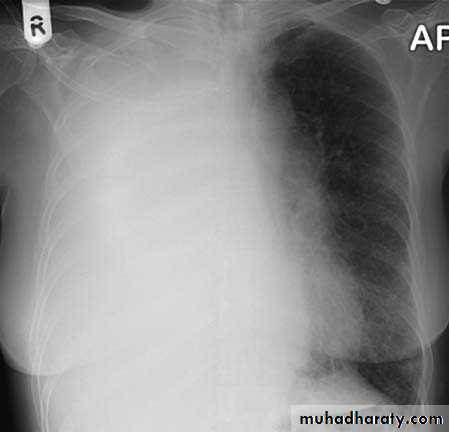
• Pleural effusion : collection of fluid within the pleural space. This can be further divided into Transudate , exudate, according to protein content .Other type of fluid collection within pleural space are
empyema (pyothorax)
chylothorax (lymph in pleural space )
haemothorax
• Chest x-rays are the most commonly used examination to assess for presence of a pleural effusion, however it should be noted that on a routine erect frontal chest x-ray as much as 200-500 ml of fluid is
• required before it becomes evident .
blunting of the costophrenic angle
blunting of the cardiophrenic angle
fluid within the horizontal or oblique fissures
eventually a meniscus will be seen, on frontal films seen laterally and gently sloping medially
with large volume effusions, mediastinal shift occurs away from the effusion
• Lateral films are able to identify a smaller amount of fluid ( about75%)as the costophrenic angles are deepest posteriorly posteriorly
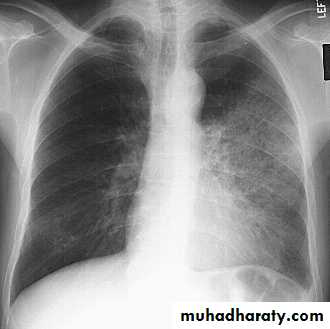
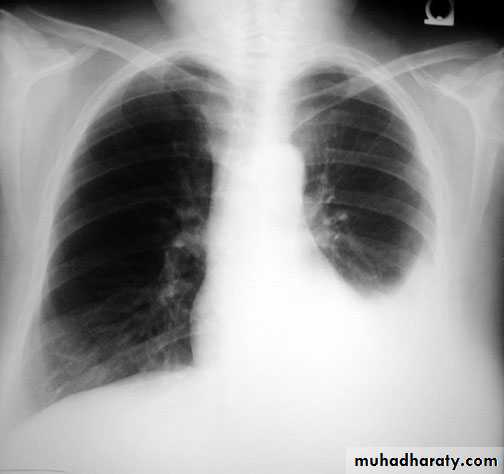
Pleura effusion signs
Obliteration of costo-pherinic anglesMeniscus sign
Lenticular sign
ٍ
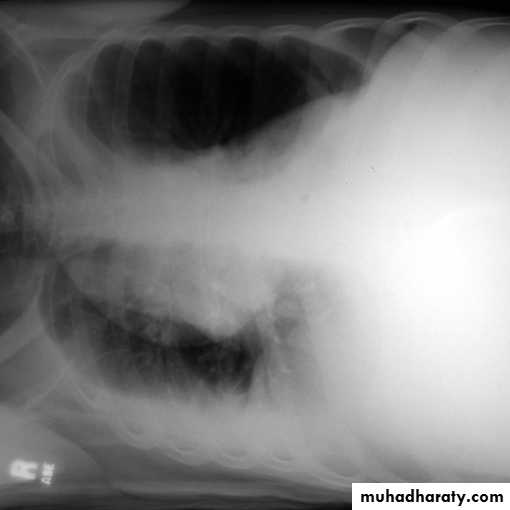
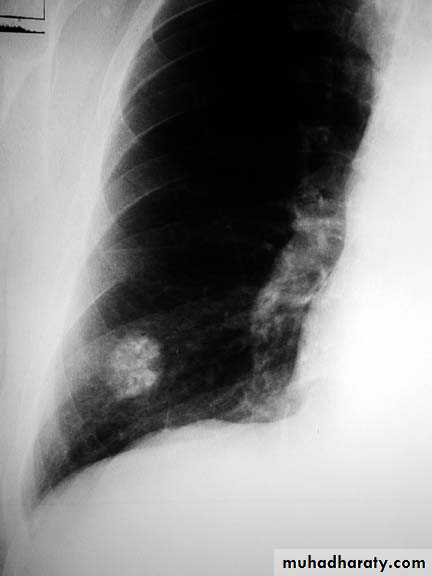
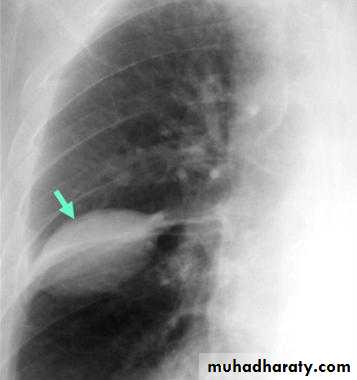
A subpulmonic effusion
(infrapulmonary effusion) accumulation of fluids between the lung & visceral pleura ..The following features are helpful :elevation of the hemidiaphragm ..right: peak of the hemidiaphragm is shifted laterally
left: increased distance between lower lobe air and gastric air bubble
Pleural effusion in supine patient
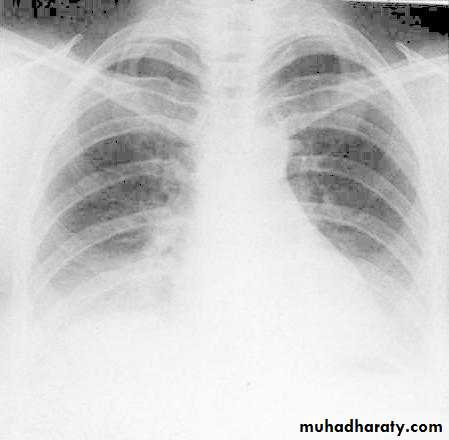
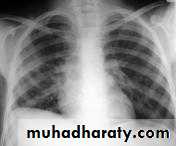
Radiopaque hemi-thoraxPneumothorax (air in pleural space )
Signs
Loss of vascular markings at the outer parts of lung fieldsDemarcating pleural line between the lung & vessels lacking area.
Well demarcating of the scapula
Epsilateral lung collapse
Tension pneumothorax
Emergency condition
Pressure effect on the mediastinum & major vessels
Treatment by chest tubes
Pulmonary blebs or bullae
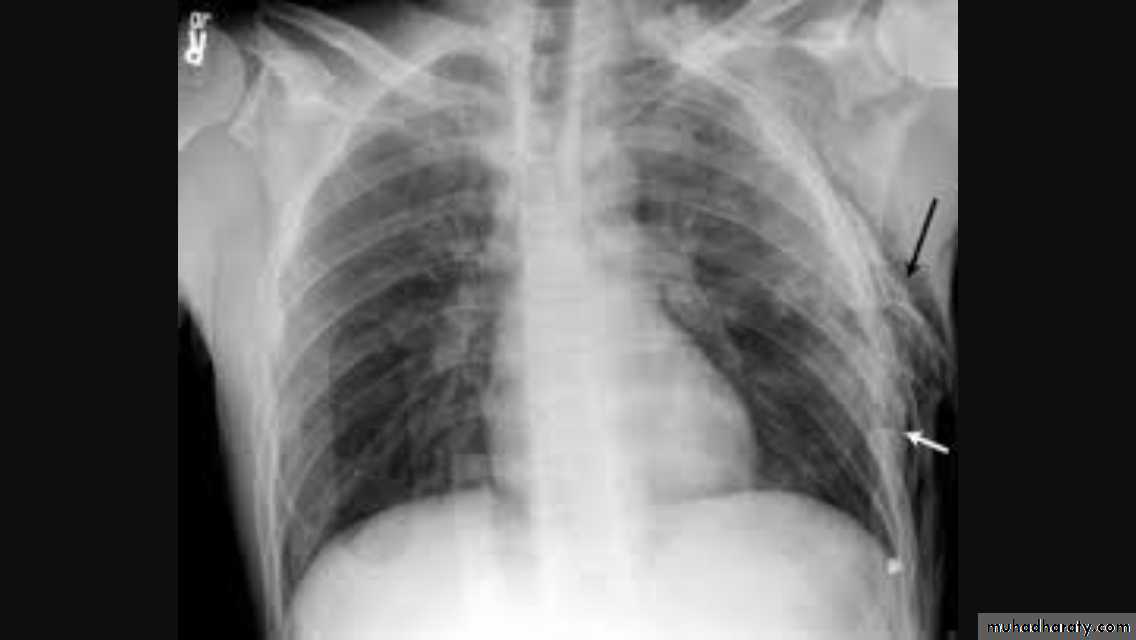
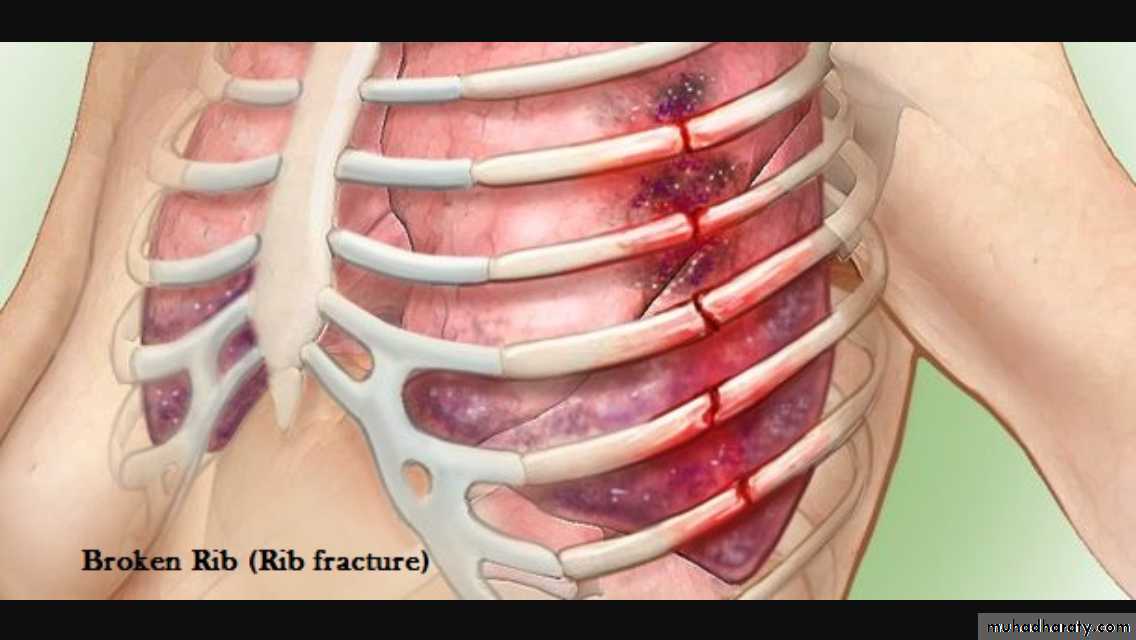
RibsRib fracture
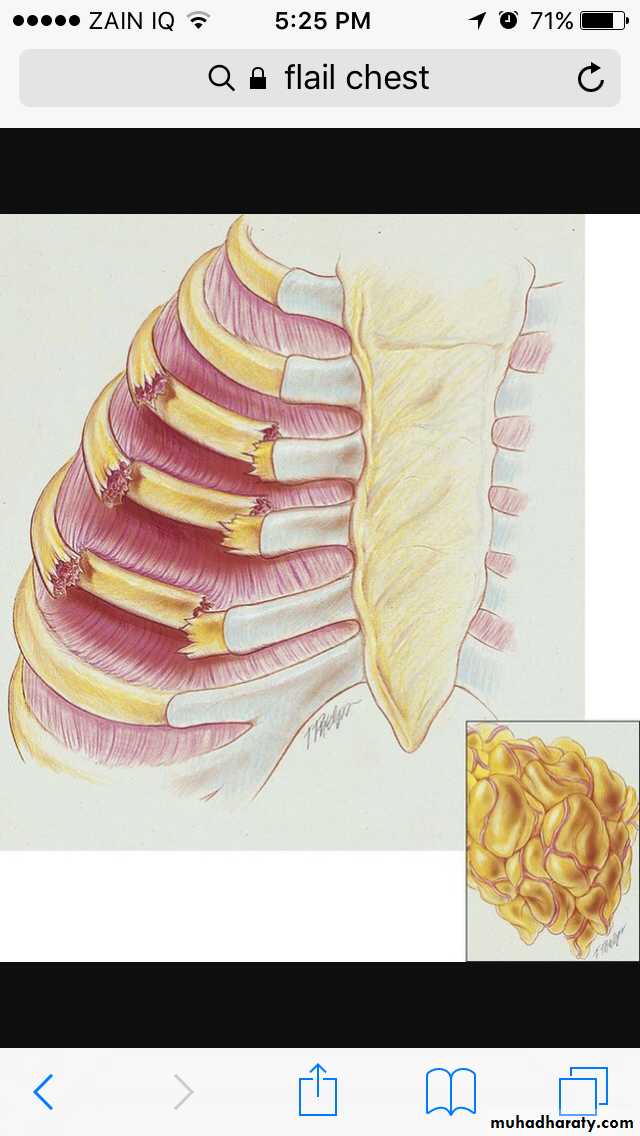
Flial chest
Surgical emphysema
Diaphragm
Diaphragmatic elevationBilateral
1) Technical ( supine or expiratory film )
2)Reduced pulmonary volume (fibrosing pulmonary diseases)
3) Abdominal distention
Unilateral
1) Diaphragmatic disease
eventration & hump
rupture
phrenic N paralysis
2)Pulmonary & pleural diseases ( collapse , pleural effusion
3) Abdominal mass or organomegaly
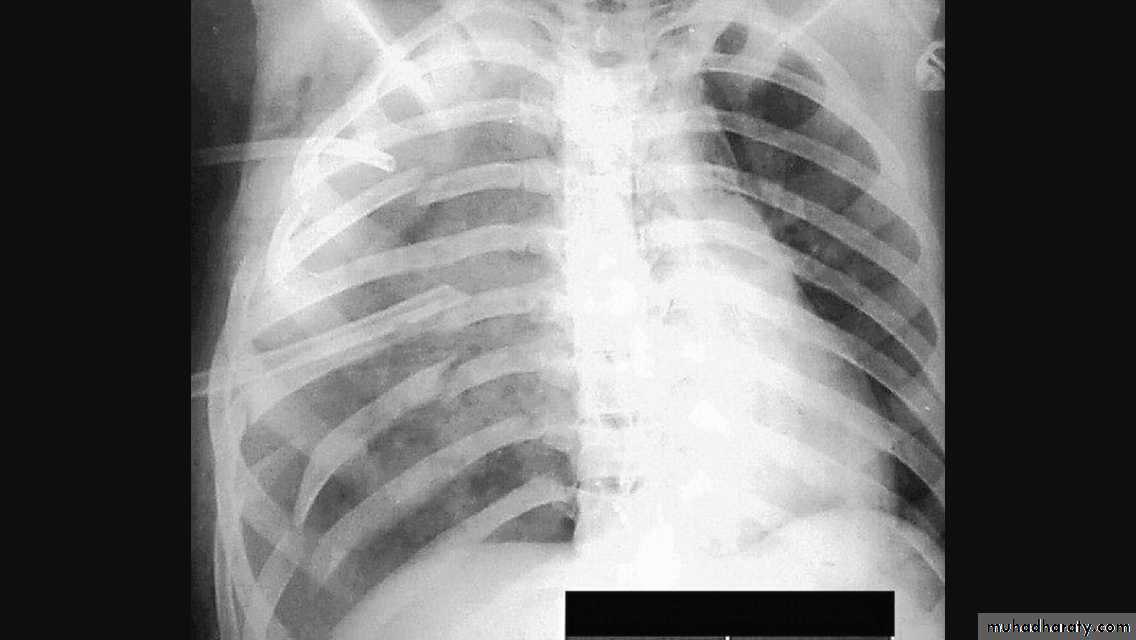
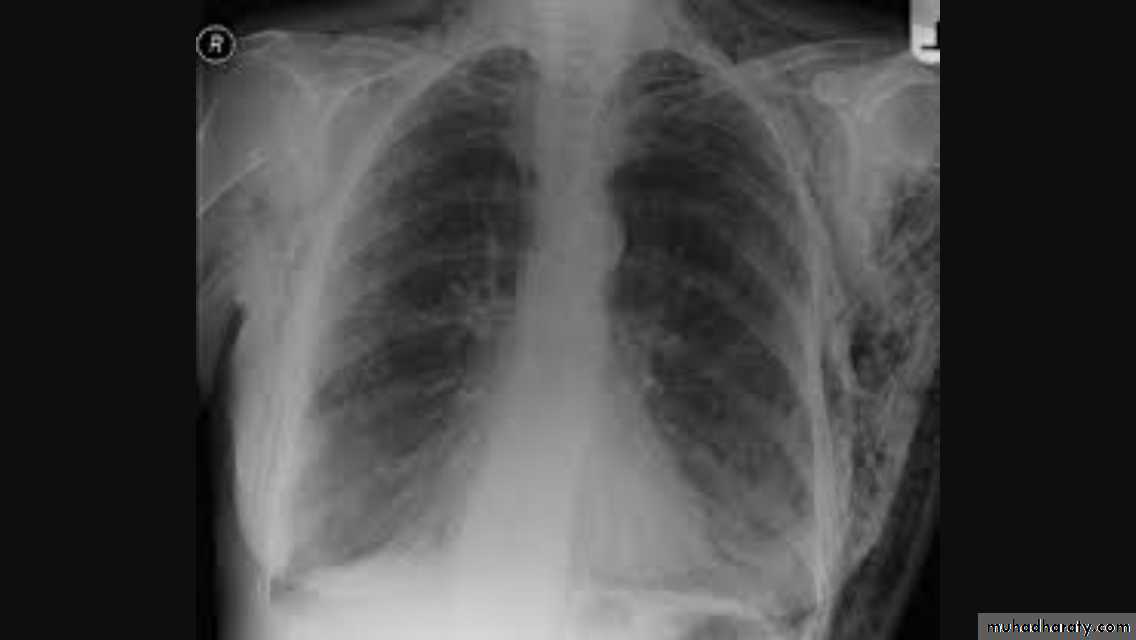
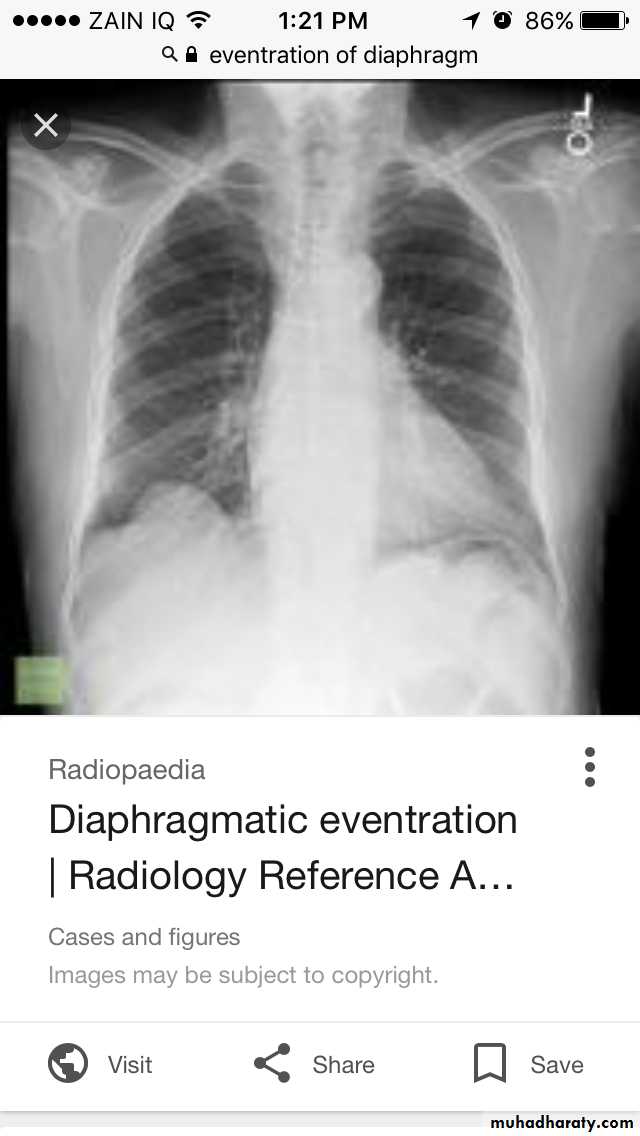
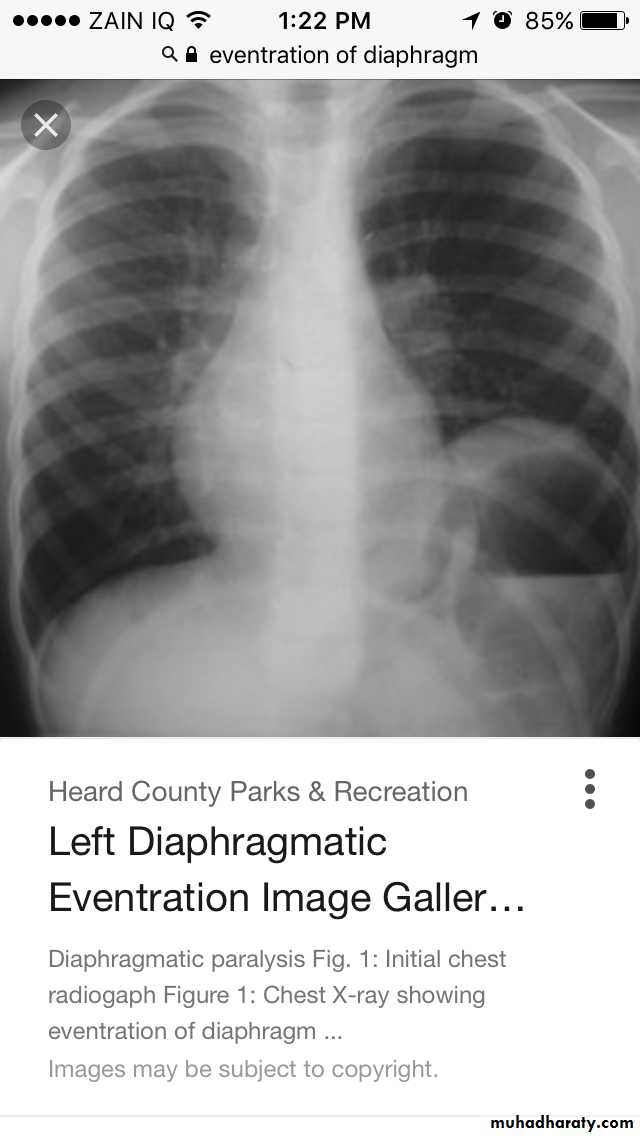
Diaphragmatic hump & eventration
Partial replacement of diaphragmatic muscle by fibrous tissue
Complete replacement of diaphragmatic muscle by fibrous tissue
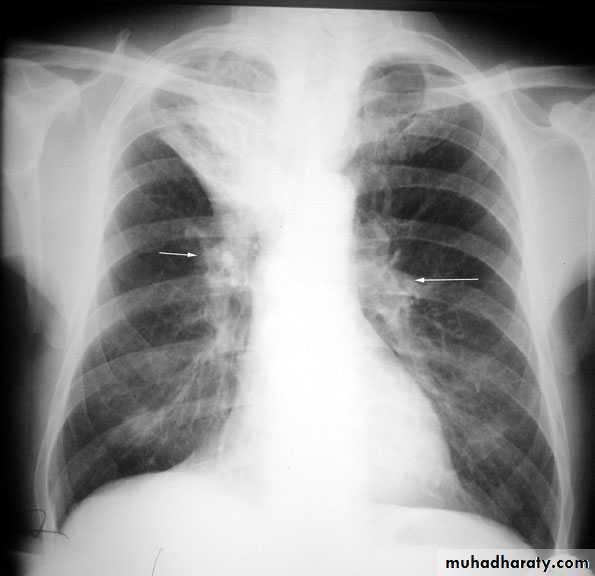
Hila
Left hilum is higher than theRt in 97%
Both hila should be equal density & size with concave lateral borders
Upper limbs of hila ( superior pulmonary veins)Lower limbs of hila ( inferior
pulmonary arteries )
Normal LNs not visible at CXR
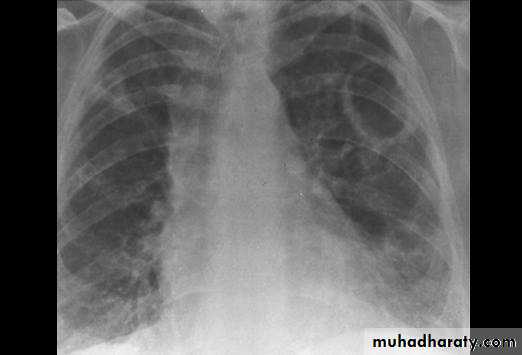
Hilar enlargement ( Bilateral )
1) Expiratory film2)LAP –hematological malignancy(leukemia, lymphoma ..)
-infections ( whooping cough or TB ?)
3) Vascular causes
Hilar enlargement ( unilateral )
1)Apparent –rotation-scoliosis
2) LAP