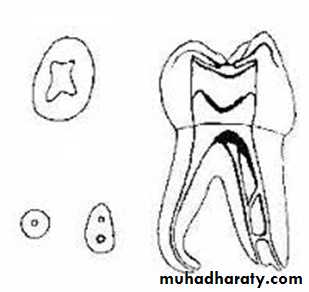
Pulp and root morphology of primary teeth
• Pulp morphology of each primary tooth• Features of the Deciduous Pulp
• Number of canals of each primary tooth
• Practical application of Understanding tooth morphology
Objectives
Considerable individual variation exists in the size of the pulp chamber and pulp canal of the primary teeth.Immediately after the eruption of the teeth, the pulp chambers are large, and in general they follow the outline of the crown.
Pulp and root morphology of primary teeth
The pulp chamber will decrease in size with an increase in age under the influence of function and of the abrasion of the occlusal and incisal surfaces.
PULP CHAMBER
it is suggested that the dentist examine critically the bite-wing radiographs of the child before undertaking operative procedures.
The root will begin to resorb as soon as the root length is completed.
The resorption causes the apical foramen to change continually, and canal length change.
Simultaneously, secondary dentin is deposited within the root canal system.The deposition produces
variations and alterations in the number and size of the root canals,as well many small connecting branches between the facial and lingual aspects of the canals.
Accessory canals, lateral canals, and apical ramifications of the pulp may be found
in 10 to 20% of primary molars
• The pulp chamber of the
deciduous toothis larger than that
of the permanent
tooth in relation to
the crown
size.
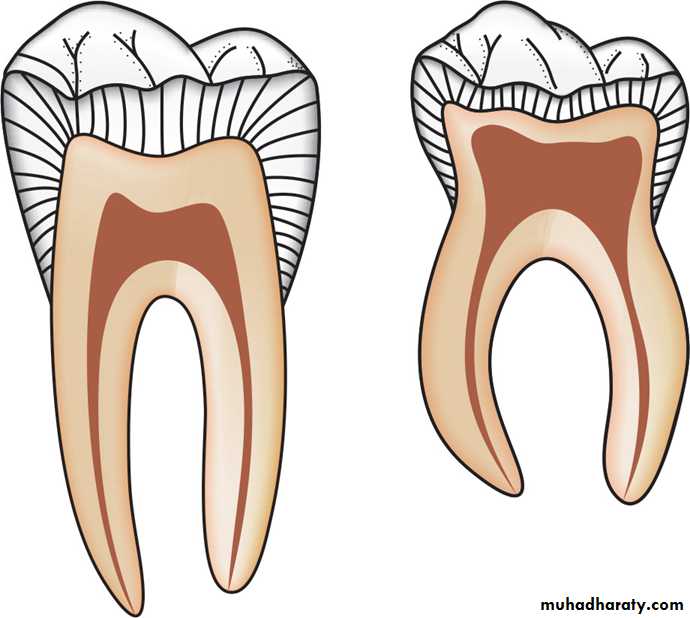
Features of a Deciduous Pulp
primary
permanent
2. The pulp horns of the deciduous tooth (especially
the mesial horns)are closer to the
outer surface of
the tooth than are
those of the
permanent tooth.
primary
permanent3. The mandibular molar has larger pulp chambers than does the maxillary molar in the deciduous tooth.
4. The form of the
pulp chamber of the
deciduous tooth
follows the surface
of the crown.
permanent
primary
5. Usually there is a pulp horn under each cusp.
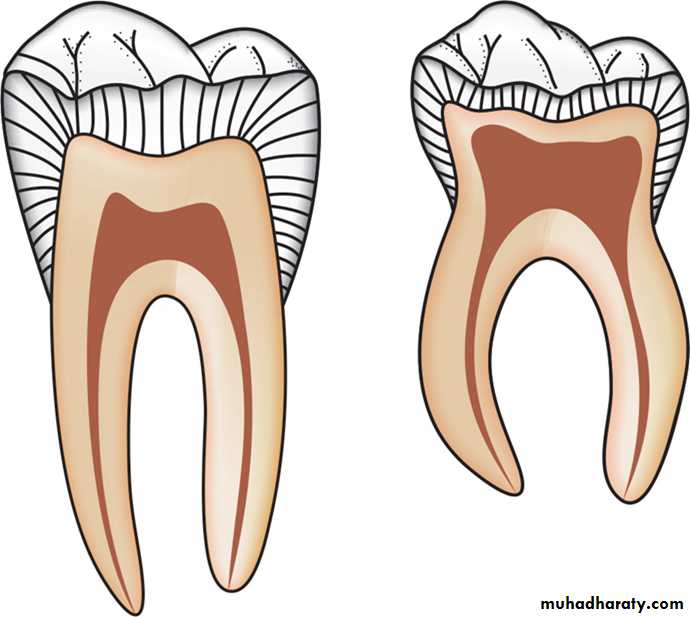
6. Thin andslender
roots pulp
canals.
primary
permanent7. Accessory canals extend from floor of the pulpal chamber to the furcation or inter-radicular area.
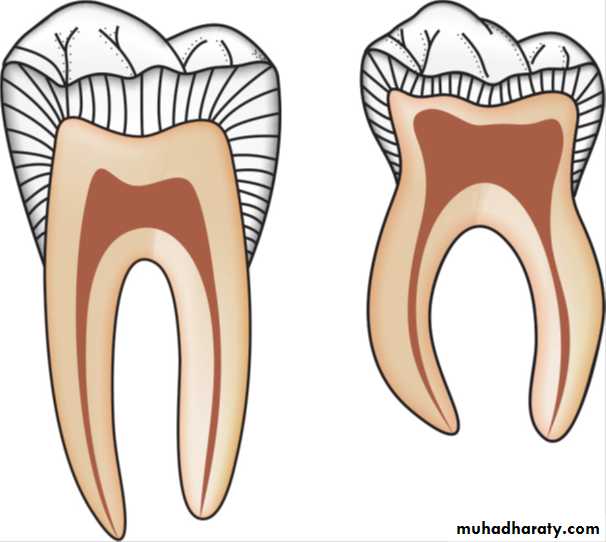
8. Increased blood supply, due to which the deciduous pulp exhibits typical inflammatory response.
9. Responds by inflammatory process, resulting in increased internal resorption.
10. Reduced sensitivity to pain—due to less number of nerve fibers.11. Poor localization
of infection and inflammation.12. Multiple ramification, making complete debridement impossible.
13. root canal narrower mesio-distally, discourages gross enlargement of the canal.
14. The roots of the posterior deciduous toothare longer and
more slender
in relation to
crown size than
are those of the
permanent tooth.
15.The roots of the deciduous molar flare more as they approach the apex (which affords the necessary room for the development of the permanent tooth buds)
than do the permanent molar roots.
Number of canals of each primary tooth
One canalRoot canals of primary maxillary incisors:
mandibular central and lateral incisorsThe pulp has
One canal10 % of mandibular incisors showed two canals in its root.
The primary canines have the simplest root canals system of all the primary teeth and offers least problems when being treated endodontically.
One canal
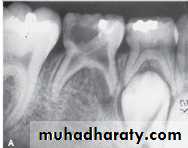
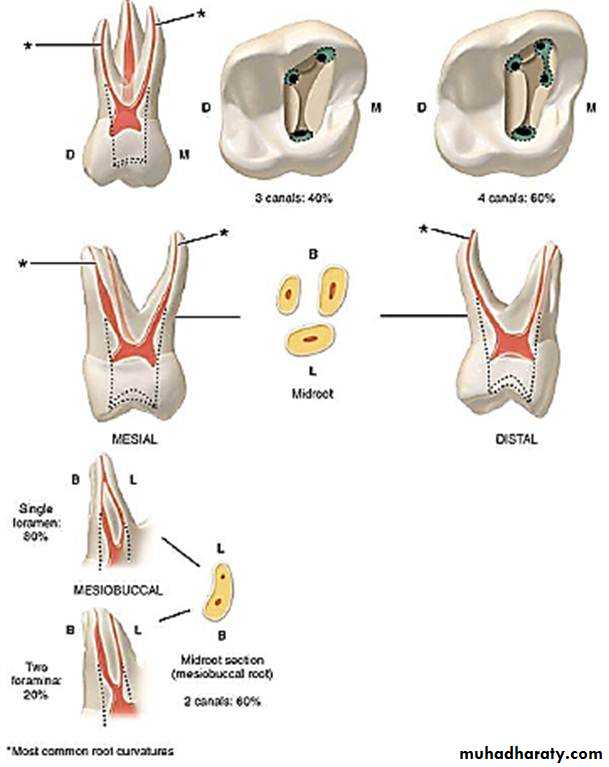
Root canals of maxillary and mandibular canines:Three to four canals are usually seen in maxillary 1st primary molars.
The palatal root is often rounded; it is often longer than the facial roots.A bifurcation of the mesiofacial roots into two canals occurs in approximately 75 percent of maxillary 1st primary molars.
Root Canals of Maxillary 1st Primary Molars
It resembles to the external root anatomy, but it may have 2 to 4 canals.
Mesial root contains 2 canals in 75% of the cases,where as only 25% of the distal root contains more than one canal.
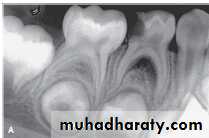
Root Canals of Mandibular 1st Primary Molars
Three to five canals are usually
It usually resembles the external root shape.Mesiofacial root normally contains two distinct canals (85 to 90%).
Root Canals of Maxillary Second MolarsIT may have 2 to 4 canals.
Mesial root has 2 canals in 85% ofwhile distal root contains more than 2 canals
In 85%Root Canals of Mandibular2nd Primary Molars
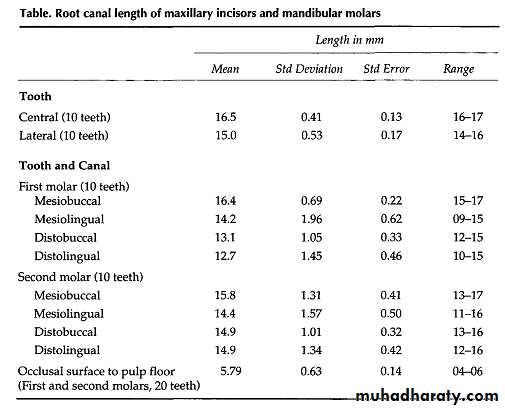
Root canal length before resorption
PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF
UNDERSTANDING TOOTH MORPHOLOGY• Modifications in the cavity depth and extension is required due to reduced thickness of enamel and dentin.
B. Width of the occlusal cavity should be very much narrow in compliance with the narrow occlusal table.
.
1. Tooth preparations
C. The inter-proximal contacts of primary teeth are broad and flat compared to those of permanent teeth. Use of a good wedge at the cervical part of the proximal box is necessary during material insertion and condensation into the proximal box
D. It is difficult to obtain an adequate gingival seat while preparing a Class II cavity due to the cervical constriction present in deciduous teeth.
Trying to prepare a gingival seat in a deep cavity may lead to encroachment into pulp chamber.
• The prominent mesiobuccal cervical ridge of mandibular and maxillary first molars must be accommodated in the preparation of stainless steel crowns, which may otherwise result in a ‘rocking’ crown.
2. Preformed Stainless steel crown preparations
• B. The gingival contour of the cervical margin that varies from the buccal to lingual to proximal aspects should be replicated while fabricating the crown.
• The cervical border of the crown must flow parallel to the gingival contour.
M
C. The cervical border of the crown must be placed below the cervical bulge of the tooth (0.5 mm)to obtain maximum retention.
• Conical roots of primary anterior teeth facilitate easy removal.
• Extraction of deciduous molar teeth must be made with great caution.• The premolar tooth bud is located between the flared roots of primary molars, which may be avulsed during deciduous tooth extraction.
3. Surgical procedures
Understanding of the
anatomy of the pulp,the number and curvature of the root canals
is important during pulp treatment procedures.
4. Pulp therapy