بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Skin in systemic diseases
Dr.RZAN
Objectives
Demonstrate skin manifestations of common systemic diseases.THE SKIN& THE PSYCH.
Psychatric problems that have dermatological presentations:Stress & anxiety may lead to trichotillomanea (hair pulling habbit resulting in alopecia with normal underling skin), nurodermatitis, lip liking dermatitis, nose picking, nail biting, ...
Obsessive compulsive nuroses may lead to irritant contact dermatitis.
Phobias: like syphliphobia, parasitopho; scabephobia,
Hysteria: may leads to dermatitis artifacta.
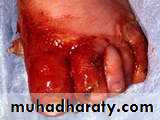
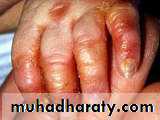
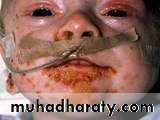
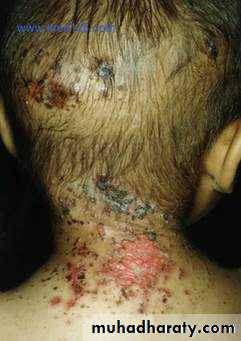
lip liking dermatitis
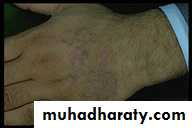
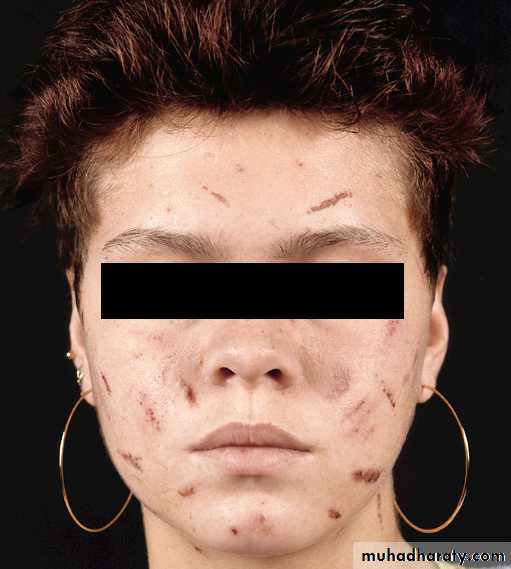
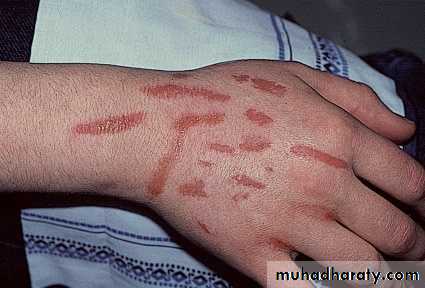
Dermatitis artifacta.
Self induced lesions.Accessible part.
Bizarre shapes.
No primary lesions.
Secondary gain
Abnormal personlity.
Commonly female.
May have some medical knowledge
Dermatitis artifacta.
Dermatological diseases that lead to psychiatric problems.Most of dermatological diseases affect the psych because they directly affect the appearance, so there effect may range from
Discomfort.
Anxiety
Dysmorphophobia (delusion of ugly body part)
Depression
Social isolation.
Suicidal ideation & attempts.
It is found that suisides occure in higher rates among dermatological patients (like those with psoriasis & acne...).
SKIN & ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Hyperthyroidism:Fine hair, hair loss.
Pruritus.
brittle nails
Onycholysis,
clubbing.
Warm smooth skin, hyperhidrosis.
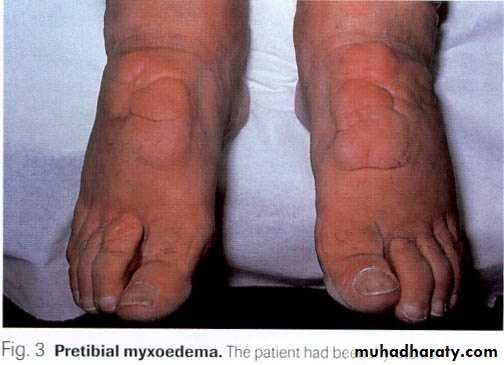
Pretibial myxedema. ±
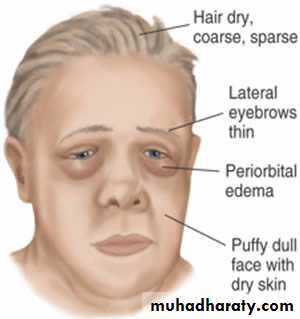
Hypothyroidism:
Coarse hair, diffuse hair, broken hair. Outer third of eyebrow lost.
Pruritus.
brittle nails.
Cold, thickened yellow dry skin (xeroderma).
myxoedemaHypothyroidism
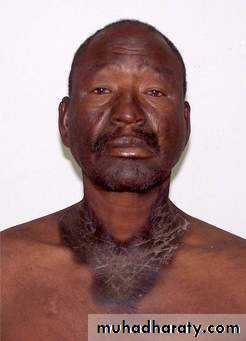
Acromegaly:
Soft tissue hypertrophy.Seborrheic dermatitis,
Acanthosis nigricans,
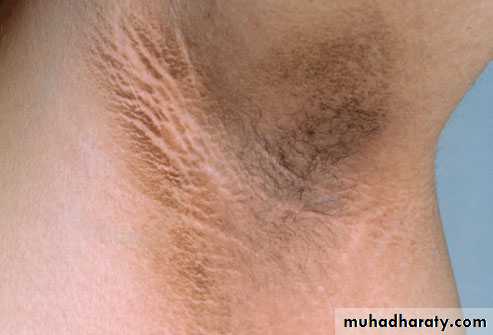
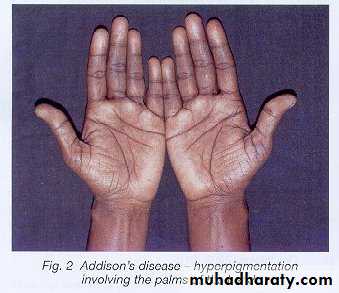
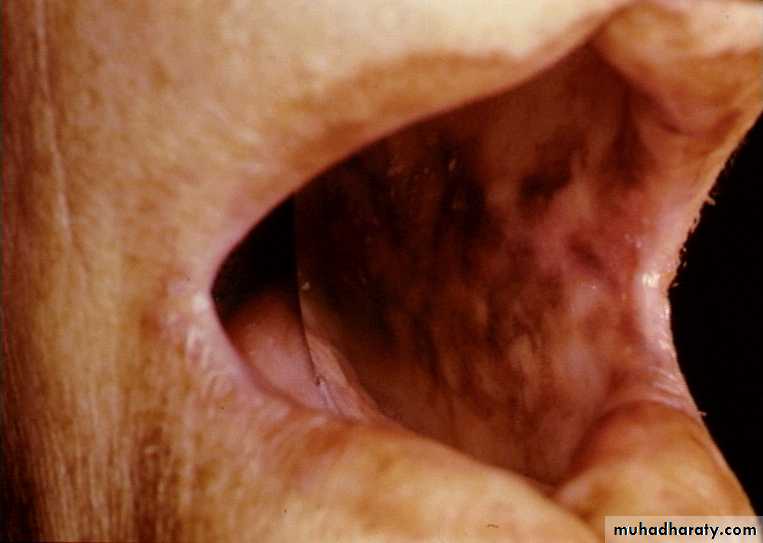
Addison’s disease:
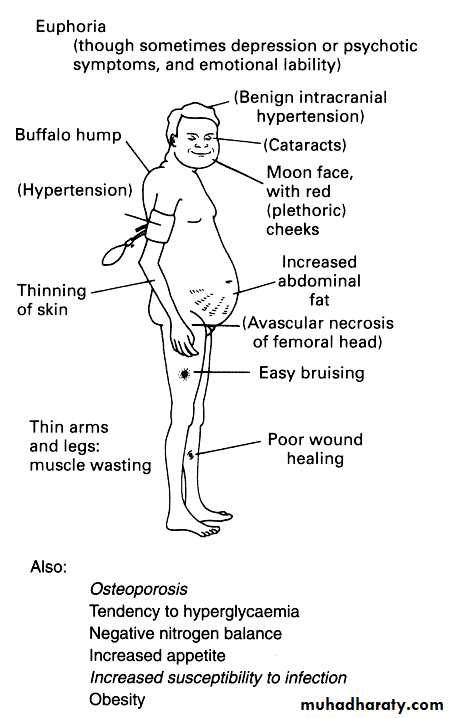
Increased skin pigmentation.Cushing’s syndrome:
fat maldistribution: Moon face& Buffalo hump. Acne.
Hirsutism.
telangiectasia,
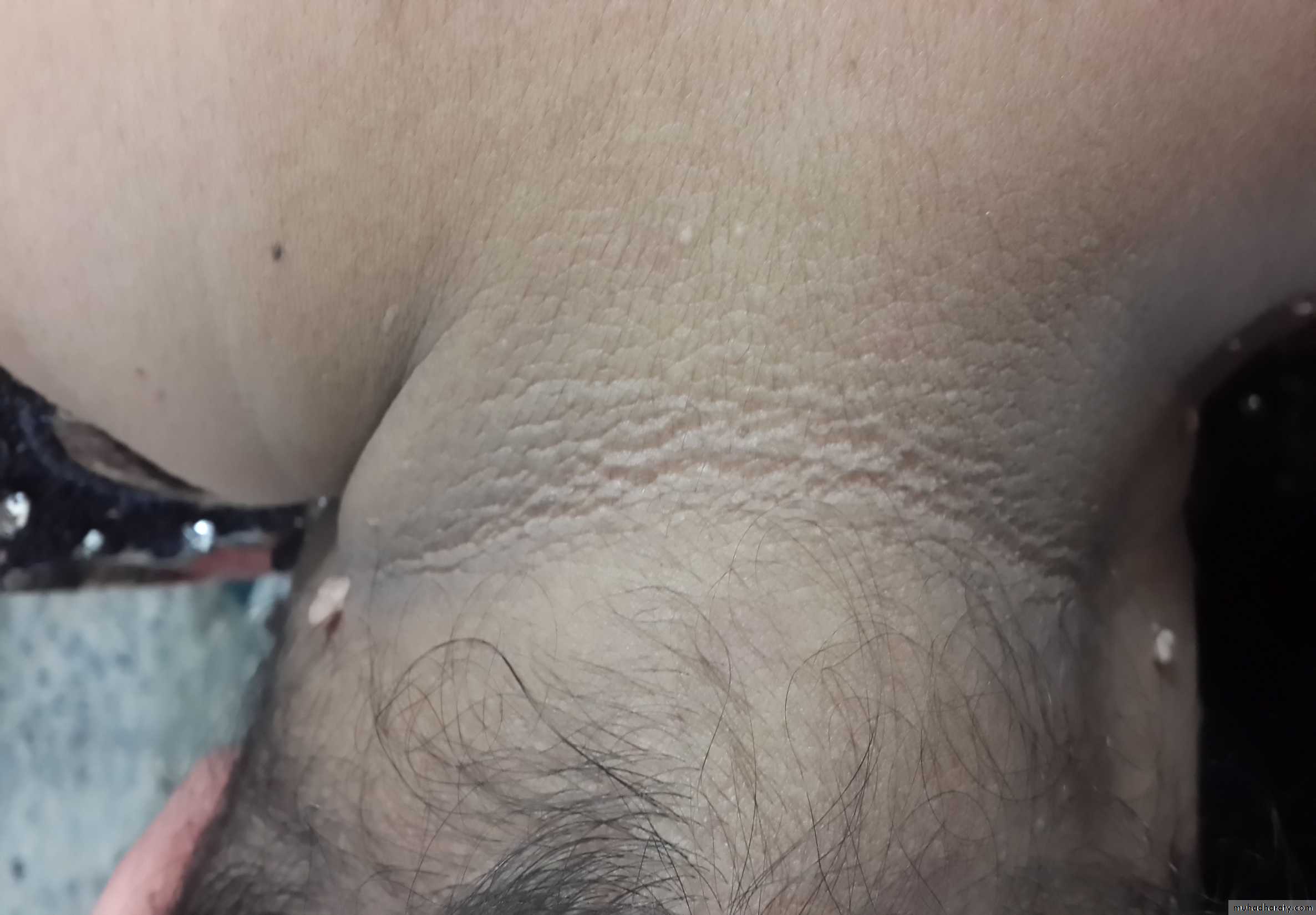
thin & atrophic skin
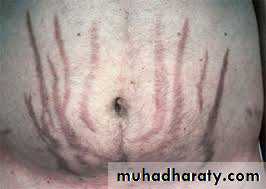
Striae.
Poor wound healing.
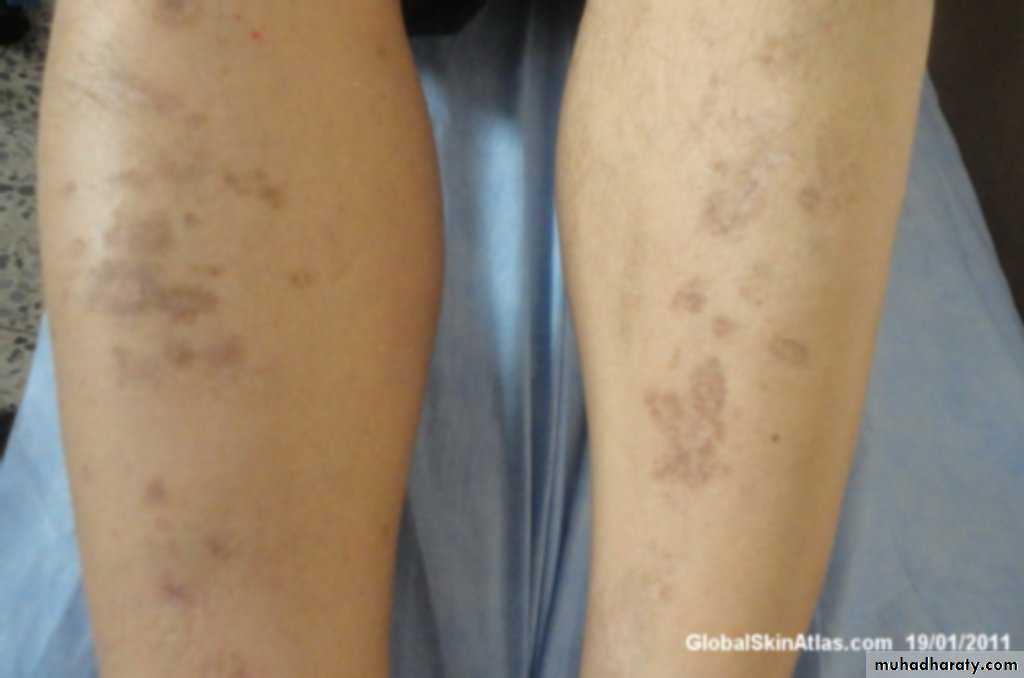
Easy bruising.
Acanthosis nigricans.
Acanthosis nigricans,
Diabetes:
• Dry skin .
• Pale skin & nails (diabetic angiopathy).
• Hair loss.
• Poor sensation (diabetic nuropathy).
• Diabetic dermopathy. is light brown, oval or round, slightly indented patches most often appearing on the shins (shin spots).
• Pruritus.
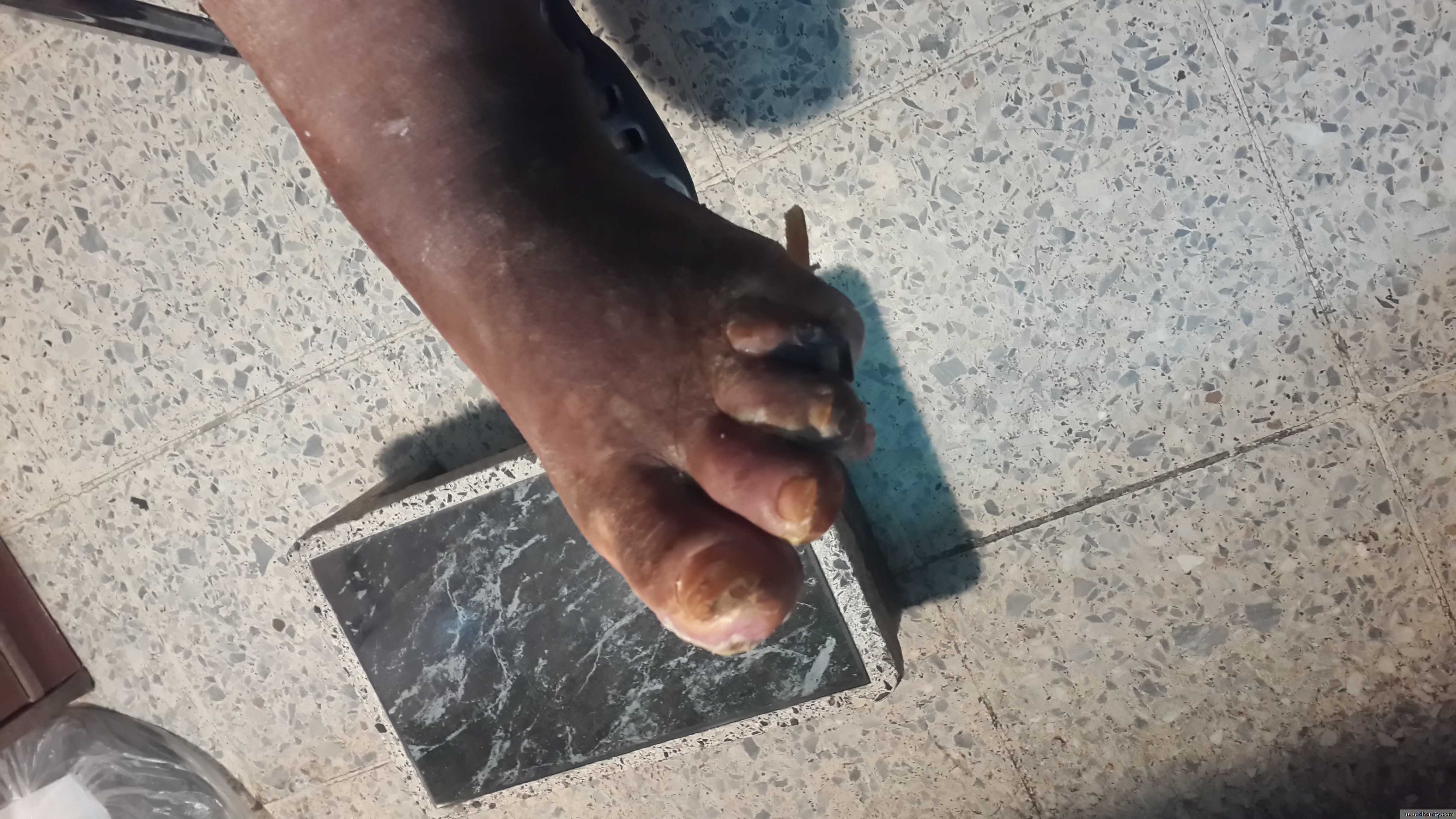
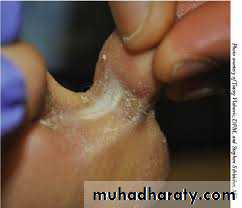
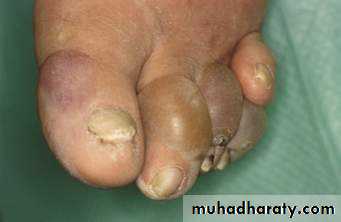
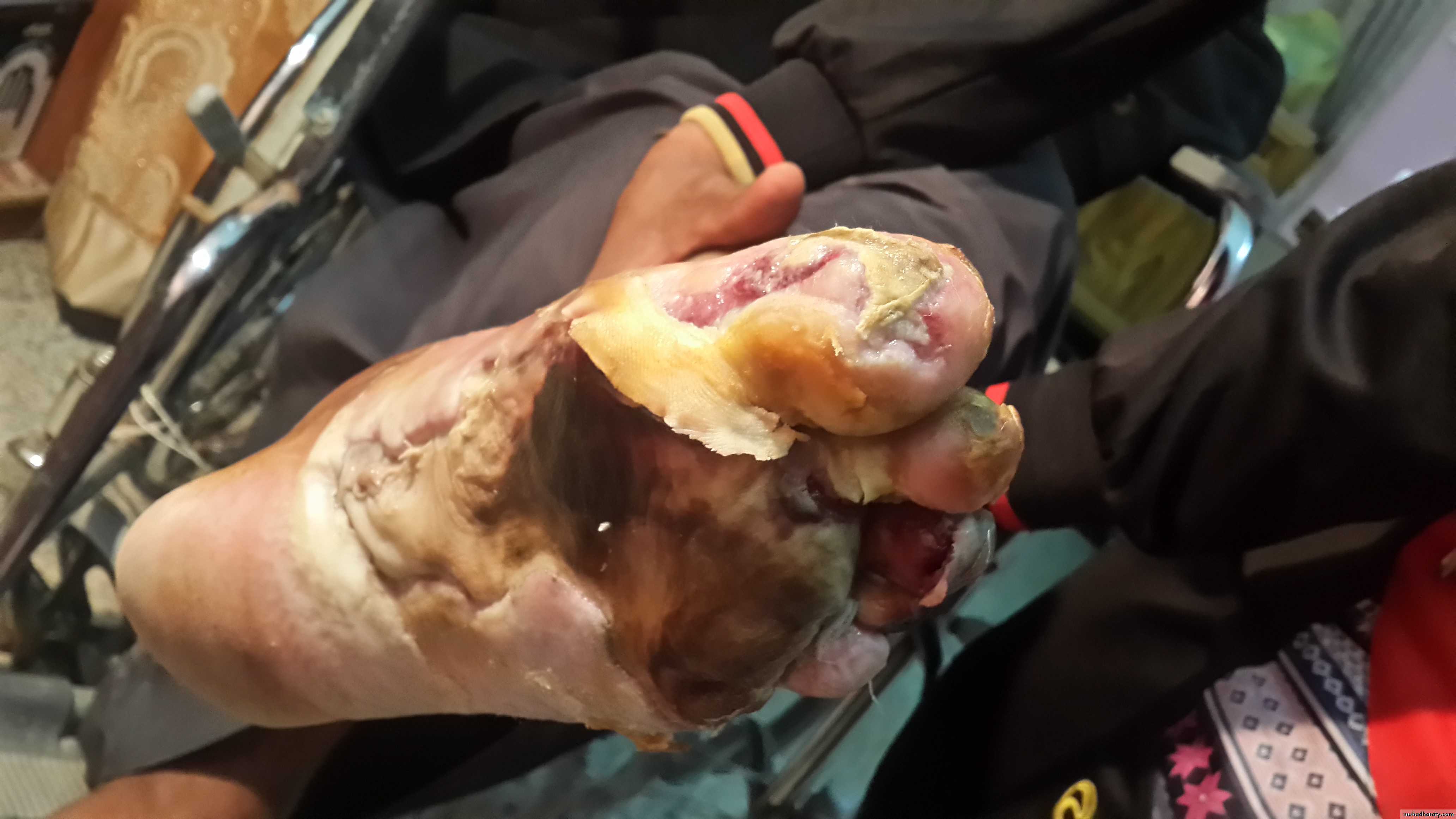
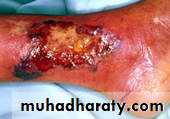
• Foot ulcers (diabetic foot).
• Fungal & bacterial skin infections.
• Poor wound healing.
• Sclerotic skin.
• Bullous diabeticorum.
• Acanthosis nigricans & skin tags.
• Necrobiosis lipoidica (diabeticorum).
• Granuloma annulare .
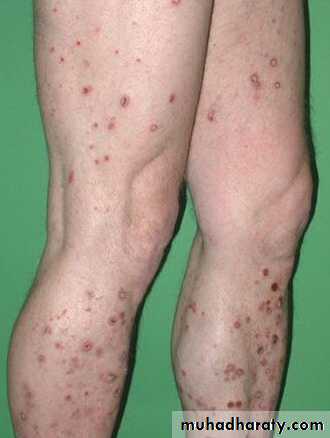
DIABETIC BULLAE
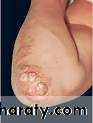
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum
Atrophic,yellow with erythematous or violet margin. The underlying blood vessels
are easily seen through the atrophic skin.
prayer sign Stiff thick skin (diabetic sclerodactyly or cheiroarthropathy) palmscannot be opposed properly
SKIN & RESPIRATORY DISEASES
Asthma associated with atopic dermatitis.TB. may be associated with TB. of skin.
CObD. : cyanosis ,clubbing of fingers.
SKIN & CARDIAC DISEASES
Cyanotic congenital heart diseases:Cyanosis.
Clubbing of fingers.
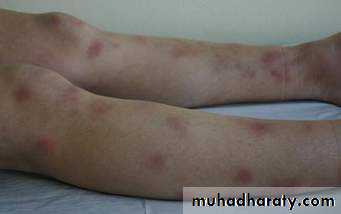
Endocarditis:
Splinter hemorrhages.
Skin & Gastrointestinal Diseases
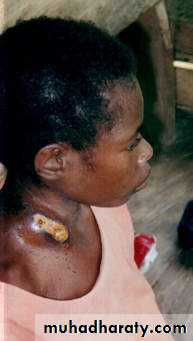
Ulcerative colitis: Erythema nodosum & pyoderma gangrinosum.
Crohn’s disease: Erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrinosum, Perineal ulceration, skin tags & sinus tracts,fistula.
Abnormality in zinc absorption: Acrodermatitis enteropathica.
Coeleac disease:Dermatitis herpetiformis:
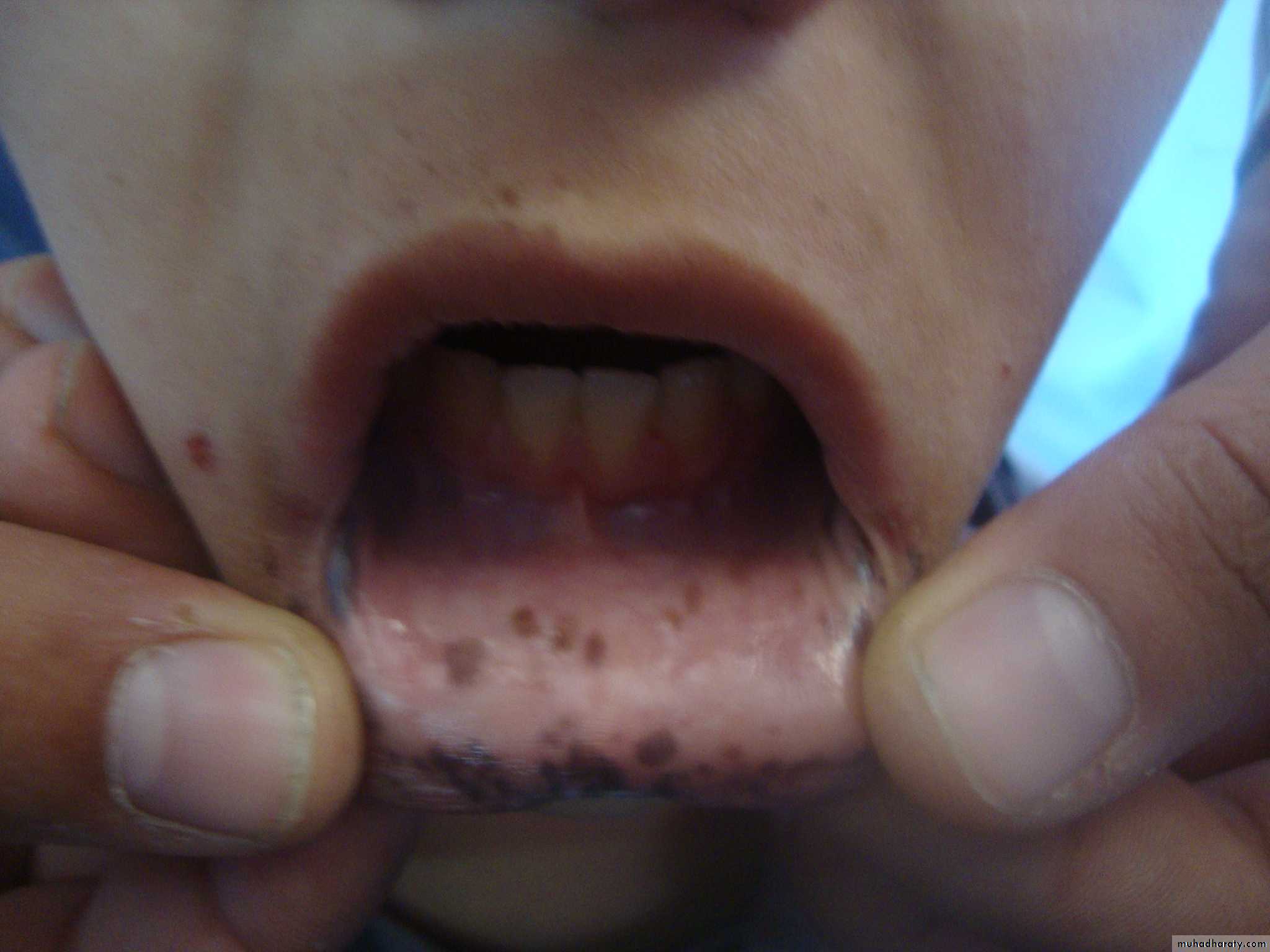
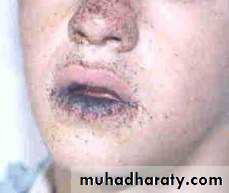
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: Small intestine polyps+ perioral pigmentitions.
PG.
EN.
ADE
pJ
Skin & Liver diseases
Jaundice.Pruritus.
Spider navae.
Palmar erythema.
doputrin contracture.
Clubbing of fingers.
Gynecomastia.
Dilated abdominal wall veins.
Spider nevus
The skin in renal disease1 Pruritus and dry skin.
2 Pigmentation. Earthy color,A yellowish sallow colour and pallor from anaemia.
3 Half-and-half nail. The proximal half is white and the distal half is pink or brownish.
4 ‘Perforating disorders’. Small papules in which collagen or elastic fibres are being extruded through the epidermis.
5 ‘Pseudoporphyria’
PSUDOPORPHYRIA
skin fragility and photosensitivity,blisters form at the sites of trauma on sun exposed skin, bursting to leave erosions.
sometimes heal with some scarring and (milia).
Perforating collagenosis.
Skin & haematology
Haemolytic anaemia’s: Pallor, jaundice.Iron deficiency anaemia: pallor, atrophic glositis,
choilonechya.
Polycythemia rubra vera: erythema,
itching.
Skin Manifestations of Metabolic Diseases
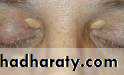
Hyperlipidemia:Xanthelasma
Xanthomas : —tendinous, tuberous, eruptive, Plane.
Porphyria: photosensitivity, skin fragility, Blister formation, hypertrichosis, milia,pigmentation.
Erruptive xanthoma.
Plane xanthoma.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavine) deficiency
Angular stomatitisSmooth purple tongue
Seborrhoeic dermatitis-like eruption
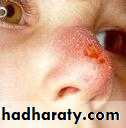
Pellagra: (nicotinic acid-Viv.B3- deficiency):
3Ds—dementia, dermatitis,diarrhea;
erythema following sun exposure.
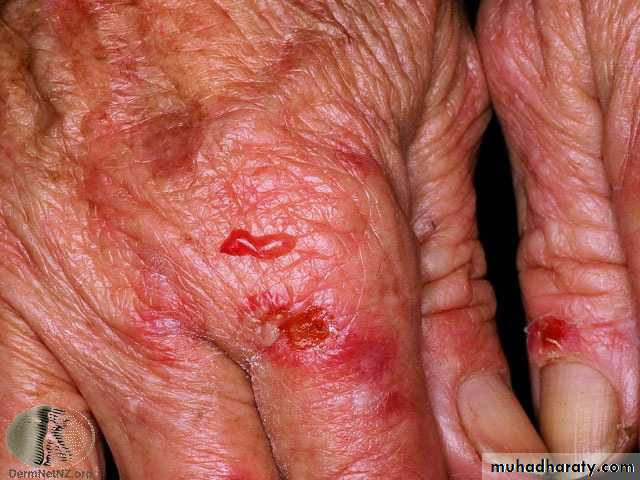
Scurvy:
Bleeding gums,
coiled hairs, perifollicular purpura,
poor wound healin
PELLAGRA
Further readings:
www.fb4d.com.