
Structure and function of cells
Cytology
The science that study the cellular organization structurally, functionally
and the relation of this organization with metabolic activities ,growth
,differentiation ,evolution ,heredity.
What Is a Cell?
The cell is the smallest and basic units of life, and new cells only come from
preexisting cells, through cell division.
How Cells Are Organized
Human cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus. The
cytoplasm
contains several types of organelles.
Cell theory
Scientists first observed living cells under the microscope in 1674 by Robert
Hooke, referred to the cavities he saw in cork as cells. Then scientists
concluded that all plant and animal tissues consisted of cells.
(1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden" all living things are made
of cells”.
Rudolf Virchow in 1858 combined the ideas and added that all cells come
from preexisting cells, formulating the cell theory:-
1-all living things are composed of one or more cells, and cell products.
2-a single cell is the smallest unite that exhibits all the characteristic of life.
3-all cells come only from preexisting cells.

The cell
All animals and plants are made up of cells, which is the smallest unite of
living materials that can exist dependently or independently .
Cells are generally members of a community and thus dependent upon other
cells for support and survival .cells come in different forms because they
have different jobs to do, although there is no such thing as a ̋typical cell̋ .so
the cell is the structural unite also the cells are the functional unite because
the functions of living organism are the result of cellular activities.
If we examine any part of the human body under microscope, we find living
cells and/or cell products. cell products include materials composed of dead
cells and substances resulting from cellular activity. all of our cells divided
from earlier cell, going to our first cell, the fertilized egg, even that original
cell come pre- existing cells ,the sperm and egg from our parents.
Cell Size
Most cells are small and can be seen only under a microscope .The small
size of cells means that they are measured using the smaller units of the
metric system. Cells are about 100 micrometers (μ m) in diameter, about the
width of a human hair . Some large cells (e.g. an egg)can be seen with the
naked eye .,figure 1 shows the differences of cells sizes.
The light microscope allows us to see objects as small as 200 nm
(nanometers) .that is very small and to see the parts of cell that are smaller
than 200nm ,we need to use an electron microscope ,which is big, more
expensive and uses beams of electrons (instead of light microscope) to show
up the cell parts and the minute details of it. We do not see the actual object
, but see it is shadow or image . so the electron microscope allows to
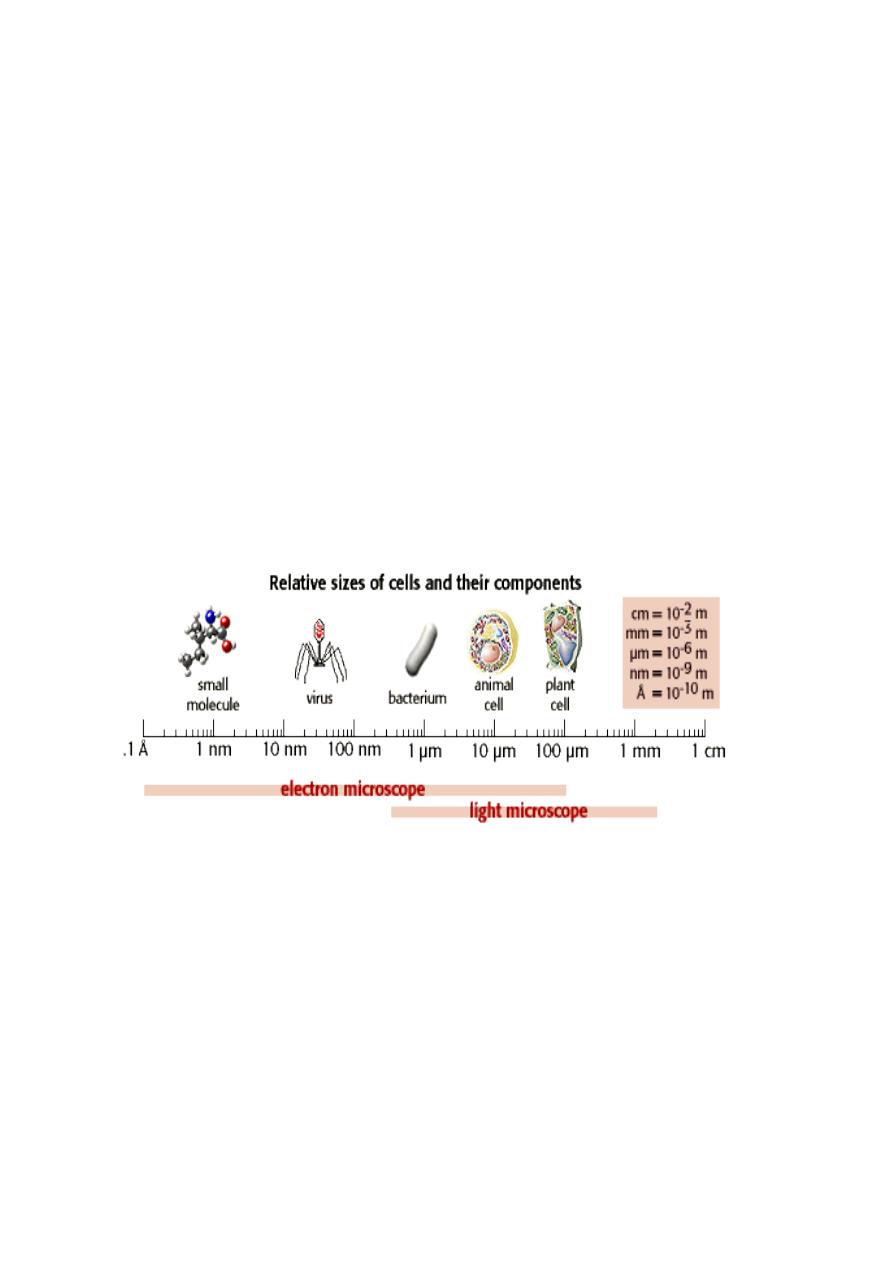
observe objects that are 0.5 nm a part (magnify more than 200,000 times)
see figure 2 A few cells, such as a hen’s egg or a frog’s egg, are large
enough to be seen by the naked eye, The small size of cells is explained by
considering the surface area-to-volume ratio of cells. Cells vary in structure
and function, but they all exchange substances with their environment.
Nutrients enter a cell, and wastes exit a cell at its surface. Therefore, the
greater the amount of surface, the greater the ability to get material in and
out of the cell. Large cells are unable to efficiently exchange nutrients and
waste with their environment because of a decreased surface area-to-volume
ratio.
As the cell increases in size, the surface area increases by the square of
the width.
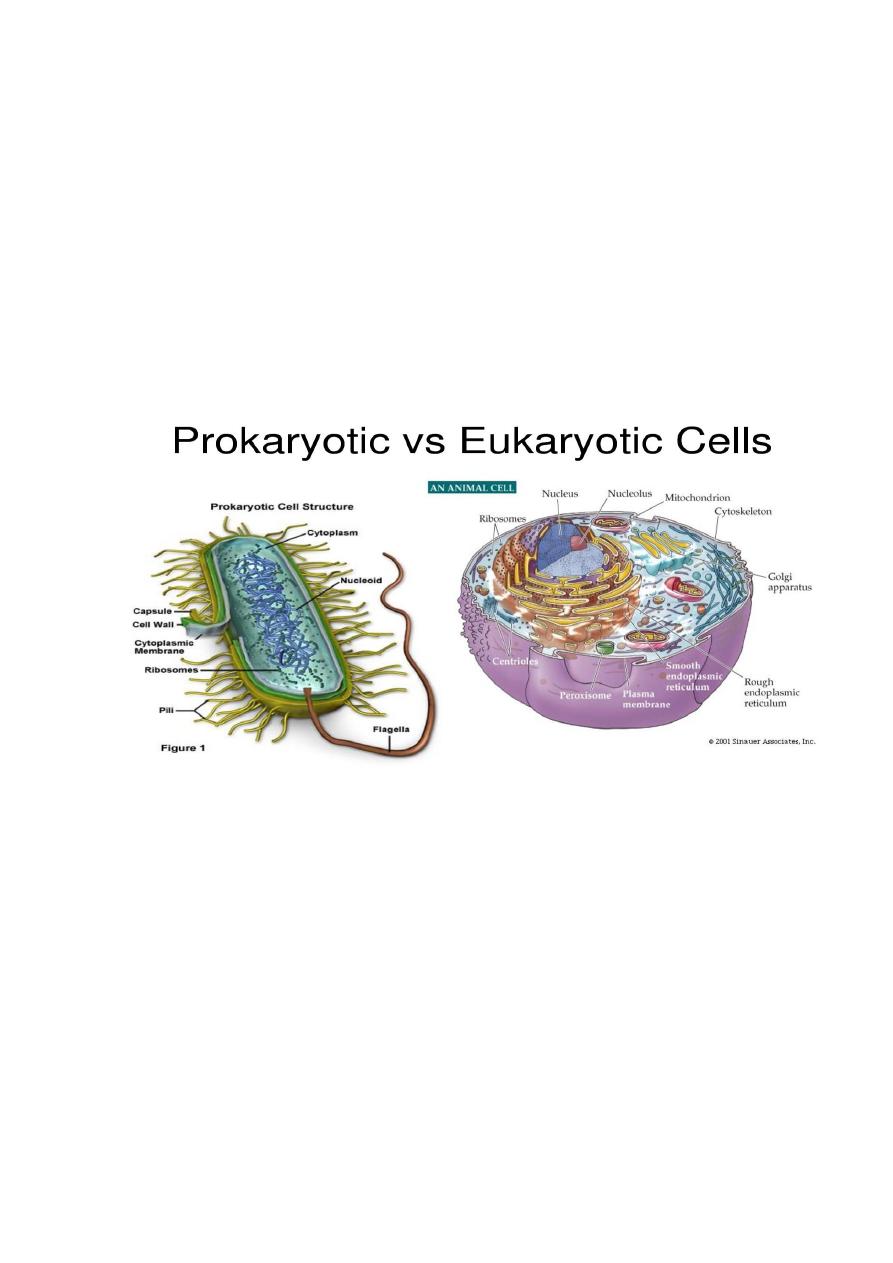
Unicellular and multicellular organisms
Cells can be classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Both types of
cells have a plasma membrane, an outer membrane that regulates what
enters and exits a cell.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. While its DNA is
centrally placed within the cell, it is not surrounded by a membrane.
Prokaryotic cells today are represented by the bacteria and archaea, which
differ mainly by their chemistry. Bacteria are well known for causing

diseases in humans, but they also have great environmental and commercial
importance.
The eukaryotic cell is believed to have evolved from the archaea. The most
prominent organelle within the eukaryotic cell is a nucleus, a membrane-
enclosed structure where DNA is found. Each type of eukaryotic organelle
has a specific function. Many organelles are surrounded by a membrane,
which allows compartmentalization of the cell. This keeps the various
cellular activities separated from one another. The distinction between
prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered to be the most important
distinction among groups of organisms. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-
bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not.
Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the
presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of
chromosomal DNA.
All organisms except viruses are made up of cells (viruses are not cells,
they have genetic materials DNA or RNA ,lack of cell membrane
,cytoplasm and the machinery for synthesizing macromolecules depending
upon host cell)either :-
1- Their bodies being made up of a single cell→ Unicellular organism like
protozoa ,yeast and bacteria.
2- Their bodies being made up of many cells → multicellular organism like
animals and plants
cells in a multicellular organism are specialized in
structure and function.
Each cell has a genetic material DNA and cytoplasm with organelles and is
bounded by a cell membrane.
In our body there are different types of cells( brain cells ,skin cells)all of
these cells have its unique function and features and there is a strong link
between structure and function.
General features of the cells
1-the use of energy .
2-maintaine the genetic information about the synthesis of cellular
molecules through the reproduction and division.
3-regulation of intracellular reaction.

Cell structure reflects cell function
All cells carry out certain activities to maintain life , and there is a strong
link between structure and function.
All cells must gather raw materials, excrete wastes, make macromolecules
,grow and reproduce.
Most of the structural differences between cells reflect differences in
function. Muscle cells contain numerous organelles to produce the energy
for muscle contraction .Nerve cells : are long ,thin carry impulses all the
way from your toes to your spinal cord. The cells line the kidney tubules :
are cube shaped.
Cells that serve the same function are remarkably similar between species.
The cell and it is organelles
A ‟generalized ” cell made up of many parts, do different jobs called
organelles (small organs) where the chemical reactions that go to make up
the living processes of the cell take place.
We see also an outer cell membrane enclosing an inner fluid jelly like are
called the cytoplasm ,which contains organelles ,and it is about 70 ٪water in
which salts (are dissolved to form a solution ) and proteins (which cannot
dissolved in the water )suspended in it as a colloid.
The total metabolic activities of a cell are proportional to it is volume of
cytoplasm ,which is in effect it is size .To support it is activities, every
cell needs raw materials in proportion to it is size, and needs a way
to
get rid of it is wastes .all these happened across the plasma membrane
.As objects get larger ,their volume increases more than there surface
area ,so some cells have numerous microscopic projection of the plasma

membrane (called microvilli) to increase surface area relative to volume
,as in cells that transport substances into and out of the body. As in
intestine, kidney tubules .
The larger a cell gets , the more likely that it is growth and metabolism
will be limited by it is ability to supply itself across the plasma
membrane, but the smaller a cell is the more effectively it can obtain
raw materials and get rid of wastes. see figure 3 view of bacterial cell
and Figure 4 view of animal cell with it is nucleus and organelles .
The Nucleus Controls the Cell
As the information center of the cell
It is the most important structure in the eukaryotic cell, because
it is contain the genetic material (DNA in chromosome controls
the structure and the function of the cell e. all the activity of the
cell)
It is larger than any cytoplasmic organelles ,may or may not be
centrally located within the cytoplasm .
It is either spherical or oval or lobes in shape with hematoxylin
stain , it is colorless ,clear and more dens than cytoplasm .
The nucleus has three regions nuclear envelope ,nucleolus and
chromatin.
The nuclear envelope : the outer surface of the nucleus consists of a
double –layered membrane called the nuclear membrane (n.m.) as outer
and inner n.m.
Outer n.m. continuous with rough endoplasmic reticulum fill with the
synthesized protein.
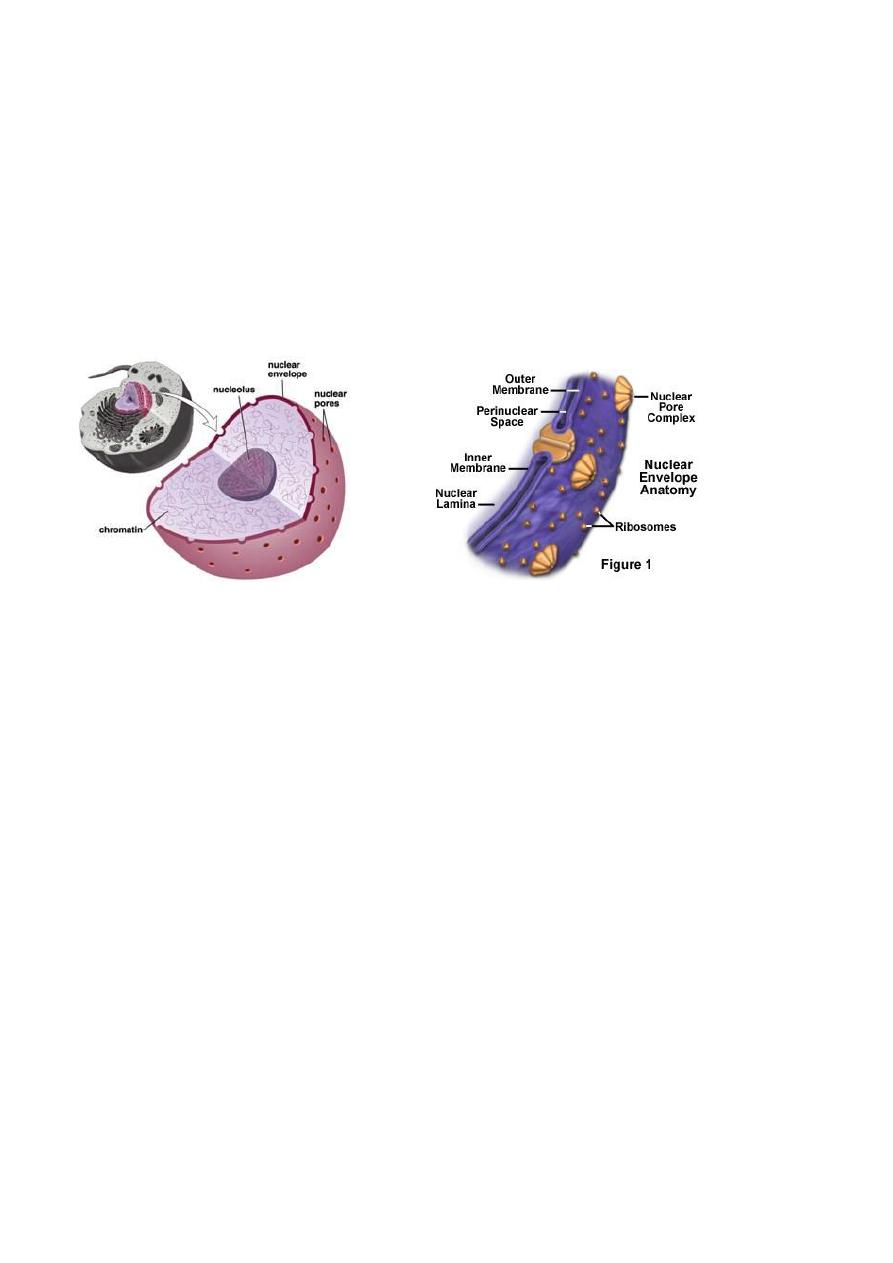
Inner n.m. continuous with outer n,m, and lumen of rough endoplasmic
reticulum fill with newly synthesized protein.
Underlying inner n.m. is a fibrous network of thin filaments called
Nuclear lamin ,surrounded the nucleus except at nuclear pores which
composed of protein called lamin .its function a site for chromatin
attachment. see figure 5
Nuclear pores of sufficient size (100 nm) to permit the passage of
proteins ,building blocks for building DNA and molecules providing
energy for genetic material production into the nucleus and ribosomal
subunits RAN out of the nucleus ,they play important role in gene
expression.
Nucleoplasim: nuclear envelop encloses a jelly like fluid called
nucleoplasim ,suspended salts, nutrients and other essential solutes .A
difference in pH between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm suggests
that the nucleoplasm has a different composition.
The nucleolus: the dense spherical darkness area. The nucleolus ,which
is the site of rRNA transcription and ribosome production so it's called
ribosome production factory. The size of the nucleolus depends on the
metabolic activity of the cell(very large in growing cells that are making
large amount of tissue protein).

The chromatin: the area within the nucleus that become colored are
called chromatin .Chromatin looks grainy, and uncoiled in electron
micrographs of the nucleus. Chromatin is immersed in a semifluid
medium nucleoplasm.
but actually it is a threadlike material that undergoes coiling into rod like
structures called chromosomes just before the cell divides. Chemical
analysis shows that chromatin, and therefore chromosomes, contains
DNA and much protein. DNA together with RNA that controls the
production of proteins by cell (DNA and RNA the inheritance factors of
cells).The protein of chromatin is histones (small protein containing
high percent of basic amino acids arginine and lysine that binding to the
DNA), there are two types of chromatin :
Euchromatin :is genetically active portion involved in transcribing
RNA to produce proteins.
Heterochromatin: is genetically inactive DNA and is the condensed
portion of chromatin when cell divides human cell contain 46
chromosomes as 23 pairs.
