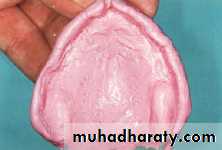
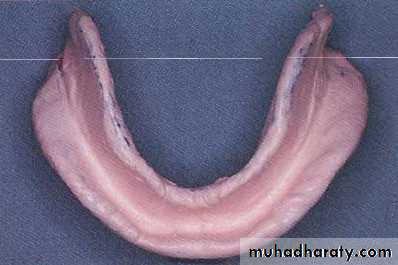
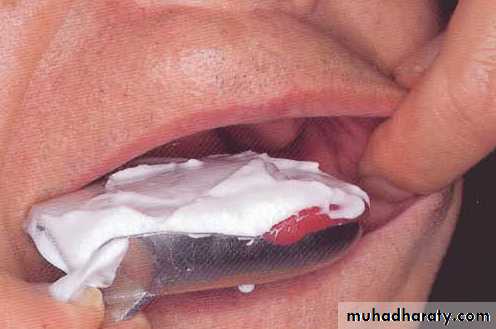
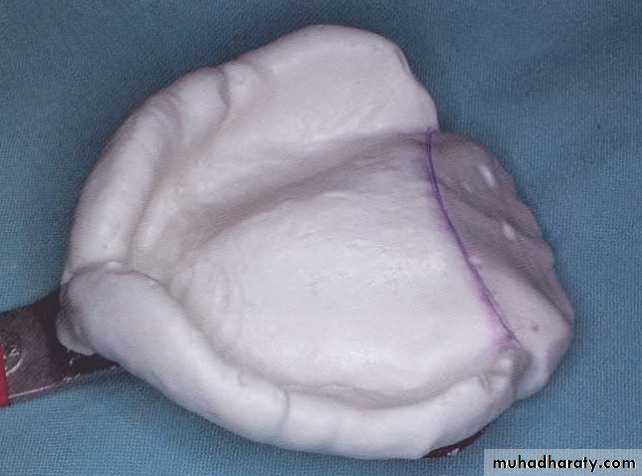
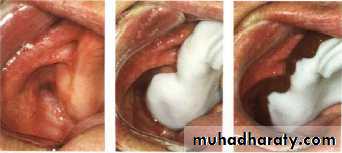
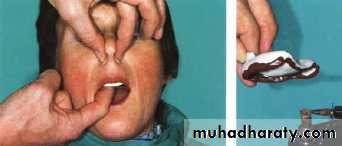
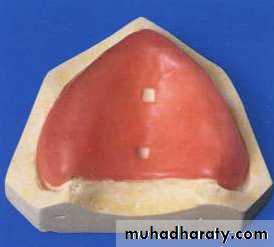
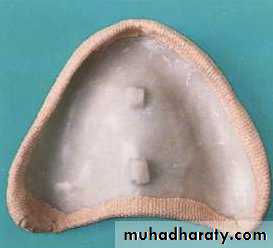
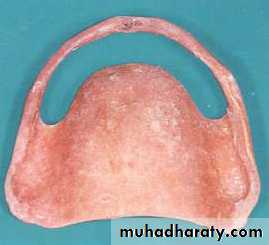
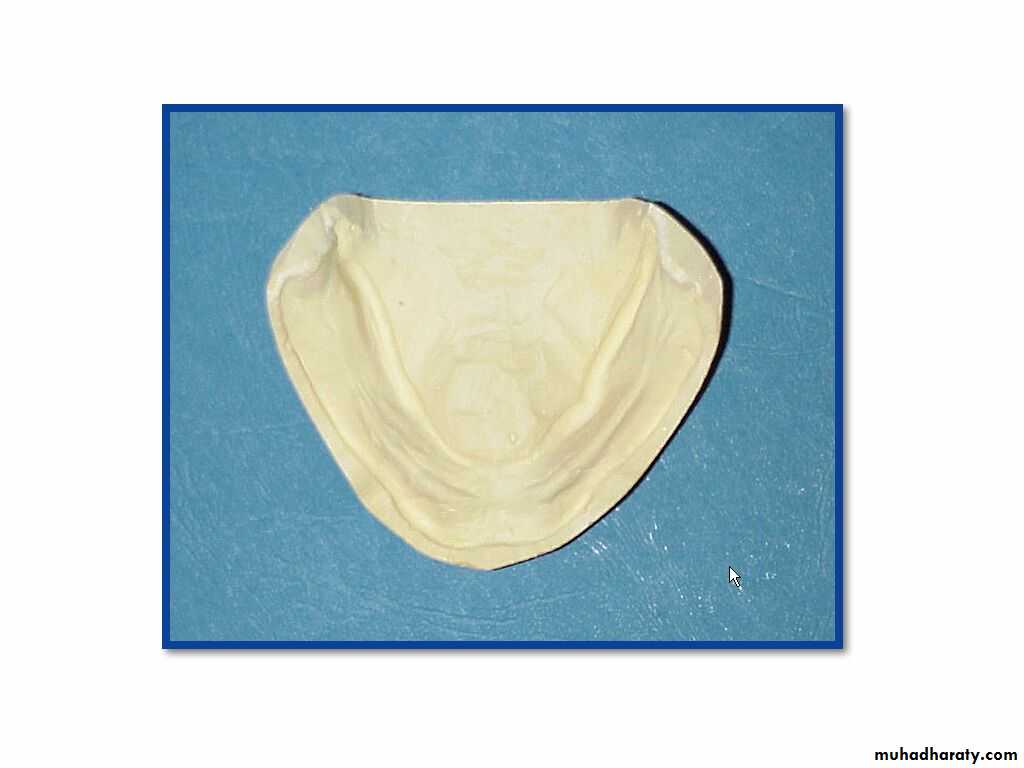
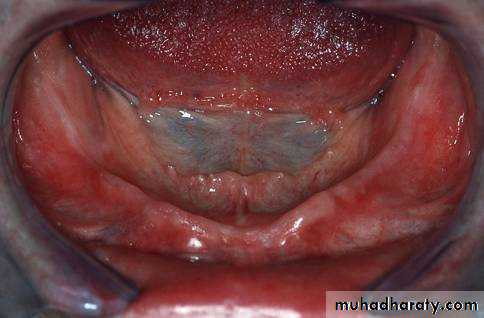
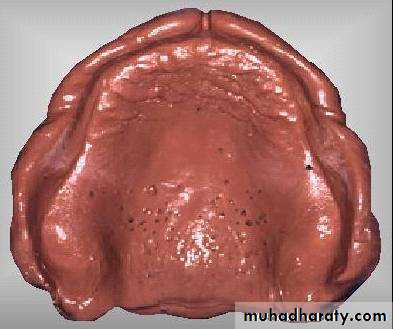
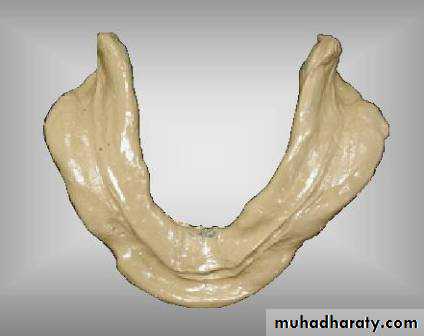
Final impressiontechniques
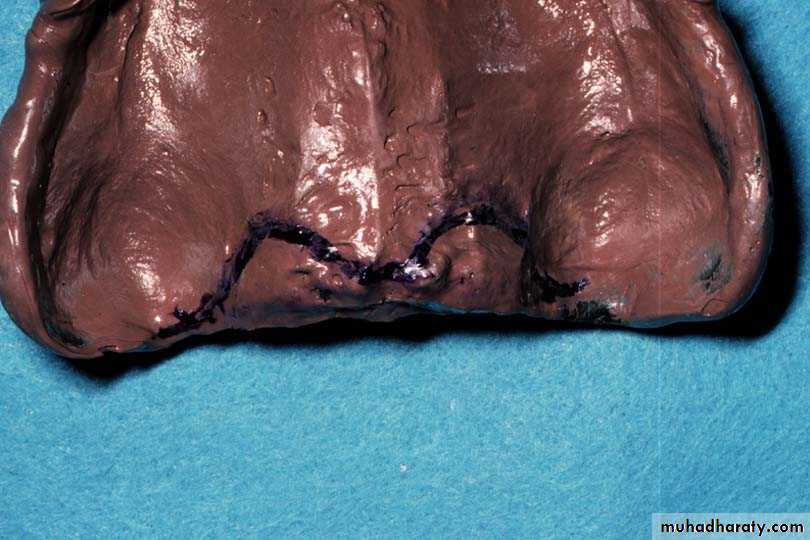
Requirements of final impression:It should include the entire denture bearing area.
It should be closely contacting the tissues and reproduce the tissues without distortion.
The periphery of the impression should be round and smooth and closely contact the resilient tissues in the vestibules.
there should be no gross surface defects in the impression such as tray exposure, fold and air voids.
The residual ridge may be said to have two forms:
The anatomic formThe anatomic form is the surface contour of the ridge when it is not supporting an occlusal load.
The functional form
The functional form of the residual ridge is the surface contour of the ridge when it is supporting a functional load.
Mucodynamic technique
Also referred as close mouth technique or mucocompressive technique.
Record the tissues in there functional position.
The patient applies pressure by closing against occlusal rims or teeth.
Patient exerts pressure and executes muscle actions.
Close fit special tray with border molding.
Mucostatic technique
Also referred as open mouth technique.Record the tissues in there undisplaced position.
Dentist exerts pressure.
Spaced special tray with no border seal.
Selective pressure technique
Selective Pressure Impression Method use those portions of the residual ridge that can withstand additional stress (primary stress bearing area) and at the same time relieve the tissue of the residual ridge that cannot withstand functional loads.Extension for maximum coverage within tissue tolerance.
Light pressure or intimate contact with the movable loosely attached tissues in the vestibules.
Special tray (special design) with border refinement.
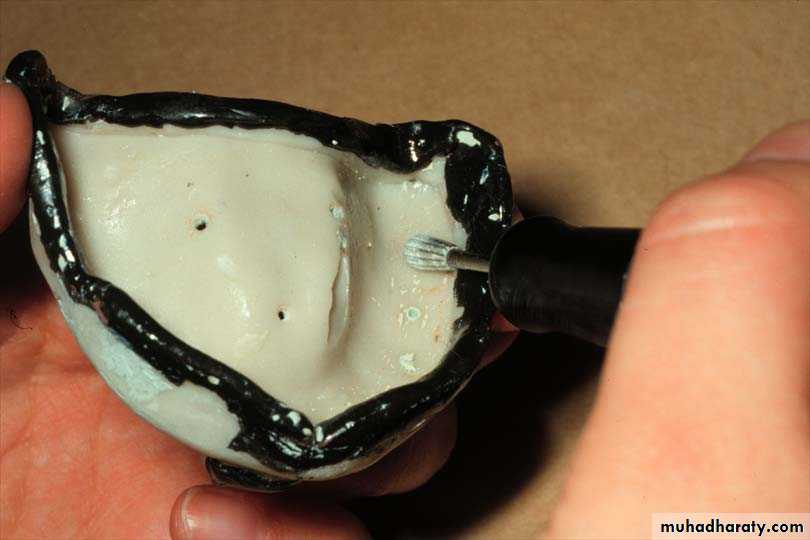
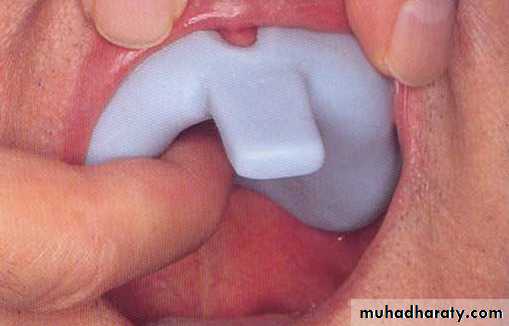
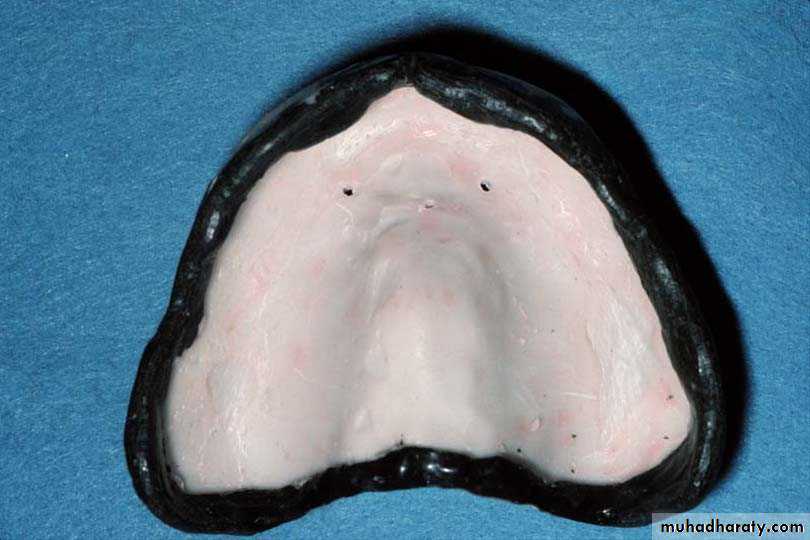
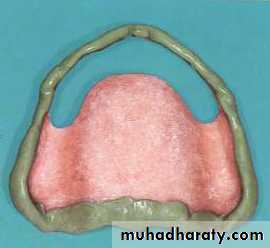
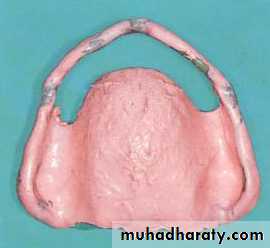
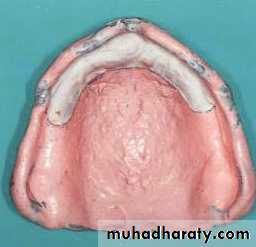
Special trayA device that is used to carry and control impression material while making a final impression.Special tray (prepared specially for each patient).
Close fit special tray
No space between the tray and oral tissue of residual ridge
No spacer is used
Used for mucodynamic impression technique
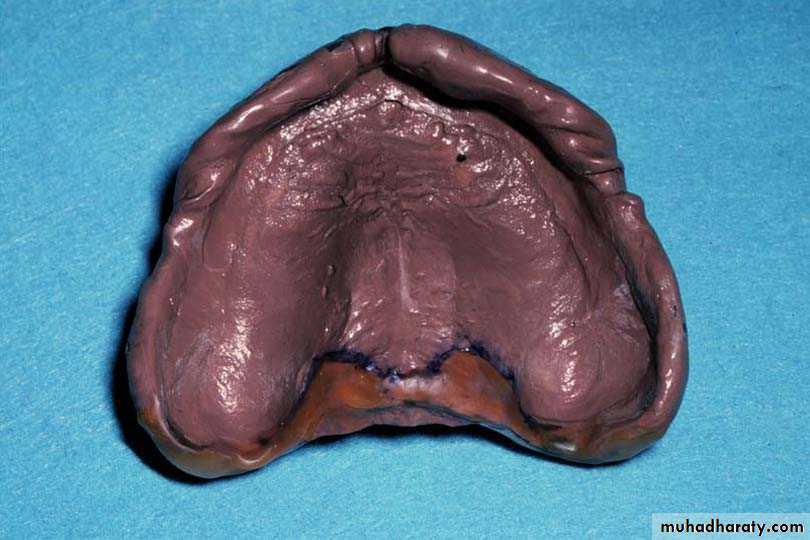
Spaced special tray
Space between the tray and oral tissue of residual ridge
Spacer is used (wax)
Used for mucostatic impression technique
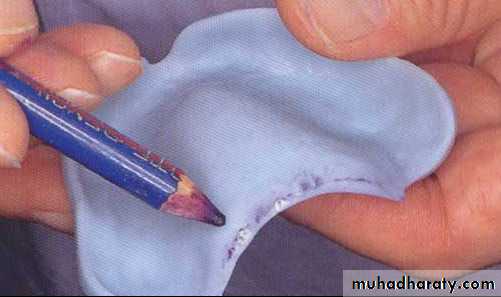
Design of spacer
Muco-compressive technique
No spacer is used
Mucostatic technique
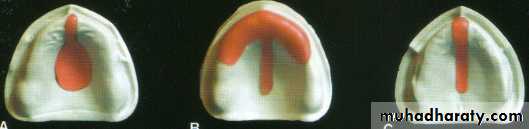
Maxilla: full coverage spacer with tissue stops in canine and molar region
Mandible: full coverage spacer with tissue stops in canine and buccal shelf area
Selective pressure technique
Maxilla: relief areas (incisive papilla and mid palatine raphe) and over flabby tissues if present.Mandible: crest of the ridge
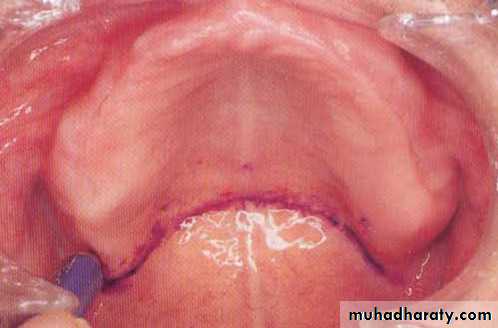
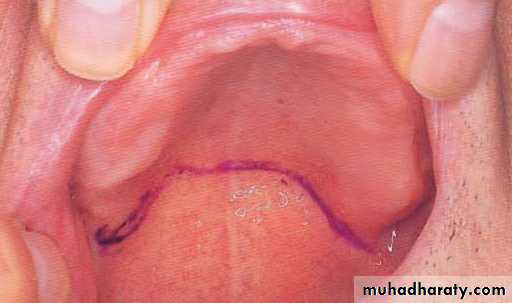
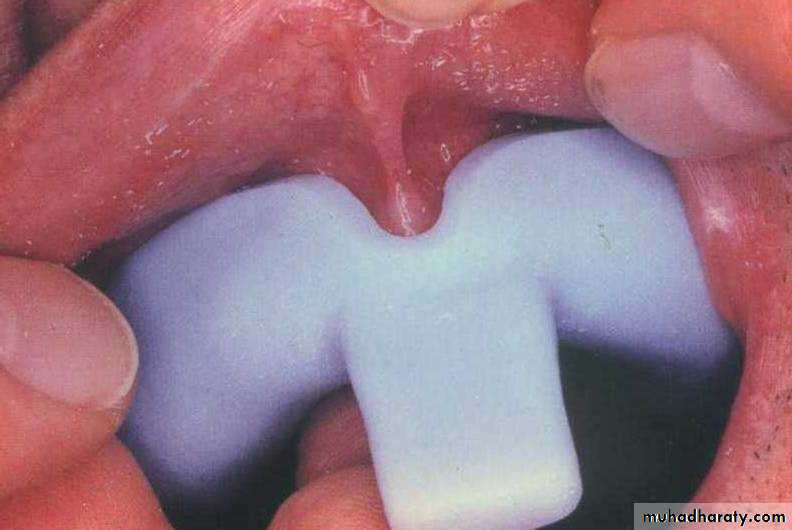
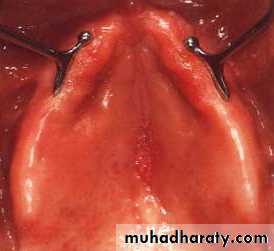
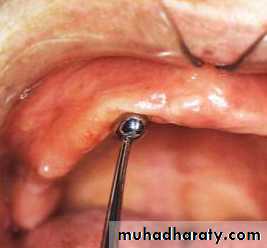
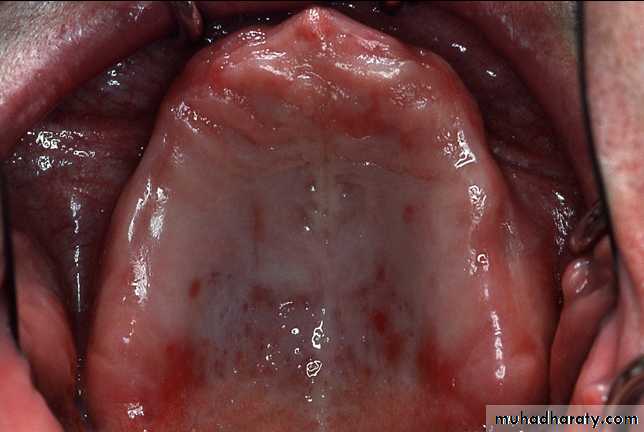
The vibrating line
an imaginary line across the posterior part of the palate marking the division between the movable and immovable tissues of the soft palate. This can be identified when the movable tissues are functioning.
The vibrating line
Its an imaginary line drawn across the palate that marks the beginning of motion in the soft palate, when the individual says “ah”.
Extends from one hamular notch to the other.
It passes about 2mm in front of the fovea palatine.
This line should lie on the soft palate.
Distal end of the denture must cover the tuberosities and extend into hamular notches. It should end 1-2mm posterior to the vibrating line.
Vibrating line
The position of fovea palatine also influences the position of posterior border of the denture. Denture can extend 1-2mm posterior to it.In patients with thick saliva, the fovea palatine should be left uncovered or else thick saliva flowing between the tissue and the denture can increase the hydrostatic pressure and displace the denture.
Anterior Vibrating Line:
“ Its an imaginary line lying at the junction between the immovable tissues over the hard palate and slightly movable tissues of the soft palate ”• Posterior Vibrating Line:
• “ Its an imaginary line at the junction of the aponeurosis of tensor veli palati muscles and muscular portion of soft palate ”• This line is usually straight.
• Its recorded by asking the patient to say “ah” in short but normal non-vigorous fashion.
• The anterior vibrating line is cupid bow shaped due to projection of posterior nasal spine.
Significance Of PPS
Prevents air passage between the tissues and denture base.Serves Primarily in denture retention by making contact with anterior portion of soft palate.
Decrease gag reflex.
Prevents food accumulation between posterior border of denture and the soft palate.
Compensates for polymerization shrinkage of denture base resin
Technique Of Recording PPS
1- Conventional Tech:By using special tray
2- By using impression
3- Arbitrary Scrapping Of The Master Cast:
Ant. & post. Vibrating lines are visualized by examining the pt’s mouth and approximately marked on master cast.The lab technician scraped 0.5 to 1mm of stone in posterior palatal seal area of the master cast and fabricates the denture.
This technique is inaccurate and not physiological and should be avoided.
Hamular notch
0 mm
0 mm
1 mm
0.5 mm
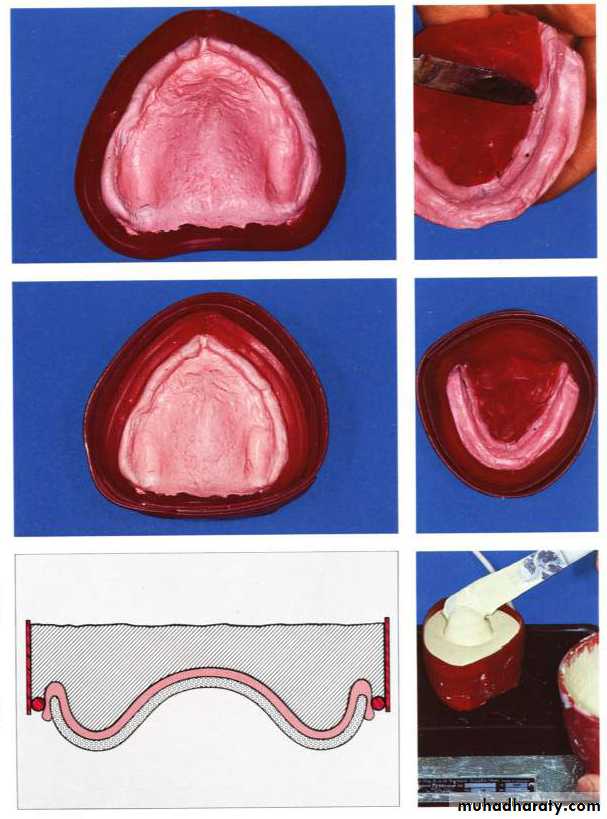
Impression procedure for flabby ridge
ObjectivesImpression of the flabby area made with pressure free technique.
Impression of the sound edentulous arch that can withstand the occlusal load made with pressure technique.
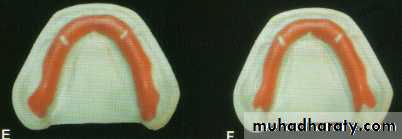
Final impression of ridge flabby in all areas
Wax spacer
Spaced special tray
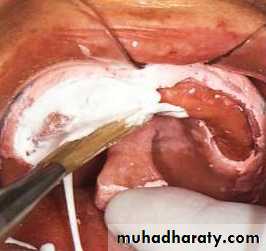
Final impression with impression plaster
Flabby ridgeFinal impression of ridge flabby in anterior region
Flabby anterior ridge
A window is made in special tray
Border molding of the special tray
Final impression of the entire ridge except the flabby ridge with ZOE
Final impression of the anterior flabby ridge with impression plaster without pressure
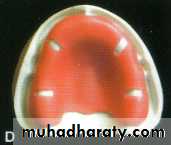
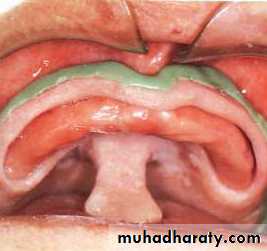
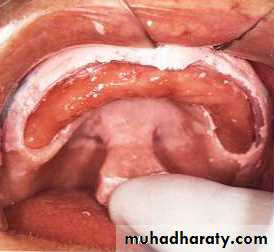
incisive papilla
b. palatal rugaec. median palatine raphe
d. maxillary tuberosity
e. pterygomaxillary notch
f. fovea palatini and vibrating line area
i. residual alveolar ridge
j. buccal frenum
k. labial frenum
MAXILLARY IMPRESSION
A
B
C
D
D
E
E
I
J
K
a. retromolar pad
b. mylohyoid (internal oblique line)c. masseteric notch
d. residual alveolar ridge
e. lingual frenum
f. external oblique line
g. buccal frenum
h. labial frenum
MANDIBULAR IMPRESSION
H
D
A
E
B
F
G
C
G
A
Disinfection of impressions
The disinfectant should be compatible with the impression materials.After taking the impression, it should be rinsed with water, excess water shaken off, and disinfectant sprayed or impression immersed in disinfectant solution.
Protective gloves should be worn.
Rinse after disinfection is complete.
28
METHODS OF POURING A CAST
INVERSION METHODBOXING IN METHOD
Inversion method:
The dental stone is mixed in proper consistency and poured at one end of the impression and gently tapped so that the material flows evenly throughout the impression (avoid incorporation of voids).
Fill the impression completely.
The remaining mix of stone is placed over the slab and the poured impression is inverted over the mix.
The land area and the base are carefully developed.
Boxing in method:
The beading wax is adapted and sealed around the periphery of the impression.Adapt and seal a sheet of base plate wax around the beading wax.
Pour the dental stone with vibration.