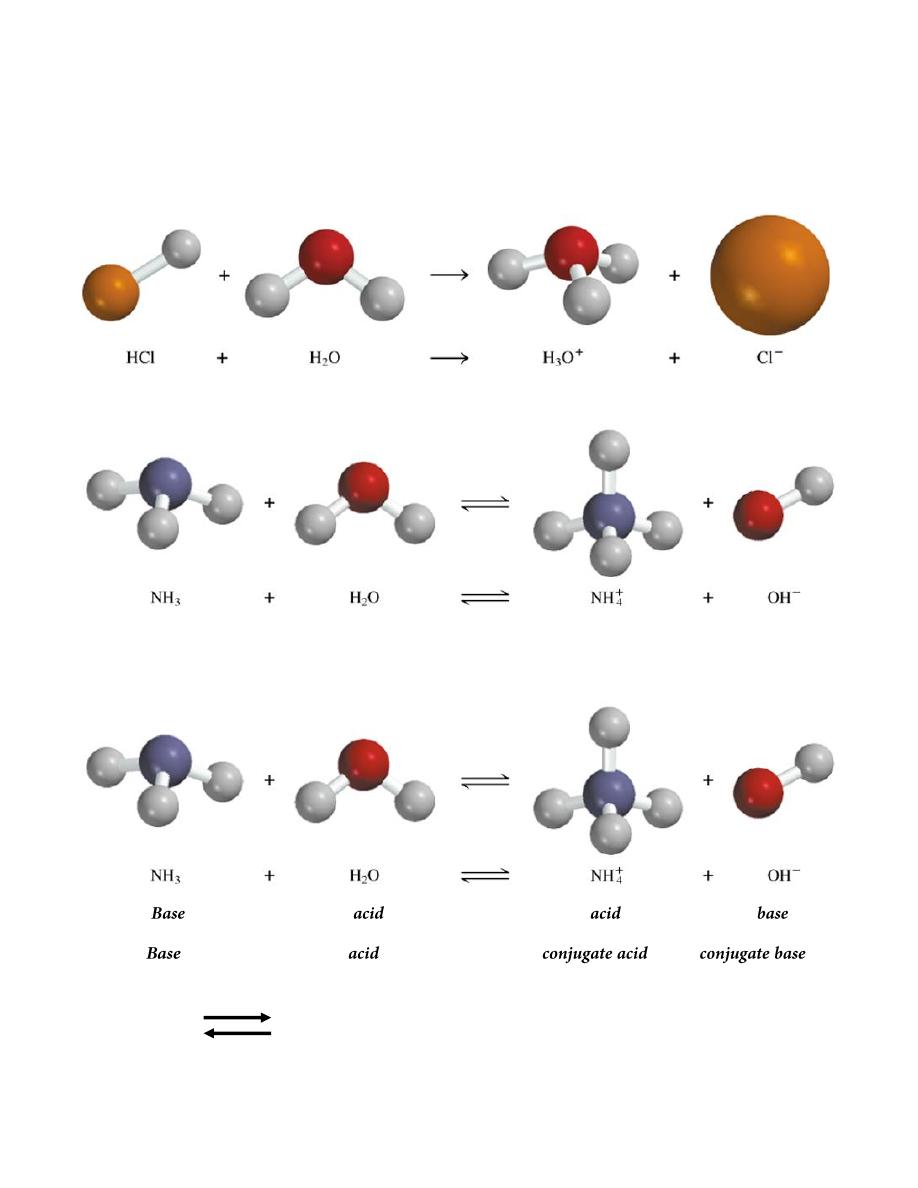
Acids and Bases
Arrhenius acid is a substance that produces H
+
(H
3
O
+
) in water
Arrhenius base is a substance that produces OH
-
in water
A Brønsted acid is a proton donor
A Brønsted base is a proton acceptor
Acid-Base Properties of Water
autoionization of water
H
2
O
(l)
H
+
(aq)
+ OH
-
Base Conjugate Acid
Acid conjugate base
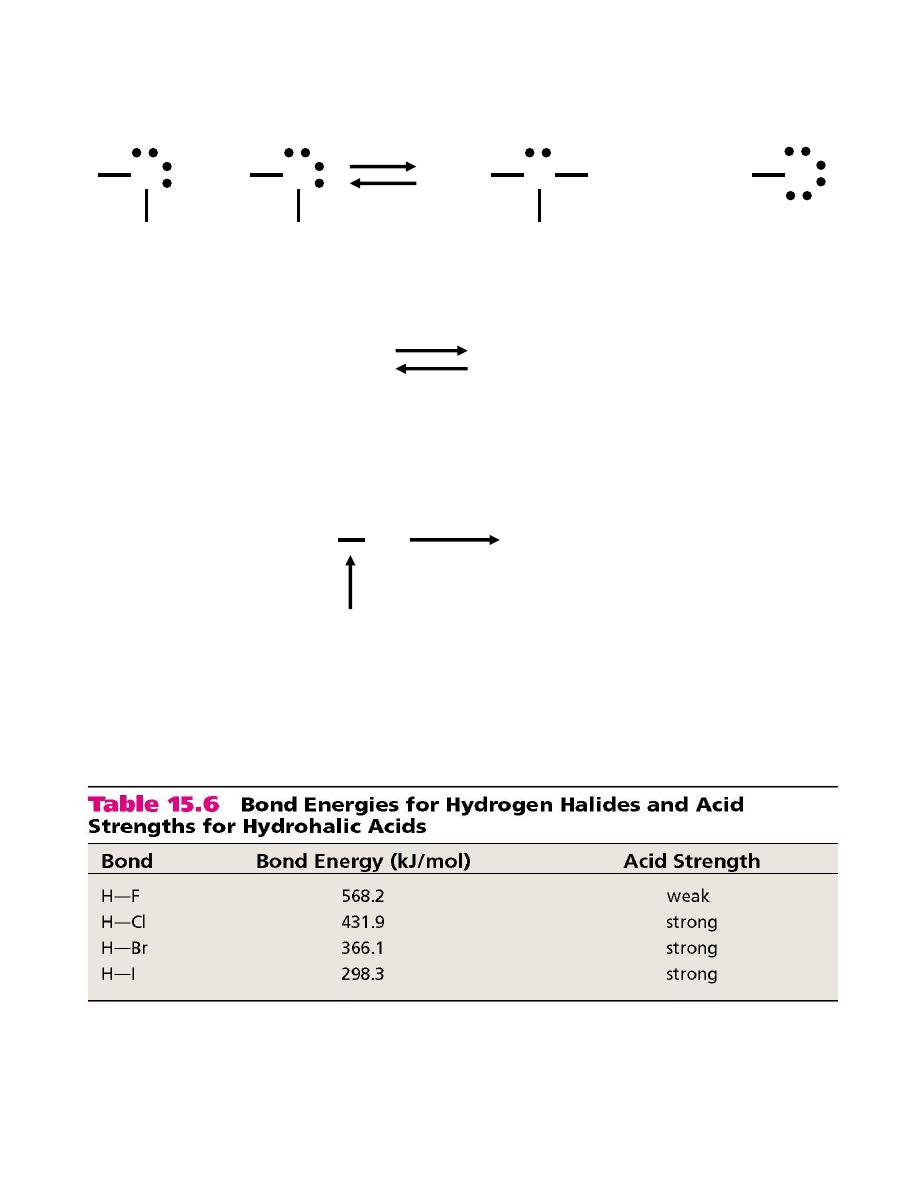
Molecular Structure and Acid Strength
HF << HCl < HBr < HI
Molecular Structure and Acid Strength
O
H
H
+
O
H
H
O
H
H
H
O
H
-
+
[
]
+
H
2
O + H
2
O H
3
O
+
+ OH
-
H X
H
+
+ X
-
The
stronger
the bond
The
weaker
the acid
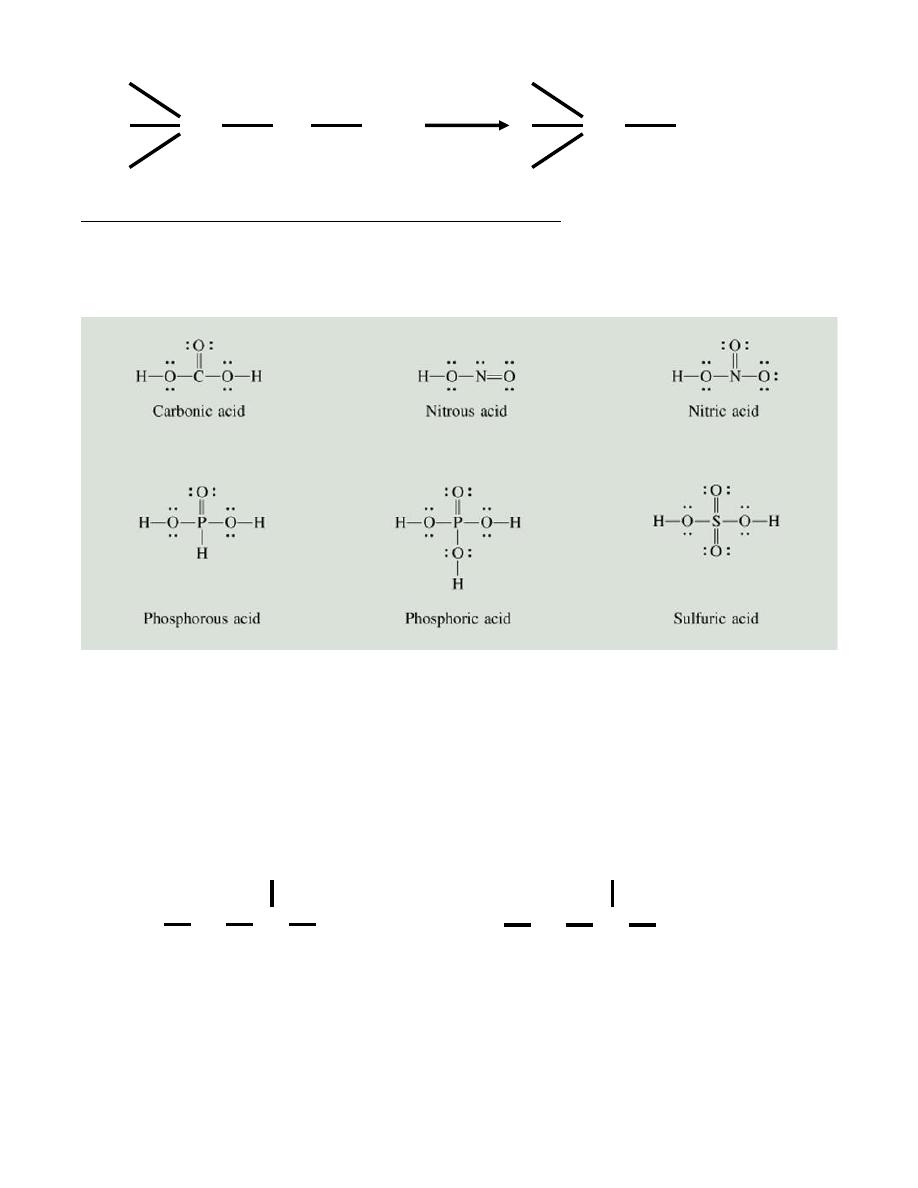
The O-H bond will be more polar and easier to break if:
• Z is very electronegative or
• Z is in a high oxidation state
1. Oxoacids having different central atoms (Z) that are from the same group and that
have the same oxidation number.
Acid strength increases with increasing electronegativity of Z
Cl is more electronegative than Br4
Z
O
H
Z
O
-
+
H
+
-
+
H O Cl O
O
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
H O Br O
O
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
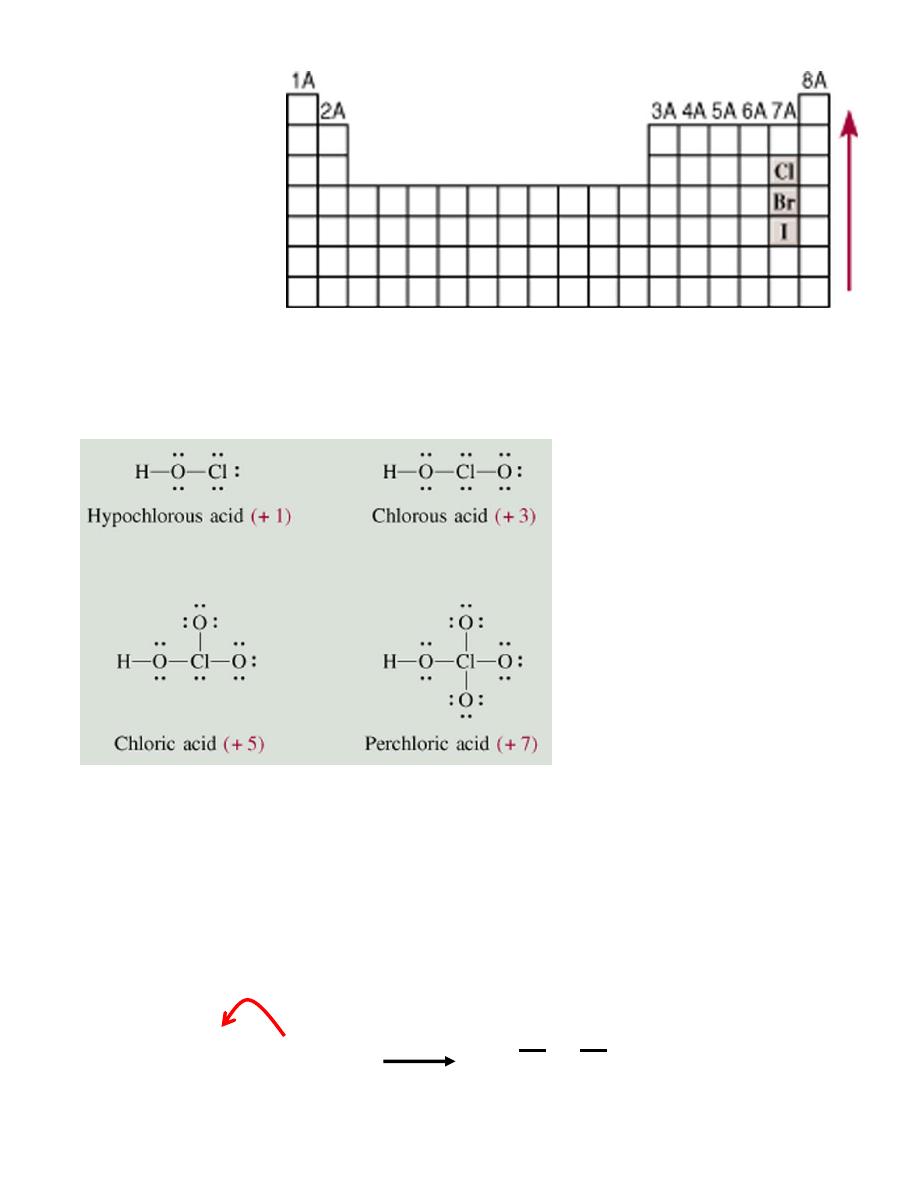
HClO
3
> HBrO
3
2. Oxoacids having the same central atom (Z) but different numbers of attached groups.
Acid strength increases as the oxidation number of Z increases.
HClO
4
> HClO
3
> HClO
2
> HClO
Definition of An Acid
Arrhenius acid is a substance that produces H
+
(H
3
O
+
) in water
A Brønsted acid is a proton donor
A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons
A Lewis base is a substance that can donate a pair of electrons
Acid Base
H
+
H O H
•
•
•
•
+ OH
-
•
•
•
•
•
•
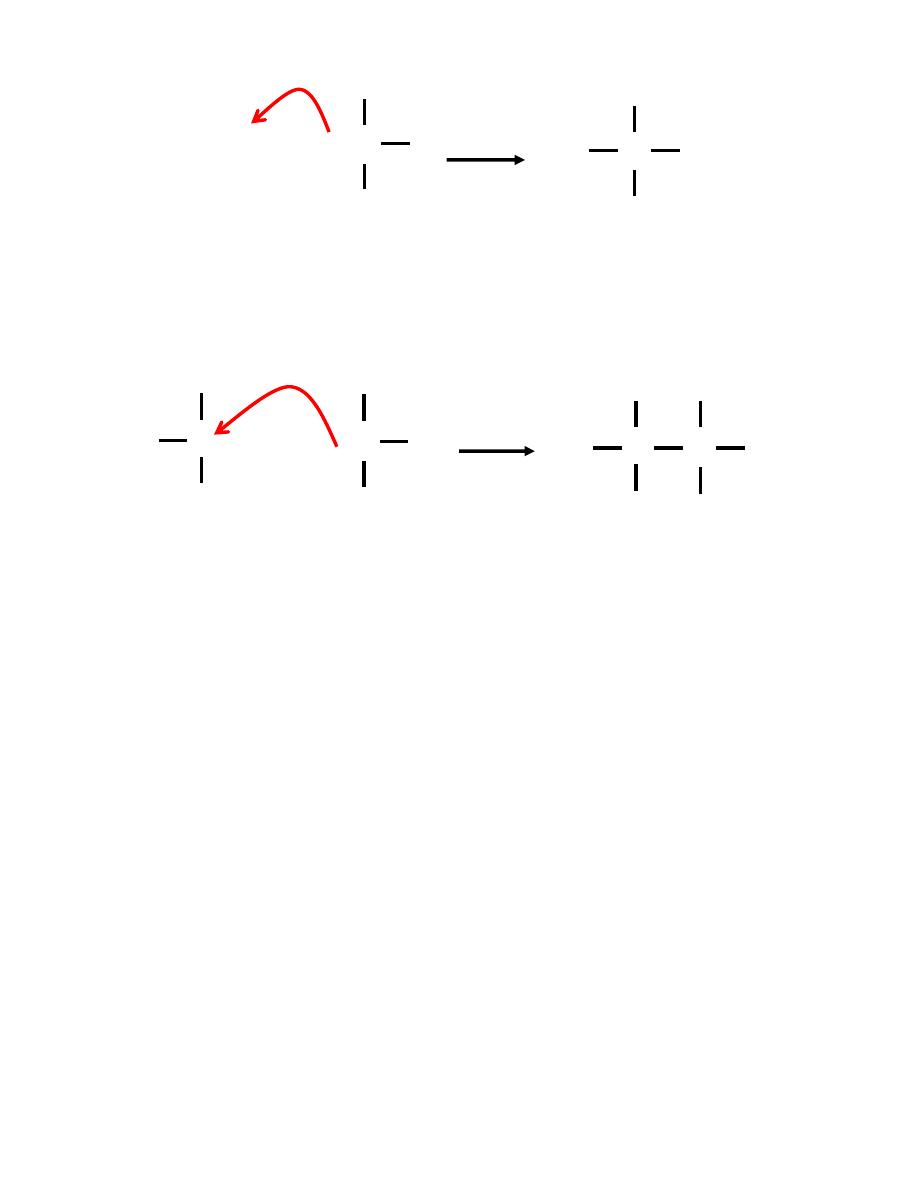
Lewis Acids and Bases
No protons donated or accepted!
Let’s look at this reaction, and others like it more closely.
To see what’s really going on we need to look at the MOs.
According to
Arrhenius, an acid is any substance that produce H
+
ions in a solution
HCl → H
+
+ Cl
-
It is the Hydrogen ion (H
+
) that is produced that makes HCl an acid.
Some other common acids include:
HNO
3
nitric acid
H
2
SO
4
sulphuric acid
HC
2
H
5
O
2
acetic acid
H
3
C
6
H
5
O
7
citric acid
Note the H
+
at the beginning of each formula
These are the acidic Hydrogen. The ones that separate in solution
A base is any substance that produce hydroxide ion (OH
-
) when it dissolved in water. For example :
NaOH → Na
+
+ OH
-
N H
•
•
H
H
H
+
+
N H
H
H
H
acid
base
N H
•
•
H
H
acid
(electrophile)
base
(nucleophile)
F B
F
F
+
F B
F
F
N H
H
H

Is produced that makes NaOH a base .
Some common base include:
KOH potassium hydroxide
Ca(OH)
2
calcium hydroxide
NH
3
amonia
Q- How can NH
3
be abase when it does not contain a hydroxide/
Remember, the definition of abase says that it must produce OH
-
ions when it dissolves in water. It
does not necessary have to contain the OH
-
ion.
NH
3
react with water molecules to produce NH4 ions and OH
-
ions, so it is considered a base
NH
3
+ H
2
O → NH
4
+
+ OH
Buffer solution
When a week acid is dissolved in water the acid partially dissociates into a hydrogen ion
and a conjugate base. The molecular acid, hydrogen ion and base in equilibrium
:
CH
3
COOH ↔ H
+
+CHOO
When a base is added to the buffer, the OH
-
combine with the H
+
in solution , forming
water. The acid molecular dissociates releasing more H
+
and CH
3
COO
-
. The pH remains
constant.
CH
3
COOH ↔ H
+
+CH
3
COO
-
H
+
+CH
3
COO
-
+ OH
-
↔
CH
3
COOH +H
2
O
