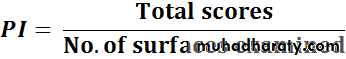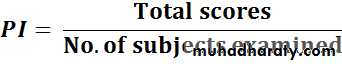Index
Indices of periodontal diseasesMany indicators has been used in research and clinical studies to measure the prevalence and severity of periodontal diseases
The most common or popular indices have evaluated the following parameters:
Extent of supra-and sub- gingival plaque.Gingival inflammation.
Bleeding of gingiva.
Supra- and sub-gingival calculi.
Contour of gingiva.
Colour of gingiva.
Pocket depth.
Tooth mobility.
Loss of epithelial attachment measured from cemento-enamel junction.
For individual patient:
1. Provide individual evaluation to help patient to recognize an oral problem.2. Reveal the degree of effectiveness of present oral hygiene practice.
3. Motivate the person in preventive or professional care for elimination and control of disease.
4. Evaluated the success of individual and professional treatment over a period of time by comparing index scores.
B. For a community:
1) Mark distribution of disease(prevalence of disease):In population group.
Within each dentition.
Around each individual tooth.
2) Provide base-line data to show existing dental health practice and needs of a community.
3) Compare the effects of community programs and evaluate the results.
There are four main categories in periodontal disease for which indices are needed
1. Dental plaque: It is soft non mineralized, bacterial deposit formed on the tooth surface.
2. Gingivitis: It is an inflammation of gingival tissue mainly caused by dental plaque.
3. Periodontitis: It is an inflammation of periodontal ligament which mainly followed un treated gingivitis.
4. Calculus: It is a hard deposit that forms by mineralization of dental plaque.
Periodontal indices are needed in four main types of study
1. Experimental study.2. Clinical trials.
3. Large population survey on prevalence and incidence.
4. Survey of treatment needed.
Indices used for plaque and debris assessment:
I. Plaque Index by Löe and Silness(1964)This index measures plaque thickness. It has very good reproducibility and is wide in use (used in clinical trial).
Each of the four surface of the tooth near the gingival margin is scored from “0”to “3”, then the mean score, first for each tooth, then the individual and finally the group, is calculated. The original 6 teeth used are:16,12,24,36,32,and 44.
Score Criteria
46 2
6 2
4
0 : No plaque.
1 : A film of plaque adhering to the free gingival margin and adjacent area of the tooth , which cannot be seen with the naked eye. But the plaque only be recognized by using disclosing solution or by running a probe across the tooth surface .
2 : Moderate accumulation of deposits within the gingival pocket, on the gingival margin and/ or adjacent tooth surface, which can be seen with the naked eye.
3 : Heavy accumulation of soft matter within the gingival pocket and/or on the tooth and gingival margin.
Calculation of plaque index:1- For Individual:
• 2- For Population:
II. Oral Hygiene Index (OHI) by Green and Vermillion(1960)
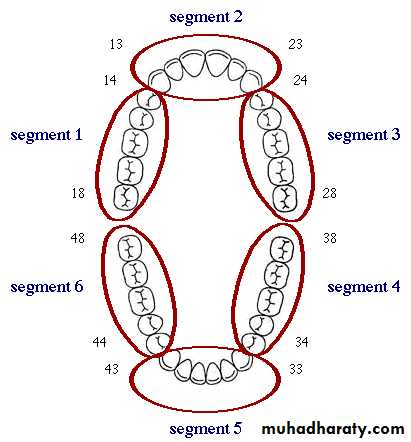
This index has 2 components: The debris index (DI) and the calculus index (CI). The scores for each are added to give the total score for the OHI. Debris index: measures plaque areas.Selection of Teeth and Scoring:
The mouth is scored in 6 segments: Anterior and right and left posterior in each jaw. The teeth are examined buccally and lingually in each segment, giving 12 scores in all. The score for the buccal of an entire segment is the highest score for the buccal surface of an individual tooth in that segment. The lingual surface scored similarly and not necessarily be on the same tooth.
The maximum score is 12 x 3=36
The DI is then determined by dividing the score (36 maximum) by the number of segments scores (6). The maximum score for the DI is thus 6 .The two combined indices (DI and CI) give an OHI with range of 0-12.
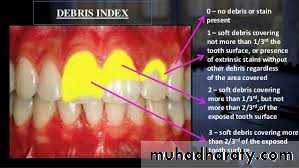
Criteria of DI:(debris is removed with the aid of the probe along the tooth)
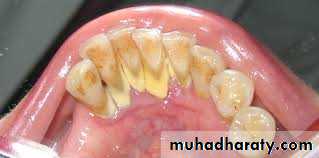
0: No debris or stain.1: Soft debris covering up to 1/3rd of the tooth surface or the presence of extrinsic stains without debris regardless of surface area covered.
2: Soft debris covering 1/3rd – 2/3rd of the tooth surface.
3: Soft debris covering over 2/3rd of the tooth surface.
III. Oral Hygiene Index simplified (OHI - S) by Green and Vermillion (1964)
Selection of teeth and Scoring :
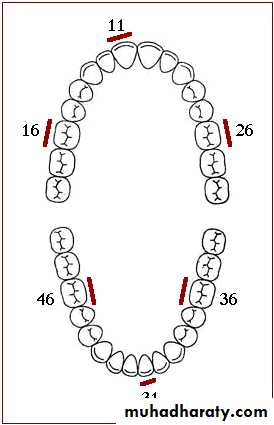
The surface examined are the buccal surface of 16, and 26, the lingual surface of 36 and 46, and the labial surface of 11 and 31.
If the first molar is absent, the first standing molar is substituted.
The DI-S for individual is calculated by dividing the total score by the number of surface examined which gives a range of 0-3.
maximum score for OHI-S is 6 not 12 as in the OHI.
• Criteria of DI-S:
• The same as DI.• 0: No debris or stain.
• 1: Soft debris covering up to 1/3rd of the tooth surface or the presence of extrinsic stains without debris regardless of surface area covered.
• 2: Soft debris covering 1/3rd – 2/3rd of the tooth surface.
3: Soft debris covering over 2/3rd of the tooth surface.
For DI-S & CI-S score –
For OHI-S score -
IV. Patients Hygiene Performance Index by Podshadley and Haley (1968).
This index was the first developed for the purpose of assessing an individual performance in removing debris after tooth brushing instruction.Selection of teeth and Scoring :
Same as OHI-S index teeth . If the first molar is absent, the First standing molar is substituted. The scoring is preceded by use of a disclosing agent (tablet or solution).
The tooth is divided into five areas:
Three longitudinal thirds (distal , middle , mesial) with the middle third subdivided horizontally into (incisal , middle, gingival thirds) .The assess of debris presence or absence is 1 or 0 .Calculation of score:
The patient hygiene performance index score per person is obtained by totaling the five subdivision scores of each teeth surface and dividing the total by the number of tooth surface examined.Advantages of Patients Hygiene Performance Index
Patients Hygiene Performance Index is relatively more sensitive than OHI-S because it divides each tooth surface into five areas.It can be used in group studies of dental health education.
Its chief value lies in its application as an education aid.
V. WHO System (1977)
This is a simple prevalence index. That teeth are not dried or stained , and no probe is used.Selection of teeth and scoring: The mouth is divided into 6 segments: posterior right and left, and anterior, in each jaw.
This system is used for all the periodontal indices advocated by WHO. All surface are examined; each segment is scored as one unit. The maximum score for an individual is 6.
Criteria of WHO system:
0: no soft deposit visible1: any soft deposit on any surface clearly visible by the naked eye.
Indices for measurement of calculus:
I. Oral Hygiene index (OHI) by Greene and Vermillion (1960):
Calculus index.
Selection of teeth and scoring: The same as DI.
Criteria of CI:
0: no calculus.1: supragingival calculus covering not more than 1/3rd of surface.
2: supragingival calculus covering 1/3rd – 2/3rd of surface or flecks of subgingival calculus.
3: supragingival calculus covering 2/3rd of surface or continuous heavy blend of subgingival calculus.
II. Oral Hygiene Index- Simplified (OHI-S) by Greene and Vermillion (1964) Calculus index.
Selection of teeth and scoring:The same as DI-S.
Criteria of CI- S:
The same as CI.
III. Calculus Surface Index (CSI) BY Sturzenberger and Radike (1961):
Selection of teeth and scoring:The teeth are 31,32,41,42. Each surface of each tooth examined therefore the maximum score is 16
.
Criteria of CSI: 2 1 1 2
0: no calculus present on surface
1: any calculus present on surface.IV. Ramfjord periodontal disease index- calculus component (1959)
Only six selected teeth are scored for assessment of the periodontal status of the mouth; 16,21,24,36,41 and 44 . The score for an individual is the total score divided by number of teeth . There is no substitution for missing teeth.Criteria :
C0 : no calculus.
C1 : supragingival calculus extending not more than 1 mm below gingival margin.
C2 : moderate amount of supragingival and subgingival calculus or subgingival calculus alone .
C3 : heavy calculus of both supra – and subgingival
V.WHO System (1977):
Selection of teeth and scoring :
The mouth is divided into 6 segments posterior right and left , and anterior ,
in each jaw . All surfaces are examined , each segment is scored as one unit.
The maximum score for an individual is 6.
Criteria :
0 : if the deposit is soft ,or there is no suspected calculus.1 : if there is calculus clearly present on visual examination on at least one tooth in the segment .
If a deposit is suspected of being calcified , a probe may be used to confirm this.
V. Calculus surface Severity index (CSSI) by Ennever et al.(1961)
Selection of teeth and scoring :Same as CSI
2 1 1 2
Criteria :
0: no calculus .
1 : less than 0.5 mm width thickness of calculus.
2 : 0.5-1 mm width thickness of calculus.
3 : over 1mm thickness of calculus.