CHAPTER 5
ENERGY, WORK AND POWER OF THE BODYBy;
Dr. Khalid ghanim al ghabsha
In the physics of the body, energy is of primary importance .All activities of the body including thinking ,involve energy changes.
The conversion of energy into work such as lifting a weight or riding a bicycle represents only a small fraction of the total energy conversions of the body.
Under resting (basal) conditions about;
25% of the body’s energy is being used by the skeletal muscles and the heart.
19% is being used by the brain.
10% is being used by the kidneys.
27% is being used by the liver and spleen.
The body’s basic energy (fuel) source is food. We can consider the body to be an energy converter that is subject to the law of conservation of energy.
The body uses the food energy to operate it’s various organs, maintain a constant body temperature, and do external work.
The energy used to operate the organs eventually appears as body heat .Some of this heat is useful in maintaining the body at it’s normal temperature . Any energy that is left over is stored as body heat.
The conservation of energy in the body can be written as;
∆U=∆Q- ∆W
∆U; change in stored energy.
∆Q ; the heat lost or gained.
∆W ; the work done by the body in some interval of time.
Met ; A convenient unit for expressing the rate of energy consumption of the body.
The (met) is defined as 50 K Cal/m2of body surface area per hour. For a normal person (1 met) is about equal to the energy consumption under resting condition.
Thus ; by measuring the oxygen consumed by the body , we can get a good estimate of the energy released.
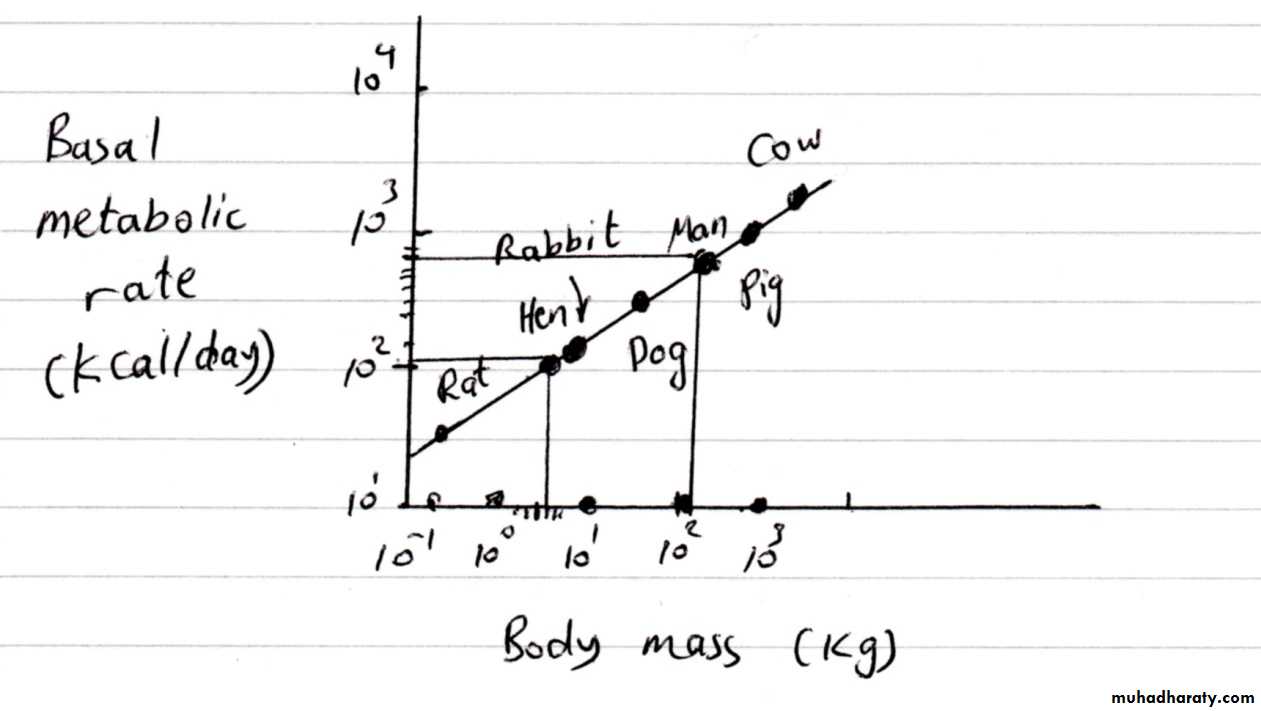
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) ;
BMR ; the lowest rate of energy consumption at rest , it is the amount of energy needed to perform minimal body function such as breathing and pumping the blood through the arteries .
Clinically an individual’s BMR is compared to normal values for a person of the same sex, age, height, and weight.
The BMR depends on the mass of the body and temperature.
The BMR depends primarily upon thyroid function . A person with an overactive thyroid has a higher BMR than a person with normal thyroid function .
Mass
BMR( Hen ) 3
100
( Man ) 100
700
Dependence of metabolic rate on temperature ;
Temperature Metabolic rate
1 C 10%
3 C X
X = 30%Metabolic rate greater than normal.
The BMR is sometimes determined from the oxygen consumption when resting. We can also estimate the food energy used in various physical activities by measuring the oxygen consumption.
WORK AND POWER;
Chemical energy stored in the body is converted into external mechanical work as well as into life- preserving function.The external work (∆W), defined as a force (F) moved through a distance (∆X).
∆W= F. ∆X
The force and the motion (∆X) must be in the same direction.
The rate of the doing work is (power) P.
P= ∆W ( J )∆t (Sec. ) = F.∆X∆t = F V
∆x∆t= velocity (v)
External work (different cases);
Case1: w = m g h
(mgis weight of the body )
( h is vertical distance )
Case 2 : w=zero
(constant speed on a level surface (F)perpendicular to the motion).
External work is done when a person is climbing a hill or walking up stairs. We can calculate the work done by multiplying the person’s weight (mg) by the vertical distance (h) moved.
When a man is walking or running at constant speed on a level surface , most of the forces act in the direction perpendicular to his motion .Thus , the external work done by him appears to be zero.
The muscles are doing internal work which appears as heat in muscle , and causes a rise in it’s temperature. This additional heat in muscle is removed by blood flowing through the muscle , by conduction to the skin , and by sweating.
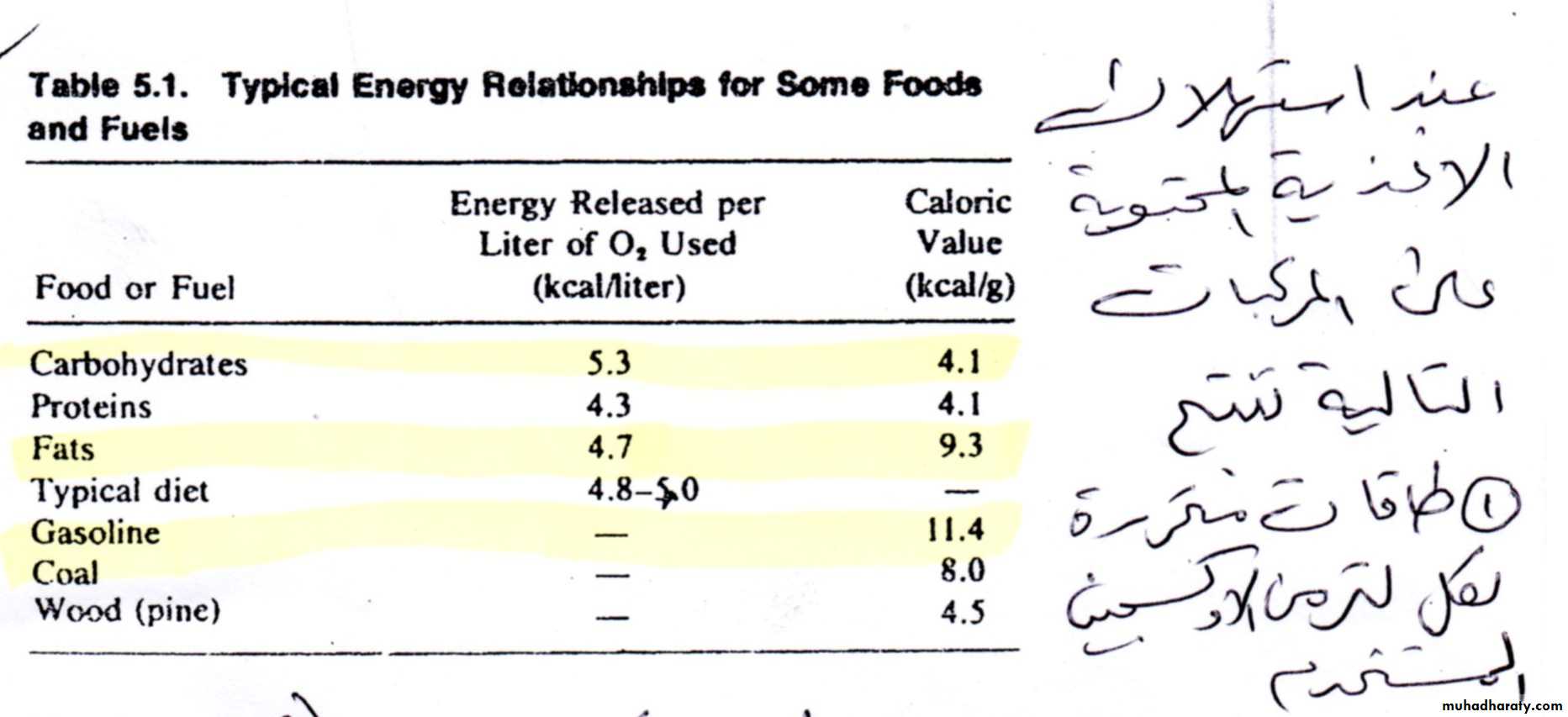
The total food energy consumed can be calculated since 4.8 to 5.0 Kcal are produced for each liter of oxygen consumed.
The efficiency of the human body as a machine ;
E = work doneenergy consumed
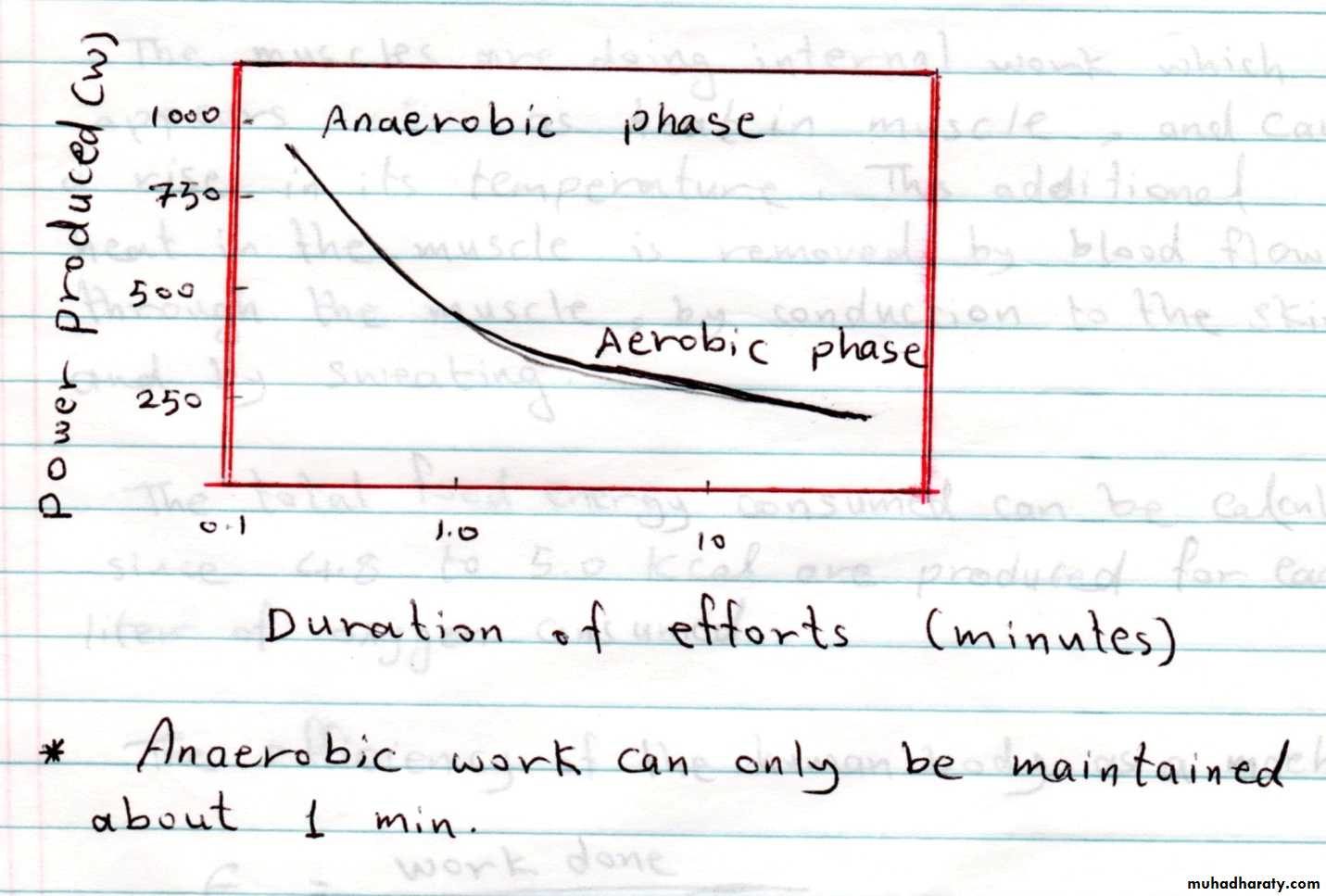
An aerobic phase of work (without oxygen);
The body supplies instantaneous energy for short- term power needs by splitting energy rich phosphates and glycogen, leaving an oxygen deficit in the body.
This process can last about a minute.
AEROBIC WORK;
Long_ term activity requires oxygen.HOMEOTHERMIC AND POIKILOTHERMIC ;
Birds and mammals are referred to as homeothermic (warm_blooded) , have a mechanisms to keep their body temperature constant, other animals are considered poikilothermic (cold_ blooded) like a frog and snake.The normal body temperature is 37OC or 98.6oF.
The temperature depends on;
The temperature of the environment.Time of the day (lower in the morning )
A mount of clothing.
Amount of recent physical activity.
Health of the individual.
The main heat loss mechanisms are;
Radiation.
Convection.
Evaporation (of perspiration ).
Eating hot or cold food.
Cooling of the body due to inspired air in lungs.
HYPOTHALAMUS ;
The hypothalamus of the brain contains the body’s thermostat.If the core temperature rises, for example , due to heavy exertion, the hypothalamus initiates sweating and vasodilation , which increase the skin temperature.
If the skin temperature drops , the thermo receptor on the skin inform the hypothalamus and it initiates shivering , which causes an increase in the core temperature.