Digestive Tract
It consists of long muscular tube starting from the mouth to the anus. There are many associated glands that produce their secretions into the tube (liver, pancreas, gall bladder).The digestive process starts with eating the food which is followed by mechanical and chemical break down of the ingested material, the products of digestion pass from the intestinal lumen to the blood stream and lymph, also the digestive tract is the site of absorption of end products of digestion.
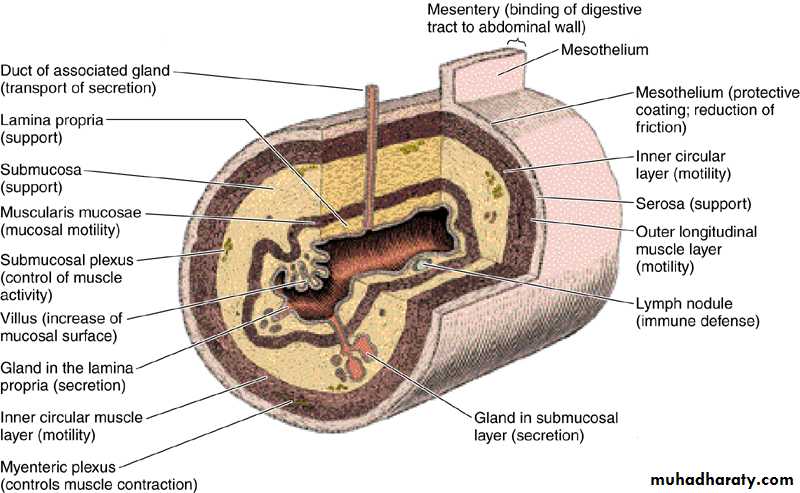
The general histological structure of the digestive tract consists of
Mucosa:Surface epithelium.
Lamina propria : ( fibroblast, collagen fibers, blood vessels, nerves,immune cells)
Muscularis mucosa
Submucosa : fibroblast, collagen fibers, blood vessels, nerves, ganglion cells, lymphoid tissue aggregations.
Muscular coat : inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle fibers.
Adventitia + mesothelium: large blood vessels & nerves, +adipose tissue.
Digestive tract include:-
Mouth - pharynx- oesophagus – stomach - small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum) - large intestine (caecum, appendix, colon and rectum).
Glandular organs included in the process of digestion are:
Salivary glands, Liver , pancreas and gall bladder.
Mouth:
It extends from the lips to the pharyngeal isthmus, it is divided into:
Vestibule: lies between the lips and cheeks externally and gum and teeth internally.
Oral cavity lies between gum and teeth and pharyngeal isthmus.
The mouth is lined by stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium. The underlying connective tissue consists of collagen and elastic fibers with small glands which secrete both serous and mucous fluids.
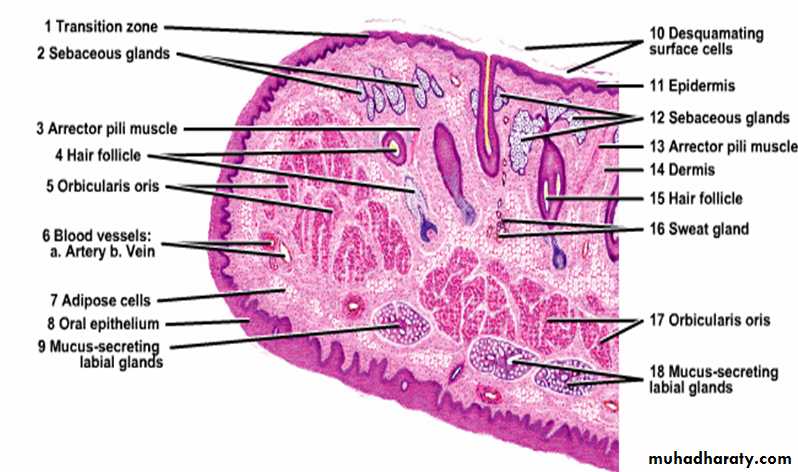
Lips:
Each lip composed of a core of skeletal muscle (orbicularis oris) embedded in a fibro-elastic connective tissues. The external surface of the lips is covered by skin that contains many hair follicle, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. At the free margin of the lip there is an area of transitional zone between the outer skin and the mucous membrane of the mouth cavity. The epith. covering this margin ( red margin) is not heavily keratinized (translucent), therefore, prominent blood vessels can be easily seen.The inner surface of the lip is lined by mucuos membrane and consist of str. sq. non kera.epithelium lying on a connective tissue lamina propria, small groups of mucous glands called labial glands are situated inside the lip and produce their secretion to the surface of the lip by small ducts, because there are no sweat gland or sebaceous gland on the lip margin, the lips must be weted with the saliva by liking them with the tip of the tongue, failure to do this will cause will cause the lips to be dried.
Cheek:
Have the same structure of the lip which is core of skeletal muscle (buccinator) covered from outside by skin and subcutaneous connective tissue and lined from inside by thick non keratinized sq. epit. & sub mucosa contains minor salivary gland (buccal glands) and few sebaceous gland.Tongue:
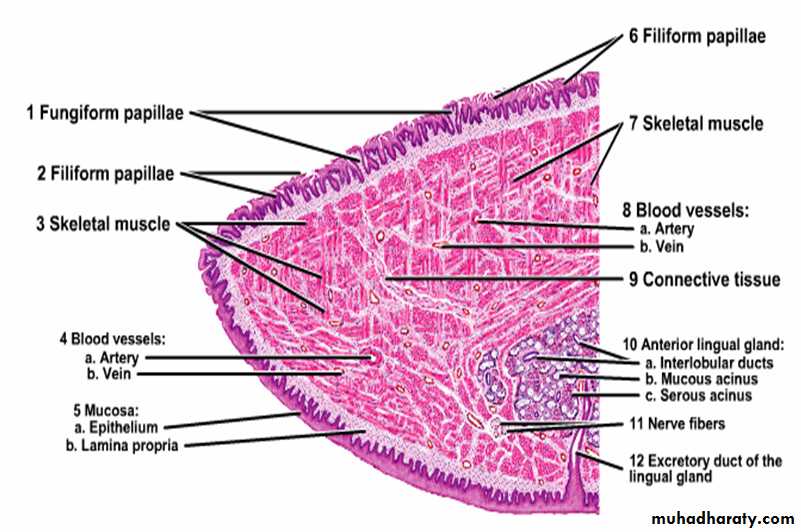
Is a highly muscular organ composed of striated muscle that function is chewing, swallowing, and speech.The upper surface of the tongue is divided into anterior two thirds and posterior one third by V- shaped sulcus called (sulcus terminalis) which is marked by foramen cecum.
The upper surface of anterior two third shows small projections called papillae which are four types:
Filiform papillae.
Fungiform papillae.
Circumvallate papillae.
Foliate papillae.
FILIFORM PAPILLAE :
Tall, narrow and pointed.
The most numerous type, found all over the upper surface of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
Each papilla has connective tissue core covered by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Does not contains taste buds.
FUNGIFORM PAPILLAE:
Mushroom shape.
Less numerous scattered among the filiform papillae, found at the lateral border and at the tip of the tongue
The covering epithelium is non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Taste buds are present.
CIRCUMVALLATE (VALLATE) PAPILLAE
Dome- shape present below the level of the surface epithelium.
6-10 in number lie in a row immediately in front of the sulcus terminalis.
Their epithelium is non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, each papillae is surrounded by 2 circular furrows.
Contains taste buds.
The duct of Von Ebners (serous) glands open at the base of the furrows surrounding each papillae.
FOLIATE PAPILAE
Regular identical shape consist of two or more parallel ridges and furrows.
Lie on the lateral surface of the dorsum of the tongue.
Their epithelium is non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Contains many taste buds.
Not well developed in the human.
Functions of the papillae:
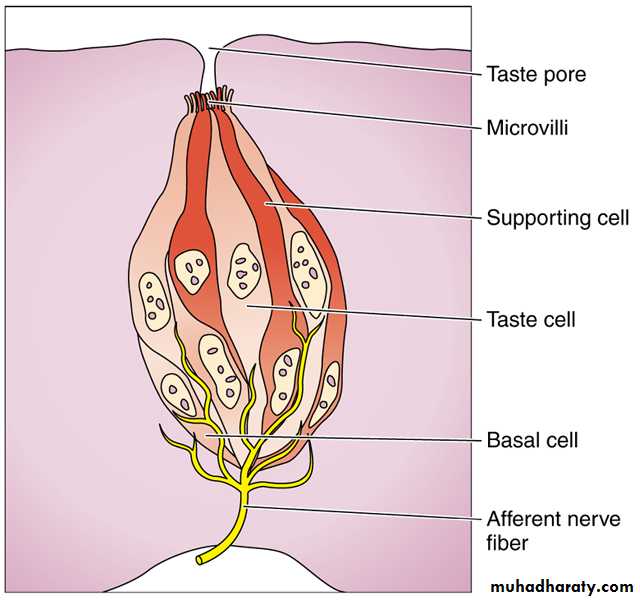
Fungiform, Foliate and all circumvallate papillae contain taste buds which are specialized sensory organs consist of oval cluster of cells
having apical surface microvilli (taste hair) which on being stimulated give rise to nerve impulses pass through afferent nerve fibers to the brain resulting in sensation of taste, at the apex of the bud there is small taste pore that connects the innervation of the bud with the oral cavity. Four types of taste sensation: sweet, salt, acid and bitter, most taste buds respond to all these stimulation to varying extent.
Three types of cells in the taste buds:-
Taste cells (sensory cells).
Supporting (sustentacular) cells.
Basal cells ( primitive stem cells) : rounded in shape lie at the base of the bud, can replace the other two type of cells.
The taste and supporting cells resemble each other they are long spindle- shaped cells, their pointed distal end are covered by microvilli, the supporting cells have dark elongated nucleus and dark stained cytoplasm while the sensory cells (taste cells) have an oval light nucleus and light stained cytoplasm, their life span is short about 10-14 days then replaced from the basal cells.
Pharynx:
Lies at the back of the mouth and divided into:
Upper part (naso pharynx) lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells (respiratory epithelium).
Middle part (oropharynx).
Lower part (laryngopharynx) both middle and lower part lined by non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium continous with that of the esophagus.
Prominent lymphoid tissue in the nasopharynx called (adenoid) while lymphoid tissue in the oropharynx called (palatine tonsil).
The muscle coat consists of striated muscle of constrictors of the pharynx.