
Asthma

Chronic inflammatory disorder of the
airways.
Airway inflammation (AI) contributes
to hyperresponsiveness.
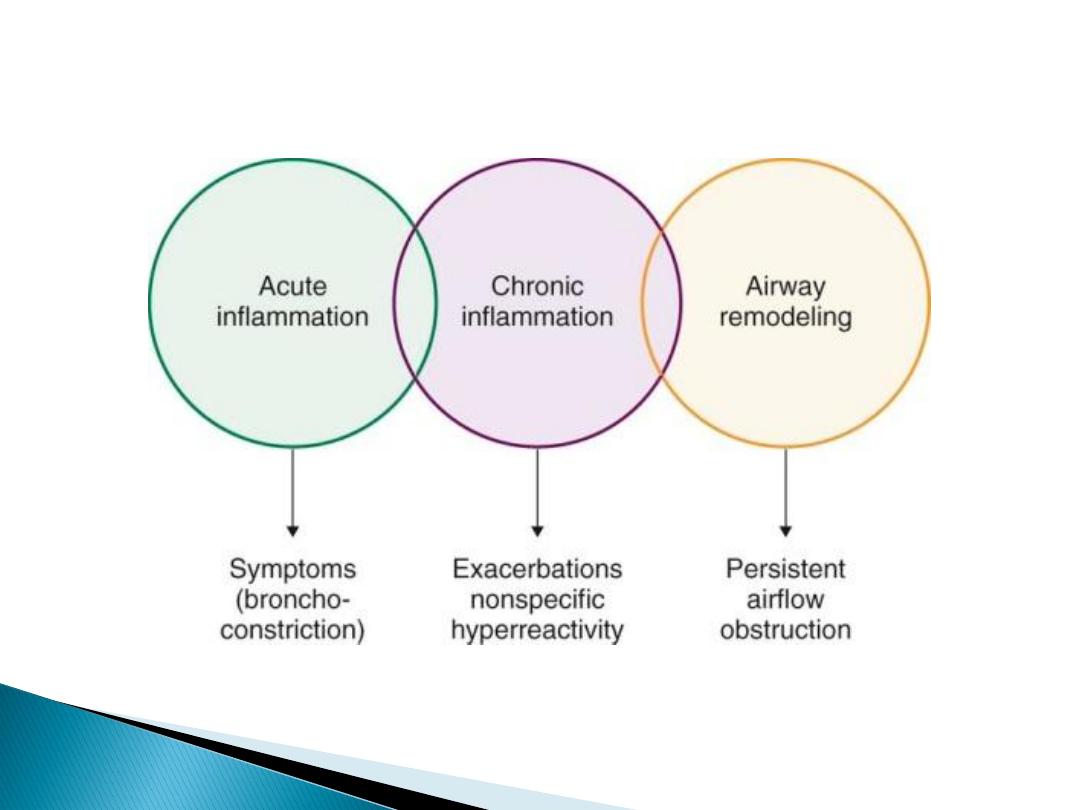
Airflow limitation symptoms &
chronicity.
mast cell activation
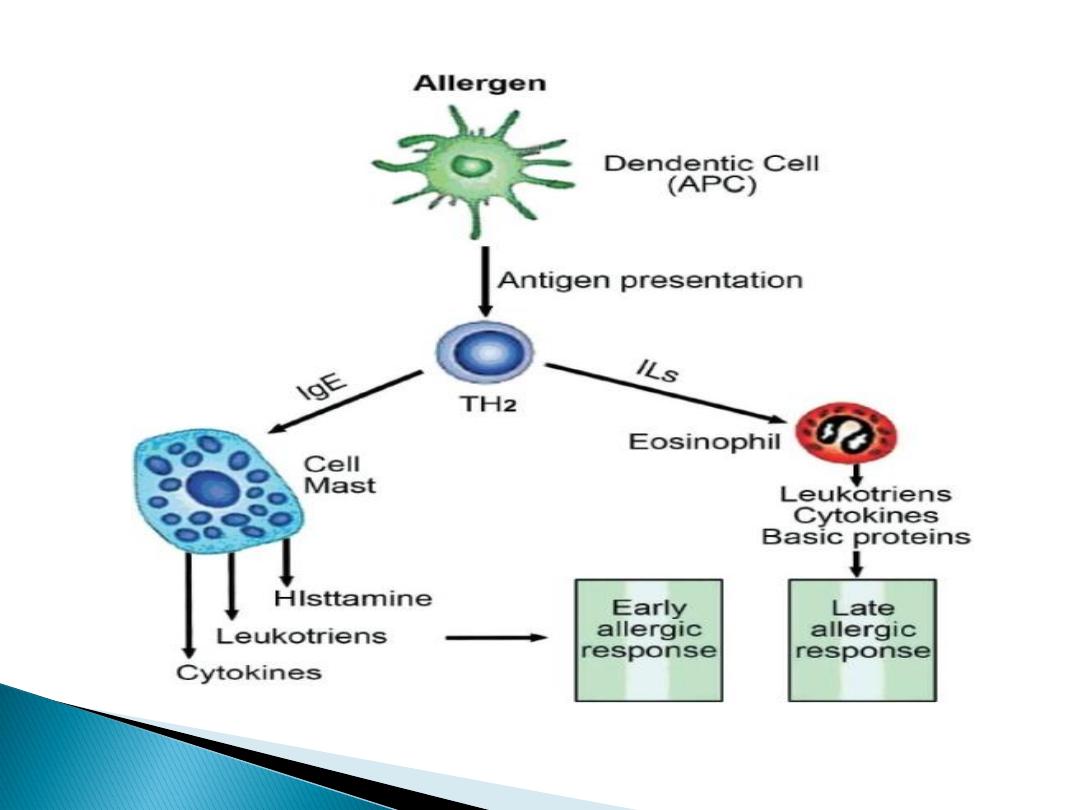
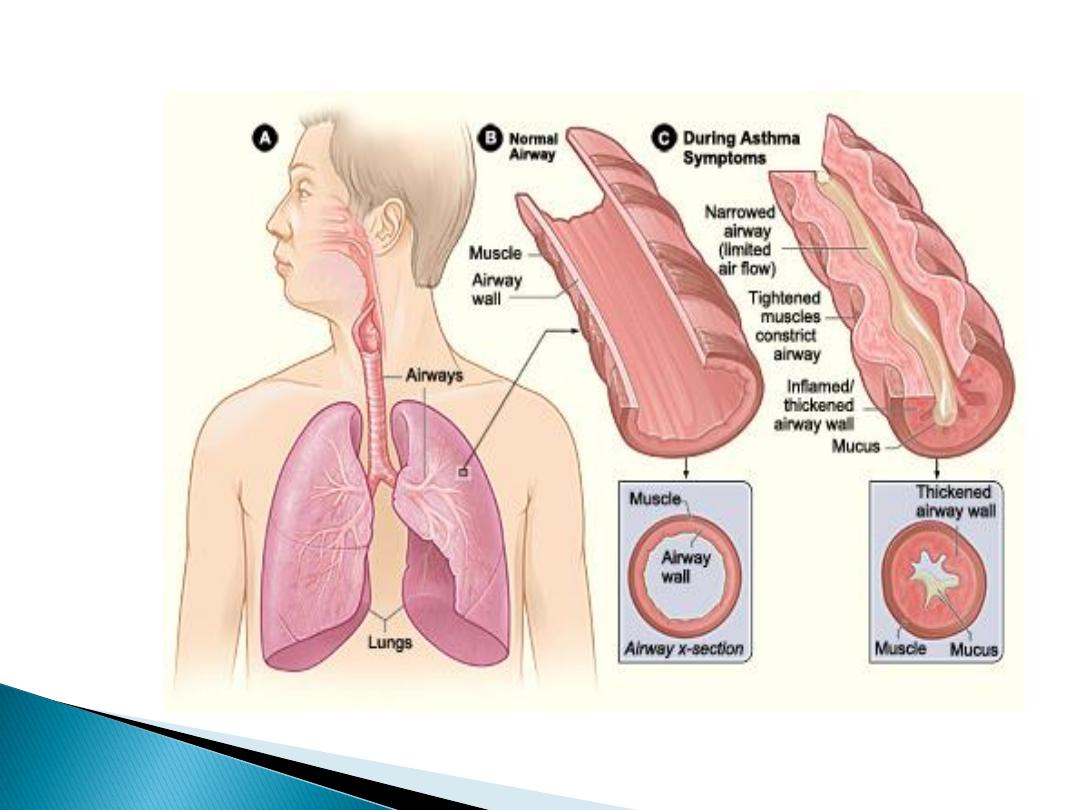

Bronchoconstriction
Edema
Mucus plug formation
Airway remodeling
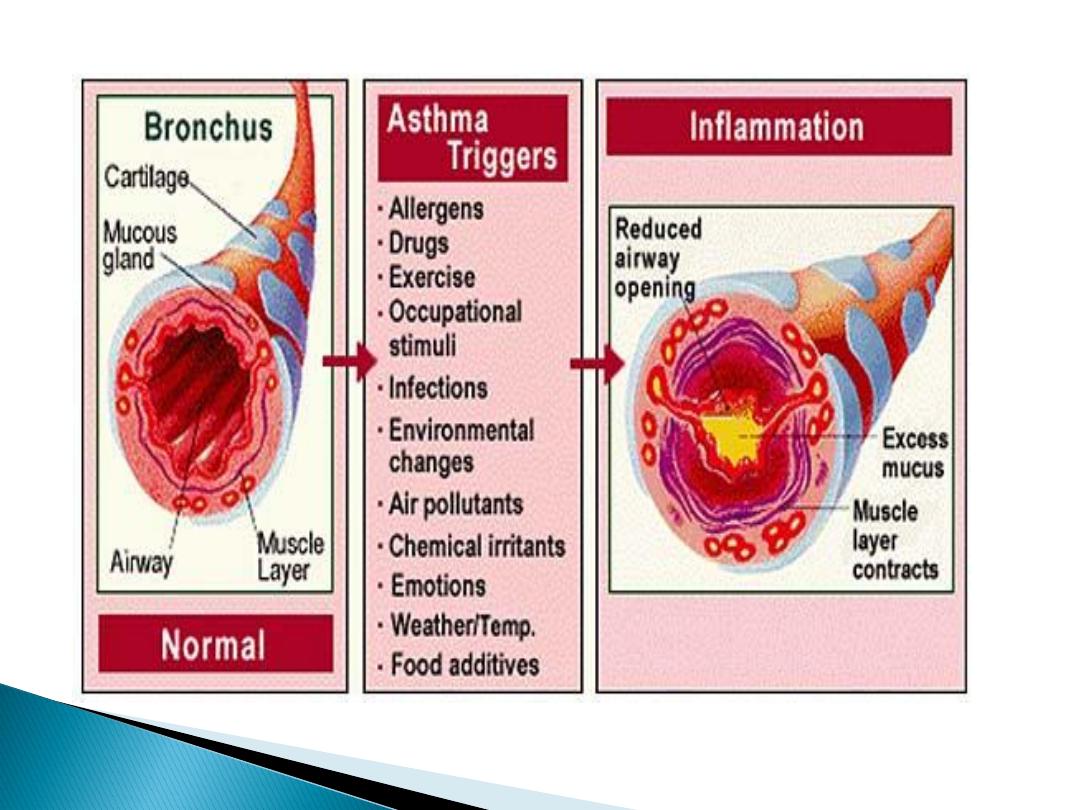

In susceptible individuals recurrent episodes of
wheezing
Breathlessness
Chest tightness
Coughing
These episodes are associated with variable airflow
obstruction often reversible
spontaneously/treatment

Asthma diagnosis criteria
Episodic symptoms of airflow obstruction
Airflow obstruction partially reversible
Rull out alternative diagnosis

To establish diagnosis
History
Physical examamination
Spirometry to demonstrate
reversibility
Additional studies

Long-term control medications
Inhaled/systemic corticosteroids
Long-acting beta2-agonists;
salmeterol
Methylxanthines; theophylline
Leukotriene modifiers; montilukast

Quick relief medications
Oxygen
Short acting beta2-agonists;
salbutamol
Anticholinergics; ipratropium
bromide
Systemic steroids

Elective dental care should be deferred in
severe asthmatics until they are in a better
phase.
Sedatives in general are better avoided as, in
an acute asthmatic attack, even
benzodiazepines can precipitate respiratory
failure.

Acute asthmatic attacks may also
occasionally be precipitated by anxiety; it is
important to attempt to lessen fear of dental
treatment by gentle handling and reassurance
General anaesthesia is best avoided as it
may be complicated by hypoxia and
hypercapnia

Aspirin
NSAIDs
Benzodiazepines

Thank you
