University of kirkukCollege of dentistry
Oral HistologyLip Cleft
Dr. Asmaa sedeekDefinition
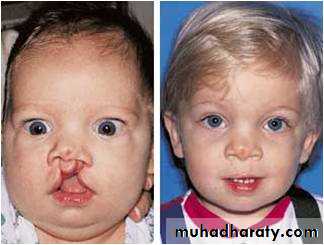
A cleft lip or palate is an abnormal separation in the oral-facial region that happens because tissue of the mouth or lip does not form correctly in fetal development.Anatomic Principles
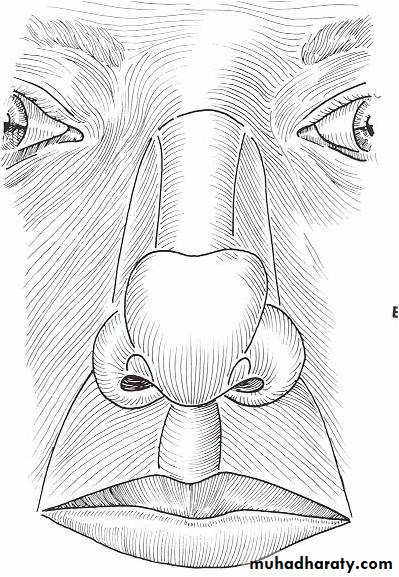
A- Normal Lip consists of:1) Central Philtrum
It is consists of:Lateral margins - philtral columns
Inferior border - Cupids bow and tubercle
2) Vermillion-cutaneous border
Embryology of Clefting
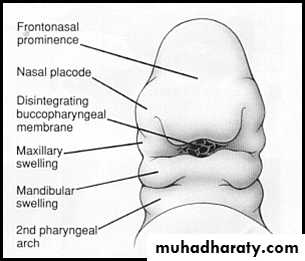
Facial Development - 4th - 10th week of developmentFormed by the fusion of five prominences
Unpaired frontonasal processPaired maxillary swellings
Paired mandibular swellingCleft Variants
Great anatomic variation in types of clefts!
Anatomic Classification based on:
1) Location2) Completeness (Incomplete/Complete)
3) Extent
Since lip, alveolus, and hard palate differ in embryologic origin, any combination can occur
Classification
Standardized methodsKey anatomic structure
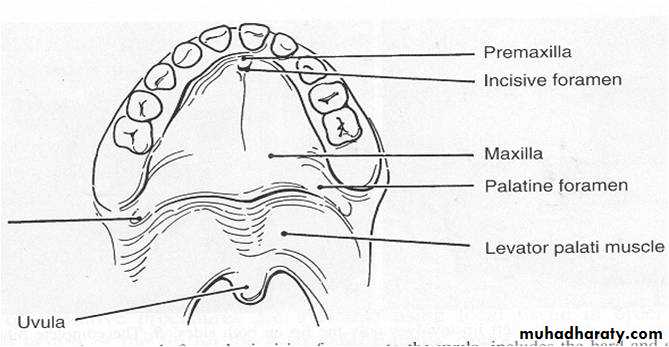
Incisive foramen
Primary palate
Lip
Premaxilla
Alveolus
Secondary palate
Soft palate
Hard palate
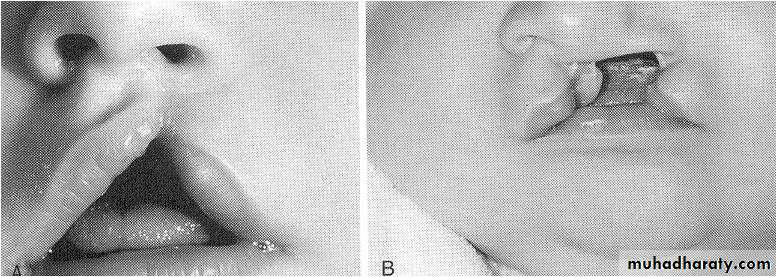
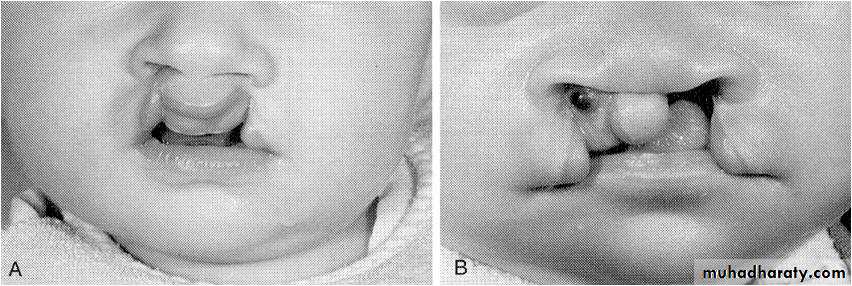
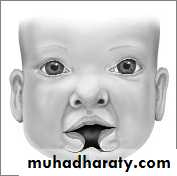
Cleft of primary palate (cleft lip)
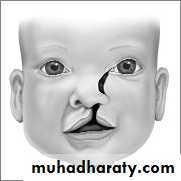
UnilateralIncomplete
Lip only
Complete
Primary palate
Lip, nasal floor, alveolus
Result from deficiency of mesenchyme in the maxillary prominences and intermaxillary segment
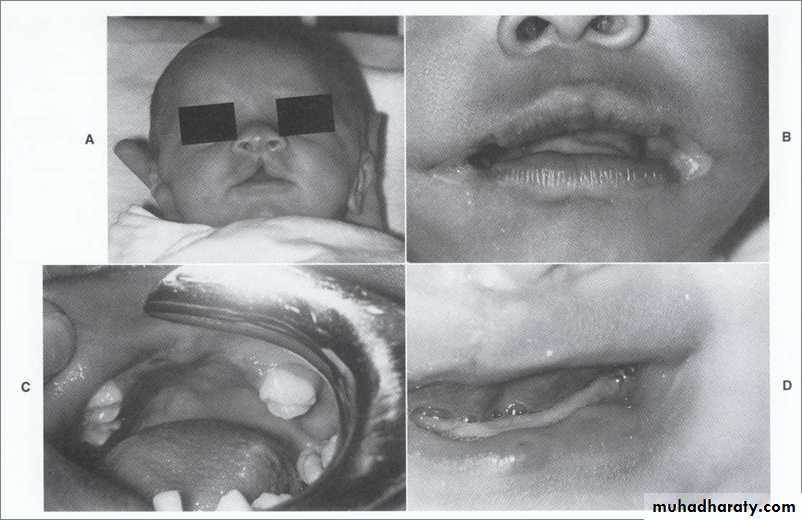
Cleft of primary palate (cleft lip)
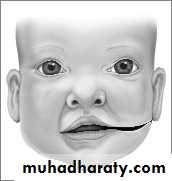
BilateralIncomplete
Lip only
Complete
Primary palate
Lip, nasal floor, alveolus
Cleft of secondary palate- Soft palat only (incomplete cleft palat) Soft and hard palat (complete cleft palat) Submucus cleft
• Caused by defective development of the secondary palate and result from the growth distortions of the lateral palatine processes (shelves) which prevent their medial migration and fusion
Epidemiology
Cleft lip and palateRacial heterogeneity
Asians
2.1 in 1000 live births
Whites
1 in 1000 live births
African Americans
0.41 in 1000
Isolated cleft palate
Constant incidence
0.5 in 1000 live births
Environmental agents
Chemical agentsAlcohol
No increased risk of cleft with low quantities of EtOH
Increased risk of clefting with higher quantities of EtOH
Dilantin , sodium valproate, benzodiazepines and corticosteroids.
10X higher risk of cleft lipSmoking
Dose response relationshipIncreased risk of clefting
Environmental agents
Folic acidBeneficial effect
Reduced incidence of unilateral cleft lip and palate with at risk mothers
Isotretinoin
Accutane dysmorphic syndrome
Rudimentary external ears
Absent/imperforate auditory canals
Triangular microcephalic skull
Cleft palate
Depressed midface
Brain/jaw/heart anomalies
Treatment
Treatment involves many things which include plastic surgery, orthodontics, and speech therapy
Other facial anomalies
• Median clefts (rare)Upper
• Mesenchymal deficiency causing partial or complete failure of medial nasal prominences to merge and form the intermaxillary segment
Lower
• Failure of mesenchymal masses in the mandibular prominences to merge completely and smooth out the embryonic cleft between them
Facial clefts
Macrostomia
Microstomia
Failure of fusion between maxillary process and lateral nasal process
Failure of fusion between maxillary process and mandibular processOver fusion between maxillary process and mandibular process
Done by: Asmaa Aljumaily