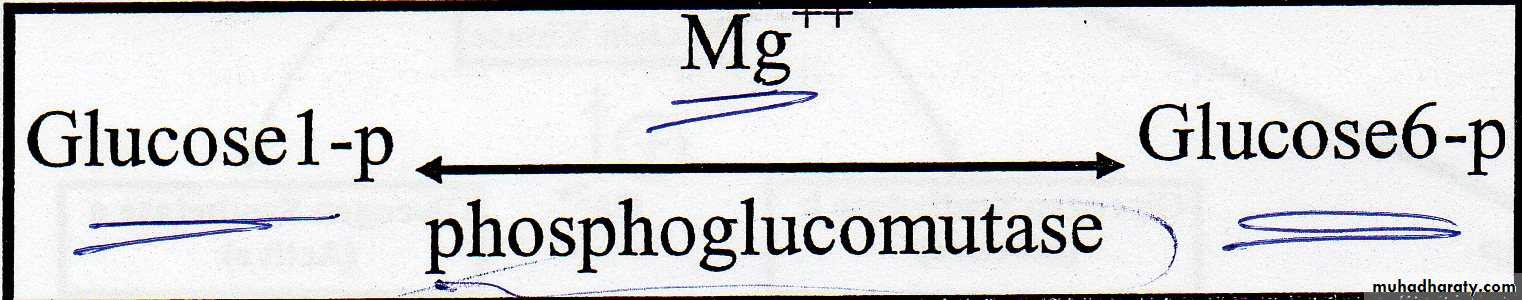glycogenolysis
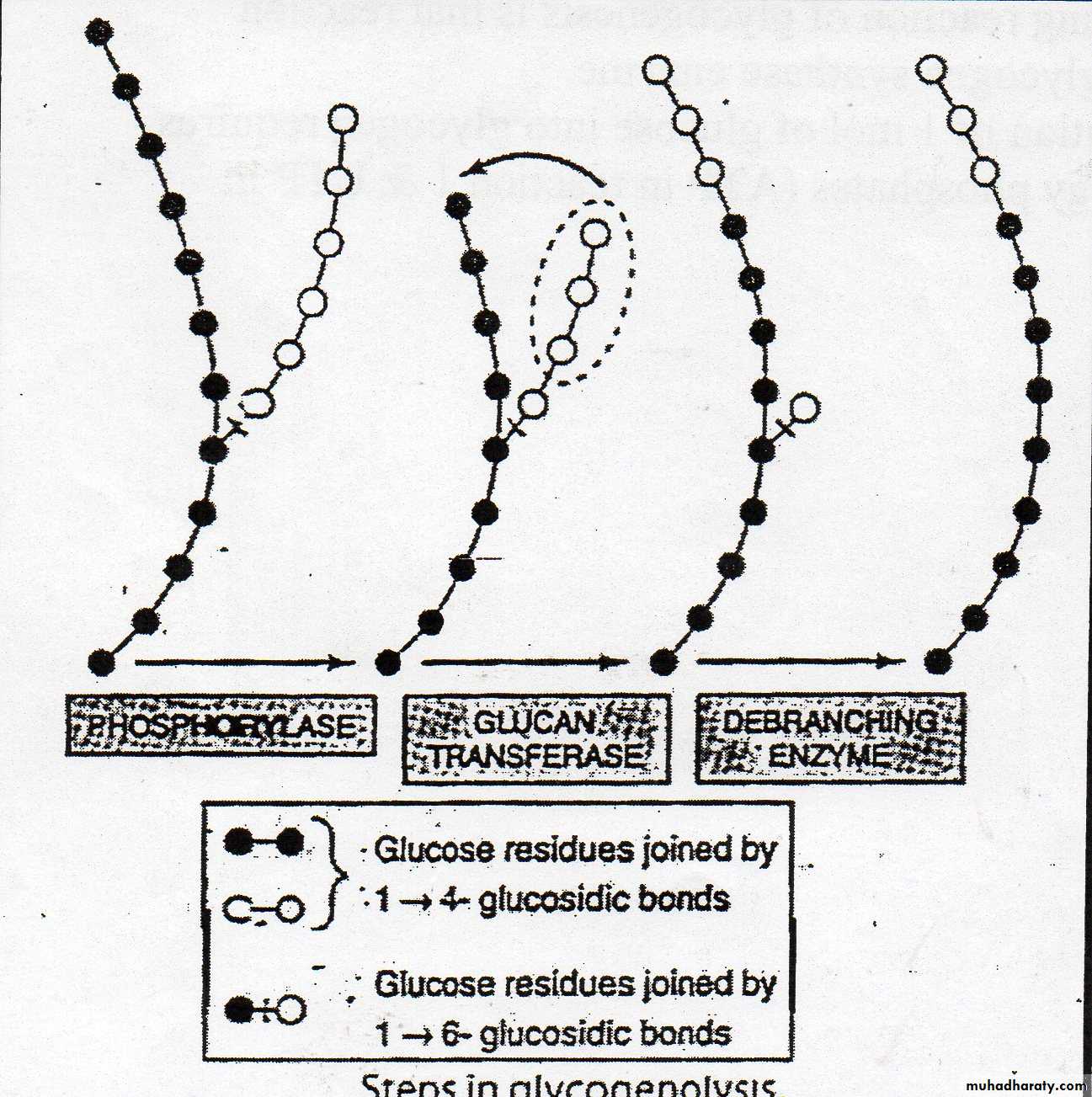
Glycogenolysis is initiated by the reaction catalyzed by glycogen phosphorylase enzyme which cause phosphoryltic cleavage of 1,4 bond until aproximately 4 glucose residuee remain on either side of 1,6 branch where another enzyme called (α 1→4 to α 1→4 glucan transferase) that transfers a trisaccharide unit from one branch to another exposing 1→6 point.Hydrolysis of the 1→6 linkage requires debranching enzyme .further phosphorylase action can now proceed.
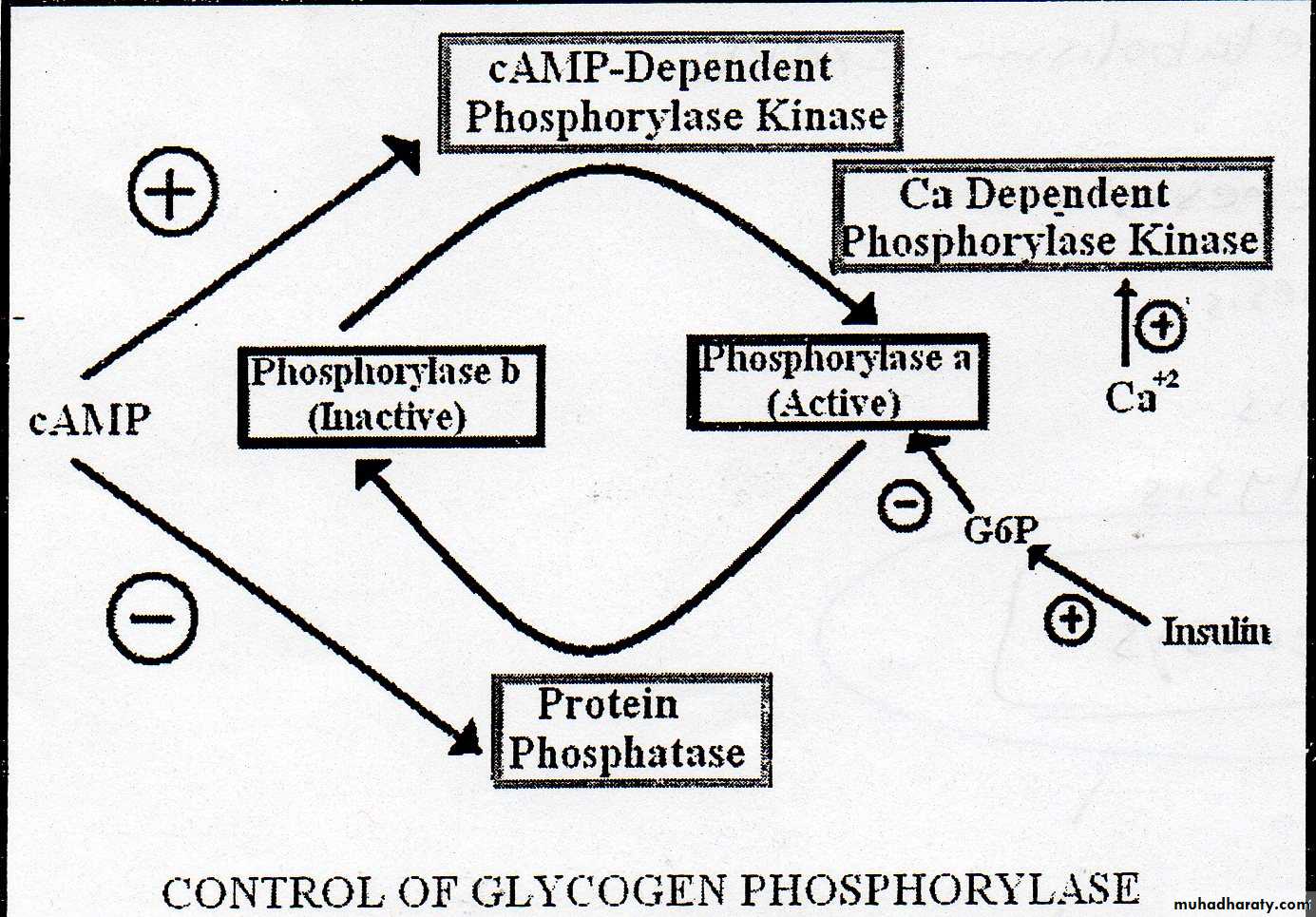
The rate limiting step is that catalyzed by phosphorylase .
The combined action of irreversible reactions catalyzed by these three enzymes convert glycogen into glucose 1 phosphate.
Glucose 1 phosphate is converted to glu 6 phosphate by reversible reaction catalyzed by phosphoglucomutase in presence of Mg˖˖
Removal of phosphate occur only in liver and kidney but not in muscle ,enabling glucose to diffuses from cells to blood ,this irreversible reaction is catalyzed by glucose 6 phosphatase enzyme.
Effects of hormones
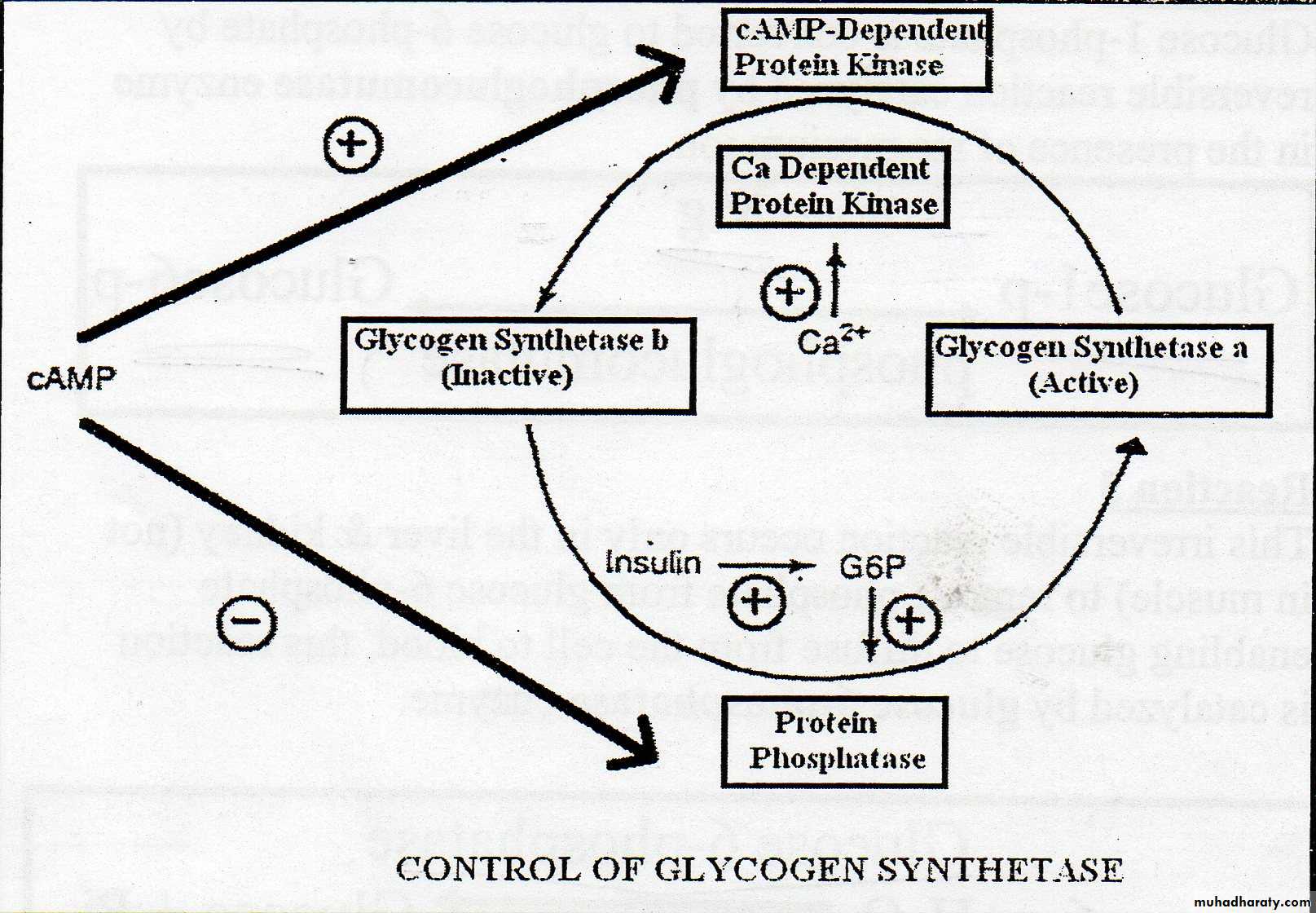
Epinephrine in muscle ,glucagon in liver inhibit glycogenesis and activate glycogenolysis.Insulin inhibits glycogenolysis and activates glycogenesis controlling blood glucose.
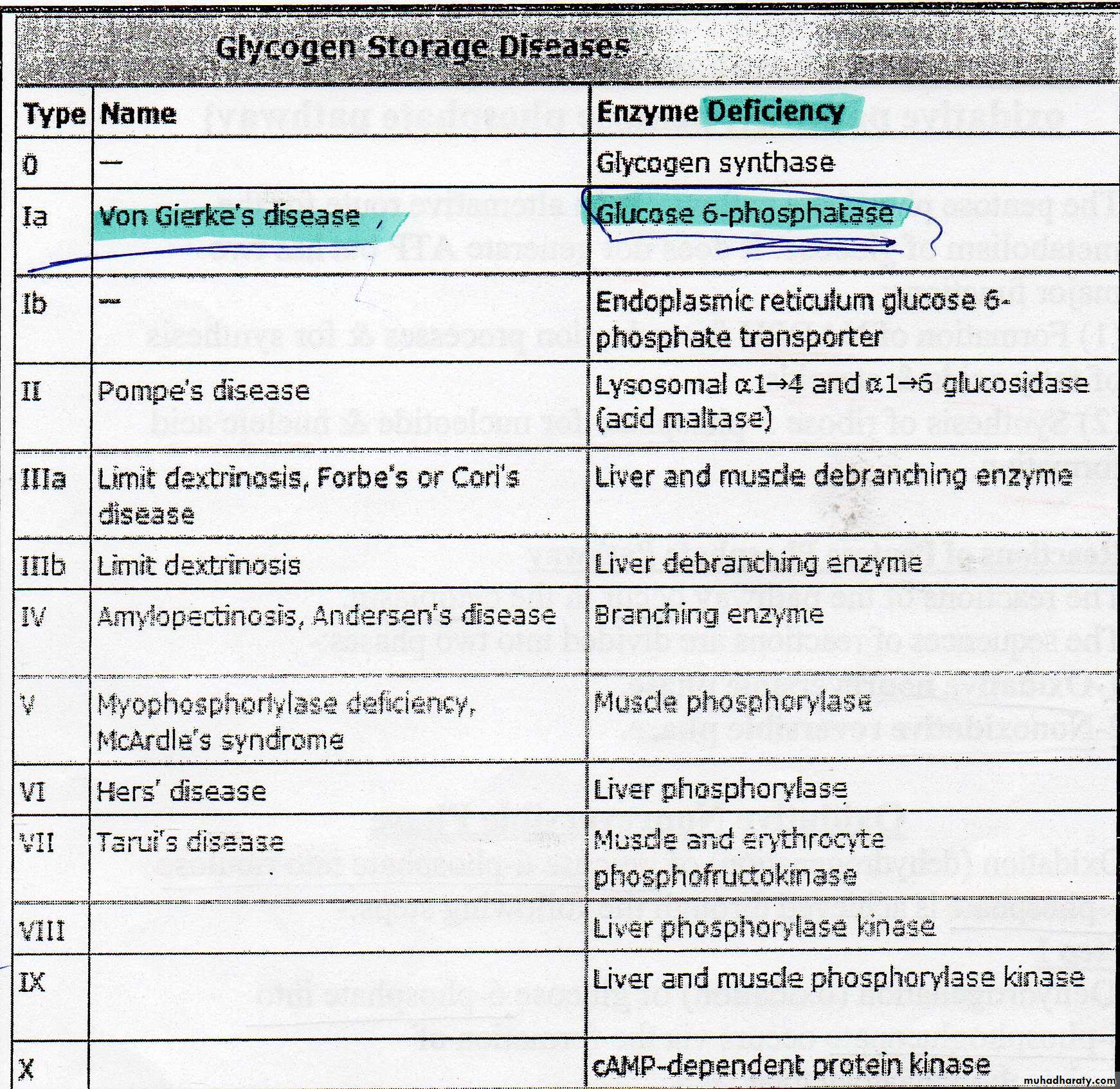
Glycogen storage disease
The term glycogen storage is a generic term that describes a group of inhereted disorders characterized by deposition of abnormal type or quantity of glycogen due to partial or complete absence of certain enzymes.Since glycogen moecule can be enormously large ,an inability to degrade glycogen causes the cells to become pathologically engorged and leads to functional loss of glycogen as a source of cell energy and as a blood glucose buffer.
Pentose phosphate pathway p.p.p.(hexose monophosphate shunt)
This is an ulternative pathway for glucose metrabolism,it does not generate ATP but has two majour functions :Formation of NADPH for reduction processes
and for synthesis of fatty acids and steroids.Synthesis of ribose 5 phosphate for nucleotides and nucleic acid synthesis.