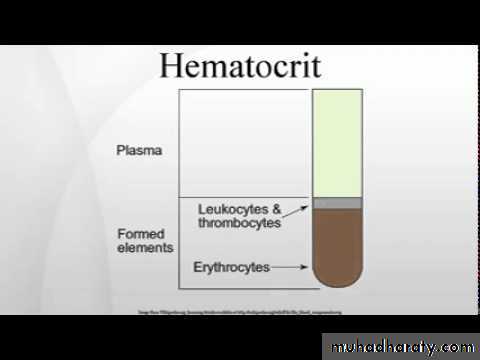
Packed cell volume (PCV) or
Heamatocrit(HCT) valueObjectives : to determine the volume or the amount of the red blood cells in 100 ml (dl) of blood .
Methods :
1/ Microheamatocrit: it requires less blood and also less time to determine a heamatocrit .
2/ Macroheamatocrit or wintrobe method : this method is little use today since it is more time consuming , requires large amount of blood and contains ahigher degree of plasma trapping .
3/ Electronic cell counting – coulter counter.
Microheamatocrit Method
Material and instruments :
1-Microheamatocrit tube 75 mm in length and 1 mm in diameter which contain heparin and show a red ring at the end of the tube.
2-Microheamatocrit centrifuge capable of producing a relative centrifugal force of 10000 to 15000.
3-Plastic seal or Bunsen burner flame to seal one end of microheamatocrit tube.
4-Microheamatocrit reader.
Procedure :
1-Blood is drawen into the tubes by capillary action by holding the tube in horizontal manner and allow 2/3 or 3/4 filled with blood . Air bubbles denote poor technique but do not affect the results of the test .
2-Seal the dry end of the tube by plastic seal or by heating dry end of the tube rapidly on a fine flame of Bunsen burner combined with rotation.
3-The sealed tube is then placed in the radial grooves of the microheamatocrit centrifuge with the sealed end away from the centre of the centrifuge and centrifuge for 5 minutes .
4-When looking at acenterfuged heamatocrit tube , you can see three distinct layers . Atop layer of clear slightly milky plasma , abuffy coat layer (consisting of WBC and platelets ) and adark packed RBC.
5-Obtain the results using the microheamatocrit tube reading device . Adjust the movable line to touch the top of the RBCs in the tube .
Results :
Normal range in adult men : 44 -54 %Normal range in adult women : 38-48 %
Blood indices
Introduction and principle:The RBCs indices are used to define the size and hemoglobin content of red blood cell. They consist of mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration.
Objectives
Are used as an aid in differentiating anemia.
Information required
1-RBC count in millions / c.mm
2-Hb estimating in g/dl.
3-PCV estimating as %.
Calculations
1-MEAN CORPUSCULAR VOLUME (MCV):
The MCV indicates the average volume of single RBCin femtoliters (FL).
MCV= PCV % / RBC count ×10⁶/c.mm
= (PCV / RBC ) × 10 Fl
2-MEAN CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN (MCH):
The MCH indicates the average weight of Hb in single RBC in pigogram(pg).
MCH =Hb (gm / dl )/RBC count ×10⁶/c.mm
=(Hb / RBC ) × 10 Pg
3-MEAN CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRTION(MCHC):
MCHC is an expression of the average concentration of Hb in the red blood cells. Its expressed as %.
MCHC = Hb ( gm /dl) / PCV (%)
=(Hb / pcv ) × 100
= %
Or MCHC = (MCH / MCV ) × 100
Results :
1-MCV : normal range 80 – 100 fl so the RBCs are normocytic .
2-MCH : normal range 27 – 31 pg.
3-MCHC : 31 – 36 % so the RBCs is normrchromic.
Discussion
Find the MCV , MCH and MCHC and identify type of anaemia from the following data :
1-Hb = 11.8 g/dl.
Pcv = 41%
RBC =4.5 × 10⁶ / c.mm
2-Hb = 9 g/dl
PCV = 30 %
RBC= 4.5 × 10⁶ / c.mm