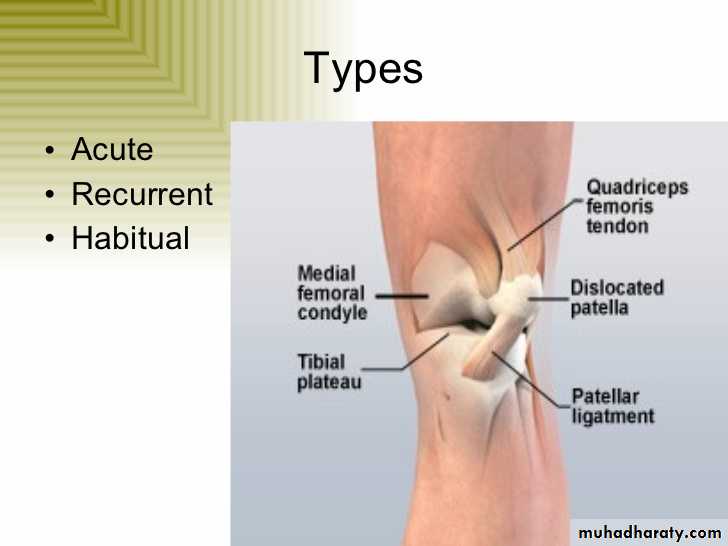
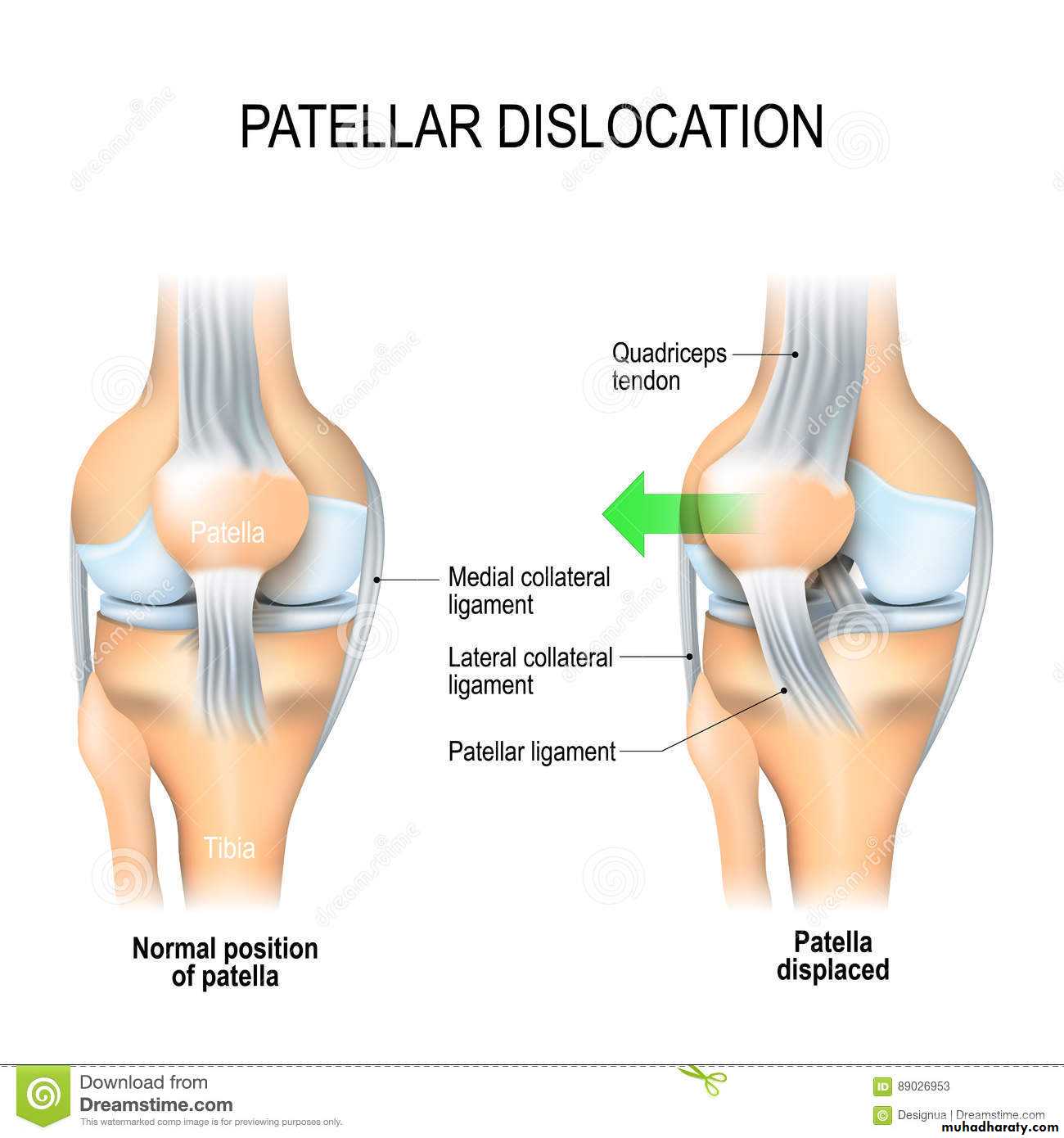
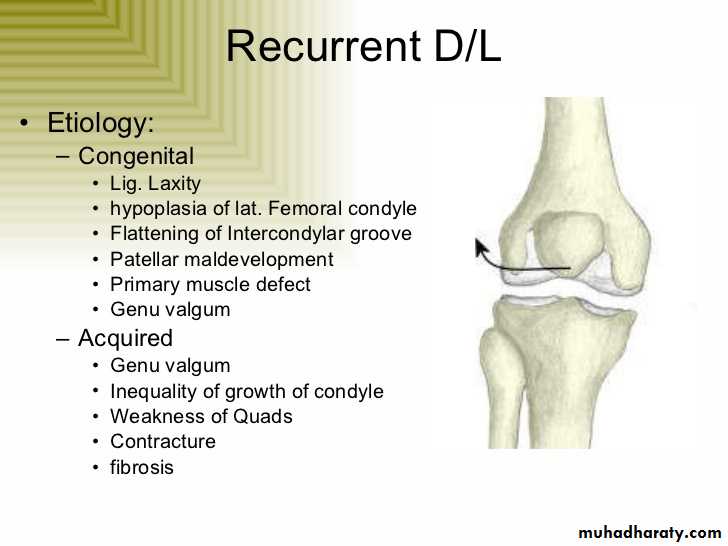
• Traumatic dislocation of patella
• Traumatic dislocation of patella occurs when it's subjected to direct lateral violence with the knee flexed, this leads to either subluxation with the patella over-riding the lateral femoral condyle (usually it slips back) or it's completely dislocated laterally.This injury is usually associated with damage to the medial side of extensor expansion and haemarthosis•
• Clinical features• Patient collapses and unable to straighten his leg stands or walk.
• Knee is swollen by haemarthosis
• Deformity is evident but sometimes misleading because the medial condyle may be prominent and mistaken for the patella.
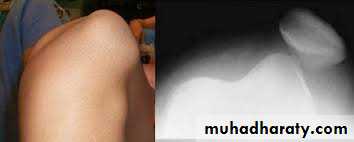
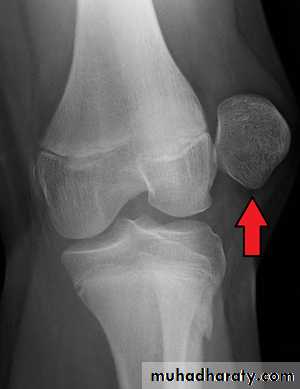
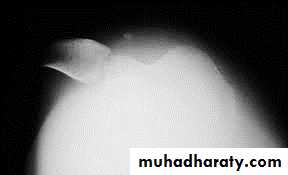
• X-ray
• It shows the displaced patella and the possible associated osteochondral fracture that occurs in 15% of the cases.
•
•
• Treatment
• Urgent reduction with or without anaesthesia by pushing the patella medially backwards while straightening the leg sometimes we need to aspirate a tender haemarthosis.• When there is severe medial joint bruise it means that there is serious underlying soft tissue damage which needs surgical suturing and repair to avoid future recurrence of dislocation.
• Immobilisation by a backslab for 3-4 weeks followed by Q-exercises.
• Operative treatment also indicated when there is associated fracture.
•
•