د.لمى العلاف HISTOLOGY
Lecture 4.Large intestine
Large intestine consists of Cecum, ascending, transverse and descending Colon, Sigmoid colon and Rectum. Its main function is reabsorption of water and soluble salts from the bowel contents converting the liquid contents into fecal material, also production of mucin to lubricate the passage of fecal material along the bowel lumen.
Histological structure:-
Mucosa:
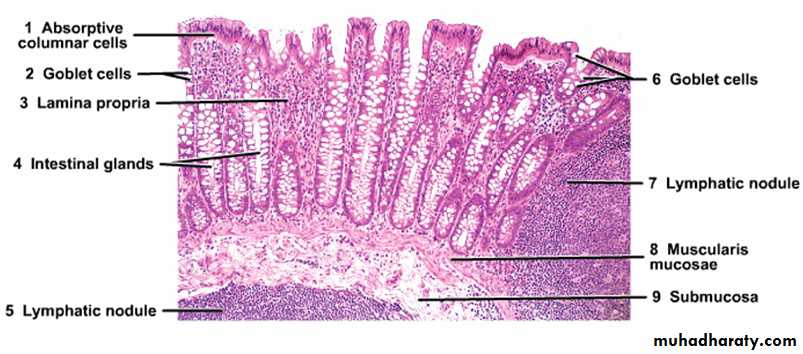
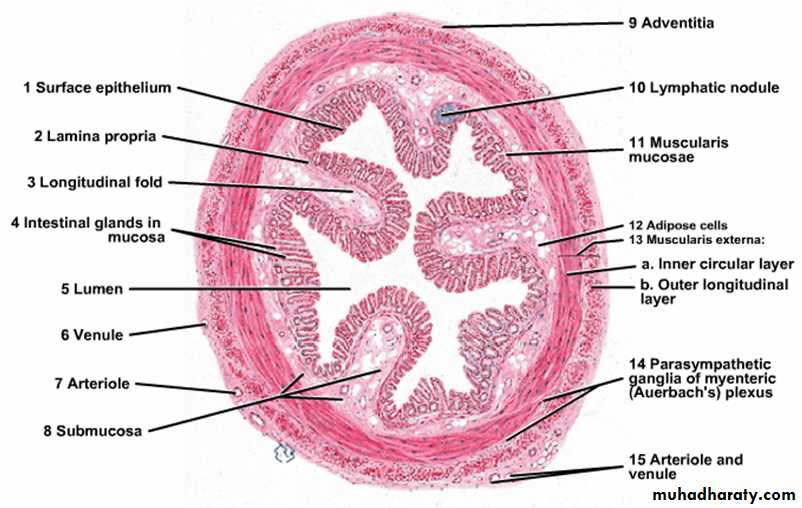
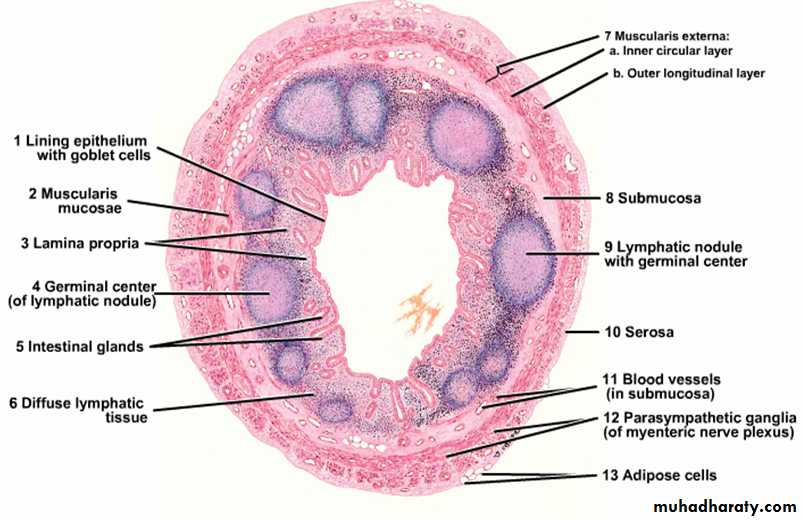
The epithelium of large intestine: contains no folds and no villi but there is a mixture of absorptive cells and mucous cells (goblet cells) arranged as simple, straight, non branching tubular glands (intestinal glands). The absorptive cells are columnar and have short irregular microvilli, they are less numerous because they are compressed between the large mucous (goblet cells) which are filled with large mucin granules. Stem cells which are able to replace other types of cells lie at the bases of the intestinal glands, also few endocrine cells are scattered among these types of cells.
Lamina propria: consists of loose connective tissue containing collagen, reticular and fibroblasts, lamina propria rich in lymphatic nodules which may extend into the submucosa.
Muscularis mucosae: composed of smooth muscle fibers.
Submucosa:
Loose connective tissue containing nerve plexus, blood vessels and lymphatics.
Muscular coat:
Consists of inner circular and outer longitudinal layers. The longitudinal layer of smooth muscle fibers is not continuous but it is converted into 3 bands called Taenia Coli which are responsible for propulsion of the gut contents by their contraction, also they cause sacculation or haustration of large intestine.
Appendix
The appendix is a blind- ending tubular diverticulum arising from the cecum, it has a narrow lumen caused by the presence of lymphoid follicles in its wall. The general structure is similar to that of large intestine although it contains fewer and shorter intestinal glands and has no taenia coli and the lymphoid tissues arranged around the lumen.
The anal canal
The anal canal is a muscular tube which transports the feces from the rectum to the exterior for elimination in the process of defecation. It is about 3-4 cm in length.
It has 2 sphincter systems:
Internal anal sphincter: is a localized thickening of inner circular muscle of the lower rectum, it is under autonomic control and responds to the distension of rectal lumen.
External anal sphinter: composed of skeletal muscle and is continuous with the muscle and fascia of pelvic floor and it is under voluntary control.
Histological structure of the anal canal:
Anal canal lined by columnar epithelium, at it’s upper end and this changes to a non keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium at the level of pectinate or dentate line which is a line of small crescentic valve- like mucosal extrusions with small vertical folds called the anal columns arising from their junctions
Small branched tubular (anal glands) open into the anal canal just above the pectinate line while apocrine glands of the peri anal skin lies at the lower end of the anal canal called (circum anal) gland.
Internal sphinecter is a continuation of circular smooth muscle layer of rectum while the external sphincter is composed of skeletal muscle.
The internal hemorrhoidal plexus lies in the submucosa of the upper end of the anal canal above the level of pectinate line while the external hemorrhoidal plexus lies in the submucosa of the lower end in the region of the junction between the anal canal and perianal skin which is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium ( piles result from enlargement of the hemorrhoidal plexus).
The external longitudinal muscle of the rectum loses it’s fibers at the level of puborectalis muscle of pelvic floor and continuous as a fibroelastic septum between the internal and external sphincter.
Large Intestine: