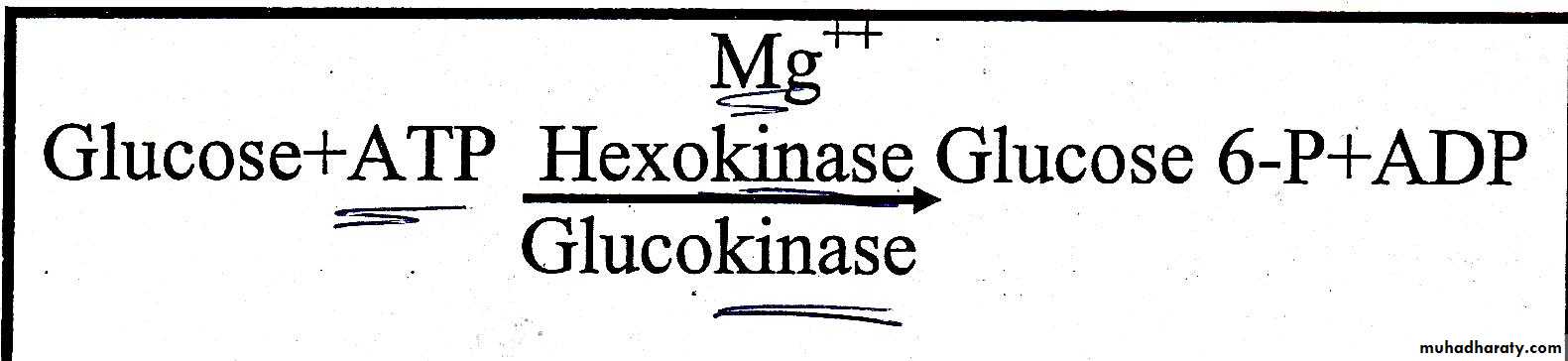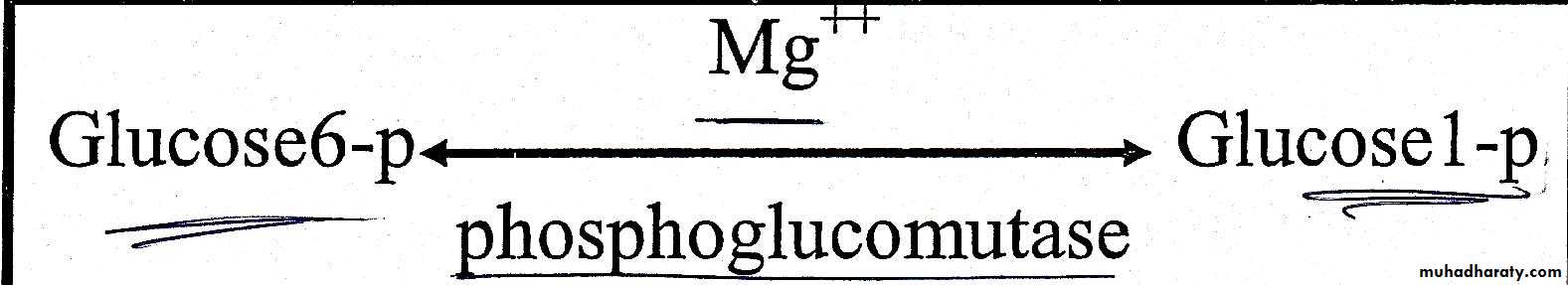د.احسان كيمياء حياتية 22\11\2017
عدد الاوراق( 4 ) م\2\موصل LEC:3Reaction 4 oxidative decarboxylation
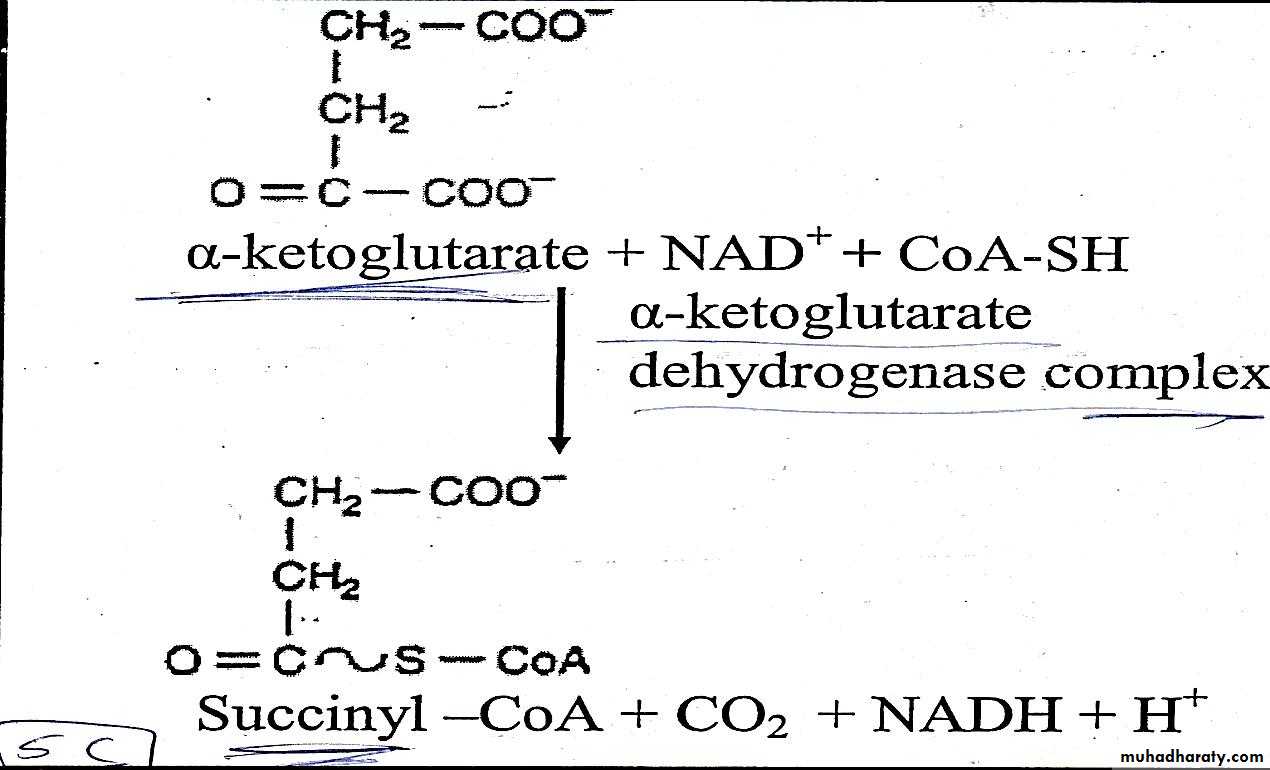
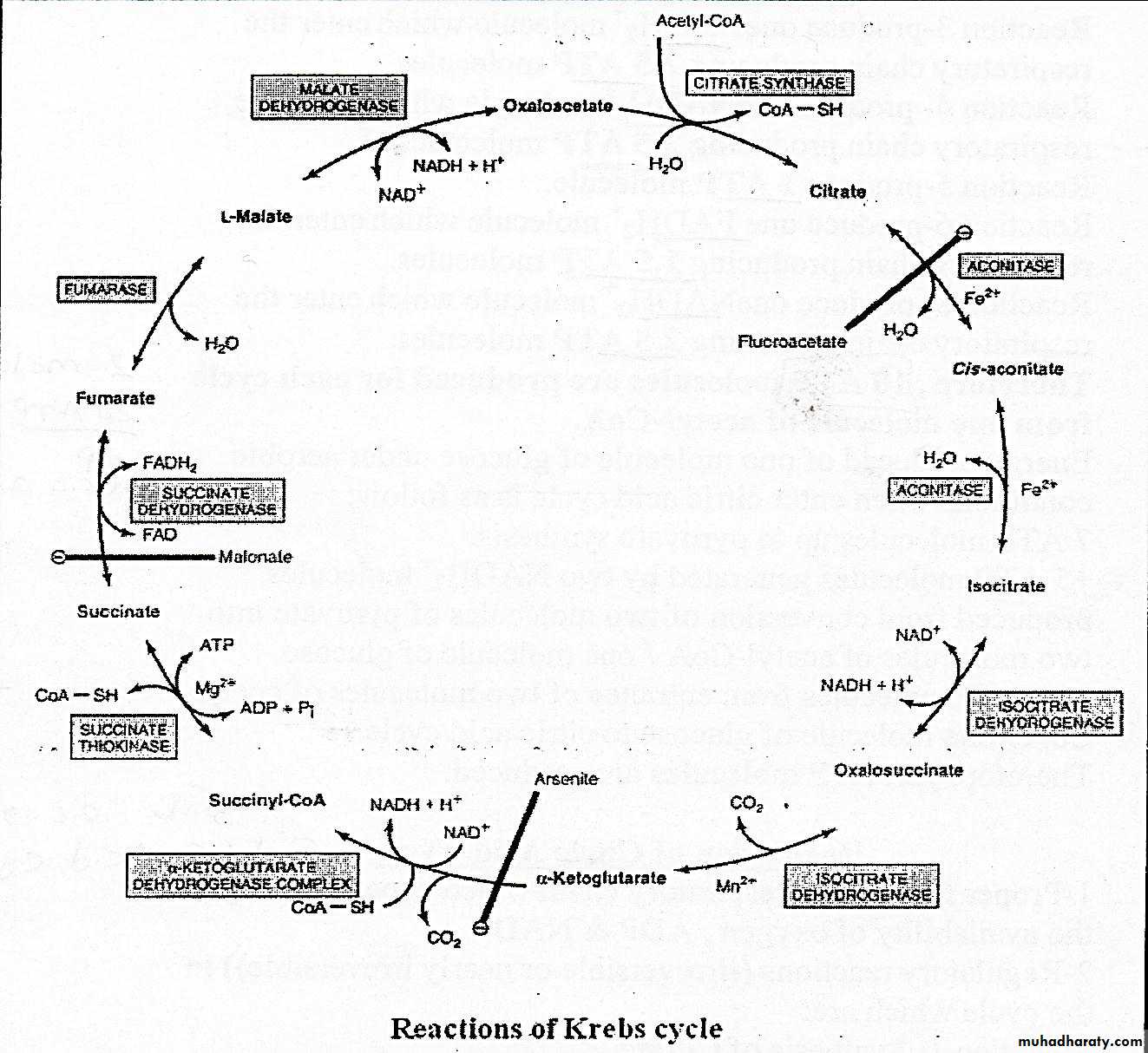
Α ketoglutarate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation .this irreversible reaction is catalyzed by α ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex which require also identical cofactors to that of pyruvate dehydrogenase as thiamin diphosphate and is inhibited by arsenate causing accumulation of α ketoglutarate.In this reaction α ketoglutarate in the presence of NAD˖ and Co A SH result in formation of
succinyl Co A +NADH+ H˖+CO2
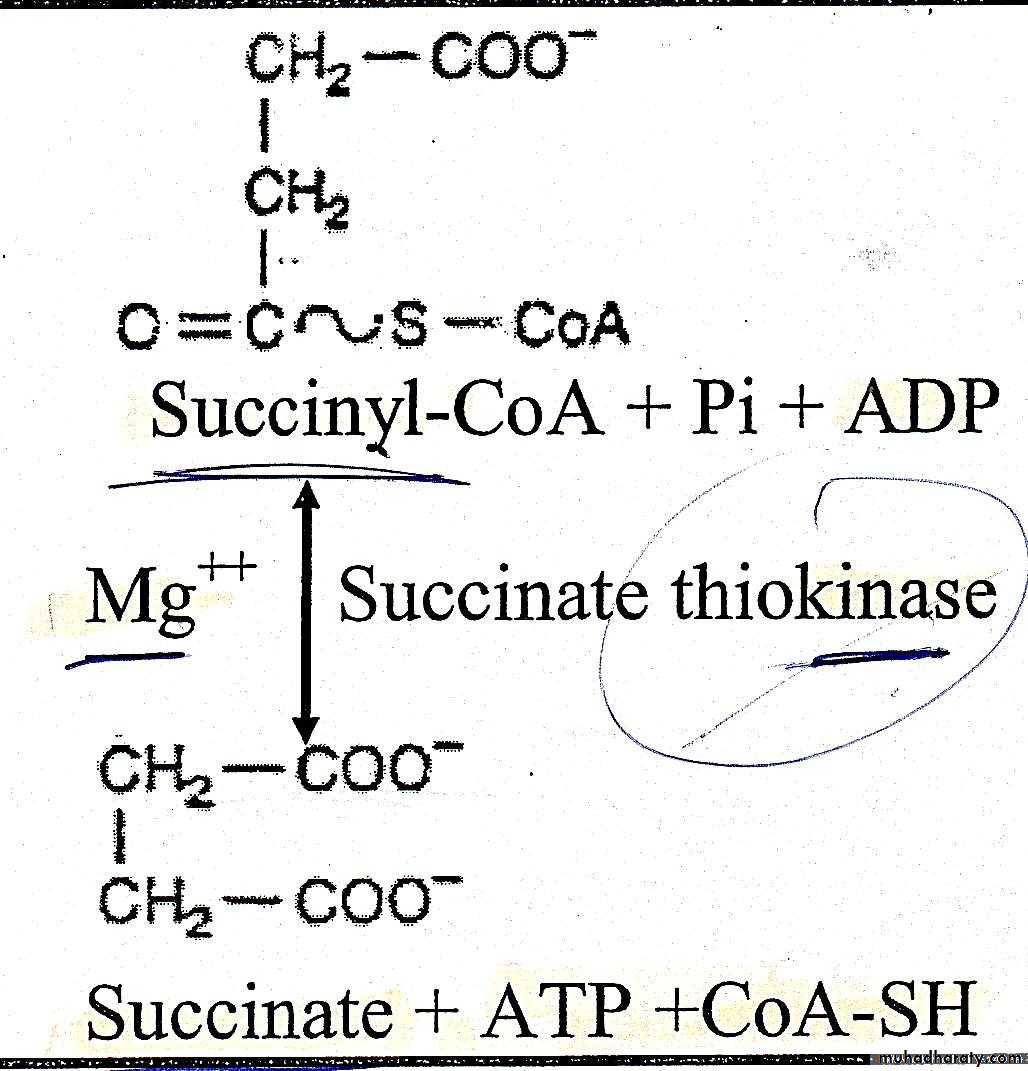
5.Hydrolysis of succinyl Co A
Succinyl Co A in the presence of ADP and inorganic phosphate is converted into succinate +ATP+CO A SH. this is the only reaction in citric acid cycle include the generation of ATP at substrate level. this reversible reaction is catalyzed by succinate thiokinase in the presence of Mg˖˖.succinate thiokinase also share in gluconeogenesis.6 dehydrogenation
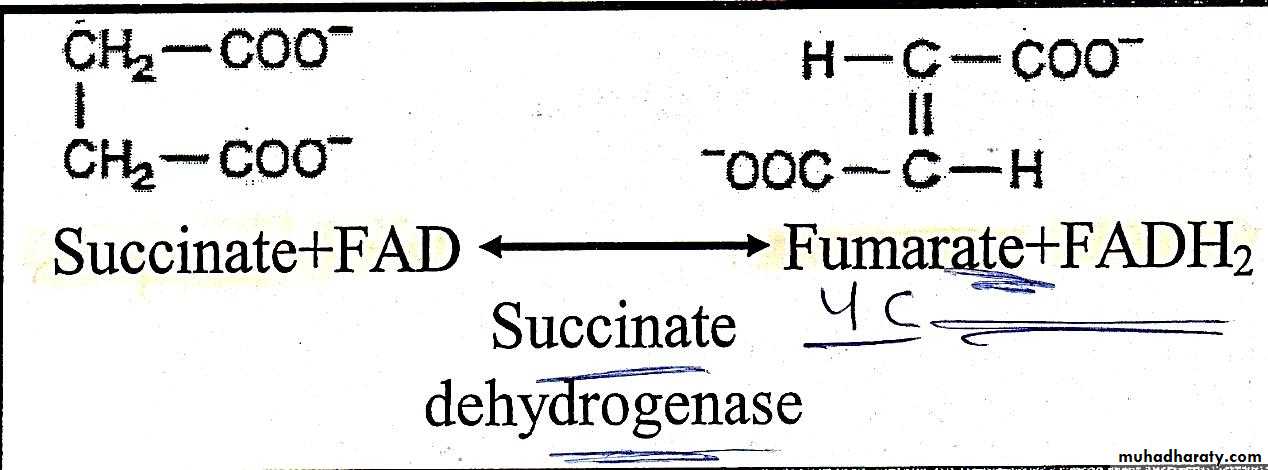
Dehydrogenation of succinate into fumarate by transfer of hydrogen directly from substrate into a flavoprotein,it is the only dehydrogenation reaction in the cycle involving direct transfer of hydrogen from substrate without participation of NAD ,this reversible reaction is catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase .Reaction 7
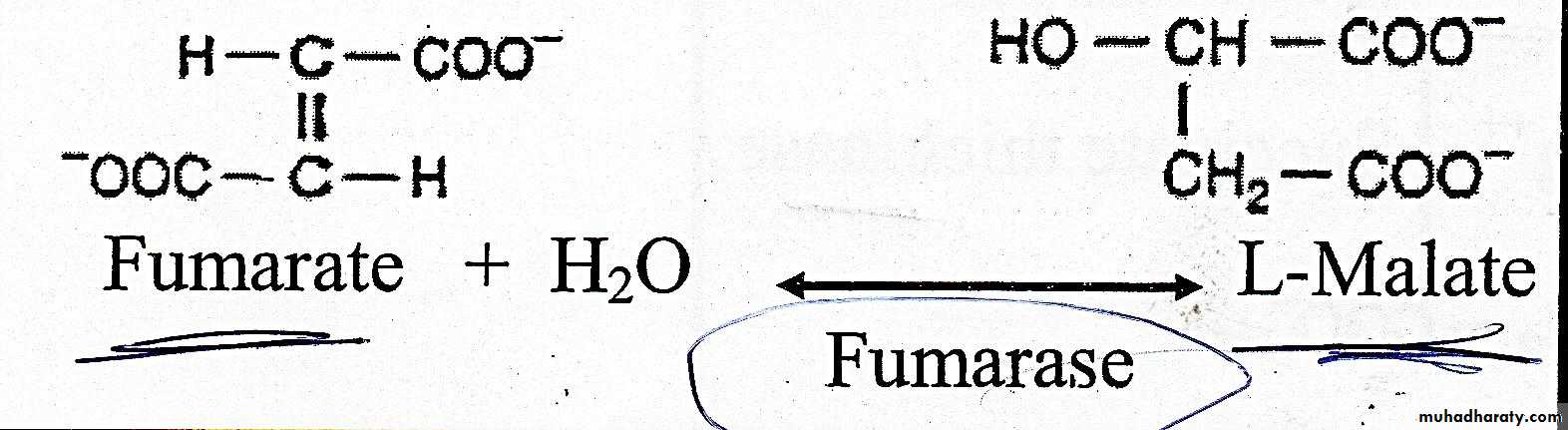
Hydration of the double bond of fumerate to form L-malate .this reversible reaction is catalyzed by fumerase (fumerate hydratase)Reaction 8
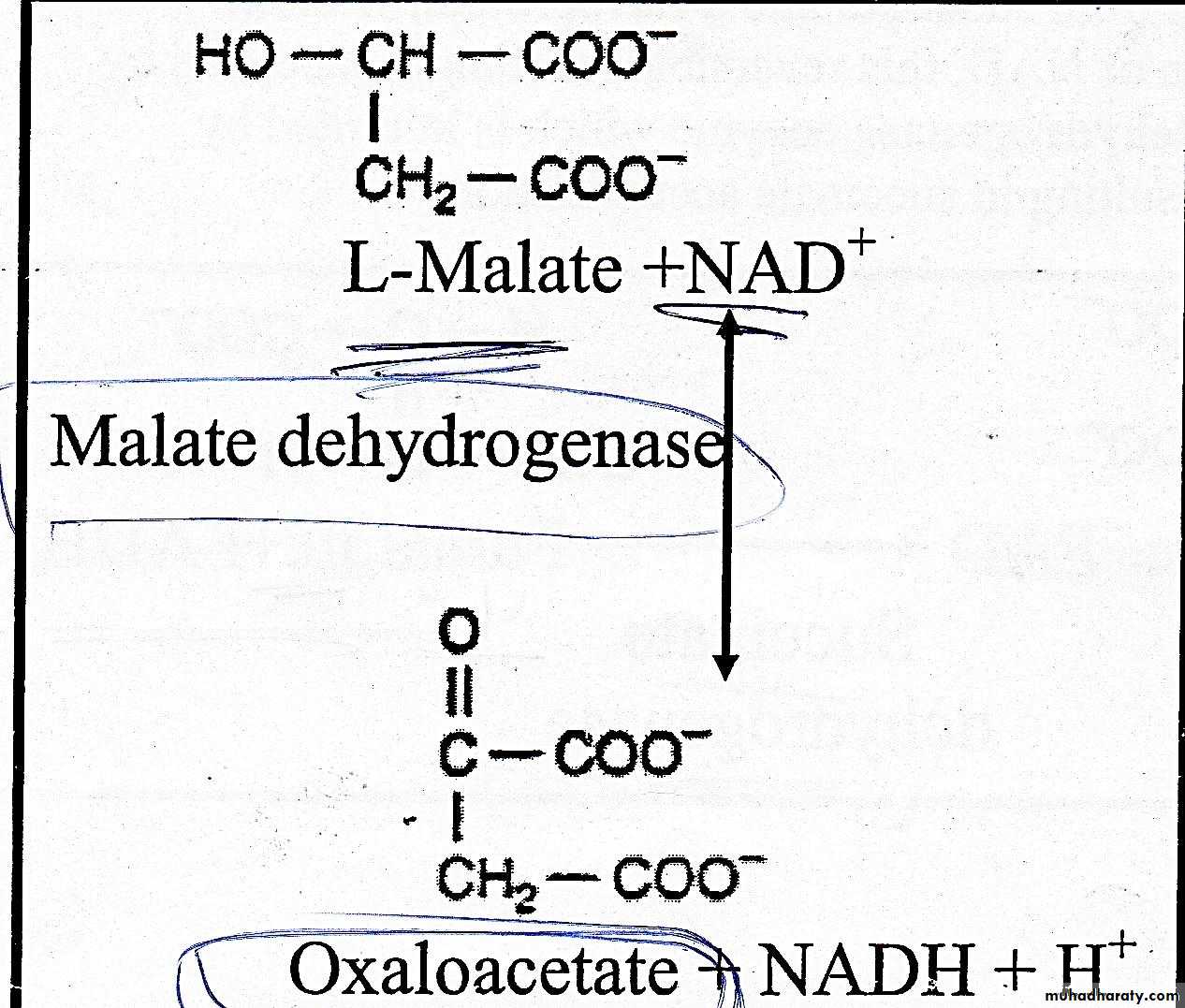
The final reaction of Kreps cycle where dehydrogenatin of malate in the presence of NAD˖ninto oxaloacetate +NADH+H˖. this is reversible reaction is catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase.The oxaloacetate produced in this reaction condense with acetyl Co A (reaction 1)and so the cycle continue again.
Energetic of citric acid cycle
Reaction 3 produces one NADH2 molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATPReaction 4 the same as above
Reaction 5 produce one ATP
reaction 6 produce FADH2 molecule that enter the respiratory chain producing 1.5
reaction 8 produces one NADH2 molecule which enter the respiratory chain producing 2.5 ATP
Therefore,10 ATP molecules are produced for each cycle of molecule of acetyl Co A.
ENERGY PRODUCED OF ONE MOLECULE OF GLUCOSE UNDER AEROBIC CONDITION IS AS FOLLOWS:
7 ATP molecules up to pyruvate synthesis.
+ 5 ATP molecules generated by two NADH 2 molecules produced from conversion of two molecules of pyruvate into two molecules of acetyl Co A per molecule of glucose
+20 ATP molecules from entrance of two molecule of acetyl CoA per one molecule of glucose to citric acid cycle
Therefore,32 ATP molecules are produced.
Role of vitamins in citric acid cycle
Riboflavin ,in the form of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)in reaction 6Niacin in the form nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) in reaction 3 ,4 and 8 thiamin as thiamin diphosphate the coenzyme for α ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Pantothenic acid as part of Co A
Glycogen metabolism
Glycogen is the major carbohydrate storage in animal and human it presents mainly in:
Liver glycogen represent 5% of liver weight. its concern with maintenance of blood glucose between meals. after 12 -18 hours of fasting the liver glycogen is almost totally finished or depleted.
Muscles glycogen represent up to 0.7% of muscle weight. But because of great muscle mass it is 3-4 times that of liver it is concerned as a source of glucose for glycolysis within the muscle itself.
Glycogenesis
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis in which glucose molecules are added to chain of glycogen . It depends on the demand for glucose and ATP . If both are present in relatively high amount,then the excess insulin promotes the glucose conversion into glycogen for storage in liver and muscle cells.Reaction 1
Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose 6 phosphate in irreversible reaction catalyzed by hexokinase in muscle and glucokinase in liver in the presence of Mg˖˖.
Reaction 2
Glucose 6 phosphate is isomerized to glucose 1 phosphate in reversible reaction catalyzed by phosphoglucomutase in presence of Mg˖˖.Step 3
Glucose 1 phosphate reacts with uridine tri phosphate (UDP) to form active nucleoside uridine diphosphate glucose and in organic phosphate this reaction is catalyzed by UDPGlu pyrophosphorylase .Number 4
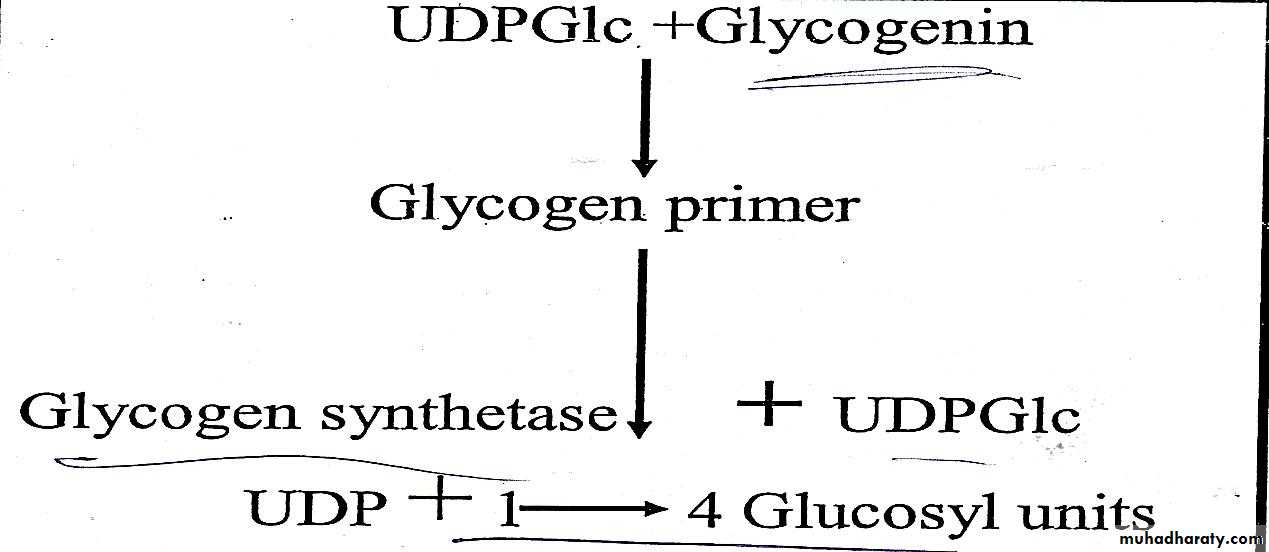
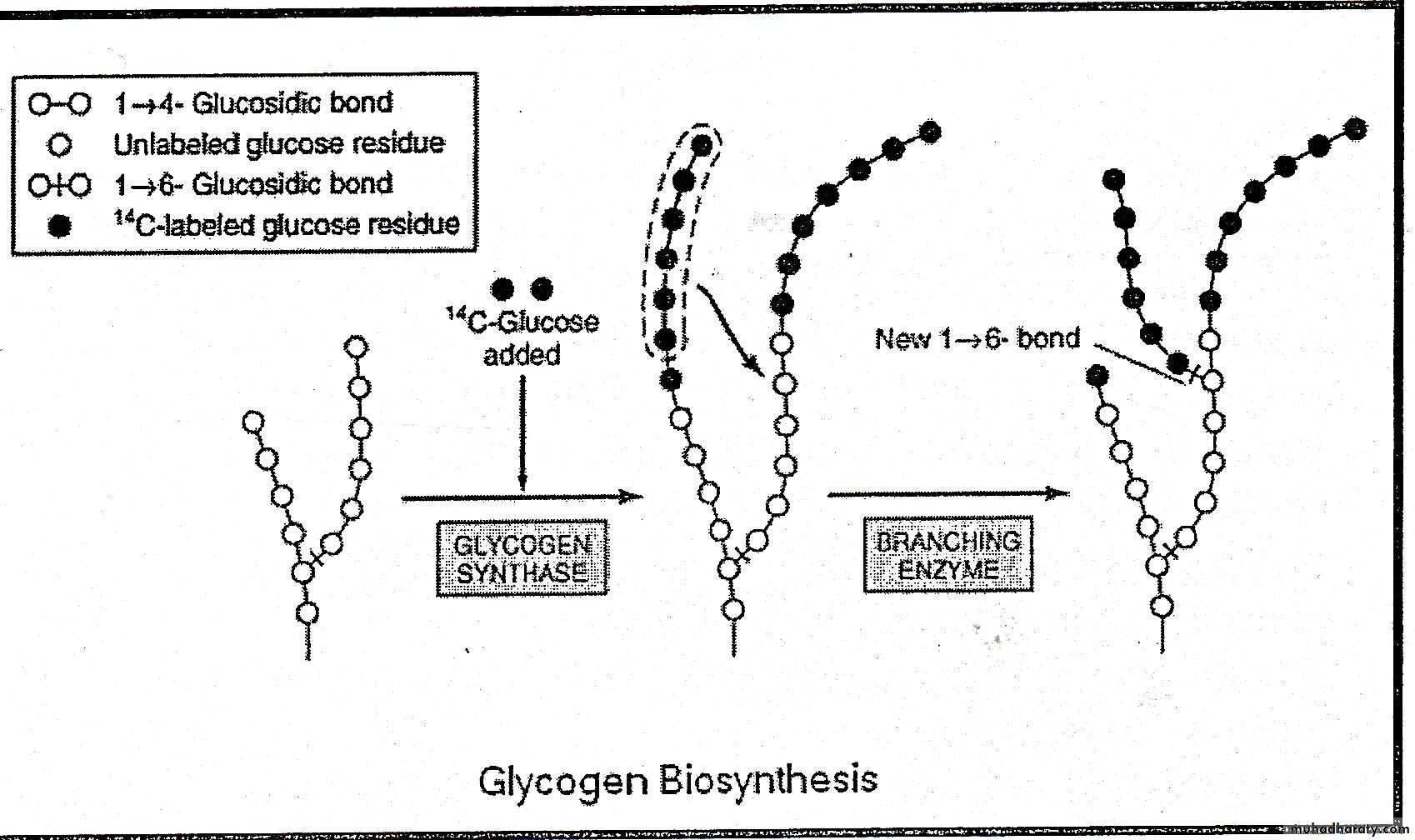
Glycogen synthase catalyzes the formation of glycosidic bond between C1 of active glucose of UDPGlu and C4 of a terminal glucose residue of glycogen primer producing 1→4 glucosyl unit with liberation of uridie diphosphate .therefore, the primer must be present to initiate the glycogen synthesis .this reaction is irreversible.5
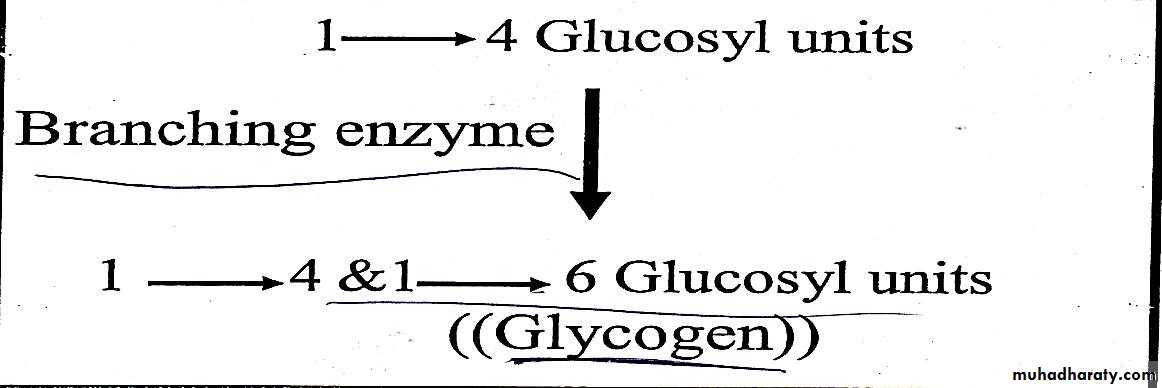
In reaction 4 the branches of glycogen tree become elongated as successive 1→4 linkages are added and when the chain becomes at least 11 glucose residue a second enzyme called branching enzyme transfer a part of 1,4 chain (minimum of 6 glucose residue) to a neighboring chain to form 1,6 linkage thus establishing a branch point in the molecule then the branches grow by further addition of 1→4 glycosyl units .this reaction is reversible.