
Pediatric radiology

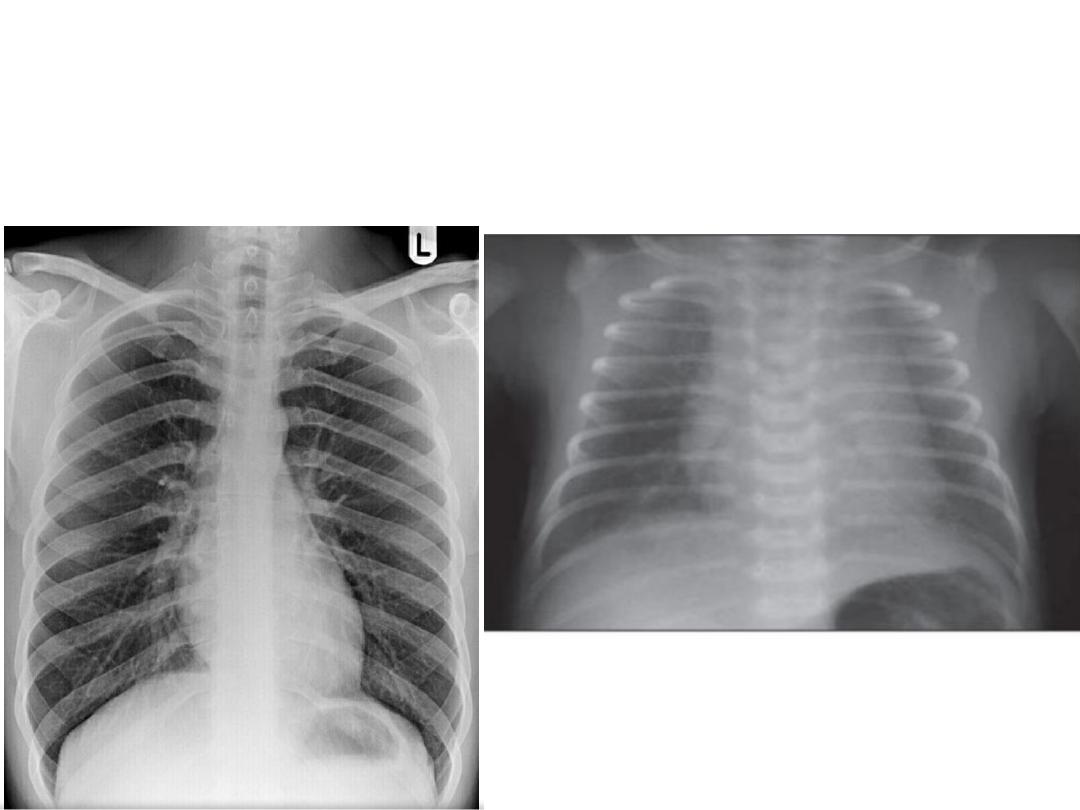
The normal thymus
• The thymus is a lymphatic organ that plays a vital role
in the development and maturation of the immune
system during childhood, specifically T cells, which are
instrumental in regulating cellular immunity, and B
cells, which are instrumental in regulating humeral
immunity. The thymus is sensitive to any kind of bodily
stress, including systemic infection, neoplasms, surgery,
and chemotherapy, and responds with rapid atrophy,
only to regrow to its original size or even larger. The
thymus is disproportionately larger in infants but
gradually becomes replaced by fat and involutes
throughout maturation. Nevertheless, the thymus
maintains its ability to grow back at any time and at
any age.
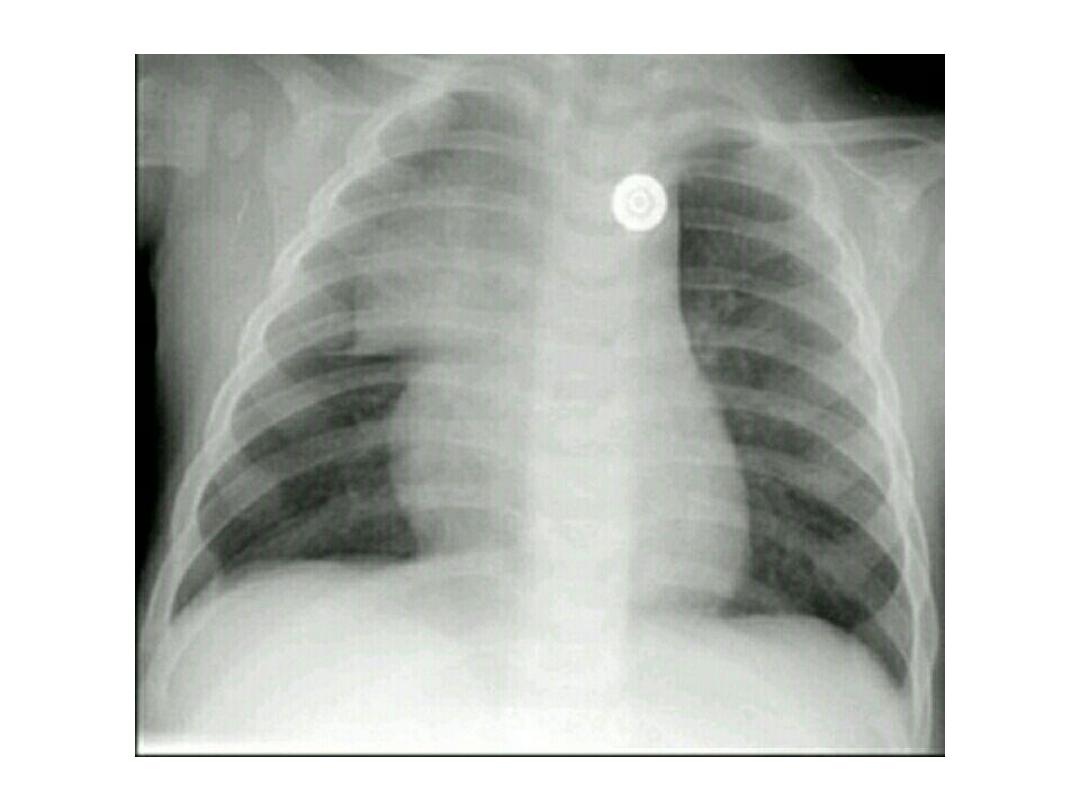

• It is relatively large in infancy
(weighing 25g at birth) reaching a
maximal weight in adolescence
between 12 and 19 years (35g), and
gradually involutes with age
(between 20 and 60 years) with
progressive fatty replacement
•
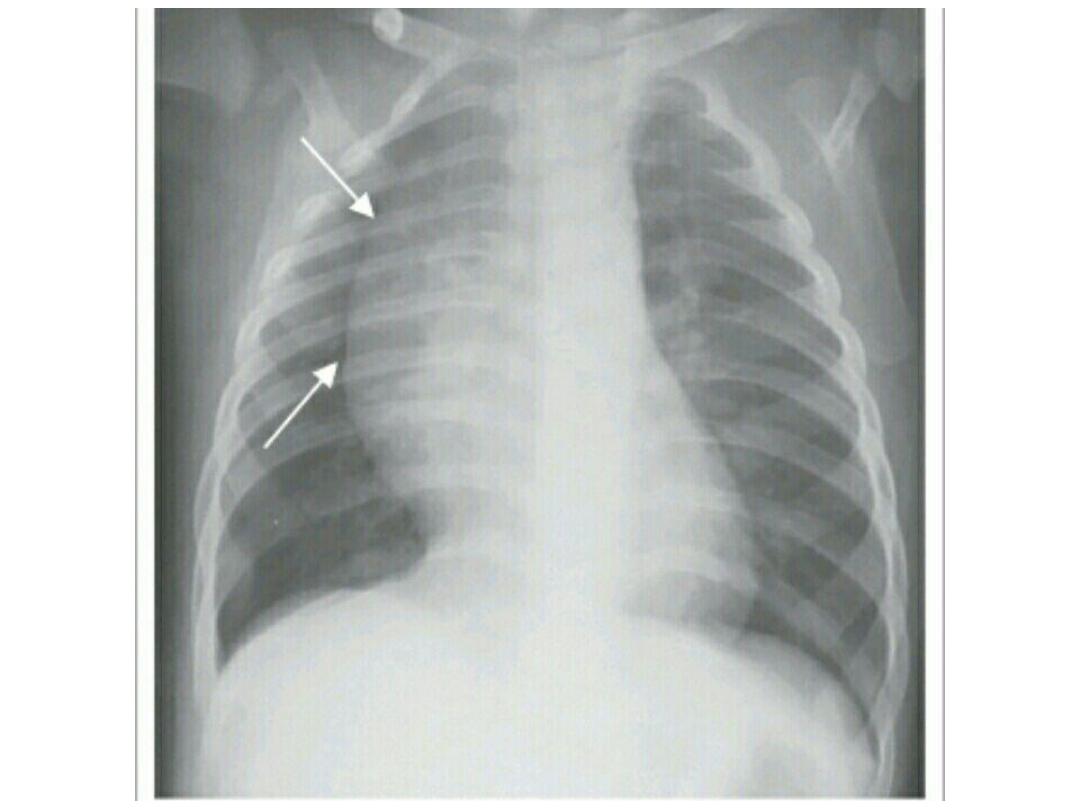
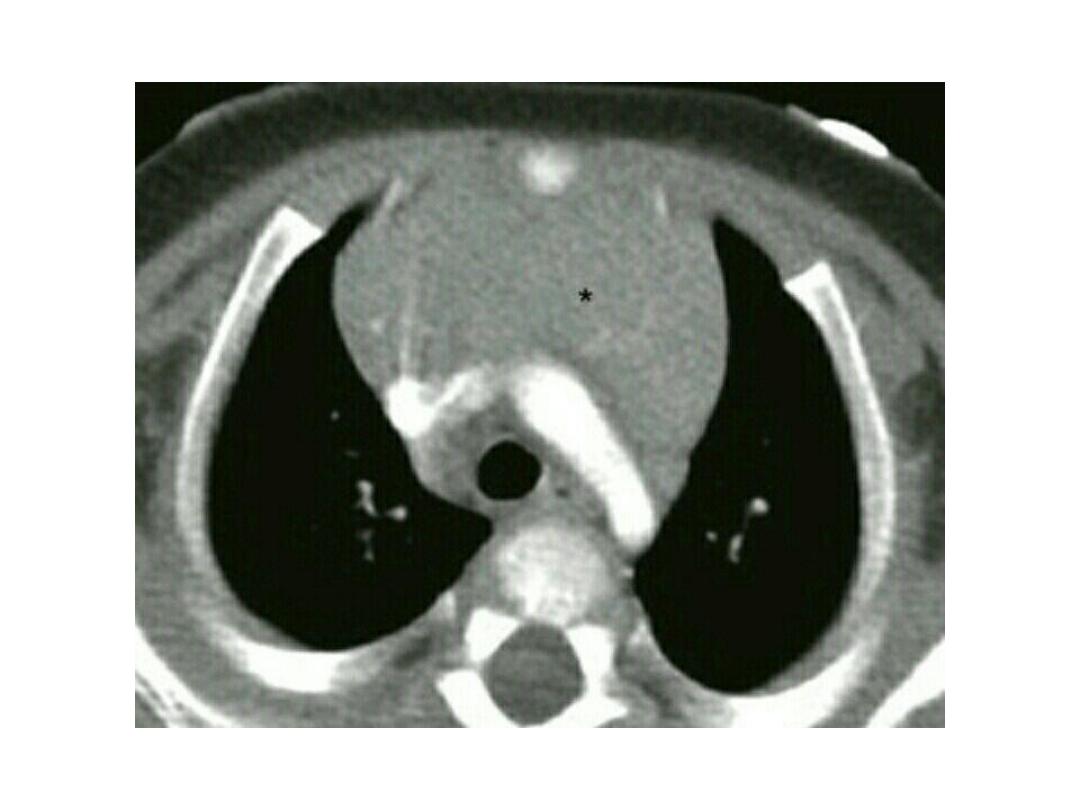
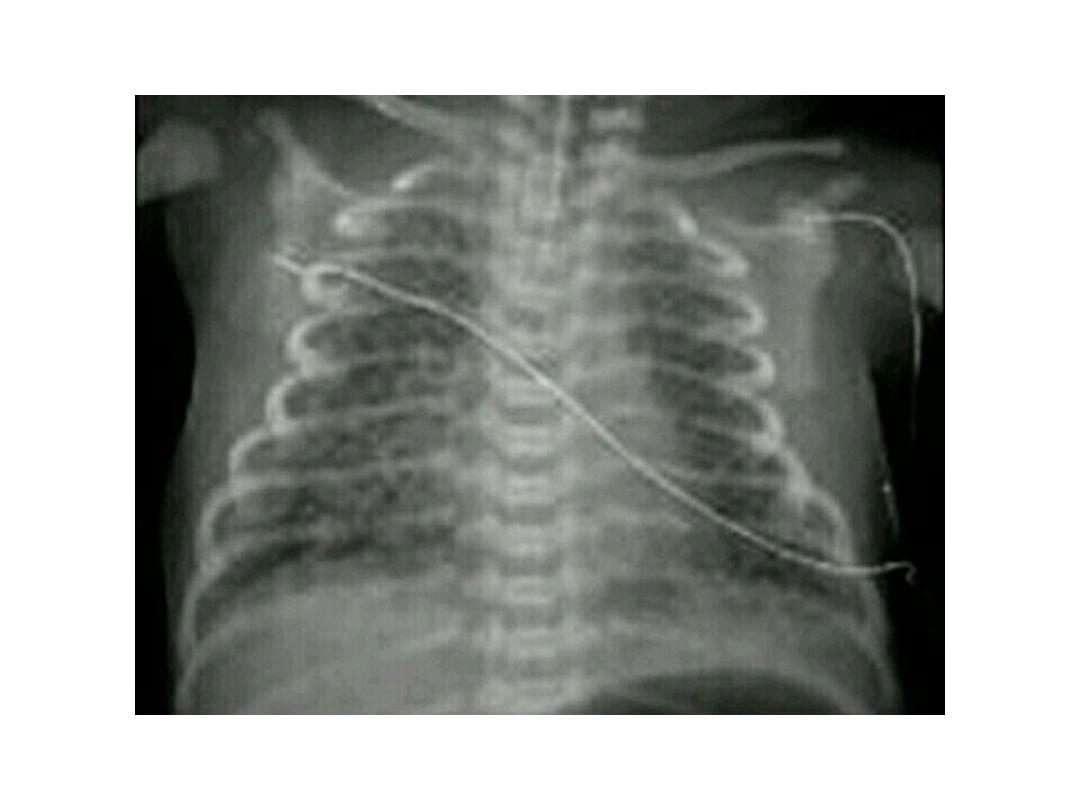
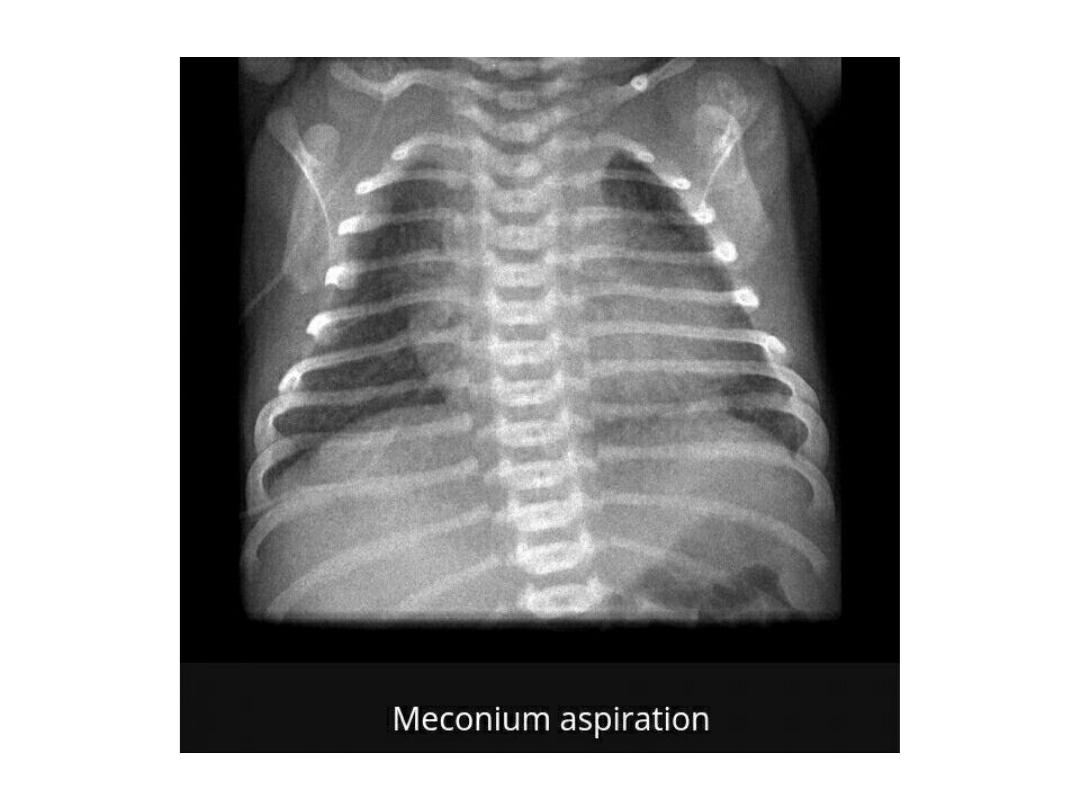
Meconium aspirate syndrome
• (MAS, alternatively "Neonatal aspiration of
meconium") is a medical condition affecting
newborn infants. It occurs when
is
present in their lungs during or before
delivery. Meconium is the first
of an
, composed of materials ingested during
the time the infant spends in the
.

• Meconium is normally stored in the
infant's intestines until after birth,
but sometimes (often in response to
fetal distress and hypoxia) it is
expelled into the amniotic fluid prior
to birth, or during labor. If the baby
then inhales the contaminated fluid,
respiratory problems may occur

• A chest x-ray may show
patchy
or
streaky areas in the infant's lungs
with
hyper inflation related to air
leak
causing
pneumo thorax ,
pneumo mediastinum and even
pneumo
pericardium.

Infant respiratory distress syndrome
(IRDS),
Hyaline membrane disease
• also called neonatal respiratory distress
syndrome, respiratory distress syndrome of
newborn, or increasingly surfactant
deficiency disorder (SDD and previously called
hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a
caused by
developmental insufficiency of
production and structural immaturity in the

• also called neonatal respiratory distress
syndrome, respiratory distress syndrome of
newborn, or increasingly surfactant
deficiency disorder (SDD and previously called
hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a
caused by
developmental insufficiency of
production and structural immaturity in the

Diagnosis
• Clinical ..with rad . Findings
• Air bronchogram..
• Absent thymus
• Reduce lung volume.
• Ground glass lung appearance
( decrease
alveolar air contents with out total
obliteration of the alveoli )
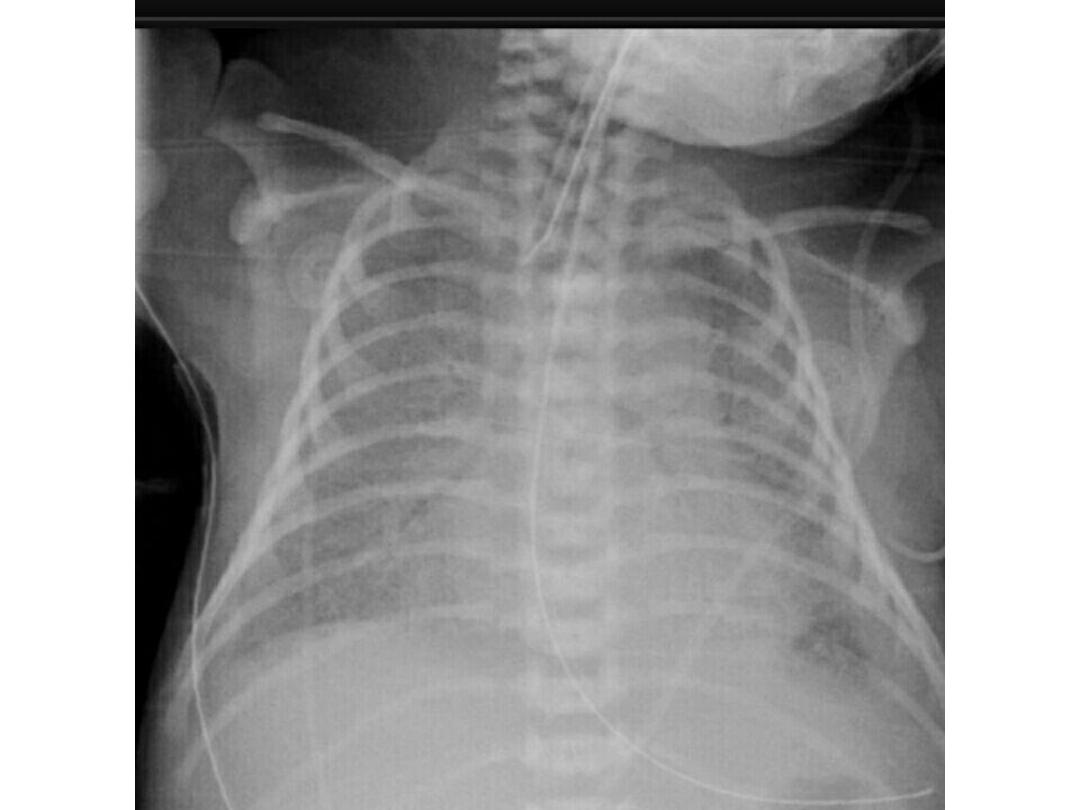
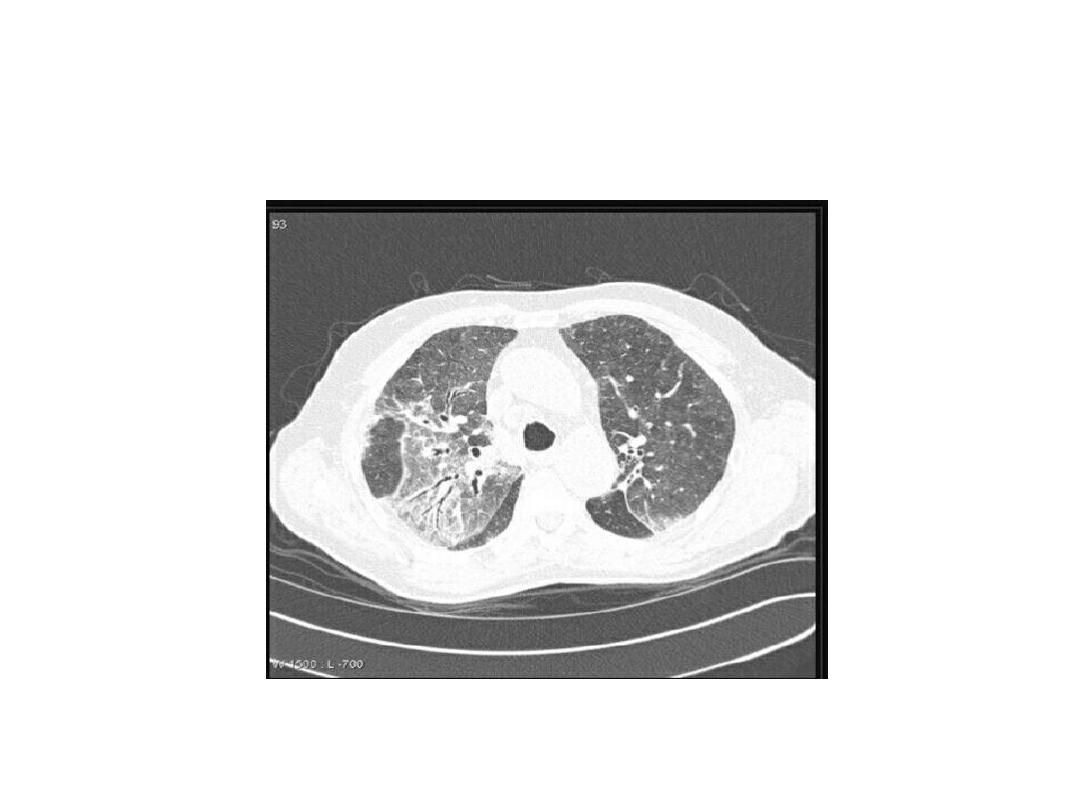
Ground glass opacification
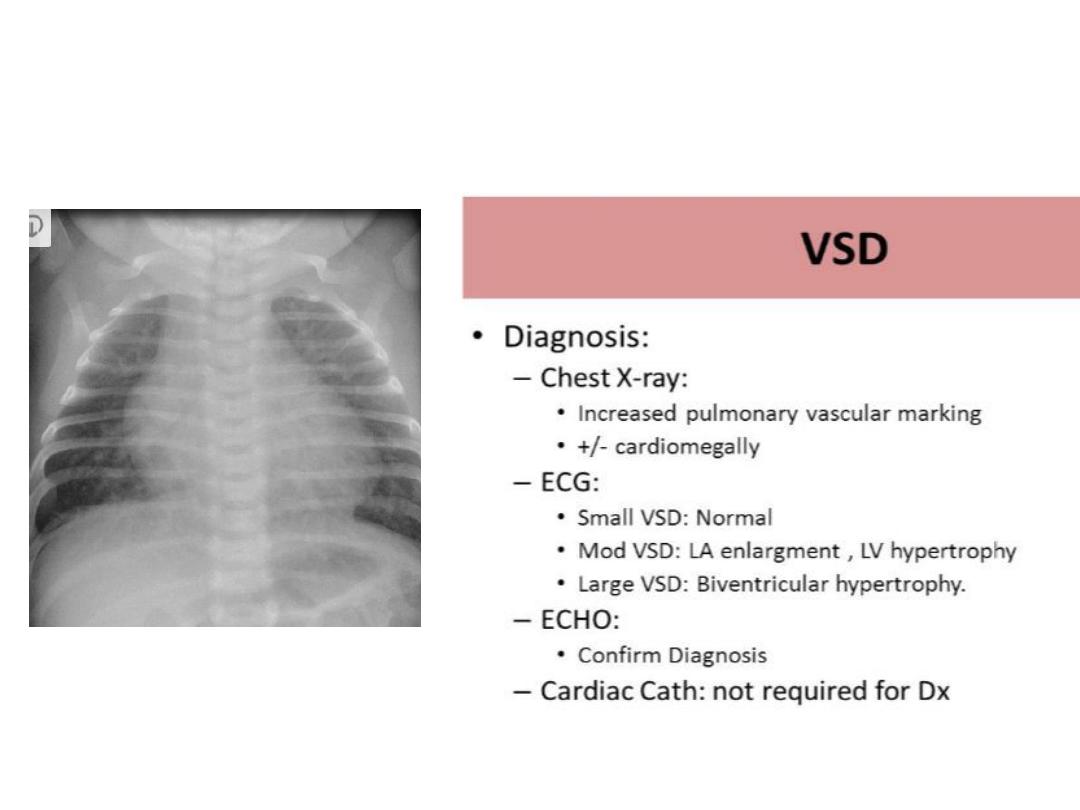
Congenital heart disease
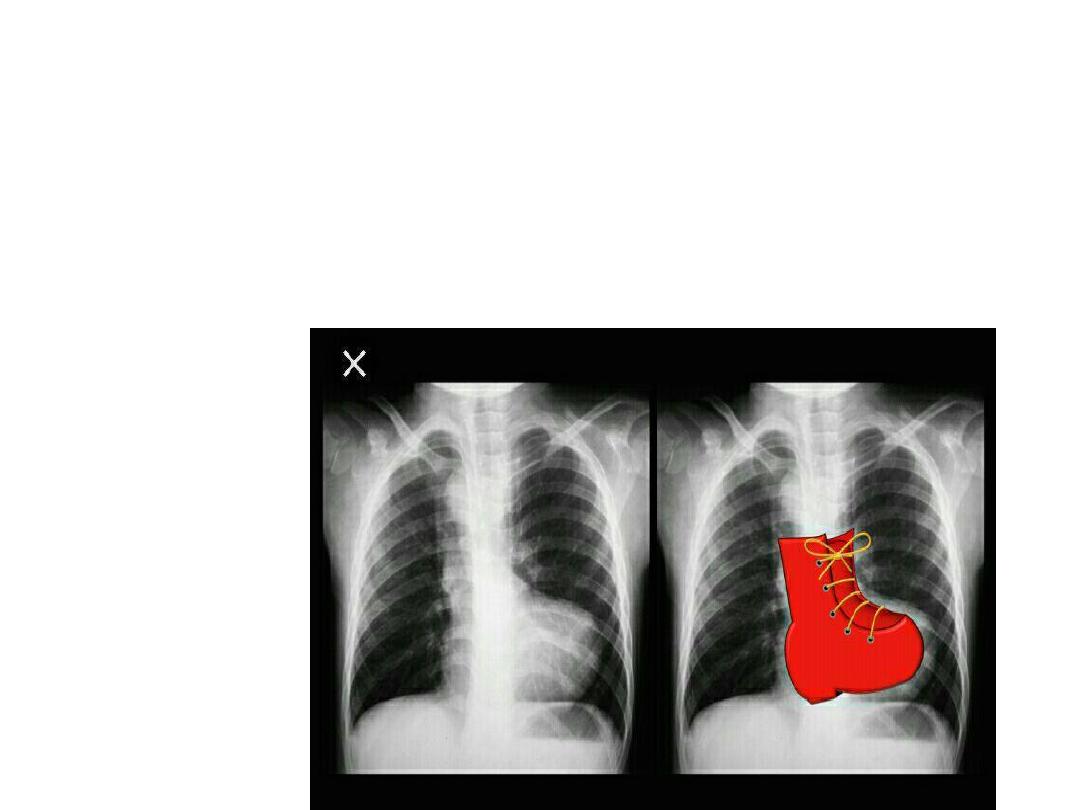
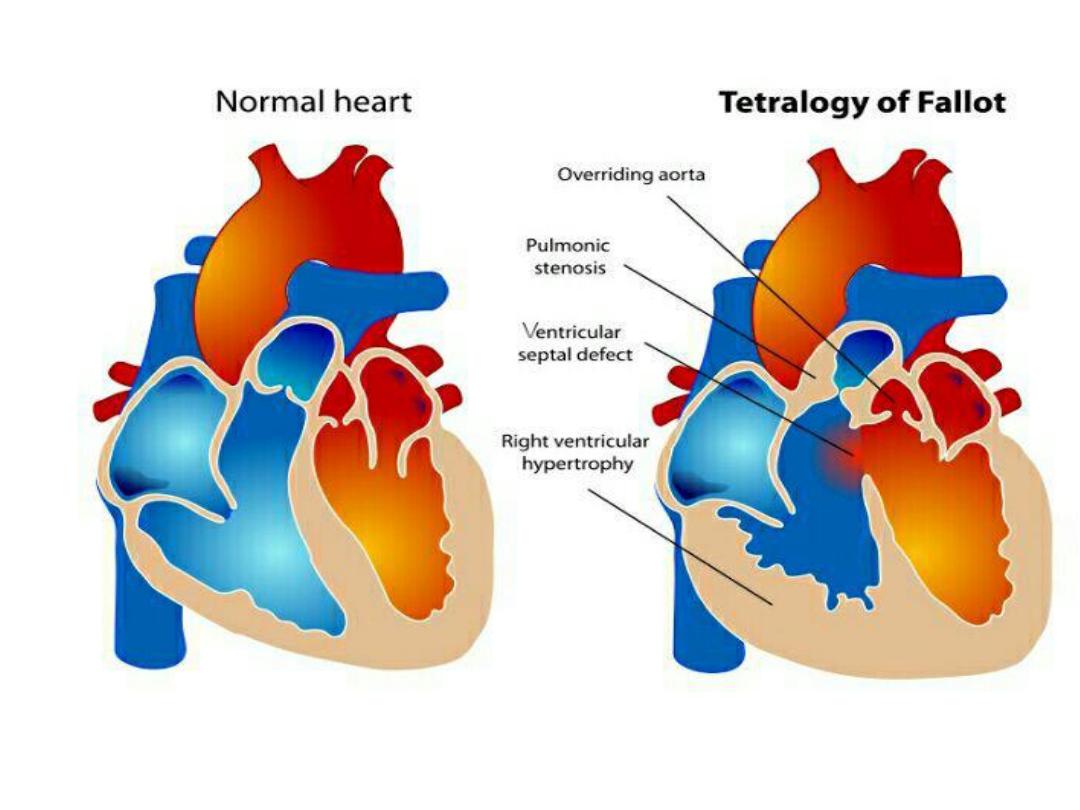
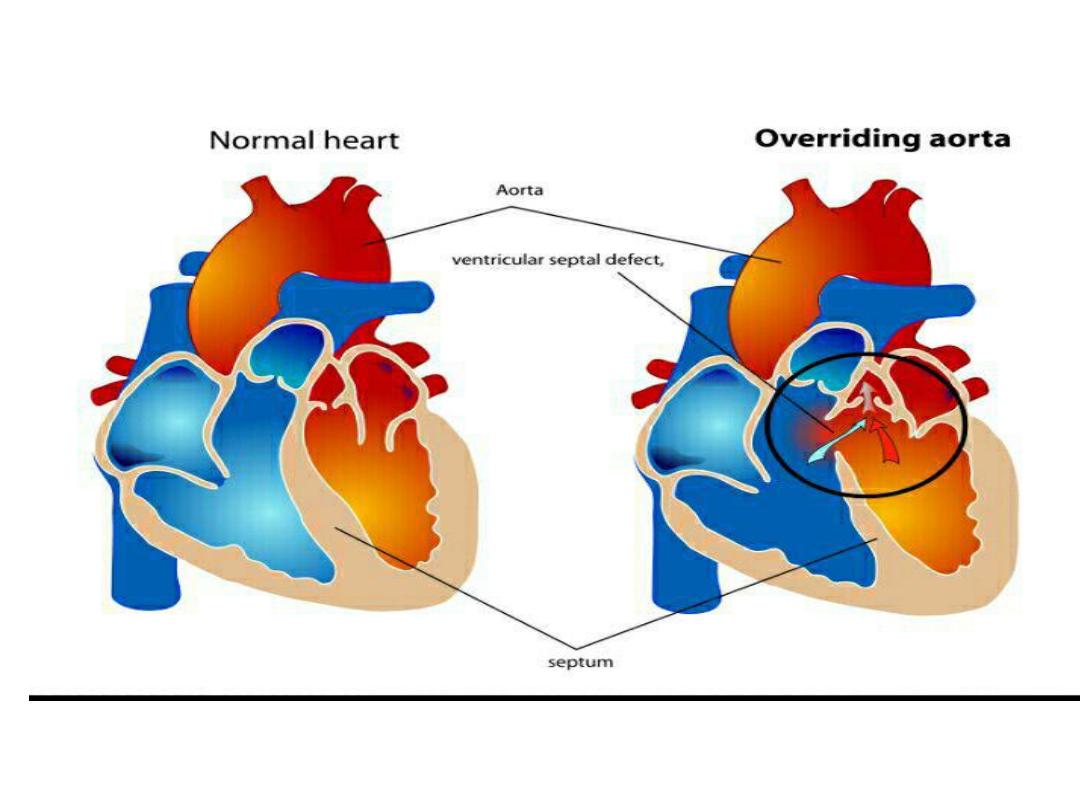
Tetralogy of Falot
• Cyanotic Congenital heart disease
• Difficult breathing ,finger clubbing , heart
murmur.

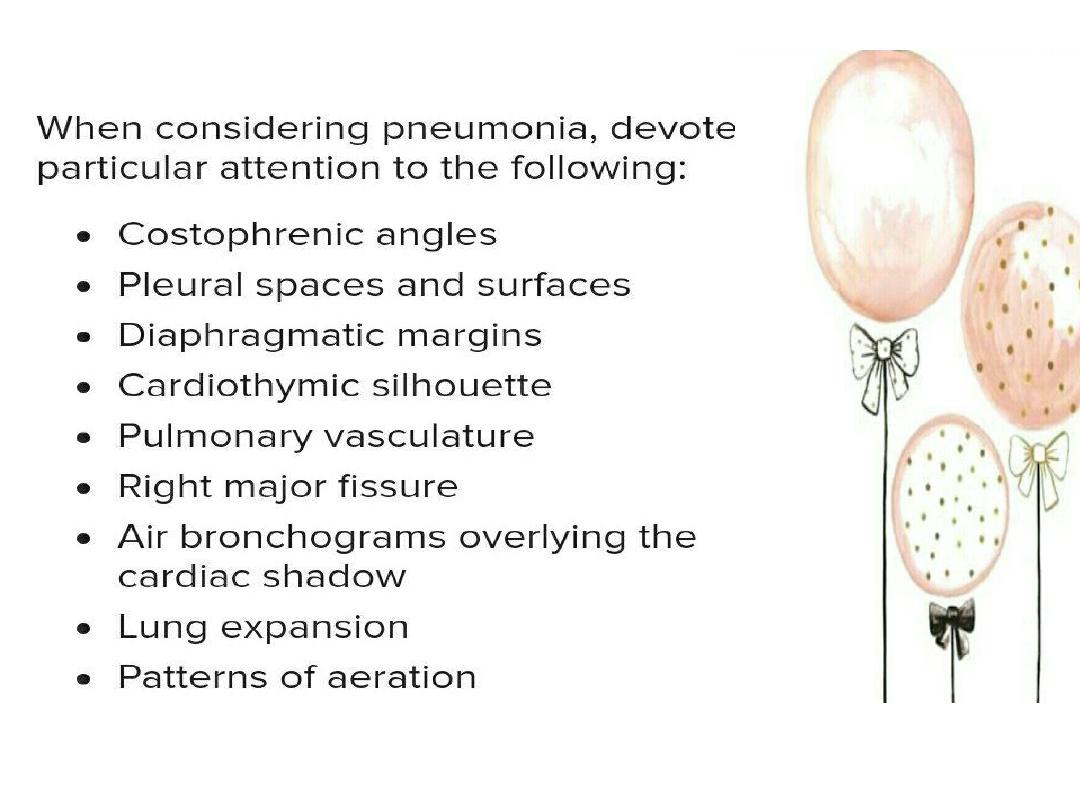
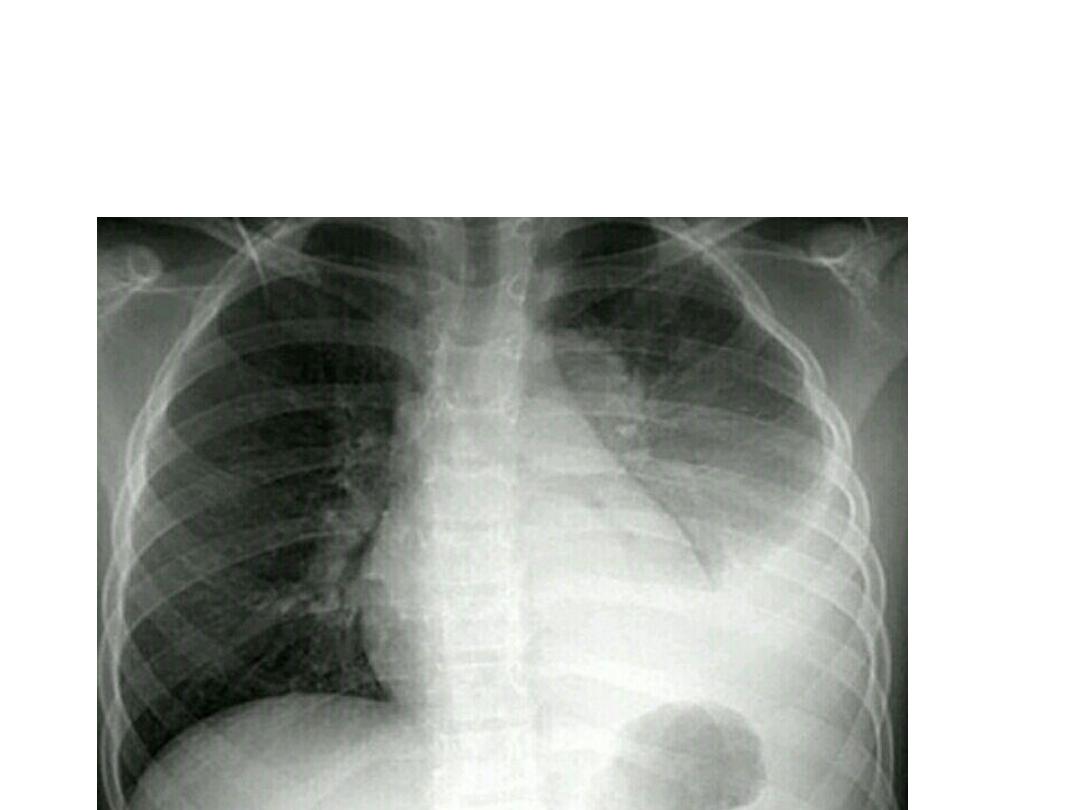
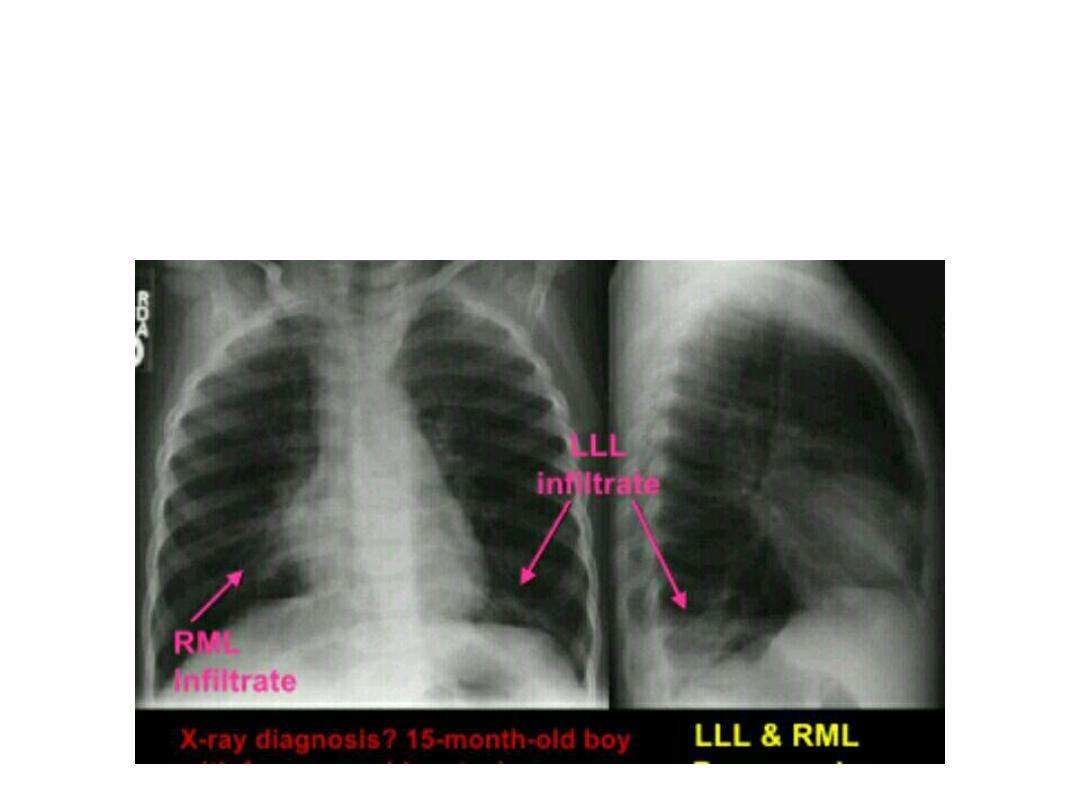
pneumonia
• Imaging investigation is
recommended when there is non
specific clinical presentations ,
when there is deteriorating
symptoms and for follow up
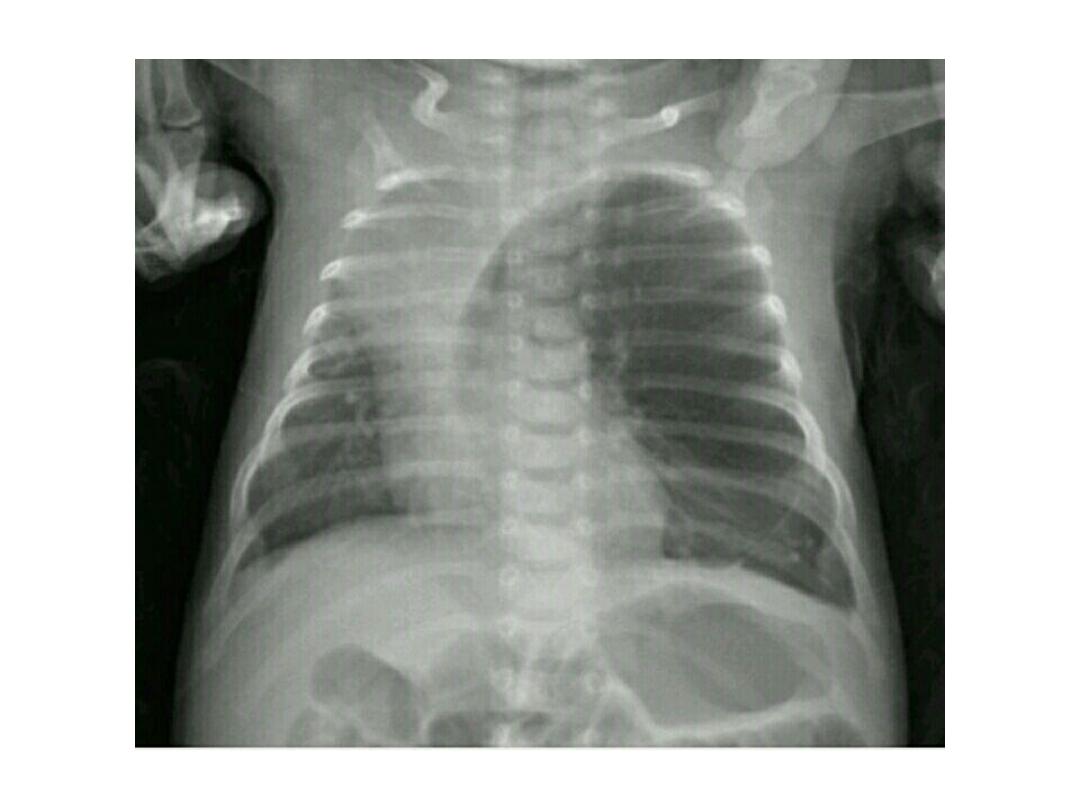
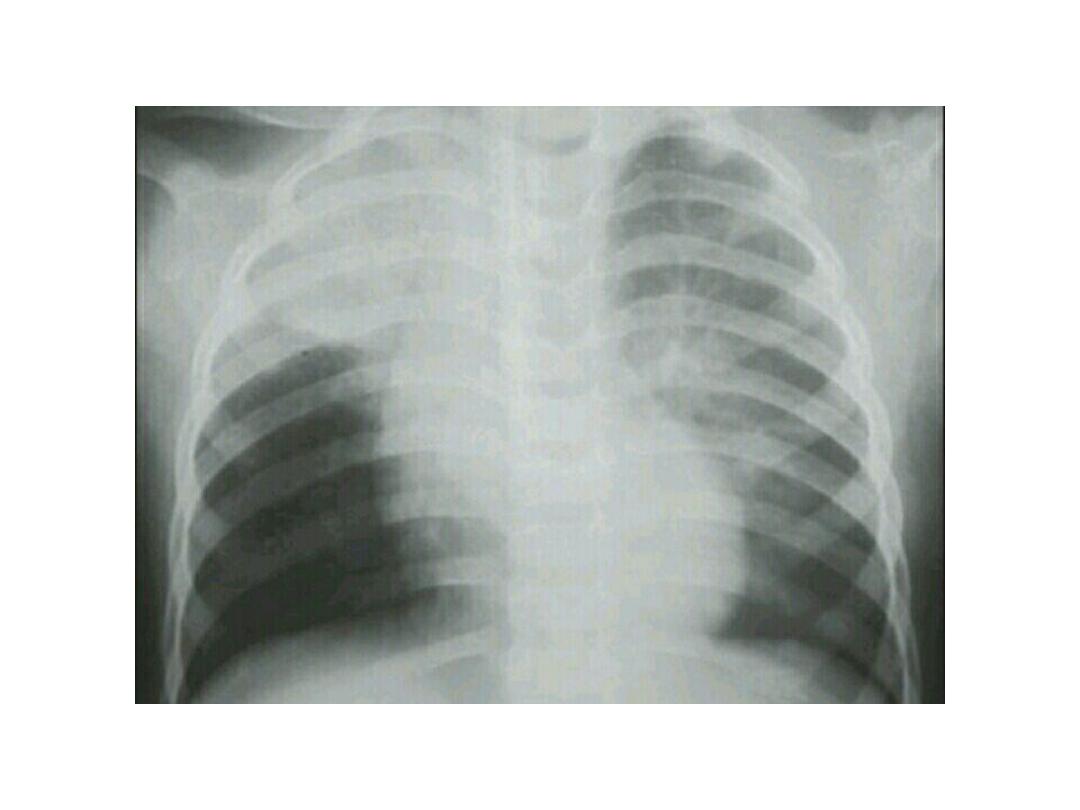
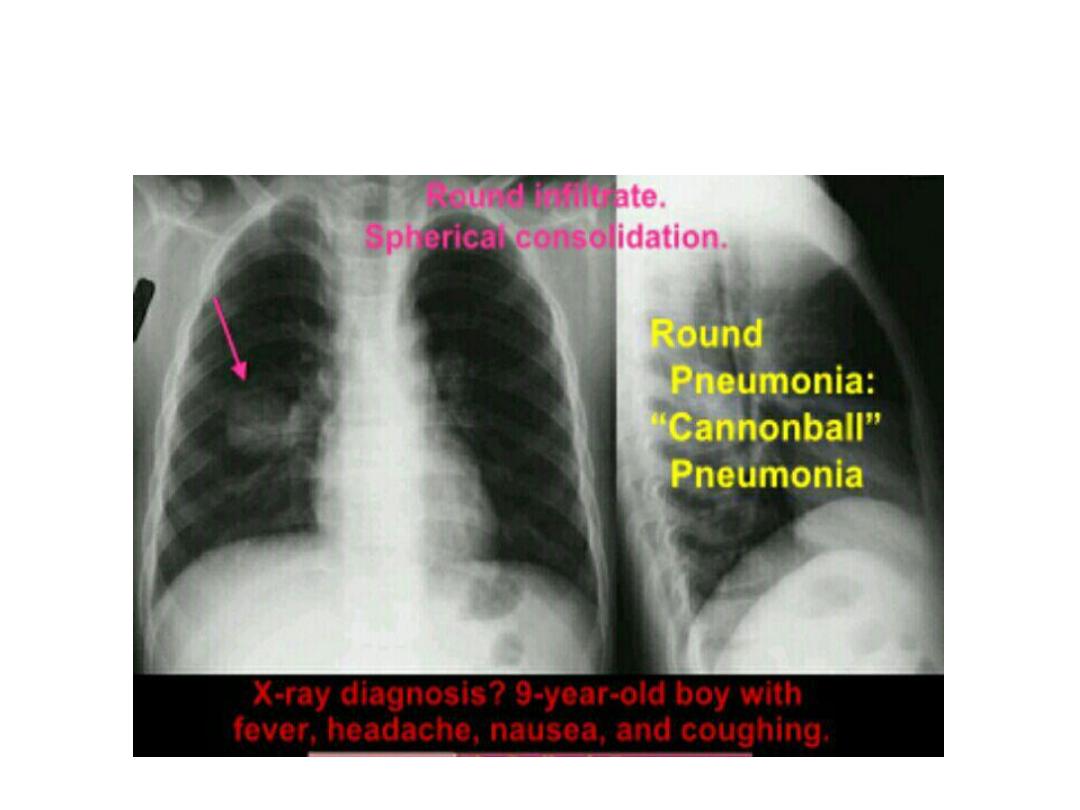
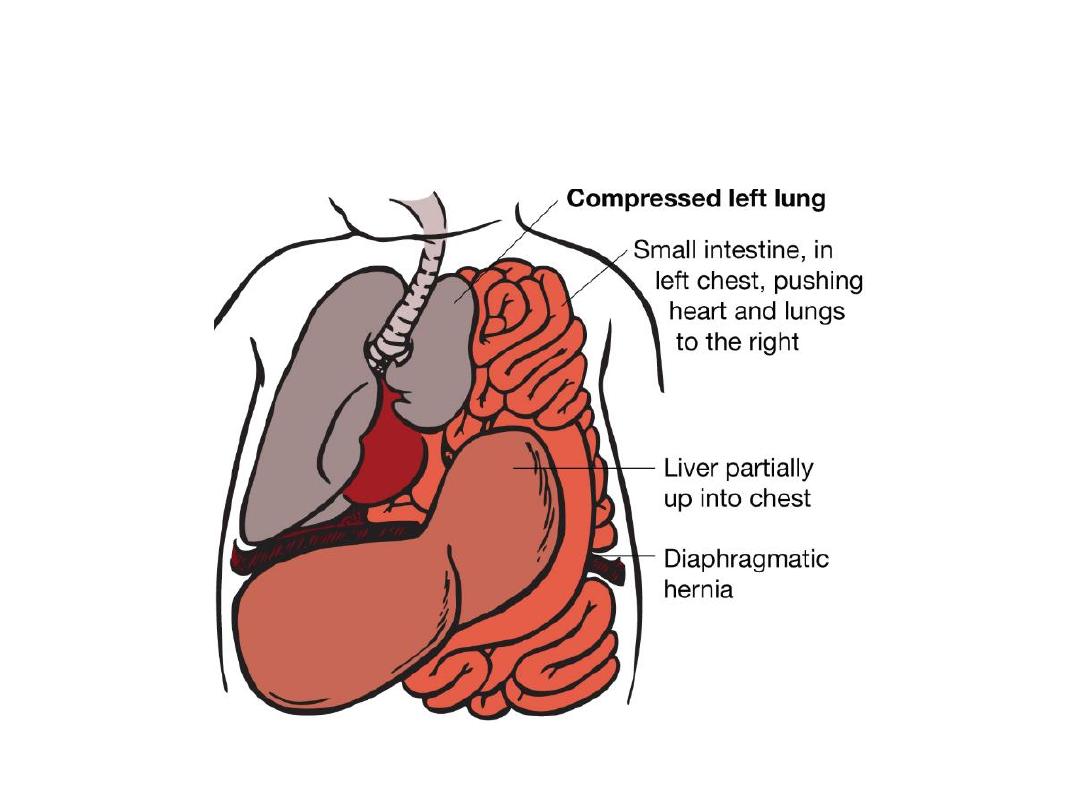
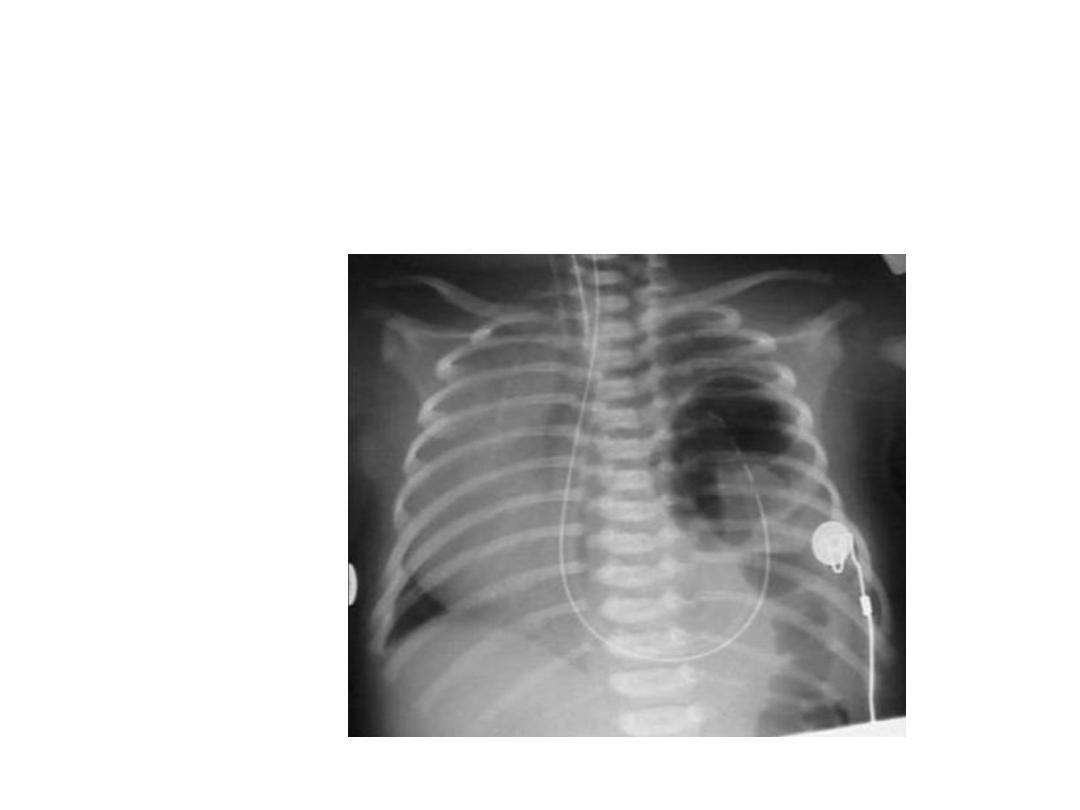
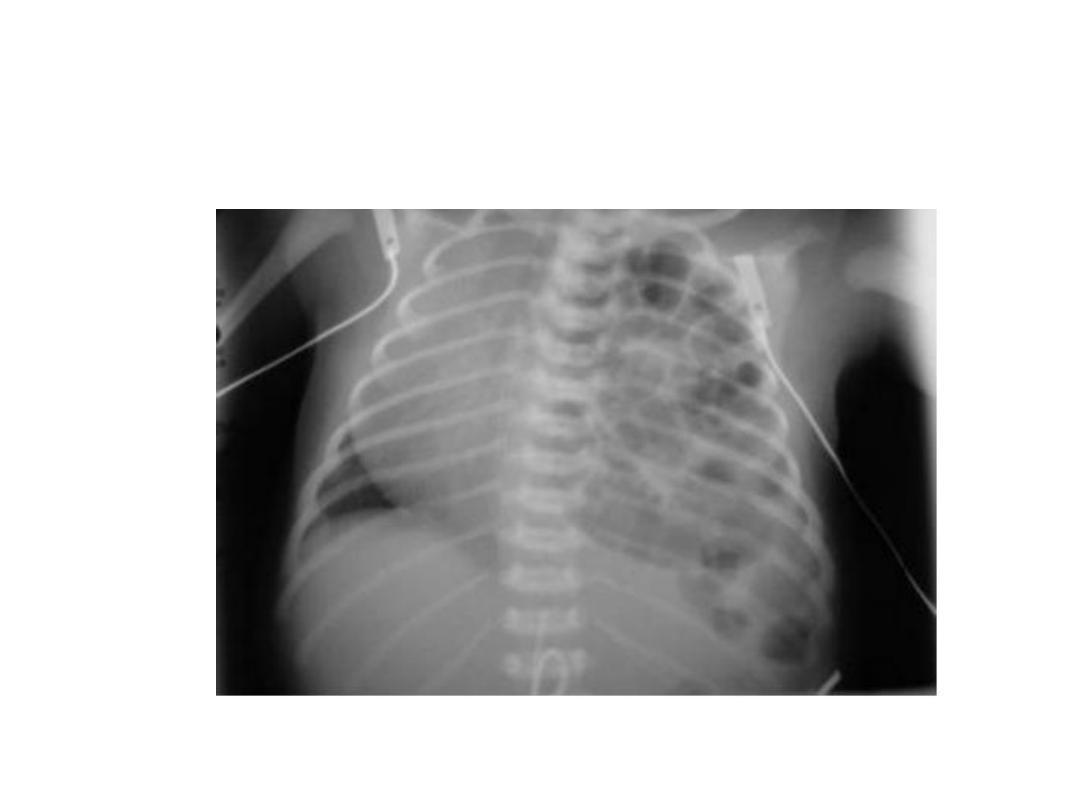
Diaphragmatic hernia
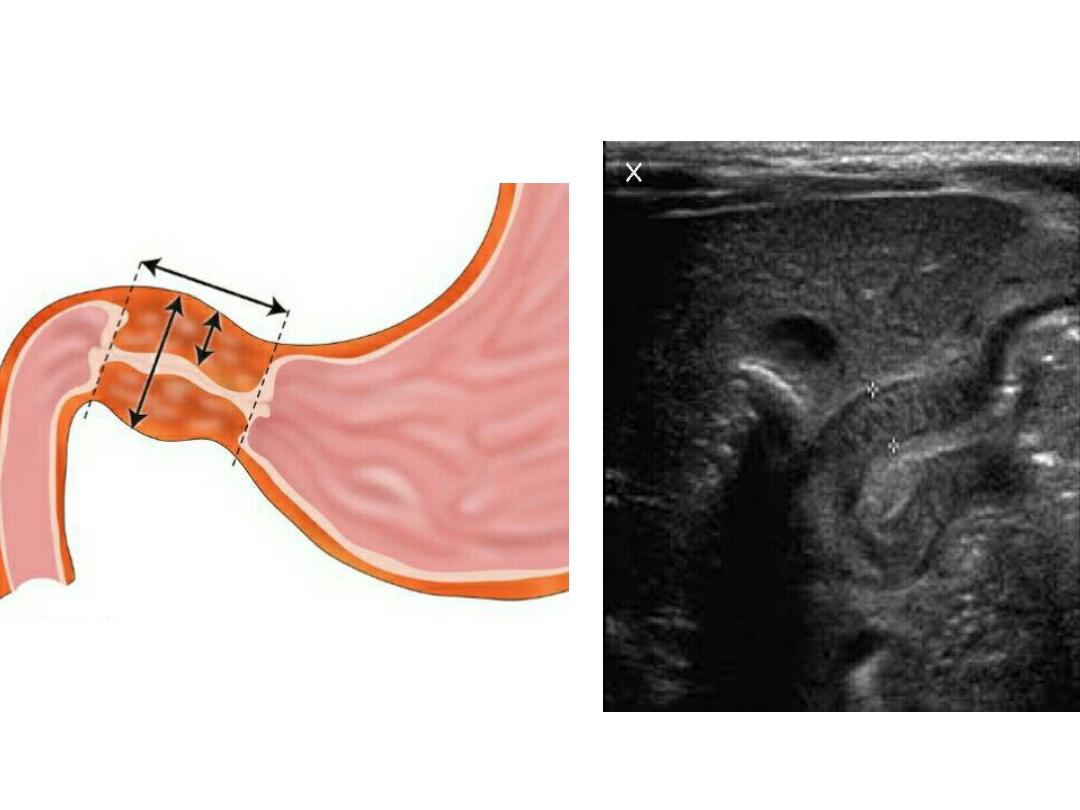
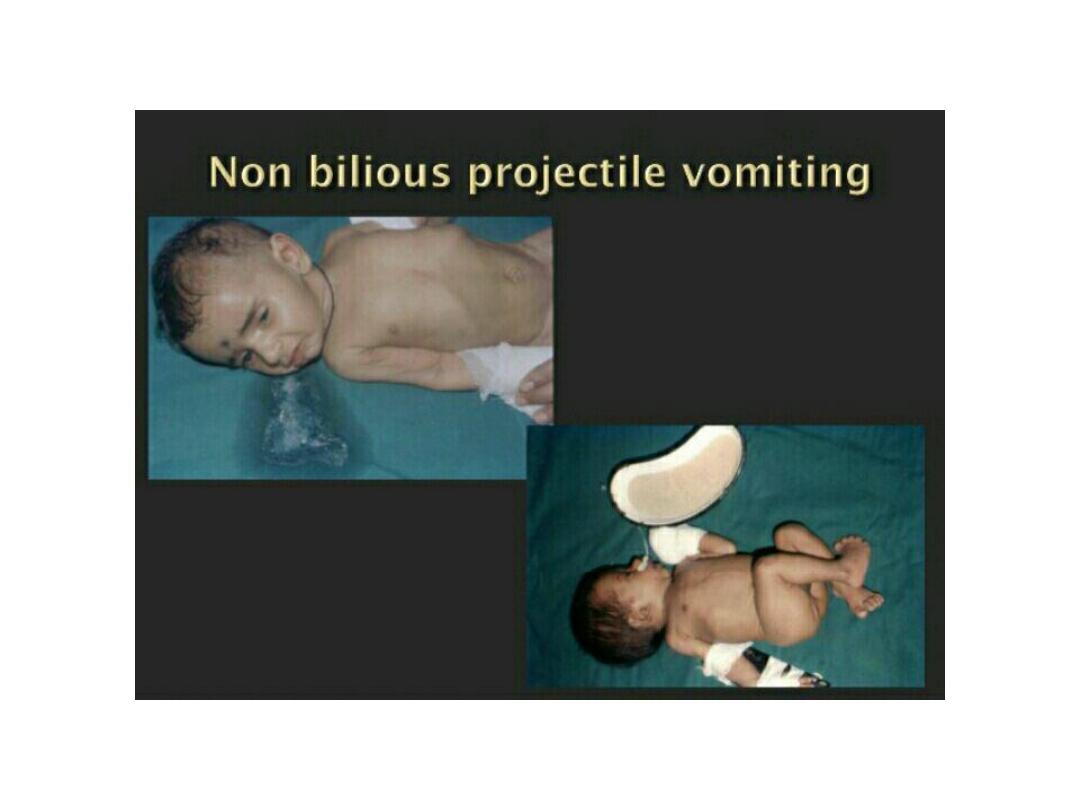
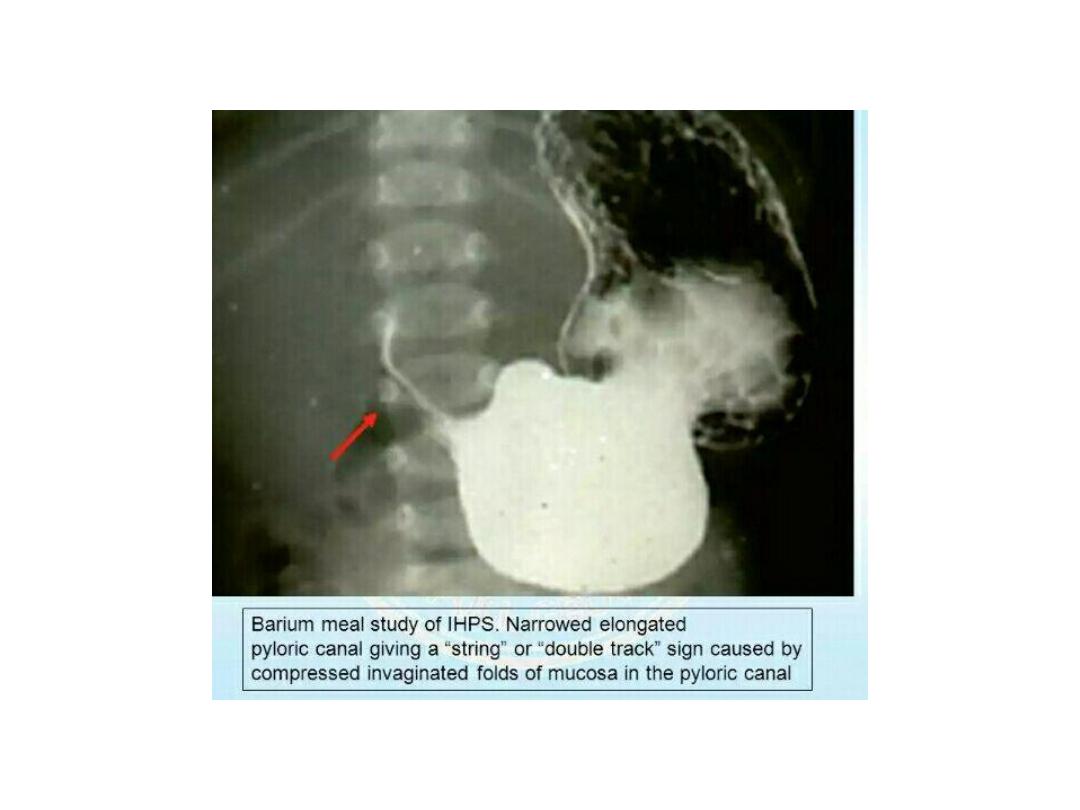
Pyloric stenosis


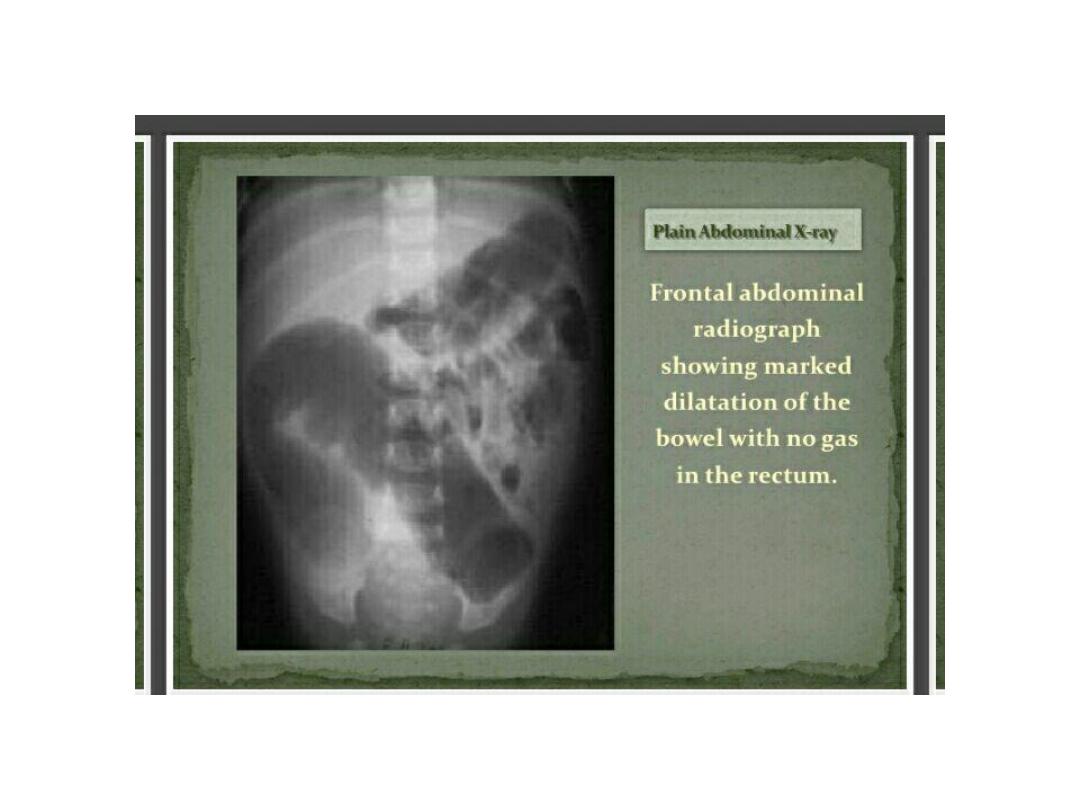
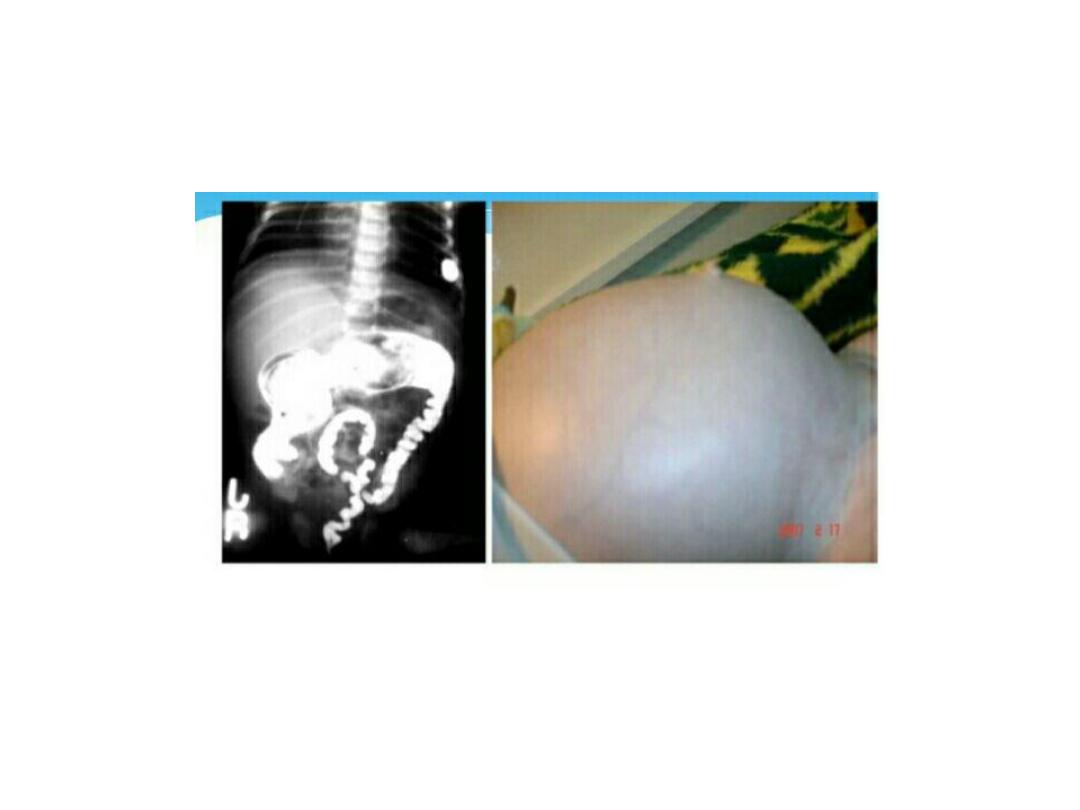
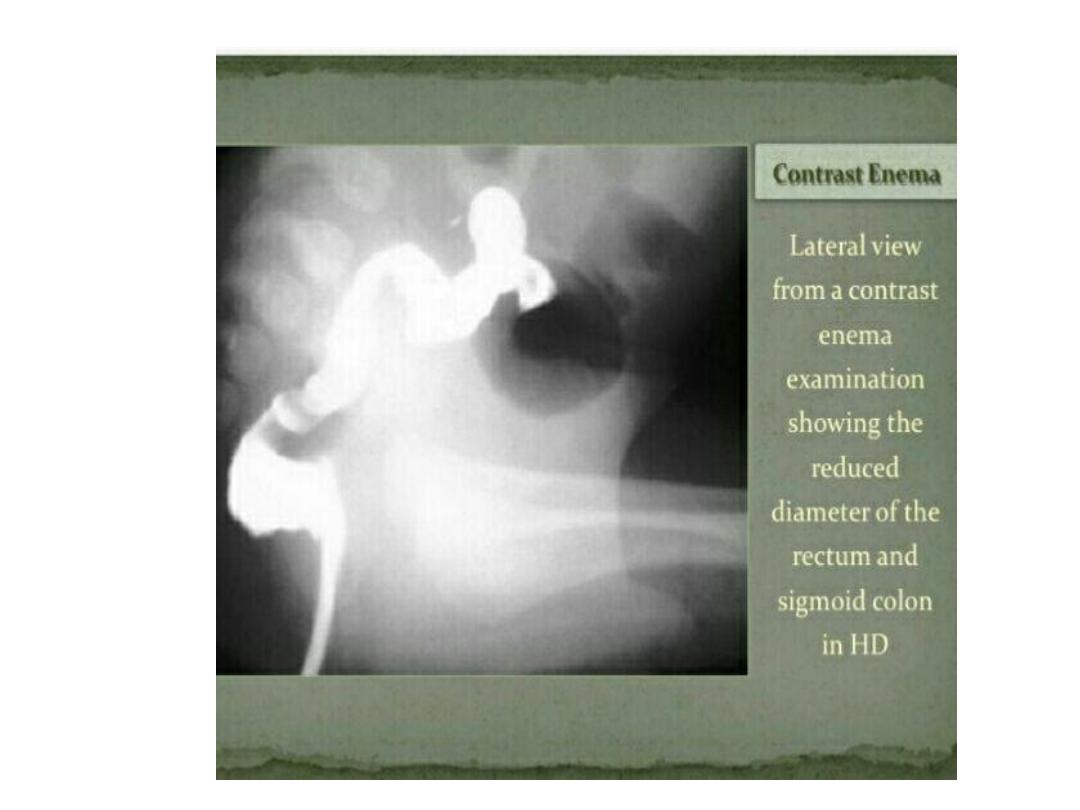
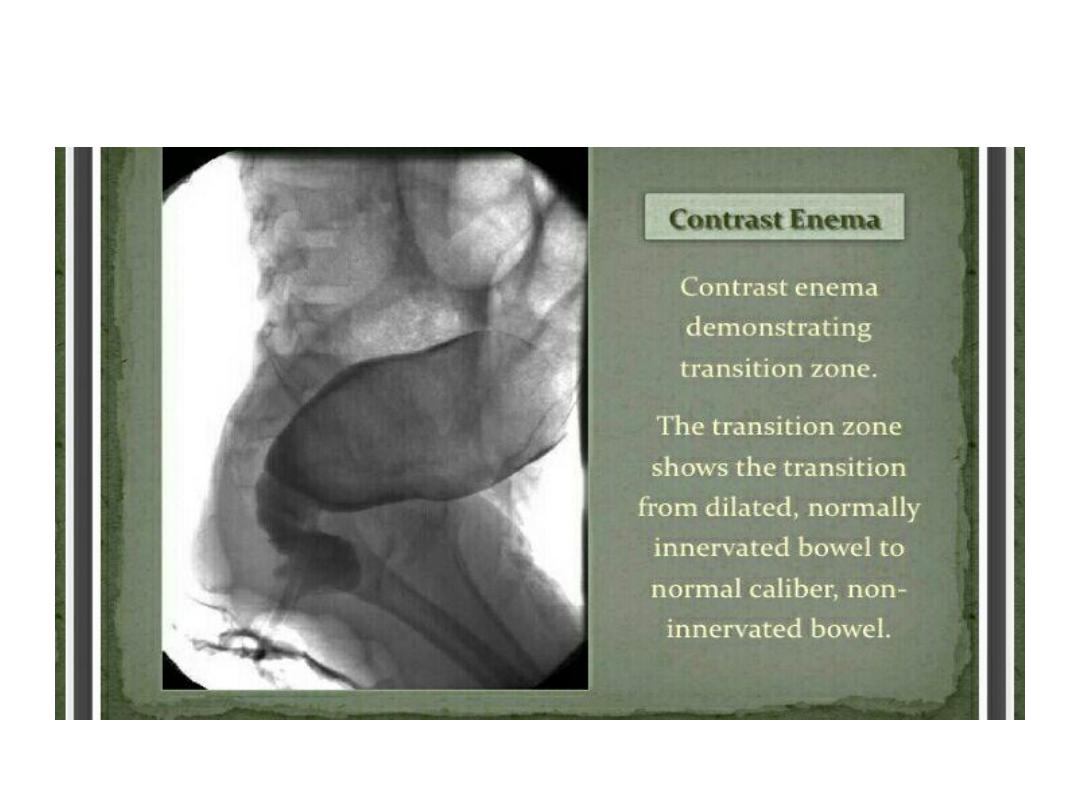
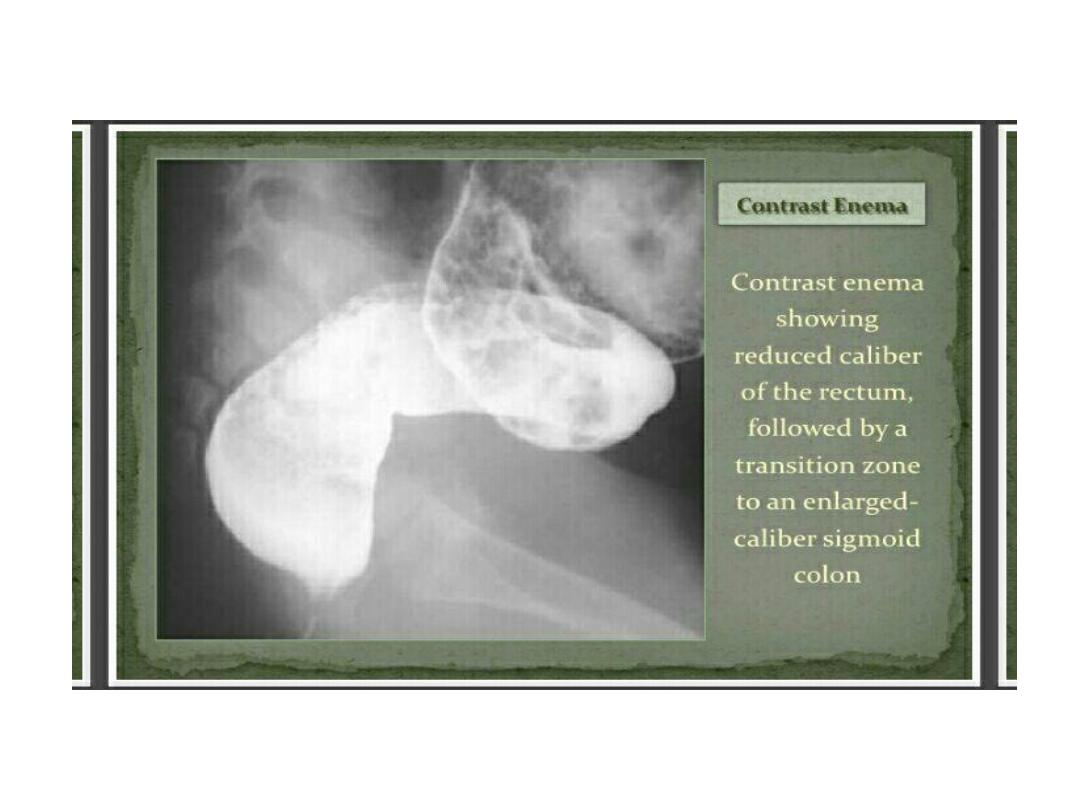
Hirchsprung
• Abasement parasympathetic ganglia in the
mucosa and sub mucosa of the colonic wall.
• The most common site is the rectosegmoid.
• Total colonic involvement is rare.
• May present with failure to pass meconium ,
prolonged constipation with paradoxical
diarrhea

• The most common cause of lower intestinal
obstruction in the .
• Associated with pre maturity and trisomy 21
• Failure to pass meconium in the 1
st
24 hr. of
life.
• Neonatal intestinal obstruction ( bilious
vomiting , abdominal distension , poor feeding
)

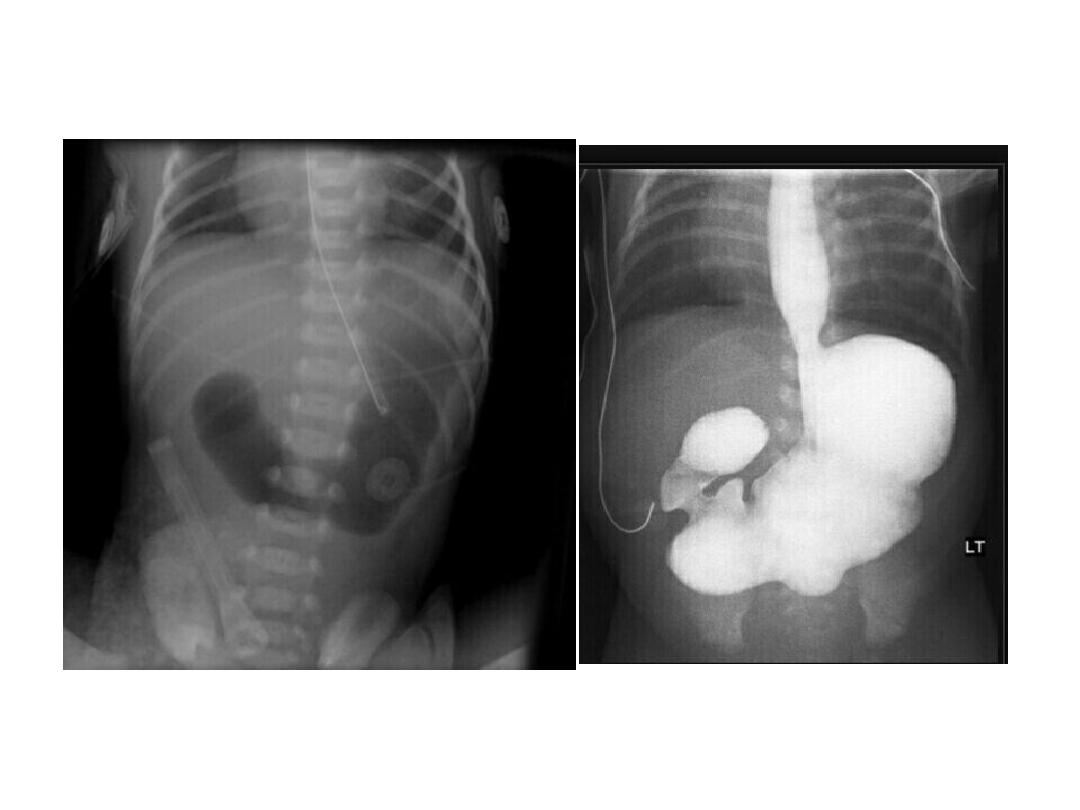
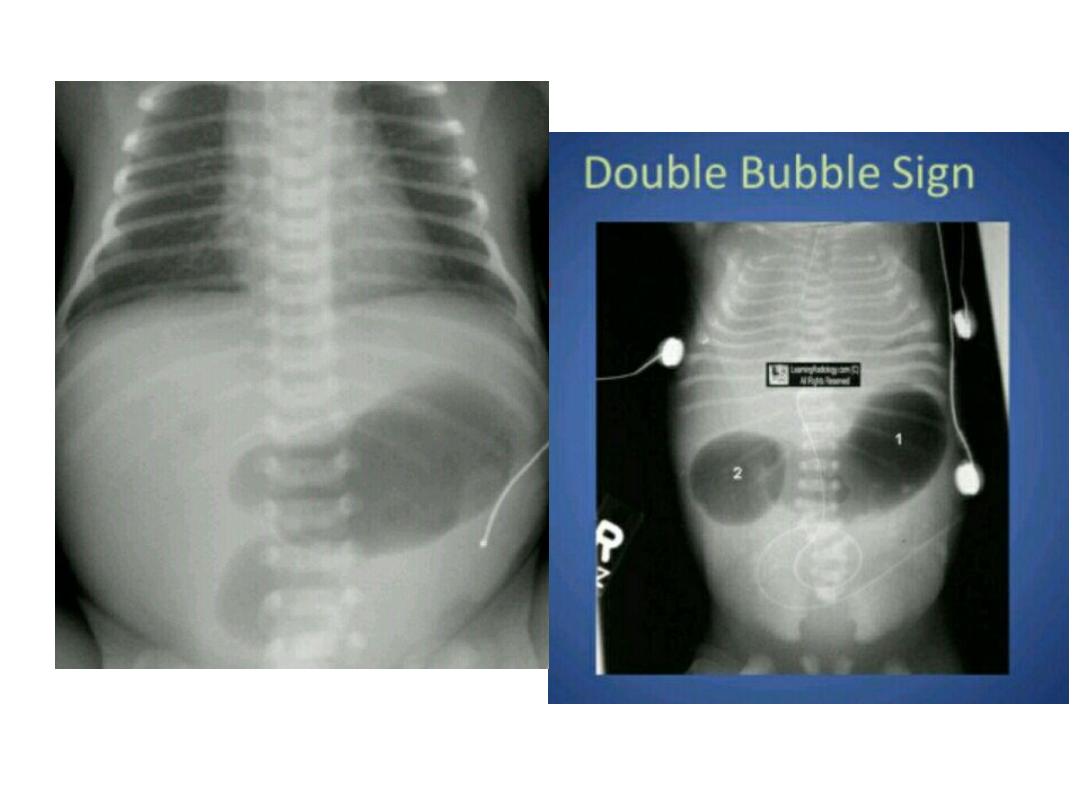
Duodenal atresia
• Double bubble singe ..gas filling distended
stomach and proximal duodenum with absent
of distal gas
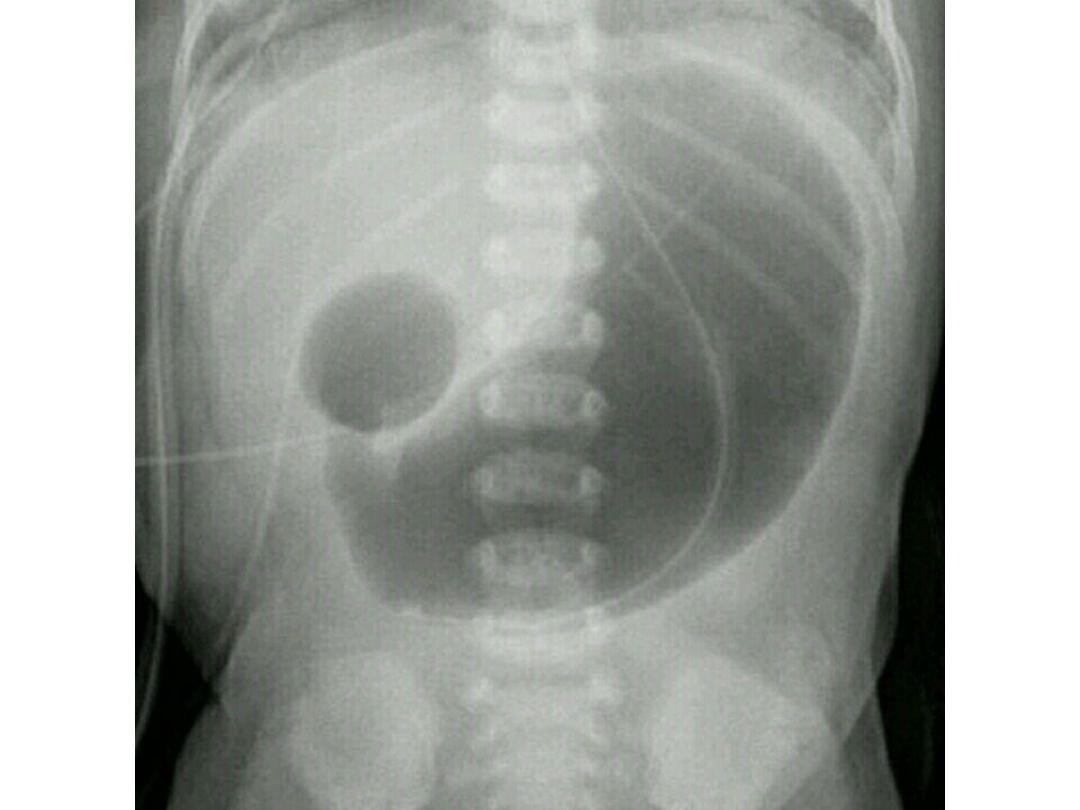

Imaging investigation of pediatric
abdominal distension
• Not all distension is pathological , healthy
infants may have variable degree of
distension.
• Neonate … .PUJ obstruction, PUV
(EU)
• Infant … Neuroblastoma…hepatoblastoma ..
( U/S , MRI , CT scan )
• 2 – 5 yrs. Wilms tumor
.( U/S , MRI , CT Scan)

