Carbohydrate metabolism
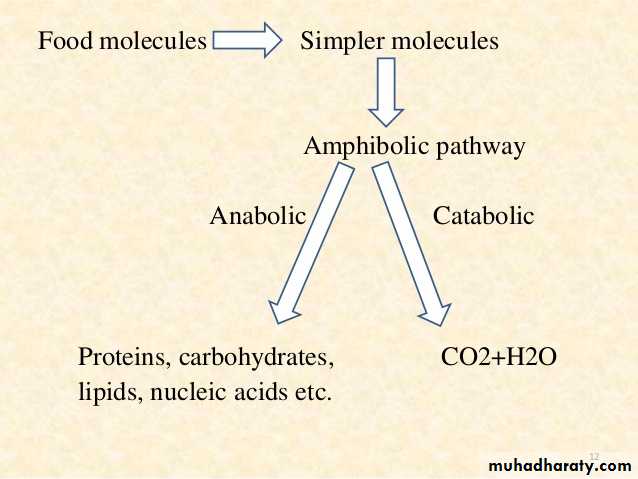
The mechanism of storing the energy available from outside so that it can be spent in installments when the energy source is not there, and the mechanism of converting the stored form in to active energy to utilize for useful purpose for the activities to carry on is called metabolism.Carbohydrates form a most important source of the activities in the body. The various biochemical processes responsible for the formation, breakdown, and The conversion of carbohydrates in to smaller sugars which will help in easily getting converted in to energy with the help of enzymes and hormones is the carbohydrate metabolism.
What is The Function of Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates have verities of functions and in human context the functions are more varied:1- Carbohydrates help supply instant energy for all kinds body functions and each gram of carbohydrates yields 4000 calories irrespective of source
2- Carbohydrates provides the carbon chain for non-essential amino acids synthesis
3- Carbohydrates are essential for the oxidation of fats
4- Carbohydrates when taken in adequate amount could help in sparing protein
5- Carbohydrates help in providing flavour to the daily diet
6- Carbohydrates are present in the tissues as constituents
7- Carbohydrates is a major part in energy requirements of the body
8- Carbohydrates derivatives acts as precursor to nucleic acid compounds, connective tissues and nervous tissue galactosides
9- Carbohydrates are very much essential for proper functioning of the central nervous system. Adequate storage of hepatic glycogen helps in detoxifying a normal liver
10- Carbohydrates help in synthesising glycol-proteins and glycolipids
11- Carbohydrates is basically the main fibre of the diet or provide the bulk fibre for better digestion.
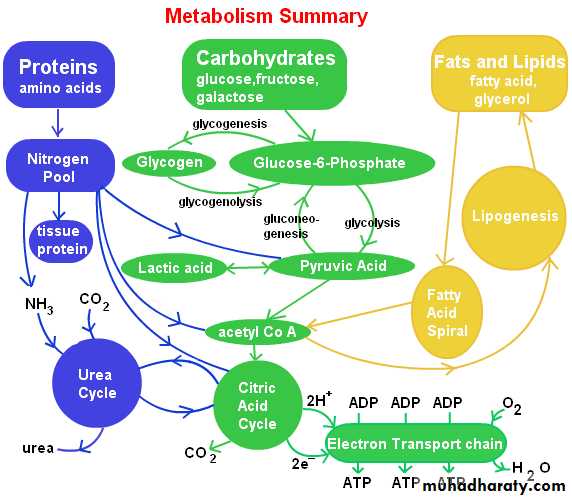
Metabolic pathways
1- Glycolysis
2- Citric acid cycle
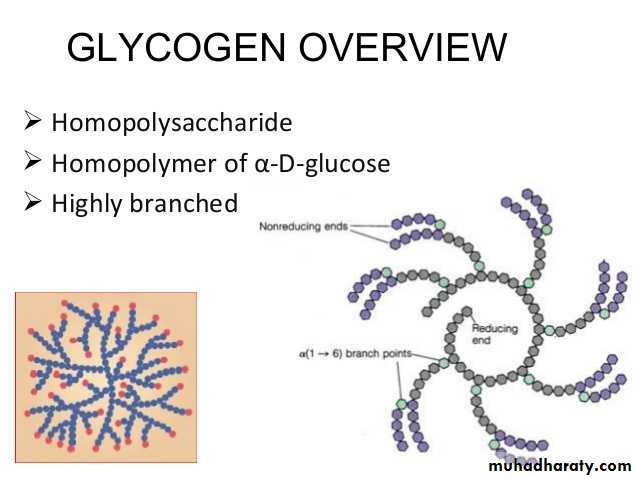
3- Glycogenolysis
4- Glycogenesis
5- Gluconeogenesis
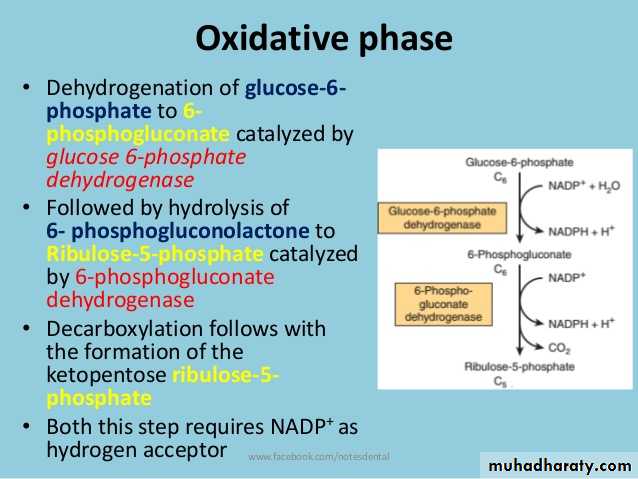
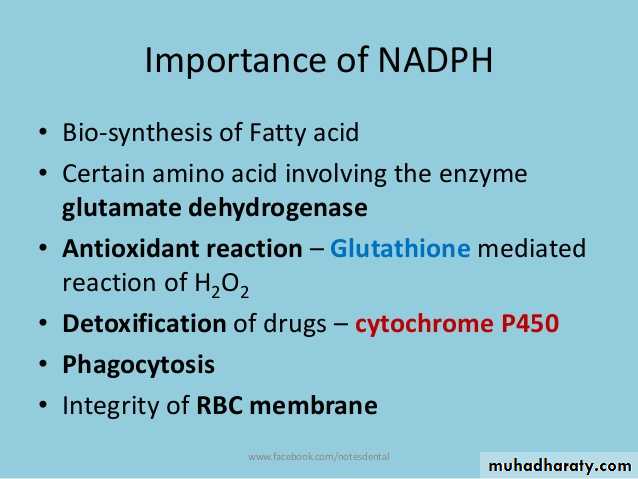
6- Pentose phosphate pathway
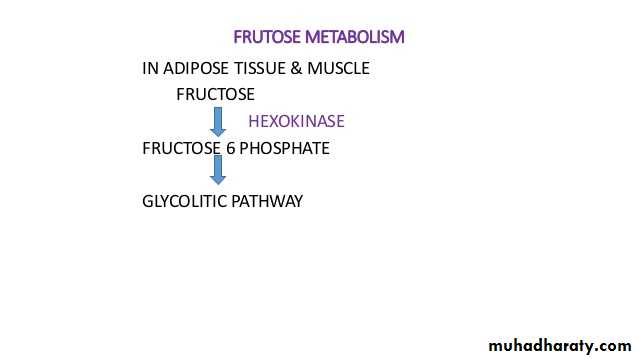
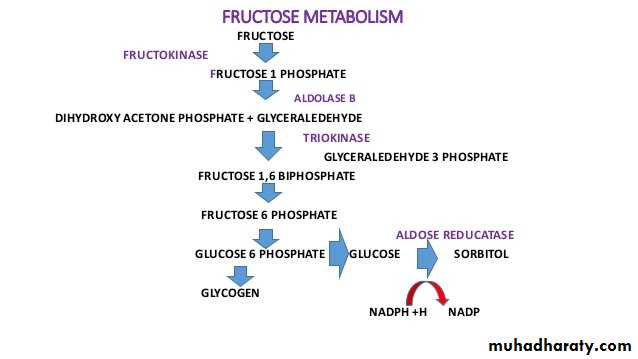
7- Fructose metabolism
8- Galactose metabolism
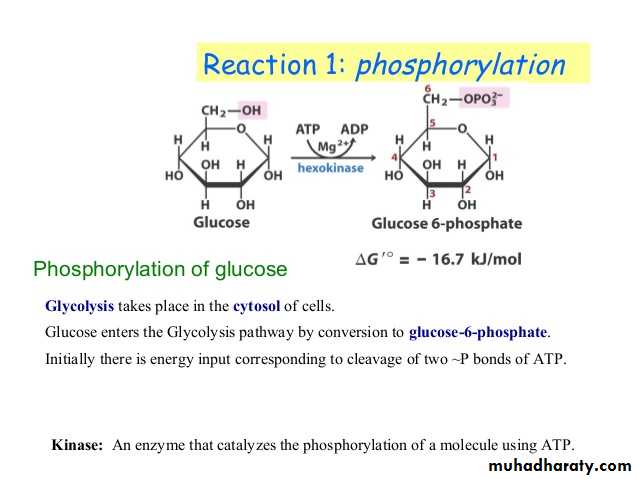
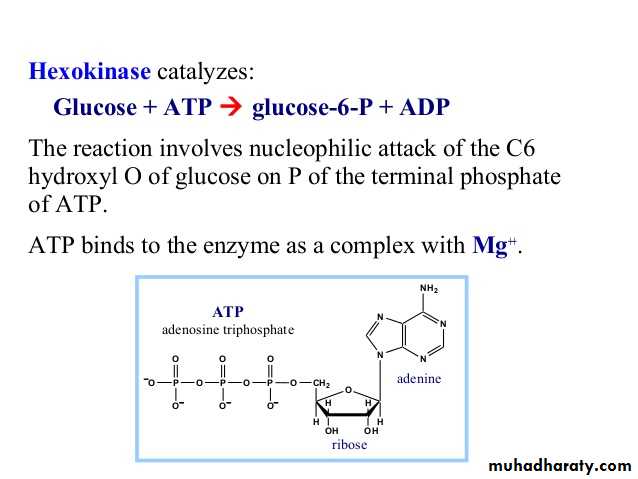
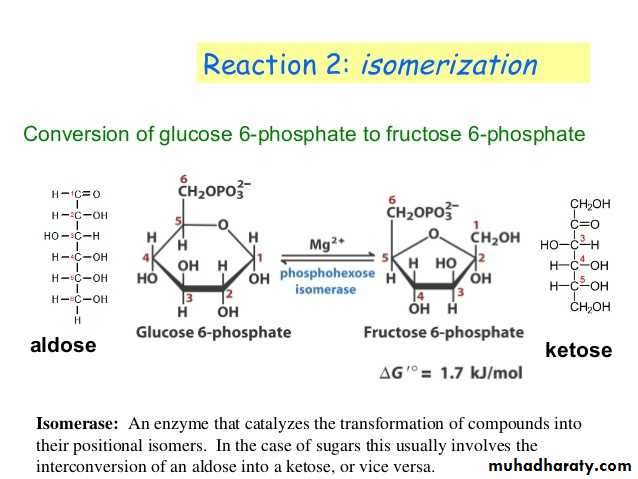
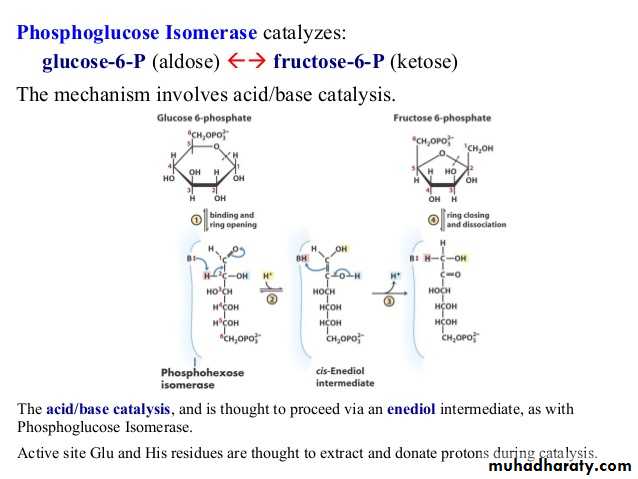
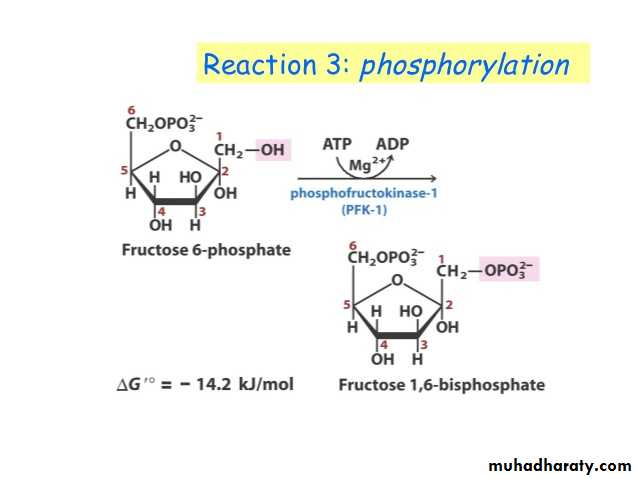
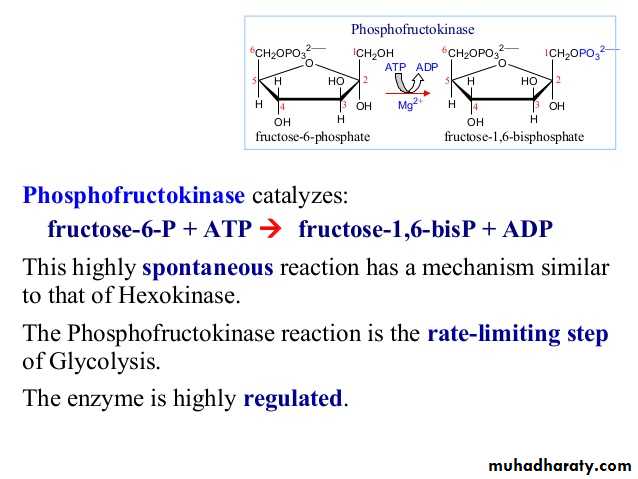
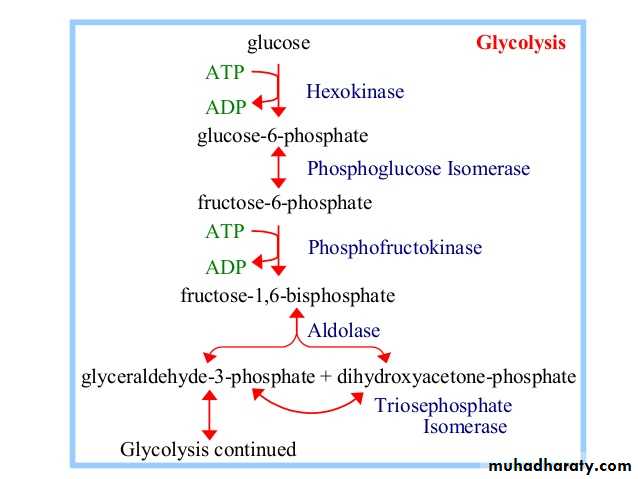
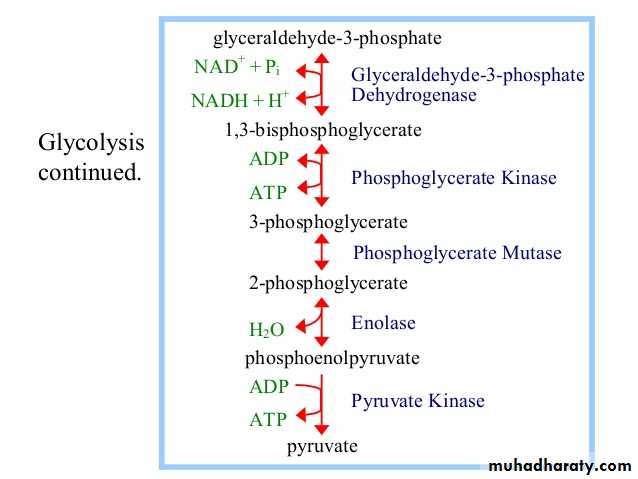
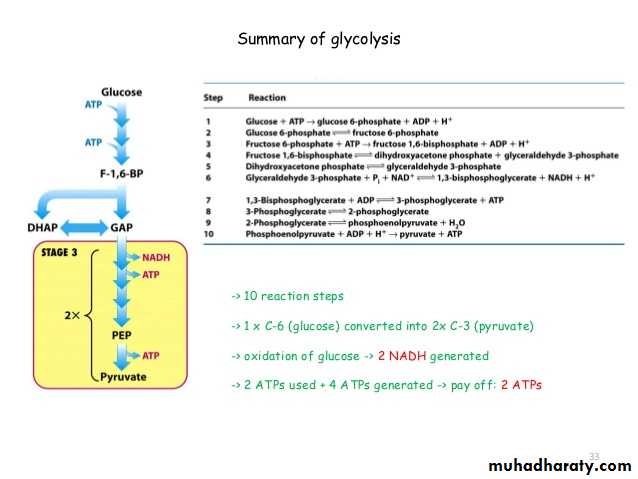
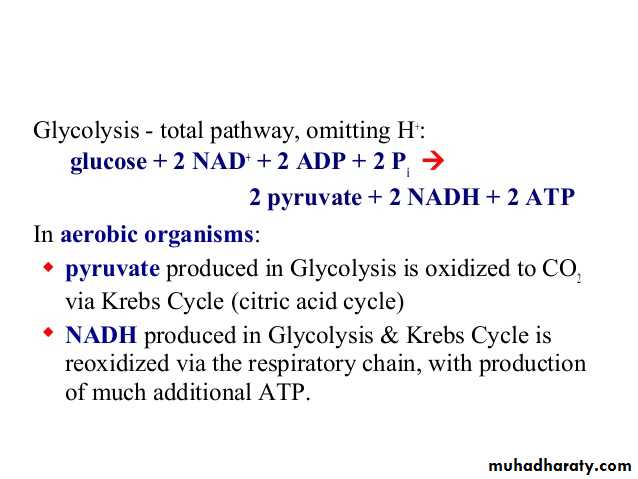
Glycolysis 1-
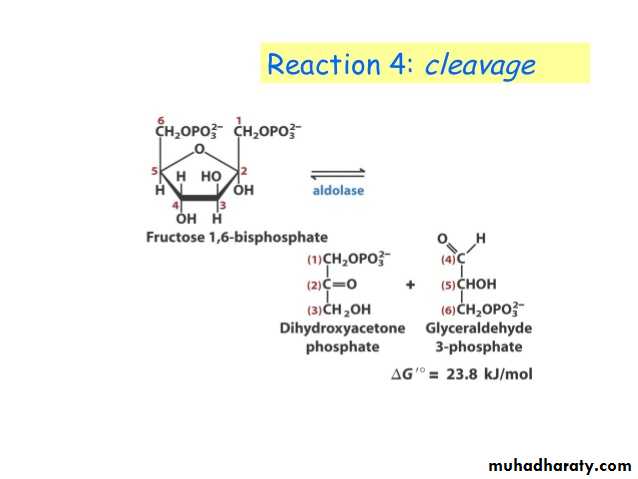
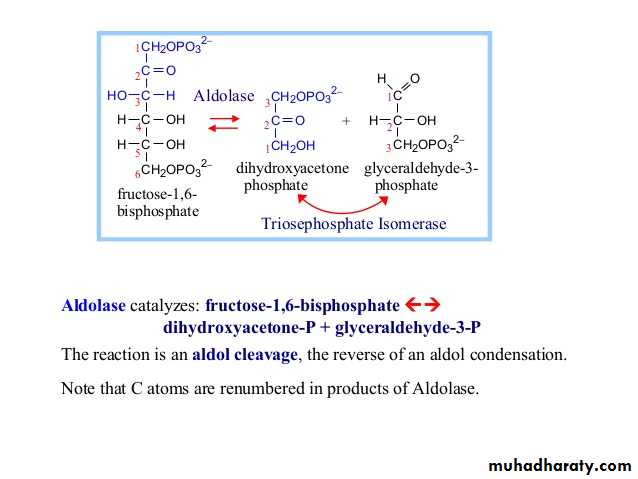
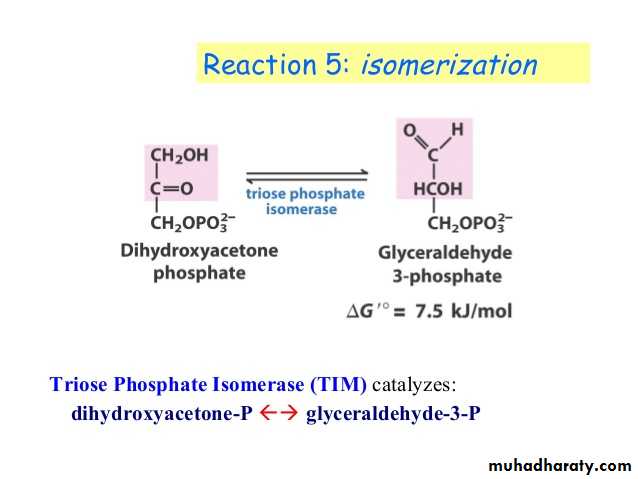
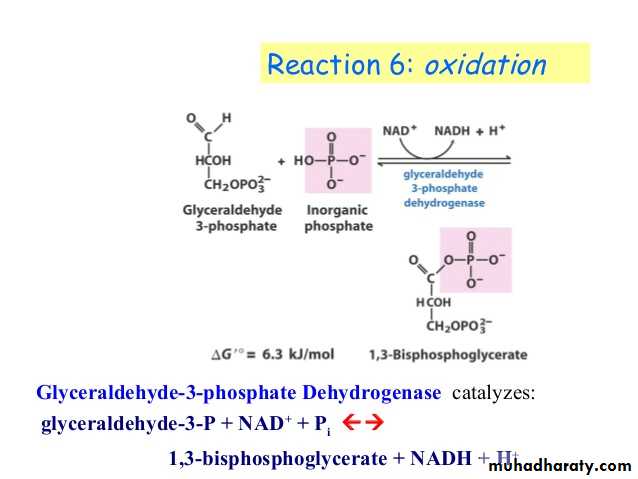
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, while storing energy released during this process as ATP and NADH. Nearly all organisms that break down glucose utilize glycolysis. Glucose regulation and product use are the primary categories in which these pathways differ between organisms. In some tissues and organisms, glycolysis is the sole method of energy production. This pathway is anaerobic, because it doesn’t require oxygen. Glycolysis consists of ten steps, split into two phases. During the first phase, it requires the breakdown of two ATP molecules. During the second phase, chemical energy from the intermediates is transferred into ATP and NADH. The breakdown of one molecule of glucose results in two molecules of pyruvate, which can be further oxidized to access more energy in later processes.
.
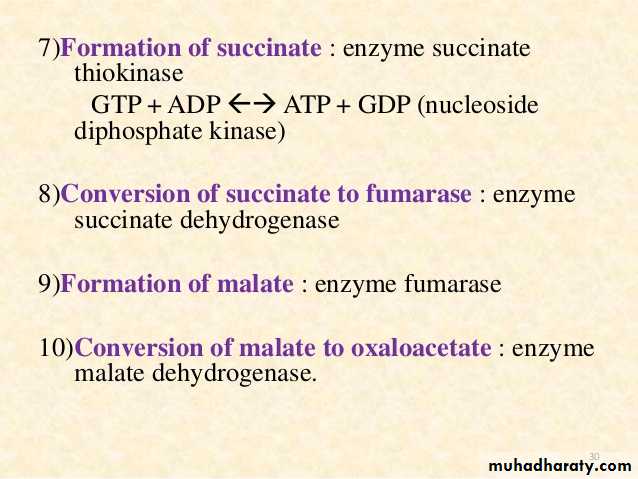
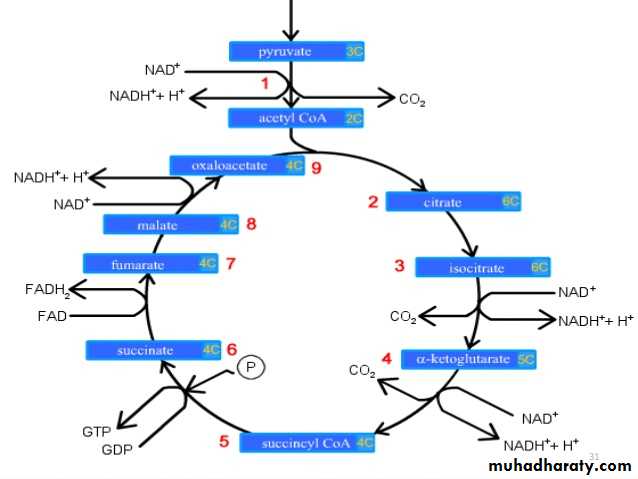
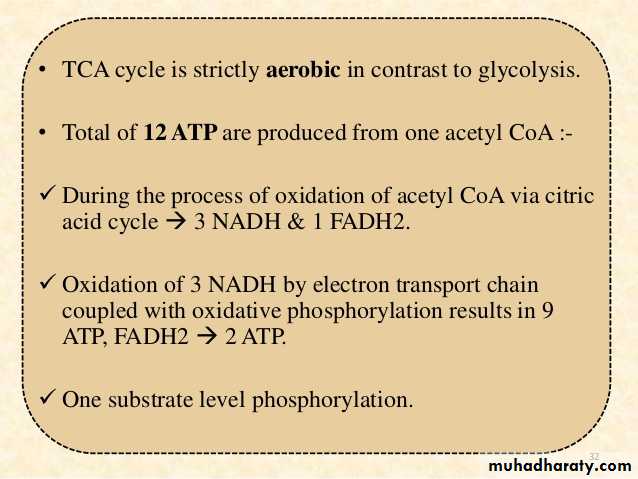
2- Citric acid cycle
Glycogenolysis: Glycogenolysis refers to the breakdown of glycogen. In the liver, muscles, and the kidney, this process occurs to provide glucose when necessary.
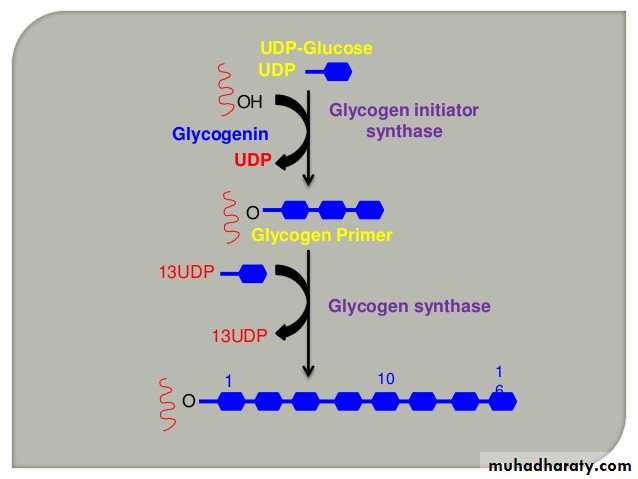
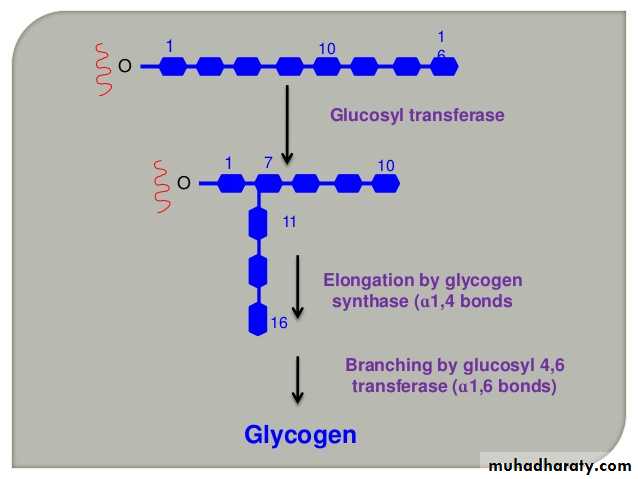
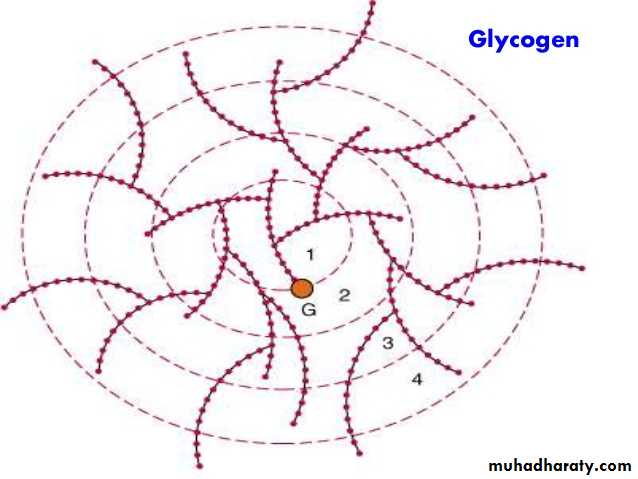
Glycogenesis:
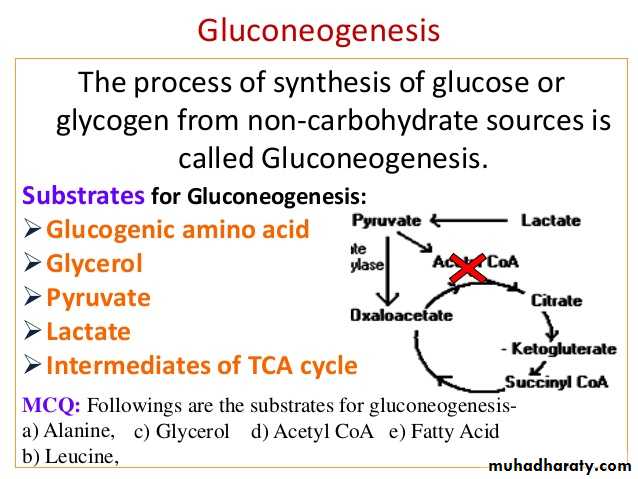
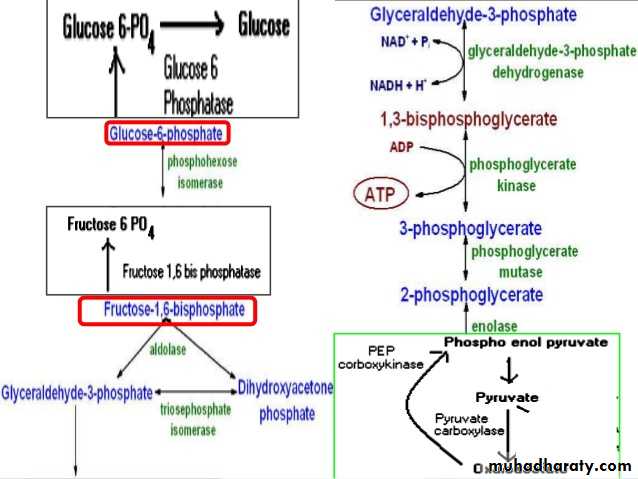
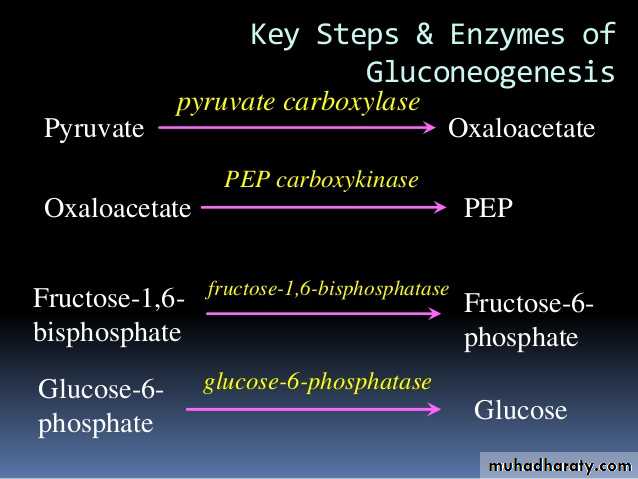
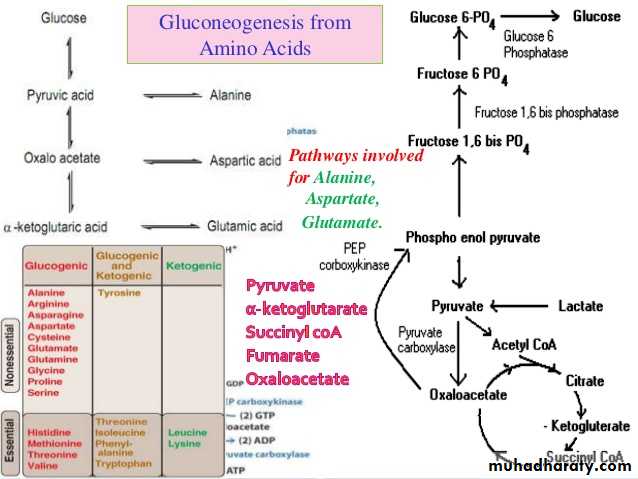
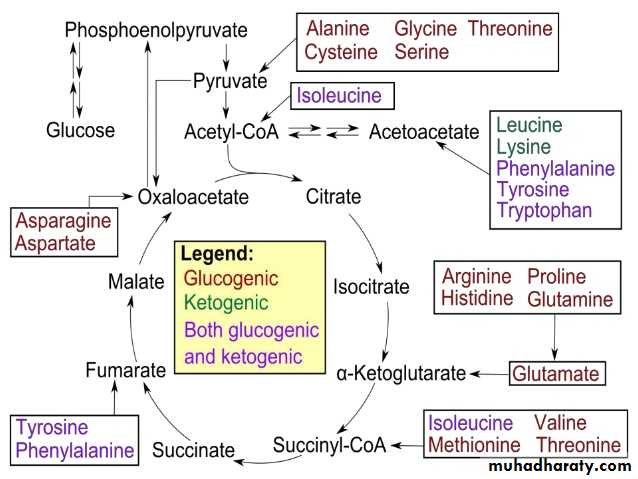
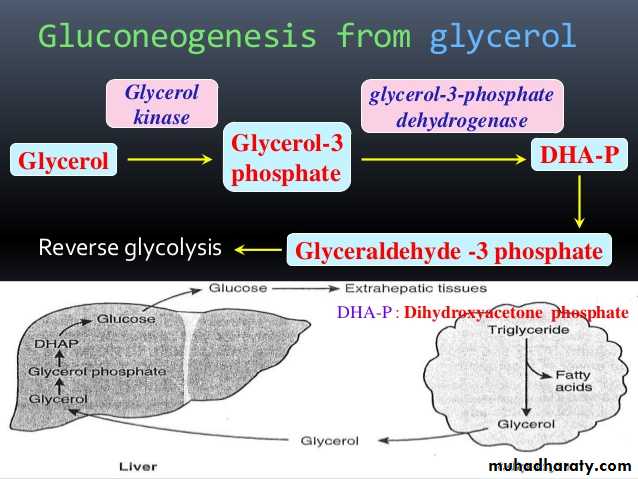
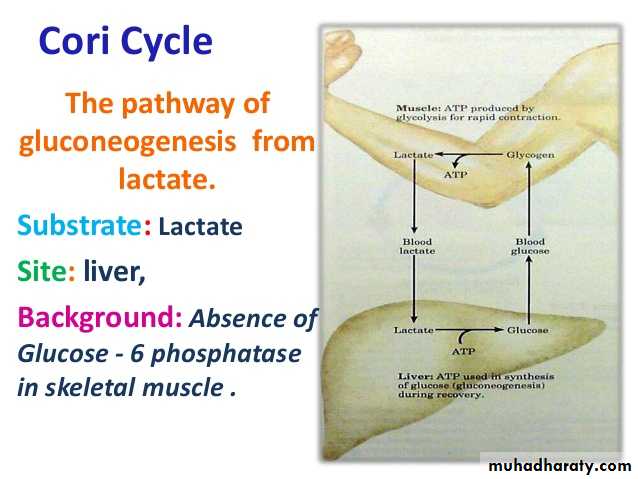
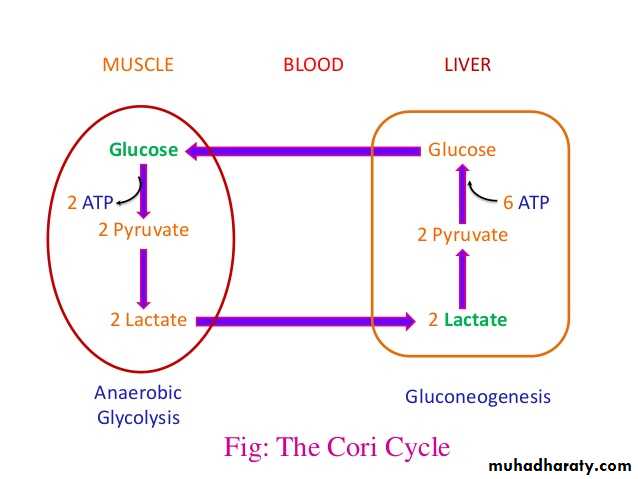
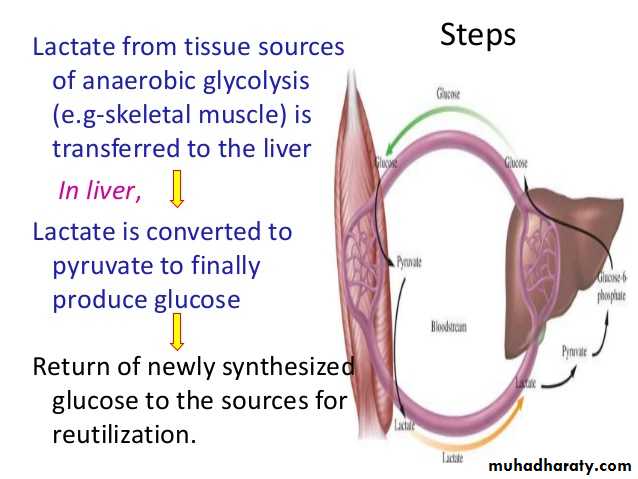
4- Gluconeogenesis:
Pentose phosphate pathway:
6- Fructose metabolism
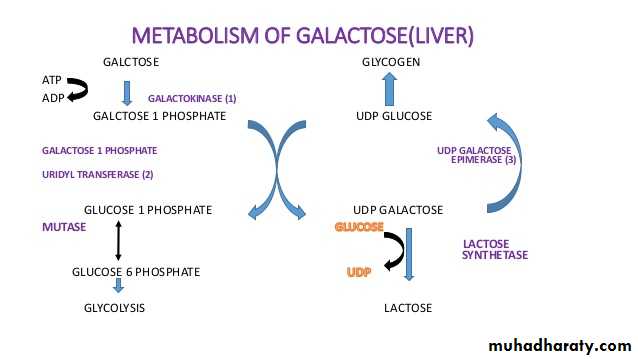
7- Galactose metabolism
Human diseases
Diabetes mellitusLactose intolerance
Fructose malabsorption
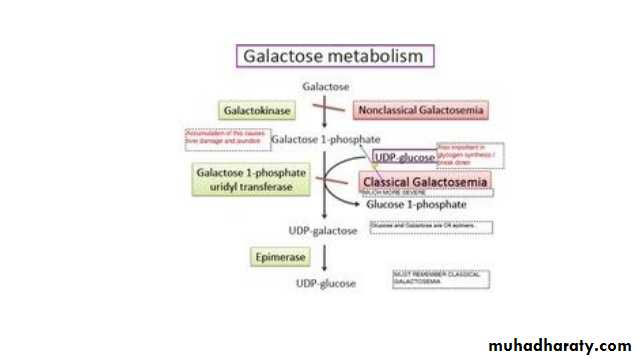
Galactosemia
Glycogen storage disease