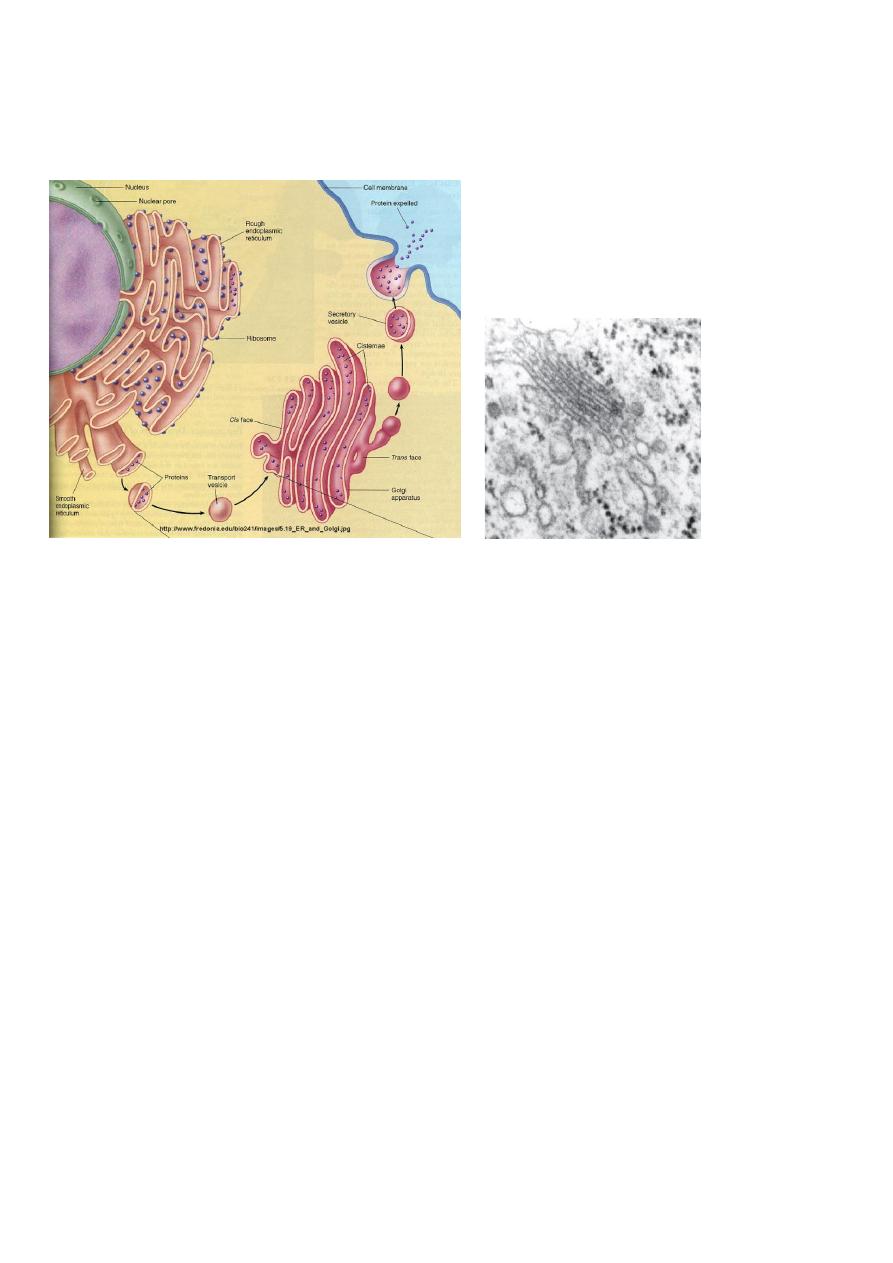
The Endomembrane System
Endoplasmic reticulum:
All eukaryotic cells have an endoplasmic reticulum.
The E.R. is organized into a network of branching tubules, vesicles and
flattened sacs (cisternae) that are interconnected and extending throughout the
cytosol ,so the E.R .membrane forms a continuous sheet inclosing a single
internal space called E.R. lumen or E.R cisternal space. A portion of the ER
connects to the nuclear membrane.
Some regions in the outer surface of the E.R are dotted with ribosomes called
rough E.R (R.E.R),a granular appearance .Regions without ribosomes are
called smooth E.R(S.E.R)
R.E.R S.E.R
Have attached ribosomes doesn't have attached ribosomes
Continuous with n. envelope continuous with R.E.R beside Golgi apparatus
Primary site of protein synthesis primary site of macromolecules
(Antibodies ,enzymes ,hormones) (other than proteins phospholipids ,cholesterol)
In R.E.R most of the protein synthesized in cisternae by the attached
ribosomes are released into the E.R. lumen ,enter S.E.R where they are
package for transfer to Golgi apparatus by transport or small vesicles.
In S.E.R synthesized macromolecules such as the phospholipids and some
hormones that occur in membranes and has various other functions, depending

on the particular cell. In the testes, it produces testosterone. In the liver, it
helps detoxify drugs.
. Numerous enzymes embedded in the inner surface of E.R. membrane
facilitated the chemicals reaction for macromolecules . S.E.R is also
responsible for packaging the proteins and lipids for delivery to the Golgi
apparatus .Synthesized protein and lipids collect in the outer most layer of
S.E.R ,then small portions of the fluid –filled space are surrounded by E.R.
membrane and pinched off forming vesicles (containing fluid proteins and
lipids) then migrate to the Golgi apparatus membrane and release their
contents into the Golgi apparatus for further processing .The dangerous
chemicals are destroyed (detoxified)by enzymes located on SER as detoxify
drugs in the liver cell.
Golgi apparatus:
Is named for Italian scientist Camillo Golgi .
Golgi apparatus consists of a stack of three to twenty slightly curved saccules.
and present in cells that are actively involved in secretion.
Golgi apparatus have two sides (is a polarized structure)
1-Cis face (entry face )is concave face toward nucleus near ER,
2-Trans face (exit face ) is concave face toward the plasma membrane.
The Golgi apparatus receives protein and/or lipid-filled vesicles that bud from
the E.R.
The Golgi apparatus contains enzymes that modify proteins and lipids. For
example, it can add a chain of sugars to proteins, thereby making them
glycoproteins and glycolipids, which are molecules found in the plasma
membrane.
The vesicles that leave the Golgi apparatus move about the cell. Some
vesicles proceed to the plasma membrane, where they discharge their contents.
Because this secretion, it is often said that the Golgi apparatus is involved in
processing, packaging, and secretion. Other vesicles that leave the Golgi apparatus
are lysosomes.
The Golgi apparatus works closely with R.E.R:
Protein is made in R.E.R→ stored in a small membrane bound called
transferring or transporting vesicles→ float through the cytoplasm→ fuse
with Golgi apparatus membrane in cis face →in this side the G.A. protein
pass through the separate layer modified in different ways, carbohydrate are
added → secretory vesicles is formed → leave the G.A. in trans face side to
different location in the cell →some vesicles proceed to the plasma
membrane .discharge their content by exocytosis. Other vesicles are
lysosomes.
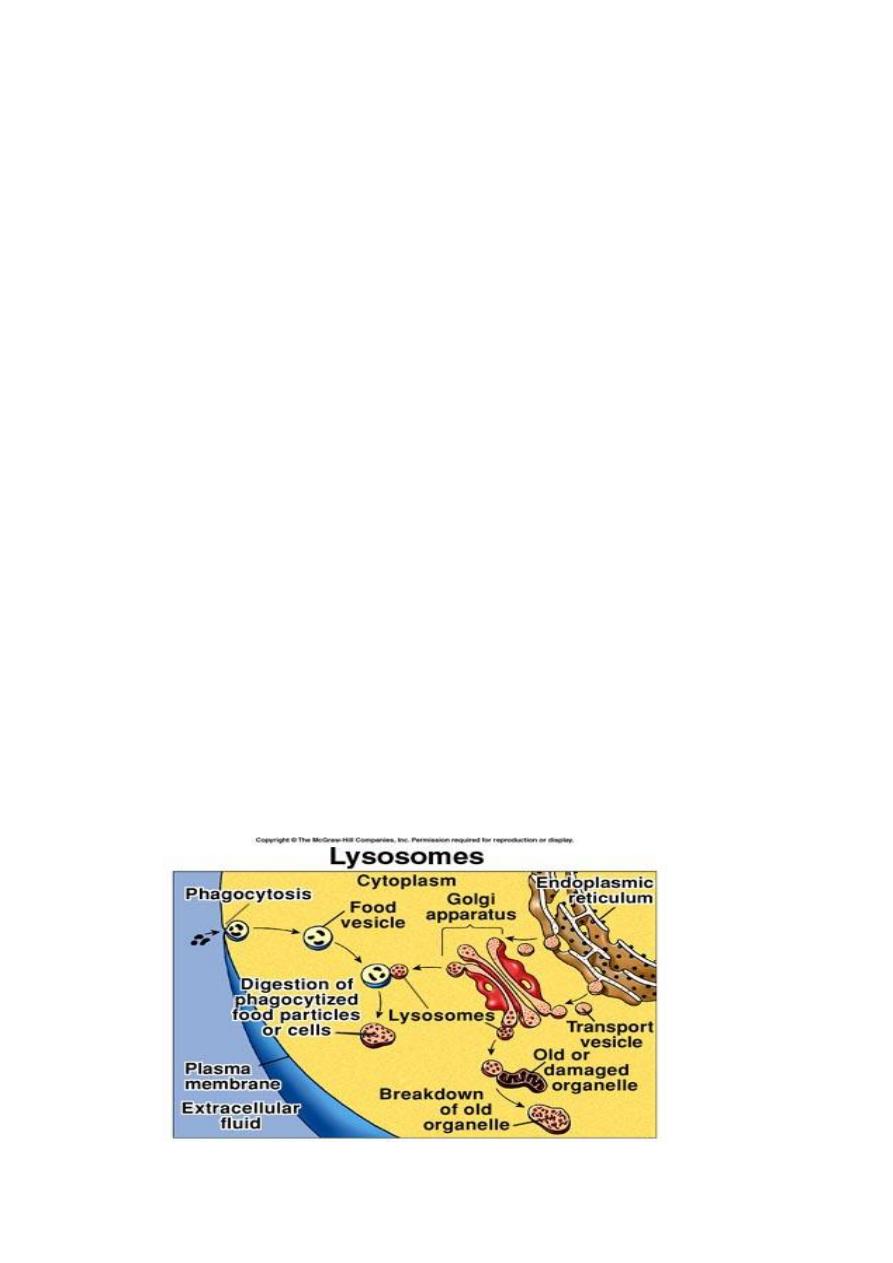
Lysosomes and Peroxisomes
Both are produce by Golgi apparatus
vacuoles contain enzymes so powerful that they must kept within
the vacuole to avoid damaging of the cell.
Peroxisome destroy various toxic wastes products in cell (like
H
2
O
2
)and component that have entered the cell from outside (like
alcohol)by detoxification process.
Lysosomes (lyses +soma from Greek→ dissolution bodies)these vacuoles
contain enzymes that break down the cell material itself by a process of
self digestion or auto digestion so they are so dangerous to the life of the
cell
Lysosomes, contain hydrolytic digestive enzymes. Sometimes
macromolecules are brought into a cell by vesicle formation at the
plasma membrane. When a lysosome fuses with such a vesicle, its
contents are digested by lysosomal enzymes into simpler subunits that
then enter the cytoplasm.
Even parts of a cell are digested by its own lysosomes (called auto
digestion). Auto digestion is also important during development. For
example, the fingers of a human embryo are at first webbed, but they
are freed from one another as a result of lysosomal action.

Lec:3
The Plasma Membrane
A human cell, like all cells, is surrounded by an outer plasma membrane.
The plasma membrane marks the boundary between the outside and the
inside of the cell. Cell membrane are vital because they separate the
intracellular and extracellular environment and prevent the loss of
enzymes nucleotides and other cellular molecules that are water soluble .
Its function :
1-Regulate transport in and out of cell or sub cellular parts by its selective
permability features .
2-Allow cell recognition
3-Play role for cell-junction
4-Receive signals through receptors from the outside environment and
transmits signals to organelles within cells like receptors for antigen ,hormones
The structure:
It’s a double structure like ER by electron microscope show it as sandwich of
fully material (phospholipids) The plasma membrane is a phospholipid
bilayer with attached or embedded proteins between two layers of proteins
(this structure called unite membrane).
Recently talk about the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure (Singer and
Nicolson 1972) that the PM composed of lipid and protein which arranged in
mosaic model: lipids 50% are a bilayer amphipathic they have
1-hydrophilic polar heads, being charged, are hydrophilic (attracted to
water). They position themselves to face toward the watery environment
outside and inside the cell.
2- hydrophobic non polar tail
(not attracted to water). They turn
inward toward one another, where there is no water.
Proteins 25-75% are embedded in the bilayer:
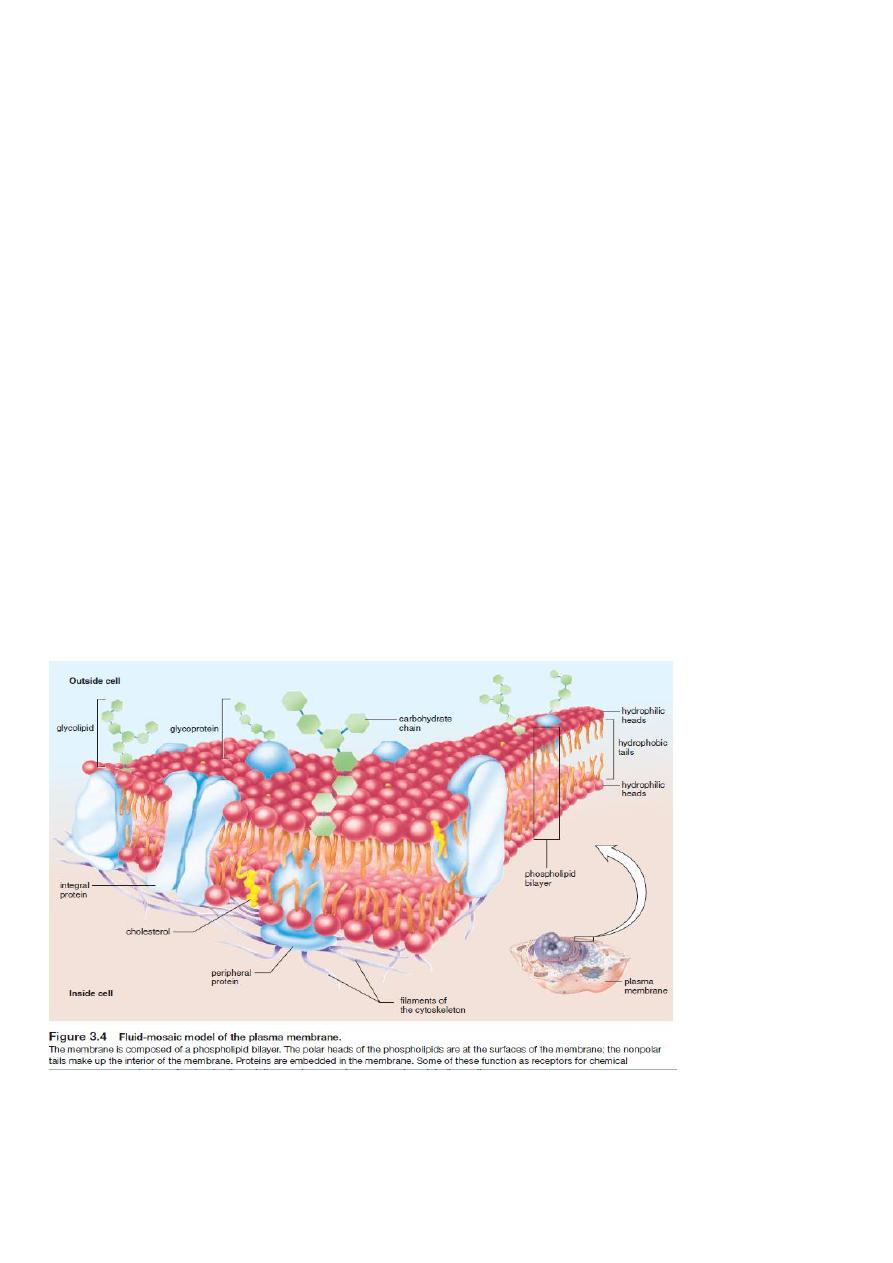
1-As trans membrane protein or integral protein(pass through the lipid
layer)
2-as peripheral proteins (may be inserted in the cytoplasm or exterior face
not inserted into the lipid layer. At body temperature, the phospholipid bilayer
is a liquid. It has the consistency of olive oil. The proteins are able to change
their position by moving laterally .see Figure 3.4
There is also cholesterol whish lends support to the membrane and
carbohydrate in the form of glycolipid and glycoprotein present in the outer
surface of the c.m.
The fluid mosaic model allows us to explain the changing permeability of
membranes from time to time and place to place.
Its not identical wherever it is found because it has different jobs in different
place.

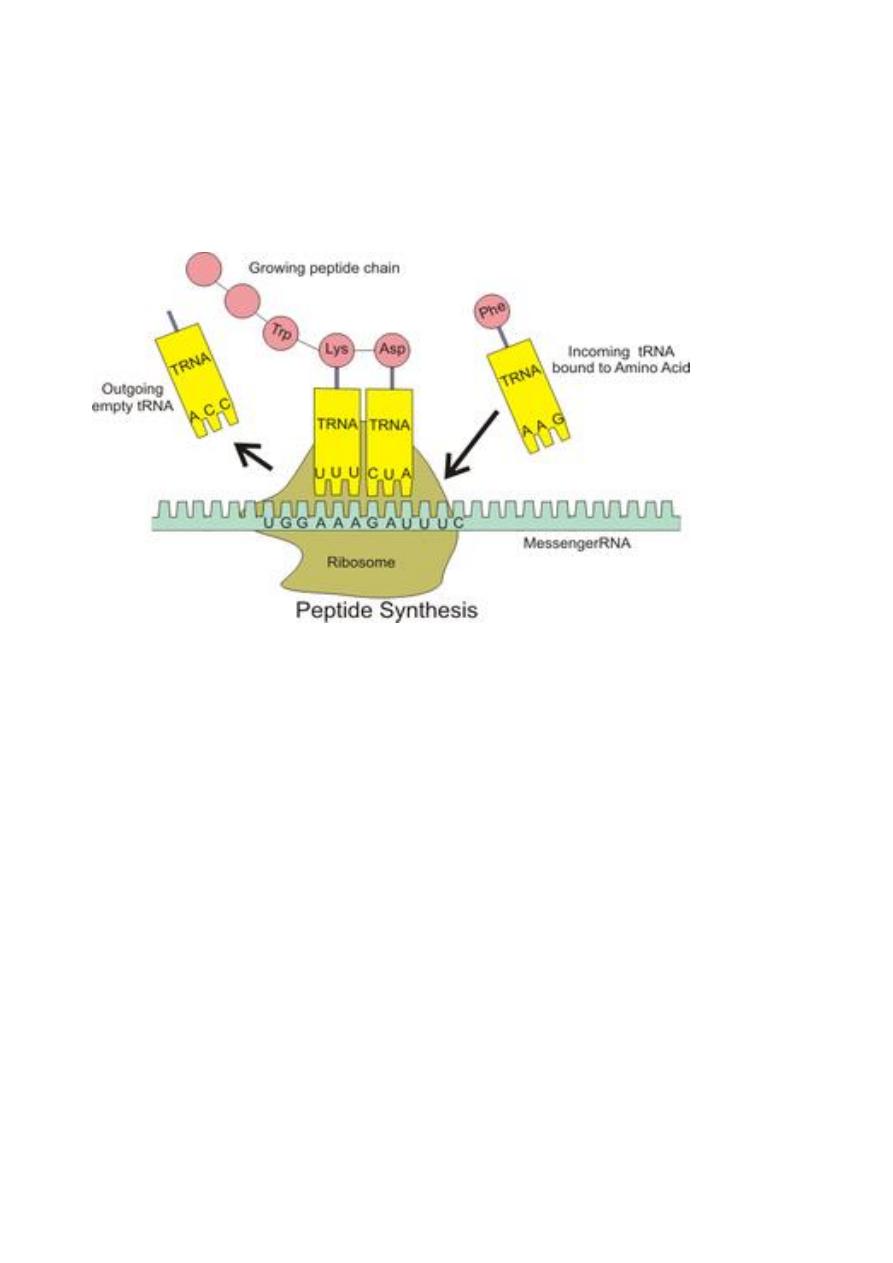
Ribosomes
Are dense slightly angular structures about 15 nm in diameter.
Found in any type of cells ,occur single or in a cluster know as polyribosomes
,freely in cytoplasm or attached to RER(those on RER may dissociate
themselves and become free).
Ribosomes are organelles composed of proteins and rRNA. Protein
synthesis occurs at the ribosomes.
Proteins synthesized at ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
have a different destination from that of proteins manufactured at ribosomes
free in the cytoplasm.
Each ribosome consist of two sub unite and its size measured in Svedberg
(S)unite (derived from sedimentation in ultracentrifuge use before electron
microscope available ).
In prokaryote →ribosome made of 30S and 50S subunites →70S
In eukaryote → ribosome made of 40S and 60S subunites →80S
A ribosome is made of about 40% protein and 60%nuclic acid (RNA).It
composed of four molecules of (rRNA) which form part of a structure of
ribosome found in the nucleus and nucleolus and may be synthesized in the
nucleolus.
Its function :1-as protein factory of the cells because it’s the place where
protein are produced according to the genetic information in mRNA which
contain the code for the synthesize of specific protein.
2-rRNA serve as enzymes called ribozymes for many of the reactions in the
ribosome required for protein synthesis.
Non active ribosome split into two subunite ,large and small in protein
synthesis begins one small and one large subunite come together to form
active ribosome.F12
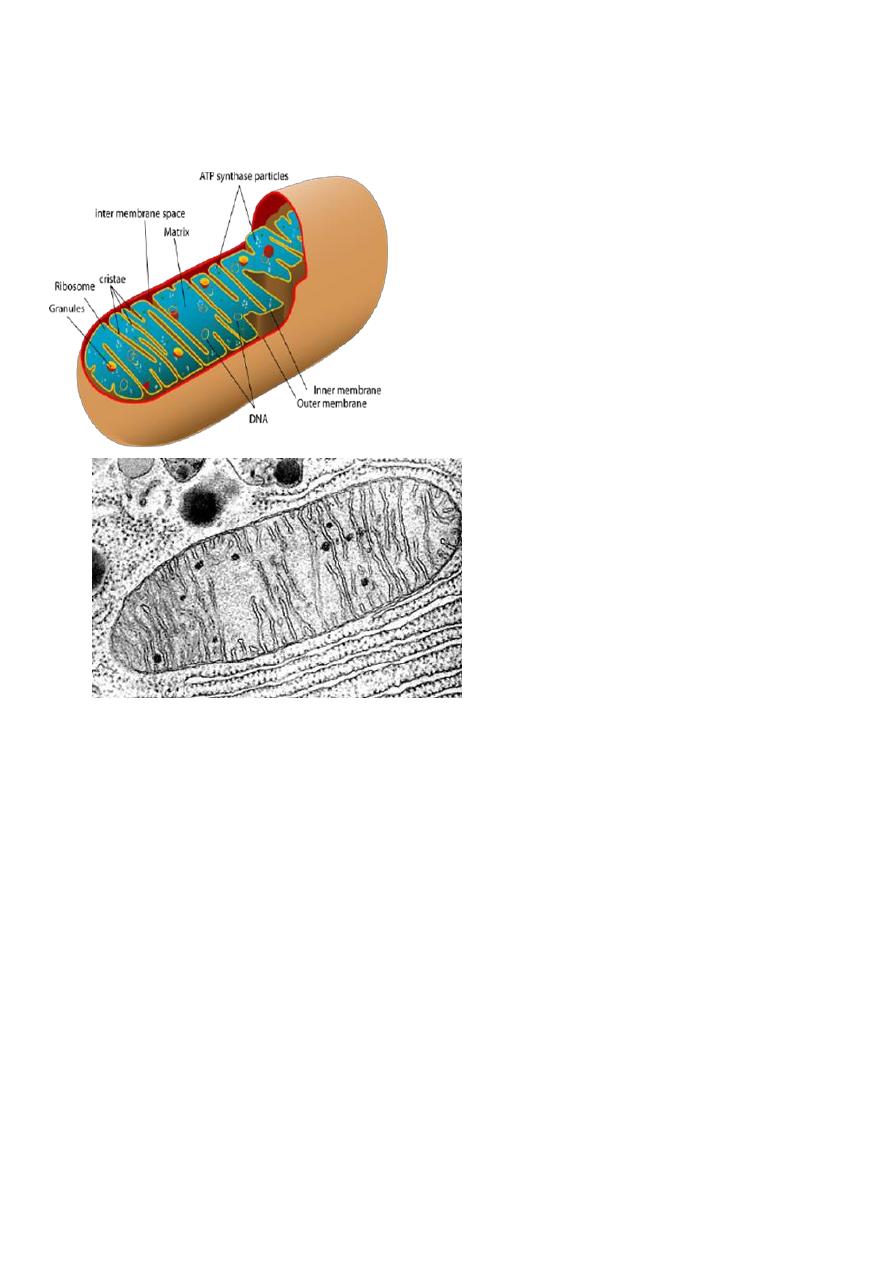
Mitochondria –the energy producing organelles
Are free flouting within the cytosol described as the power house of the
cell.
Found in most eukaryote cells ,including plants ,animals ,fungi.(plants in
addition have chloroplasts organelles containing the green pigment
chlorophyll that is able to transform sunlight energy into chemical energy that
can be used by plants).
Described as power house of the cell because here cellular respiration
takes place and energy stored in ATP is produced.
Its called cellular respiration because the cell take up the O
2
that it respire
and the glucose produced by digestion of the food that we eat and convert it to
carbon dioxide and water in a chemical reaction that’s give off energy ,by the
process of oxidative phosphorylation :
1glucose + O
2
→CO
2
+H
2
O +36 ATP (Krebs cycle)

A few cells have a single large mitochondria but usually a cell has 100-1000 of
mitochondria (e.g. muscle cells have many of it but skin cells have a very few).
A mitochondria is a fluid –fluid tubular structure surrounded by a double
membrane which are much like a typical cell membrane.
The outer membrane
1- enclose the complete organelle and protects it.
2-composed of 50%phospholipids +50%protein
3-composed of a varity enzymes as a the oxidative enzymes.
4-contain many integral proteins ,specialized proteins called porins which
contains a large internal channels allow ion and small molecules to move
into the intra membranous space (space between inner and outer membranes
without using energy.
The lower membrane
1- enclose the matrix.
2-composed of 30%phospholipids + 70% protein.
3-Dose not contain porins.
4-Is folded into projection called cristae ,fill the inner cavity or matrix and
increase the surface area of the inner membrane allowing more area for energy
production and on it the energy producing enzymes are located.
The matrix
1- encloses the respiratory chain enzymes ,so it’s the place for chemical
reaction.
2-Contain ribosomes and several molecules of DNA(their own genetic
material and it made their own RNAs and proteins).
3-ATP synthase particles for energy production by a processes oxidative
phosphorylation.
Mitochondria also play role in many metabolic activity like heme
synthesis ,steroid synthesis ,heat production (enabling the organism to stay
warm).