DENTAL X-RAY IMAGE CHARACTERISTICS
The image characteristics of dental radiograph include : 1.Density. 2.Contrast . 3.Geometric characteristic of sharpness with minimal magnification and distortion.DENSITY:Is the overall degree of blackness or darkness of the dental radiography. Influencing Factors: 1- Exposure Factors.2-Patient Parameter .3. D-Development condition.
1- Exposure Factors
a-Milliamperage: An increase in milliamperage produce more x-ray that expose the film and therefore the film density increase and the radiograph appears darker.
b-Operating kilovoltage peak: Increasing the kilovoltage increase the density of the film by increasing the mean energy of the x-ray beam and produce higher energy x-ray.
c-Exposure time: An increase in exposure time increase film density by increasing the total number of x-rays that reach the film surface and the film appears darker.
2-Patient Parameter :
a. Subject thickness :The thicker the subject (greater tissue thickness), the more the beam is attenuated and the lighter the resultant image .Large patients with greater tissue thickness will required longer exposure time or increased milliamper setting.b. Object density : Denser objects (strong absorbers such as bone, ,enamel,dentin,cementum,restoration) cause the radiographic image to be light and are said to be radiopaque. Objects with low densities are weak absorbers.They allow most photons to pass through, and they cast a dark area on the film that corresponds to the radiolucent object.
c.Source-film distance: The inverse square law stated that the intensity of x-ray beam varies inversely with square of distance from source and must be compensate by increasing exposure time.
3.-Development condition: Film density may increase by prolonging the development time during processing or increasing temperature of developer.
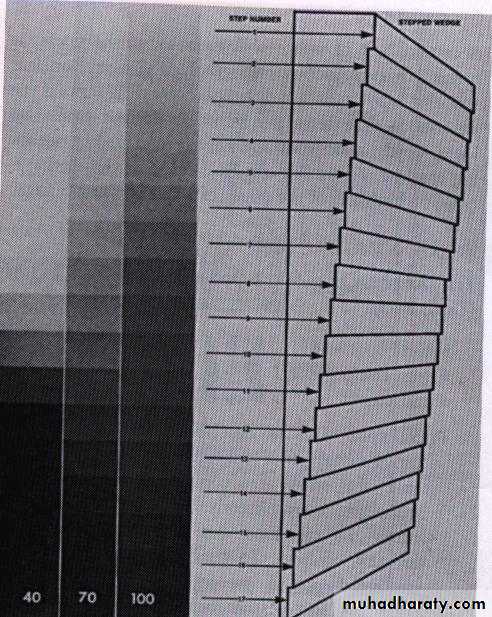
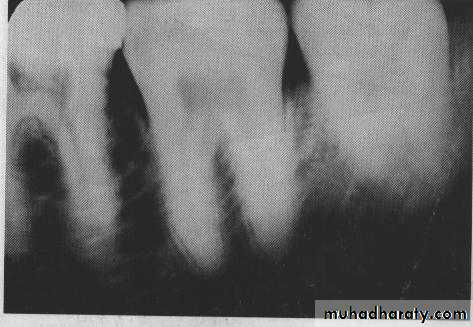
CONTRAST: It is the difference in densities between light and dark regions on a radiograph.
Densities on radiograph are not simply black and white but encompass multiple shade of gray called scale of contrast.
High-contrast image(short scale contrast)would be black and white with few gray shade.
Low-contrast images(long-scale contrast)usually contain a wide rang of shades of gray.
The radiographic contrast of an image is the result of
subject contrast, film contrast, and scattered radiation.The exposure factors has direct influence on the contrast of dental radiograph .
Increasing the kVp affect film contrast by increasing the mean energy of x-ray and by producing higher energy x-ray ,x-ray with higher energy are better able to penetrate tissue as a result more variations in tissue density are record on the film and appear as varying shade of gray.
GEOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS:
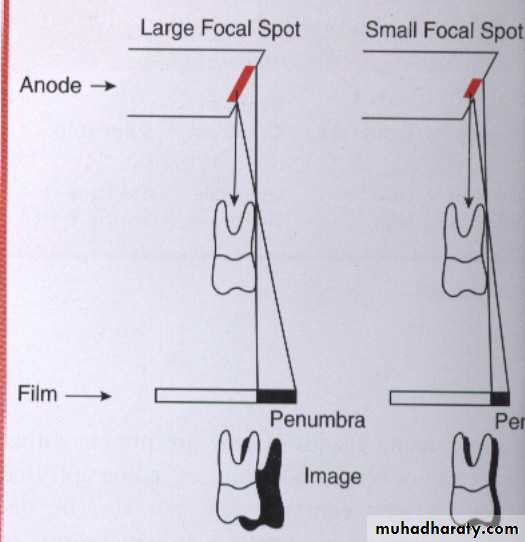
Sharpness: Sharpness also known as( detail, resolution, or definition) refers to capability of the x-ray film to reproduce the distinct outline of an object or how well the smallest detail of an object are reproduce on dental radiograph.Penumbra:Is a fuzzy unclear area that surround a dental radiograph.
Influencing factors:
Focal spot size.
Film composition.
Movement.
Focal spot size: The smaller the focal spot area the sharper the image appears. The larger the focal spot area the greater the loss of image sharpness.
Film composition: The sharpness of the film is relative to the size of crystals found in emulsion, The emulsion of faster film contains larger crystals that produce less image sharpness, where as slower film contains smaller crystals that produce more image sharpness.
Movement: A loss of image sharpness occurs if either the film or patient moves during x-ray exposure.
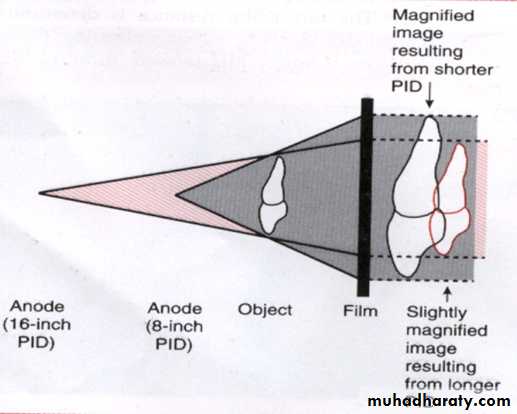
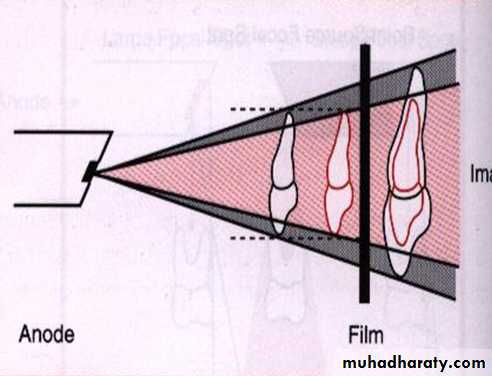
MAGNIFICATION: Image magnification refers to radiographic image that appears larger than the size of the object due to the divergent paths of x-ray beam.
Influencing factors:
1.Target-film distance: Is the distance between source of x-rays to the film.The target film distance is determined by length of cone, when a longer cone is used more parallel rays from the middle of the x-ray beam strike the object rather than the diverging x-ray from the periphery of beam.
2.Object-film distance: Is the distance between the object being radiographed and x-ray film .The tooth and object should always be placed as close together as possible, the closer the proximity of the tooth to the film the less image enlargement.
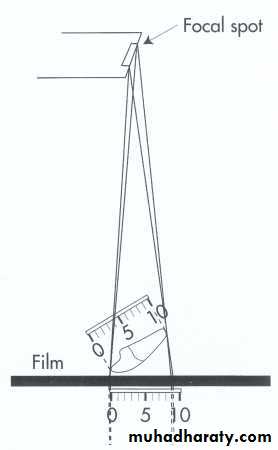
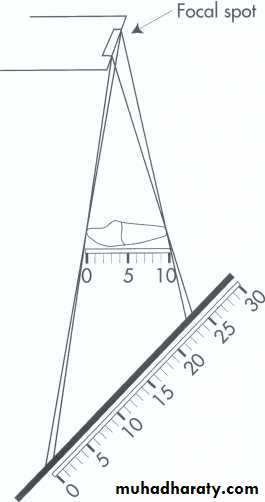
DISTORTION:Is a variation in the true size and shape of the object being radiographed.A distorted image dose not have the same size and shape of the object. Distortion result from unequal magnification of different parts of same object.
Influencing factors:
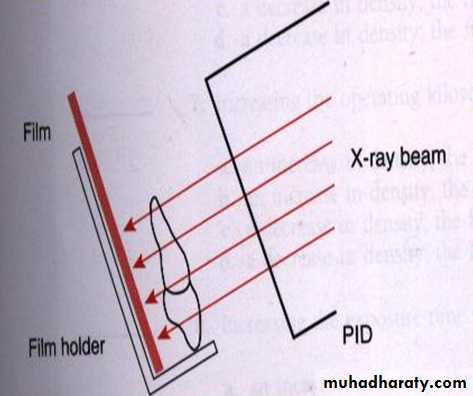
1.Object-film alignment: The object and film must be parallel to each other if the object and film
are not parallel an angular
relationship result and this
produce variation of distance
between the tooth and the film.
Image shortening
Image elongation2.X-ray beam angulation: The x-ray beam must be direct perpendicular to the tooth and film in order to record the adjacent structures in their true spatial relationships.