GENERAL FACTORS
Etiology of MalocclusionGENERAL FACTORS
• Heredity• 2. Congenital
• 3. Environmental
• Pre-natal
• b. Post-natal
• 4. Pre-disposing metabolic climate and disease
• a. Endocrine imbalanace
• b. Metabolic disturbance
• c. Infectious diseases
5. Dietary problems(nutritional deficiency)
6. Abnormal pressure habits and functional aberrations• a. Thumb and finger sucking
• b. Tongue thrust
• c. Lip and nail biting
• d. Mouth breathing
7. Posture
8. Trauma and accidents
Heredity
Heredity has for long been attributed as one of causes of malocclusion. The child is a product of parents who have dissimilar genetic material. The child may inherit conflicting traits from both the parents resulting in abnormalities of the dentofacial region.According to Lundstrom there exist a number of human trait that are influenced by the genes that include:
Tooth size: Abnormalities of tooth size such as microdontia and macrodontia are attributed to heredity.
Arch : The dental arch length and arch width are believed to be inherited.
Height of the palatal vault
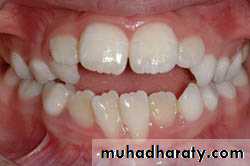
Crowding /spacing : Crowing and spacing of teeth are believed to be of genetic origin. most of these conditions are believed to be a uncoordinated inheritance of arch length and tooth material.
Position and configuration of muscles
• Tongue size and shape
• Character of the oral mucosa
Abnormalities of tooth shape: Anomalies of tooth shape such as the presence of peg shaped lateral is another trait that shows high genetics predisposition.
Abnormalities of tooth number : Presence of either more or less number of teeth can also be inherited .
Overjet :The horizontal overlap upper and lower dentition referred to as the overjet is believed to be genetically influenced.
Inter –arch variations: Discrepancies in the transvers , sagittal and vartical plane between upper and lower jaws can be inherited
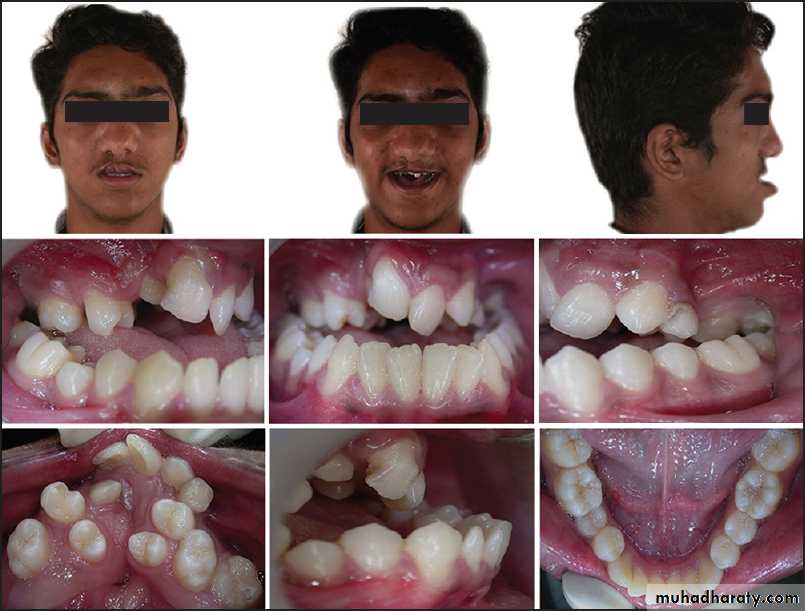
CONGENITAL
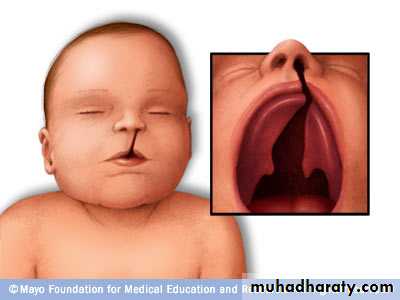
Congenital defects are malformations seen at the time of birth. It may be caused by a variety of factors including genetic, radiologic, chemical, endocrine , infection and mechanical factors. The congenital abnormalities that cause malocclusion are:1- CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE:- Clefts involving the lip and palate are the most commonly seen development defects that occur as a result of non-fusion between the various embryonic processes. The following characteristic features of malocclusion are always concurrent with congenital cleft lip and palate:
a) Anterior cross-bite
b) Bilateral or unilateral posterior crossbitec) Malpositioning and rotation of the maxillary incisors
d) Deflect the teeth from their normal eruptive path.
e) Anterior openbite
F) Class III malocclusion
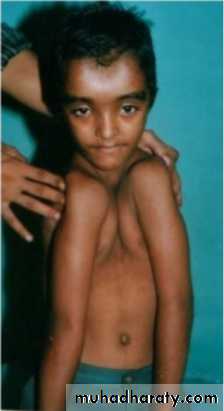
2- CLELDOCRANIAIL DYSOSTOSIS:- This is a congenital condition characterized by unilater or bilateral ,partial or complete absence of the clavical. The patient may exhibit the following features:
a. Maxillary retrusion and possible mandibular protrusion
b. Over retained deciduous teeth and retarded eruption of permanent teeth
c. Presence of supernumerary teeth
3- CEREBRAL PALSY:- This is a condition where in the patient lacks muscular co-ordination. It uncontrolled and aberrant muscle activity upsets the muscle the balance resulting malocclusion
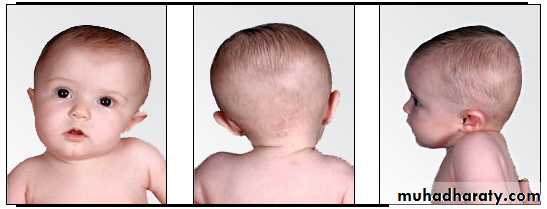
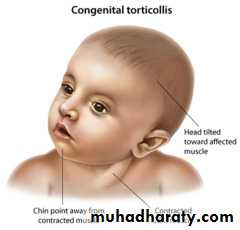
4- Torticollis : Shortening of the sternocleido mastoid muscle causing profound changes in the bony morphology of the cranium and the face Characterised by “wry neck” Bizarre facial asymmetries and uncorrectable malocclusions if not treated early
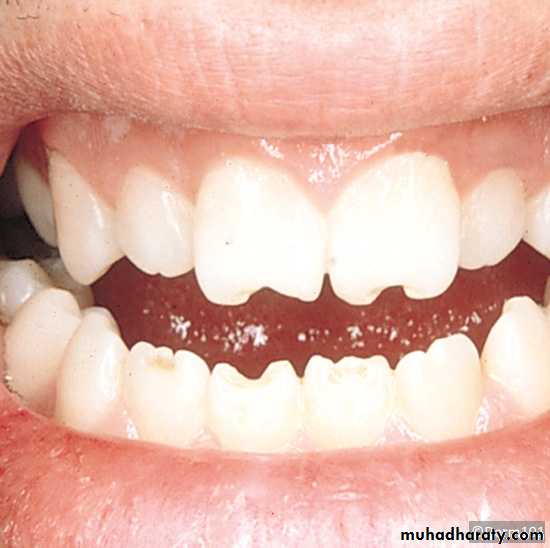
CONGENITAL SYPHILIS:- Syphilis of congenital origin is transmitted from the infected mother to the child. The child exhibits one or more of the following features:
a. Hutchinson’s incisors
b. Mulberry molars
c. Enamel deficiencies
d. Extensive dental decay
e. The maxilla may be smaller in size relative to the mandible
f. Anterior crossbite
ENVIRONMENT
Various prenatal and postnatal environmental factors can cause malocclusion:1. Prenatal factors : The foetus is well protected against injuries and nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy . but there are certain factor , the presence of which can result in abnormal growth of the oro-facial region thereby predisposing to malocclusion. abnormal fetal posture during gestastion is said to interfere with symmertric development of the face.
The other prenatal influences include maternal fibroids, fibroids , amniotic lesions , maternaldiet and metabolism. Maternal infection such as German measles and use of certain drugs during pregnancy such as Thalidomide can cause gross congenital deformities including clefts.
2.Postnatal factors: The following are some of the postnatal factors that can cause malocclusion:
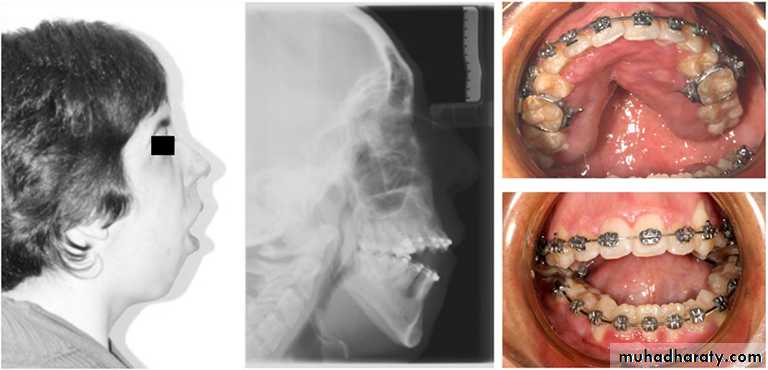
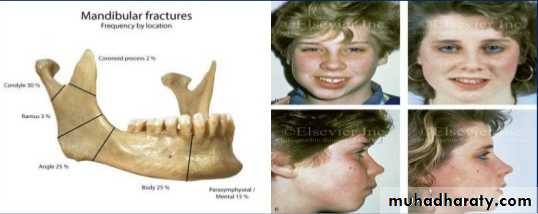
a). Forceps delivery can result in injury to the temporomandibular joint joint area, which can undergo ankylosis. Such patients show retarded mandibular growth and thus have a hypoplastic mandible.
b). Traumatic injuries that cause condylar fracture can cause growth retardation resulting in marked facial asymmetry.
PREDISPOSING METABOLIC CLIMATE AND DISEASE
A number of endocrinal disorders , infectious conditions and metabolic disturbances can predispose to malocclusion. (1). Endocrine imbalance: - Certain endocrinal disorders may result in malocclusion .Hypopituitarism :
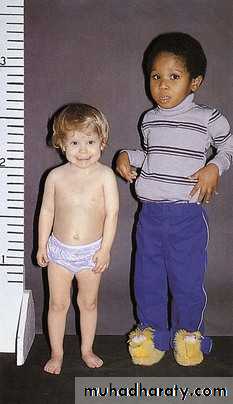
DwarfismDelayed eruption of permanent teeth and delayed shedding of primary teeth.
Crowding due to smaller arch size. Mandibular growth more affected than maxilla.
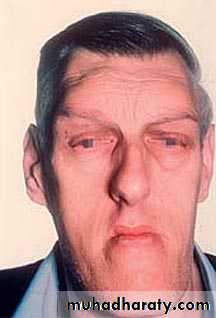
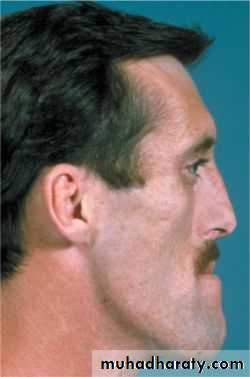
Hyperpituitarism: Gigantism-large teeth and jaws. Acromegaly-occurs after growth and ossification is complete. Lips thick,tongue enlarged,shows scalloping. Accelerated condylar growth-large mandible. Teeth tipped buccally due to large tongue.
Hypothyroidism: Delayed eruption. Abnormal resorption pattern. Retained deciduous teeth. Malposed teeth-deflected from eruption path. Gingival disturbances.
Hyperthyroidism: Early shedding and eruption Atrophy of alveolar bone.
(2). Metabolic disturbance: - Acute febrile diseases are believed to slow down the pace of growth and development . These condition may cause a disturbance in tooth eruption and shedding thereby increasing the risk of malocclusion.
DIETARY PROBLEMS
Nutritional deficiencies during growth may result in abnormal development , causing malocclusion. These diseases are more common in the developing countries than in the development world. Nutritional related disturbances such as rickets, scurvy and beriberi can produce severe malocclusion and may upset the dental developmental timetable.Abnormal pressure habits
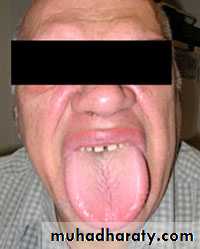
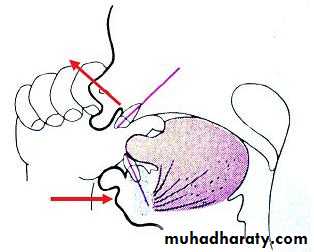
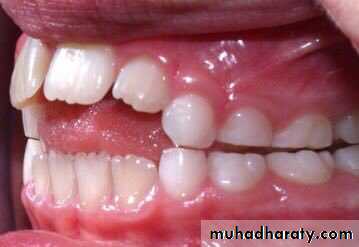
• Thumb and finger sucking: Thumb sucking is defined as the repeated and forceful sucking of thumb with associated strong buccal and lip contractions. It causes• proclination of upper incisors
• retroclination of mandibular incisors
• Increased overjet decreased over bite
• class II occlusion
• Anterior openbite
• Posterior cross bites
•
Abnormal pressure habits
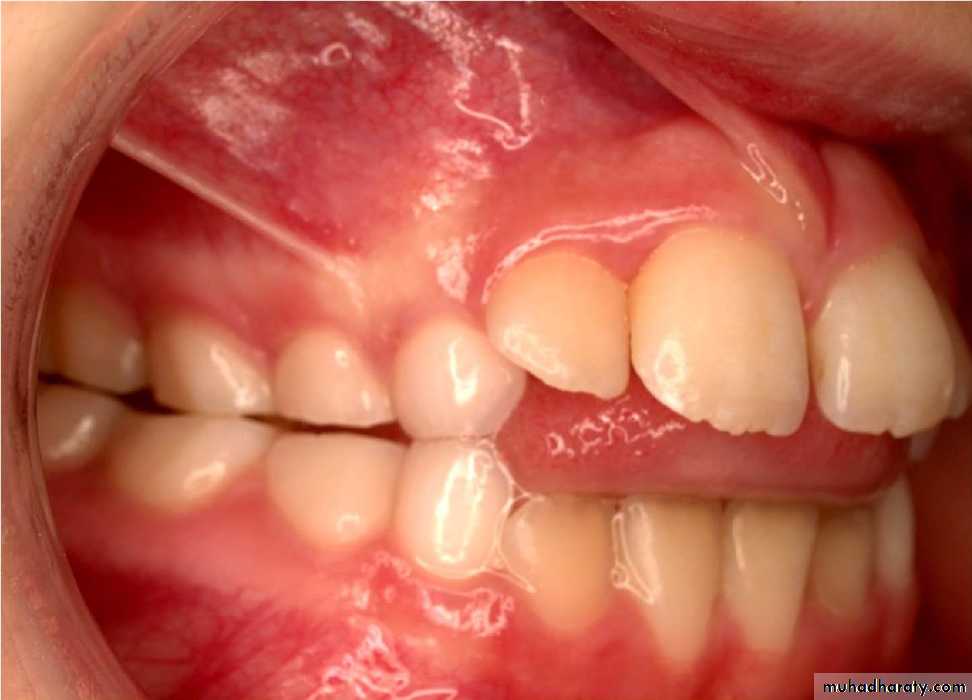
b. Tongue thrust: placement of the tongue tip forcefully forward between the upper and lower incisors during swallowing.1. Anterior open bite
2. Proclination of anterior teeth
3. Increased overjet
4. Class II malocclusion
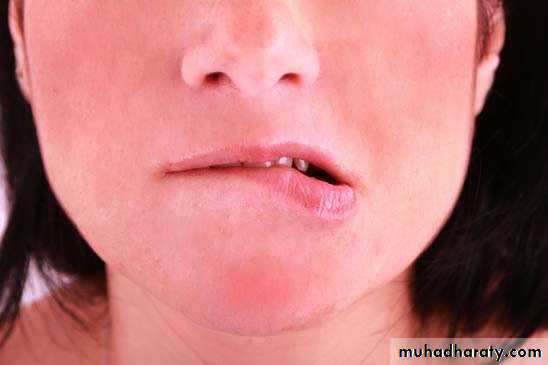
Lip sucking and biting
c. Lip sucking and biting: it most often involves the lower lip which is turned inwards and pressure is exerted on lingual surfaces of upper incisors and labial surface of lower incisors. It causes1. Proclination of the upper incisors
2. Retroclination of the lower incisors
3. Increased overjet
Nail Biting
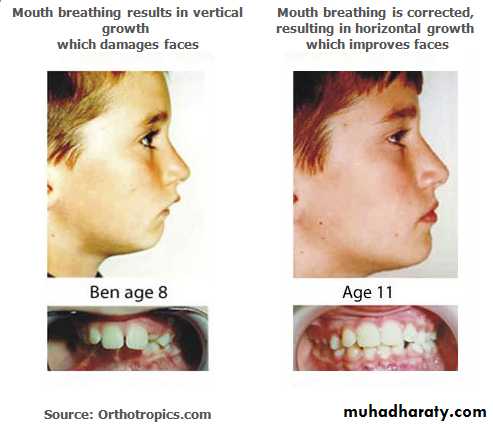
It causes minor teeth irrigularities such as rotation , wear of incisal edge and minor crowding.Mouth Breathing
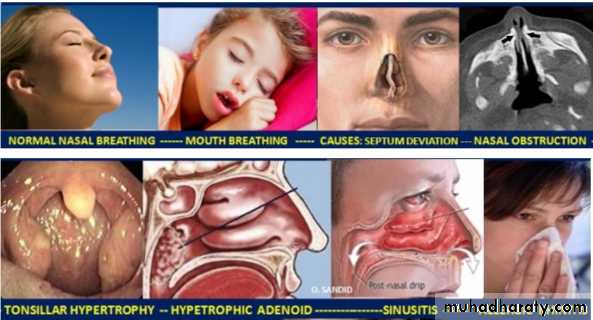
d. Mouth Breathing: Partial blockage of the nose leads to resistance of airflow and the person shifts to mouth breathingThe blockage occurs due to
• Chronic respiratory infection
• Enlarged tonsils &adenoids
• Nasal polyp
Mouth Breathing
d. Mouth Breathing effects• Over eruption of posterior teeth.
• Open bite anteriorly.
• Increase in overjet.
• narrow maxillary arch.
• Posterior crossbite .
• class II malocclusion.