
Anatomy and Physiology
By
Dr. Marwan Arbilei

What Is Anatomy and Physiology?
• Anatomy is the study of the
structure and relationship
between body parts.
• Physiology is the study of the
function of body parts and
the body as a whole.
SYSTEMS INSIDE THE BODY
• Skeletal system
• Muscular system
• Cardiovascular system
• Digestive system
• Endocrine system
• Nervous system
• Respiratory system
• Immune/ Lymphatic system
• Urinary system
• Male and Female Reproductive system
• Integumentary system
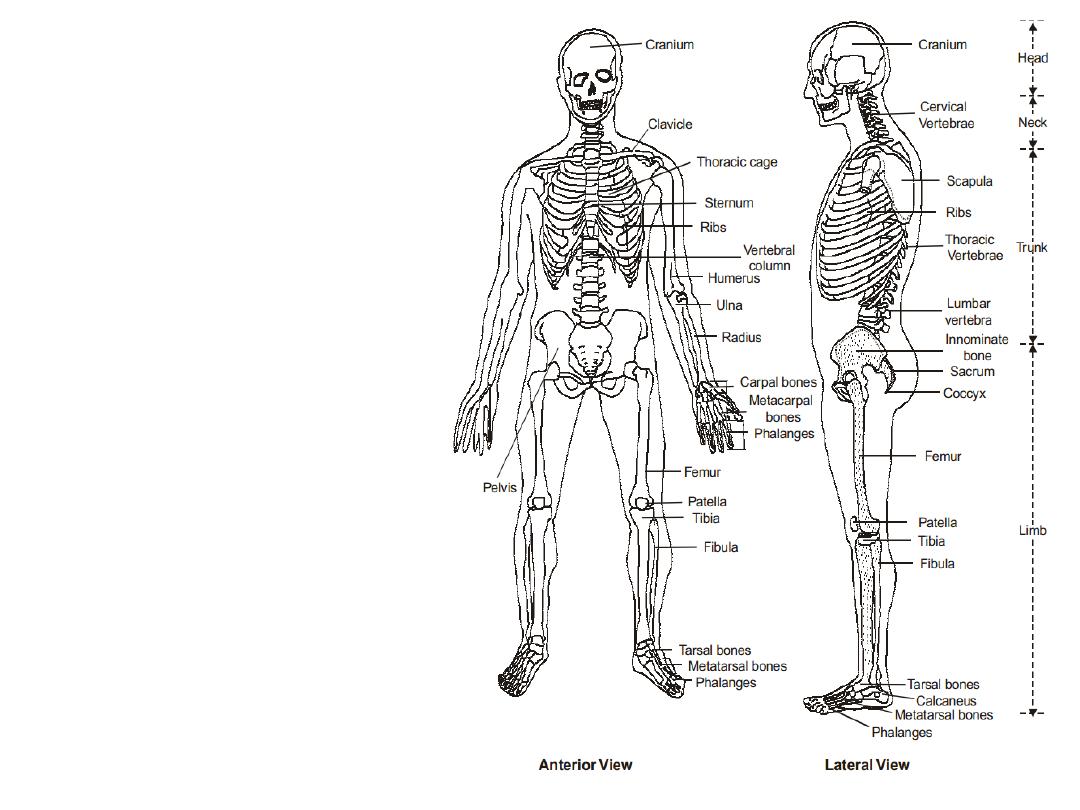
Skeletal system
The axial skeleton runs along the
body’s midline axis and is made up
of 80 bones in the following
regions:
Skull
Hyoid
Auditory ossicles
Ribs
Sternum
Vertebral column
The appendicular skeleton is made
up of 126 bones in the following
regions:
Upper limbs
Lower limbs
Pelvic girdle
Pectoral (shoulder) girdle
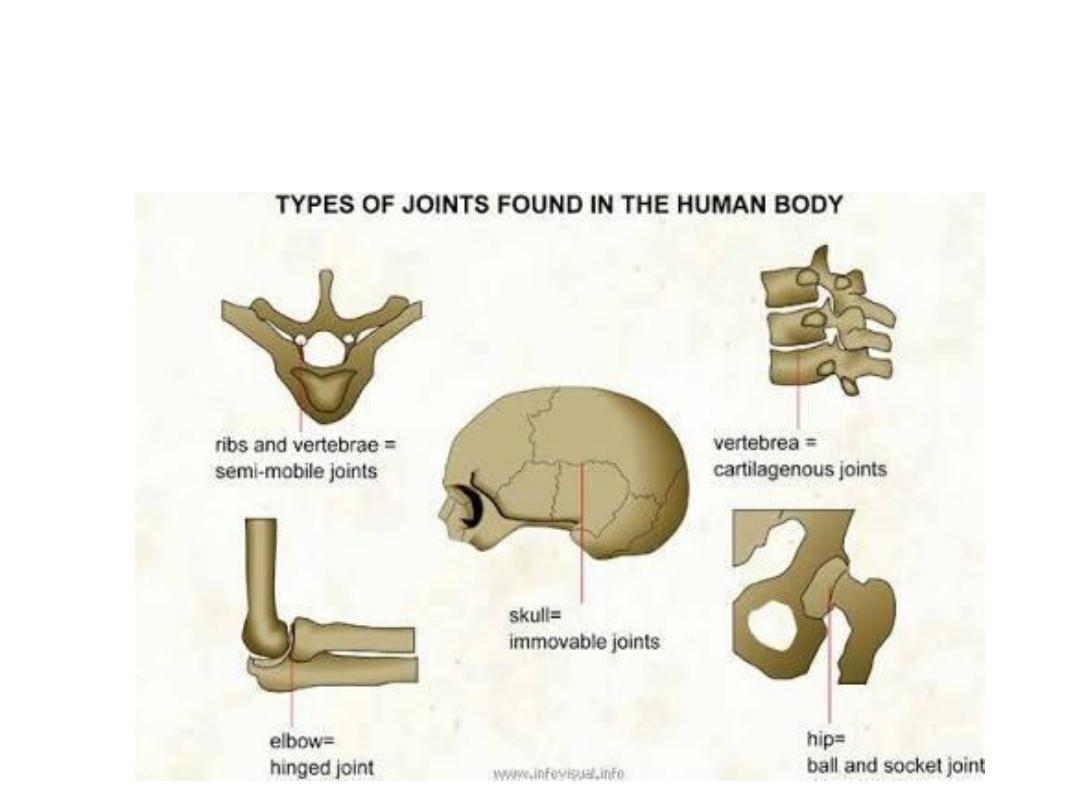
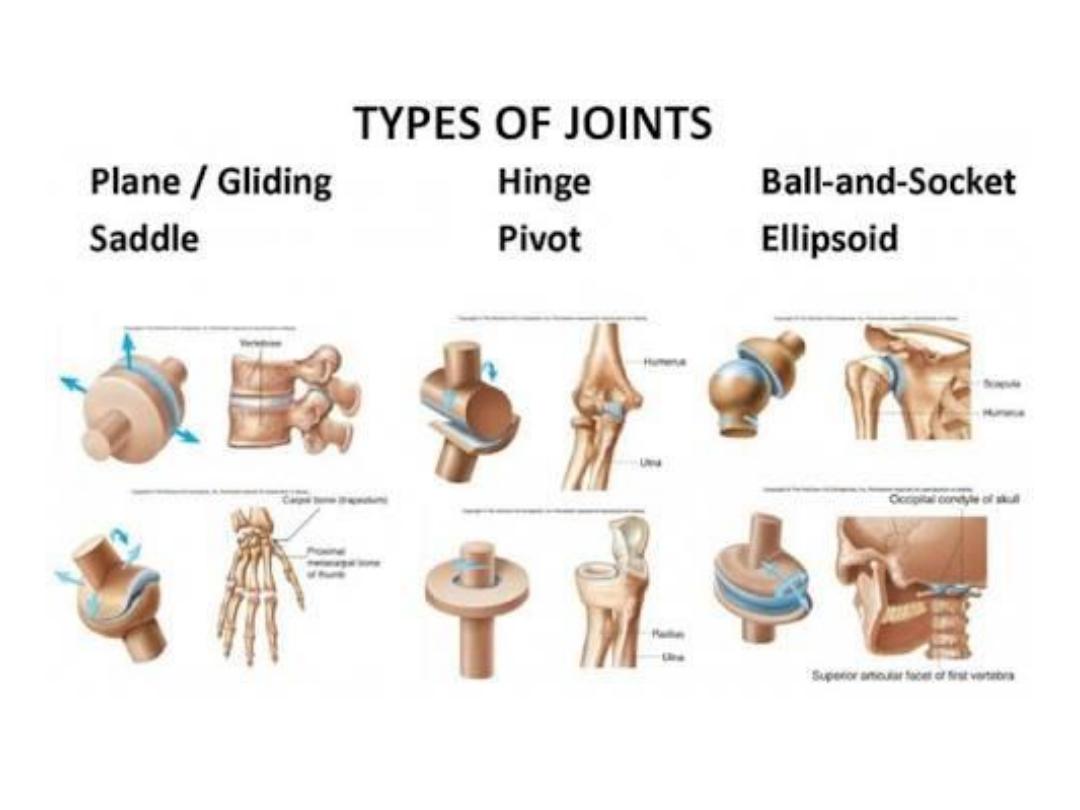
Joints
Fibrous Joint -non movable. eg: skull
Cartilaginous Joint –chest bone, vertebrae
Synovial Joint – elbow,knee,hip,shoulder,finger
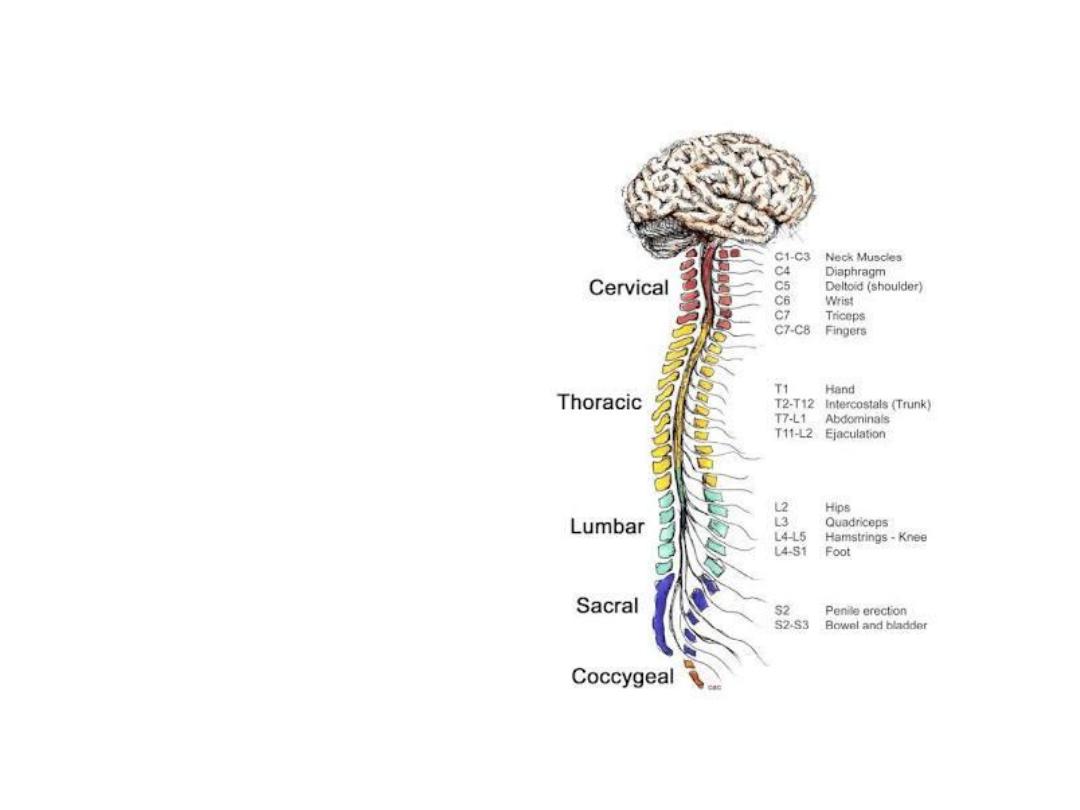
• Vertebral column
• Total 33
vertebrae
• Cervical 7
• Thoracic 12
• Lumber 5
• Sacral 5
• Coccygeial
4
Vertebral column
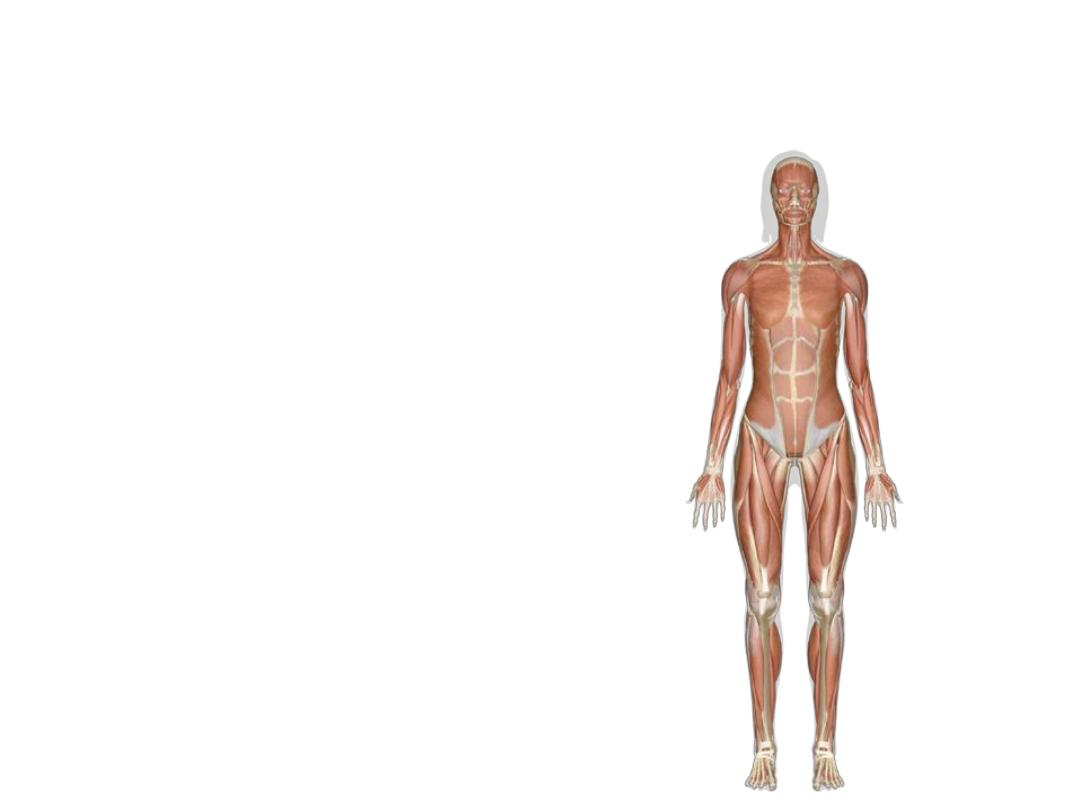
Muscular system
There are three types of
muscle tissue:
Visceral
Stomach, intestines, blood vessels
Cardiac
Heart
Skeletal
Muscles attached to two bones across
a joint
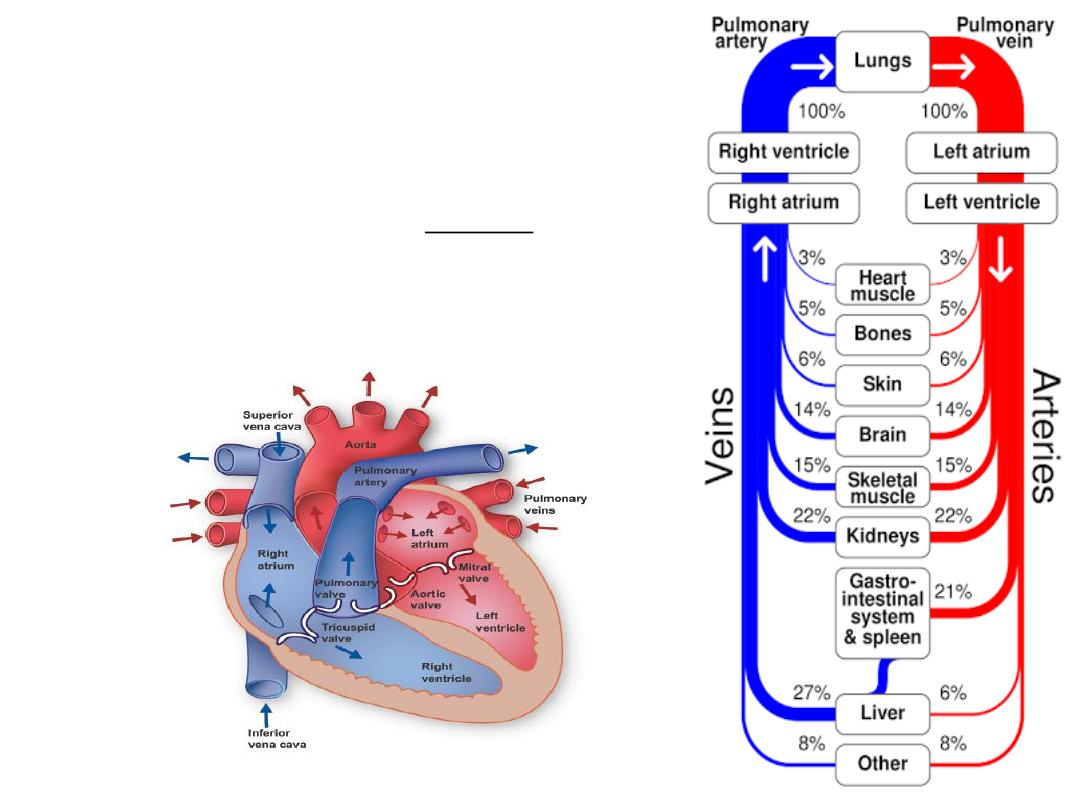
Cardiovascular system
Anatomy
• The Heart
• Circulatory Loops
• Blood Vessels
• Coronary Circulation
• Hepatic Portal Circulation
• Blood
Functions
Transportation
Protection
Regulation
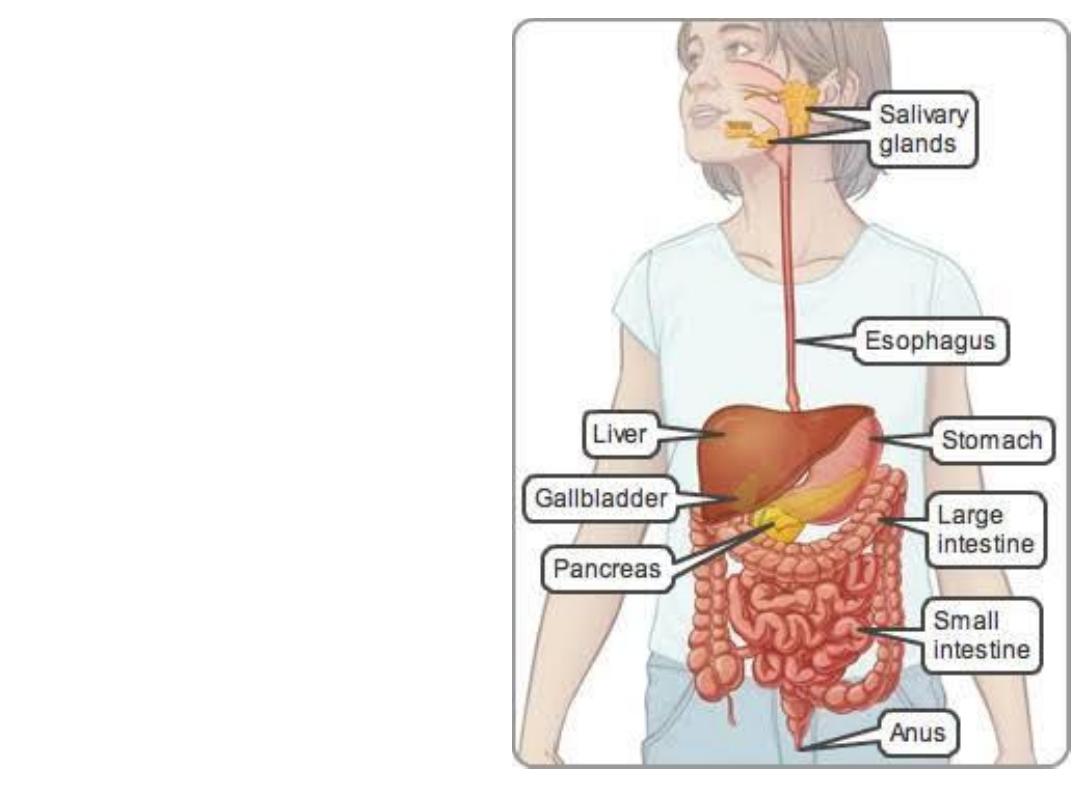
Digestive system
Anatomy
Mouth-Pharynx –
Esophagus – Stomach -
Small Intestine - Liver and
Gallbladder – Pancreas -
Large Intestine - Rectum
Physiology
Ingestion
Secretion
Mixing and movement
Digestion
Absorption
Excretion
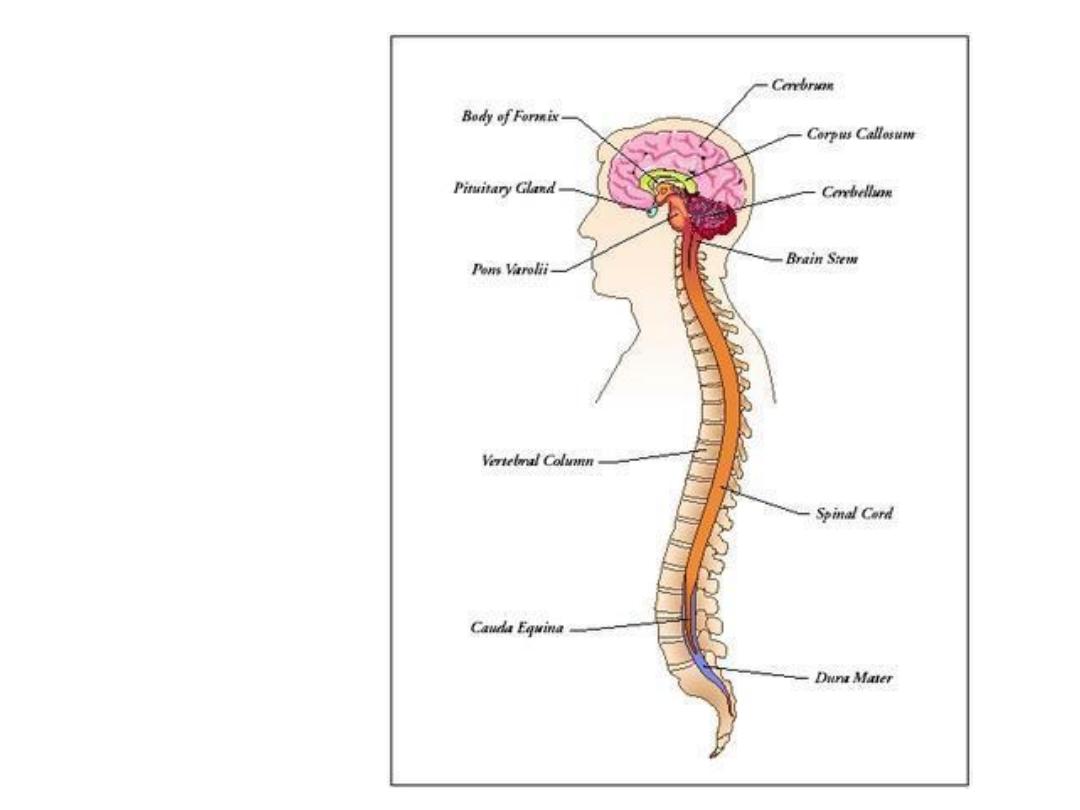
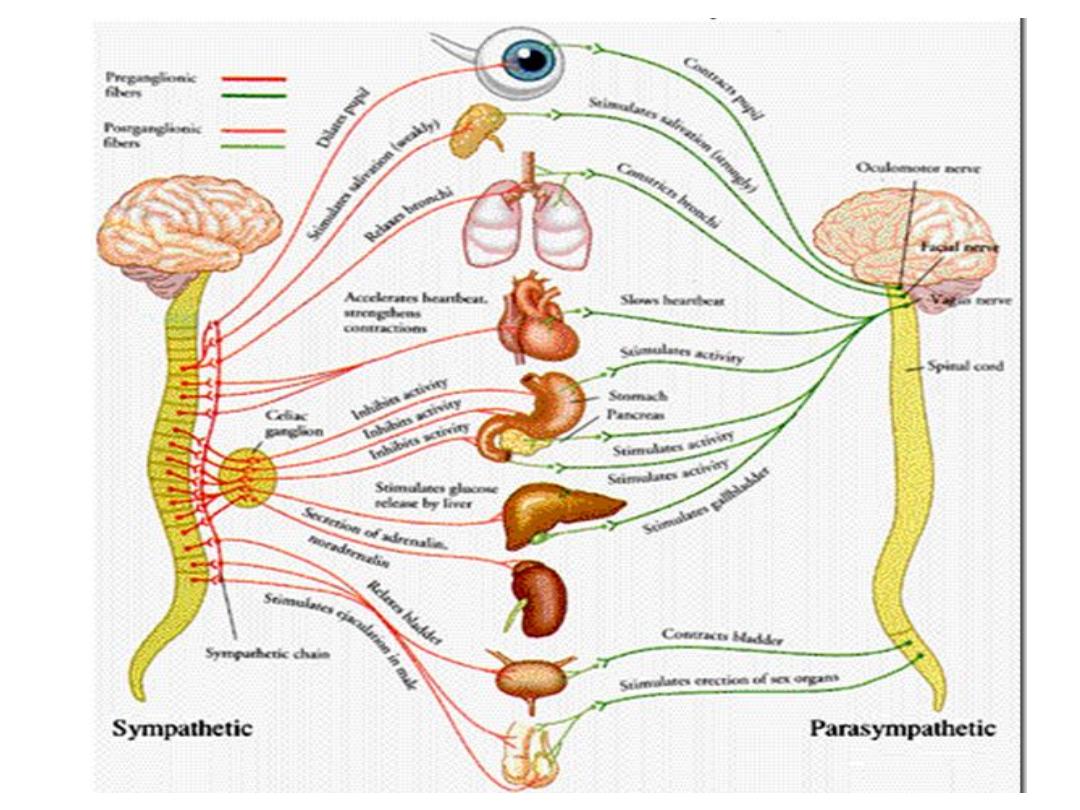
Nervous
system
Anatomy
Nervous tissue
Brain
Spinal cord
Nerves
Meninges
Cerebrospinal fluid
Sense organs
Physiology
Sensory
Integration
motor
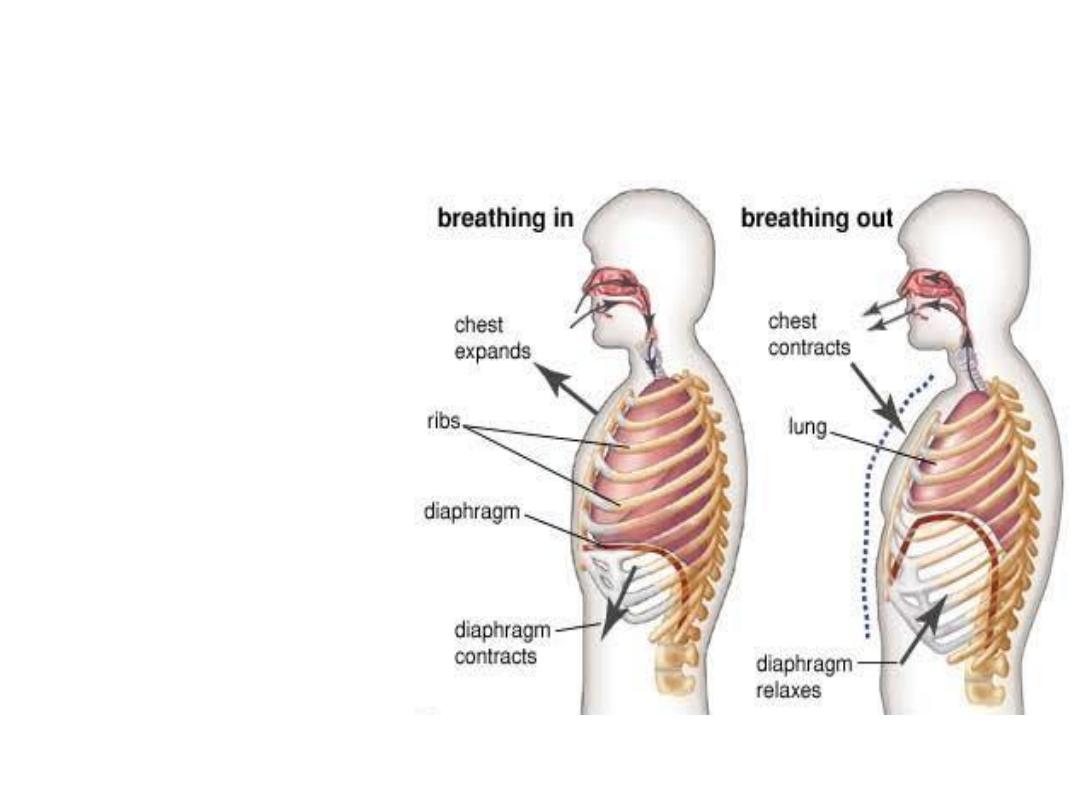
Respiratory system
Anatomy
Nose and Nasal Cavity,
Mouth, Pharynx, Larynx,
Trachea, Bronchi and
Bronchioles, Lungs,
Muscles of Respiration
Physiology
Pulmonary Ventilation,
External respiration,
Internal respiration,
transportation of gases,
Homeostatic Control of
Respiration
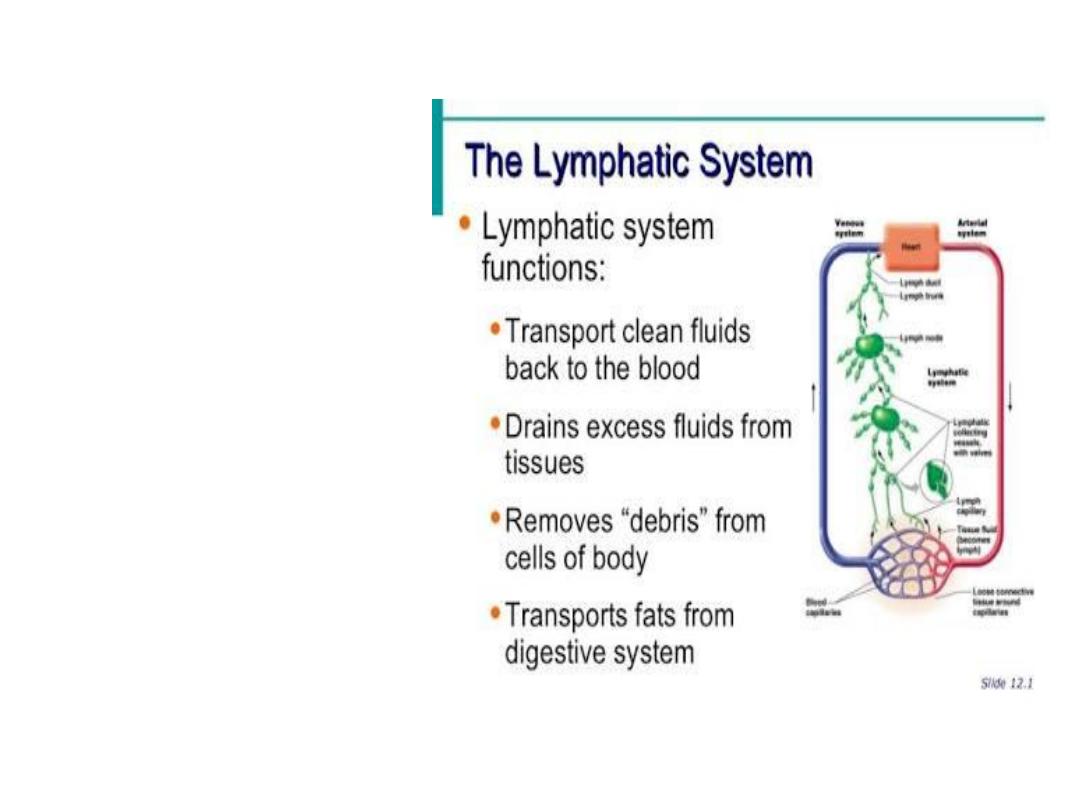
Immune / Lymphatic system
Anatomy
Spleen ,Thymus ,
Lymphatic Vessels,
Lymph Nodes,
Lymphatic Ducts,
Tonsils
Physiology
Defends against
infection, Return
tissue fluids to
the blood stream
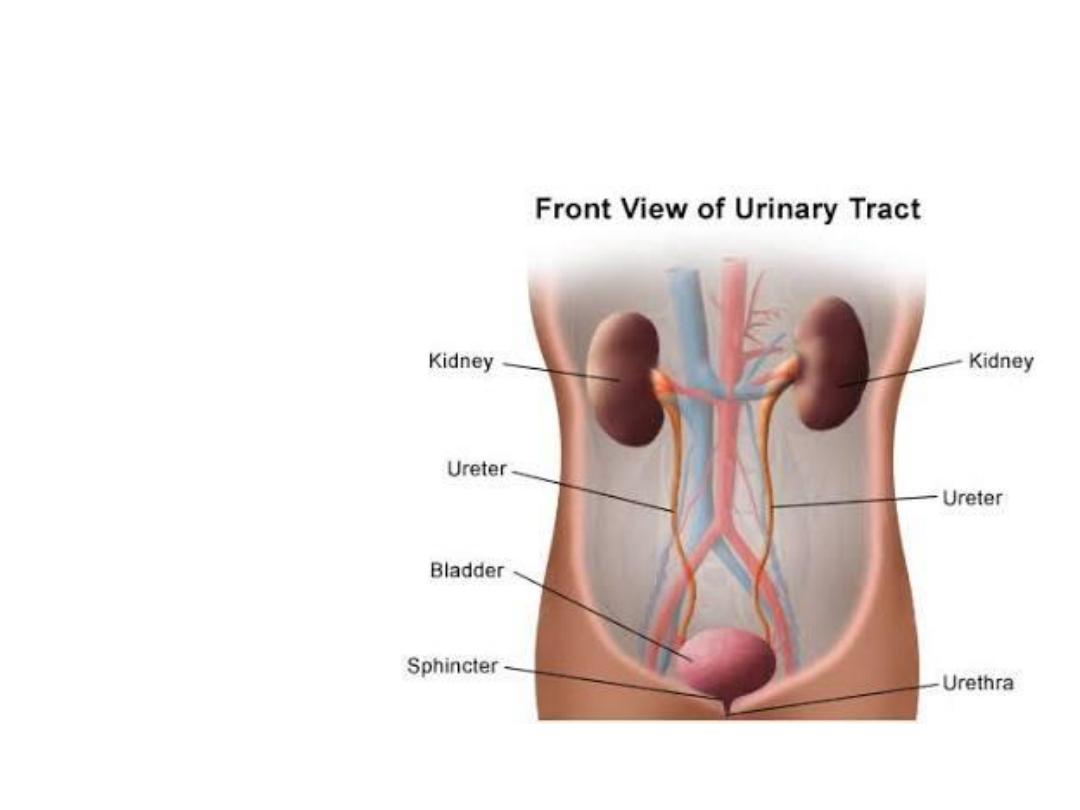
Urinary system
Anatomy
Kidneys
Ureter
Urinary bladder
Urethra
Physiology
Maintenance of
Homeostasis
Filtration
Storage and Excretion
of Wastes
Production of
Hormones
