د.صفية الجلبي
Lec. 1,2,3
علوم سلوكية
Life Cycle Growth and Development
Is the scientific study of the changes that occur in people as they age, from conception until death.
Nature versus nurture
Nature: refers to heredity, the influence of inherited characteristics on:
Personality
Physical growth
Intellectual growth, and
Social interactions
Nurture: refers to the influence of the environment on all of those same things and includes:
Parenting stile,
Physical surroundings,
Economic factors, and
Anything that can have an influence on development that does not come from within the person.
Most developmental psychologist agree that the most likely explanation for most human development is based on the interaction between nature and nurture.
Behavioral genetics: is relatively new field that attempts to identify genetic basis of behavior. (try to determine how much of behavior is the result of genetic inheritance and how much is due to a person’s experiences).
Prenatal development
From conception to the actual birth of the baby
It is a period of approximately 9 months,
during which a single cell becomes a complete infant.
It is also during this time that many things can have a positive or negative influence on the developing infant.
Infancy and childhood development
Preferential looking:
The longer an infant spends looking at stimulus, the more the infant prefers that stimulus over others.
Habituation:
Is the tendency for infant (and adult) to stop paining attention to a stimulus that does not change.
Physical development
Respiratory system begin to function.
The blood circulate only within the infant’s system.
Temperature regulated by:
Infants own activity
Body fat (act as insulation).
The digestive system takes the longest time to adjust to life outside the womb.
Reflexes
Innate,
Involuntary behavior
existing from birth
It is a means of interaction with the surrounding world.
Help the infant to survive
Used to determine whether nervous system is working properly.
It is a five reflexes:
Grasping
Startle (moro)
Rooting
Stepping
sucking
Motor development
Infant manage a tremendous amount of development in motor skills from birth to about 2 years of age (milestone).
An infant may reach these milestones earlier or later than the average and still be considered to be developing normally.
Infant sensory abilities
Touch
Skin to womb contact in the last months of pregnancy
Smell
Differentiate between Mother’s milk scent & another woman’s milk scent within few days after birth.
Taste
At birth preference for sweet.
At 4ms preference for salty.
Hearing
Vision
Cognitive development
5 years
Brain : 90% of its adult wt
Development of:
#Thinking
#Problem solving
#memory
5 years
Brain : 90% of its adult wt
Development of:
#Thinking
#Problem solving
#memory
2 years
Brain triples its wt
Brain: 75% of its adult wt
Piaget’s theory
Pioneered by Jean Piaget.
Jean Piaget developed his theory from detailed observations of infants and children most especially his own three children.
Piaget believe that children form mental concept or “schemes” as they experience new situation or events.
Piaget also believe that children first try to understand new things in terms of schemes they already possess, a process called “assimilaton”.
The process of altering or adjusting old schemes to fit new information and experiences is “accommodation”.
Piaget’s stages of cognitive development
Cognitive developmentAge
Stage
Children explore the world using their senses and ability to move. They develop object permanence & the understanding that concepts and mental images represent objects, people, and events (symbolic thought).
Birth 2yrs
Sensorimotor
1
Young children can mentally represent and refer to object and event with words or pictures (use language) and they can pretend .however, they can’t conserve , logically reason, or simultaneously consider many characteristic of an object (centration), or unable to mentally reverse actions ( irreversibility).
Another limitation is “ egocentrism”, the unability to see the world through any one else’s eyes but one’s own.
They believe that any thing that move is alive (animism).
They tend to believe that what they see is literally true, (e.g. Santa Claus)
27 yrs
Preoperational
2
Children at this stage able to conserve, reverse their thinking, and classify object in terms of their many characteristic.
They can also think logically and understand analogies but only about concrete events.
712 yrs
Concrete operational
3
People at this stage can use abstract reasoning about hypothetical events or situation, think about logical possibilities, use abstract analogies, and systematically examine and test hypotheses. Not everyone can eventually reason in all these ways.
12yrs adult-
Hood
Formal operational
4
Language Development
Child directed speech: the way adults and older children talk to infants and very young children, with higher pitched, repetitious, sing-song speech pattern.
Receptive-productive lag: Infants seem understand far more than they can produce.
Autism spectrum disorder
It is a neurodevelopmental disorder.
It cause problems in
Thinking
Feeling
Language
Social skills
Causes are still being investigated but do not appear to be linked childhood immunization.
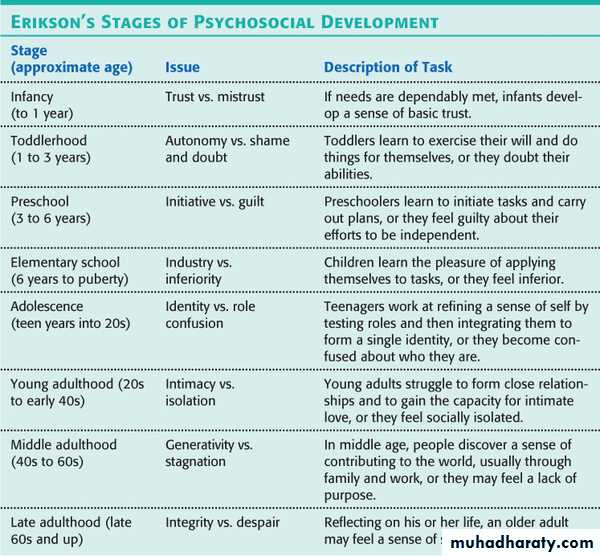
Psychosocial development
TemperamentThe behavior and emotional characteristics that are fairly established at birth.
Thomas and Chess have identified three basic temperament styles of infant:
AttachmentThe emotional bond that forms between an infant and primary care giver.
Attachment is an important first step in forming relationships with others.
Usually forming with in the 1st 6 ms.
During the 2nd 6 ms can be showing up in a no. of ways:
Stranger anxiety (wariness of stranger)
Separation anxiety (fear of being separated from the caregiver)
Harlow and contact comfort
Psychologist at first assumed that attachment to the mother occurred because the mother was associated with satisfaction of primary drives (hunger & thirst).
food __________ 1ry reinforcer (primary drive).
mother __________ 2ry reinforcer (pleasurable feeling).
Psychologist Harry Harlow felt that attachment had to be influenced by more than just the provision of food.
Harlow and his colleagues conclude that contact comfort was an important basic affectional or love variable.
Harlow ‘s work represent one of the earliest investigations into the importance of touch in the attachment process and remains an important study in human development.
adolescence
adolescence
Physical development in adolescence
Physical development in adolescenceCognitive development in adolescence
Piaget’s formal operations revisedAbstract thinking become possible
Thinking about hypothetical situation (teenagers).
Egocentric thought (preoccupied with their own thoughts).
They do a lot of introspection (turning inward).
Convinced that their thoughts are as important to others as they are to themselves.
Personal fable (they are special, they feel unique).
Imaginary audience (every one is looking at them, they are the center of everyone else world, just as they are the center of their own).
Physical development (use it or lose it)
Physical development (use it or lose it)Cognitive development
Cognitive development
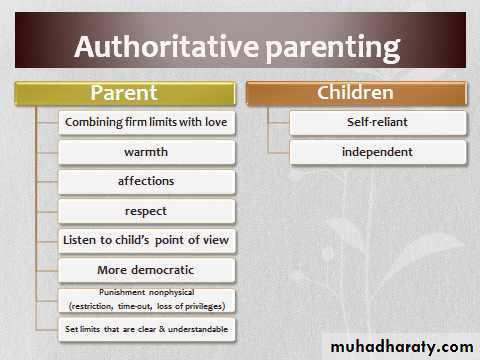
Parenting style
Parenting stylePsychosocial development
Psychosocial development